Switch parser function on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In electrical engineering, a switch is an
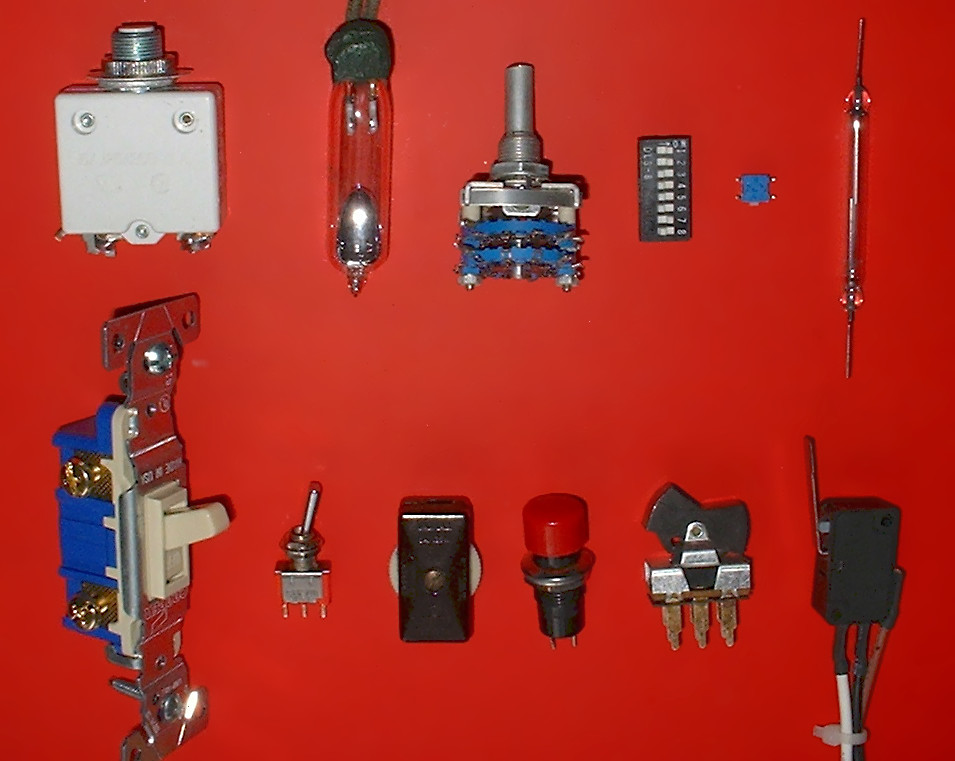 The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of
 In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often
In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often
 In electronics, switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts. A pair of contacts is said to be "''closed''" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "''open''", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "''make''" for closure of contacts and "''break''" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "''poles''" is the number of electrically separate switches which are controlled by a single physical actuator. For example, a "''2-pole''" switch has two separate, parallel sets of contacts that open and close in unison via the same mechanism. The number of "''throws''" is the number of separate wiring path choices other than "open" that the switch can adopt for each pole. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
In a switch where the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, such as a push-button switch, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c." or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a ''changeover switch'' or ''double-throw switch''. These may be "make-before-break" ("MBB" or shorting) which momentarily connects both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" ("BBM" or non-shorting) which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
These terms have given rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the
In electronics, switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts. A pair of contacts is said to be "''closed''" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "''open''", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "''make''" for closure of contacts and "''break''" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "''poles''" is the number of electrically separate switches which are controlled by a single physical actuator. For example, a "''2-pole''" switch has two separate, parallel sets of contacts that open and close in unison via the same mechanism. The number of "''throws''" is the number of separate wiring path choices other than "open" that the switch can adopt for each pole. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
In a switch where the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, such as a push-button switch, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c." or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a ''changeover switch'' or ''double-throw switch''. These may be "make-before-break" ("MBB" or shorting) which momentarily connects both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" ("BBM" or non-shorting) which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
These terms have given rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the
 Contact bounce (also called ''chatter'') is a common problem with mechanical switches and
Contact bounce (also called ''chatter'') is a common problem with mechanical switches and
See also Keyboard technology #Debouncing. * Bounce in SPDT ("single-pole, double-throw") switch contacts signals can be filtered out using an SR flip-flop (latch) or
 When turned on, an incandescent lamp draws a large
When turned on, an incandescent lamp draws a large
 A rotary switch operates with a twisting motion of the operating handle with at least two positions. One or more positions of the switch may be momentary (biased with a spring), requiring the operator to hold the switch in the position. Other positions may have a detent to hold the position when released. A rotary switch may have multiple levels or "decks" in order to allow it to control multiple circuits.
One form of rotary switch consists of a spindle or "rotor" that has a contact arm or "spoke" which projects from its surface like a cam. It has an array of terminals, arranged in a circle around the rotor, each of which serves as a contact for the "spoke" through which any one of a number of different electrical circuits can be connected to the rotor. The switch is layered to allow the use of multiple poles, each layer is equivalent to one pole. Usually such a switch has a detent mechanism so it "clicks" from one active position to another rather than stalls in an intermediate position. Thus a rotary switch provides greater pole and throw capabilities than simpler switches do.
Other types use a cam mechanism to operate multiple independent sets of contacts.
Rotary switches were used as channel selectors on television receivers until the early 1970s, as range selectors on electrical metering equipment, as band selectors on multi-band radios and other similar purposes. In industry, rotary switches are used for control of measuring instruments,
A rotary switch operates with a twisting motion of the operating handle with at least two positions. One or more positions of the switch may be momentary (biased with a spring), requiring the operator to hold the switch in the position. Other positions may have a detent to hold the position when released. A rotary switch may have multiple levels or "decks" in order to allow it to control multiple circuits.
One form of rotary switch consists of a spindle or "rotor" that has a contact arm or "spoke" which projects from its surface like a cam. It has an array of terminals, arranged in a circle around the rotor, each of which serves as a contact for the "spoke" through which any one of a number of different electrical circuits can be connected to the rotor. The switch is layered to allow the use of multiple poles, each layer is equivalent to one pole. Usually such a switch has a detent mechanism so it "clicks" from one active position to another rather than stalls in an intermediate position. Thus a rotary switch provides greater pole and throw capabilities than simpler switches do.
Other types use a cam mechanism to operate multiple independent sets of contacts.
Rotary switches were used as channel selectors on television receivers until the early 1970s, as range selectors on electrical metering equipment, as band selectors on multi-band radios and other similar purposes. In industry, rotary switches are used for control of measuring instruments,

 A toggle switch or tumbler switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical
A toggle switch or tumbler switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical
 Switches can be designed to respond to any type of mechanical stimulus: for example, vibration (the trembler switch), tilt, air pressure, fluid level (a
Switches can be designed to respond to any type of mechanical stimulus: for example, vibration (the trembler switch), tilt, air pressure, fluid level (a
 Knife switches consist of a flat metal blade, hinged at one end, with an insulating handle for operation, and a fixed contact. When the switch is closed, current flows through the hinged pivot and blade and through the fixed contact. Such switches are usually not enclosed. The knife and contacts are typically formed of
Knife switches consist of a flat metal blade, hinged at one end, with an insulating handle for operation, and a fixed contact. When the switch is closed, current flows through the hinged pivot and blade and through the fixed contact. Such switches are usually not enclosed. The knife and contacts are typically formed of
 A
A
electrical component
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not ...
that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contact
An electrical contact is an electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they c ...
s connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow.
Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch
In electrical wiring, a light switch is a switch most commonly used to operate electric lights, permanently connected equipment, or electrical outlets. Portable lamps such as table lamps may have a light switch mounted on the socket, base, or i ...
or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of ...
, rotary switch
A rotary switch is a switch operated by rotation. These are often chosen when more than 2 positions are needed, such as a three-speed fan or a CB radio with multiple frequencies of reception or "channels".
A rotary switch consists of a spindl ...
, mercury switch
A mercury switch is an electrical switch that opens and closes a circuit when a small amount of the liquid metal mercury connects metal electrodes to close the circuit. There are several different basic designs (tilt, displacement, radial, etc ...
, push-button switch, reversing switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of ...
, relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
, and circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the ris ...
. A common use is control of lighting, where multiple switches may be wired into one circuit to allow convenient control of light fixtures. Switches in high-powered circuits must have special construction to prevent destructive arcing when they are opened.
Description
 The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts
An electrical contact is an electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they c ...
, which are connected to external circuits. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) is usually (there are other types of actions) either an "''alternate action''" (flip the switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "''momentary''" (push for "on" and release for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch
In electrical wiring, a light switch is a switch most commonly used to operate electric lights, permanently connected equipment, or electrical outlets. Portable lamps such as table lamps may have a light switch mounted on the socket, base, or i ...
. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensors in a process and used to automatically control a system. For example, a thermostat is a temperature-operated switch used to control a heating process. A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be padlocked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock.
An ideal switch would have no voltage drop when closed, and would have no limits on voltage or current rating. It would have zero rise time In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equivale ...
and fall time
In electronics, fall time (pulse decay time) t_f is the time taken for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease (fall) from a specified value (usually 90% of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot) to another specified value (usually 10 ...
during state changes, and would change state without "bouncing" between on and off positions.
Practical switches fall short of this ideal; as the result of roughness and oxide films, they exhibit contact resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is describe ...
, limits on the current and voltage they can handle, finite switching time, etc. The ideal switch is often used in circuit analysis as it greatly simplifies the system of equations to be solved, but this can lead to a less accurate solution. Theoretical treatment of the effects of non-ideal properties is required in the design of large networks of switches, as for example used in telephone exchanges.
Contacts
 In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often
In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
, called ''contacts'', connected to an external circuit, that touch to complete (make) the circuit, and separate to open (break) the circuit. The contact material is chosen for its resistance to corrosion, because most metals form insulating oxides that would prevent the switch from working. Contact materials are also chosen on the basis of electrical conductivity, hardness (resistance to abrasive wear), mechanical strength, low cost and low toxicity. The formation of oxide layers at contact surface, as well as surface roughness and contact pressure, determine the contact resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is describe ...
, and wetting current
In electrical and electronics engineering, wetting current is the minimum electric current needing to flow through a contact to break through the surface film resistance at a contact. It is typically far below the contact's nominal maximum curr ...
of a mechanical switch. Sometimes the contacts are plated
Plating is a surface covering in which a metal is deposited on a conductive surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improv ...
with noble metal
A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals ( ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, o ...
s, for their excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. They may be designed to wipe against each other to clean off any contamination. Nonmetallic conductors, such as conductive plastic, are sometimes used. To prevent the formation of insulating oxides, a minimum wetting current
In electrical and electronics engineering, wetting current is the minimum electric current needing to flow through a contact to break through the surface film resistance at a contact. It is typically far below the contact's nominal maximum curr ...
may be specified for a given switch design.
Contact terminology
 In electronics, switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts. A pair of contacts is said to be "''closed''" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "''open''", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "''make''" for closure of contacts and "''break''" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "''poles''" is the number of electrically separate switches which are controlled by a single physical actuator. For example, a "''2-pole''" switch has two separate, parallel sets of contacts that open and close in unison via the same mechanism. The number of "''throws''" is the number of separate wiring path choices other than "open" that the switch can adopt for each pole. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
In a switch where the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, such as a push-button switch, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c." or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a ''changeover switch'' or ''double-throw switch''. These may be "make-before-break" ("MBB" or shorting) which momentarily connects both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" ("BBM" or non-shorting) which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
These terms have given rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the
In electronics, switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts. A pair of contacts is said to be "''closed''" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "''open''", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "''make''" for closure of contacts and "''break''" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "''poles''" is the number of electrically separate switches which are controlled by a single physical actuator. For example, a "''2-pole''" switch has two separate, parallel sets of contacts that open and close in unison via the same mechanism. The number of "''throws''" is the number of separate wiring path choices other than "open" that the switch can adopt for each pole. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
In a switch where the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, such as a push-button switch, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c." or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a ''changeover switch'' or ''double-throw switch''. These may be "make-before-break" ("MBB" or shorting) which momentarily connects both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" ("BBM" or non-shorting) which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
These terms have given rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
industry such as "''single-pole, single-throw''" (SPST) (the simplest type, "on or off") or "''single-pole, double-throw''" (SPDT), connecting either of two terminals to the common terminal. In electrical power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions o ...
wiring (i.e., house and building wiring by electrician
An electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance ...
s), names generally involve the suffix ''"-way"''; however, these terms differ between British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
and American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances i ...
(i.e., the terms ''two way'' and ''three way'' are used with different meanings).
Switches with larger numbers of poles or throws can be described by replacing the "S" or "D" with a number (e.g. 3PST, SP4T, etc.) or in some cases the letter "T" (for "triple") or "Q" (for "quadruple"). In the rest of this article the terms ''SPST'', ''SPDT'' and ''intermediate'' will be used to avoid the ambiguity.
Contact bounce
Bounce
 Contact bounce (also called ''chatter'') is a common problem with mechanical switches and
Contact bounce (also called ''chatter'') is a common problem with mechanical switches and relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
s, which arises as the result of electrical contact resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is describe ...
(ECR) phenomena at interfaces. Switch and relay contacts are usually made of springy metals. When the contacts strike together, their momentum and elasticity act together to cause them to bounce apart one or more times before making steady contact. The result is a rapidly pulsed electric current instead of a clean transition from zero to full current. The effect is usually unimportant in power circuits, but causes problems in some analogue and logic circuit
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gat ...
s that respond fast enough to misinterpret the on‑off pulses as a data stream.Walker, PMB, ''Chambers Science and Technology Dictionary'', Edinburgh, 1988, In the design of micro-contacts, controlling surface structure ( surface roughness) and minimizing the formation of passivated layers on metallic surfaces are instrumental in inhibiting chatter.
In the Hammond organ, multiple wires are pressed together under the piano keys of the manuals. Their bouncing and non-synchronous closing of the switches is known as ''Hammond Click'' and compositions exist that use and emphasize this feature. Some electronic organ
An electric organ, also known as electronic organ, is an electronic keyboard instrument which was derived from the harmonium, pipe organ and theatre organ. Originally designed to imitate their sound, or orchestral sounds, it has since developed ...
s have a switchable replica of this sound effect.
Debouncing
The effects of contact bounce can be eliminated by: * use of mercury-wetted contacts, but these are now infrequently used because of the hazards of mercury. * Alternatively, contact circuit voltages can below-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
ed to reduce or eliminate multiple pulses from appearing.
* In digital systems, multiple samples of the contact state can be taken at a low rate and examined for a steady sequence, so that contacts can settle before the contact level is considered reliable and acted upon.See also Keyboard technology #Debouncing. * Bounce in SPDT ("single-pole, double-throw") switch contacts signals can be filtered out using an SR flip-flop (latch) or
Schmitt trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input ...
.
All of these methods are referred to as 'debouncing'.
Arcs and quenching
When the power being switched is sufficiently large, the electron flow across opening switch contacts is sufficient toionize
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
the air molecules across the tiny gap between the contacts as the switch is opened, forming a gas plasma, also known as an electric arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An ...
. The plasma is of low resistance and is able to sustain power flow, even with the separation distance between the switch contacts steadily increasing. The plasma is also very hot and is capable of eroding the metal surfaces of the switch contacts (the same true for vacuum switches). Electric current arcing causes significant degradation of the contacts and also significant electromagnetic interference (EMI), requiring the use of arc suppression methods.
Where the voltage is sufficiently high, an arc can also form as the switch is closed and the contacts approach. If the voltage potential is sufficient to exceed the breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that mak ...
of the air separating the contacts, an arc forms which is sustained until the switch closes completely and the switch surfaces make contact.
In either case, the standard method for minimizing arc formation and preventing contact damage is to use a fast-moving switch mechanism, typically using a spring-operated tipping-point mechanism to assure quick motion of switch contacts, regardless of the speed at which the switch control is operated by the user. Movement of the switch control lever applies tension to a spring until a tipping point is reached, and the contacts suddenly snap open or closed as the spring tension is released.
As the power being switched increases, other methods are used to minimize or prevent arc formation. A plasma is hot and will rise due to convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the conve ...
air currents. The arc can be quenched with a series of non-conductive blades spanning the distance between switch contacts, and as the arc rises, its length increases as it forms ridges rising into the spaces between the blades, until the arc is too long to stay sustained and is extinguished. A ''puffer'' may be used to blow a sudden high velocity burst of gas across the switch contacts, which rapidly extends the length of the arc to extinguish it quickly.
Extremely large switches often have switch contacts surrounded by something other than air to more rapidly extinguish the arc. For example, the switch contacts may operate in a vacuum, immersed in mineral oil
Mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils.
The name 'mineral oil' by itself is imprecise, ...
, or in sulfur hexafluoride.
In AC power service, the current periodically passes through zero; this effect makes it harder to sustain an arc on opening. Manufacturers may rate switches with lower voltage or current rating when used in DC circuits.
Power switching
When a switch is designed to switch significant power, the transitional state of the switch as well as the ability to withstand continuous operating currents must be considered. When a switch is in the on state, its resistance is near zero and very little power is dropped in the contacts; when a switch is in the off state, its resistance is extremely high and even less power is dropped in the contacts. However, when the switch is flicked, the resistance must pass through a state where a quarter of the load's rated power (or worse if the load is not purely resistive) is briefly dropped in the switch. For this reason, power switches intended to interrupt a load current have spring mechanisms to make sure the transition between on and off is as short as possible regardless of the speed at which the user moves the rocker. Power switches usually come in two types. A momentary on‑off switch (such as on alaser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a small handheld device with a power source (usually a battery) and a laser diode emitting a very narrow coherent low-powered laser beam of visible light, intended to be used to highlight something of interest by ...
) usually takes the form of a button and only closes the circuit when the button is depressed. A regular on‑off switch (such as on a flashlight) has a constant on-off feature. Dual-action switches incorporate both of these features.
Inductive loads
When a strongly inductive load such as anelectric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate for ...
is switched off, the current cannot drop instantaneously to zero; a spark
Spark commonly refers to:
* Spark (fire), a small glowing particle or ember
* Electric spark, a form of electrical discharge
Spark may also refer to:
Places
* Spark Point, a rocky point in the South Shetland Islands
People
* Spark (surname)
* ...
will jump across the opening contacts. Switches for inductive loads must be rated to handle these cases. The spark will cause electromagnetic interference if not suppressed; a snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems.
Ele ...
network of a resistor and capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
in series will quell the spark.
Incandescent loads
 When turned on, an incandescent lamp draws a large
When turned on, an incandescent lamp draws a large inrush current
Inrush current, input surge current, or switch-on surge is the maximal instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when first turned on. Alternating-current electric motors and transformers may draw several times their normal full-lo ...
of about ten times the steady-state current; as the filament heats up, its resistance rises and the current decreases to a steady-state value. A switch designed for an incandescent lamp load can withstand this inrush current.
Wetting current
''Wetting current
In electrical and electronics engineering, wetting current is the minimum electric current needing to flow through a contact to break through the surface film resistance at a contact. It is typically far below the contact's nominal maximum curr ...
'' is the minimum current needing to flow through a mechanical switch while it is operated to break through any film of oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
that may have been deposited on the switch contacts. The film of oxidation occurs often in areas with high humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
. Providing a sufficient amount of wetting current is a crucial step in designing systems that use delicate switches with small contact pressure as sensor inputs. Failing to do this might result in switches remaining electrically "open" due to contact oxidation.
Actuator
The moving part that applies the operating force to the contacts is called the '' actuator'', and may be a toggle or ''dolly'', a rocker, a push-button or any type of mechanical linkage ''(see photo).''Biased switches
A switch normally maintains its set position once operated. A biased switch contains a mechanism that springs it into another position when released by an operator. The momentary push-button switch is a type of biased switch. The most common type is a "push-to-make" (or normally-open or NO) switch, which makes contact when the button is pressed and breaks when the button is released. Each key of a computer keyboard, for example, is a normally-open "push-to-make" switch. A "push-to-break" (or normally-closed or NC) switch, on the other hand, breaks contact when the button is pressed and makes contact when it is released. An example of a push-to-break switch is a button used to release a door held closed by anelectromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in ...
. The interior lamp of a household refrigerator is controlled by a switch that is held open when the door is closed.
Rotary switch
 A rotary switch operates with a twisting motion of the operating handle with at least two positions. One or more positions of the switch may be momentary (biased with a spring), requiring the operator to hold the switch in the position. Other positions may have a detent to hold the position when released. A rotary switch may have multiple levels or "decks" in order to allow it to control multiple circuits.
One form of rotary switch consists of a spindle or "rotor" that has a contact arm or "spoke" which projects from its surface like a cam. It has an array of terminals, arranged in a circle around the rotor, each of which serves as a contact for the "spoke" through which any one of a number of different electrical circuits can be connected to the rotor. The switch is layered to allow the use of multiple poles, each layer is equivalent to one pole. Usually such a switch has a detent mechanism so it "clicks" from one active position to another rather than stalls in an intermediate position. Thus a rotary switch provides greater pole and throw capabilities than simpler switches do.
Other types use a cam mechanism to operate multiple independent sets of contacts.
Rotary switches were used as channel selectors on television receivers until the early 1970s, as range selectors on electrical metering equipment, as band selectors on multi-band radios and other similar purposes. In industry, rotary switches are used for control of measuring instruments,
A rotary switch operates with a twisting motion of the operating handle with at least two positions. One or more positions of the switch may be momentary (biased with a spring), requiring the operator to hold the switch in the position. Other positions may have a detent to hold the position when released. A rotary switch may have multiple levels or "decks" in order to allow it to control multiple circuits.
One form of rotary switch consists of a spindle or "rotor" that has a contact arm or "spoke" which projects from its surface like a cam. It has an array of terminals, arranged in a circle around the rotor, each of which serves as a contact for the "spoke" through which any one of a number of different electrical circuits can be connected to the rotor. The switch is layered to allow the use of multiple poles, each layer is equivalent to one pole. Usually such a switch has a detent mechanism so it "clicks" from one active position to another rather than stalls in an intermediate position. Thus a rotary switch provides greater pole and throw capabilities than simpler switches do.
Other types use a cam mechanism to operate multiple independent sets of contacts.
Rotary switches were used as channel selectors on television receivers until the early 1970s, as range selectors on electrical metering equipment, as band selectors on multi-band radios and other similar purposes. In industry, rotary switches are used for control of measuring instruments, switchgear
In an electric power system, a switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be ...
, or in control circuits. For example, a radio controlled overhead crane may have a large multi-circuit rotary switch to transfer hard-wired control signals from the local manual controls in the cab to the outputs of the remote control receiver.
Toggle switch


 A toggle switch or tumbler switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical
A toggle switch or tumbler switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is d ...
, handle, or rocking mechanism.
Toggle switches are available in many different styles and sizes, and are used in numerous applications. Many are designed to provide the simultaneous actuation of multiple sets of electrical contact
An electrical contact is an electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they c ...
s, or the control of large amounts of electric current or mains voltages.
The word "toggle" is a reference to a kind of mechanism or joint consisting of two arms, which are almost in line with each other, connected with an elbow-like pivot. However, the phrase "toggle switch" is applied to a switch with a short handle and a positive snap-action, whether it actually contains a toggle mechanism or not. Similarly, a switch where a definitive click is heard, is called a "positive on-off switch". A very common use of this type of switch is to switch lights or other electrical equipment on or off. Multiple toggle switches may be mechanically interlocked to prevent forbidden combinations.
In some contexts, particularly computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
, a toggle switch, or the action of toggling, is understood in the different sense of a mechanical or software switch that alternates between two states each time it is activated, regardless of mechanical construction. For example, the caps lock key on a computer causes all letters to be generated in capitals after it is pressed once; pressing it again reverts to lower-case letters.
Special types
 Switches can be designed to respond to any type of mechanical stimulus: for example, vibration (the trembler switch), tilt, air pressure, fluid level (a
Switches can be designed to respond to any type of mechanical stimulus: for example, vibration (the trembler switch), tilt, air pressure, fluid level (a float switch A float switch is a type of level sensor, a device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank. The switch may be used to control a pump, as an indicator, an alarm, or to control other devices.
One type of float switch uses a mercury switch ...
), the turning of a key (key switch
A key switch (sometimes called a keyswitch or lock switch) is a key-operated switch. Key switches are used in situations where access needs to be restricted to the switch's functions.
Key switches are available as components with solder connecti ...
), linear or rotary movement (a limit switch In electrical engineering, a limit switch is a switch operated by the motion of a machine part or the presence of an object. A limit switch can be used for controlling machinery as part of a control system, as a safety interlock, or as a counter en ...
or microswitch
A miniature snap-action switch, also trademarked and frequently known as a micro switch, is an electric switch that is actuated by very little physical force, through the use of a tipping-point mechanism, sometimes called an "over-center" mechan ...
), or presence of a magnetic field (the reed switch). Many switches are operated automatically by changes in some environmental condition or by motion of machinery. A limit switch In electrical engineering, a limit switch is a switch operated by the motion of a machine part or the presence of an object. A limit switch can be used for controlling machinery as part of a control system, as a safety interlock, or as a counter en ...
is used, for example, in machine tools to interlock operation with the proper position of tools. In heating or cooling systems a sail switch ensures that air flow is adequate in a duct. Pressure switch
A pressure switch is a form of switch that operates an electrical contact when a certain set fluid pressure has been reached on its input. The switch may be designed to make contact either on pressure rise or on pressure fall. Pressure switches ar ...
es respond to fluid pressure.
Mercury tilt switch
The mercury switch consists of a drop of mercury inside aglass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
bulb with two or more contacts. The two contacts pass through the glass, and are connected by the mercury when the bulb is tilted to make the mercury roll on to them.
This type of switch performs much better than the ball tilt switch, as the liquid metal
A liquid metal is a metal or a metal alloy which is liquid at or near room temperature.
The only stable liquid elemental metal at room temperature is mercury (Hg), which is molten above −38.8 °C (234.3 K, −37.9 °F). Three more ...
connection is unaffected by dirt, debris and oxidation, it wets the contacts ensuring a very low resistance bounce-free connection, and movement and vibration do not produce a poor contact. These types can be used for precision works.
It can also be used where arcing is dangerous (such as in the presence of explosive vapour) as the entire unit is sealed.
Knife switch
copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, steel, or brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
, depending on the application. Fixed contacts may be backed up with a spring. Several parallel blades can be operated at the same time by one handle. The parts may be mounted on an insulating base with terminals for wiring, or may be directly bolted to an insulated switch board in a large assembly. Since the electrical contacts are exposed, the switch is used only where people cannot accidentally come in contact with the switch or where the voltage is so low as to not present a hazard.
Knife switches are made in many sizes from miniature switches to large devices used to carry thousands of amperes. In electrical transmission and distribution, gang-operated switches are used in circuits up to the highest voltages.
The disadvantages of the knife switch are the slow opening speed and the proximity of the operator to exposed live parts. Metal-enclosed safety disconnect switches are used for isolation of circuits in industrial power distribution. Sometimes spring-loaded auxiliary blades are fitted which momentarily carry the full current during opening, then quickly part to rapidly extinguish the arc.
Footswitch
A footswitch is a rugged switch which is operated by foot pressure. An example of use is in the control of a machine tool, allowing the operator to have both hands free to manipulate the workpiece. The foot controls of an electric guitarist'seffects pedals
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in ele ...
and amp #REDIRECT Amp
{{Redirect category shell, {{R from other capitalisation{{R from ambiguous page ...
are also footswitches.
Reversing switch
A DPDT switch has six connections, but since polarity reversal is a very common usage of DPDT switches, some variations of the DPDT switch are internally wired specifically for polarity reversal. These crossover switches only have four terminals rather than six. Two of the terminals are inputs and two are outputs. When connected to a battery or other DC source, the 4-way switch selects from either normal or reversed polarity. Such switches can also be used as intermediate switches in amultiway switching
In building wiring, multiway switching is the interconnection of two or more electrical switches to control an electrical load from more than one location. A common application is in lighting, where it allows the control of lamps from multiple ...
system for control of lamps by more than two switches.
Light switches
In building wiring, light switches are installed at convenient locations to control lighting and occasionally other circuits. By use of multiple-pole switches,multiway switching
In building wiring, multiway switching is the interconnection of two or more electrical switches to control an electrical load from more than one location. A common application is in lighting, where it allows the control of lamps from multiple ...
control of a lamp can be obtained from two or more places, such as the ends of a corridor or stairwell. A wireless light switch
A wireless light switch is a light switch that commands a light or home appliance to turn itself off or on, instead of interrupting the power line going to the light fixture. There are different ways to communicate between the switch and the fixt ...
allows remote control of lamps for convenience; some lamps include a touch switch A touch switch is a type of switch that only has to be touched by an object to operate. It is used in many lamps and wall switches that have a metal exterior as well as on public computer terminals. A touchscreen includes an array of touch switches ...
which electronically controls the lamp if touched anywhere. In public buildings several types of vandal resistant switches are used to prevent unauthorized use.
Slide switches
Slide switches are mechanical switches using a slider that moves (slides) from the open (off) position to the closed (on) position.Electronic switches
 A
A relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching—often a silicon-controlled rectifier or TRIAC, triac.
The analogue switch uses two MOSFET transistors in a transmission gate arrangement as a switch that works much like a relay, with some advantages and several limitations compared to an electromechanical relay.
The Power transistor, power transistor(s) in a switching voltage regulator, such as a power supply unit (computer), power supply unit, are used like a switch to alternately let power flow and block power from flowing.
Many people use metonymy to call a variety of devices "switches" that conceptually connect or disconnect signals and communication paths between electrical devices, analogous to the way mechanical switches connect and disconnect paths for electrons to flow between two conductors. Early telephone systems used an automatically operated Strowger switch to connect telephone callers; telephone exchanges contain one or more crossbar switches today.
Since the advent of digital logic in the 1950s, the term ''switch'' has spread to a variety of digital active devices such as transistors and logic gates whose function is to change their output state between two logic levels or connect different Digital signal (electronics), signal lines, and even computers, network switches, whose function is to provide connections between different computer port (hardware), ports in a computer network. The most widely used electronic switch in digital circuits is the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET).
The term 'switched' is also applied to telecommunications networks, and signifies a network that is circuit switched, providing dedicated circuits for communication between end nodes, such as the public switched telephone network. The common feature of all these usages is they refer to devices that control a binary numeral system, binary State (computer science), state: they are either ''on'' or ''off'', ''closed'' or ''open'', ''connected'' or ''not connected''.
Other switches
* Centrifugal switch * Company switch * Dead man's switch * Fireman's switch * Hall-effect switch * Inertial switch * Isolator switch * Key switch * Kill switch * Latching switch * Light switch * Load control switch * Membrane switch * MEMS switch * Optical switch * Piezo switch * Pull switch * Push switch * Railroad switch * Sense switch * Slotted optical switch * Stepping switch * Thermal switch * Time switch * Touch switch * Transfer switch * Trolleybus#Wire switches, Wire switches * Zero speed switchSee also
* Circuit breaker * Commutator (electric) * Contact resistance * DIN rail * Electric switchboard * Fuse cutout * RF switch matrix * Switch access * SwitchgearReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Switches, Electrical components Human–machine interaction