Hispania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in
 Latin was the official language of Hispania during the Roman Empire's rule, which exceeded 600 years. By the empire's end in Hispania around 460 AD, all the original Iberian languages, except the ancestor of modern Basque, were extinct. Even after the fall of Rome and the invasion of the Germanic
Latin was the official language of Hispania during the Roman Empire's rule, which exceeded 600 years. By the empire's end in Hispania around 460 AD, all the original Iberian languages, except the ancestor of modern Basque, were extinct. Even after the fall of Rome and the invasion of the Germanic
 After its defeat by the
After its defeat by the
 The Umayyad governor
The Umayyad governor
Hispania
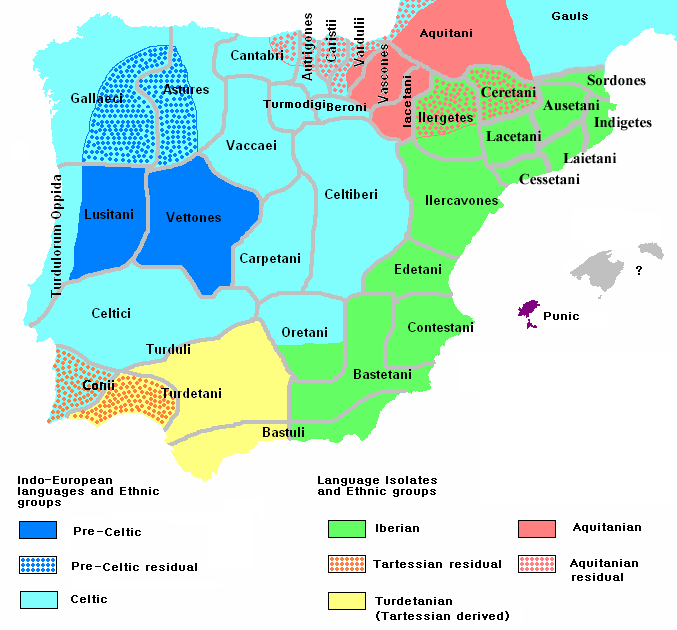
Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC)HISPANIA
A Map of Roman Spain and Portugal.
Amphorae ex HispaniaHispania EpigraphicaEx Officina Hispana- Ancient Ceramics in Spain
{{Authority control Ancient history of the Iberian Peninsula * * Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula New Testament places States and territories established in the 3rd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 5th century 218 BC Pauline churches 210s BC establishments 3rd-century BC establishments in the Roman Republic 5th-century disestablishments in the Roman Empire 3rd-century BC establishments in Spain 5th-century disestablishments
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Catalan, and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, first as Hispania Nova, later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
, whence modern Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 284) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Carthaginensis
Hispania Carthaginensis was a Roman province segregated from Hispania Tarraconensis in the new division of Hispania by emperor Diocletian in 298.
The capital of the new province was settled in Carthago Nova, now Cartagena.
It encompassed ...
, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a civil diocese
In the Late Roman Empire, usually dated 284 AD to 602 AD, the regional governance district known as the Roman or civil diocese was made up of a grouping of provinces each headed by a ''Vicarius'', who were the representatives of praet ...
headed by a ''vicarius
''Vicarius'' is a Latin word, meaning ''substitute'' or ''deputy''. It is the root of the English word "vicar".
History
Originally, in ancient Rome, this office was equivalent to the later English " vice-" (as in "deputy"), used as part of th ...
''. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic rule.
The modern place names Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Hispaniola are both derived from ''Hispania''.
Etymology
The origin of the word ''Hispania'' is much disputed. The evidence for the various speculations is based merely upon what are at best mere resemblances, likely to be accidental, and suspect supporting evidence. The most commonly held theory holds it to be ofPunic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of t ...
origin, from the Phoenician language of colonizing Carthage. Specifically, it may derive from a Punic cognate () of Hebrew () meaning 'island of the hyrax', referring to the European rabbit
The European rabbit (''Oryctolagus cuniculus'') or coney is a species of rabbit native to the Iberian Peninsula (including Spain, Portugal, and southwestern France), western France, and the northern Atlas Mountains in northwest Africa. It has b ...
(Phoenician-Punic and Hebrew are both Canaanite languages and therefore closely related to each other). Some Roman coins of the Emperor Hadrian, born in Hispania, depict Hispania and a rabbit. Others derive the word from Phoenician , meaning 'hidden', and make it indicate "a hidden", that is, "a remote", or "far-distant land".
Other far-fetched theories have been proposed. Isidore of Sevilla
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish people, Spanish scholar, theologian, and Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Seville, archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-cen ...
considered ''Hispania'' of Iberian origin and derived it from the pre-Roman name for Seville, ''Hispalis''. This was revived for instance by the etymologist Eric Partridge
Eric Honeywood Partridge (6 February 1894 – 1 June 1979) was a New Zealand– British lexicographer of the English language, particularly of its slang. His writing career was interrupted only by his service in the Army Education Corps an ...
(in his work ''Origins'') who felt that this might strongly hint at an ancient name for the country of ''*Hispa'', presumably an Iberian or Celtic root whose meaning is now lost. ''Hispalis'' may alternatively derive from '' Heliopolis'' (Greek for 'city of the sun'). However, according to modern research by Manuel Pellicer Catalán, the name derives from Phoenician 'lowland', rendering the above explanations of ''Hispania'' highly unlikely. Occasionally Hispania was called 'farthest western land' by Roman writers since the name ''Hesperia'' 'western land' had already been used by the Greeks to refer to the Italian peninsula.
During the 18th and 19th centuries, Jesuits scholars like Larramendi and José Francisco de Isla tied the name to the Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
word 'lip', but also 'border, edge', thus meaning the farthest area or place.
During Antiquity and Middle Ages, the literary texts derive the term ''Hispania'' from an eponymous hero named Hispan, who is mentioned for the first time in the work of the Roman historian Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus
Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus also anglicized as was a Gallo-Roman historian from the Celtic Vocontii tribe in Narbonese Gaul who lived during the reign of the emperor Augustus. He was nearly contemporary with Livy.
Life
Pompeius Trogus's grandfathe ...
, in the 1st century BC.
Although is the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
root for the modern name ''Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
'', the words ''Spanish'' for or ''Hispanic'', or ''Spain'' for , are not easily interchangeable, depending on context. The ('The History of Spain') written on the initiative of Alfonso X of Castile
Alfonso X (also known as the Wise, es, el Sabio; 23 November 1221 – 4 April 1284) was King of Castile, León and Galicia from 30 May 1252 until his death in 1284. During the election of 1257, a dissident faction chose him to be king of Ger ...
('the Wise'), between 1260 and 1274, during the '' Reconquista'' ('reconquest') of Spain, is believed to be the first extended history of Spain in Old Spanish using the words ('Spain') and ('Spaniards') to refer to Medieval Hispania. The use of Latin , Castilian , Catalan and Old French , among others, to refer to Roman Hispania or Visigothic Hispania was common throughout all the Late Middle Ages. A document dated 1292 mentions the names of foreigners from Medieval Spain as . Latin expressions using or (e.g. ) were often used in the Middle Ages, while the Spain Romance languages of the ''Reconquista'' use the Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
version interchangeably. In the James Ist Chronicle '' Llibre dels fets'', written between 1208 and 1276, there are many instances of this. The borders of modern Spain do not coincide with those of the Roman province of Hispania or of the Visigothic Kingdom, and thus medieval Spain and modern Spain exist in separate contexts. The Latin term , often used during Antiquity and the Low Middle Ages, like with Roman Hispania, as a geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
and political name, continued to be used geographically and politically in the Visigothic Spania, as shown in the expression , 'Praise to Hispania', to describe the history of the peoples of the Iberian Peninsula of Isidore of Seville's ''Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum
The ''Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum'' ("History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals and Suevi") is a Latin history of the Goths from 265 to 624, written by Isidore of Seville. It is a condensed account and, due to its diver ...
'':
You are, OIn modern history, ''Spain'' and ''Spanish'' have become increasingly associated with the Kingdom of Spain alone, although this process took several centuries. After the union of the central peninsular Kingdom of Castile with the eastern peninsular Kingdom of Aragon in the 15th century under theSpain , image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , i ..., holy and always happy mother of princes and peoples, the most beautiful of all the lands that extend far from the West toIndia India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so .... You, by right, are now the queen of all provinces, from whom the lights are given not only the sunset, but also the East. You are the honor and ornament of the orb and the most illustrious portion of the Earth ... And for this reason, long ago, the goldenRome , established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption ...desired you
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
in 1492, only Navarra and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
were left to complete the whole peninsula under one monarchy. Navarre followed soon after in 1512, and Portugal, after over 400 years as an independent and sovereign nation, in 1580. During this time, the concept of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
was still unchanged. It was after the restoration of Portugal's independence in 1640 when the concept of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
started to shift and be applied to all the Peninsula except Portugal.
Pre-Roman history
The Iberian peninsula has long been inhabited, first by early hominids such as '' Homo erectus'', ''Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' i ...
'' and '' Homo antecessor''. In the Paleolithic period, the Neanderthals entered Iberia and eventually took refuge from the advancing migrations of modern humans. In the 40th millennium BC, during the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
and the last ice age, the first large settlement of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
by modern humans occurred. These were nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
hunter-gatherers originating on the steppes
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grassland ...
of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. When the last ice age reached its maximum extent, during the 30th millennium BC, these modern humans took refuge in Southern Europe, namely in Iberia, after retreating through Southern France. In the millennia that followed, the Neanderthals became extinct and local modern human cultures thrived, producing pre-historic art such as that found in L'Arbreda Cave and in the Côa Valley.
In the Mesolithic period, beginning in the 10th millennium BC, the Allerød Oscillation
The Allerød oscillation ( da, Allerødtiden) was a warm and moist global interstadial that occurred c.13,900 to 12,900 BP, nearly at the end of the Last Glacial Period. It raised temperatures in the northern Atlantic region to almost present-da ...
occurred. This was an interstadial deglaciation that lessened the harsh conditions of the Ice Age. The populations sheltered in Iberian Peninsula (descendants of the Cro-Magnon) migrated and recolonized all of Western Europe. In this period one finds the Azilian
The Azilian is a Mesolithic industry of the Franco-Cantabrian region of northern Spain and Southern France. It dates approximately 10,000–12,500 years ago. Diagnostic artifacts from the culture include projectile points (microliths with ro ...
culture in Southern France and Northern Iberia (to the mouth of the Douro
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part o ...
river), as well as the Muge Culture in the Tagus valley.
The Neolithic brought changes to the human landscape of Iberia (from the 5th millennium BC onwards), with the development of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
and the beginning of the European Megalith Culture. This spread to most of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and had one of its oldest and main centres in the territory of modern Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, as well as the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
and Beaker cultures.
During the 1st millennium BC, in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, the first wave of migrations into Iberia of speakers of Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
occurred. These were later (7th and 5th centuries BC) followed by others that can be identified as Celts. Eventually urban cultures developed in southern Iberia, such as Tartessos
Tartessos ( es, Tarteso) is, as defined by archaeological discoveries, a historical civilization settled in the region of Southern Spain characterized by its mixture of local Paleohispanic and Phoenician traits. It had a proper writing system ...
, influenced by the Phoenician colonization of coastal Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
Iberia, with strong competition from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonization. These two processes defined Iberia's cultural landscape – Mediterranean towards the southeast and Continental in the northwest.
Languages
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
and Suebi, Latin was spoken by nearly all of the population, but in its common form known as Vulgar Latin, and the regional changes which led to the modern Iberian Romance languages had already begun.
Carthaginian Hispania
 After its defeat by the
After its defeat by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
in the First Punic War (264 BC–241 BC), Carthage compensated for its loss of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
by rebuilding a commercial empire in Hispania.
The major part of the Punic Wars, fought between the Punic Carthaginians and the Romans, was fought on the Iberian Peninsula. Carthage gave control of the Iberian Peninsula and much of its empire to Rome in 201 BC as part of the peace treaty after its defeat in the Second Punic War, and Rome completed its replacement of Carthage as the dominant power in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
area. By then the Romans had adopted the Carthaginian name, romanized first as ''Ispania''. The term later received an ''H'', much like what happened with ''Hibernia
''Hibernia'' () is the Classical Latin name for Ireland. The name ''Hibernia'' was taken from Greek geographical accounts. During his exploration of northwest Europe (c. 320 BC), Pytheas of Massalia called the island ''Iérnē'' (written ). ...
'', and was pluralized as ''Hispaniae'', as had been done with the Three Gauls.
Roman conquest
Roman armies invaded the Iberian peninsula in 218 BC and used it as a training ground for officers and as a proving ground for tactics during campaigns against the Carthaginians, the Iberians, theLusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. ...
, the Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
ns and other Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
. It was not until 19 BC that the Roman emperor Augustus (r. 27 BC–AD 14) was able to complete the conquest (see Cantabrian Wars). Until then, much of Hispania remained autonomous.
Romanization proceeded quickly in some regions where there are references to the togati, and very slowly in others, after the time of Augustus, and Hispania was divided into three separately governed provinces, and nine provinces by the 4th century. More importantly, Hispania was for 500 years part of a cosmopolitan world empire bound together by law, language, and the Roman road. But the impact of Hispania in the newcomers was also substantial. Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
wrote on the Civil Wars that the soldiers from the Second Legion had become Hispanicized and regarded themselves as ''hispanici''.
Some of the peninsula's population were admitted into the Roman aristocratic class and they participated in governing Hispania and the Roman Empire, although there was a native aristocracy class who ruled each local tribe. The ''latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious" and ''fundus'', "farm, estate") is a very extensive parcel of privately owned land. The latifundia of Roman history were great landed estates specializing in agriculture destined for export: grain, o ...
'' (sing., ''latifundium''), large estates controlled by the aristocracy, were superimposed on the existing Iberian landholding system.
The Romans improved existing cities, such as Lisbon (''Olissipo'') and Tarragona (''Tarraco''), established Zaragoza (''Caesaraugusta''), Mérida (''Augusta Emerita''), and Valencia (''Valentia''), and reduced other native cities to mere villages. The peninsula's economy expanded under Roman tutelage. Hispania served as a granary and a major source of metals for the Roman market, and its harbors exported gold, tin, silver, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, wool, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, olive oil, wine, fish, and garum
Garum is a fermented fish sauce that was used as a condiment in the cuisines of Phoenicia, ancient Greece, Rome, Carthage and later Byzantium. Liquamen is a similar preparation, and at times they were synonymous. Although garum enjoyed its gre ...
. Agricultural production increased with the introduction of irrigation projects, some of which remain in use today. The Romanized Iberian populations and the Iberian-born descendants of Roman soldiers and colonists had all achieved the status of full Roman citizenship by the end of the 1st century. The emperors Trajan (r. 98–117), Hadrian (r. 117–138), and Theodosius (r. 379–395) were of Hispanic origin. The Iberian denarii, also called ''argentum oscense'' by Roman soldiers, circulated until the 1st century BC, after which it was replaced by Roman coins.
Hispania was separated into two provinces (in 197 BC), each ruled by a praetor: '' Hispania Citerior'' ("Hither Hispania") and ''Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
'' ("Farther Hispania"). The long wars of conquest lasted two centuries, and only by the time of Augustus did Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
managed to control Hispania Ulterior. Hispania was divided into three provinces in the 1st century BC.
In the 4th century, Latinius Pacatus Drepanius, a Gallic rhetorician, dedicated part of his work to the depiction of the geography, climate and inhabitants of the peninsula, writing:
This Hispania produces tough soldiers, very skilled captains, prolific speakers, luminous bards. It is a mother of judges and princes; it has given Trajan, Hadrian, and Theodosius to the Empire.With time, the name Hispania was used to describe the collective names of the Iberian Peninsula kingdoms of the Middle Ages, which came to designate all of the Iberian Peninsula plus the Balearic Islands.
The Hispaniae
During the first stages of Romanization, the peninsula was divided in two by the Romans for administrative purposes. The closest one to Rome was called ''Citerior'' and the more remote one ''Ulterior''. The frontier between both was a sinuous line which ran from Cartago Nova (now Cartagena) to theCantabrian Sea
The Cantabrian Sea; french: Mer Cantabrique, gl, Mar Cantábrico, ast, Mar Cantábricu, eu, Kantauri. is the term used mostly in Spain to describe the coastal sea of the Atlantic Ocean that borders the northern coast of Spain and the southwe ...
.
''Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
'' comprised what are now Andalusia, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, Extremadura
Extremadura (; ext, Estremaúra; pt, Estremadura; Fala: ''Extremaúra'') is an autonomous community of Spain. Its capital city is Mérida, and its largest city is Badajoz. Located in the central-western part of the Iberian Peninsula, it ...
, León, a great portion of the former Castilla la Vieja, Galicia, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, and the Basque Country.
'' Hispania Citerior'' comprised the eastern part of former Castilla la Vieja, and what are now Aragon, Valencia, Catalonia, and a major part of former Castilla la Nueva
New Castile ( ) is a historic region of Spain. It roughly corresponds to the historic Moorish Taifa of Toledo, taken during the '' Reconquista'' of the peninsula by Christians and thus becoming the southern part of Castile. The extension o ...
.
In 27 BC, the general and politician Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa divided Hispania into three parts, namely dividing Hispania Ulterior into Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
(basically Andalusia) and Lusitania (including Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
) and attaching Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east ...
and the Basque Country to Hispania Citerior.
The emperor Augustus in that same year returned to make a new division leaving the provinces as follows:
*''Provincia Hispania Ulterior Baetica'' (or '' Hispania Baetica''), whose capital was Corduba, presently Córdoba. It included a little less territory than present-day Andalusia—since modern Almería and a great portion of what today is Granada and Jaén were left outside—plus the southern zone of present-day Badajoz. The river ''Anas'' or ''Annas'' ( Guadiana, from Wadi-Anas) separated Hispania Baetica from Lusitania.
*''Provincia Hispania Ulterior Lusitania'' ('' Lusitania''), whose capital was Emerita Augusta (now Mérida) and without Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
.
*''Provincia Hispania Citerior'' (or ''Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
''), whose capital was Tarraco (Tarragona). After gaining maximum importance this province was simply known as ''Tarraconensis'' and it comprised Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
(modern Galicia and northern Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
) and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
.
By the 3rd century the emperor Caracalla made a new division which lasted only a short time. He split Hispania Citerior again into two parts, creating the new provinces ''Provincia Hispania Nova Citerior'' and ''Asturiae-Calleciae''. In the year 238 the unified province ''Tarraconensis'' or ''Hispania Citerior'' was re-established.
In the 3rd century, under the Soldier Emperors, Hispania Nova (the northwestern corner of Spain) was split off from Tarraconensis, as a small province but the home of the only permanent legion in Hispania, Legio VII Gemina
__NOTOC__
Legio VII Gemina (Latin for "The Twins' Seventh Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was raised in AD 68 in Hispania by the general Galba to take part in his rebellion against the emperor Nero. "Gemina" means the legion ...
. After Diocletian's Tetrarchy reform in AD 293, the new ''Diocese of Hispania
The Diocese of Hispania was a late antique administrative unit ('' Dioecesis'') of the Roman Empire on the Iberian Peninsula. It existed from 314 to about 409 AD. Its capital was Augusta Emerita. The Diocese was governed by a vicarius responsibl ...
'' became one of the four dioceses
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
—governed by a ''vicarius''—of the praetorian prefecture of Gaul
The Praetorian Prefecture of Gaul ( la, praefectura praetorio Galliarum) was one of four large prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.
History
The prefecture was established after the death of Constantine I in 337, when the ...
(also comprising the provinces of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, Germania and Britannia), after the abolition of the imperial Tetrarchs under the Western Emperor (in Rome itself, later Ravenna). The diocese, with its capital at Emerita Augusta (modern Mérida), comprised the five peninsular Iberian provinces (Baetica, Gallaecia and Lusitania, each under a governor styled ''consularis ''Consularis'' is a Latin adjective indicating something pertaining to the position or rank of consul. In Ancient Rome it was also used as a noun (plural ''consulares'') to designate those senators who had held the office of consul or attained co ...
''; and Carthaginiensis, Tarraconensis, each under a '' praeses''), the Insulae Baleares, which were detached from Tarraconensis in the 4th century, and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
was introduced into Hispania in the 1st century and it became popular in the cities in the 2nd century. Little headway was made in the countryside, however, until the late 4th century, by which time Christianity was the official religion of the Roman Empire. Some heretical sects emerged in Hispania, most notably Priscillianism, but overall the local bishops remained subordinate to the Pope. Bishops who had official civil as well as ecclesiastical status in the late empire continued to exercise their authority to maintain order when civil governments broke down there in the 5th century. The Council of Bishops became an important instrument of stability during the ascendancy of the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
. The last vestiges of (Western·classical) Roman rule ended in 472.
Germanic conquest
The undoing of (Western classical) Roman Spain was the result of four tribes crossing the Rhine on 31 December 406. After three years of depredation and wandering about northern and western Gaul, the Germanic Buri, Suevi and Vandals, together with theSarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
moved into Iberia in September or October 409 at the request of Gerontius, a Roman usurper. Thus began the history of the end of (Western classical) Roman Spain, which came in 472. The Suevi established a kingdom in Gallaecia in what is today modern Galicia and northern Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
. The Alans' allies, the Hasdingi Vandals, also established a kingdom in another part of Gallaecia. The Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
established a kingdom in Lusitania – modern Alentejo and Algarve
The Algarve (, , ; from ) is the southernmost NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities ( ''concelhos'' or ''municípios'' in Portuguese).
The region has it ...
, in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
. The Silingi Vandals briefly occupied parts of South Iberia in the province of Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
. In an effort to retrieve the region, the Western Roman emperor, Honorius (r. 395–423), promised the Visigoths a home in southwest Gaul if they destroyed the invaders in Spain. They all but wiped out the Silingi and Alans. The remnant joined the Asding Vandals who had settled first in the northwest with the Sueves but south to Baetica. It is a mystery why the Visigoths were recalled by patrician Constantius (who in 418 married Honorius' sister who had been married briefly to the Visigothic king Ataulf). The Visigoths, the remnants of the two tribes who joined them and the Sueves were confined to a small area in the northwest of the peninsula. The diocese may even have been re-established with its capital at Mérida in 418. The Roman attempt under General Castorius to dislodge the Vandals from Cordoba failed in 422.
The Vandals and Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
crossed over to North Africa in 429, an event which is considered to have been decisive in hastening the decline of the Western Roman Empire. However their departure allowed the Romans to recover 90% of the Iberian peninsula until 439. After the departure of the Vandals only the Sueves remained in a northwest corner of the peninsula. Roman rule which had survived in the eastern quadrant was restored over most of Iberia until the Sueves occupied Mérida in 439, a move which coincides to the Vandal occupation of Carthage late the same year. Rome made attempts to restore control in 446 and 458. Success was temporary. After the death of emperor Majorian in 461 Roman authority collapsed except in Tarraconensis the northeastern quadrant of the peninsula. The Visigoths, a Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, whose kingdom was located in southwest Gaul, took the province when they occupied Tarragona in 472. They also confined the Sueves who had ruled most of the region to Galicia and northern Portugal. In 484 the Visigoths established Toledo as the capital of their kingdom. Successive Visigothic kings ruled Hispania as patricians who held imperial commissions to govern in the name of the Roman emperor. In 585 the Visigoths conquered the Suebic Kingdom of Galicia
The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from ...
, and thus controlled almost all of Hispania.
A century later, taking advantage of a struggle for the throne between the Visigothic kings Agila and Athanagild
Athanagild ( 517 – December 567) was Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania. He had rebelled against his predecessor, Agila I, in 551. The armies of Agila and Athanagild met at Seville, where Agila met a second defeat. Following the death of ...
, the Byzantine emperor Justinian I sent an army under the command of Liberius to take back the peninsula from the Visigoths. This short-lived reconquest recovered only a small strip of land along the Mediterranean coast roughly corresponding to the ancient province of Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
, known as Spania
Spania ( la, Provincia Spaniae) was a province of the Eastern Roman Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the Emperor Justinian I in an effort to restore the western prov ...
.
Under the Visigoths, culture was not as highly developed as it had been under Roman rule, when a goal of higher education had been to prepare gentlemen to take their places in municipal and imperial administration. With the collapse of the imperial administrative super-structure above the provincial level (which was practically moribund) the task of maintaining formal education and government shifted to the Church from the old ruling class of educated aristocrats and gentry. The clergy, for the most part, emerged as the qualified personnel to manage higher administration in concert with local powerful notables who gradually displaced the old town councils. As elsewhere in early medieval Europe, the church in Hispania stood as society's most cohesive institution. The Visigoths are also responsible for the introduction of mainstream Christianity to the Iberian peninsula; the earliest representation of Christ in Spanish religious art can be found in a Visigothic hermitage, Santa Maria de Lara
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnight ...
. It also embodied the continuity of Roman order. Native Hispano-Romans continued to run the civil administration and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
continued to be the language of government and of commerce on behalf of the Visigoths.
Religion was the most persistent source of friction between the Chalcedonian (Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
) native Hispano-Romans and their Arian Visigothic overlords, whom the former considered heretical. At times this tension invited open rebellion, and restive factions within the Visigothic aristocracy exploited it to weaken the monarchy. In 589, Recared, a Visigothic ruler, renounced his Arianism before the Council of Bishops at Toledo and accepted Chalcedonian Christianity (Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
), thus assuring an alliance between the Visigothic monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restric ...
and the native Hispano-Romans. This alliance would not mark the last time in the history of the peninsula that political unity would be sought through religious unity.
Court ceremonials – from Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
– that proclaimed the imperial sovereignty and unity of the Visigothic state were introduced at Toledo. Still, civil war, royal assassinations, and usurpation were commonplace, and warlords and great landholders assumed wide discretionary powers. Bloody family feuds went unchecked. The Visigoths had acquired and cultivated the apparatus of the Roman state but not the ability to make it operate to their advantage. In the absence of a well-defined hereditary system of succession to the throne, rival factions encouraged foreign intervention by the Greeks, the Franks, and finally the Muslims in internal disputes and in royal elections.
According to Isidore of Seville, it is with the Visigothic domination of the zone that the idea of a peninsular unity is sought after, and the phrase ''Mother Hispania'' is first spoken. Up to that date, ''Hispania'' designated all of the peninsula's lands. In '' Historia Gothorum'', the Visigoth Suinthila
Suintila, or ''Suinthila'', ''Swinthila'', ''Svinthila''; (ca. 588 – 633/635) was Visigothic King of Hispania, Septimania and Galicia from 621 to 631. He was a son of Reccared I and his wife Bado, and a brother of the general Geila. Under Suintil ...
appears as the first monarch where Hispania is dealt with as a Gothic nation.
Umayyad conquest
Tariq ibn Ziyad
Ṭāriq ibn Ziyād ( ar, طارق بن زياد), also known simply as Tarik in English, was a Berber commander who served the Umayyad Caliphate and initiated the Muslim Umayyad conquest of Visigothic Hispania (present-day Spain and Portugal) ...
led a raiding force of approximately 1,700 men from North Africa to southern Hispania in April 711. They defeated the Visigothic army, in a decisive battle at Guadalete in 712. Tariq's forces were then reinforced and within a few years they took control of more than two-thirds of the Iberian Peninsula. The second invasion of the Umayyads comprised 18 thousand mostly Arab troops, who rapidly captured Seville and then defeated Roderick's supporters at Mérida and met up with Tariq's troops at Talavera. The following year the combined forces continued into Galicia and the northeast, capturing Léon, Astorga and Zaragoza.
The Umayyads called the area they controlled ' Al-Andalus' ( ar, الأندلس). Al-Andalus, then at its greatest extent, was divided into five administrative units.
In the chronicles and documents of the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
the terms derived from Hispania, ''Spania'', ''España'' or ''Espanha'', continued to be used by the Christians but only in reference to Muslim controlled areas.
Catholic reconquest
From the mid 13th to the late 15th century, the only remaining domain of Al-Andalus was the Emirate of Granada, the last Muslim stronghold in the Iberian Peninsula. Then there was a war of Granada which resulted with the defeat of Emirate of Granada and its annexation by Castile, ending Islamic rule on the Iberian peninsula. In the last years of the 12th century the whole Iberian Peninsula, Muslim and Christian, became known as "Spain" (''España'', ''Espanya'' or ''Espanha'') and the denomination "the Five Kingdoms of Spain" became used to refer to the MuslimKingdom of Granada
)
, common_languages = Official language:Classical ArabicOther languages: Andalusi Arabic, Mozarabic, Berber, Ladino
, capital = Granada
, religion = Majority religion:Sunni IslamMinority religions:Roman ...
and the Christian kingdoms of Aragon, Castile, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, and Navarre.
Economy
Before the Punic Wars, Hispania was a land with much untapped mineral and agricultural wealth, limited by the primitive subsistence economies of her native peoples outside of a few trading ports along theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
. Occupations by the Carthaginians and then by the Romans for her abundant silver deposits developed Hispania into a thriving multifaceted economy. Several metals, olives, oil from Baetica, salted fish and garum
Garum is a fermented fish sauce that was used as a condiment in the cuisines of Phoenicia, ancient Greece, Rome, Carthage and later Byzantium. Liquamen is a similar preparation, and at times they were synonymous. Although garum enjoyed its gre ...
, and wines were some of the goods produced in Hispania and traded throughout the Empire. Gold mining was the most important activity in the north-west parts of the peninsula. This activity is attested in archaeological sites as Las Médulas
Las Médulas () is a historic gold-mining site near the town of Ponferrada in the comarca of El Bierzo (province of León, Castile and León, Spain). It was the most important gold mine, as well as the largest open-pit gold mine in the entire ...
(Spain) and Casais (Ponte de Lima
Ponte de Lima () is the oldest ''vila'' (chartered town, head of a municipality) in Portugal. It is part of the district of Viana do Castelo. The population in 2011 was 43,498, in an area of 320.25 km2. The town proper has about 2,800 inhabi ...
, Portugal).
Climate
Precipitation levels were unusually high during the so-called Iberian–Roman Humid Period. Roman Spain experienced its three phases: the most humid interval in 550–190 BC, an arid interval in 190 BC–150 AD and another humid period in 150–350. In 134 BC the army ofScipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the ...
in Spain had to march at night due to extreme heat, when some of its horses and mules died of thirst (even though earlier, in 181 BC, heavy spring rains prevented the Celtiberians from relieving the Roman siege of Contrebia
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
). Through the 2nd century AD warm temperatures dominated particularly in the mountains along the north coast, punctuated by further cool spells from to 180. After about 200 the temperatures fluctuated, trending toward cool.
Sources and references
Modern sources in Spanish and Portuguese
*Altamira y Crevea, Rafael ''Historia de España y de la civilización española''. Tomo I. Barcelona, 1900. Altamira was a professor at the University of Oviedo, a member of the Royal Academy of History, of the Geographic Society of Lisbon and of the Instituto de Coimbra. (In Spanish.) *Aznar, José Camón, ''Las artes y los pueblos de la España primitiva''. Editorial Espasa Calpe, S.A. Madrid, 1954. Camón was a professor at the University of Madrid. (In Spanish.) *Bosch Gimpera, Pedro;Aguado Bleye, Pedro Aguado may refer to:
People
Aguado is a Spanish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Alexandre Marie Aguado, Spanish banker
*Dionisio Aguado, Spanish classical guitarist and composer
*José Sanz Aguado, Spanish chess master
*Xavier ...
; and Ferrandis, José. ''Historia de España. España romana, I'', created under the direction of Ramón Menéndez Pidal. Editorial Espasa-Calpe S.A., Madrid 1935. (In Spanish.)
*García y Bellido, Antonio, ''España y los españoles hace dos mil años (según la Geografía de Estrabón)''. Colección Austral de Espasa Calpe S.A., Madrid 1945 (first edition 8-XI-1945). García y Bellido was an archeologist and a professor at the University of Madrid. (In Spanish.)
*Mattoso, José (dir.), ''História de Portugal. Primeiro Volume: Antes de Portugal'', Lisboa, Círculo de Leitores, 1992. (in Portuguese)
*Melón, Amando, ''Geografía histórica española'' Editorial Volvntad, S.A., Tomo primero, Vol. I Serie E. Madrid 1928. Melón was a member of the Royal Geographical Society of Madrid and a professor of geography at the Universities of Valladolid and Madrid. (In Spanish.)
*Pellón, José R., ''Diccionario Espasa Íberos''. Espasa Calpe S.A. Madrid 2001. (In Spanish.)
*Urbieto Arteta, Antonio, ''Historia ilustrada de España'', Volumen II. Editorial Debate, Madrid 1994. (In Spanish.)
* El Housin Helal Ouriachen, 2009, La ciudad bética durante la Antigüedad Tardía. Persistencias y mutaciones locales en relación con la realidad urbana del Mediterraneo y del Atlántico, Tesis doctoral, Universidad de Granada, Granada.
Other modern sources
*Westermann ''Grosser Atlas zur Weltgeschichte'' (in German)Hispania
Classical sources
*The notitia dignitatum (c. AD 400; one edition online is http://www.intratext.com/IXT/LAT0212/_PJ.HTM#1WJ) Other classical sources have been accessed second-hand (see references above): * Strabo, ''Geographiká. Book III, Iberia'', written between the years 29 and 7 BC and touched up in AD 18. The most prestigious and widely used edition is Karl Müller's, published in Paris at the end of the 19th century, one volume, with 2 columns,Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
. The most reputed French translation is Tardieu, París 1886. The most reputed English translation (with Greek text) is H.L. Jones, vol. I–VIII, London 1917ff., ND London 1931ff.
* Ptolemy (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
astronomer of the 2nd century) ''Geographiké Hyphaégesis'', geographic guidebook.
*Pacatus
Latinius Pacatus Drepanius''PLRE'' I, p. 272 ( 389–393), one of the Latin panegyrists, flourished at the end of the 4th century AD.
Life
He probably came from Aginnum (Agen), in the south of France, in the territory of the Nitiobriges, and rec ...
( Gallic rhetorician) directed a panegyric on Hispania to the emperor Theodosius I in 389, which he read to the Senate.
*Paulus Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in ''Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), th ...
(390–418) historian, follower of Saint Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
and author of ''Historiae adversus paganos'', the first Christian universal history
A universal history is a work aiming at the presentation of a history of all of mankind as a whole, coherent unit. A universal chronicle or world chronicle typically traces history from the beginning of written information about the past up to t ...
, and of ''Hispania Universa'', an historical guide translated into Anglo-Saxon by Alfred the Great and into Arabic by Abd-ar-Rahman III.
*Lucius Anneus Florus
Three main sets of works are attributed to Florus (a Roman cognomen): ''Virgilius orator an poeta'', an Epitome of Roman History and a collection of 14 short poems (66 lines in all). As to whether these were composed by the same person, or set of ...
(between 1st and 2nd century). ''Compendium of Roman History'' and ''Epitome of the History of Titus Livius (Livy)''. The relevant texts of Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
have been lost, but we can read them via Florus.
*Trogus Pompeius
Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus also anglicized as was a Gallo-Roman historian from the Celtic Vocontii tribe in Narbonese Gaul who lived during the reign of the emperor Augustus. He was nearly contemporary with Livy.
Life
Pompeius Trogus's grandfathe ...
. Believed to be a Gaul with Roman citizenship. ''Historia universal'' written in Latin in the times of Augustus Caesar.
*Titus Livius (Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
) (59 BC–17 BC). ''Ab urbe condita'', Book CXLII of Livy's surviving work.
Neo-modern references
* E. Hübner, ''La Arqueologia de España'' (Barcelona, 1888) *E. S. Bouchier, ''Spain under the Roman Empire'' (Oxford, 1914)Further reading
* Abad Casal, Lorenzo, Simon Keay, and Sebastián F. Ramallo Asensio, eds. 2006. ''Early Roman Towns in Hispania Tarraconensis.'' Portsmouth, RI: Journal of Roman Archaeology. * Bowes, Kim, and Michael Kulikowski, eds. and trans. 2005. ''Hispania in Late Antiquity: Current Perspectives.'' Medieval and Early Modern Iberian World 24. Leiden, The Netherlands, and Boston: Brill. * Curchin, Leonard A. 1991. ''Roman Spain: Conquest and Assimilation.'' London and New York: Routledge. * Curchin, Leonard A. 2003. ''The Romanization of Central Spain: Complexity, Diversity, and Change in a Provincial Hinterland.'' Routledge Classical Monographs. London and New York: Routledge. * * Keay, Simon J. 2001. "Romanization and the Hispaniae." In ''Italy and the West: Comparative Issues in Romanization.'' Edited by Simon Keay and Nicola Terrenato, 117–144. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press. * Keay, Simon, ed. 1998. ''The Archaeology of Early Roman Baetica.'' Portsmouth, RI: Journal of Roman Archaeology * Kulikowski, Michael. 2004. ''Late Roman Spain and its Cities.'' Ancient Society and History. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Univ. Press. * Lowe, Benedict. 2009. ''Roman Iberia: Economy, Society and Culture.'' London: Duckworth. * Mierse, William E. 1999. ''Temples and Towns of Roman Iberia: The Social and Architectural Dynamics of Sanctuary Designs from the Third century B.C. to the Third century A.D.'' Berkeley: Univ. of California Press. * Richardson, J. S. 1996. ''The Romans in Spain. History of Spain.'' Oxford: Blackwell.See also
* List of Roman sites in Spain * Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula * Iberian peninsula *Carthaginian Iberia
The Carthaginian presence in Iberia is long and has been influential on the region.
Background
The Phoenicians were a people from the eastern Mediterranean who were mainly traders from the cities of Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. They established ...
* Iberian languages (all languages spoken, past & present, in Iberia)
*Tartessos
Tartessos ( es, Tarteso) is, as defined by archaeological discoveries, a historical civilization settled in the region of Southern Spain characterized by its mixture of local Paleohispanic and Phoenician traits. It had a proper writing system ...
(Early Iberian civilization)
**Tartessian language
The Tartessian language is the extinct Paleo-Hispanic language of inscriptions in the Southwestern script found in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula, mainly in the south of Portugal (Algarve and southern Alentejo), and the southwest of Sp ...
** Southwest script
* Ophiussa
**Oestriminis
In Latin poetry Oestreminis ("Extreme West") was a name given to the territory of what is today modern Portugal and Galicia, comparable to ''Finis terrae'', the "end of the earth" from a Mediterranean perspective. Its inhabitants were named Oestri ...
* Iberians
** Iberian language
**Iberian scripts
The Iberian scripts are the Paleohispanic scripts that were used to represent the extinct Iberian language. Most of them are typologically unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic.Ferrer, J., Moncunill, N., V ...
*Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. ...
**Lusitanian language
Lusitanian (so named after the Lusitani or Lusitanians) was an Indo-European Paleohispanic language. There has been support for either a connection with the ancient Italic languages or Celtic languages. It is known from only six sizeable inscri ...
** Lusitanian mythology
* Cynetes
* Celtiberians
**Celtiberian language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebr ...
** Celtiberian script
* Hispania Citerior
*Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
*Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
* Lusitania
*Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
*Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
* Suevi Gallaecia
* Vandals in Hispania
* Alans in Hispania
* Visigothic Hispania
* Al-Andalus (Muslim Medieval Iberia)
** Umayyad conquest of Hispania
** Timeline of the Muslim Occupation of the Iberian peninsula
** History of Andalucía
* Reconquista
*Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
**History of Portugal
The history of Portugal can be traced from circa 400,000 years ago, when the region of present-day Portugal was inhabited by Homo heidelbergensis.
The Roman invasion in the 3rd century BC lasted several centuries, and developed the Roman provin ...
** Timeline of Portuguese history
*Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
** History of Spain
References
Footnotes CitationsExternal links
Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC)
A Map of Roman Spain and Portugal.
{{Authority control Ancient history of the Iberian Peninsula * * Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula New Testament places States and territories established in the 3rd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 5th century 218 BC Pauline churches 210s BC establishments 3rd-century BC establishments in the Roman Republic 5th-century disestablishments in the Roman Empire 3rd-century BC establishments in Spain 5th-century disestablishments