Hexacene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hexacene is an
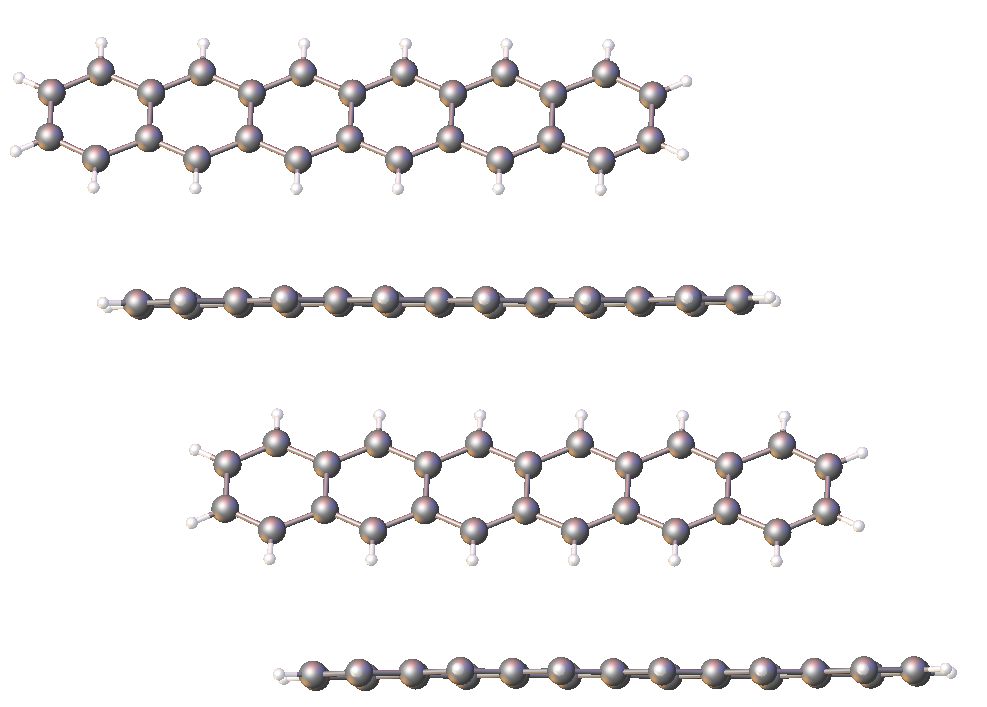
Molecular graphics representation of the X-ray crystallographic structure determined for 6,15-bis(tri-t-butylsilylethynyl)hexacene
Ćöhexacene with bulky, protective substituents in the reactive 6- and 15- ring positions, see rotating graphic at base of page.
Sander-Wise Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Structure Index entry for hexacene
NIST Special Publication 922.
aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ...
compound consisting of six linearly-fused benzene rings. It is a blue-green, air-stable solid with low solubility.
Hexacene is one of a series of linear polycyclic molecules created by such aromatic ring fusions, a series termed acene
In organic chemistry, the acenes or polyacenes are a class of organic compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons made up of benzene () rings which have been linearly fused. They follow the general molecular formula .
The larger represent ...
sŌĆöthe previous in the series being pentacene
Pentacene () is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and t ...
(with five fused rings) and the next being heptacene
Heptacene is an organic compound and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the seventh member of the acene or polyacene family of linear fused benzene rings. This compound has long been pursued by chemists because of its potential interest in elec ...
(with seven). It and other acenes and their derivatives have been investigated in potential applications related to organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and ŌĆō at times ŌĆō heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or ...
s. Like larger acenes, hexacene is poorly soluble, but derivatives have been prepared with improved solubility. 6,15-Bis(tri-t-butylsilylethynyl)hexacene, which melts with decomposition at 96 ┬░C.
Syntheses and structure
Hexacene has been the subject of many syntheses. One route entails by thermaldecarbonylation
Decarbonylation is a type of organic reaction that involves loss of CO. It is often an undesirable reaction since it represents a degradation. In the chemistry of metal carbonyls, decarbonylation describes a substitution process, whereby a CO lig ...
of monoketone precursor.

Further reading
*First synthesis: **Marschalk, C. Linear hexacenes. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 6, 1112ŌĆō1121 (1939). ** ** *Bydehydrogenation
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At ...
of ''hexacosahydrohexacene'' by palladium on carbon
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used as a catalyst. The metal is supported on activated carbon to maximize its surface area and activity.
Uses Hydrogenation
Palladium on carbon is used for catalytic hydrog ...
*Isolation:
*By decarbonylation of a diketone
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls ...
precursor:
*Deoxygenation route:
External links
Molecular graphics representation of the X-ray crystallographic structure determined for 6,15-bis(tri-t-butylsilylethynyl)hexacene
Ćöhexacene with bulky, protective substituents in the reactive 6- and 15- ring positions, see rotating graphic at base of page.
Sander-Wise Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Structure Index entry for hexacene
NIST Special Publication 922.
References
{{PAHs Organic semiconductors Acenes Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons