History of Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other
 The history of
The history of 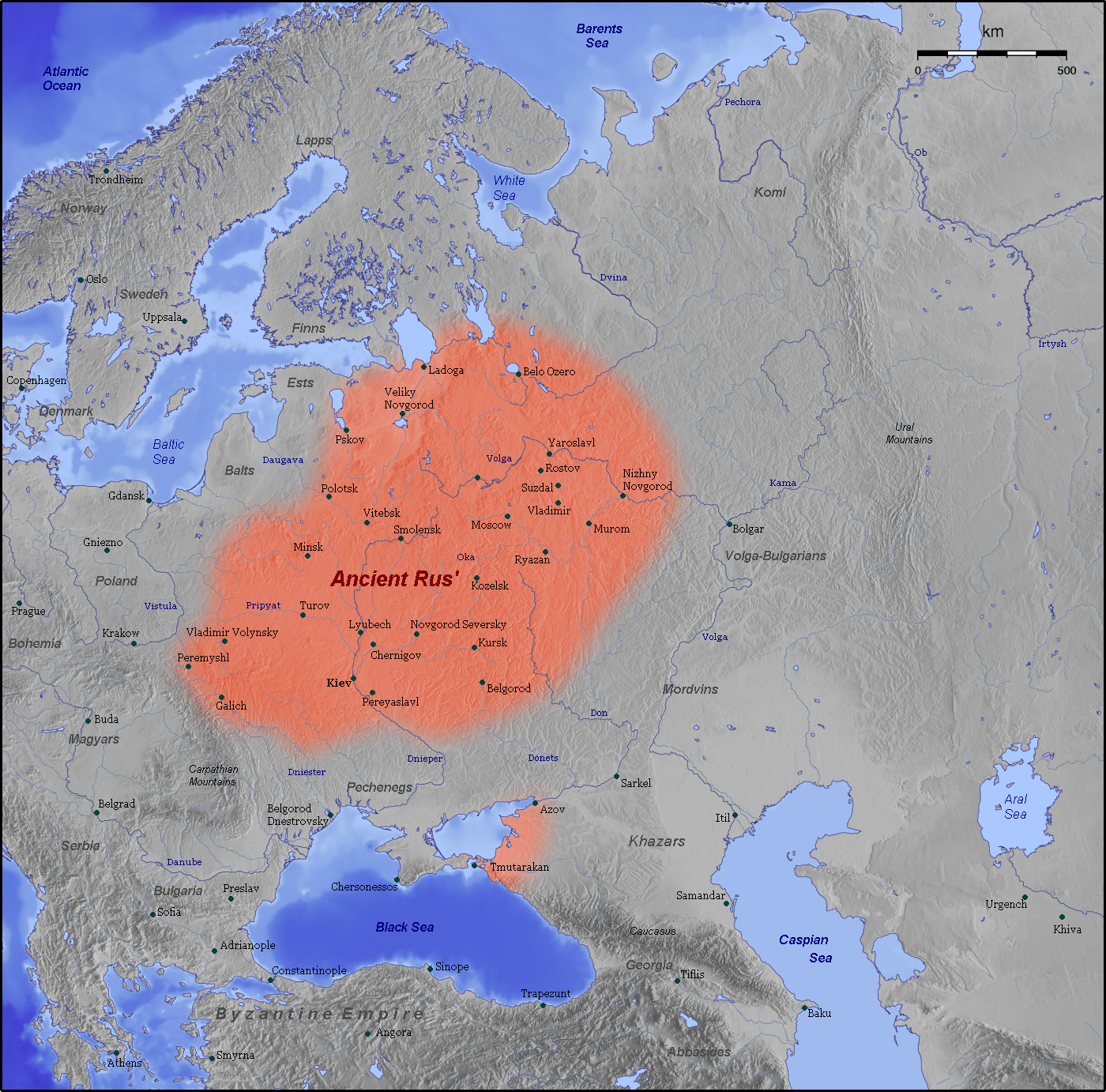 During the 9th and 10th centuries,
During the 9th and 10th centuries,
 Between the 9th and 12th centuries, the
Between the 9th and 12th centuries, the
 Construction of Orthodox churches in some parts of present-day Belarus had been initially prohibited, as was the case in
Construction of Orthodox churches in some parts of present-day Belarus had been initially prohibited, as was the case in
 The Lublin Union of 1569 constituted the
The Lublin Union of 1569 constituted the  Also, with time the religious conflicts started to arise. The gentry with time started to adopt
Also, with time the religious conflicts started to arise. The gentry with time started to adopt
Table of Contents online
From 1569, the Despite the abovementioned conflicts, the literary tradition of Belarus evolved. Until the 17th century, the Ruthenian language, the predecessor of modern Belarusian, was used in Grand Duchy as a ''chancery language'', that is the language used for official documents. Afterwards, it was replaced with the
Despite the abovementioned conflicts, the literary tradition of Belarus evolved. Until the 17th century, the Ruthenian language, the predecessor of modern Belarusian, was used in Grand Duchy as a ''chancery language'', that is the language used for official documents. Afterwards, it was replaced with the
 Under Russian administration, the territory of Belarus was divided into the '' guberniyas'' of
Under Russian administration, the territory of Belarus was divided into the '' guberniyas'' of


 On 21 February 1918, Minsk was captured by German troops.
On 21 February 1918, Minsk was captured by German troops.
 The Polish part of Belarus was subject to
The Polish part of Belarus was subject to

 When the Soviet Union invaded Poland on September 17, 1939, following the terms of the
When the Soviet Union invaded Poland on September 17, 1939, following the terms of the
 More than 200,000 ethnic Poles left or were expelled to Poland in late 1940s and late 1950s, some killed by the
More than 200,000 ethnic Poles left or were expelled to Poland in late 1940s and late 1950s, some killed by the
 On 27 July 1990, Belarus declared its national sovereignty, a key step toward independence from the Soviet Union. Around that time,
On 27 July 1990, Belarus declared its national sovereignty, a key step toward independence from the Soviet Union. Around that time,
 A new Belarusian constitution enacted in early 1994 paved the way for the first democratic presidential election on 23 June and 10 July.
A new Belarusian constitution enacted in early 1994 paved the way for the first democratic presidential election on 23 June and 10 July.
U.S. no longer recognizes Lukashenko as legitimate president of Belarus
''Axios'' (24 September 2020). On 23 May 2021,
online
* Defense Technical Information Center. ''The Role of Small States in the Post-Cold War Era: The Case of Belarus'' (2012
online
* Fedor, Helen, ''Belarus and Moldova: country studies'' (Library of Congress. Federal Research Division, 1995
online
with brief history pp 18–25. * Epstein, Barbara. ''The Minsk Ghetto 1941–1943: Jewish Resistance and Soviet Internationalism'' (U of California Press, 2008). * Guthier, Steven L. "The Belorussians: National identification and assimilation, 1897–1970: Part 1, 1897–1939." ''Soviet Studies'' 29.1 (1977): 37–61. * Horak, Stephan M. "Belorussia: Modernization, Human Rights, Nationalism." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers'' 16.3 (1974): 403–423. * Korosteleva, Elena A., Lawson Colin W. and Marsh, Rosalind J., eds. ''Contemporary Belarus'' (Routledge 2003) * Loftus, John J., 'The Belarus Secret'(Knopf, 1982) * Lubachko, Ivan S. ''Belorussia: Under Soviet Rule, 1917–1957'' (U Press of Kentucky, 2015). * Marples, David R. "Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia Under Soviet Occupation: The Development of Socialist Farming, 1939–1941." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers 27.2 (1985): 158–177
online
* Marples, David. Our Glorious Past': Lukashenka's Belarus and the Great Patriotic War'' (Columbia University Press, 2014) * * * * Rudling, Pers Anders. ''The Rise and Fall of Belarusian Nationalism, 1906–1931'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2014) 436 pages * * * Skinner, Barbara. (2012) ''The Western Front of the Eastern Church: Uniate and Orthodox Conflict in Eighteenth-Century Poland, Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia'' * Smilovitsky, Leonid. "Righteous Gentiles, the Partisans, and Jewish Survival in Belorussia, 1941–1944." ''Holocaust and Genocide Studies'' 11.3 (1997): 301-329. * Snyder, Timothy. (2004) ''The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999'
excerpt and text search
* Strategic Studies Institute. ''Political Trends in the New Eastern Europe – Ukraine and Belarus'' (2007
online
* Strużyńska, Nina. ''Anti-Soviet conspiracy and partisan struggle of the Green Oak Party in Belarus'', in ''Non Provincial Europe'', London 1999, * * Szporluk, Roman. "West Ukraine and West Belorussia: Historical tradition, social communication, and linguistic assimilation." ''Soviet Studies'' 31.1 (1979): 76-98
online
* Szporluk, Roman. "The press in Belorussia, 1955–65." ''Europe‐Asia Studies'' 18.4 (1967): 482–493. * * Urban, Michael E. ''An Algebra of Soviet Power: Elite Circulation in the Belorussian Republic 1966–86'' (Cambridge UP, 1989). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: the making of a nation: a case study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A bibliographical guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * * Wexler, Paul. "Belorussification, Russification and Polonization Trends in the Belorussian Language 1890–1982." in Kreindler, ed., ''Sociolinguistic Perspectives'' (1985): 37–56. * Zaprudnik, Jan. ''Historical dictionary of Belarus'' (Scarecrow Pr, 1998) * Zaprudnik. Jan. ''Belarus: At A Crossroads In History'' (Westview Press, 1993
online free to borrow
Belarus National Republic
— the Belarusian Government in exile
Stary Hetman
— forums and library (in Belarusian and Russian) on Belarusian history
Belarus
by CIA World Factbook, 2000
Belarus
by
Belarusian diaspora
History of Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Belarus history
on th
Official Website of the Republic of Belarus
Belarusian Historical Review. Independent Academic Journal dedicated to history of Belarus (Belarusian and English versions)
History of Belarus in five minutes
YouTube {{European history by country
East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert H ...
.
Belarus is a successor of some Ruthenian principalities (Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
, Turov, Novogrudok, etc.), the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (with Republic of Lithuania
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
), the BPR, the LBSR, and the BSSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
.
After an initial period of independent feudal consolidation, Belarusian lands were incorporated into the Kingdom of Lithuania
The Kingdom of Lithuania was a Lithuanian state, which existed roughly from 1251 to 1263. King Mindaugas was the first and only Lithuanian monarch crowned King of Lithuania with the assent of the Pope. The formation of the Kingdom of Lithuani ...
, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and eventually the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. Apart from a brief attempt at independence, known as the Belarusian People's Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; be, Беларуская Народная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Narodnaja Respublika, ), or Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic R ...
, following the political vacuum created by the World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
only became an independent country in 1991 after declaring itself free from the Soviet Union.
Early history
 The history of
The history of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, or more precisely of the Belarusian ethnicity, begins with the migration and expansion of the Slavic peoples through Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
between the 6th and 8th centuries. East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert H ...
settled on the territory of present-day Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, assimilating local Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
(Yotvingians
Yotvingians (also called: Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians; Yotvingian: ''Jotvingai''; lt, Jotvingiai, ; lv, Jātvingi; pl, Jaćwingowie, be, Яцвягі, ger, Sudauer) were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prus ...
, Dniepr Balts), Finns
Finns or Finnish people ( fi, suomalaiset, ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland.
Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these ...
(in Russia) and steppe nomads (in Ukraine) already living there, their early ethnic integrations contributed to the gradual differentiation of the three East Slavic nations. These East Slavs, pagan, animistic
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning ' breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, ...
, agrarian people, had an economy which included trade in agricultural produce, game, fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
s, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, beeswax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive work ...
and amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In ...
.
The modern Belarusian ethnos was probably formed on the basis of the three Slavic tribes— Kryvians, Drehovian
The Dregoviches or Dregovichi ( Belarusian: дрыгавічы, ''dryhavičy'', ; russian: дреговичи, dregovichi; ua, дреговичі, drehovychi) were one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs, and inhabited the territories ...
s, and Radzimians—as well as several Baltic tribes
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
.
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
n Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
established trade posts on the way from Scandinavia to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The network of lakes and rivers crossing East Slav territory provided a lucrative trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
between the two civilizations. In the course of trade, they gradually took sovereignty over the tribes of East Slavs, at least to the point required by improvements in trade.
The Rus' rulers invaded the Byzantine Empire on few occasions, but eventually they allied against the Bulgars. The condition underlying this alliance was to open the country for Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
and acculturation from the Byzantine Empire.
The common cultural bond of Eastern Orthodox Christianity and written Church Slavonic (a literary and liturgical Slavic language
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Ea ...
developed by 8th-century missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited wi ...
) fostered the emergence of a new geopolitical entity, Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
— a loose-knit multi-ethnic network of principalities,John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.16. established along preexisting trade routes, with major centers in Novgorod (currently Russia), Polatsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
(in Belarus) and Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
(currently in Ukraine) — which claimed a sometimes precarious preeminence among them.
First Belarusian states
 Between the 9th and 12th centuries, the
Between the 9th and 12th centuries, the Principality of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk ( be, По́лацкае кня́ства, ''Polackaje kniastva''; la, Polocensis Ducatus), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs. The origin and ...
(northern Belarus) emerged as the dominant center of power on the Belarusian territory, while the Principality of Turaŭ in the south had a lesser power.
The Principality of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk ( be, По́лацкае кня́ства, ''Polackaje kniastva''; la, Polocensis Ducatus), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs. The origin and ...
repeatedly asserted its sovereignty in relation to the other centers of Rus', becoming a political capital, the episcopal see of a bishopric and the controller of vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
territories among Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
in the west. The city's Cathedral of the Holy Wisdom (1044–66), though completely rebuilt over the years, remains a symbol of this independent-mindedness, rivaling churches of the same name in Novgorod and Kiev, referring to the original Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
(and hence to claims of imperial prestige, authority and sovereignty). Cultural achievements of the Polatsk period include the work of the nun Euphrosyne of Polatsk (1120–1173), who built monasteries, transcribed books, promoted literacy and sponsored art (including local artisan Lazarus Bohsha's famous " Cross of Euphrosyne", a national symbol and treasure stolen during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
), and the prolific, original Church Slavonic sermons and writings of Bishop Cyril of Turau (1130–1182).
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
In the 13th century, the fragile unity of Kievan Rus' disintegrated due to nomadic incursions fromAsia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, which climaxed with the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
sacking of Kiev (1240), leaving a geopolitical vacuum in the region. The East Slavs splintered into a number of independent and competing principalities. Due to military conquest and dynastic marriages, the West Ruthenian (Belarusian) principalities were acquired by the expanding Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, beginning with the rule of Lithuanian King Mindaugas
Mindaugas (german: Myndowen, la, Mindowe, orv, Мендог, be, Міндоўг, pl, Mendog, c. 1203–1263) is the first known Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only crowned King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or ...
(1240–1263). From the 13th to 15th century, Ruthenian principalities were either conquered or willingly joined Grand Duchy of Lithuania, with its initial capital unknown, but which presumably could have been Voruta
Voruta may have been the capital city of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Lithuania during the reign of king Mindaugas in the 13th century. Voruta is mentioned briefly in a written source only once and its exact location is unknown ...
. Beginning in the 14th century, Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
was the only official capital of the state.
The Lithuanians' smaller numbers in this medieval state gave the Ruthenians (present-day Belarusians and Ukrainians) an important role in the everyday cultural life of the state. Owing to the prevalence of East Slavs and the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
faith among the population in eastern and southern regions of the state, the Ruthenian language was a widely used colloquial language.
An East Slavic variety (''rus'ka mova'', ''Old Belarusian'' or ''West Russian Chancellery language''), gradually influenced by Polish, was the language of administration in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from at least Vytautas
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
' reign until the late 17th century when it was replaced by Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
.
This period of political breakdown and reorganization also saw the rise of written local vernaculars in place of the literary and liturgical Church Slavonic language, a further stage in the evolving differentiation between the Belarusian, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
and Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
languages.
Several Lithuanian monarchs — the last being Švitrigaila
Švitrigaila (before 1370 – 10 February 1452; sometimes spelled Svidrigiello) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1430 to 1432. He spent most of his life in largely unsuccessful dynastic struggles against his cousins Vytautas and Sigismund K� ...
in 1432–36 — relied on the Eastern Orthodox Ruthenian majority, while most monarchs and magnates increasingly came to reflect the opinions of the Roman Catholics.
Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest c ...
in 1480. On the other hand, further unification of the mostly Orthodox Grand Duchy with mostly Catholic Poland led to liberalization and a partial solving of the religious problem. In 1511, King and Grand Duke Sigismund I the Old granted the Orthodox clergy an autonomy previously enjoyed only by Catholic clergy. The privilege was enhanced in 1531, when the Orthodox church was no longer responsible to the Catholic bishop and instead the metropolitan was responsible only to the '' sobor'' of eight Orthodox bishops, the Grand Duke and the Patriarch of Constantinople. The privilege also extended the jurisdiction of the Orthodox hierarchy over all Orthodox people.
In such circumstances, a vibrant Ruthenian culture flourished, mostly in the major cities of present-day Belarus.
Despite the legal usage of the Old Ruthenian language (the predecessor of both modern Belarusian and Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
languages), which was used as a chancellery language in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, literature was mostly non-existent, apart from several chronicles. The first Belarusian book printed with the first printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
in the Cyrillic alphabet was published in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
in 1517 by Francysk Skaryna
Francysk Skaryna (alternative transcriptions of his name: ''Francišak Skaryna'' or ''Francisk Skaryna''; lat, Franciscus Scorina, be, Францыск (Францішак) Скарына ; pl, Franciszek Skaryna, cs, František Skorina; ...
, a leading representative of Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
Belarusian culture. Soon afterwards he founded a similar printing press in Polatsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
and started an extensive undertaking of publishing the Bible and other religious works there. Apart from the Bible itself, before his death in 1551 he published 22 other books, thus laying the foundations for the evolution of the Ruthenian language into the modern Belarusian language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some p ...
.
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
as an influential player in European politics and the largest multinational state in Europe. While Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Podlaskie
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest ci ...
became subjects to the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
, present-day Belarus territory was still regarded as part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
. The new polity was dominated by densely populated Poland, which had 134 representatives in the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
as compared to 46 representatives from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. However the Grand Duchy of Lithuania retained much autonomy, and was governed by a separate code of laws called the Lithuanian Statutes
The Statutes of Lithuania, originally known as the Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, were a 16th-century codification of all the legislation of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and its successor, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Stat ...
, which codified both civil and property rights. Mogilyov
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
was the largest urban centre of the territory of present-day Belarus, followed by Vitebsk, Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
, Pinsk
Pinsk ( be, Пі́нск; russian: Пи́нск ; Polish: Pińsk; ) is a city located in the Brest Region of Belarus, in the Polesia region, at the confluence of the Pina River and the Pripyat River. The region was known as the Marsh of Pinsk ...
, Slutsk
Slutsk ( officially transliterated as Sluck, be, Слуцк; russian: Слуцк; pl, Słuck, lt, Sluckas, Yiddish/Hebrew: סלוצק ''Slutsk'') is a city in Belarus, located on the Sluch River south of Minsk. As of 2022, its population i ...
, and Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
* Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
* Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
** Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Br ...
, whose population exceeded 10,000. In addition, Vilna (Vilnius), the capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, also had a significant Ruthenian population.
With time, the ethnic pattern did not evolve much. Throughout their existence as a separate culture, Ruthenians formed in most cases rural population, with the power held by local szlachta and boyars, often of Lithuanian, Polish or Russian descent. By this time, a significant Jewish presence had also formed in this region of German Jews
The history of the Jews in Germany goes back at least to the year 321, and continued through the Early Middle Ages (5th to 10th centuries CE) and High Middle Ages (''circa'' 1000–1299 CE) when Jewish immigrants founded the Ashkenazi Jewish ...
fleeing persecution from the Northern and Baltic Crusaders. Since the Union of Horodlo
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
of 1413, local nobility was assimilated into the traditional clan system by means of the formal procedure of adoption by the '' szlachta'' (Polish gentry
Gentry (from Old French ''genterie'', from ''gentil'', "high-born, noble") are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past.
Word similar to gentle imple and decentfamilies
''Gentry'', in its widest c ...
). Eventually it formed a significant part of the szlachta. Initially mostly Ruthenian and Orthodox, with time most of them became polonized
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
. This was especially true for major magnate families (Sapieha
The House of Sapieha (; be, Сапега, ''Sapieha''; lt, Sapiega) is a Polish-Lithuanian noble and magnate family of Lithuanian and Ruthenian origin,Энцыклапедыя ВКЛ. Т.2, арт. "Сапегі" descending from the med ...
and Radziwiłł clans being the most notable), whose personal fortunes and properties often surpassed those of the royal families and were huge enough to be called a state within a state. Many of them founded their own cities and settled them with settlers from other parts of Europe. Indeed, there were Scots, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and Dutch people
The Dutch ( Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aru ...
inhabiting major towns of the area, as well as several Italian artists who had been "imported" to the lands of modern Belarus by the magnates. Contrary to Poland, in the lands of the Grand Duchy, the peasants had little personal freedom in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. However, with time, the magnates and the gentry gradually limited the few liberties of the serfs, at the same time increasing their taxation, often in labour for the local gentry. This made many Ruthenians flee to the scarcely populated lands, ''Dzikie Pola'' (Wild Fields), the Polish name of the Zaporizhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich ( ua, Запорозька Січ, ; also uk, Вольностi Вiйська Запорозького Низового, ; Free lands of the Zaporozhian Host the Lower) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of C ...
, where they formed a large part of the Cossacks. Others sought refuge in the lands of other magnates or in Russia.
 Also, with time the religious conflicts started to arise. The gentry with time started to adopt
Also, with time the religious conflicts started to arise. The gentry with time started to adopt Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
while the common people by large remained faithful to Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
. Initially the Warsaw Compact of 1573 codified the preexisting freedom of worship
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedo ...
. However, the rule of an ultra-Catholic King Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
was marked by numerous attempts to spread the Catholicism, mostly through his support for counterreformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
and the Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
. Possibly to avoid such conflicts, in 1595 the Orthodox hierarchs of Kiev signed the Union of Brest
The Union of Brest (; ; ; ) was the 1595–96 decision of the Ruthenian Orthodox Church eparchies (dioceses) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth to break relations with the Eastern Orthodox Church and to enter into communion with, and place i ...
, breaking their links with the Patriarch of Constantinople and placing themselves under the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
. Although the union was generally supported by most local Orthodox bishops and the king himself, it was opposed by some prominent nobles and, more importantly, by the nascent Cossack movement. This led to a series of conflicts and rebellions against the local authorities. The first of such happened in 1595, when the Cossack insurgents under Severyn Nalivaiko took the towns of Slutsk
Slutsk ( officially transliterated as Sluck, be, Слуцк; russian: Слуцк; pl, Słuck, lt, Sluckas, Yiddish/Hebrew: סלוצק ''Slutsk'') is a city in Belarus, located on the Sluch River south of Minsk. As of 2022, its population i ...
and Mogilyov
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
and executed Polish magistrates there. Other such clashes took place in Mogilyov
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
(1606–10), Vitebsk (1623), and Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
(1623, 1633). This left the population of the Grand Duchy divided between Greek Catholic The term Greek Catholic Church can refer to a number of Eastern Catholic Churches following the Byzantine (Greek) liturgy, considered collectively or individually.
The terms Greek Catholic, Greek Catholic church or Byzantine Catholic, Byzantine Ca ...
and Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
parts. At the same time, after the schism in the Orthodox Church (Raskol
The Schism of the Russian Church, also known as Raskol (russian: раскол, , meaning "split" or "schism"), was the splitting of the Russian Orthodox Church into an official church and the Old Believers movement in the mid-17th century. It ...
), some Old Believers migrated west, seeking refuge in the Rzeczpospolita, which allowed them to freely practice their faith. Jerzy Czajewski, ''Zbiegostwo ludności Rosji w granice Rzeczypospolitej'' (Russian population exodus into the Rzeczpospolita), Promemoria journal, October 2004 nr. (5/15), ISSN 1509-9091Table of Contents online
From 1569, the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
suffered a series of Tatar raids, the goal of which was to loot, pillage and capture slaves into jasyr
Slavery in the Ottoman Empire was a lawful institution and a significant part of the Ottoman Empire's economy and traditional society. The main sources of slaves were wars and politically organized enslavement expeditions in the Caucasus, Easte ...
. The borderland area to the south-east was in a state of semi-permanent warfare until the 18th century. Some researchers estimate that altogether more than 3 million people, predominantly Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
but also Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Belarusians and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
, were captured and enslaved during the time of the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
.
 Despite the abovementioned conflicts, the literary tradition of Belarus evolved. Until the 17th century, the Ruthenian language, the predecessor of modern Belarusian, was used in Grand Duchy as a ''chancery language'', that is the language used for official documents. Afterwards, it was replaced with the
Despite the abovementioned conflicts, the literary tradition of Belarus evolved. Until the 17th century, the Ruthenian language, the predecessor of modern Belarusian, was used in Grand Duchy as a ''chancery language'', that is the language used for official documents. Afterwards, it was replaced with the Polish language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In a ...
, commonly spoken by the upper classes of Belarusian society. Both Polish and Ruthenian cultures gained a major cultural centre with the foundation of the Academy of Vilna. At the same time the Belarusian lands entered a path of economic growth, with the formation of numerous towns that served as centres of trade on the east–west routes.
However, both economic and cultural growth came to an end in mid-17th century with a series of violent wars against Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
, Sweden, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
and Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, as well as internal conflicts, known collectively as The Deluge
The Genesis flood narrative (chapters 6–9 of the Book of Genesis) is the Hebrew version of the universal flood myth. It tells of God's decision to return the universe to its pre- creation state of watery chaos and remake it through the microc ...
. The misfortunes were started in 1648 by Bohdan Chmielnicki, who started a large-scale Cossack uprising in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Although the Cossacks were defeated in 1651 in the battle of Beresteczko
The Battle of Berestechko ( pl, Bitwa pod Beresteczkiem; uk, Берестецька битва, Битва під Берестечком) was fought between the Ukrainian Cossacks, led by Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky, aided by their Crimean Ta ...
, Khmelnytsky sought help from Russian tsar, and by the Treaty of Pereyaslav
The Pereiaslav AgreementPereyaslav Agreement
Russia dominated and partially occupied the eastern lands of the Commonwealth since 1655. The Swedes invaded and occupied the rest in the same year. The wars had shown internal problems of the state, with some people of the Grand Duchy supporting Russia while others (most notably Janusz Radziwiłł) supporting the Swedes. Although the Swedes were finally driven back in 1657 and the Russians were defeated in 1662, most of the country was ruined. It is estimated that the Commonwealth lost a third of its population, with some regions of Belarus losing as much as 50%. This broke the power of the once-powerful Commonwealth and the country gradually became vulnerable to foreign influence.
Subsequent wars in the area (Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
and the War of Polish succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their ...
) damaged its economy even further. In addition, Russian armies raided the Commonwealth under the pretext of the returning of fugitive peasants. By mid-18th century their presence in the lands of modern Belarus became almost permanent.
The last attempt to save the Commonwealth's independence was a Polish–Belarusian–Lithuanian national uprising of 1794 led by Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko ( be, Andréj Tadévuš Banavientúra Kasciúška, en, Andrew Thaddeus Bonaventure Kosciuszko; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish military engineer, statesman, and military leader who ...
, however it was eventually quenched.
Eventually by 1795 Poland was partitioned by its neighbors. Thus a new period in Belarusian history started, with all its lands annexed by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, in a continuing endeavor of Russian tsars of "gathering the Rus lands" started after the liberation from the Tatar yoke
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, destroying numerous southern cities, including the largest cities, Kiev (50,000 inhabitants) and Chernihiv (30,000 inhabitants), with the only major cities escaping destr ...
by Grand Duke Ivan III of Russia
Ivan III Vasilyevich (russian: Иван III Васильевич; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was a Grand Prince of Moscow and Grand Prince of all Rus'. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his blin ...
.
Russian Empire
 Under Russian administration, the territory of Belarus was divided into the '' guberniyas'' of
Under Russian administration, the territory of Belarus was divided into the '' guberniyas'' of Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest c ...
, Mogilyov
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
, and Hrodno. Belarusians were active in the guerrilla movement against Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's occupation.. With Napoleon's defeat, Belarus again became a part of Imperial Russia and its ''guberniyas'' constituted part of the Northwestern Krai. The anti-Russian uprisings of the gentryŻytko, Anatol (1999) ''Russian policy towards the Belarussian gentry in 1861–1914'', Minsk, p. 551. in 1830 and 1863
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Abraham Lincoln signs the Emancipation Proclamation during the third year of the American Civil War, making the abolition of slavery in the Confederate states an official war goal. It proclaim ...
were subdued by government forces.
Although under Nicholas I and Alexander III the national cultures were repressed due to the policies of de-Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
and Russification, which included the return to Orthodoxy, the 19th century signifies the rise of the modern Belarusian nation and self-confidence. A number of authors started publishing in the Belarusian language, including Jan Czeczot
Jan Czeczot of Ostoja ( be, Ян Чачот, ''Jan Čačot,'' lt, Jonas Čečiotas, 1796–1847) was a Polish romantic poet and ethnographer. Fascinated by the folklore and the traditional folk songs of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania, a c ...
, Władysław Syrokomla
Ludwik Władysław Franciszek Kondratowicz (29 September 1823 – 15 September 1862), better known as Władysław Syrokomla, was a Polish romantic poet, writer and translator working in Vilnius and Vilna Governorate, then Russian Empire.
Biogr ...
and Konstanty Kalinowski. In 1862-1863 Kalinowski published first newspaper in modern Belarusian language, ''Mużyckaja prauda
''Mużyckaja prauda'' (''Peasants' Truth'' or ''Folk's Truth'') was the first Belarusian language newspaper printed in 1862-1863 by a collective led by a revolutionary Kastuś Kalinoŭski in the Belarusian Latin alphabet in a form of letters. Se ...
'' (''Peasants' Truth''), in a Latin script.
In a Russification drive in the 1840s, Nicholas I forbade the use of the term ''Belarusia'' and renamed the region the "North-Western Territory". He also prohibited the use of Belarusian language in public schools, campaigned against Belarusian publications and tried to pressure those who had converted to Catholicism under the Poles to reconvert to the Orthodox faith. In 1863, economic and cultural pressure exploded into a revolt, led by Kalinowski. After the failed revolt, the Russian government reintroduced the use of Cyrillic to Belarusian in 1864 and banned the use of the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and th ...
.
In the second half of the 19th century, the Belarusian economy, like that of the entire Europe, was experiencing significant growth due to the spread of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
to Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, particularly after the emancipation of the serfs
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
in 1861. Peasants sought a better lot in foreign industrial centres, with some 1.5 million people leaving Belarus in the half-century preceding the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
.
20th century
BNR and LBSSR

World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
was the short period when Belarusian culture
The culture of Belarus is the product of a millennium of development under the impact of a number of diverse factors. These include the physical environment; the ethnographic background of Belarusians (the merger of Slavic newcomers with Baltic ...
started to flourish. German administration allowed schools with Belarusian language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some p ...
, previously banned in Russia; a number of Belarusian schools were created until 1919 when they were banned again by the Polish military administration. At the end of World War I, when Belarus was still occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
by Germans, according to the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
, the short-lived People's Republic of Belarus was pronounced on 25 March 1918, as part of the German Mitteleuropa
(), meaning Middle Europe, is one of the German terms for Central Europe. The term has acquired diverse cultural, political and historical connotations. University of Warsaw, Johnson, Lonnie (1996) ''Central Europe: Enemies, Neighbors, Friends'p ...
plan.
In December 1918, Mitteleuropa was obsolete as the German Empire withdrew from the Ober-Ost territory, and for the next few years in the newly created power vacuum
In political science and political history, the term power vacuum, also known as a power void, is an analogy between a physical vacuum to the political condition "when someone in a place of power, has lost control of something and no one has repla ...
the territories of Belarus would witness the struggle of various national and foreign factions. On 3 December 1918 the Germans withdrew from Minsk. On 10 December 1918 Soviet troops occupied Minsk. The Rada (Council) of the People's Republic of Belarus went into exile, first to Kaunas, then to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and finally to Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
. On 2 January 1919, the Soviet Socialist Republic of Byelorussia
The Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia or Soviet Socialist Republic of Belarus (SSRB; be, Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка Беларусь, Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika Biełaruś; russian: � ...
was declared. On 17 February 1919 it was disbanded. Part of it was included into Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
, and part was joined to the Lithuanian SSR
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; lt, Lietuvos Tarybų Socialistinė Respublika; russian: Литовская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Litovskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialistiche ...
to form the LBSSR, Lithuanian–Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, informally known as ''Litbel'', whose capital was Vilnius. While Belarus National Republic faced off with Litbel, foreign powers were preparing to reclaim what they saw as their territories: Polish forces were moving from the West, and Russians from the East. When Vilnius was captured by Polish forces on 17 April 1919, the capital of the Soviet puppet state Litbel was moved to Minsk. On 17 July 1919 Lenin dissolved Litbel because of the pressure of Polish forces advancing from the West. Polish troops captured Minsk on 8 August 1919.
Republic of Central Lithuania
TheRepublic of Central Lithuania
The Republic of Central Lithuania ( pl, Republika Litwy Środkowej, ), commonly known as the Central Lithuania, and the Middle Lithuania ( pl, Litwa Środkowa, , be, Сярэдняя Літва, translit=Siaredniaja Litva), was an unrecognize ...
was a short-lived political entity, which was the last attempt to restore Lithuania in the historical confederacy state (it was also supposed to create Lithuania Upper and Lithuania Lower). The republic was created in 1920 following the staged rebellion of soldiers of the 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division of the Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stre ...
under Lucjan Żeligowski. Centered on the historical capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, Vilna
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
( lt, Vilnius, pl, Wilno), for 18 months the entity served as a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
between Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, upon which it depended, and Lithuania, which claimed the area. After a variety of delays, a disputed election took place on 8 January 1922, and the territory was annexed to Poland. Żeligowski later in his memoir which was published in London in 1943 condemned the annexation of Republic by Poland, as well as the policy of closing Belarusian schools and general disregard of Marshal Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
's confederation plans by Polish ally.
Belarusian Soviet Republic and West Belarus
Some time in 1918 or 1919,Sergiusz Piasecki
Sergiusz Piasecki (; 1901 in Lachowicze near Baranowicze – 1964 in Penley, London) was one of the best known Belarusian-Polish writers of the mid 20th century. He was mainly portraying life of criminals and lowlifes of Minsk, which he knew ...
returned to Belarus, joining Belarusian anti-Soviet units, the "Green Oak" (in Polish, ''Zielony Dąb''), led by Ataman Wiaczesław Adamowicz (pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individua ...
: J. Dziergacz). When on 8 August 1919, the Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stre ...
captured Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, Adamowicz decided to work with them. Thus Belarusian units were created, and Piasecki was transferred to a Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
school of infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
cadets. In the summer of 1920, during the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
, Piasecki fought in the Battle of Radzymin.
The frontiers between Poland, which had established an independent government after World War I, and the former Russian Empire were not recognized by the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
. Poland's Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
, who envisioned the formation of an Intermarium
Intermarium ( pl, Międzymorze, ) was a post-World War I geopolitical plan conceived by Józef Piłsudski to unite former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth lands within a single polity. The plan went through several iterations, some of which antic ...
federation as a Central and East European bloc that would be a bulwark against Germany to the west and Russia to the east, carried out a Kiev Offensive into Ukraine in 1920. This met with a Red Army counter-offensive that drove into Polish territory almost to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Minsk itself was re-captured by the Soviet Red Army on 11 July 1920 and a new Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic was declared on 31 July 1920. Piłsudski, however, halted the Soviet advance at the Battle of Warsaw and resumed his eastward offensive. Finally the Treaty of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet War.
...
, ending the Polish–Soviet War, divided Belarus between Poland and Soviet Russia. Over the next two years, the People's Republic of Belarus prepared a national uprising, ceasing the preparations only when the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
recognized the Soviet Union's western borders on 15 March 1923. The Soviets terrorised Western Belarus, the most radical case being Soviet raid on Stołpce Soviet raid on Stołpce refers to the events of the night of August 3/4, 1924, when a group of 150 Soviet agents, commanded by Lieutenant Boryshkevich, raided the town of Stołpce (now Stowbtsy, Belarus), which back then was a railroad border cross ...
. Poland created Border Protection Corps
The Border Protection Corps ( pl, Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza, KOP) was a military formation of the Second Polish Republic that was created in 1924 to defend the country's eastern borders against armed Soviet incursions and local bandits. Other b ...
in 1924.
 The Polish part of Belarus was subject to
The Polish part of Belarus was subject to Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
policies (especially in the 1930s), while the Soviet Belarus was one of the original republics which formed the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. For several years, the national culture and language enjoyed a significant boost of revival in the Soviet Belarus. A Polish Autonomous District
Polish National Districts (called in Russian "полрайоны", ''polrajony'', an abbreviation for "польские национальные районы", "Polish national raions") were in the interbellum period possessing some form of a na ...
was also formed. This was however soon ended during the Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secret ...
, when almost all prominent Belarusian national intelligentsia were executed, many of them buried in Kurapaty
Kurapaty ( be, Курапаты, ) is a wooded area on the outskirts of Minsk, Belarus, in which a vast number of people were executed between 1937 and 1941 during the Great Purge by the Soviet secret police, the NKVD.
The exact count of victi ...
. Thousands were deported to Asia. As the result of Polish operation of the NKVD
The ''Polish Operation'' of the NKVD (Soviet security service) in 1937–1938 was an anti-Polish mass-ethnic cleansing operation of the NKVD carried out in the Soviet Union against Poles (labeled by the Soviets as "agents") during the period of ...
tens of thousands people of many nationalities were killed. Belarusian orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
was Russified
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
in 1933 and use of Belarusian language was discouraged as exhibiting anti-soviet attitude.Janowicz, Sokrat (1999). ''Forming of the Belarussian nation''. RYTM. pp. 247–248.
In West Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus ( be, Заходняя Беларусь, translit=Zachodniaja Bielaruś; pl, Zachodnia Białoruś; russian: Западная Белоруссия, translit=Zapadnaya Belorussiya) is a historical region of mod ...
, up to 30,000 families of Polish veteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that h ...
s (''osadnik
Osadniks ( pl, osadnik/osadnicy, "settler/settlers, colonist/colonists") were veterans of the Polish Army and civilians who were given or sold state land in the ''Kresy'' (current Western Belarus and Western Ukraine) territory ceded to Poland by P ...
s'') were settled in the lands formerly belonging to the Russian tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
family and Russian aristocracy. Belarusian representation in Polish parliament
The parliament of Poland is the bicameral legislature of Poland. It is composed of an upper house (the Senate) and a lower house (the Sejm). Both houses are accommodated in the ''Sejm'' complex in Warsaw. The Constitution of Poland does not ...
was reduced as a result of the 1930 elections. Since the early 1930s, the Polish government introduced a set of policies designed to Polonize all minorities (Belarusians, Ukrainians, Jews, etc.). The usage of Belarusian language was discouraged and the Belarusian schools were facing severe financial problems. In spring of 1939, there already was neither single Belarusian official organisation in Poland nor a single exclusively Belarusian school (with only 44 schools teaching Belarusian language left).
Belarus in World War II

 When the Soviet Union invaded Poland on September 17, 1939, following the terms of the
When the Soviet Union invaded Poland on September 17, 1939, following the terms of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
's secret protocol, Western Byelorussia, which was part of Poland, is included in the BSSR. Similarly to the times of German occupation during World War I, Belarusian language and Soviet culture enjoyed relative prosperity in this short period. Already in October 1940, over 75% of schools used the Belarusian language, also in the regions where no Belarus people lived, e.g. around Łomża
Łomża (), in English known as Lomza, is a city in north-eastern Poland, approximately 150 kilometers (90 miles) to the north-east of Warsaw and west of Białystok. It is situated alongside the Narew river as part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship ...
, what was Ruthenization. Western Belarus was sovietised, tens of thousands were imprisoned, deported, murdered. The victims were mostly Polish and Jewish.
After twenty months of Soviet rule, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and its Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
allies invaded the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941. Soviet authorities immediately evacuated about 20% of the population of Belarus, killed thousands of prisoners and destroyed all the food supplies. The country suffered particularly heavily during the fighting and the German occupation. Minsk was captured by the Germans on 28 June 1941. Following bloody encirclement battles, all of the present-day Belarus territory was occupied by the Germans by the end of August 1941.
During World War II, the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
attempted to establish a puppet Belarusian government, Belarusian Central Rada
The Belarusian Central Council ( be, Беларуская цэнтральная рада, in lacinka: Biełaruskaja centralnaja rada; german: Weißruthenischer Zentralrat) was a puppet administrative body in German-occupied Belarus during World ...
, with the symbolics similar to BNR. In reality, however, the Germans imposed a brutal racist regime, burning down some 9,000 Belarusian villages, deporting some 380,000 people for slave labour, and killing hundreds of thousands of civilians more. Local police took part in many of those crimes. Almost the whole, previously very numerous, Jewish populations of Belarus that did not evacuate were killed. One of the first uprisings of a Jewish ghetto
A ghetto, often called ''the'' ghetto, is a part of a city in which members of a minority group live, especially as a result of political, social, legal, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished t ...
against the Nazis occurred in 1942 in Belarus, in the small town of Lakhva
Lakhva (or Lachva, Lachwa; Belarusian and Russian: Лахва, pl, Łachwa, yi, לאַכװע, Lakhve) is a small town in southern Belarus, with a population of approximately 2,100. Lakhva is considered to have been the location of one of the fi ...
.
Since the early days of the occupation, a powerful and increasingly well-coordinated Belarusian resistance movement
Belarusian resistance movement are the resistance movements on the territory of contemporary Belarus. Wars in the area - Great Northern War and the War of the Polish Succession - damaged its economy further. In addition, Russian armies raided the P ...
emerged. Hiding in the woods and swamps, the partisans inflicted heavy damage to German supply lines and communications, disrupting railway tracks, bridges, telegraph wires, attacking supply depots, fuel dumps and transports and ambushing German soldiers. Not all anti-German partisans were pro-Soviet. In the largest partisan sabotage action of the entire Second World War, the so-called Asipovichy
Asipovichy ( be, Асiповiчы; Łacinka: Asipovičy, pl, Osipowicze) or Osipovichi (russian: Осипо́вичи) is a town in Mahilyow Oblast, Belarus, located 136 km southwest of Mahilyow, 3 km south of the Minsk-Homyel expresswa ...
diversion of 30 July 1943 four German trains with supplies and Tiger tank Tiger tank may refer to:
*Tiger I, or ''Panzerkampfwagen'' Tiger ''Ausf. E'', a German heavy tank produced from 1942 to 1944
*Tiger II, or ''Panzerkampfwagen'' Tiger ''Ausf. B'', a German heavy tank produced from 1943 to 1945, also known as ''Kön ...
s were destroyed. To fight partisan activity, the Germans had to withdraw considerable forces behind their front line. On 22 June 1944 the huge Soviet offensive Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration (; russian: Операция Багратио́н, Operatsiya Bagration) was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (russian: Белорусская наступательная оп ...
was launched, Minsk was re-captured on 3 July 1944, and all of Belarus was regained by the end of August. Hundred thousand of Poles were expelled after 1944. As part of the Nazis' effort to combat the enormous Belarusian resistance during World War II
The Belarusian resistance during World War II opposed Nazi Germany from 1941 until 1944. Belarus was one of the Soviet republics occupied during Operation Barbarossa. The term Belarusian partisans may refer to Soviet-formed irregular milita ...
, special units of local collaborationists were trained by the SS's Otto Skorzeny
Otto Johann Anton Skorzeny (12 June 1908 – 5 July 1975) was an Austrian-born German SS-''Obersturmbannführer'' (lieutenant colonel) in the Waffen-SS during World War II. During the war, he was involved in a number of operations, including th ...
to infiltrate the Soviet rear. In 1944 thirty Belarusians (known as Čorny Kot (''Black Cat'') and personally led by Michał Vituška) were airdrop
An airdrop is a type of airlift in which items including weapons, equipment, humanitarian aid or leaflets are delivered by military or civilian aircraft without their landing. Developed during World War II to resupply otherwise inaccessible tr ...
ped by the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
behind the lines of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
, which had already liberated Belarus during Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration (; russian: Операция Багратио́н, Operatsiya Bagration) was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (russian: Белорусская наступательная оп ...
. They experienced some initial success due to disorganization in the rear of the Red Army, and some other German-trained Belarusian nationalist units also slipped through the Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest; lt, Baltvyžių giria; pl, Puszcza Białowieska ; russian: Беловежская пуща, Belovezhskaya Pushcha is a forest on the border between Belarus and Poland. It is one of the last and largest remaining pa ...
in 1945. The NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
, however, had already infiltrated these units. Vituška himself was hunted down, captured and executed, although he continued to live on in Belarusian nationalist hagiography.
In total, Belarus lost a quarter of its pre-war population in World War II including practically all its intellectual elite. About 9,200 villages and 1.2 million houses were destroyed. The major towns of Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
and Vitsebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
lost over 80% of their buildings and city infrastructure. For the defence against the Germans, and the tenacity during the German occupation, the capital Minsk was awarded the title '' Hero City'' after the war. The fortress of Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
* Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
* Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
** Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Br ...
was awarded the title ''Hero-Fortress
Hero Fortress ( Russian: крепость-герой, ''krepost'-geroy'') is the honorary title awarded in 1965 to the Soviet Brest Fortress in Brest, Belarus, (previously part of the Byelorussian SSR) for the defence of the frontier stronghold du ...
''.
BSSR from 1945 to 1990
After the end of War in 1945, Belarus became one of the founding members of theUnited Nations Organisation
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
. Joining Belarus was the Soviet Union itself and another republic Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. In exchange for Belarus and Ukraine joining the UN, the United States had the right to seek two more votes, a right that has never been exercised.
 More than 200,000 ethnic Poles left or were expelled to Poland in late 1940s and late 1950s, some killed by the
More than 200,000 ethnic Poles left or were expelled to Poland in late 1940s and late 1950s, some killed by the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
or deported to Siberia. Armia Krajowa and post-AK resistance was the strongest in the Hrodna
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
, Vaŭkavysk
Vawkavysk ( be, Ваўкавы́ск, ; russian: Волковы́ск; pl, Wołkowysk; lt, Valkaviskas; yi, וואלקאוויסק; Names of European cities in different languages: U-Z#V, names in other languages) is one of the oldest towns in ...
, Lida
Lida ( be, Лі́да ; russian: Ли́да ; lt, Lyda; lv, Ļida; pl, Lida ; yi, לידע, Lyde) is a city 168 km (104 mi) west of Minsk in western Belarus in Grodno Region.
Etymology
The name ''Lida'' arises from its Lithuan ...
and Ščučyn regions.
The Belarusian economy was completely devastated by the events of the war. Most of the industry, including whole production plants were removed either to Russia or Germany. Industrial production of Belarus in 1945 amounted for less than 20% of its pre-war size. Most of the factories evacuated to Russia, with several spectacular exceptions, were not returned to Belarus after 1945. During the immediate postwar period, the Soviet Union first rebuilt and then expanded the BSSR's economy, with control always exerted exclusively from Moscow. During this time, Belarus became a major center of manufacturing in the western region of the USSR. Huge industrial objects like the BelAZ
BelAZ ( be, Беларускі аўтамабільны завод, translit=Belaruski autamabilny zavod, lit=Belarusian Automobile Plant, russian: Белорусский автомобильный завод or БелАЗ) is a Belarusian aut ...
, MAZ
Maz or MAZ may refer to:
* IATA code for Eugenio María de Hostos Airport, Mayagüez, Puerto Rico
* Minsk Automobile Plant, abbreviated in Belarusian as MAZ
* Myc-associated zinc finger protein, a protein encoded by the ''MAZ'' gene
* Maz, a vill ...
, and the Minsk Tractor Plant were built in the country. The increase in jobs resulted in a huge immigrant population of Russians in Belarus. Russian became the official language of administration and the peasant class, which traditionally was the base for Belarusian nation, ceased to exist.
On 26 April 1986, the Chernobyl disaster occurred at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (ChNPP; ; ), is a nuclear power plant undergoing decommissioning. ChNPP is located near the abandoned city of Pripyat in northern Ukraine northwest of the city of Chernobyl, from the Belarus–Ukraine borde ...
in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
situated close to the border with Belarus. It is regarded as the worst nuclear accident
A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility. Examples include lethal effects to individuals, lar ...
in the history of nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
. It produced a plume of radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
debris that drifted over parts of the western Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, and Scandinavia. Large areas of Belarus, Ukraine and Russia were contaminated, resulting in the evacuation and resettlement of roughly 200,000 people. About 60% of the radioactive fallout landed in Belarus. The effects of the Chernobyl accident in Belarus were dramatic: about 50,000 km2 (or about a quarter of the territory of Belarus) formerly populated by 2.2 million people (or a fifth of the Belarusian population) now require permanent radioactive monitoring (after receiving doses over 37 kBq/m2 of caesium-137). 135,000 persons were permanently resettled and many more were resettled temporarily. After 10 years since the accident, the occurrences of thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. C ...
among children increased fifteenfold (the sharp rise started in about four years after the accident).
Republic of Belarus
Pre-Alexander Lukashenko period
 On 27 July 1990, Belarus declared its national sovereignty, a key step toward independence from the Soviet Union. Around that time,
On 27 July 1990, Belarus declared its national sovereignty, a key step toward independence from the Soviet Union. Around that time, Stanislau Shushkevich
Stanislav Stanislavovich Shushkevich ( be, Станісла́ў Станісла́вавіч Шушке́віч, translit=Stanisłáŭ Stanisłávavič Šuškiévič,; russian: Станисла́в Станисла́вович Шушке́вич; ...
became the chairman of the Supreme Soviet of Belarus, the top leadership position in Belarus.
On 25 August 1991, after the failure of the August coup
August is the eighth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars, and the fifth of seven months to have a length of 31 days. Its zodiac sign is Leo and was originally named ''Sextilis'' in Latin because it was the 6th month in ...
in Moscow, Belarus declared full independence from the USSR by granting the declaration of state sovereignty a constitutional status that it did not have before. On 8 December 1991, Shushkevich met with Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
of Russia and Leonid Kravchuk
Leonid Makarovych Kravchuk ( uk, Леонід Макарович Кравчук; 10 January 1934 – 10 May 2022) was a Ukrainian politician and the first president of Ukraine, serving from 5 December 1991 until 19 July 1994. In 1992, he signed ...
of Ukraine, in Belavezhskaya Pushcha, to formally declare the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
.
Alexander Lukashenko period
 A new Belarusian constitution enacted in early 1994 paved the way for the first democratic presidential election on 23 June and 10 July.
A new Belarusian constitution enacted in early 1994 paved the way for the first democratic presidential election on 23 June and 10 July. Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (as transliterated from Russian; also transliterated from Belarusian as Alyaksand(a)r Ryhoravich Lukashenka;, ; rus, Александр Григорьевич Лукашенко, Aleksandr Grigoryevich Luk ...
was elected president of Belarus. Having assumed the rights and responsibilities of the Soviet Union on the territory of Byelarus, in December 1994 Lukashenko signed the Budapest Memorandum
The Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances comprises three substantially identical political agreements signed at the OSCE conference in Budapest, Hungary, on 5 December 1994, to provide security assurances by its signatories relating to the ...
along with the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
,
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
and the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
acting as guarantors and thereby denuclearized the nation.
The 1996 referendum resulted in amendments to the constitution that removed key powers from the parliament.
In 1999 opposition leaders Yury Zacharanka
Colonel Yury Zakharanka ( Belarusian: ''Юрый Захаранка'', Russian: ''Юрий Захаренко'', ''Yuri Zakharenko''; January 1, 1952 – 1999) was the Belarusian Minister of Internal Affairs and opposition politician abducted ...
and Viktar Hanchar
Viktar Hanchar, or Viktar Hančar ( be, Віктар Ганчар, russian: Виктор Гончар, Viktor Gonchar, September 7, 1957 – September 16, 1999?) was a Belarusian politician who disappeared and was presumably murdered in 1999. He w ...
disappeared
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person by a state or political organization, or by a third party with the authorization, support, or acquiescence of a state or political organi ...
and were presumably killed. In 2001, Lukashenko was re-elected* as president in elections described as undemocratic by Western observers. At the same time, the west began criticizing him as authoritarian. In 2006, Lukashenko was once again re-elected in presidential elections again criticized as flawed by most European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
countries.
In 2010, Lukashenko was re-elected once again in presidential elections which were again described as falsified by most EU countries and organizations such as the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
. A peaceful protest against the electoral flaws turned into a riot when demonstrators tried to storm a government building. The police used batons to quell the riot. Seven presidential candidates and hundreds of rioters were arrested by KGB
The KGB (russian: links=no, lit=Committee for State Security, Комитет государственной безопасности (КГБ), a=ru-KGB.ogg, p=kəmʲɪˈtʲet ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əj bʲɪzɐˈpasnəsʲtʲɪ, Komitet gosud ...
.
Lukashenko's disputed victory in the country's 2020 presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
**C ...
led to widespread allegations of vote rigging
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share of ...
, which strongly amplified anti-government protests, the largest during his rule. Protesters have faced violent persecution by the authorities. A statement by the United Nations Human Rights Office on 1 September cited more than 450 documented cases of torture and ill-treatment of detainees, as well as reports of sexual abuse and rape. Several protesters were killed. Following the contested election, Lukashenko is not recognized by the United Kingdom, the European Union, or the United States as the legitimate president of Belarus.Dave LawlerU.S. no longer recognizes Lukashenko as legitimate president of Belarus
''Axios'' (24 September 2020). On 23 May 2021,
Ryanair Flight 4978
Ryanair Flight 4978 was a regularly scheduled international passenger flight from Athens International Airport, Greece, to Vilnius Airport, Lithuania, operated by the Polish subsidiary Buzz. On 23 May 2021, while in Belarusian airspace, it was d ...
was diverted by the Belarusian government to Minsk National Airport, where two of its passengers, opposition activist and former editor-in-chief of the Telegram channel Nexta
Nexta (pronounced ''niekh-ta'', ) is a Belarusian media outlet that is primarily distributed through Telegram and YouTube channels. The YouTube channel was founded by then 17-year-old student Stsiapan Putsila. The channel's headquarters are loc ...
Roman Protasevich
Roman Dmitriyevich Protasevich (russian: Роман Дмитриевич Протасевич; born 5 May 1995), or Raman Dzmitryyevich Pratasyevich ( be, Раман Дзмітрыевіч Пратасевіч, translit=Raman Dzmitryjevič Prat ...
and his girlfriend Sofia Sapega, were arrested by authorities. In summer of the same year, Belarusian authorities organized the 2021–2022 Belarus–European Union border crisis consisting of an influx of tens of thousands of immigrants, primarily from Iraqi Kurdistan, to Lithuania, Latvia, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
via those countries' borders with Belarus.
Belarus allowed its territory to be used by Putin's army in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. ...
to stage and launch forces from the north into Ukraine.
On 25 June 2022 Putin announced that Russia would supply Belarus with nuclear-capable Iskander-M missile systems. Both conventional and nuclear versions of the missile would be provided to the Belarusians. Additionally, Putin said that he would facilitate the modifications necessary for the Belarusian fleet of Su-25 bombers to carry nuclear missiles. It was then noted that Lukashenko had purchased the month before some units of the S-400
The S-400 Triumf (russian: link=no, C-400 Триумф – Triumf; translation: Triumph; NATO reporting name: SA-21 Growler), previously known as the S-300 PMU-3, is a mobile, surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed in the 1990s by Russ ...
anti-aircraft and anti-missile system. At the same news conference Lukashenko talked of the "aggressive", "confrontational" and "repulsive" policies of Belarus' neighbours Poland and Lithuania.
On 9 July 2022 it was reported that a communiqué had been broadcast by the officers of the fifth brigade of the Special Forces of Belarus. They said they had "observed the most serious infringement of Clause One of the Constitution of Belarus
The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Канстытуцыя Рэспублікі Беларусь, russian: Конституция Республики Беларусь) is the ultimate law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed o ...
by Russia's highest political leadership. According to this Clause, the Republic of Belarus maintains supremacy and full authority on its own territory. It also enjoys independence over its internal and foreign politics."
See also
*History of the Jews in Belarus
The history of the Jews in Belarus begins as early as the 8th century. Jews lived in all parts of the lands of modern Belarus. Jews were the third largest ethnic group in the country in the first half of the 20th century. In 1897, the Jewish po ...
* History of Lithuania
The history of Lithuania dates back to settlements founded many thousands of years ago, but the first written record of the name for the country dates back to 1009 AD. Lithuanians, one of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands an ...
* History of Poland
The history of Poland spans over a thousand years, from medieval tribes, Christianization and monarchy; through Poland's Golden Age, expansionism and becoming one of the largest European powers; to its collapse and partitions, two world wars ...
* History of Russia
The history of Russia begins with the histories of the East Slavs. The traditional start-date of specifically Russian history is the establishment of the Rus' people, Rus' state in the north in 862, ruled by Varangians. Staraya Ladoga and Veli ...
* History of Ukraine
Prehistoric Ukraine, as a part of the Pontic steppe in Eastern Europe, played an important role in Eurasian cultural contacts, including the spread of the Chalcolithic, the Bronze Age, Indo-European migrations and the domestication of the hor ...
* List of people from Belarus
* List of Belarusian rulers
Belarusian statehood can be traced to the medieval Principality of Polotsk. From the 13th century, the lands of modern-day Belarus became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania which later evolved into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In the 19t ...
* Polish Autonomous District
Polish National Districts (called in Russian "полрайоны", ''polrajony'', an abbreviation for "польские национальные районы", "Polish national raions") were in the interbellum period possessing some form of a na ...
s: Dzierzynszczyzna, Marchlewszczyzna
* White Ruthenia
White Ruthenia ( cu, Бѣла Роусь, Bela Rous'; be, Белая Русь, Biełaja Ruś; pl, Ruś Biała; russian: Белая Русь, Belaya Rus'; ukr, Біла Русь, Bila Rus') alternatively known as Russia Alba, White Rus' or W ...
References
Further reading
* Baranova, Olga. "Nationalism, anti-Bolshevism or the will to survive? Collaboration in Belarus under the Nazi occupation of 1941–1944." ''European Review of History—Revue européenne d'histoire'' 15.2 (2008): 113–128. * Bekus, Nelly. ''Struggle over Identity: The Official and the Alternative “Belarussianness” ''(Budapest: Central European University Press, 2010); * Bemporad, Elissa. ''Becoming Soviet Jews: The Bolshevik Experiment in Minsk'' (Indiana UP, 2013). * Bennett, Brian M. ''The last dictatorship in Europe: Belarus under Lukashenko'' (Columbia University Press, 2011) * Defense Technical Information Center. ''Democratization and Instability in Ukraine, Georgia, and Belarus'' (2014online
* Defense Technical Information Center. ''The Role of Small States in the Post-Cold War Era: The Case of Belarus'' (2012
online
* Fedor, Helen, ''Belarus and Moldova: country studies'' (Library of Congress. Federal Research Division, 1995
online
with brief history pp 18–25. * Epstein, Barbara. ''The Minsk Ghetto 1941–1943: Jewish Resistance and Soviet Internationalism'' (U of California Press, 2008). * Guthier, Steven L. "The Belorussians: National identification and assimilation, 1897–1970: Part 1, 1897–1939." ''Soviet Studies'' 29.1 (1977): 37–61. * Horak, Stephan M. "Belorussia: Modernization, Human Rights, Nationalism." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers'' 16.3 (1974): 403–423. * Korosteleva, Elena A., Lawson Colin W. and Marsh, Rosalind J., eds. ''Contemporary Belarus'' (Routledge 2003) * Loftus, John J., 'The Belarus Secret'(Knopf, 1982) * Lubachko, Ivan S. ''Belorussia: Under Soviet Rule, 1917–1957'' (U Press of Kentucky, 2015). * Marples, David R. "Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia Under Soviet Occupation: The Development of Socialist Farming, 1939–1941." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers 27.2 (1985): 158–177
online
* Marples, David. Our Glorious Past': Lukashenka's Belarus and the Great Patriotic War'' (Columbia University Press, 2014) * * * * Rudling, Pers Anders. ''The Rise and Fall of Belarusian Nationalism, 1906–1931'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2014) 436 pages * * * Skinner, Barbara. (2012) ''The Western Front of the Eastern Church: Uniate and Orthodox Conflict in Eighteenth-Century Poland, Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia'' * Smilovitsky, Leonid. "Righteous Gentiles, the Partisans, and Jewish Survival in Belorussia, 1941–1944." ''Holocaust and Genocide Studies'' 11.3 (1997): 301-329. * Snyder, Timothy. (2004) ''The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999'
excerpt and text search
* Strategic Studies Institute. ''Political Trends in the New Eastern Europe – Ukraine and Belarus'' (2007
online
* Strużyńska, Nina. ''Anti-Soviet conspiracy and partisan struggle of the Green Oak Party in Belarus'', in ''Non Provincial Europe'', London 1999, * * Szporluk, Roman. "West Ukraine and West Belorussia: Historical tradition, social communication, and linguistic assimilation." ''Soviet Studies'' 31.1 (1979): 76-98
online
* Szporluk, Roman. "The press in Belorussia, 1955–65." ''Europe‐Asia Studies'' 18.4 (1967): 482–493. * * Urban, Michael E. ''An Algebra of Soviet Power: Elite Circulation in the Belorussian Republic 1966–86'' (Cambridge UP, 1989). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: the making of a nation: a case study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A bibliographical guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * * Wexler, Paul. "Belorussification, Russification and Polonization Trends in the Belorussian Language 1890–1982." in Kreindler, ed., ''Sociolinguistic Perspectives'' (1985): 37–56. * Zaprudnik, Jan. ''Historical dictionary of Belarus'' (Scarecrow Pr, 1998) * Zaprudnik. Jan. ''Belarus: At A Crossroads In History'' (Westview Press, 1993
online free to borrow
In Polish
*Piotr Eberhardt
Piotr Eberhardt (December 27, 1935 – September 10, 2020) was a Polish geographer, a professor at the Polish Academy of Science and author of studies in the field of demography and population geography. His works included the ethnic problems of Ce ...
, ''Problematyka narodowościowa Białorusi w XX wieku'' ("Nationality issue of Belarus in the 20th century"), Lublin, 1996,
* Ryszard Radzik Ryszard () is the Polish equivalent of "Richard", and may refer to:
*Ryszard Andrzejewski (born 1976), Polish rap musician, songwriter and producer
*Ryszard Bakst (1926–1999), Polish and British pianist and piano teacher of Jewish/Polish/Russian ...
, ''Kim są Białorusini?'' (''Who are the Belarusians?''), Toruń 2003,
* Małgorzata Ruchniewicz, ''Stosunki narodowościowe w latach 1939–1948 na obszarze tzw. Zachodniej Białorusi'' in ''Przemiany narodowościowe na kresach wschodnich II Rzeczypospolitej 1931–1948'' (''Nationality relations in 1939–1948 on the territory of so-called Western Belarus''), Toruń, 2004,
External links
Belarus National Republic
— the Belarusian Government in exile
Stary Hetman
— forums and library (in Belarusian and Russian) on Belarusian history
Belarus
by CIA World Factbook, 2000
Belarus
by
United States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
Belarusian diaspora
History of Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Belarus history
on th
Official Website of the Republic of Belarus
Belarusian Historical Review. Independent Academic Journal dedicated to history of Belarus (Belarusian and English versions)
History of Belarus in five minutes
YouTube {{European history by country