Hindi language (Hindi belt) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
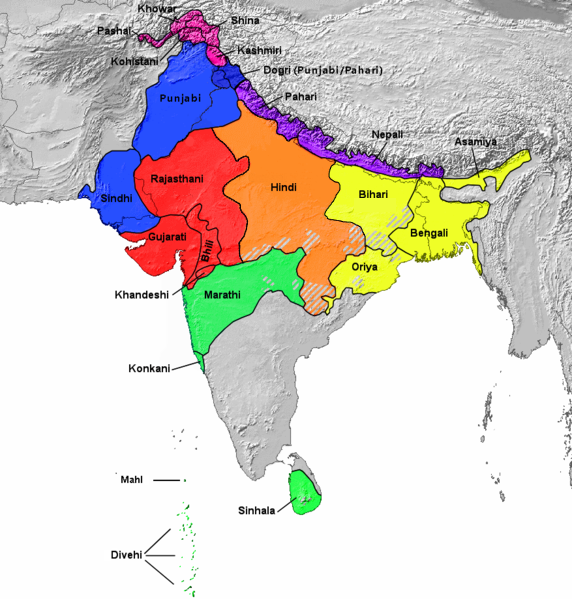
 The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central,
The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central,
 The highly fertile, flat, alluvial Gangetic plain occupies the northern portion of the Hindi Heartland, the Vindhyas in Madhya Pradesh demarcate the southern boundary and the hills and dense forests of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh lie in the east. The region has a predominantly subtropical climate, with cool winters, hot summers and moderate monsoons. The climate does vary with latitude somewhat, with winters getting cooler and rainfall decreasing. It can vary significantly with altitude, especially in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
The Hindi Heartland supports about a third of India's population and occupies about a quarter of its geographical area. The population is concentrated along the fertile Ganges plain in the states of
The highly fertile, flat, alluvial Gangetic plain occupies the northern portion of the Hindi Heartland, the Vindhyas in Madhya Pradesh demarcate the southern boundary and the hills and dense forests of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh lie in the east. The region has a predominantly subtropical climate, with cool winters, hot summers and moderate monsoons. The climate does vary with latitude somewhat, with winters getting cooler and rainfall decreasing. It can vary significantly with altitude, especially in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
The Hindi Heartland supports about a third of India's population and occupies about a quarter of its geographical area. The population is concentrated along the fertile Ganges plain in the states of
On The Problems Of The Hindi Belt: A Seminar
(Archived 1 June 2012) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hindi Belt regions Articles containing video clips

eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
and western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
where various Central Indo-Aryan languages subsumed under the term 'Hindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
' (for example, by the Indian census
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 16 times, as of 2021. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by ...
) are spoken. The Hindi belt is sometimes also used to refer to nine Indian states whose official language is ''Hindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
'', namely Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, Chhattisgarh, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land a ...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern s ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
, Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
and the union territory of Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which a ...
and the National Capital Territory of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
. It is also referred to as the Hindi–Urdu
Hindustani (; Devanagari: ,
*
*
*
* ; Perso-Arabic: , , ) is the ''lingua franca'' of Northern and Central India and Pakistan. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu. Thus, the langua ...
Belt or Hindustani Belt by some writers.
Hindi as a dialect continuum
Hindi is part of the Indo-Aryandialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated varie ...
that lies within the cultural Hindi Belt in the northern plains of India. Hindi in this broad sense is a sociolinguistic rather than an ethnic concept.
This definition of Hindi is one of the ones used in the Indian census
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 16 times, as of 2021. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by ...
, and results in more than forty percent of Indians being reported to be speakers of Hindi, though Hindi-area respondents vary as to whether they call their language Hindi or use a local language name to distinguish their language from Hindi. As defined in the 1991 census, Hindi has a broad and a narrow sense. The name "Hindi" is thus ambiguous. Before being identified as a separate language Maithili was identified as a Hindi dialect. Many such languages still struggle for recognition.
The broad sense covers a number of Central, East-Central, Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
, and Northern Zone languages, including the Bihari languages
Bihari is a group of the Indo-Aryan languages. The Bihari languages are mainly spoken in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh and also in Nepal.Brass, Paul R. (1974). ''Language, Religion and Politics in North ...
except Maithili, all the Rajasthani languages
Rajasthani (Devanagari: ) refers to a group of Indo-Aryan languages and dialects spoken primarily in the state of Rajasthan and adjacent areas of Haryana, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh in India. There are also speakers in the Pakistani provinces ...
, and the Central Pahari languages
The Northern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Pahāṛi languages, are a proposed group of Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east, through the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhan ...
. This is an area bounded on the west by Punjabi and Sindhi; on the south by Gujarati, Marathi, and Odia; on the east by Maithili and Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
; and on the north by Nepali, Kashmiri, Western Pahari
The Western Pahari languages are a group of Northern Indo-Aryan languages that are spoken in the state of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Uttarakhand and Punjab
Languages
The following lists the languages cla ...
and Tibetic languages
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descended from Old Tibetan (7th to 9th centuries).Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptiv ...
. The varieties of this belt can be considered separate languages rather than dialects of a single language.
In a narrower sense, Hindi is equated with the Central Zone Indic languages. Based on their linguistic features, these are divided into Western Hindi
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the ...
and Eastern Hindi
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the ...
. The narrowest definition of Hindi is that of the official language, Modern Standard Hindi or ''Mānak Hindi'', a standardised register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), th ...
of Hindustani, one of the varieties of Western Hindi. Standardised Hindustani—including both Mānak Hindi and Urdu—is historically based on the Khariboli
Kauravi ( hi, कौरवी, ur, ), also known as Khaṛībolī is a set of Western Hindi varieties of Shauraseni Prakrit mainly spoken in Northwestern Uttar Pradesh.
Standard Hindi and Urdu are based on Khariboli, specifically on its De ...
of 17th-century Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
.
Also, in many provinces like Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
, Hindi is the official language but many oppose the Hindi Belt tag due to the region being part of the Western Pahari
The Western Pahari languages are a group of Northern Indo-Aryan languages that are spoken in the state of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Uttarakhand and Punjab
Languages
The following lists the languages cla ...
linguistic Belt which also includes Jammu
Jammu is the winter capital of the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is the headquarters and the largest city in Jammu district of the union territory. Lying on the banks of the river Tawi, the city of Jammu, with an area of ...
areas of the Jammu and Kashmir (princely state)
Jammu and Kashmir, officially known as the Princely State of Kashmir and Jammu, was a princely state during the Company rule in India from 1757 to 1858 as well as the British Raj in India from 1846 to 1952. The princely state was created aft ...
further extending to Pakistan's Pothohar Plateau
The Pothohar Plateau ( ur, ) is a plateau in north-eastern Pakistan, located between Indus River and the Jhelum River, forming the northern part of Punjab.
Geography
Potohar Plateau is bounded on the east by the Jhelum River, on the west by the ...
.
Number of speakers
Population data from 2011 Indian Census is as follows: *Central zone
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the ...
(Hindi proper)
**Western Hindi
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the ...
(West Central zone)
***240 M Hindustani excluding Urdu
***9.8 M Haryanvi
Haryanvi ( ' or '), also known as Bangru, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the state of Haryana in India, and to a lesser extent in Delhi. Haryanvi is considered to be part of the dialect group of Western Hindi, which also includes Kharib ...
***1.5 M Braj Bhasha
***9.5 M Kanauji
***5.6 M Bundeli
**Eastern Hindi
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the ...
(East Central zone)
***4.5 M Awadhi
Awadhi (; ), also known as Audhi (), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern India and Nepal. It is primarily spoken in the Awadh region of present-day Uttar Pradesh, India. The name ''Awadh'' is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient city ...
***16.2 M Chhattisgarhi
***2.6 M Bagheli
Bagheli (Devanagari: बघेली) or Baghelkhandi is a Central Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Baghelkhand region of central India.
Classification
An independent language belonging to the Eastern Hindi subgroup, Bagheli is one of the ...
***1.7 M Surgujia
*Bihari languages
Bihari is a group of the Indo-Aryan languages. The Bihari languages are mainly spoken in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh and also in Nepal.Brass, Paul R. (1974). ''Language, Religion and Politics in North ...
apart from Maithili (East Zone)
**51 M: Bhojpuri
**13 M: Magadhi
**8 M: Khortha
**5.1 M: Nagpuri
**0.5 M: Kurmali
* Rajasthani (part of Western Zone, which also includes Gujarati and Bhili)
**7.8 M Marwari-Merwari
**5.2 M Malvi
**2.3 M Nimadi
**4.8M Lambadi
Lambadi, Gor Boli, Banjara, Labanki or Banjari is a language spoken by the once nomadic Banjara people across India,Ancient Pastoral Nomadic Community of India Ancient Warrior Community/Raajputs Medieval Traders/Grain Carriers Modern Grain Tra ...
**2.9 M Harauti
**3 M Godwari
Godwari is a dialect of Marwari spoken in Godwar
Gorwar or Godwar, (in different periods also was called Chandravati Kingdom, Sirohi State) is a region of Rajasthan state in India, which lies in the southwest Rajasthan and borders with the ...
**2 M Bagri
According to the 2001 Indian census, 258 million people in India (25% of the population) regarded their native language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
to be "Hindi", however, including other Hindi dialects this figure becomes 422 million Hindi speakers (41% of the population). These figures do not count 52 million Indians who considered their mother tongue to be "Urdu". The numbers are also not directly comparable to the table above; for example, while independent estimates in 2001 counted 37 million speakers of Awadhi, in the 2001 census only 2½ million of these identified their language as "Awadhi" rather than as "Hindi".
There have been demands to include Awadhi
Awadhi (; ), also known as Audhi (), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern India and Nepal. It is primarily spoken in the Awadh region of present-day Uttar Pradesh, India. The name ''Awadh'' is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient city ...
, Bhojpuri, Kumaoni, Bundeli, Chhattisgarhi, Garhwali, Kurmali, Magahi
The Magahi language (), also known as Magadhi (), is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name derives. ...
, Nagpuri, and Rajasthani in the Eighth Schedule; these are otherwise regarded as Hindi dialects however these languages don't have any direct relation with modern day Hindi. Some academics oppose inclusion of Hindi dialects in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution as full-fledged Indian languages. According to them recognition of Hindi dialects as separate languages would deprive Hindi of millions of its speakers and eventually no Hindi will be left.
Outside the Indian subcontinent
Much of the Hindi spoken outside of the subcontinent is distinct from the Indian standard language. Fiji Hindi is a derived form of Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and including some English and very few native Fijian words. It is spoken by majority of Indo-Fijians. Mauritian Bhojpuri, once widely spoken as a mother tongue, has become less commonly spoken over the years. According to the 2011 census, Bhojpuri was spoken by 5% of the population compare.Geography and demography
 The highly fertile, flat, alluvial Gangetic plain occupies the northern portion of the Hindi Heartland, the Vindhyas in Madhya Pradesh demarcate the southern boundary and the hills and dense forests of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh lie in the east. The region has a predominantly subtropical climate, with cool winters, hot summers and moderate monsoons. The climate does vary with latitude somewhat, with winters getting cooler and rainfall decreasing. It can vary significantly with altitude, especially in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
The Hindi Heartland supports about a third of India's population and occupies about a quarter of its geographical area. The population is concentrated along the fertile Ganges plain in the states of
The highly fertile, flat, alluvial Gangetic plain occupies the northern portion of the Hindi Heartland, the Vindhyas in Madhya Pradesh demarcate the southern boundary and the hills and dense forests of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh lie in the east. The region has a predominantly subtropical climate, with cool winters, hot summers and moderate monsoons. The climate does vary with latitude somewhat, with winters getting cooler and rainfall decreasing. It can vary significantly with altitude, especially in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
The Hindi Heartland supports about a third of India's population and occupies about a quarter of its geographical area. The population is concentrated along the fertile Ganges plain in the states of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
.
Although the vast majority of the population is rural, significant urban cities include Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which a ...
, Panchkula
Panchkula (PKL) is a planned city and district headquarter in the Panchkula district, part of the Ambala division in Haryana, India. The origin of the name Panchkula came from the place where five irrigation canals meet. Panchkula establis ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
, Lucknow
Lucknow (, ) is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is also the second largest urban agglomeration in Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and division ...
, Kanpur, Raipur
Raipur ( ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Raipur is also the administrative headquarters of Raipur district and Raipur division, and the largest city of the state. It was a part of Madhya Pradesh before the state of Ch ...
, Allahabad, Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had a population of 3.1 million, making it the tenth most populous city in the country. Jaipur is also known ...
, Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra i ...
, Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
, Indore
Indore () is the largest and most populous city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of both Indore District and Indore Division. It is also considered as an education hub of the state and is the only city to ...
, Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
, Jamshedpur and Ranchi. The region hosts a diverse population, with various dialects of Hindi being spoken along with other Indian languages, and multi-religious population including Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Sikhs along with people from various castes and a significant tribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
population. The geography is also varied, with the flat, alluvial Gangetic plain occupying the northern portion, the Vindhyas
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
in Madhya Pradesh demarcating the southern boundary and the hills and dense forests of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh separate the region from West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
.
Political sphere
Over the years political development in some of these states has been dominated by caste-based politics, but this has changed somewhat in recent years. In 2019 election, 226 members from the Hindi belt states had been elected to the Lok Sabha.See also
*BIMARU states BIMARU (Hindi: बीमारू ''Bīmārū'') is an acronym formed from the first letters of the names of the Indian states of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. It was coined by Ashish Bose in the mid-1980s. BIMARU has a rese ...
Bibliography
* Grierson, G. A. ''Linguistic Survey of India'' Vol I-XI, Calcutta, 1928, *. *.Notes
References
External links
On The Problems Of The Hindi Belt: A Seminar
(Archived 1 June 2012) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hindi Belt regions Articles containing video clips