History of Hanover on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hanover (german: link=no, Hannover) is a territory that was at various times a principality within the
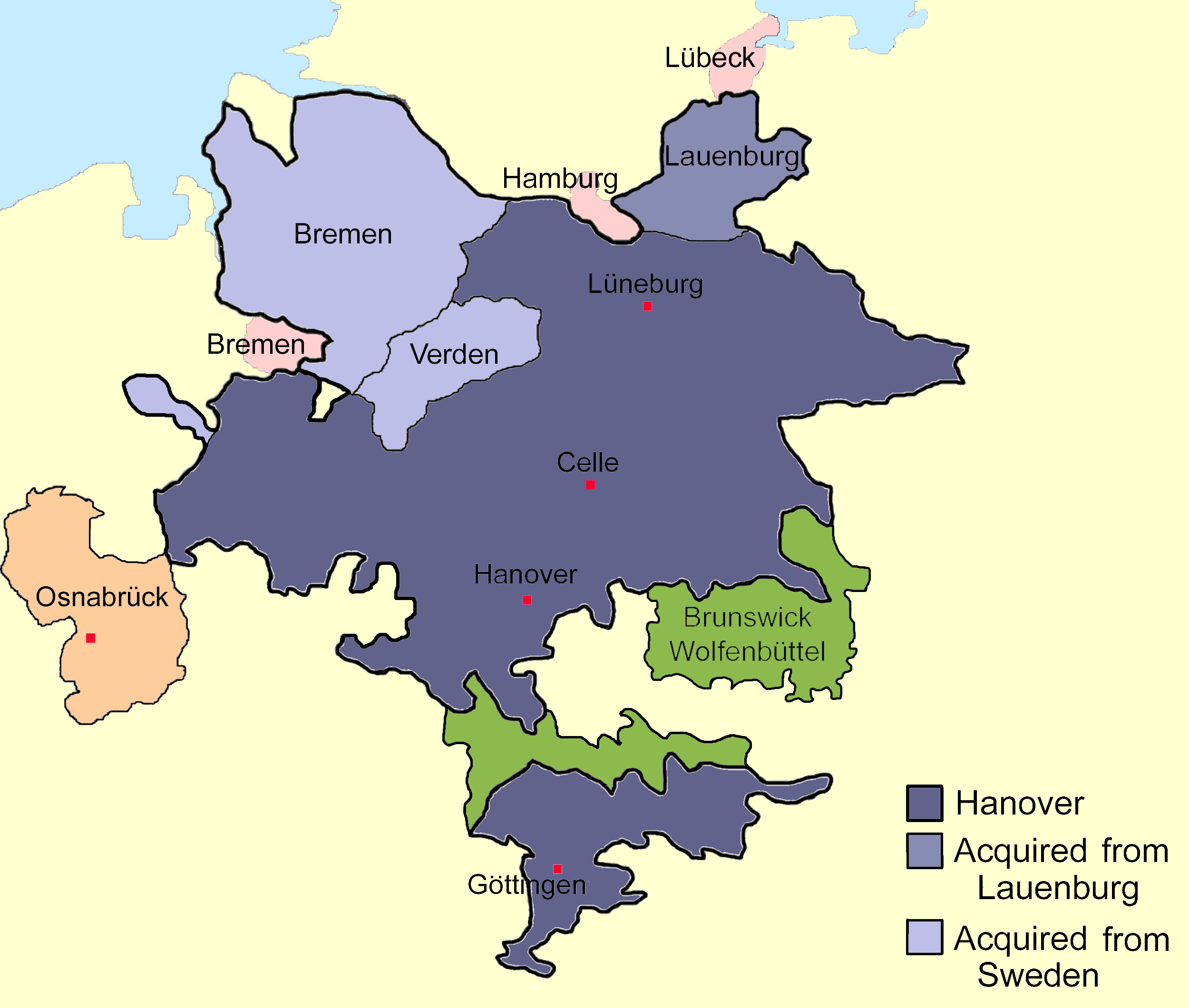 The Electorate was legally bound to be indivisible: it could add to its territory, but not alienate territory or be split up among several heirs; and its succession was to follow male primogeniture. The territory assigned to the Electorate included the Brunswick-Lüneburg principalities of Calenberg, Grubenhagen, and Lüneburg (even though at the time Lüneburg was ruled by Ernest Augustus's older brother) and the counties of
The Electorate was legally bound to be indivisible: it could add to its territory, but not alienate territory or be split up among several heirs; and its succession was to follow male primogeniture. The territory assigned to the Electorate included the Brunswick-Lüneburg principalities of Calenberg, Grubenhagen, and Lüneburg (even though at the time Lüneburg was ruled by Ernest Augustus's older brother) and the counties of


Map of Lower Saxony 1789
Die Welfen
the official homepage of the House of Welf. {{Rulers of Hanover
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, an Electorate within the same, an independent Kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
, and a subordinate Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
within the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
. The territory was named after its capital, the city of Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, which was the principal town of the region from 1636. In contemporary usage, the name is only used for the city; most of the historical territory of Hanover forms the greater part of the German ''Land'' of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
but excludes certain areas.
Formation
Hanover was formed by the union of severaldynastic
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
divisions of the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, with the sole exception of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. From 1714 to 1837, it was joined in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
with the United Kingdom, which terminated upon the accession in Britain of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
, as in Hanover, a woman could not rule if there was a male descendant. Until 1803, when it was occupied by French and Prussian troops, Hanover was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
; when it regained independence in 1814, Hanover was raised to a kingdom, which lasted until 1866.
Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg
The title " Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg" (german: link=no, Herzog zu Braunschweig und Lüneburg) was held, from 1235, by various members of the Welf family who ruled several small territories in northwest Germany. These holdings did not have all of the formal characteristics of a state, being neither compact nor indivisible. When several sons of a Duke competed for power, the lands were often divided between them; when a branch of the family lost power or became extinct, the lands were reallocated among surviving members of the family; different dukes might also exchange territories. The territories were named after notable towns where the dukes had (or had had at one time) their residences, e.g. Calenberg,Göttingen
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the capital of the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911.
General information
The ori ...
, Grubenhagen, Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also called ...
, Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel (; nds, Wulfenbüddel) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel District. It is best known as the location of the internationally renowned Herzog August Library and for having the largest ...
. The unifying element of all these territories was that they were ruled by male-line descendants of Duke Otto I, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Otto I of Brunswick-Lüneburg (about 1204 – 9 June 1252), a member of the House of Welf, was the first duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg from 1235 until his death. He is called Otto the Child to distinguish him from his uncle, Emperor Otto IV. ...
, nephew of the Holy Roman Emperor Otto IV.
Principality of Lüneburg
The line that would lead to the House of Hanover was that of Bernard, one of the three sons of Duke Magnus II who had jointly ruled a united Duchy of Brunswick since 1388, but who partitioned the territory in 1428 and 1432. Bernard received the territory ofLüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also called ...
, whose principal town was Celle.
From 1527 until 1642 the Principality of Harburg, seated in Harburg, was partitioned from Lüneburg. In 1569, Lüneburg was divided between Henry III (''line of Dannenberg'') and William VI (''line of Lüneburg''), the sons of Ernest the Confessor, Bernard's great-great-grandson.
A distant cousin of the line of Lüneburg, Frederick Ulrich, who ruled the territories of Wolfenbüttel and Calenberg, died in 1634. After some dispute, his territories were divided in 1635 between the Dannenberg and Celle branches of the Lüneburg line. Henry III's son Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
became Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and his descendants eventually ruled the Duchy of Brunswick.
William's first four sons ruled Lüneburg in sequence from their father's death in 1592 to 1648. The fifth son, George
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presid ...
received the territories of Calenberg and Göttingen in 1635. In 1636 he moved the seat of the Dukes of Calenberg from Pattensen
Pattensen () is a town in the district of Hanover, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately south of Hanover.
Geography
Pattensen is located in the historic landscape Calenberg Land between the Leine and the Deister hills. The ...
to the town of Hannover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
in the Calenberg territory. This was the nucleus of the state of Hanover, though the territory would have to wait until 1814 before receiving "Hanover" as its official name.
In 1648, the Duke of Calenberg inherited Lüneburg from his uncle Frederick, the last survivor of William's five sons. From 1648 to 1705, Lüneburg (the larger territory) was held by the senior of the Lüneburg line, and Calenberg by the next junior.
In 1692, the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
promised to raise the Duke of Calenberg, Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg to the rank of Elector
Elector may refer to:
* Prince-elector or elector, a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors
* Elector, a member of an electoral college
** Confederate elector, a member of ...
. This promotion did not become effective until it was recognized by the Imperial Diet in 1708, ten years after Ernest Augustus's death.
In the meantime, his son, George Louis, inherited Lüneburg from his uncle in 1705, doubling Hanover's size.
Electorate of Hanover 1708–1814
In 1692, the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold I, elevated George's son, Duke Ernest Augustus to the rank ofElector
Elector may refer to:
* Prince-elector or elector, a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors
* Elector, a member of an electoral college
** Confederate elector, a member of ...
of the Empire as a reward for aid given in the War of the Grand Alliance
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
. There were protests against the addition of a new Elector, and the elevation did not become official (with the approval of the Imperial Diet) until 1708, in the person of Ernest Augustus's son, George Louis. Though the Elector's titles were properly ''Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg'' and ''Elector of the Holy Roman Empire'', he is commonly referred to as the ''Elector of Hanover'' after his residence.
 The Electorate was legally bound to be indivisible: it could add to its territory, but not alienate territory or be split up among several heirs; and its succession was to follow male primogeniture. The territory assigned to the Electorate included the Brunswick-Lüneburg principalities of Calenberg, Grubenhagen, and Lüneburg (even though at the time Lüneburg was ruled by Ernest Augustus's older brother) and the counties of
The Electorate was legally bound to be indivisible: it could add to its territory, but not alienate territory or be split up among several heirs; and its succession was to follow male primogeniture. The territory assigned to the Electorate included the Brunswick-Lüneburg principalities of Calenberg, Grubenhagen, and Lüneburg (even though at the time Lüneburg was ruled by Ernest Augustus's older brother) and the counties of Diepholz
Diepholz (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Deefholt'') is a town and capital of the district of Diepholz in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the rivers Hunte and Lohne, approximately 45 km northeast of Osnabrück, and 60 km southwest of ...
and Hoya.
George Louis became king of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
in 1714 (see House of Hanover
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house or ...
). The influence of the electors in Germany grew also: they inherited the formerly Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
territories of Bremen and Verden in 1719. As part of the German Mediatisation
German mediatisation (; german: deutsche Mediatisierung) was the major territorial restructuring that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany and the surrounding region by means of the mass mediatisation and secularisation of a large number ...
of 1803, the Electorate received the Prince-Bishopric of Osnabrück
The Prince-Bishopric of OsnabrückAlso known as the Prince-Bishopric of Osnaburg) (german: link=no, Hochstift Osnabrück; Fürstbistum Osnabrück, Bistum Osnabrück) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1225 until 1803. ...
.
The Electorate became a battleground during the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
following the French Invasion of Hanover. In the Convention of Klosterzeven
The Convention of Klosterzeven (or the Convention of Kloster-Zeven, german: Konvention von Kloster Zeven) was a convention signed on 10 September 1757 at Klosterzeven between France and the Electorate of Hanover during the Seven Years' War that ...
it was agreed that Hanover should be neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
with large parts of the Electorate occupied by French forces. George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089) ...
subsequently revoked the convention, and the re-formed Army of Observation An army of observation is a military body whose purpose is to monitor a given area or enemy body in preparation for possible hostilities.
Some of the more notable armies of observation include:
* Third Reserve Army of Observation, a Russian army ta ...
counter-attacked and drove the French from the Electorate. Subsequent French attacks were repulsed.
In 1803, the Electorate of Hanover was occupied by France after the Convention of Artlenburg. From 1807 to 1813, the Hanoverian territory was part of the Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the ...
. However, the government of George III did not recognize the French annexation (being at war continuously with France through the entire period) and Hanoverian ministers continued to operate from London. The Hanoverian government maintained its own separate diplomatic service, which maintained links to countries such as Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, with whom the United Kingdom itself was technically at war. The Hanoverian army was dissolved, but many of the officers and soldiers went to England, where they formed the King's German Legion. The KGL was the only German army to fight continually throughout the Napoleonic wars against the French. They played an important part in the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
in 1815.
Although the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
was dissolved in 1806, George III's government did not consider the dissolution to be final, and he continued to be styled "Elector of Hanover" down to 1814.
Kingdom of Hanover 1814–1866
In 1813,George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
was restored to his Hanoverian territories, and in October 1814 they were erected into the independent Kingdom of Hanover at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
. The Congress of Vienna instituted a territorial exchange between Hanover and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, in which Hanover increased its area substantially, gaining the Bishopric of Hildesheim, East Frisia, the Lower County of Lingen
Lingen (), officially Lingen (Ems), is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany. In 2008, its population was 52,353, and in addition there were about 5,000 people who registered the city as their secondary residence. Lingen, specifically "Lingen (Ems)" is ...
and the northern part of the Bishopric of Münster
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
. It lost those parts of the Duchy of Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (german: Herzogtum Sachsen-Lauenburg, called ''Niedersachsen'' (Lower Saxony) between the 14th and 17th centuries), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296–1803 and again from 1814–1876 in the extreme sou ...
to the right of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
, and several small exclaves in the east.
The personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
with the United Kingdom ended in 1837 on the accession of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
because the succession laws in Hanover prevented a female from inheriting the throne if there was a male descendent.
In the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, Hanover was annexed by Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
and became the Province of Hanover
The Province of Hanover (german: Provinz Hannover) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.
During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position ...
.
Province of Hanover 1866–1946
The Province of Hanover (german: link=no, Provinz Hannover) was aprovince
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
and the Free State of Prussia
The Free State of Prussia (german: Freistaat Preußen, ) was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it continued to be the domina ...
from 1868 to 1946.
In 1946, the British military administration made the Province of Hanover the main part of the land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various isla ...
of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, along with the states of Oldenburg, Brunswick, and Schaumburg-Lippe
Schaumburg-Lippe, also Lippe-Schaumburg, was created as a county in 1647, became a principality in 1807, a free state in 1918, and was until 1946 a small state in Germany, located in the present day state of Lower Saxony, with its capital at Bück ...
, with the city of Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
as the capital of the new state.
Coat of arms
See also
*Province of Hanover
The Province of Hanover (german: Provinz Hannover) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.
During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position ...
* King's German Legion
*House of Hanover
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house or ...
*Ernst zu Münster
Graf Ernst Friedrich Herbert zu Münster (born 1 March 1766 Osnabrück; died 20 May 1839 Hanover) was a German statesman, politician and minister in the service of the House of Hanover.
Biography
Ernst zu Münster was born the son of Georg zu (1 ...
*German Chancery
The German Chancery (German: ''Deutsche Kanzlei''), also known as the Hanoverian Chancery, was the official name given to the office of the Hanoverian ministry in London during the years of personal union between Great Britain (later the United K ...
* Timeline of Hanover city
Further reading
*External links
Map of Lower Saxony 1789
Die Welfen
the official homepage of the House of Welf. {{Rulers of Hanover