The history of Afghanistan as a
state began in 1823 as the
Emirate of Afghanistan after the exile of the
Sadozai monarchy to
Herat. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan
Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern
Afghanistan
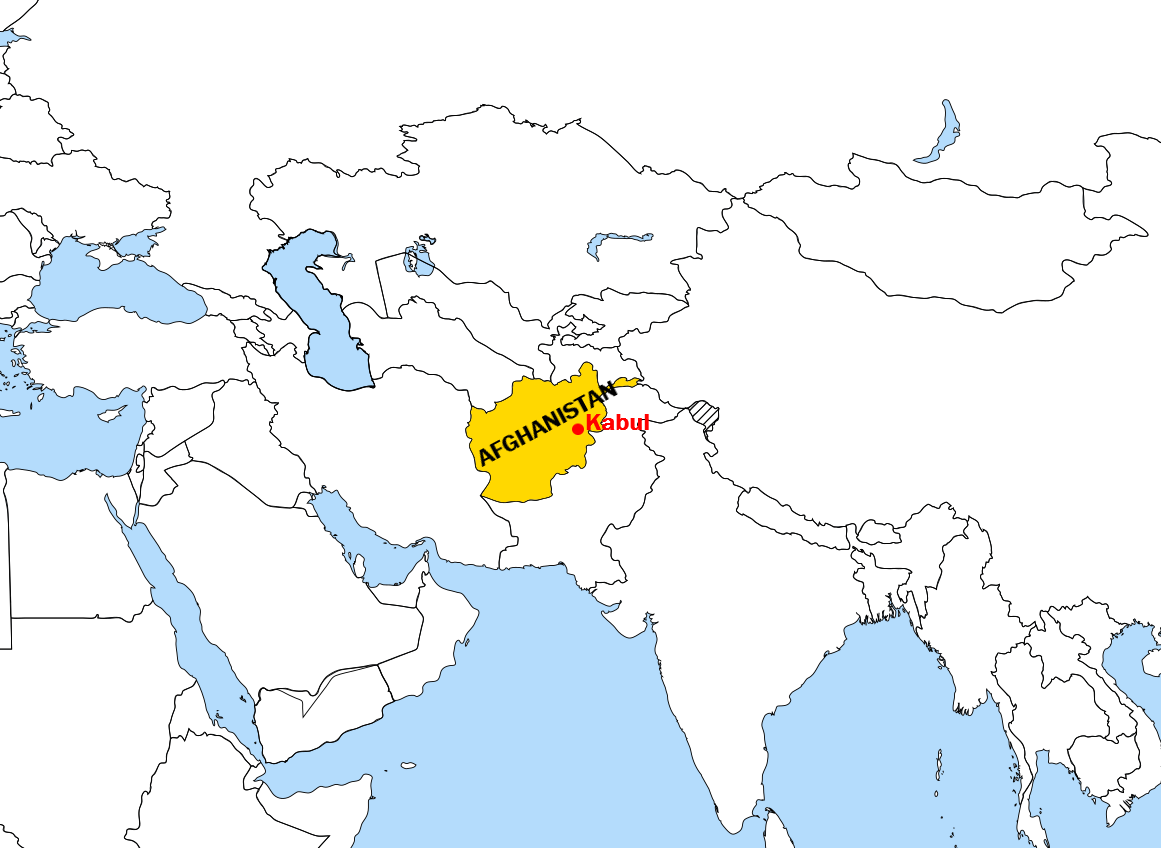
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
. The written recorded history of the land presently constituting Afghanistan can be traced back to around 500 BCE when the area was under the
Achaemenid Empire, although evidence indicates that an advanced degree of
urbanized culture has existed in the land since between 3000 and 2000 BCE.
Bactria dates back to 2500 BCE. The
Indus Valley civilisation stretched up to large parts of Afghanistan in the north.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, ß╝ł╬╗╬Ł╬Š╬▒╬Į╬┤Žü╬┐Žé, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC ŌĆō 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and his
Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
army arrived at what is now
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
in 330 BCE after
the fall of the Achaemenid Empire during the
Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, ╬ō╬▒Žģ╬│╬¼╬╝╬Ę╬╗╬▒, translit=Gaug├Īmela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, ß╝īŽü╬▓╬Ę╬╗╬▒, translit=├ürbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great a ...
.
Since then, many empires have established capitals in Afghanistan, including the
Greco-Bactrians
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Indi ...
,
Kushans,
Indo-Sassanids,
Kabul Shahi,
Saffarids,
Samanids,
Ghaznavids,
Ghurids,
Kartids,
Timurids,
Hotakis and
Durranis.
Afghanistan (meaning "land of the Afghans" or "Afghan land") has been a strategically important location throughout history. The land served as " a center of the ancient
Silk Road in central Asia, a gateway to
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, connecting China to western Asia and Europe, which carried trade from the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
to
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
". Sitting on many trade and migration routes, Afghanistan may be called the '
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
n roundabout' since routes converge from the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, ž¦┘äž┤ž▒┘é ž¦┘䞯┘łž│žĘ, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, from the
Indus Valley through the passes over the
Hindu Kush, from the Far East via the
Tarim Basin, and from the adjacent
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
n Steppe.
The
Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
were developed by one branch of these people; the
Pashto language
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
spoken today in Afghanistan by the ethnic Pashtuns, is one of the
Eastern Iranian languages. Elena E. Kuz'mina argues that the tents of Iranic-speaking nomads of Afghanistan developed from the light surface houses of the Eurasian steppe belt in the Bronze Age.
Mirwais Hotak
Mir Ways ibn Shah 'Alam, also known as Mirwais Khan Hotak ( Pashto/ Dari: ) (1673ŌĆō1715) was an Afghan ruler from the Ghilji tribe of Kandahar, Afghanistan, and the founder of the Hotak dynasty.
In 1709, after overthrowing and assassinating ...
, followed by
Ahmad Shah Durrani unified Afghanistan's tribes such as
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
,
Tajiks,
Hazaras
The Hazaras ( fa, , H╔Öz─ür╔Ö; haz, , ─Ćz╔Ör╔Ö) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scat ...
, and
Uzbeks and
Turkmens under one banner and founded the last
Afghan Empire in the early 18th century CE.
Afghanistan is inhabited by many and diverse peoples: the
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
,
Tajiks,
Hazaras
The Hazaras ( fa, , H╔Öz─ür╔Ö; haz, , ─Ćz╔Ör╔Ö) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scat ...
,
Uzbeks,
Turkmen,
Qizilbash,
Aimak,
Pashayi,
Baloch,
Pamiris,
Nuristanis, and others.
Prehistory

Excavations of prehistoric sites by
Louis Dupree and others at
Darra-e Kur in 1966 where 800 stone implements were recovered along with a fragment of Neanderthal right
temporal bone, suggest that early humans were living in what is now Afghanistan at least 52,000 years ago. A cave called Kara Kamar contained
Upper Paleolithic blades
Carbon-14 dated at 34,000 years old.
Farming communities in Afghanistan were among the earliest in the world.
Artifacts indicate that the
indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
were small farmers and herdsmen, very probably grouped into tribes, with small local kingdoms rising and falling through the ages. Urbanization may have begun as early as 3000 BCE.
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
predominated as the religion in the area; even the modern Afghan solar calendar shows the influence of Zoroastrianism in the names of the months. Other religions such as
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2ŌĆō1.35 billion followers, or 15ŌĆō16% of the global p ...
flourished later, leaving a major mark in the region.
Gandhara is the name of an ancient kingdom from the Vedic period and its capital city located between the
Hindukush and
Sulaiman Mountains (mountains of
Solomon), although Kandahar in modern times and the ancient Gandhara are not geographically identical.
Early inhabitants, around 3000 BCE were likely to have been connected through culture and trade to neighboring civilizations like
Jiroft
Jiroft ( fa, ž¼█īž▒┘üž¬, also Romanized as J─½roft; formerly, Sabz─üw─ür─ün, Sabzev─ür─ün, Sabzev─ür─ün-e Jiroft, and Sabzv─ür─ün) is a city and capital of Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 95,031, in ...
and
Tappeh Sialk and the
Indus Valley civilization. Urban civilization may have begun as early as 3000 BCE and it is possible that the early city of Mundigak (near
Kandahar) was a part of
Helmand culture.
The first known people were
Indo-Iranians,
but their date of arrival has been estimated widely from as early as about 3000 BCE
to 1500 BCE. (For further detail see
Indo-Aryan migration.)
Indus Valley civilization
The
Indus Valley civilisation (IVC) was a
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
civilization (3300ŌĆō1300 BCE; mature period 2600ŌĆō1900 BCE) extending from present-day northwest
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
to present-day northwest
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and present-day northeast Afghanistan.
An Indus Valley trading colony has been found on the
Oxus River at
Shortugai in northern Afghanistan. Apart from Shortughai,
Mundigak is another known site. There are several other smaller IVC sites to be found in Afghanistan as well.
Bactria-Margiana
The
Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex became prominent between 2200 and 1700 BCE (approximately). The city of
Balkh (
Bactra) was founded about this time (c. 2000ŌĆō1500 BCE).
Ancient period (c. 1500 ŌĆō 250 BCE)
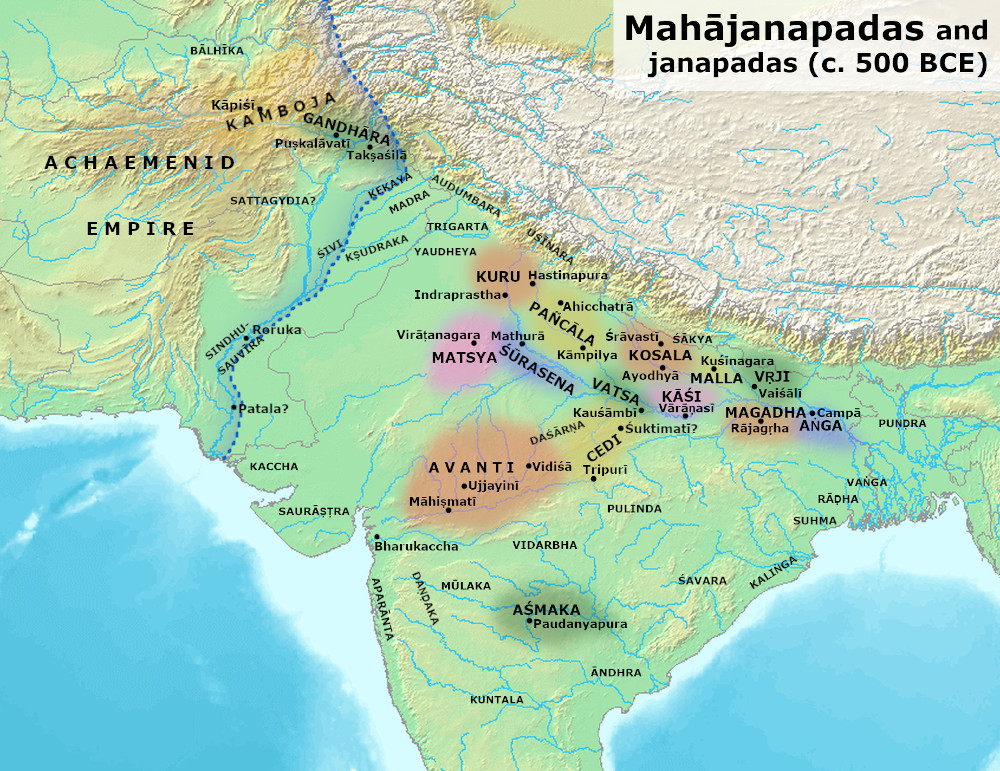
Gandhara Kingdom (c. 1500 ŌĆō 535 BCE)

The
Gandhara region centered around the
Peshawar Valley and
Swat river valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the
Taxila region in
Potohar Plateau
The Pothohar Plateau ( ur, ) is a plateau in north-eastern Pakistan, located between Indus River and the Jhelum River, forming the northern part of Punjab.
Geography
Potohar Plateau is bounded on the east by the Jhelum River, on the west by t ...
and westwards into the
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
and
Bamiyan valleys in
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, and northwards up to the
Karakoram range.
During the 6th century BCE, Gandh─üra was an important imperial power in north-west South Asia, with the
valley of Ka┼øm─½ra being part of the kingdom, while the other states of the Punjab region, such as the
Kekayas,
Madrakas,
U┼ø─½naras, and
Shivis being under G─ündh─ür─½ suzerainty. The G─ündh─ür─½ king
Pukkus─üti, who reigned around 550 BCE, engaged in expansionist ventures which brought him into conflict with the king
Pradyota of the rising power of
Avanti. Pukkus─üti was successful in this struggle with Pradyota.
By the later 6th century BCE, the founder of the
Persian Achaemenid Empire,
Cyrus
Cyrus (Persian: ┌®┘łž▒┘łž┤) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus ...
, soon after his conquests of
Media,
Lydia, and
Babylonia, marched into Gandhara and annexed it into his empire.
The scholar
Kaikhosru Danjibuoy Sethna advanced that Cyrus had conquered only the trans-Indus borderlands around Peshawar which had belonged to Gandh─üra while Pukkus─üti remained a powerful king who maintained his rule over the rest of Gandh─üra and the western Punjab.
Kamboja Kingdom (c. 700 ŌĆō 200 BCE)
The Kambojas entered into conflict with
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, ß╝ł╬╗╬Ł╬Š╬▒╬Į╬┤Žü╬┐Žé, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC ŌĆō 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
as he invaded
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
. The Macedonian conqueror made short shrift of the arrangements of
Darius and after over-running the Achaemenid Empire he dashed into today's eastern Afghanistan and western Pakistan. There he encountered resistance from the Kamboja ''Aspasioi'' and ''Assakenoi'' tribes. The Region of the
Hindukush that was inhabitanted by the Kambojas has gone through many rules such as
Vedic Mahajanapada,
Pali Kapi┼øi,
Indo-Greeks,
Kushan and
Gandharans to
Paristan and modern day being split between Pakistan and Eastern Afghanistan.
The descendants of Kambojas have mostly been assimilated into newer identities, however, some tribes remain today that still retain the names of their ancestors. The
Yusufzai Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
are said to be the
Esapzai
The Yusufzai or Yousafzai ( ps, █ī┘łž│┘üž▓█ī, ), also referred to as the Esapzai (, ) are one of the largest tribes of ethnic Pashtuns. They are natively based in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, to which they migrated to from Suliman mountains du ...
/
A┼øvakas from the Kamboja age. The
Kom
Kom or KOM may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Kom people (Afghanistan), a Nuristani tribe in Afghanistan and Pakistan
* Kom people (Cameroon), an ethnic group of northwest Cameroon
* Kom people (India) a subgroup of the Kuki in north-eastern India
* ...
/Kamoz people of
Nuristan retain their Kamboj name. The
Ashkun of Nuristan also retain the name of A┼øvakas. The
Yashkun Shina dards are another group that retain the name of the Kamboja A┼øvakans. The
Kamboj of
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: ┘Š┘åž¼ž¦ž© ; Ó©¬Ó®░Ó©£Ó©ŠÓ©¼ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panj─üb'' or ''Panj-─Ćb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
are another group that still retain the name however have integrated into new identity. The country of
Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, ß×ĆßלߤÆß×¢ß×╗ß×ćß×Č, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
derives its name from the Kamboja.
Achaemenid Empire


Afghanistan fell to the
Achaemenid Empire after it was conquered by
Darius I of Persia. The area was divided into several provinces called
satrapies
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with con ...
, which were each ruled by a governor, or
satrap. These ancient satrapies included:
Aria
In music, an aria ( Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompa ...
: The region of Aria was separated by mountain ranges from the
Paropamisadae in the east,
Parthia
Parthia ( peo, ÉÄ▒ÉÄ╝ÉÄ░ÉÄ║ ''Par╬Ėava''; xpr, ÉŁÉÉŁōÉŁĢÉŁģ ''Par╬Ėaw''; pal, ÉŁ»ÉŁ½ÉŁ«ÉŁźÉŁĪÉŁź ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
in the west and
Margiana and
Hyrcania in the north, while a desert separated it from
Carmania and
Drangiana in the south. It is described in a very detailed manner by
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, ╬ĀŽä╬┐╬╗╬Ą╬╝╬▒ß┐¢╬┐Žé, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
and
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
and corresponds, according to that, almost to the
Herat Province
Herat ( Persian: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the north-western part of the country. Together with Badghis, Farah, and Ghor provinces, it makes up the north-western region of Afghanistan. Its primary city a ...
of today's Afghanistan;
Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the In ...
, corresponds to the modern-day
Kandahar,
Lashkar Gah, and
Quetta
Quetta (; ur, ; ; ps, ┌®┘ł┘╝┘ćŌĆÄ) is the tenth most populous city in Pakistan with a population of over 1.1 million. It is situated in south-west of the country close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of th ...
. Arachosia bordered
Drangiana to the west,
Paropamisadae (i.e.
Gandahara) to the north and to the east, and
Gedrosia to the south. The inhabitants of Arachosia were
Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
, referred to as Arachosians or Arachoti.
It is assumed that they were called ''Paktyans'' by ethnicity, and that name may have been in reference to the ethnic
''Paß╣Żtun'' (Pashtun)
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
;
na was the area north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Tian Shan, with the Amu Darya flowing west through the center (
Balkh);
Sattagydia was the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire, part of its Seventh tax district according to Herodotus, along with Gand─ürae, Dadicae and Aparytae. It is believed to have been situated east of the Sulaiman Mountains up to the Indus River in the basin around Bannu.
(Ghazni);_and__
Gandhara_which_corresponds_to_modern_day_Kabul.html" ;"title="Ghazni.html" ;"title="(Ghazni">(Ghazni); and Gandhara which corresponds to modern day Kabul">Ghazni.html" ;"title="(Ghazni">(Ghazni); and Gandhara which corresponds to modern day Kabul, Jalalabad, and Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, ┘Š█É┌Ü┘łž▒ ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
.
Alexander and the Seleucus
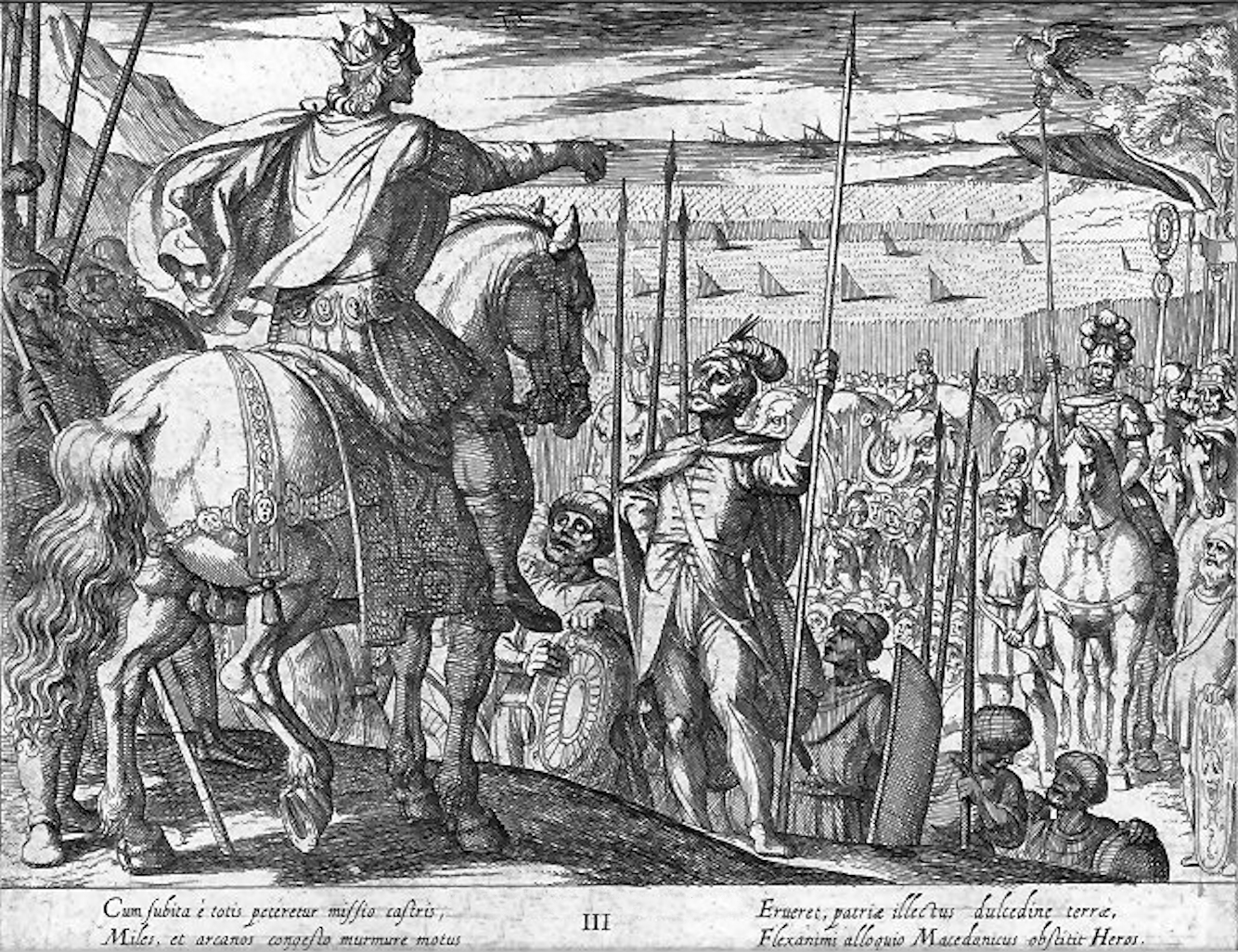
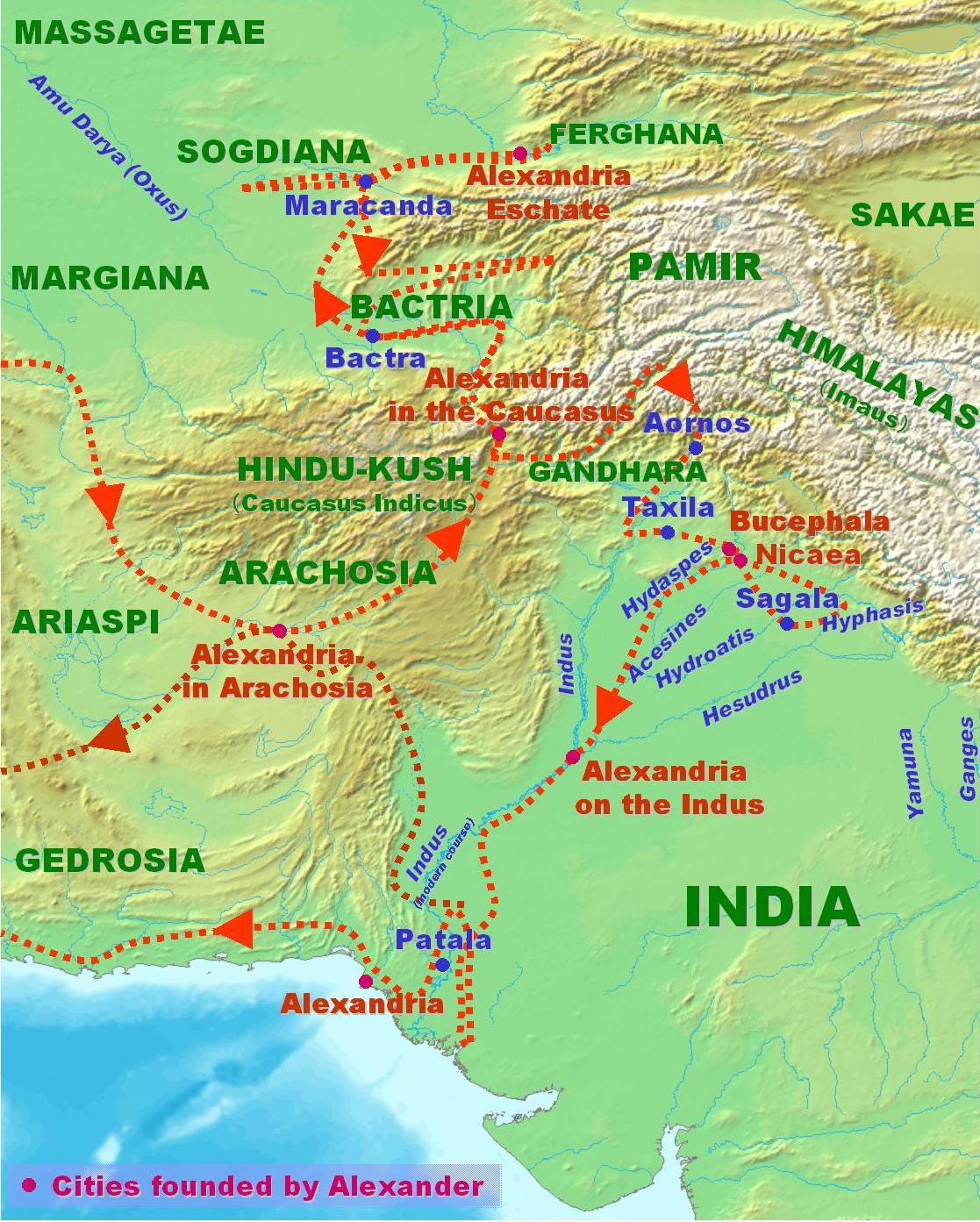

Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, ß╝ł╬╗╬Ł╬Š╬▒╬Į╬┤Žü╬┐Žé, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC ŌĆō 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
arrived in the area of Afghanistan in 330 BCE after defeating Darius III of Persia a year earlier at the Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, ╬ō╬▒Žģ╬│╬¼╬╝╬Ę╬╗╬▒, translit=Gaug├Īmela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, ß╝īŽü╬▓╬Ę╬╗╬▒, translit=├ürbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great a ...
.Begram
Bagram (; Pashto/ fa, ž©┌»ž▒ž¦┘ģ) is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir V ...
, at Bordj-i-Abdullah); and finally, Alexandria-Eschate (near Kojend), in the north. After Alexander's death, his loosely connected empire was divided. Seleucus, a Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
officer during Alexander's campaign, declared himself ruler of his own Seleucid Empire, which also included present-day Afghanistan.
Mauryan Empire
Maurya Empire, c.250 BCE.png, Maurya Empire under Ashoka the Great.
Mes Aynak stupa.jpg, Newly excavated Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
stupa
A stupa ( sa, ÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźéÓż¬, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''┼øar─½ra'' ŌĆō typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circum ...
at Mes Aynak
Mes Aynak (Pashto/Persian: , meaning "little source of copper"), also called Mis Ainak or Mis-e-Ainak, was a major Buddhist settlement southeast of Kabul, Afghanistan, located in a barren region of Logar Province. The site is also the location ...
in Logar Province of Afghanistan. Similar stupas have been discovered in neighboring Ghazni Province
Ghazni ( Dari: ) is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in southeastern Afghanistan. The province contains 19 districts, encompassing over a thousand villages and roughly 1.3 million people, making it the 5th most populous province. Th ...
, including in the northern Samangan Province.
Aramaic inscription of Laghman.jpg, Aramaic Inscription of Laghman
The Aramaic inscription of Laghman, also called the Laghman I inscription to differentiate from the Laghman II inscription discovered later, is an inscription on a slab of natural rock in the area of Laghmân, Afghanistan, written in Aramaic b ...
is an inscription on a slab of natural rock in the area of Laghmân, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, written in Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ▄É▄¬▄Ī▄Ø▄É, Ar─üm─üy─ü; oar, ÉżĆÉżōÉżīÉżēÉżĆ; arc, ÉĪĆÉĪōÉĪīÉĪēÉĪĆ; tmr, ūÉų▓ū©ųĖū×ų┤ūÖū¬), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
by the Indian emperor Ashoka about 260 BCE, and often categorized as one of Minor Rock Edicts of Ashoka.
Kandahar Greek inscription.jpg, Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka is among the Major Rock Edicts of the Indian Emperor Ashoka (reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, ╬Ģ╬╗╬╗╬Ę╬Į╬╣╬║╬¼, Ellinik├Ī, ; grc, ß╝Ö╬╗╬╗╬Ę╬Į╬╣╬║╬«, Hell─ōnikßĖŚ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), souther ...
and Prakrit language.
The territory fell to the Maurya Empire, which was led by Chandragupta Maurya. The Mauryas further entrenched Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2ŌĆō1.35 billion followers, or 15ŌĆō16% of the global p ...
and introduced Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
to the region, and were planning to capture more territory of Central Asia until they faced local Greco-Bactrian forces. Seleucus is said to have reached a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
with Chandragupta by giving control of the territory south of the Hindu Kush to the Mauryas upon intermarriage and 500 elephants.
Having consolidated power in the northwest, Chandragupta pushed east towards the Nanda Empire. Afghanistan's significant ancient tangible and intangible Buddhist heritage is recorded through wide-ranging archeological finds, including religious and artistic remnants. Buddhist doctrines are reported to have reached as far as Balkh even during the life of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
(563 BCE to 483 BCE), as recorded by Husang Tsang.
Classical Period (c. 250 BCE ŌĆō 565 CE)
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
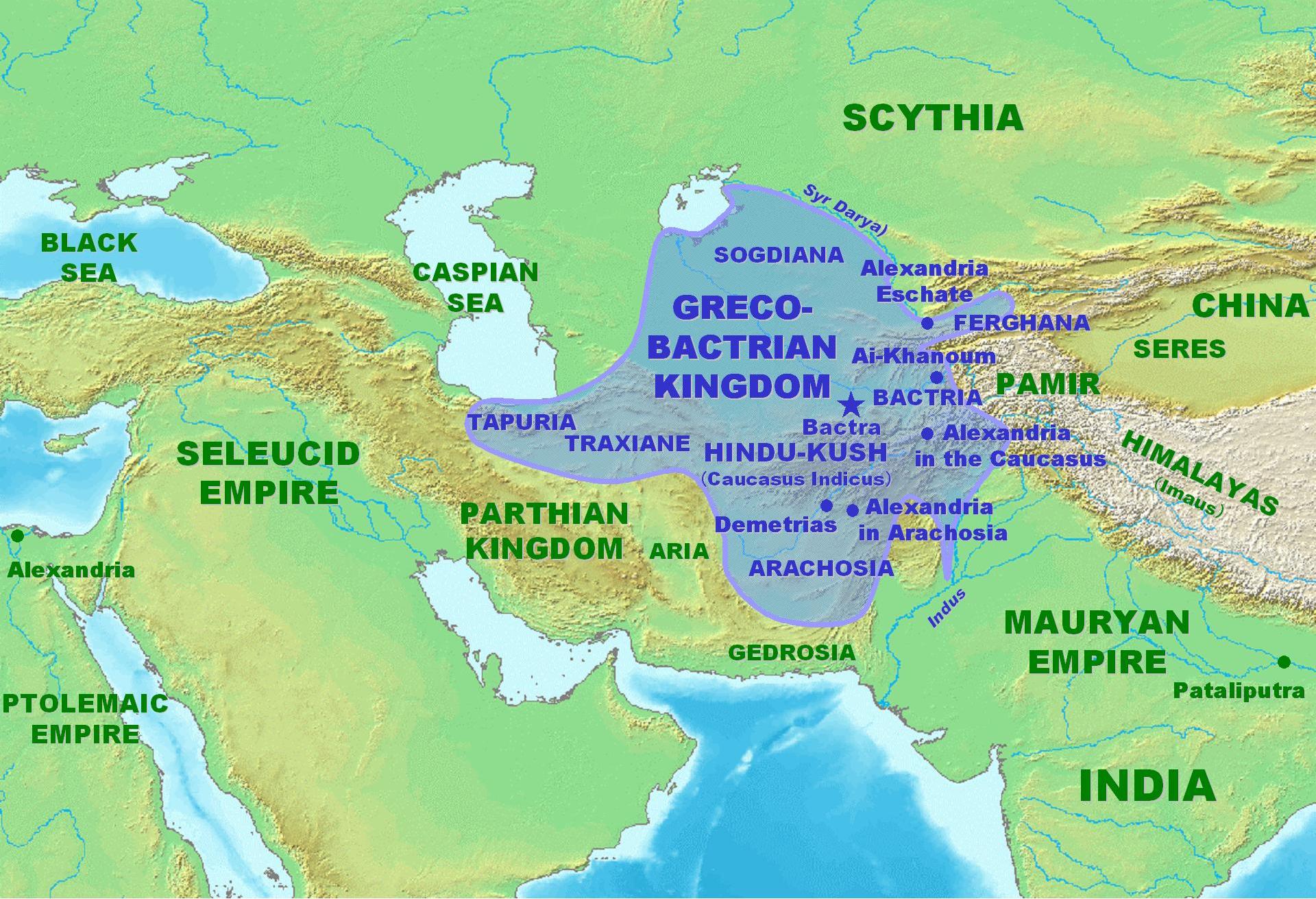 The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was a
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was a Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
kingdom,Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
and Alexandria of the Caucasus until 70 BCE when King Hermaeus was also defeated by the Yuezhi.
Indo-Greek Kingdom
One of Demetrius I's successors, Menander I, brought the Indo-Greek Kingdom (now isolated from the rest of the Hellenistic world after the fall of Bactria) to its height between 165 and 130 BCE, expanding the kingdom in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
to even larger proportions than Demetrius. After Menander's death, the Indo-Greeks steadily declined and the last Indo-Greek kings ( Strato II and Strato III) were defeated in c. 10 CE. The Indo-Greek Kingdom was succeeded by the Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
.
Indo-Scythians
 The
The Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
were descended from the Sakas (Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
) who migrated from southern Siberia to Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the In ...
from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century BCE. They displaced the Indo-Greeks and ruled a kingdom that stretched from Gandhara to Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
. The power of the Saka rulers started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Scythians were defeated by the south Indian Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni
Gautamiputra Satakarni (Brahmi: æĆĢæüäæĆóæĆ½æĆ║æƦæĆ╝æĆó æĆ▓æĆĖæĆóæĆōæĆĪæĆ║, ''Gotamiputa S─ütakaß╣ći'', IAST: ) was a ruler of the Satavahana Empire in present-day Deccan region of India. He was mentioned as the important an ...
of the Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''S─üdav─ühana'' or ''S─ütav─ühana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the la ...
. Later the Saka kingdom was completely destroyed by Chandragupta II of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
from eastern India in the 4th century.
Indo-Parthians
 The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was ruled by the Gondopharid dynasty, named after its eponymous first ruler Gondophares. They ruled parts of present-day
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was ruled by the Gondopharid dynasty, named after its eponymous first ruler Gondophares. They ruled parts of present-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
,India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, during or slightly before the 1st century AD. For most of their history, the leading Gondopharid kings held Taxila (in the present Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: ┘Š┘åž¼ž¦ž© ; Ó©¬Ó®░Ó©£Ó©ŠÓ©¼ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panj─üb'' or ''Panj-─Ćb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
province of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
) as their residence, but during their last few years of existence the capital shifted between Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
and Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, ┘Š█É┌Ü┘łž▒ ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
. These kings have traditionally been referred to as Indo-Parthians, as their coinage was often inspired by the Arsacid dynasty, but they probably belonged to a wider groups of Iranic tribes who lived east of Parthia
Parthia ( peo, ÉÄ▒ÉÄ╝ÉÄ░ÉÄ║ ''Par╬Ėava''; xpr, ÉŁÉÉŁōÉŁĢÉŁģ ''Par╬Ėaw''; pal, ÉŁ»ÉŁ½ÉŁ«ÉŁźÉŁĪÉŁź ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
proper, and there is no evidence that all the kings who assumed the title ''Gondophares'', which means "Holder of Glory", were even related. Christian writings claim that the Apostle Saint Thomas ŌĆō an architect and skilled carpenter ŌĆō had a long sojourn in the court of king Gondophares, had built a palace for the king at Taxila and had also ordained leaders for the Church before leaving for the Indus Valley in a chariot, for sailing out to eventually reach Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing ...
.
Kushans
 The Kushan Empire expanded out of Bactria (Central Asia) into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises, about the middle of the 1st century CE. They came from an Indo-European language speaking Central Asian tribe called the Yuezhi, a branch of which was known as the Kushans. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka the Great, the empire spread to encompass much of
The Kushan Empire expanded out of Bactria (Central Asia) into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises, about the middle of the 1st century CE. They came from an Indo-European language speaking Central Asian tribe called the Yuezhi, a branch of which was known as the Kushans. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka the Great, the empire spread to encompass much of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, and then the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
(Benares).
Emperor Kanishka was a great patron of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
; however, as Kushans expanded southward, the deities of their later coinage came to reflect its new Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
majority.
They played an important role in the establishment of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent and its spread to Central Asia and China.
Historian Vincent Smith said about Kanishka:
The empire linked the Indian Ocean maritime trade with the commerce of the Silk Road through the Indus valley, encouraging long-distance trade, particularly between China and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. The Kushans brought new trends to the budding and blossoming Gandhara Art, which reached its peak during Kushan Rule.
H. G. Rowlinson commented:
By the 3rd century, their empire in India was disintegrating and their last known great emperor was Vasudeva I.
BuddhistTriad.JPG, Early Mahayana Buddhist
''Mah─üy─üna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mah─üy─üna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing bran ...
triad. From left to right, a Kushan devotee, Maitreya, the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
, Avalokitesvara, and a Buddhist monk. 2ndŌĆō3rd century, Gandhara.
Kumara, The Divine General LACMA M.85.279.3.jpg, Kumara or Kartikeya
Kartikeya ( sa, ÓżĢÓżŠÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓźŹÓżżÓż┐ÓżĢÓźćÓż», K─ürttikeya), also known as Skanda, Subrahmanya, Shanmukha (), and Murugan ( ta, Ó««Ó»üÓ«░Ó»üÓ«ĢÓ«®Ó»Ź), is the Hindu god of war. He is the son of Parvati and Shiva, the brother of Ganesh ...
with a Kushan devotee, 2nd century CE.
Gandhara, omaggio di un re kushana al bodhisattva, II-III sec.JPG, Kushan prince, said to be Huvishka, making a donation to a Boddhisattva.
Relief Showing Shiva Linga Worshipped by Saka Devotees - Kushan Period - Dampier Nagar - ACCN 36-2661 - Government Museum - Mathura 2013-02-23 5614.JPG, Shiva
Shiva (; sa, ÓżČÓż┐ÓżĄ, lit=The Auspicious One, ┼Üiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ╔É╔”a╦Éd╠¬e╦É╩ŗ╔É, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
Linga
A lingam ( sa, Óż▓Óż┐ÓżÖÓźŹÓżŚ , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary ''murti'' or devotional ...
worshipped by Kushan devotees, circa 2nd century CE.
Sassanian Empire
 After the Kushan Empire's rule was ended by SassanidsŌĆö officially known as the Empire of IraniansŌĆö was the last kingdom of the Persian Empire before the rise of Islam. Named after the House of Sasan, it ruled from 224 to 651 AD. In the east around 325, Shapur II regained the upper hand against the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom and took control of large territories in areas now known as Afghanistan and Pakistan. Much of modern-day
After the Kushan Empire's rule was ended by SassanidsŌĆö officially known as the Empire of IraniansŌĆö was the last kingdom of the Persian Empire before the rise of Islam. Named after the House of Sasan, it ruled from 224 to 651 AD. In the east around 325, Shapur II regained the upper hand against the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom and took control of large territories in areas now known as Afghanistan and Pakistan. Much of modern-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
became part of the Sasanian Empire, since Shapur I extended his authority eastwards into Afghanistan and the previously autonomous Kushans were obliged to accept his suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
.
From around 370, however, towards the end of the reign of Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, ÉŁ▒ÉŁ¦ÉŁ»ÉŁźÉŁ¦ÉŁźÉŁ® ; New Persian: , ''┼Ā─üpur'', 309 ŌĆō 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian King of Kings ( Shahanshah) of Iran. The longest-reigning monarch in Iranian history, he reign ...
, the Sassanids lost the control of Bactria to invaders from the north. These were the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, the Alchon Huns, and the Nezaks
The Nezak Huns ( Pahlavi: ÉŁŁÉŁ®ÉŁ░ÉŁ¬ÉŁ® ''nycky''), also Nezak Shahs, formed a major principality in the south of the Hindu Kush region, active from circa 484 to 665 CE. Despite being traditionally identified as the last of the Hunnic stat ...
: The four Huna tribes to rule Afghanistan. These invaders initially issued coins based on Sasanian designs.
Huna
The Hunas were peoples who were of a group of Central Asian tribes. Four of the Huna tribe conquered and ruled Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
: the Kidarites, Hepthalites, Alchon Huns and the Nezaks
The Nezak Huns ( Pahlavi: ÉŁŁÉŁ®ÉŁ░ÉŁ¬ÉŁ® ''nycky''), also Nezak Shahs, formed a major principality in the south of the Hindu Kush region, active from circa 484 to 665 CE. Despite being traditionally identified as the last of the Hunnic stat ...
.
Kidarites
The Kidarites were a nomadic clan, the first of the four Huna people
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''H┼½ß╣ć─ü'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
in Afghanistan. They are supposed to have originated in Western China and arrived in Bactria with the great migrations of the second half of the 4th century.
Alchon Huns
 The Alchons are one of the four
The Alchons are one of the four Huna people
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''H┼½ß╣ć─ü'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
that ruled in Afghanistan. A group of Central Asian tribes, Hunas or Huna, via the Khyber Pass, entered India at the end of the 5th or early 6th century and successfully occupied areas as far as Eran and Kausambi, greatly weakening the Gupta Empire. The 6th-century Roman historian Procopius of Caesarea (Book I. ch. 3), related the Huns of Europe with the Hephthalites or "White Huns" who subjugated the Sassanids and invaded northwestern India, stating that they were of the same stock, "in fact as well as in name", although he contrasted the Huns with the Hephthalites, in that the Hephthalites were sedentary, white-skinned, and possessed "not ugly" features.
Song Yun and Hui Zheng, who visited the chief of the Hephthalite nomads at his summer residence in Badakshan and later in Gandhara, observed that they had no belief in the Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
law and served a large number of divinities."
The White Huns
The Hephthalites (or Ephthalites), also known as the White Huns and one of the four Huna people
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''H┼½ß╣ć─ü'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
in Afghanistan, were a nomadic confederation in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
during the late antiquity period. The White Huns established themselves in modern-day Afghanistan by the first half of the 5th century. Led by the Hun military leader Toramana, they overran the northern region of Pakistan and North India. Toramana's son Mihirakula, a Saivite
Shaivism (; sa, ÓżČÓźłÓżĄÓżĖÓż«ÓźŹÓż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż”ÓżŠÓż»Óżā, ┼Üaivasamprad─üyaßĖź) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangi ...
Hindu, moved up to near Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
to the east and Gwalior to central India. Hiuen Tsiang narrates Mihirakula's merciless persecution of Buddhists and destruction of monasteries, though the description is disputed as far as the authenticity is concerned. The Huns were defeated by the Indian kings Yasodharman of Malwa and Narasimhagupta in the 6th century. Some of them were driven out of India and others were assimilated in the Indian society.
Nezak Huns
The Nezaks are one of the four Huna people
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''H┼½ß╣ć─ü'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
that ruled in Afghanistan.
Middle Ages (565ŌĆō1504 CE)
 From the
From the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
to around 1750 the eastern part of Afghanistan was recognized as being a part of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
while its western parts were included in Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
.Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
), was called Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, which loosely covered a wide area between the Hindu Kush and the Indus River, principally around the Sulaiman Mountains.Afghan
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
*Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
**Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pash ...
"'' (''"Abgân"'') being mentioned is by Shapur I of the Sassanid Empire during the 3rd century CEAfghana
Afghana or Avagana is a tribal chief or prince of Pashtuns, who is traditionally considered the progenitor of modern-day Pashtuns,Socio-economic Behaviour of Pukhtun Tribe By Dipali Saha, Dipali Saha - 2006 - 282 pages - Page 124.India and the ...
"'', grandson of King Saul of Israel. Hiven Tsiang, a Chinese pilgrim, visiting the Afghanistan area several times between 630 and 644 CE also speaks about them.culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
and language of the Pashtun tribes already present there. Among these were the Khalaj people which are known today as Ghilzai.
Kabul Shahi
The Kabul Shahi dynasties ruled the Kabul Valley and Gandhara from the decline of the Kushan Empire in the 3rd century to the early 9th century.[Shahi Family. Encyclop├”dia Britannica. 2006. Encyclop├”dia Britannica Online. 16 October 2006]
The Shahis are generally split up into two eras: the Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
Shahis and the Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Shahis, with the change-over thought to have occurred sometime around 870. The kingdom was known as the Kabul Shahan or Ratbelshahan from 565 to 670, when the capitals were located in Kapisa Province, Kapisa and Kabul, and later Udabhandapura, also known as Hund for its new capital.
The Hindu Shahis under ruler Jayapala, is known for his struggles in defending his kingdom against the Ghaznavids in the modern-day eastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
region. Jayapala saw a danger in the consolidation of the Ghaznavids and invaded their capital city of Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, ž║ž▓┘å█ī, ps, ž║ž▓┘å┘Ŗ), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, ╬æ╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬®ŽĆ╬╣╬▒╬Į╬«), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
both in the reign of Sebuktigin and in that of his son Mahmud
Mahmud is a transliteration of the male Arabic given name (), common in most parts of the Islamic world. It comes from the Arabic triconsonantal root ßĖż-M-D, meaning ''praise'', along with ''Muhammad''.
Siam Mahmud
*Mahmood (singer) (born 19 ...
, which initiated the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘å, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
Ghaznavid and Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Shahi struggles.Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, ┘Š█É┌Ü┘łž▒ ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
. After the Battle of Peshawar, he committed suicide because his subjects thought he had brought disaster and disgrace to the Shahi dynasty.Siwalik
The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian ...
Hills.
Islamic conquest
In 642 CE, Rashidun Arabs had conquered most of West Asia from the Sassanids and Byzantines, and from the western city of Herat they introduced the religion of Islam as they entered new cities. Afghanistan at that period had a number of different independent rulers, depending on the area. Ancestors of Ab┼½ ßĖżan─½fa
Nu╩┐m─ün ibn Th─übit ibn Z┼½ß╣Ł─ü ibn Marzub─ün ( ar, ┘åž╣┘ģž¦┘å ž©┘å ž½ž¦ž©ž¬ ž©┘å ž▓┘łžĘž¦ ž©┘å ┘ģž▒ž▓ž©ž¦┘å; ŌĆō767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Ab┼½ ßĖżan─½fa ( ar, žŻž©┘ł žŁ┘å┘Ŗ┘üž®), or reverently as Imam Ab┼½ ßĖżan─½fa by Sunni Musl ...
, including his father, were from the Kabul region.
The early Arab forces did not fully explore Afghanistan due to attacks by the mountain tribes. Much of the eastern parts of the country remained independent, as part of the Hindu Shahi kingdoms of Kabul and Gandhara, which lasted that way until the forces of the Muslim Saffarid dynasty followed by the Ghaznavids conquered them.
Ghaznavids
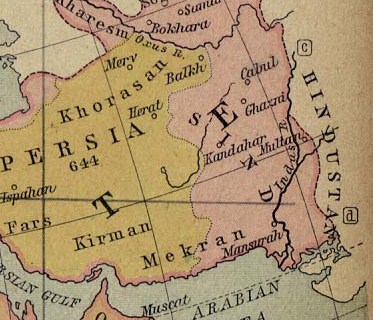
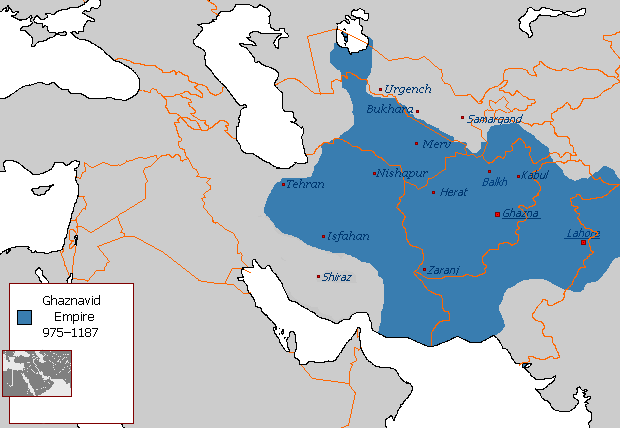 The Ghaznavid dynasty ruled from the city of
The Ghaznavid dynasty ruled from the city of Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, ž║ž▓┘å█ī, ps, ž║ž▓┘å┘Ŗ), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, ╬æ╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬®ŽĆ╬╣╬▒╬Į╬«), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
in eastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
. From 997 to his death in 1030, Mahmud of Ghazni turned the former provincial city of Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, ž║ž▓┘å█ī, ps, ž║ž▓┘å┘Ŗ), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, ╬æ╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬®ŽĆ╬╣╬▒╬Į╬«), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
into the wealthy capital of an extensive empire which covered most of today's Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, eastern and central Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, T├╝rkmenistan / ąóę»čĆą║ą╝ąĄąĮąĖčüčéą░ąĮ, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Tojikiston; russian: ąóą░ą┤ąČąĖą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, ęČčāą╝ę│čāčĆąĖąĖ ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: ąŻąĘą▒ąĄą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ ąŻąĘą▒ąĄą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ), is a doubly landlocked co ...
. Mahmud of Ghazni (Mahmude Ghaznavi in local pronunciation) consolidated the conquests of his predecessors and the city of Ghazni became a great cultural centre as well as a base for frequent forays into the Indian subcontinent. The Nasher Khans became princes of the Kharoti until the Soviet invasion.
Ghorids
The Ghaznavid dynasty was defeated in 1148 by the Ghurids from Ghor, but the Ghaznavid Sultans continued to live in Ghazni as the ' Nasher' until the early 20th century.[Meher, Jagmohan: ]Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, much of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
like Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, and north and central part of modern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Mongol invasion
 The Mongols invaded Afghanistan in 1221 having defeated the Khwarazmian armies. The Mongols invasion had long-term consequences with many parts of Afghanistan never recovering from the devastation. The towns and villages suffered much more than the nomads who were able to avoid attack. The destruction of irrigation systems maintained by the sedentary people led to the shift of the weight of the country towards the hills. The city of Balkh was destroyed and even 100 years later Ibn Battuta described it as a city still in ruins. While the Mongols were pursuing the forces of Jalal ad-Din Mingburnu they besieged the city of Bamyan. In the course of the siege a defender's arrow killed Genghis Khan's grandson Mutukan. The Mongols razed the city and massacred its inhabitants in revenge, with its former site known as the City of Screams. Herat, located in a fertile valley, was destroyed as well but was rebuilt under the local Kart dynasty. After the Mongol Empire splintered, Herat eventually became part of the
The Mongols invaded Afghanistan in 1221 having defeated the Khwarazmian armies. The Mongols invasion had long-term consequences with many parts of Afghanistan never recovering from the devastation. The towns and villages suffered much more than the nomads who were able to avoid attack. The destruction of irrigation systems maintained by the sedentary people led to the shift of the weight of the country towards the hills. The city of Balkh was destroyed and even 100 years later Ibn Battuta described it as a city still in ruins. While the Mongols were pursuing the forces of Jalal ad-Din Mingburnu they besieged the city of Bamyan. In the course of the siege a defender's arrow killed Genghis Khan's grandson Mutukan. The Mongols razed the city and massacred its inhabitants in revenge, with its former site known as the City of Screams. Herat, located in a fertile valley, was destroyed as well but was rebuilt under the local Kart dynasty. After the Mongol Empire splintered, Herat eventually became part of the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ž¦█ī┘ä ž«ž¦┘垦┘å, ''Ilx─ün─ün''), known to the Mongols as ''H├╝leg├╝ Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
while Balkh and the strip of land from Kabul through Ghazni to Kandahar went to the Chagatai Khanate. The Afghan tribal areas south of the Hindu Kush were usually either allied with the Khalji dynasty of northern India or independent.
Timurids

Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Tem├╝r'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Tem├╝r'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617ŌĆō19 February 1405), later Tim┼½r Gurk─ün─½ ( chg, ''Tem├╝r K├╝ ...
(Tamerlane) incorporated much of the area into his own vast Timurid Empire. The city of Herat became one of the capitals of his empire, and his grandson Pir Muhammad held the seat of Kandahar. Timur rebuilt most of Afghanistan's infrastructure which was destroyed by his early ancestor. The area was progressing under his rule. Timurid rule began declining in the early 16th century with the rise of a new ruler in Kabul, Babur.
Timur, a descendant of Genghis Khan, created a vast new empire across Russia and Persia which he ruled from his capital in Samarkand in present-day Uzbekistan. Timur captured Herat in 1381 and his son, Shah Rukh moved the capital of the Timurid empire to Herat in 1405. The Timurids, a Turkic people, brought the Turkic nomadic culture of Central Asia within the orbit of Persian civilisation, establishing Herat as one of the most cultured and refined cities in the world. This fusion of Central Asian and Persian culture was a major legacy for the future Afghanistan. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glory matched Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
of the Italian Renaissance as the center of a cultural rebirth. A century later, the emperor Babur, a descendant of Timur, visited Herat and wrote, "the whole habitable world had not such a town as Herat." For the next 300 years the eastern Afghan tribes periodically invaded India creating vast Indo-Afghan empires. In 1500 CE, Babur was driven out of his home in the Ferghana valley. By the 16th century western Afghanistan again reverted to Persian rule under the Safavid dynasty.
Modern era (1504ŌĆō1973)
Mughals, Uzbeks, and Safavids
 In 1504, Babur, a descendant of
In 1504, Babur, a descendant of Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Tem├╝r'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Tem├╝r'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617ŌĆō19 February 1405), later Tim┼½r Gurk─ün─½ ( chg, ''Tem├╝r K├╝ ...
, arrived from present-day Uzbekistan and moved to the city of Kabul. He began exploring new territories in the region, with Kabul serving as his military headquarters. Instead of looking towards the powerful Safavids towards the Persian west, Babur was more focused on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
. In 1526, he left with his army to capture the seat of the Delhi Sultanate, which at that point was possessed by the Afghan Lodi dynasty of India. After defeating Ibrahim Lodi and his army, Babur turned (Old) Delhi into the capital of his newly established Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
.
From the 16th century to the 17th century CE, Afghanistan was divided into three major areas. The north was ruled by the Khanate of Bukhara, the west was under the rule of the Iranian Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
Safavids, and the eastern section was under the Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85ŌĆō90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
Mughals of northern India, who under Akbar established in Kabul one of the original twelve subah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''sub ...
s (imperial top-level provinces), bordering Lahore, Multan and Kashmir (added to Kabul in 1596, later split-off) and short-lived Balkh Subah
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, ┌»┘Å┘åž©┘Äž», dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
and Badakhshan Subah
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic B ...
(only 1646ŌĆō47). The Kandahar region in the south served as a buffer zone between the Mughals (who shortly established a Qandahar subah 1638ŌĆō1648) and Persia's Safavids, with the native Afghans often switching support from one side to the other. Babur explored a number of cities in the region before his campaign into India. In the city of Kandahar, his personal epigraphy can be found in the Chilzina rock mountain. Like in the rest of the territories that used to make part of the Indian Mughal Empire, Afghanistan holds tombs, palaces, and forts built by the Mughals.
Hotak dynasty

 In 1704, the Safavid Shah Husayn appointed George XI (''Gurg─½n Kh─ün''), a ruthless Georgian subject, to govern their easternmost territories in the Greater Kandahar region. One of Gurg─½n's main objectives was to crush the rebellions started by native Afghans. Under his rule the revolts were successfully suppressed and he ruled Kandahar with uncompromising severity. He began imprisoning and executing the native Afghans, especially those suspected in having taken part in the rebellions. One of those arrested and imprisoned was
In 1704, the Safavid Shah Husayn appointed George XI (''Gurg─½n Kh─ün''), a ruthless Georgian subject, to govern their easternmost territories in the Greater Kandahar region. One of Gurg─½n's main objectives was to crush the rebellions started by native Afghans. Under his rule the revolts were successfully suppressed and he ruled Kandahar with uncompromising severity. He began imprisoning and executing the native Afghans, especially those suspected in having taken part in the rebellions. One of those arrested and imprisoned was Mirwais Hotak
Mir Ways ibn Shah 'Alam, also known as Mirwais Khan Hotak ( Pashto/ Dari: ) (1673ŌĆō1715) was an Afghan ruler from the Ghilji tribe of Kandahar, Afghanistan, and the founder of the Hotak dynasty.
In 1709, after overthrowing and assassinating ...
who belonged to an influential family in Kandahar. Mirwais was sent as a prisoner to the Persian court in Isfahan, but the charges against him were dismissed by the king, so he was sent back to his native land as a free man.revolted
In political science, a revolution ( Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically d ...
.uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
began when George XI and his escort were killed after a banquet that had been prepared by Mirwais at his house outside the city. Southern Afghanistan was made into an independent local Pashtun kingdom.
Southern Afghanistan was made into an independent local Pashtun kingdom.Abdul Aziz Hotak
Sh─üh Abdul Az─½z Hotak (Pashto/Dari: ; died 1717) was the second ruler of the Ghilji Hotak dynasty of Kandahar, in what is now the modern state of Afghanistan. He was crowned in 1715 after the death of his brother, Mirwais Hotak. He was the fathe ...
. Aziz was killed about two years later by Mirwais' son Mahmud Hotaki, allegedly for planning to give Kandahar's sovereignty back to Persia.Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ž¦┘ģž¦ž▒ž¬ ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
was ruled by Mahmud's younger brother Shah Hussain Hotaki. Ashraf was able to secure peace with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ą×╬ĖŽē╬╝╬▒╬Į╬╣╬║╬« ╬æŽģŽä╬┐╬║Žü╬▒Žä╬┐Žü╬»╬▒, Oth┼Źmanik─ō Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in 1727 (''See'' '' Treaty of Hamedan''), winning against a superior Ottoman army during the Ottoman-Hotaki War, but the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
took advantage of the continuing political unrest and civil strife to seize former Persian territories for themselves, limiting the amount of territory under Shah Mahmud's control.
The short lived Hotaki dynasty was a troubled and violent one from the very start as internecine conflict made it difficult for them to establish permanent control. The dynasty lived under great turmoil due to bloody succession feuds that made their hold on power tenuous. There was a massacre of thousands of civilians in Isfahan; including more than three thousand religious scholars, nobles, and members of the Safavid family.Abdali Abdali may refer to:
* An alternate name for the Durrani, one of the largest Pashtun tribes of Afghanistan and western Pakistan
** Ahmed Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, founder of the Durrani Empire in Afghanistan
* Al-Abdali, a dist ...
Pashtuns defeated him at the long Siege of Kandahar.
Afsharid Invasion and Durrani Empire
Nader Shah and his Afsharid
Afsharid Iran ( fa, ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘å ž¦┘üž┤ž¦ž▒█ī), also referred as the Afsharid Empire was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, ruling Iran (Persia). The state was ruled by the A ...
army arrived in the town of Kandahar in 1738 and defeated Hussain Hotaki subsequently absorbing all of Afghanistan in his empire and renaming Kandahar as Naderabad. Around this time, a young teenager Ahmad Khan joined Nader Shah's army for his invasion of India.  Nadir Shah was assassinated on 19 June 1747 by several of his Persian officers, and the Afsharid empire fell to pieces. At the same time the 25-year-old Ahmad Khan was busy in Afghanistan calling for a loya jirga ("grand assembly") to select a leader among his people. The Afghans gathered near Kandahar in October 1747 and chose Ahmad Shah from among the challengers, making him their new
Nadir Shah was assassinated on 19 June 1747 by several of his Persian officers, and the Afsharid empire fell to pieces. At the same time the 25-year-old Ahmad Khan was busy in Afghanistan calling for a loya jirga ("grand assembly") to select a leader among his people. The Afghans gathered near Kandahar in October 1747 and chose Ahmad Shah from among the challengers, making him their new head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110ŌĆō11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
. After the inauguration or coronation
A coronation is the act of placement or bestowal of a crown upon a monarch's head. The term also generally refers not only to the physical crowning but to the whole ceremony wherein the act of crowning occurs, along with the presentation of o ...
, he became known as Ahmad Shah Durrani. He adopted the title ''padshah durr-i dawran'' ('King, "pearl of the age") and the Abdali tribe became known as the Durrani tribe after this. Ahmad Shah not only represented the Durranis but he also united all the Pashtun tribes
The Pashtun tribes ( ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć ┘éž©ž¦┘Ŗ┘ä), historically also known as Afghan tribes, are the tribes of the Pashtun people, a large Eastern Iranian ethnic group who use the Pashto language and follow Pashtunwali code of conduct. They a ...
. By 1751, Ahmad Shah Durrani and his Afghan army conquered the entire present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and for a short time, subjugated large swathes of the Khorasan and Kohistan provinces of Iran, along with Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
in India.Shrine of the Cloak
Kirka Sharif ( ps, ž«ž▒┘é┘ć ž┤ž▒┘Ŗ┘ü┘ć Shrine of the Cloak) is an Islamic shrine located in present-day Kandahar, Afghanistan. The shrine became notable in literature during the Second Anglo-Afghan War, when the British Indian army were trying t ...
. He was succeeded by his son, Timur Shah Durrani
Timur Shah Durrani (; prs, ;), also known as Timur Shah Abdali or Taimur Shah Abdali (December 1746 ŌĆō May 20, 1793) was the second ruler of the Afghan Durrani Empire, from November 1772 until his death in 1793. An ethnic Pashtun, he was the s ...
, who transferred the capital of their Afghan Empire from Kandahar to Kabul. Timur died in 1793 and his son Zaman Shah Durrani took over the reign.
Zaman Shah and his brothers had a weak hold on the legacy left to them by their famous ancestor. They sorted out their differences through a "round robin of expulsions, blindings and executions," which resulted in the deterioration of the Afghan hold over far-flung territories, such as Attock
Attock (Punjabi and Urdu: ), formerly known as Campbellpur (), is a historical city located in the north of Pakistan's Punjab Province, not far from the country's capital Islamabad. It is the headquarters of the Attock District and is 61st lar ...
and Kashmir. Durrani's other grandson, Shuja Shah Durrani, fled the wrath of his brother and sought refuge with the Sikhs. Not only had Durrani invaded the Punjab region many times, but had destroyed the holiest shrine of the Sikhs ŌĆō the Harmandir Sahib in Amritsar, defiling its ''sarowar'' with the blood of cows and decapitating Baba Deep Singh
Baba Deep Singh (26 January 1682 ŌĆō 13 November 1757) is revered among Sikhs as one of the most hallowed martyrs in Sikhism. He is remembered for his sacrifice and devotion to the teachings of the Sikh Gurus. Baba Deep Singh was the fir ...
in 1757. The Sikhs, under Ranjit Singh, eventually wrested a large part of the Durrani Kingdom (present day Pakistan, but not including Sindh) from the Afghans while they were in civil war.
Barakzai dynasty and British influence
 The Emir Dost Mohammed Khan (1793ŌĆō1863) gained control in Kabul in 1826 after toppling his brother,
The Emir Dost Mohammed Khan (1793ŌĆō1863) gained control in Kabul in 1826 after toppling his brother, Sultan Mohammad Khan
Sultan Mohammad Khan (Pashto/ Dari: ), also known as Ghazi Sardar Sultan Mohammad Talaei, was an Afghan aristocrat, chief minister and regent. He was a powerful brother of Emir Dost Mohammad Khan, the eventual ruler of Afghanistan who seized co ...
, and founded () the Barakzai dynasty
The two branches of the Barakzai dynasty (, "sons of Barak") ruled modern day Afghanistan from 1823 to 1973 when the monarchy ended under Musahiban Mohammed Zahir Shah. The Barakzai dynasty was established by Dost Mohammad Khan after the Durr ...
. In 1837, the Afghan army
The Army of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (), also referred to as the Islamic Emirate Army and the Afghan Army, is the land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. The roots of an army in Afghanistan can be t ...
descended through the Khyber Pass on Sikh forces at Jamrud killed the Sikh general Hari Singh Nalwa but could not capture the fort. Rivalry between the expanding British and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
s in what became known as " The Great Game" significantly influenced Afghanistan during the 19th century. British concern over Russian advances in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
and over Russia's growing influence in West Asia and in Persia in particular culminated in two Anglo-Afghan wars and in the Siege of Herat (1837ŌĆō1838), in which the Persians, trying to retake Afghanistan and throw out the British, sent armies into the country and fought the British mostly around and in the city of Herat. The first Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, ž¼┘å┌» ž¦┘ł┘ä ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘å ┘ł ž¦┘å┌»┘ä█īž│) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a succession di ...
(1839ŌĆō1842) resulted in the destruction of a British army; causing great panic throughout British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and the dispatch of a second British invasion army. Following the British defeat in the First Anglo-Afghan War, where they tried to re-establish the Durrani Kingdom as a de facto vassal, Dost Mohammad could focus on reuniting Afghanistan, which was divided following the Durrani-Barakzai civil wars. Dost Mohammad began his conquest while only ruling the major cities of Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
, Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, ž║ž▓┘å█ī, ps, ž║ž▓┘å┘Ŗ), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, ╬æ╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬®ŽĆ╬╣╬▒╬Į╬«), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
, Jalalabad, and Bamyan. By the time of his death in 1863, Dost Mohammad had reunited most of Afghanistan. Following Dost Mohammad's death, a civil war broke out amongst his sons, leading to Sher Ali succeeding and beginning his rule. The Second Anglo-Afghan War (1878ŌĆō1880) resulted from the refusal by Emir Shir Ali (reigned 1863 to 1866 and from 1868 to 1879) to accept a British diplomatic mission in Kabul. In the wake of this conflict Shir Ali's nephew, Emir Abdur Rahman, known as "Iron Emir",
came to the Afghan throne. During his reign (1880ŌĆō1901), the British and Russians officially established the boundaries of what would become modern Afghanistan. The British retained effective control over Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
's foreign affairs. Abdur Rahman's reforms of the army, legal system and structure of government gave Afghanistan a degree of unity and stability which it had not before known. This, however, came at the cost of strong centralisation, of harsh punishments for crime and corruption, and of a certain degree of international isolation.[Afghanistan and the Search for Unity]
Omrani, Bijan, published in ''Asian Affairs'', Volume 38, Issue 2, 2007, pp. 145ŌĆō57.
Habibullah Khan
Habibullah Khan (Pashto/ Dari: ; 3 June 1872 ŌĆō 20 February 1919) was the Emir of Afghanistan from 1901 until his death in 1919. He was the eldest son of the Emir Abdur Rahman Khan, whom he succeeded by right of primogeniture in October 190 ...
, Abdur Rahman's son, came to the throne in 1901 and kept Afghanistan neutral during World War I, despite encouragement by Central Powers of anti-British feelings and of Afghan rebellion along the borders of India. His policy of neutrality was not universally popular within the country, and Habibullah was assassinated in 1919, possibly by family members opposed to British influence. His third son, Amanullah Amanullah or Amanallah is a male Muslim given name ( ar , žŻ┘ģž¦┘å ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć ) meaning the trust or protection of God. It may refer to:
* Am─ünull─üh Kh─ün (1892ŌĆō1960), ruler of Afghanistan from 1919 to 1929
* Amanullah Khan (disambiguation), sev ...
(), regained control of Afghanistan's foreign policy after launching the Third Anglo-Afghan War (May to August 1919) with an attack on India. During the ensuing conflict the war-weary British relinquished their control over Afghan foreign affairs by signing the Treaty of Rawalpindi
The Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919, also known as the Treaty of Rawalpindi, was a treaty which brought the Third Anglo-Afghan War to an end. It was signed on 8 August 1919 in Rawalpindi by the United Kingdom and the Emirate of Afghanistan. Britain r ...
in August 1919. In commemoration of this event Afghans celebrate 19 August as their Independence Day.
Reforms of Amanullah Khan and civil war
King Amanullah Khan
Ghazi Amanullah Khan (Pashto and Dari: ; 1 June 1892 ŌĆō 25 April 1960) was the sovereign of Afghanistan from 1919, first as Emir and after 1926 as King, until his abdication in 1929. After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War in August 1 ...
moved to end his country's traditional isolation in the years following the Third Anglo-Afghan war. After quelling the Khost rebellion in 1925, he established diplomatic relations with most major countries and, following a 1927 tour of Europe and Turkey (during which he noted the modernization and secularization advanced by Atat├╝rk), introduced several reforms intended to modernize Afghanistan. A key force behind these reforms was Mahmud Tarzi
Mahmud Tarzi ( ps, ┘ģžŁ┘ģ┘łž» žĘž▒ž▓█Ź, Dari: ┘ģžŁ┘ģ┘łž» ž©█ī┌» žĘž▒ž▓█ī; August 23, 1865 ŌĆō November 22, 1933) was an Afghan politician and intellectual. He is known as the father of Afghan journalism. He became a key figure in the history of ...
, Amanullah Khan's Foreign Minister and father-in-law ŌĆö and an ardent supporter of the education of women. He fought for Article 68 of Afghanistan's first constitution (declared through a Loya Jirga), which made elementary education compulsory. Some of the reforms that were actually put in place, such as the abolition of the traditional Muslim veil for women and the opening of a number of co-educational schools, quickly alienated many tribal and religious leaders, which led to the revolt of the Shinwari in November 1928, marking the beginning of the Afghan Civil War (1928ŌĆō1929). Although the Shinwari revolt was quelled, a concurrent Saqqawist
The Saqqawists (Pashto:ž│┘鞦┘ł█īž¦┘å prs, ž│┘鞦┘ł█īŌĆī┘枦 ''Saq─üw─½h─ü'') were an armed group in the Kingdom of Afghanistan who were active from 1924 to 1931. They were led by Habibull─üh Kalak─üni, and in January 1929, they managed to take c ...
uprising in the north eventually managed to depose Amanullah, leading to Habibull─üh Kalak─üni taking control of Kabul.
Reigns of Nadir Khan and Zahir Khan
 Mohammed Nadir Khan became King of Afghanistan on 15 October 1929 after he took control of Afghanistan by defeating the
Mohammed Nadir Khan became King of Afghanistan on 15 October 1929 after he took control of Afghanistan by defeating the Habibullah Kalakani Habibullah also spelled Habib Ullah, Habibollah, Habeeb-Allah etc. ( ar, žŁ┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘Æž©┘Ä┘Å ┘▒┘ä┘ä┘ć), is a male Muslim given name meaning in ''Beloved of God'', stemming from the male form of the name Habib. It may refer to:
People
*Raja Sir C ...
. He then executed him in 1 November of same year. He began consolidating power and regenerating the country. He abandoned the reforms of Amanullah Khan in favour of a more gradual approach to modernisation. In 1933, however, he was assassinated in a revenge killing by a student from Kabul.
Mohammad Zahir Shah, Nadir Khan's 19-year-old son, succeeded to the throne and reigned from 1933 to 1973. The Afghan tribal revolts of 1944ŌĆō1947 saw Zahir Shah's reign being challenged by Zadran, Safi and Mangal tribesmen led by Mazrak Zadran and Salemai among others. Until 1946 Zahir Shah ruled with the assistance of his uncle Sardar Mohammad Hashim Khan, who held the post of Prime Minister and continued the policies of Nadir Khan. In 1946, another of Zahir Shah's uncles, Sardar Shah Mahmud Khan
Sardar Shah Mahmud Khan (Pashto/Dari: ž│ž▒ž»ž¦ž▒ ž┤ž¦┘ć ┘ģžŁ┘ģ┘łž» ž«ž¦┘å ŌĆō b:1890 d: 27 December 1959) was the Prime Minister of Afghanistan from May 1946 to 7 September 1953, under King Mohammed Zahir Shah's monarchy. He was from the Pashtun ...
, became Prime Minister and began an experiment allowing greater political freedom, but reversed the policy when it went further than he expected. In 1953, he was replaced as Prime Minister by Mohammed Daoud Khan
Mohammed Daoud Khan ( ps, ), also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan (18 July 1909 ŌĆō 28 April 1978), was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan cou ...
, the king's cousin and brother-in-law. Daoud looked for a closer relationship with the Soviet Union and a more distant one towards Pakistan. However, disputes with Pakistan led to an economic crisis and he was asked to resign in 1963. From 1963 until 1973, Zahir Shah took a more active role.
In 1964, King Zahir Shah promulgated a liberal constitution providing for a bicameral legislature to which the king appointed one-third of the deputies. The people elected another third, and the remainder were selected indirectly by provincial assemblies. Although Zahir's "experiment in democracy" produced few lasting reforms, it permitted the growth of parties on both the left and the right. This included the communist People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA), which had close ideological ties to the Soviet Union. In 1967, the PDPA split into two major rival factions: the Khalq
Khalq ( ps, ž«┘ä┘é, ) was a faction of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA). Its historical ''de facto'' leaders were Nur Muhammad Taraki (1967ŌĆō1979), Hafizullah Amin (1979) and Sayed Mohammad Gulabzoy (1979ŌĆō1990). It was also ...
(Masses) was headed by Nur Muhammad Taraki and Hafizullah Amin who were supported by elements within the military, and the Parcham
Parcham (Pashto and prs, ┘Šž▒┌å┘ģ, ) was the name of one of the factions of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan, formed in 1967 following its split and led for most of its history by Babrak Karmal and Mohammed Najibullah. The basic ide ...
(Banner) led by Babrak Karmal.
Contemporary era (1973ŌĆōpresent)
Republic of Afghanistan and the end of the monarchy
Amid corruption charges and malfeasance against the royal family and the poor economic conditions created by the severe 1971ŌĆō72 drought, former Prime Minister Mohammad Sardar Daoud Khan seized power in a non-violent coup on July 17, 1973, while Zahir Shah was receiving treatment for eye problems and therapy for lumbago in Italy.[Barry Bearak]
Former King of Afghanistan Dies at 92
''The New York Times'', July 23, 2007. Daoud abolished the monarchy, abrogated the 1964 constitution, and declared Afghanistan a republic with himself as its first President and Prime Minister. His attempts to carry out badly needed economic and social reforms met with little success, and the new constitution promulgated in February 1977 failed to quell chronic political instability.
As disillusionment set in, in 1978 a prominent member of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA), Mir Akbar Khyber (or "Kaibar"), was killed by the government. The leaders of PDPA apparently feared that Daoud was planning to exterminate them all, especially since most of them were arrested by the government shortly after. Nonetheless, Hafizullah Amin and a number of military wing officers of the PDPA's Khalq
Khalq ( ps, ž«┘ä┘é, ) was a faction of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA). Its historical ''de facto'' leaders were Nur Muhammad Taraki (1967ŌĆō1979), Hafizullah Amin (1979) and Sayed Mohammad Gulabzoy (1979ŌĆō1990). It was also ...
faction managed to remain at large and organize a military coup.
Democratic Republic and Soviet war (1978ŌĆō1989)

 On 28 April 1978, the PDPA, led by Nur Mohammad Taraki, Babrak Karmal and Amin Taha overthrew the government of Mohammad Daoud, who was assassinated along with all his family members in a bloody military coup. The coup became known as the Saur Revolution. On 1 May, Taraki became
On 28 April 1978, the PDPA, led by Nur Mohammad Taraki, Babrak Karmal and Amin Taha overthrew the government of Mohammad Daoud, who was assassinated along with all his family members in a bloody military coup. The coup became known as the Saur Revolution. On 1 May, Taraki became head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110ŌĆō11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
, head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a ...
and General Secretary of the PDPA. The country was then renamed the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan (DRA), and the PDPA regime lasted, in some form or another, until April 1992.
In March 1979, Hafizullah Amin took over as prime minister, retaining the position of field marshal and becoming vice-president of the Supreme Defence Council. Taraki remained General Secretary, Chairman of the Revolutionary Council and in control of the Army. On 14 September, Amin overthrew Taraki, who was killed. Amin stated that "the Afghans recognize only crude force."women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countri ...
, banning forced marriages and giving state recognition of women's right to vote. A prominent example was Anahita Ratebzad
Anahita Ratebzad (Persian/ ps, žó┘垦┘ć█īž¬ž¦ ž▒ž¦ž¬ž©ž▓ž¦ž»; November 1931 ŌĆō 7 September 2014) was an Afghan socialist and Marxist-Leninist politician and a member of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) and the Revolutionary ...
, who was a major Marxist leader and a member of the Revolutionary Council. Ratebzad wrote the famous ''New Kabul Times'' editorial (May 28, 1978) which declared: "Privileges which women, by right, must have are equal education, job security, health services, and free time to rear a healthy generation for building the future of the country ... Educating and enlightening women is now the subject of close government attention." The PDPA also carried out socialist land reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultura ...
s and moved to promote state atheism. They also prohibited usury
Usury () is the practice of making unethical or immoral monetary loans that unfairly enrich the lender. The term may be used in a moral senseŌĆöcondemning taking advantage of others' misfortunesŌĆöor in a legal sense, where an interest rate is c ...
. The PDPA invited the Soviet Union to assist in modernizing its economic infrastructure (predominantly its exploration and mining of rare minerals and natural gas). The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
also sent contractors to build roads, hospitals and schools and to drill water wells; they also trained and equipped the Afghan Armed Forces
("The land belongs to Allah, the rule belongs to Allah")
, founded = 1997
, current_form =
, branches =
* Afghan Army
* Afghan Air Force
, headquarters = Kabul
, website =
, commander-in-chie ...
. Upon the PDPA's ascension to power, and the establishment of the DRA, the Soviet Union promised monetary aid amounting to at least $1.262 billion.
 At the same time, the PDPA imprisoned, tortured or murdered thousands of members of the traditional elite, the religious establishment, and the intelligentsia. The government launched a campaign of violent repression, killing some 10,000 to 27,000 people and imprisoning 14,000 to 20,000 more, mostly at Pul-e-Charkhi prison. In December 1978 the PDPA leadership signed an agreement with the Soviet Union which would allow military support for the PDPA in Afghanistan if needed. The majority of people in the cities including Kabul either welcomed or were ambivalent to these policies. However, the MarxistŌĆōLeninist and secular nature of the government as well as its heavy dependence on the Soviet Union made it unpopular with a majority of the Afghan population. Repressions plunged large parts of the country, especially the rural areas, into open revolt against the new MarxistŌĆōLeninist government. By spring 1979 unrests had reached 24 out of 28 Afghan provinces including major urban areas. Over half of the Afghan army would either desert or join the insurrection. Most of the government's new policies clashed directly with the traditional Afghan understanding of Islam, making religion one of the only forces capable of unifying the tribally and ethnically divided population against the unpopular new government, and ushering in the advent of Islamist participation in Afghan politics.
At the same time, the PDPA imprisoned, tortured or murdered thousands of members of the traditional elite, the religious establishment, and the intelligentsia. The government launched a campaign of violent repression, killing some 10,000 to 27,000 people and imprisoning 14,000 to 20,000 more, mostly at Pul-e-Charkhi prison. In December 1978 the PDPA leadership signed an agreement with the Soviet Union which would allow military support for the PDPA in Afghanistan if needed. The majority of people in the cities including Kabul either welcomed or were ambivalent to these policies. However, the MarxistŌĆōLeninist and secular nature of the government as well as its heavy dependence on the Soviet Union made it unpopular with a majority of the Afghan population. Repressions plunged large parts of the country, especially the rural areas, into open revolt against the new MarxistŌĆōLeninist government. By spring 1979 unrests had reached 24 out of 28 Afghan provinces including major urban areas. Over half of the Afghan army would either desert or join the insurrection. Most of the government's new policies clashed directly with the traditional Afghan understanding of Islam, making religion one of the only forces capable of unifying the tribally and ethnically divided population against the unpopular new government, and ushering in the advent of Islamist participation in Afghan politics.Parcham
Parcham (Pashto and prs, ┘Šž▒┌å┘ģ, ) was the name of one of the factions of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan, formed in 1967 following its split and led for most of its history by Babrak Karmal and Mohammed Najibullah. The basic ide ...
faction, the Soviet Union decided to intervene on December 27, 1979, when the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: ąĀą░ą▒ąŠ╠üč湥-ą║čĆąĄčüčéčīčÅ╠üąĮčüą║ą░čÅ ąÜčĆą░╠üčüąĮą░čÅ ą░čĆą╝ąĖčÅ),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
invaded its southern neighbor. Over 100,000 Soviet troops took part in the invasion, which was backed by another 100,000 Afghan military men and supporters of the Parcham faction. In the meantime, Hafizullah Amin was killed and replaced by Babrak Karmal.
The Carter administration started providing limited assistance to rebels before the Soviet invasion. After the Soviet occupation of Afghanistan, the U.S. began arming the Afghan mujahideen, thanks in large part to the efforts of Charlie Wilson and CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
officer Gust Avrakotos. Early reports estimated that $6ŌĆō20 billion had been spent by the U.S. and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
surface-to-air missiles
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft sys ...
, for building up Islamic groups against the Soviet Union. The U.S. handled most of its support through Pakistan's ISI
ISI or Isi may refer to:
Organizations
* Intercollegiate Studies Institute, a classical conservative organization focusing on college students
* Ice Skating Institute, a trade association for ice rinks
* Indian Standards Institute, former name of ...
.
Scholars such as W. Michael Reisman, Charles Norchi and Mohammed Kakar, believe that the Afghans were victims of genocide by the Soviet Union.Afghan refugees
Afghan refugees are citizens of Afghanistan who were compelled to abandon their country as a result of major wars, persecution, torture or genocide. The 1978 Saur Revolution followed by the 1979 Soviet invasion marked the first wave of interna ...
to Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and from there over 38,000 made it to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and many more to the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
. The Afghan refugees in Iran and Pakistan brought with them verifiable stories of murder, collective rape, torture and depopulation of civilians by the Soviet forces. Faced with mounting international pressure and great number of casualties on both sides, the Soviets withdrew in 1989. Their withdrawal from Afghanistan was seen as an ideological victory in the United States, which had backed some Mujahideen factions through three U.S. presidential administrations to counter Soviet influence in the vicinity of the oil-rich Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, ž«┘ä█īž¼ ┘üž¦ž▒ž│, translit=xalij-e f├órs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, ž¦┘Ä┘ä┘Æž«┘Ä┘ä┘É┘Ŗ┘Æž¼┘Å ┘▒┘ä┘Æž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘Å┘æ, Al-Khal─½j al-╦üArab─½), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
. The USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
continued to support Afghan leader Mohammad Najibullah (former head of the Afghan secret service, '' KHAD'') until 1992.
''Columbia Encyclopedia'': Afghanistan - History.
Foreign interference and civil war (1989ŌĆō1996)

Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
's spy agency Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), headed by Hamid Gul
Lieutenant General Hamid Gul ( ur, ; 20 November 1936 ŌĆō 15 August 2015) was a three-star rank army general in the Pakistan Army and defence analyst. Gul was notable for serving as the Director-General of the Inter-Services Intelligenc ...
at the time, was interested in a trans-national Islamic revolution which would cover Pakistan, Afghanistan and Central Asia. For this purpose the ISI masterminded an attack on Jalalabad in March 1989, for the Mujahideen to establish their own government in Afghanistan, but this failed in three months.
With the crumbling of the Najibullah regime early in 1992, Afghanistan fell into further disarray and civil war. A U.N.-supported attempt to have the mujahideen parties and armies form a coalition government shattered. Mujahideen did not abide by the mutual pledges and Ahmad Shah Masood forces because of his proximity to Kabul captured the capital before Mujahideen Govt was established. So the elected prime minister and warlord Gulbuddin Hekmatyar, started war on his president and Massod force entrenched in Kabul. This ignited civil war, because the other mujahideen parties wouldn't settle for Hekmatyar ruling alone or sharing actual power with him. Within weeks, the still frail unity of the other mujahideen forces also evaporated, and six militias were fighting each other in and around Kabul.
Sibghatuallah Mojaddedi was elected as Afghanistan's elected interim president for two months and then professor Burhanuddin Rabbani a well known Kabul university professor and the leader of Jamiat-e-Islami party of Mujahiddin who fought against Russians during the occupation was chosen by all of the Jahadi leaders except Gulbuddin Hekmatyar. Professor Rabbani reigned as the official and elected president of Afghanistan by Shurai Mujahiddin Peshawer (Peshawer Mujahiddin Council) from 1992 until 2001 when he officially handed over the presidency post to Hamid Karzai the next US appointed interim president. During Rabbani's presidency some parts of the country including a few provinces in the north such as Mazar e-Sharif, Jawzjan, Faryab, Shuburghan and some parts of Baghlan provinces were ruled by general Abdul Rashid Dostum.
During Rabbani's first five years illegal term before the emergence of the Taliban, the eastern and western provinces and some of the northern provinces such as Badakhshan, Takhar, Kunduz, the main parts of Baghlan Province, and some parts of Kandahar and other southern provinces were under the control of the central government while the other parts of southern provinces did not obey him because of his Tajik ethnicity. During the 9 year presidency of Burhanuddin Rabani, Gulbuddin Hekmatyar was directed, funded and supplied by the Pakistani army.Amin Saikal
Professor Amin Saikal (born in Kabul, Afghanistan), is Adjunct Professor of Social Sciences at the University of Western Australia, and a former University Distinguished Professor and Director of the Centre for Arab and Islamic Studies (The Mi ...
concludes in his book ''Modern Afghanistan: A History of Struggle and Survival'':
There was no time for the interim government to create working government departments, police units or a system of justice and accountability. Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
and Iran also armed and directed Afghan militias.George Washington University
, mottoeng = "God is Our Trust"
, established =
, type = Private federally chartered research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $2.8 billion (2022)
, presi ...
describes:
According to Human Rights Watch, numerous Iranian agents were assisting the Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
Hezb-i Wahdat forces of Abdul Ali Mazari, as Iran was attempting to maximize Wahdat's military power and influence.Wahhabite
Wahhabism ( ar, ┘▒┘ä┘Æ┘ł┘Ä┘ć┘Ä┘枦ž©┘É┘Ŗ┘Äž®┘Å, translit=al-Wahh─übiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, and ...
Abdul Rasul Sayyaf and his Ittihad-i Islami faction.Hezb-i Islami
Hezb-e-Islami (also ''Hezb-e Islami'', ''Hezb-i-Islami'', ''Hezbi-Islami'', ''Hezbi Islami''), lit. Islamic Party, was an Islamist organization that was commonly known for fighting the Communist Government of Afghanistan and their close ally ...
of Gulbuddin Hekmatyar directed by Pakistan, the Hezb-i Wahdat of Abdul Ali Mazari directed by Iran, the Ittehad-i Islami of Abdul Rasul Sayyaf supported by Saudi Arabia, the Junbish-i Milli of Abdul Rashid Dostum backed by Uzbekisten, the Harakat-i Islami of Hussain Anwari and the Shura-i Nazar
The Shura-e Nazar ( fa, ž┤┘łž▒ž¦žĪ ┘åžĖž¦ž▒) (known as the Supervisory Council of the North) was created by Ahmad Shah Massoud in 1984 at the northern provinces of Takhar, Badakhshan, Balkh and Kunduz, during the Soviet-Afghan War. It comprise ...
operating as the regular Islamic State forces (as agreed upon in the Peshawar Accords) under the Defence Ministry of Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975ŌĆō2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the SovietŌĆōAfghan War ...
.
Meanwhile, the southern city of Kandahar was a centre of lawlessness, crime and atrocities fuelled by complex Pashtun tribal rivalries.[Matinuddin, Kamal, ''The Taliban Phenomenon, Afghanistan 1994ŌĆō1997'', ]Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print book ...
, (1999), pp.25ŌĆō6 In 1994, the Taliban (a movement originating from Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam-run religious schools for Afghan refugees in Pakistan) also developed in Afghanistan as a politico-religious force, reportedly in opposition to the tyranny of the local governor.Mullah Omar
Mullah Muhammad Omar (; ŌĆōApril 2013) was an Afghan Islamic revolutionary who founded the Taliban and served as the supreme leader of Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001.
Born into a religious family of Kandahar, Omar was educated at local ''madras ...
started his movement with fewer than 50 armed madrassah students in his hometown of Kandahar.Amin Saikal
Professor Amin Saikal (born in Kabul, Afghanistan), is Adjunct Professor of Social Sciences at the University of Western Australia, and a former University Distinguished Professor and Director of the Centre for Arab and Islamic Studies (The Mi ...
describe the Taliban as developing into a proxy force for Pakistan's regional interests.
Taliban and the United Front (1996ŌĆō2001)


 The Taliban started shelling Kabul in early 1995 but were defeated by forces of the Islamic State government under Ahmad Shah Massoud.
The Taliban started shelling Kabul in early 1995 but were defeated by forces of the Islamic State government under Ahmad Shah Massoud.[Amnesty International. "Document ŌĆō Afghanistan: Further Information on Fear for Safety and New Concern: Deliberate and Arbitrary Killings: Civilians in Kabul". 16 November 1995 Accessed at* ] Amnesty International, referring to the Taliban offensive, wrote in a 1995 report:
On September 26, 1996, as the Taliban, with military support by Pakistan and financial support by Saudi Arabia, prepared for another major offensive, Massoud ordered a full retreat from Kabul. The Taliban seized Kabul on September 27, 1996, and established the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. They imposed on the parts of Afghanistan under their control their political and judicial interpretation of Islam, issuing edicts forbidding women from working outside the home, attending school or leaving their homes unless accompanied by a male relative.Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975ŌĆō2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the SovietŌĆōAfghan War ...
and Abdul Rashid Dostum, two former enemies, created the United Front ( Northern Alliance) against the Taliban, who were preparing offensives against the remaining areas under the control of Massoud and Dostum. The United Front included beside the dominantly Tajik forces of Massoud and the Uzbek forces of Dostum, Hazara factions and Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
forces under the leadership of commanders such as Abdul Haq, Haji Abdul Qadir
Abd al-Qadir or Abdulkadir ( ar, ž╣ž©ž» ž¦┘ä┘鞦ž»ž▒) is a male Muslim given name. It is formed from the Arabic words '' Abd'', '' al-'' and '' Qadir''. The name means "servant of the powerful", ''Al-Q─üdir'' being one of the names of God in th ...
, Qari Baba or diplomat Abdul Rahim Ghafoorzai. From the Taliban conquest in 1996 until November 2001 the United Front controlled roughly 30% of Afghanistan's population in provinces such as Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic ...
, Kapisa Province, Kapisa, Takhar and parts of Parwan, Kunar, Nuristan, Laghman, Samangan, Kunduz, Gh┼Źr and Bamyan.
According to a 55-page report by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
, the Taliban, while trying to consolidate control over northern and western Afghanistan, committed systematic massacres against civilians.Mullah Omar
Mullah Muhammad Omar (; ŌĆōApril 2013) was an Afghan Islamic revolutionary who founded the Taliban and served as the supreme leader of Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001.
Born into a religious family of Kandahar, Omar was educated at local ''madras ...
himself."civilian
Civilians under international humanitarian law are "persons who are not members of the armed forces" and they are not " combatants if they carry arms openly and respect the laws and customs of war". It is slightly different from a non-combatant ...
s were executed by the Taliban and many more reported torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts ...
. Among those killed in Mazari Sharif were several Iranian diplomats. Others were kidnapped by the Taliban, touching off a hostage crisis that nearly escalated to a full-scale war, with 150,000 Iranian soldiers massed on the Afghan border at one time. It was later admitted that the diplomats were killed by the Taliban, and their bodies were returned to Iran.
The documents also reveal the role of Arab and Pakistani support troops in these killings.055 Brigade
The 055 Brigade (or 55th Arab Brigade) was a guerrilla organization sponsored and trained by Al Qaeda that was integrated into the Taliban army between 1995 and 2001.
Composition and role
The unit consisted mostly of foreign guerrilla fighters ( ...
was responsible for mass-killings of Afghan civilians.U.S. State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other n ...
confirms that "20ŌĆō40 percent of egularTaliban soldiers are Pakistani."Ayman al-Zawahiri
Ayman Mohammed Rabie al-Zawahiri (June 19, 1951 ŌĆō July 31, 2022) was an Egyptian-born terrorist and physician who served as the second emir of al-Qaeda from June 16, 2011, until his death.
Al-Zawahiri graduated from Cairo University with a ...
became a state within the Taliban state.Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975ŌĆō2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the SovietŌĆōAfghan War ...
set up democratic institutions and signed the Women's Rights Charter.Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975ŌĆō2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the SovietŌĆōAfghan War ...
.European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, R├®gion de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
asking the international community to provide humanitarian help to the people of Afghanistan.
NATO presence, the Emergency Loya Jirga, Taliban takeover and Panjshir uprising
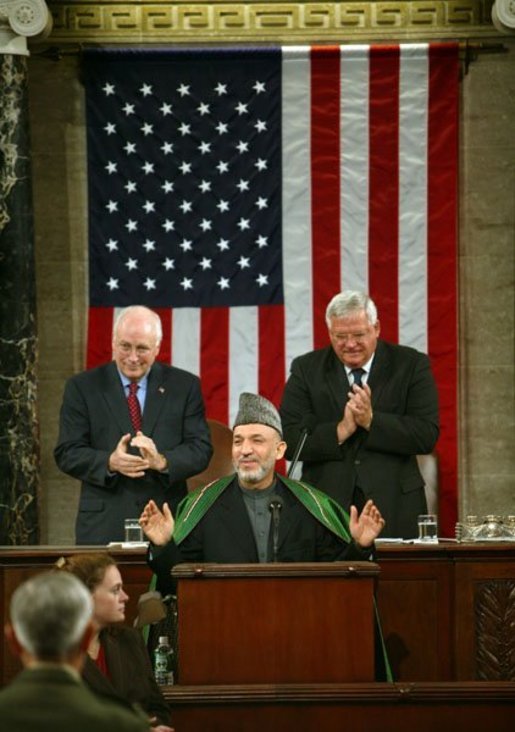 On 9 September 2001,
On 9 September 2001, Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975ŌĆō2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the SovietŌĆōAfghan War ...
was assassinated by two Arab suicide attack
A suicide attack is any violent attack, usually entailing the attacker detonating an explosive, where the attacker has accepted their own death as a direct result of the attacking method used. Suicide attacks have occurred throughout histor ...
ers inside Afghanistan. Two days later about 3,000 people became victims of the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
in the United States, when Afghan-based Al-Qaeda suicide bombers hijacked planes and flew them into four targets in the Northeastern United States. Then US President George W. Bush accused Osama bin Laden and Khalid Sheikh Mohammed as the faces behind the attacks. When the Taliban refused to hand over bin Laden to US authorities and to disband al-Qaeda bases in Afghanistan, Operation Enduring Freedom was launched in which teams of American and British special forces worked with commanders of the United Front (Northern Alliance) against the Taliban.International Security Assistance Force
The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was a multinational military mission in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2014. It was established by United Nations Security Council United Nations Security Council Resolution 1386, Resolution 1386 pursua ...
(ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration
Hamid Karzai (; Pashto/ fa, žŁž¦┘ģž» ┌®ž▒ž▓█ī, , ; born 24 December 1957) is an Afghan statesman who served as the fourth president of Afghanistan from July 2002 to September 2014, including as the first elected president of the Islamic Republ ...
and provide basic security to the Afghan people
Afghans ( ps, ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘垦┘å, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘å ┘枦, translit=afgh─ünh─ü; Persian: ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å█ī, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry f ...
. The majority of Afghans supported the American invasion of their country. While the Taliban began regrouping inside Pakistan, the rebuilding of war-torn Afghanistan kicked off in 2002 (see also
While the Taliban began regrouping inside Pakistan, the rebuilding of war-torn Afghanistan kicked off in 2002 (see also War in Afghanistan (2001ŌĆō2021)
The War in Afghanistan was an armed conflict that began when an Participants in Operation Enduring Freedom, international military coalition led by the United States launched United States invasion of Afghanistan, an invasion of Afghanistan, ...
). The Afghan nation was able to build democratic structures over the years by the creation of an emergency loya jirga to set up the modern Afghan government, and some progress was made in key areas such as governance, economy, health, education, transport, and agriculture. NATO had been training the Afghan armed forces
("The land belongs to Allah, the rule belongs to Allah")
, founded = 1997
, current_form =
, branches =
* Afghan Army
* Afghan Air Force
, headquarters = Kabul
, website =
, commander-in-chie ...
as well its national police. ISAF and Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban but failed to fully defeat them. By 2009, a Taliban-led shadow government began to form in many parts of the country complete with their own version of mediation court. After U.S. President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
announced the deployment of another 30,000 soldiers in 2010 for a period of two years, Der Spiegel published images of the US soldiers who killed unarmed Afghan civilians.
In 2009, the United States resettled 328 refugees from Afghanistan. Over five million Afghan refugees
Afghan refugees are citizens of Afghanistan who were compelled to abandon their country as a result of major wars, persecution, torture or genocide. The 1978 Saur Revolution followed by the 1979 Soviet invasion marked the first wave of interna ...
were repatriated in the last decade, including many who were forcefully deported from NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du trait├® de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states ŌĆō 28 European and two N ...
countries. This large return of Afghans may have helped the nation's economy but the country still remains one of the poorest in the world due to the decades of war, lack of foreign investment, ongoing government corruption and the Pakistani-backed Taliban insurgency. The United States also accuses neighboring Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
of providing small level of support to the Taliban insurgents. In October 2008 U.S. Defense Secretary Gates had asserted that a political settlement with the Taliban was the endgame for the Afghanistan war. "There has to be ultimately ŌĆō and I'll underscore ultimately ŌĆō reconciliation as part of a political outcome to this," Gates stated. By 2010 peace efforts began. In early January, Taliban commanders held secret exploratory talks with a United Nations special envoy to discuss peace terms. Regional commanders on the Taliban's leadership council, the Quetta Shura, sought a meeting with the UN special representative in Afghanistan,
In October 2008 U.S. Defense Secretary Gates had asserted that a political settlement with the Taliban was the endgame for the Afghanistan war. "There has to be ultimately ŌĆō and I'll underscore ultimately ŌĆō reconciliation as part of a political outcome to this," Gates stated. By 2010 peace efforts began. In early January, Taliban commanders held secret exploratory talks with a United Nations special envoy to discuss peace terms. Regional commanders on the Taliban's leadership council, the Quetta Shura, sought a meeting with the UN special representative in Afghanistan, Kai Eide
Kai Aage Eide (born 28 February 1949 in Sarpsborg) is a Norwegian diplomat and writer. He was appointed the United Nations Special Representative to Afghanistan and Head of the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) on 7 Marc ...
, and it took place in Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, wikt:ž»ž©┘Ŗ, ž»ž©┘Ŗ, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the List of cities in the United Arab Emirates#Major cities, most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 ...
on January 8. It was the first such meeting between the UN and senior members of the Taliban.Afghan President
The president of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was constitutionally the head of state and head of government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004ŌĆō2021) and Commander-in-Chief of the Afghan Armed Forces.
On 15 August 2021, as th ...
Hamid Karzai said he intends to reach out to the Taliban leadership (including Mullah Omar
Mullah Muhammad Omar (; ŌĆōApril 2013) was an Afghan Islamic revolutionary who founded the Taliban and served as the supreme leader of Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001.
Born into a religious family of Kandahar, Omar was educated at local ''madras ...
, Sirajuddin Haqqani and Gulbuddin Hekmatyar). Supported by NATO, Karzai called on the group's leadership to take part in a loya jirga meeting to initiate peace talks. These steps have resulted in an intensification of bombings, assassinations and ambushes.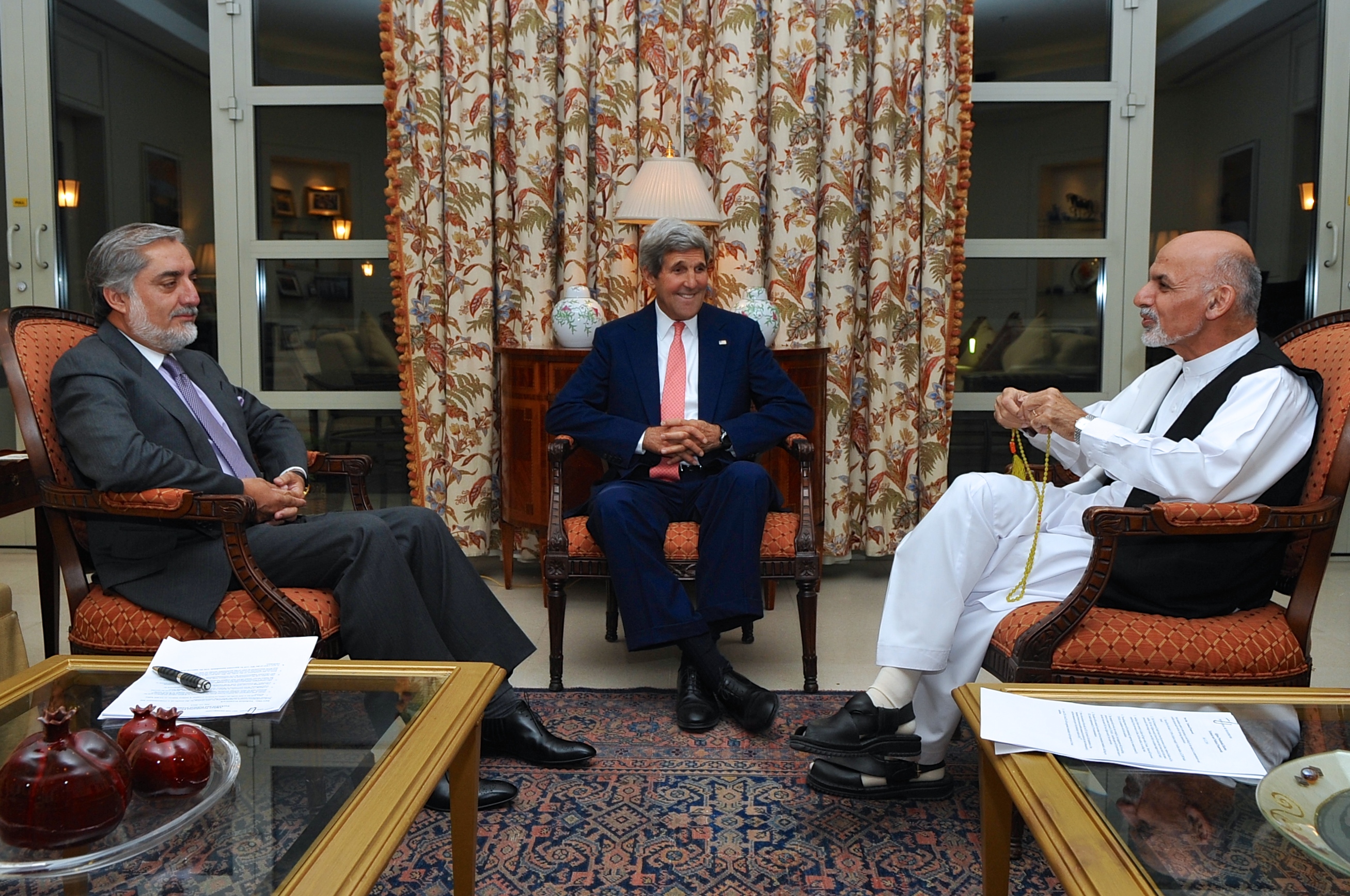 Afghan President Hamid Karzai told world leaders during the London conference that he intends to reach out to the top echelons of the Taliban within a few weeks with a peace initiative.
Afghan President Hamid Karzai told world leaders during the London conference that he intends to reach out to the top echelons of the Taliban within a few weeks with a peace initiative.Ahmad Wali Karzai
Ahmed Wali Karzai ( ps, ž¦žŁ┘ģž» ┘ł┘ä┘Ŗ ┌®ž▒ž▓█ī, , 1961 ŌĆō 12 July 2011) was a politician in Afghanis ...
, Jan Mohammad Khan
Jan Mohammad Khan (died July 17, 2011) was a politician in Afghanistan, who served as Governor of Oruzgan Province from January 2002 to March 2006, member of the National Assembly, and a special adviser to President Hamid Karzai.
He was an el ...
, Ghulam Haider Hamidi
Ghulam Haider Hamidi ( ps, ž║┘䞦┘ģ žŁ█īž»ž▒ žŁ┘ģ█īž»█ī, also spelled Ghulam Haidar Hameedi and also known as Henry Hamidi; 1945 ŌĆō 27 July 2011) was the Mayor of Kandahar in Afghanistan. his family fled to Pakistan, then to the United St ...
, Burhanuddin Rabbani and others.ISI
ISI or Isi may refer to:
Organizations
* Intercollegiate Studies Institute, a classical conservative organization focusing on college students
* Ice Skating Institute, a trade association for ice rinks
* Indian Standards Institute, former name of ...
spy network as the masterminds behind all of this.[
The U.S. ambassador to Pakistan, Cameron Munter, told Radio Pakistan that "The attack that took place in Kabul a few days ago, that was the work of the Haqqani network. There is evidence linking the Haqqani Network to the Pakistan government. This is something that must stop." Other top U.S. officials such as ]Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
and Leon Panetta made similar statements.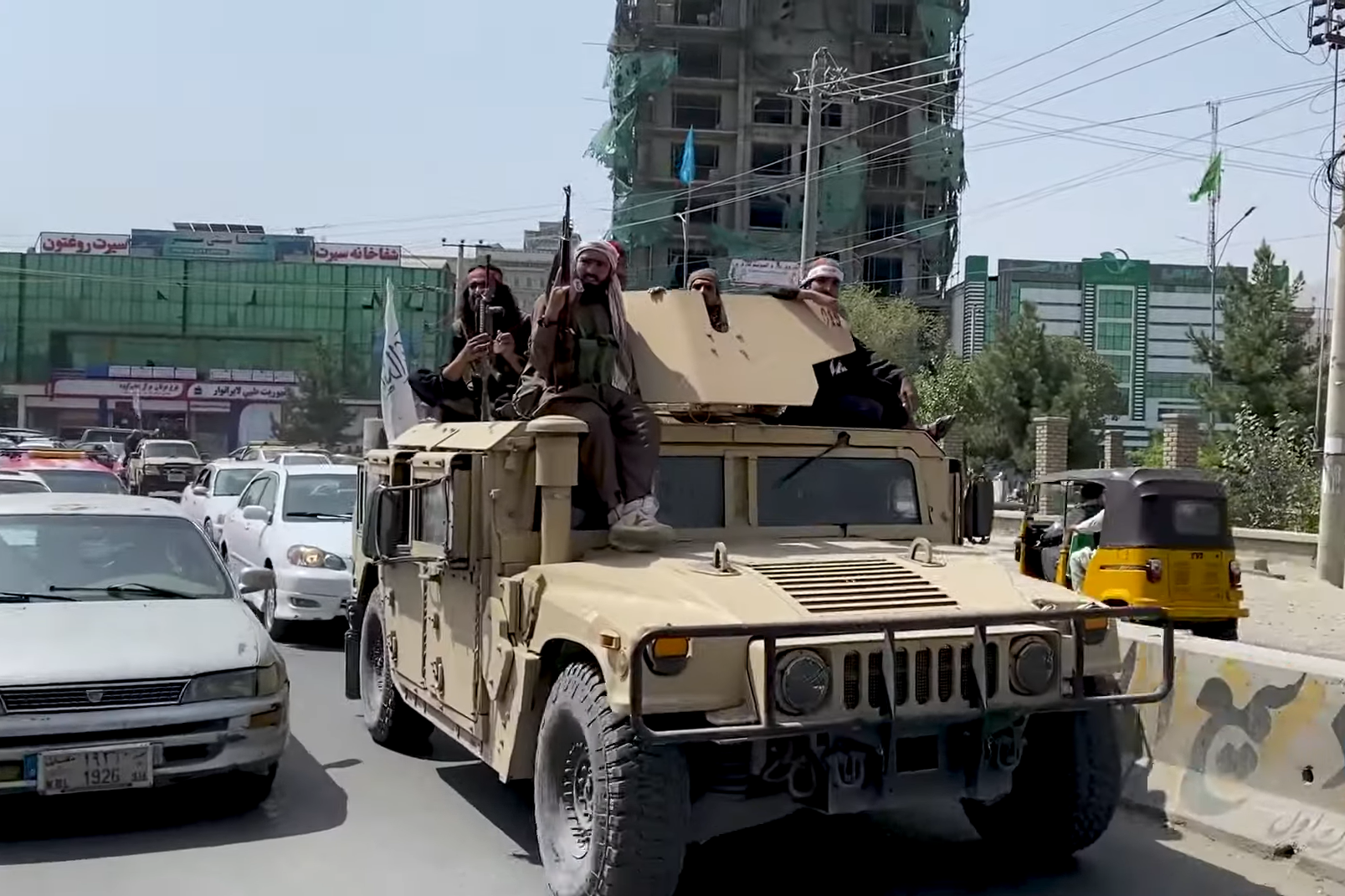 In 2021, the United States forces and allies withdrew from Afghanistan, which allowed the Taliban to intensify their insurgency. On 15 August 2021, as the Taliban entered Kabul, President Ghani fled to
In 2021, the United States forces and allies withdrew from Afghanistan, which allowed the Taliban to intensify their insurgency. On 15 August 2021, as the Taliban entered Kabul, President Ghani fled to Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Tojikiston; russian: ąóą░ą┤ąČąĖą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, ęČčāą╝ę│čāčĆąĖąĖ ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, and the U.S.-backed Afghan government collapsed. Anti-Taliban forces formed the National Resistance Front of Afghanistan and launched an uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
from the Panjshir Valley.
On 7 September 2021 Taliban announced an interim government headed by Mohammad Hassan Akhund
Mohammad Hasan Akhund (born or ) is an Afghan mullah, politician and Taliban leader who is currently the acting prime minister of Afghanistan.
Akhund is one of the founding members of the Taliban and has been a senior leading member of th ...
, although the government remained unrecognized internationally.
Western countries have suspended most humanitarian aid to Afghanistan following the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021. The United States has frozen about $9 billion in assets belonging to the Afghan central bank, blocking the Taliban from accessing billions of dollars held in U.S. bank accounts. In October 2021, more than half of Afghanistan's 39 million people faced an acute food shortage. On 11 November 2021, the ''Human Rights Watch'' reported that Afghanistan is facing widespread famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
due to collapsed economy and broken banking system. The UN World Food Program has also issued multiple warnings of worsening food insecurity.
See also
* Fall of Kabul (2021)
* Invasions of Afghanistan
* List of Pashtun empires and dynasties
* List of heads of state of Afghanistan
This article lists the heads of state of Afghanistan since the foundation of the first modern Afghan state, the Hotak Empire, in 1709.
History
The Hotak Empire was formed after a successful uprising led by Mirwais Hotak and other Afghan t ...
* Politics of Afghanistan
* Timeline of Kabul
The following is a timeline of the history of Kabul, Afghanistan.
Prior to 20th century
* Circa 1500ŌĆō1200 B.C. ŌĆō The '' Rigveda'', a book of Vedic Sanskrit hymns, called this town "Kubha". By about 1000 BC the Zend Avesta of Zoroastrian ...
* Timeline of Herat
References
Further reading
* Adamec, Ludwig W. ''Historical dictionary of Afghanistan'' (Scarecrow Press, 2011).
* Adamec, Ludwig W. ''Historical dictionary of Afghan wars, revolutions, and insurgencies'' (Scarecrow Press, 2005).
* Adamec, Ludwig W. ''Afghanistan's foreign affairs to the mid-twentieth century: relations with the USSR, Germany, and Britain'' (University of Arizona Press, 1974).
* Banting, Erinn.
Afghanistan the People
'. Crabtree Publishing Company, 2003. .
* Barfield, Thomas. ''Afghanistan: A Cultural and Political History'' (Princeton U.P. 2010
excerpt and text search
* Bleaney, C. H; Mar├Ła ├üngeles Gallego.
Afghanistan: a bibliography
'. Brill, 2006. .
* Caroe, Olaf (1958).
The Pathans: 500 B.C.ŌĆōA.D. 1957
'. Oxford in Asia Historical Reprints. Oxford University Press, 1983. .
* Clements, Frank.
Conflict in Afghanistan: a historical encyclopedia
'. ABC-CLIO, 2003. .
* Dupree, Louis.
Afghanistan
'. Princeton University Press, 1973. .
* Dupree, Nancy Hatch.
An Historical Guide to Afghanistan
'. 2nd Edition. Revised and Enlarged. Afghan Air Authority, Afghan Tourist Organization, 1977.
* Ewans, Martin. ''Afghanistan ŌĆō a new history'' (Routledge, 2013).
* Fowler, Corinne.
Chasing tales: travel writing, journalism and the history of British ideas about Afghanistan
'. Rodopi, 2007. Amsterdam and New York. .
* Griffiths, John C. (1981).
Afghanistan: a history of conflict
'. Carlton Books, 2001. .
* Gommans, Jos J. L.
The rise of the Indo-Afghan empire, c. 1710ŌĆō1780
'. Brill, 1995. .
* Gregorian, Vartan.
The emergence of modern Afghanistan: politics of reform and modernization, 1880ŌĆō1946
'. Stanford University Press, 1969.
* Habibi, Abdul Hai.
Afghanistan: An Abridged History
'. Fenestra Books, 2003. .
* Harmatta, J├Īnos.
History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The development of sedentary and nomadic civilizations, 700 B.C. to A.D. 250
'. Motilal Banarsidass Publ., 1999. .
* Hiebert, Fredrik Talmage.
Afghanistan: hidden treasures from the National Museum, Kabul
'. National Geographic Society, 2008. .
* Hill, John E. 2003. "Annotated Translation of the Chapter on the Western Regions according to the ''Hou Hanshu''." 2nd Draft Edition.
* Holt, Frank.
Into the Land of Bones: Alexander the Great in Afghanistan
'. University of California Press, 2006. .
* Hopkins, B. D. 2008.
The Making of Modern Afghanistan
'. Palgrave Macmillan, 2008. .
* Jabeen, Mussarat, Prof Dr Muhammad Saleem Mazhar, and Naheed S. Goraya. "US Afghan Relations: A Historical Perspective of Events of 9/11." ''South Asian Studies'' 25.1 (2020).
* Kakar, M. Hassan. ''A Political and Diplomatic History of Afghanistan, 1863-1901'' (Brill, 2006)
online
* Malleson, George Bruce (1878).
History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878
'. Elibron Classic Replica Edition. Adamant Media Corporation, 2005. .
* Olson, Gillia M.
Afghanistan
'. Capstone Press, 2005. .
* Omrani, Bijan & Leeming, Matthew
Afghanistan: A Companion and Guide
'. Odyssey Publications, 2nd Edition, 2011. .
* Reddy, L. R.
Inside Afghanistan: end of the Taliban era?
'. APH Publishing, 2002. .
* Romano, Amy.
A Historical Atlas of Afghanistan
'. The Rosen Publishing Group, 2003. .
* Runion, Meredith L.
The history of Afghanistan
'. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. .
* Saikal, Amin, A.G. Ravan Farhadi, and Kirill Nourzhanov. ''Modern Afghanistan: a history of struggle and survival'' (IB Tauris, 2012).
* Shahrani, M Nazif, ed. ''Modern Afghanistan: The Impact of 40 Years of War'' (Indiana UP, 2018)
* Siddique, Abubakar. ''The Pashtun Question The Unresolved Key to the Future of Pakistan and Afghanistan'' (Hurst, 2014)
* Tanner, Stephen. ''Afghanistan: a military history from Alexander the Great to the war against the Taliban'' (Da Capo Press, 2009).
* Wahab, Shaista; Barry Youngerman.
A brief history of Afghanistan
'. Infobase Publishing, 2007.
* Vogelsang, Willem.
The Afghans
'. Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. Oxford, UK & Massachusetts, US. .
Primary sources
* "Durand's Curse: A Line Across the Pathan Heart" by Rajiv Dogra, Publisher: Rupa Publications India
* Green, Nile, ed. ''Afghan History Through Afghan Eyes'' (Oxford University Press, 2016) online edition for libraries:
* Elliot, Henry Miers.
The history of India, as told by its own historians: The Muhammadan period
'. Elibron.com, 1952. Volume 8.
* Elphinstone, Mountstuart. 1819.
An account of the kingdom of Caubul, and its dependencies in Persia, Tartary, and India: Comprising a view of the Afghaun nation, and a history of the Dooraunee monarchy
'. Printed for Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, and J. Murry, 1819.
* Hill, John E. 2004. ''The Peoples of the West from the Weilue'' ķŁÅńĢź ''by Yu Huan'' ķŁÜĶ▒ó'': A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE.'' Draft annotated English translation.
* Levi, Peter. 1972.
The light garden of the angel king: journeys in Afghanistan
'. Collins, 1972. .
* Wood, John (1872).
A Journey to the Source of the River Oxus
'. New Edition, edited by his son, with an essay on the "Geography of the Valley of the Oxus" by Henry Yule. John Murray, London. Gregg Division McGraw-Hill, 1971, .
External links
*
ŌĆō Library of Congress Country Studies
Video on Afghan-Soviet War
from th
Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
Encyclop├”dia Britannica ŌĆō History of Afghanistan
by Abdul Hai Habibi
An Historical Guide to Kabul
by Nancy Hatch Dupree
Afghanistan Online ŌĆō History of Afghanistan
*
British Museum Lecture: An Introduction to the History of Afghanistan by Bijan Omrani
Ten Myths about Afghanistan
Ćö''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers '' The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the ...
''
{{History of Asia
Articles containing video clips
History of Central Asia
Kabul Shahi
 The history of Afghanistan as a state began in 1823 as the Emirate of Afghanistan after the exile of the Sadozai monarchy to Herat. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern
The history of Afghanistan as a state began in 1823 as the Emirate of Afghanistan after the exile of the Sadozai monarchy to Herat. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern  Excavations of prehistoric sites by Louis Dupree and others at Darra-e Kur in 1966 where 800 stone implements were recovered along with a fragment of Neanderthal right temporal bone, suggest that early humans were living in what is now Afghanistan at least 52,000 years ago. A cave called Kara Kamar contained Upper Paleolithic blades Carbon-14 dated at 34,000 years old. Farming communities in Afghanistan were among the earliest in the world. Artifacts indicate that the
Excavations of prehistoric sites by Louis Dupree and others at Darra-e Kur in 1966 where 800 stone implements were recovered along with a fragment of Neanderthal right temporal bone, suggest that early humans were living in what is now Afghanistan at least 52,000 years ago. A cave called Kara Kamar contained Upper Paleolithic blades Carbon-14 dated at 34,000 years old. Farming communities in Afghanistan were among the earliest in the world. Artifacts indicate that the 
 The Gandhara region centered around the Peshawar Valley and Swat river valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region in
The Gandhara region centered around the Peshawar Valley and Swat river valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region in 
 Afghanistan fell to the Achaemenid Empire after it was conquered by Darius I of Persia. The area was divided into several provinces called
Afghanistan fell to the Achaemenid Empire after it was conquered by Darius I of Persia. The area was divided into several provinces called 

 The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was a
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was a  The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was ruled by the Gondopharid dynasty, named after its eponymous first ruler Gondophares. They ruled parts of present-day
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was ruled by the Gondopharid dynasty, named after its eponymous first ruler Gondophares. They ruled parts of present-day  The Kushan Empire expanded out of Bactria (Central Asia) into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises, about the middle of the 1st century CE. They came from an Indo-European language speaking Central Asian tribe called the Yuezhi, a branch of which was known as the Kushans. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka the Great, the empire spread to encompass much of
The Kushan Empire expanded out of Bactria (Central Asia) into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises, about the middle of the 1st century CE. They came from an Indo-European language speaking Central Asian tribe called the Yuezhi, a branch of which was known as the Kushans. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka the Great, the empire spread to encompass much of  After the Kushan Empire's rule was ended by SassanidsŌĆö officially known as the Empire of IraniansŌĆö was the last kingdom of the Persian Empire before the rise of Islam. Named after the House of Sasan, it ruled from 224 to 651 AD. In the east around 325, Shapur II regained the upper hand against the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom and took control of large territories in areas now known as Afghanistan and Pakistan. Much of modern-day
After the Kushan Empire's rule was ended by SassanidsŌĆö officially known as the Empire of IraniansŌĆö was the last kingdom of the Persian Empire before the rise of Islam. Named after the House of Sasan, it ruled from 224 to 651 AD. In the east around 325, Shapur II regained the upper hand against the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom and took control of large territories in areas now known as Afghanistan and Pakistan. Much of modern-day  From the
From the 
 In 1504, Babur, a descendant of
In 1504, Babur, a descendant of 
 In 1704, the Safavid Shah Husayn appointed George XI (''Gurg─½n Kh─ün''), a ruthless Georgian subject, to govern their easternmost territories in the Greater Kandahar region. One of Gurg─½n's main objectives was to crush the rebellions started by native Afghans. Under his rule the revolts were successfully suppressed and he ruled Kandahar with uncompromising severity. He began imprisoning and executing the native Afghans, especially those suspected in having taken part in the rebellions. One of those arrested and imprisoned was
In 1704, the Safavid Shah Husayn appointed George XI (''Gurg─½n Kh─ün''), a ruthless Georgian subject, to govern their easternmost territories in the Greater Kandahar region. One of Gurg─½n's main objectives was to crush the rebellions started by native Afghans. Under his rule the revolts were successfully suppressed and he ruled Kandahar with uncompromising severity. He began imprisoning and executing the native Afghans, especially those suspected in having taken part in the rebellions. One of those arrested and imprisoned was  Southern Afghanistan was made into an independent local Pashtun kingdom. Refusing the title of king, Mirwais was called "Prince of Qandah├Īr and general of the national troops" by his Afghan countrymen. He died of natural causes in November 1715 and was succeeded by his brother
Southern Afghanistan was made into an independent local Pashtun kingdom. Refusing the title of king, Mirwais was called "Prince of Qandah├Īr and general of the national troops" by his Afghan countrymen. He died of natural causes in November 1715 and was succeeded by his brother  Nadir Shah was assassinated on 19 June 1747 by several of his Persian officers, and the Afsharid empire fell to pieces. At the same time the 25-year-old Ahmad Khan was busy in Afghanistan calling for a loya jirga ("grand assembly") to select a leader among his people. The Afghans gathered near Kandahar in October 1747 and chose Ahmad Shah from among the challengers, making him their new
Nadir Shah was assassinated on 19 June 1747 by several of his Persian officers, and the Afsharid empire fell to pieces. At the same time the 25-year-old Ahmad Khan was busy in Afghanistan calling for a loya jirga ("grand assembly") to select a leader among his people. The Afghans gathered near Kandahar in October 1747 and chose Ahmad Shah from among the challengers, making him their new 
 The Emir Dost Mohammed Khan (1793ŌĆō1863) gained control in Kabul in 1826 after toppling his brother,
The Emir Dost Mohammed Khan (1793ŌĆō1863) gained control in Kabul in 1826 after toppling his brother,  Mohammed Nadir Khan became King of Afghanistan on 15 October 1929 after he took control of Afghanistan by defeating the
Mohammed Nadir Khan became King of Afghanistan on 15 October 1929 after he took control of Afghanistan by defeating the 
 At the same time, the PDPA imprisoned, tortured or murdered thousands of members of the traditional elite, the religious establishment, and the intelligentsia. The government launched a campaign of violent repression, killing some 10,000 to 27,000 people and imprisoning 14,000 to 20,000 more, mostly at Pul-e-Charkhi prison. In December 1978 the PDPA leadership signed an agreement with the Soviet Union which would allow military support for the PDPA in Afghanistan if needed. The majority of people in the cities including Kabul either welcomed or were ambivalent to these policies. However, the MarxistŌĆōLeninist and secular nature of the government as well as its heavy dependence on the Soviet Union made it unpopular with a majority of the Afghan population. Repressions plunged large parts of the country, especially the rural areas, into open revolt against the new MarxistŌĆōLeninist government. By spring 1979 unrests had reached 24 out of 28 Afghan provinces including major urban areas. Over half of the Afghan army would either desert or join the insurrection. Most of the government's new policies clashed directly with the traditional Afghan understanding of Islam, making religion one of the only forces capable of unifying the tribally and ethnically divided population against the unpopular new government, and ushering in the advent of Islamist participation in Afghan politics.
To bolster the
At the same time, the PDPA imprisoned, tortured or murdered thousands of members of the traditional elite, the religious establishment, and the intelligentsia. The government launched a campaign of violent repression, killing some 10,000 to 27,000 people and imprisoning 14,000 to 20,000 more, mostly at Pul-e-Charkhi prison. In December 1978 the PDPA leadership signed an agreement with the Soviet Union which would allow military support for the PDPA in Afghanistan if needed. The majority of people in the cities including Kabul either welcomed or were ambivalent to these policies. However, the MarxistŌĆōLeninist and secular nature of the government as well as its heavy dependence on the Soviet Union made it unpopular with a majority of the Afghan population. Repressions plunged large parts of the country, especially the rural areas, into open revolt against the new MarxistŌĆōLeninist government. By spring 1979 unrests had reached 24 out of 28 Afghan provinces including major urban areas. Over half of the Afghan army would either desert or join the insurrection. Most of the government's new policies clashed directly with the traditional Afghan understanding of Islam, making religion one of the only forces capable of unifying the tribally and ethnically divided population against the unpopular new government, and ushering in the advent of Islamist participation in Afghan politics.
To bolster the 


 On 9 September 2001,
On 9 September 2001,  While the Taliban began regrouping inside Pakistan, the rebuilding of war-torn Afghanistan kicked off in 2002 (see also
While the Taliban began regrouping inside Pakistan, the rebuilding of war-torn Afghanistan kicked off in 2002 (see also  In October 2008 U.S. Defense Secretary Gates had asserted that a political settlement with the Taliban was the endgame for the Afghanistan war. "There has to be ultimately ŌĆō and I'll underscore ultimately ŌĆō reconciliation as part of a political outcome to this," Gates stated. By 2010 peace efforts began. In early January, Taliban commanders held secret exploratory talks with a United Nations special envoy to discuss peace terms. Regional commanders on the Taliban's leadership council, the Quetta Shura, sought a meeting with the UN special representative in Afghanistan,
In October 2008 U.S. Defense Secretary Gates had asserted that a political settlement with the Taliban was the endgame for the Afghanistan war. "There has to be ultimately ŌĆō and I'll underscore ultimately ŌĆō reconciliation as part of a political outcome to this," Gates stated. By 2010 peace efforts began. In early January, Taliban commanders held secret exploratory talks with a United Nations special envoy to discuss peace terms. Regional commanders on the Taliban's leadership council, the Quetta Shura, sought a meeting with the UN special representative in Afghanistan,  Afghan President Hamid Karzai told world leaders during the London conference that he intends to reach out to the top echelons of the Taliban within a few weeks with a peace initiative. Karzai set the framework for dialogue with Taliban leaders when he called on the group's leadership to take part in a "loya jirga" ŌĆō or large assembly of elders ŌĆō to initiate peace talks. Karzai also asked for creation of a new peacemaking organization, to be called the National Council for Peace, Reconciliation and Reintegration. Karzai's top adviser on the reconciliation process with the insurgents said that the country must learn to forgive the Taliban. In March 2010, the Karzai government held preliminary talks with Hezb-i-Islami, who presented a plan which included the withdrawal of all foreign troops by the end of 2010. The Taliban declined to participate, saying "The Islamic Emirate has a clear position. We have said this many, many times. There will be no talks when there are foreign troops on Afghanistan's soil killing innocent Afghans on daily basis." In June 2010 the Afghan Peace Jirga 2010 took place. In September 2010 General David Petraeus commented on the progress of peace talks to date, stating, "The prospect for reconciliation with senior Taliban leaders certainly looms out there...and there have been approaches at (a) very senior level that hold some promise."
After the May 2011 death of Osama bin Laden in Pakistan, many prominent Afghan figures began being assassinated, including Mohammed Daud Daud,
Afghan President Hamid Karzai told world leaders during the London conference that he intends to reach out to the top echelons of the Taliban within a few weeks with a peace initiative. Karzai set the framework for dialogue with Taliban leaders when he called on the group's leadership to take part in a "loya jirga" ŌĆō or large assembly of elders ŌĆō to initiate peace talks. Karzai also asked for creation of a new peacemaking organization, to be called the National Council for Peace, Reconciliation and Reintegration. Karzai's top adviser on the reconciliation process with the insurgents said that the country must learn to forgive the Taliban. In March 2010, the Karzai government held preliminary talks with Hezb-i-Islami, who presented a plan which included the withdrawal of all foreign troops by the end of 2010. The Taliban declined to participate, saying "The Islamic Emirate has a clear position. We have said this many, many times. There will be no talks when there are foreign troops on Afghanistan's soil killing innocent Afghans on daily basis." In June 2010 the Afghan Peace Jirga 2010 took place. In September 2010 General David Petraeus commented on the progress of peace talks to date, stating, "The prospect for reconciliation with senior Taliban leaders certainly looms out there...and there have been approaches at (a) very senior level that hold some promise."
After the May 2011 death of Osama bin Laden in Pakistan, many prominent Afghan figures began being assassinated, including Mohammed Daud Daud,  In 2021, the United States forces and allies withdrew from Afghanistan, which allowed the Taliban to intensify their insurgency. On 15 August 2021, as the Taliban entered Kabul, President Ghani fled to
In 2021, the United States forces and allies withdrew from Afghanistan, which allowed the Taliban to intensify their insurgency. On 15 August 2021, as the Taliban entered Kabul, President Ghani fled to