Heidelberg Observatory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heidelberg (; Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the German state of
 Heidelberg is located on the eastern edge of the
Heidelberg is located on the eastern edge of the 
 Heidelberg is a unitary authority within the Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. The
Heidelberg is a unitary authority within the Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. The


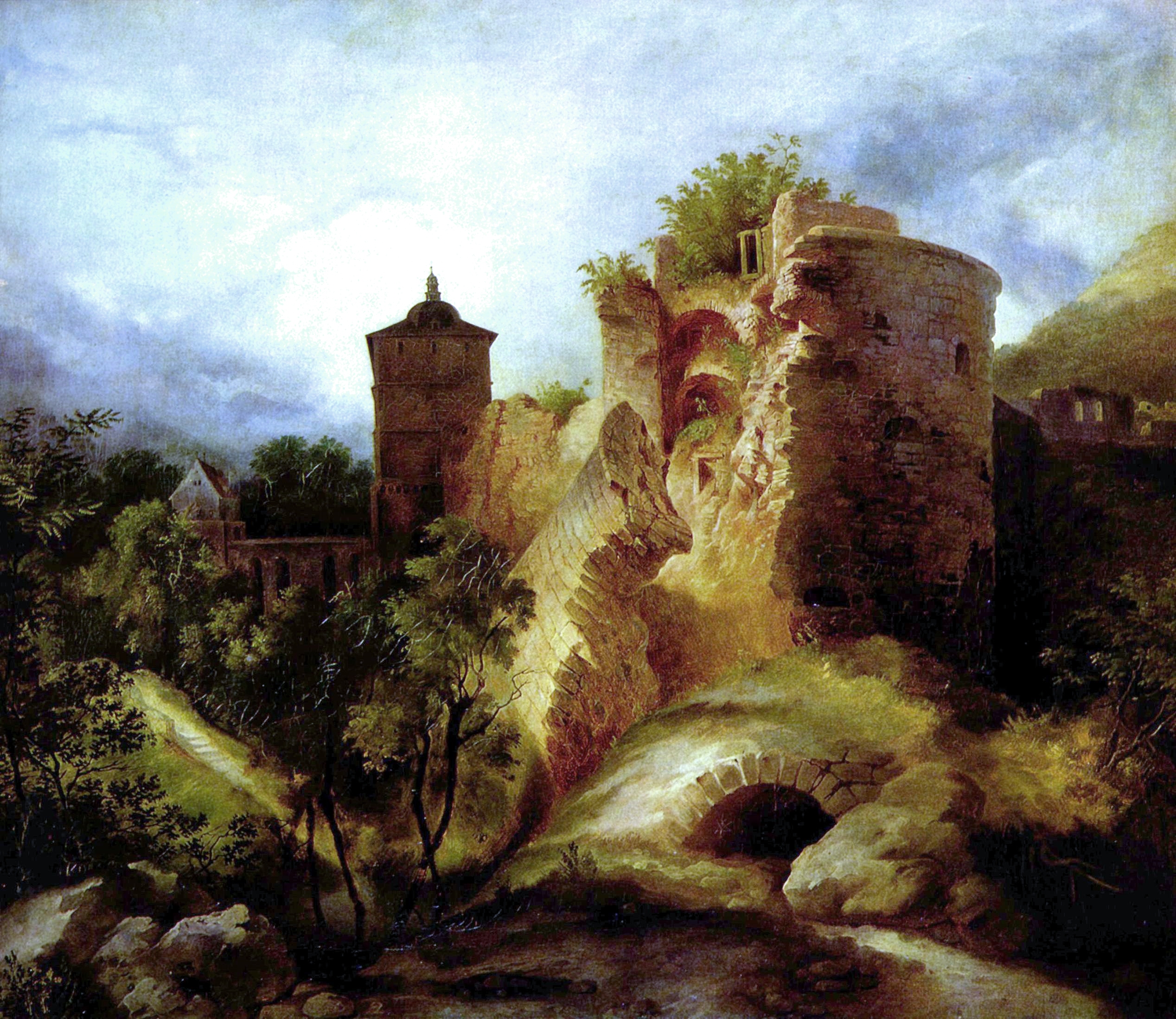 Modern Heidelberg can trace its beginnings to the fifth century. The village ''Bergheim'' ("Mountain Home") is first mentioned for that period in documents dated to 769 AD. ''Bergheim'' now lies in the middle of modern Heidelberg. The people gradually converted to Christianity. In 870 AD, the
Modern Heidelberg can trace its beginnings to the fifth century. The village ''Bergheim'' ("Mountain Home") is first mentioned for that period in documents dated to 769 AD. ''Bergheim'' now lies in the middle of modern Heidelberg. The people gradually converted to Christianity. In 870 AD, the


 In November 1619, the Royal
In November 1619, the Royal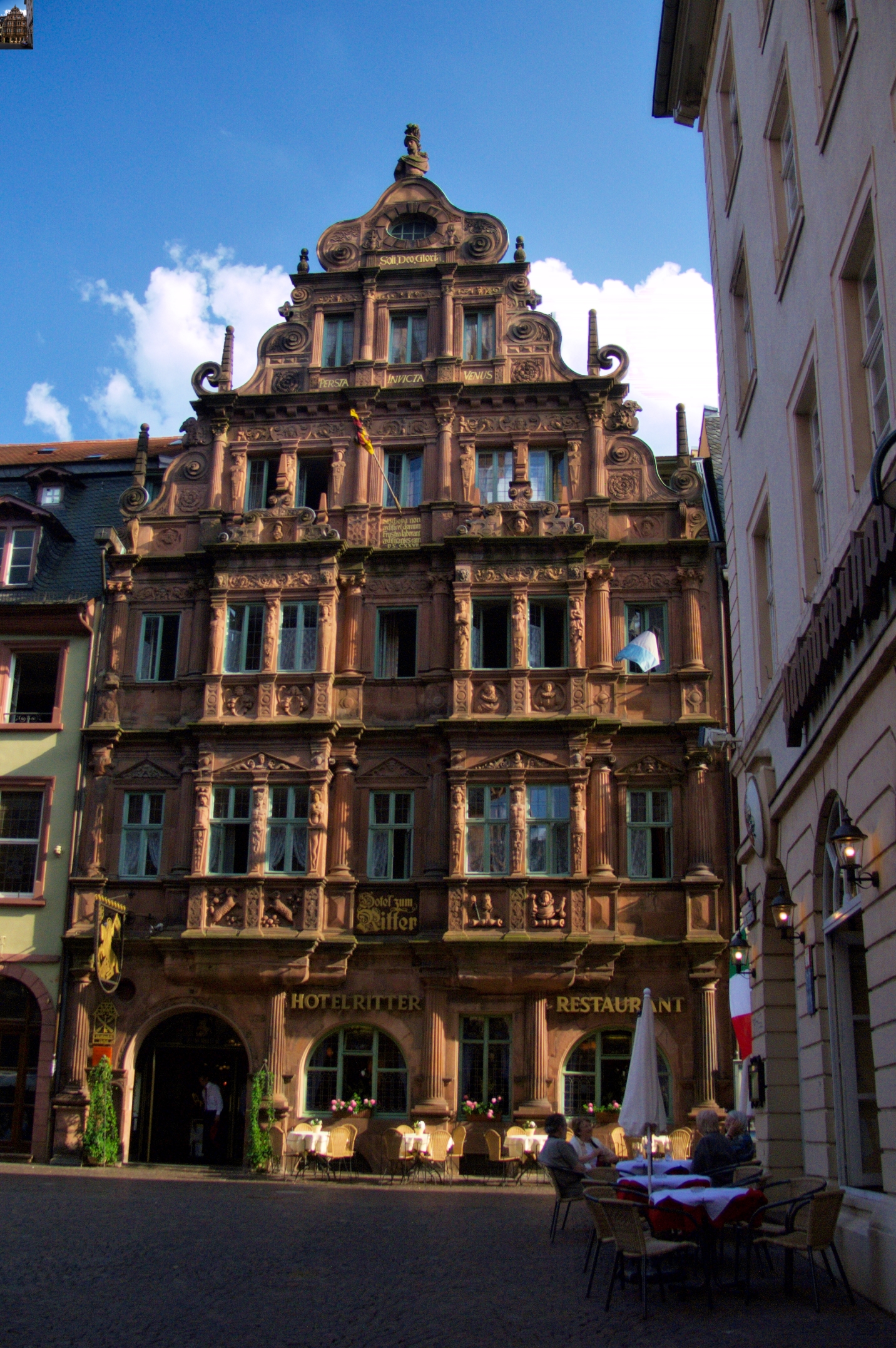 
 In late 1634, after the Swedish army had conquered Heidelberg, imperial forces attempted to recapture the city. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by
In late 1634, after the Swedish army had conquered Heidelberg, imperial forces attempted to recapture the city. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by
 During the ''
During the ''
 The population of the city of Heidelberg exceeded 100,000 for the first time in 1946. It is a city with an international population, including one of the largest American communities outside North America, but this is not analysed in the Heidelberg population statistics. At the end of December 2011, the city had 149,633 inhabitants with an official primary residence in Heidelberg (not including the soldiers and employees of the U.S. Army and their dependents, a total of about 20,000 people), a historic high.
The following table shows the number of inhabitants within the boundaries of the city at the time. To 1833 they are mostly estimates, then census results or official updates of the statistical offices of the time or the city administration. The data refer from 1843 to the "local population", from 1925 to the resident population and since 1987 the "population at the site of their main dwelling." Prior to 1843 the population was determined by non-uniform collection procedures.
¹ Census results
With a
The population of the city of Heidelberg exceeded 100,000 for the first time in 1946. It is a city with an international population, including one of the largest American communities outside North America, but this is not analysed in the Heidelberg population statistics. At the end of December 2011, the city had 149,633 inhabitants with an official primary residence in Heidelberg (not including the soldiers and employees of the U.S. Army and their dependents, a total of about 20,000 people), a historic high.
The following table shows the number of inhabitants within the boundaries of the city at the time. To 1833 they are mostly estimates, then census results or official updates of the statistical offices of the time or the city administration. The data refer from 1843 to the "local population", from 1925 to the resident population and since 1987 the "population at the site of their main dwelling." Prior to 1843 the population was determined by non-uniform collection procedures.
¹ Census results
With a
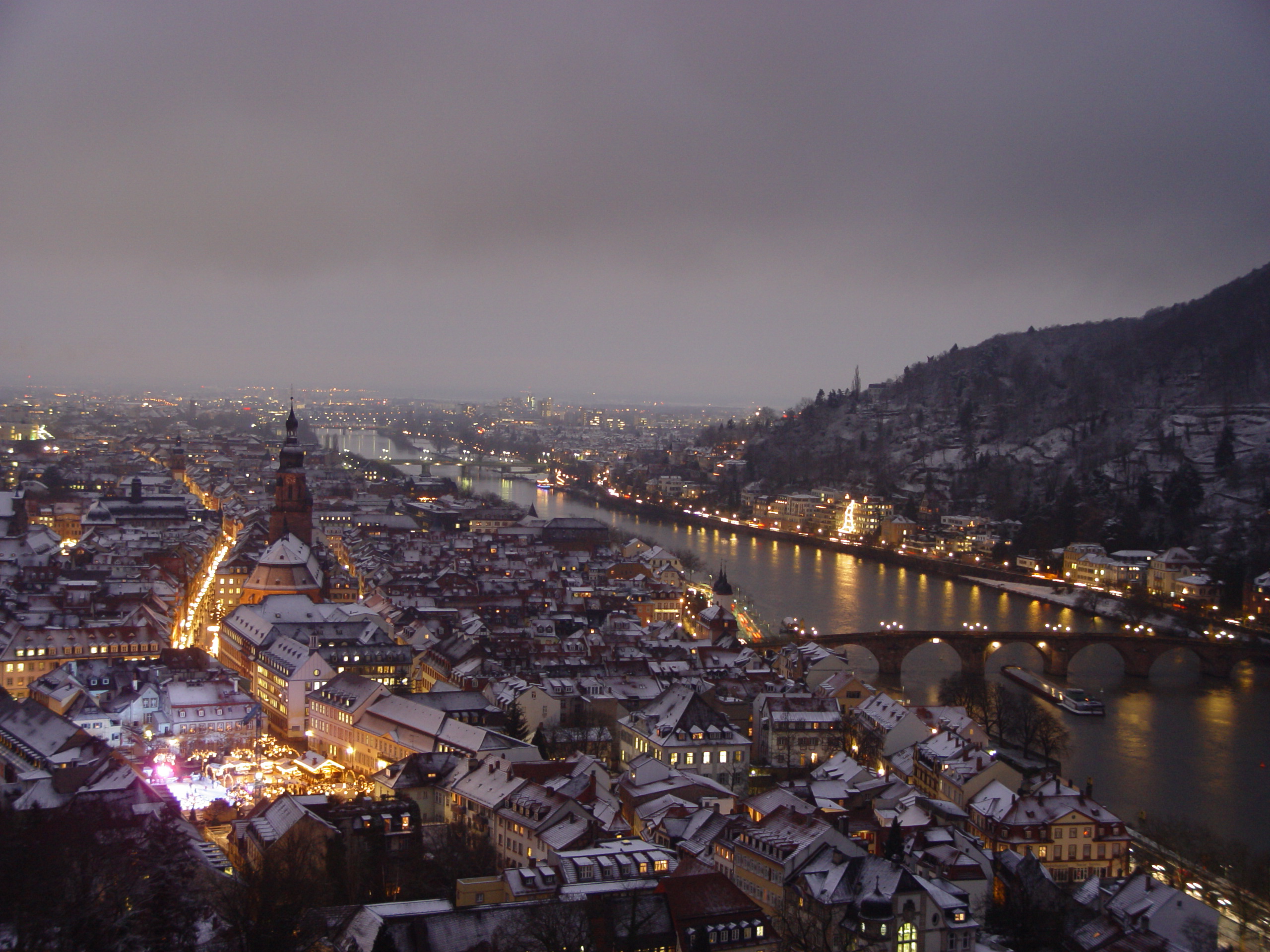


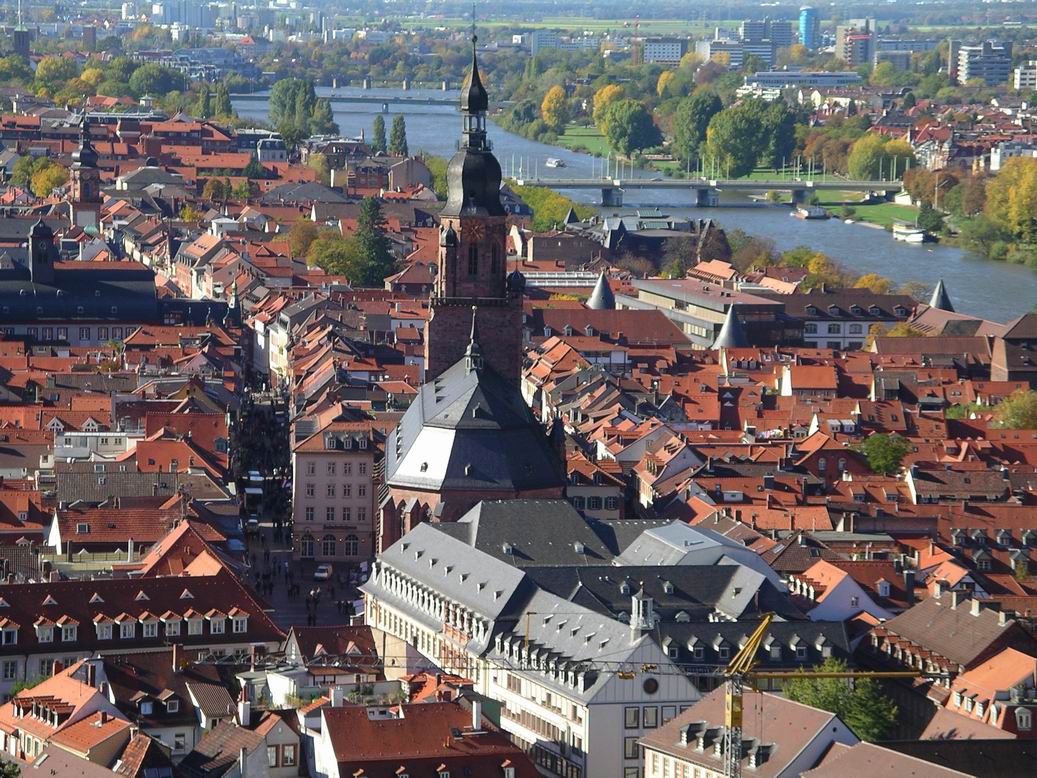
 The "old town" (german: link=no, Altstadt), on the south bank of the Neckar, is long and narrow. It is dominated by the ruins of Heidelberg Castle, 80 metres above the Neckar on the steep wooded slopes of the Königstuhl (''King's chair or throne'') hill.
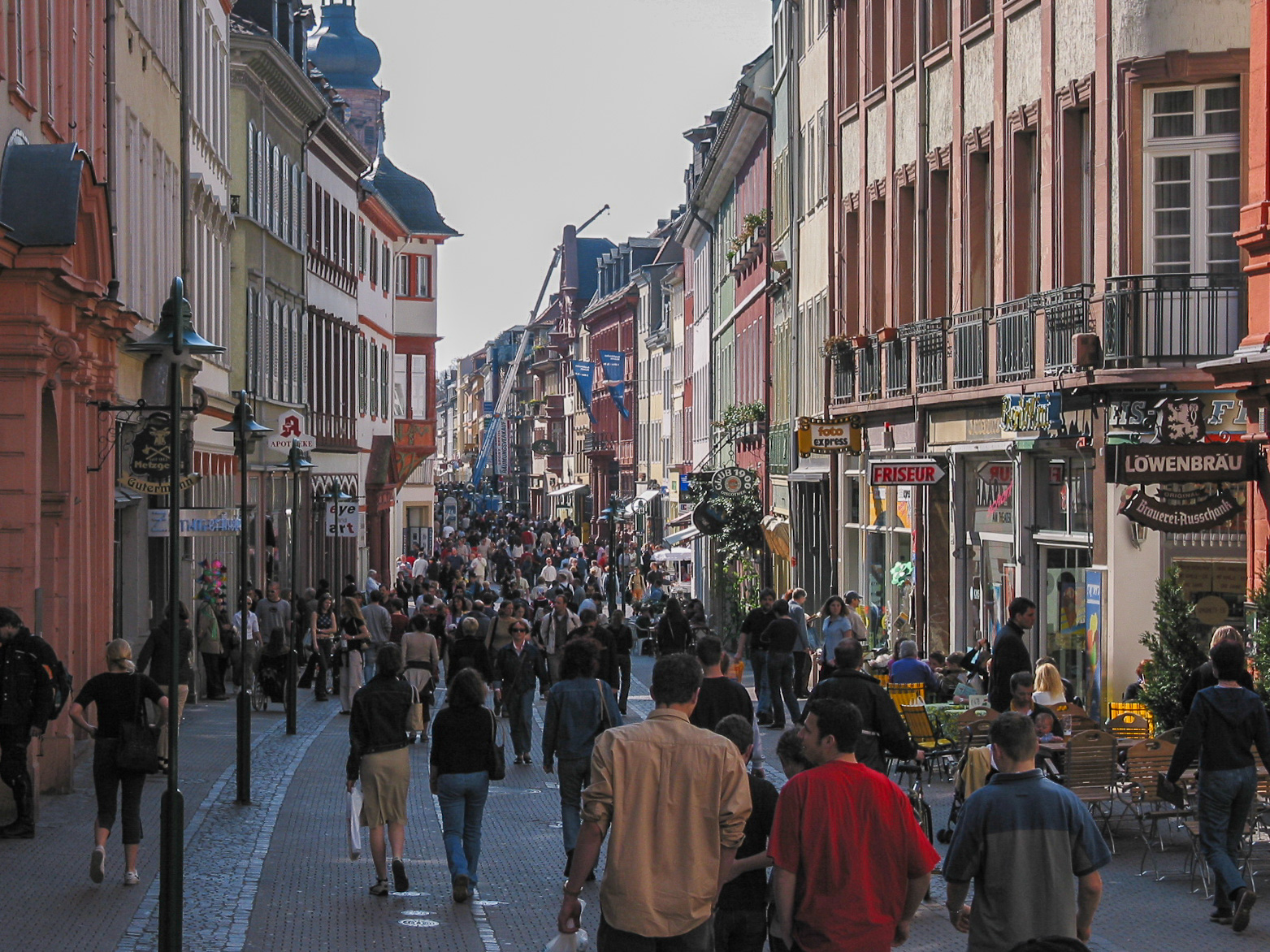
*The Main Street (''Hauptstrasse''), a mile-long pedestrian street, running the length of the old town.
*The old stone bridge was erected 1786–1788. A medieval bridge gate is on the side of the old town, and was originally part of the town wall. Baroque tower helmets were added as part of the erection of the stone bridge in 1788.
*The Church of the Holy Spirit (''Heiliggeistkirche''), a late Gothic church in the marketplace of the old town.
*The Karls‘ gate (''Karlstor'') is a triumphal arch in honour of the Prince Elector Karl Theodor, located at Heidelberg's east side. It was built 1775–1781 and designed by Nicolas de Pigage.
*The house ''Zum Ritter Sankt Georg'' (Knight St. George) is one of the few buildings to survive the War of Succession. Standing across from the Church of the Holy Spirit, it was built in the style of the late
The "old town" (german: link=no, Altstadt), on the south bank of the Neckar, is long and narrow. It is dominated by the ruins of Heidelberg Castle, 80 metres above the Neckar on the steep wooded slopes of the Königstuhl (''King's chair or throne'') hill.
*The Main Street (''Hauptstrasse''), a mile-long pedestrian street, running the length of the old town.
*The old stone bridge was erected 1786–1788. A medieval bridge gate is on the side of the old town, and was originally part of the town wall. Baroque tower helmets were added as part of the erection of the stone bridge in 1788.
*The Church of the Holy Spirit (''Heiliggeistkirche''), a late Gothic church in the marketplace of the old town.
*The Karls‘ gate (''Karlstor'') is a triumphal arch in honour of the Prince Elector Karl Theodor, located at Heidelberg's east side. It was built 1775–1781 and designed by Nicolas de Pigage.
*The house ''Zum Ritter Sankt Georg'' (Knight St. George) is one of the few buildings to survive the War of Succession. Standing across from the Church of the Holy Spirit, it was built in the style of the late


 The castle is a mix of styles from
The castle is a mix of styles from
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students.
Located about south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is the fifth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg. Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region.
Heidelberg University, founded in 1386, is Germany's oldest and one of Europe's most reputable universities. Heidelberg is a scientific hub in Germany and home to several internationally renowned research facilities adjacent to its university, including the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and four Max Planck Institutes. The city has also been a hub for the arts, especially literature, throughout the centuries, and it was designated a "City of Literature
UNESCO's City of Literature programme is part of the wider Creative Cities Network.
The ''Network'' was launched in 2004, and now has member cities in seven creative fields. The other creative fields are: Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gas ...
" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a project of UNESCO launched in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities which recognized creativity as a major factor in their urban development.Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
and is a popular tourist destination due to its romantic cityscape, including Heidelberg Castle, the Philosophers' Walk, and the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including th ...
old town.
Geography
Upper Rhine Plain
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben ( German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the ...
(German: "Oberrheinebene"), at the place where the river Neckar leaves its narrow valley through the Odenwald
The Odenwald () is a low mountain range in the Germany, German states of Hesse, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg.
Location
The Odenwald is located between the Upper Rhine Plain with the Bergstraße Route, Bergstraße and the ''Hessisches Ried' ...
mountains and begins the last leg of its journey across the plain towards Mannheim, where it merges into the Rhine about 20 kilometers downstream.
A part of Heidelberg, including the historical old town and the famous Heidelberg Castle, is located in the narrow Neckar valley. Other parts (mostly quarters from around the 19th century or newer, or originally independent, later incorporated villages) sprawl out into the Rhine Plain and along the Bergstraße (route)
The Bergstraße ("Mountain Road") is ancient trade route in the south-west of Germany. The route and the area around it is a mountainous " theme route" running north–south along the western edge of the Odenwald forest in southern Hesse and no ...
("mountain road"), the narrow strip of characteristic landscape along the sharp border between the plain and the Odenwald mountains.
The town is bordered by the Königsstuhl (568 m), the Gaisberg (375 m) and the Heiligenberg
Heiligenberg is a municipality and a village in the Bodensee district in Baden-Württemberg, about seven kilometres north of Salem, in Germany.
Location and climate
Heiligenberg (literally: the Holy Mountain or the Mountain of Saints) is loca ...
(445 m) mountains.
Heidelberg is on European walking route E1 ( Sweden-Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
).

Flora and fauna
Heidelberg is among the warmest regions of Germany and plants atypical of the central-European climate flourish there, including almond and fig trees, many kinds of palm trees and olive trees. Alongside the ''Philosophenweg'' (Philosophers' Walk) on the opposite side of the Old Town,winegrowing
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
was restarted in 2000.
There is a wild population of African rose-ringed parakeets, and a wild population of Siberian swan geese, which can be seen mainly on the islands in the Neckar near the district of Bergheim.
Administrative structures
 Heidelberg is a unitary authority within the Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. The
Heidelberg is a unitary authority within the Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. The Rhein-Neckar-Kreis
The Rhein-Neckar-Kreis is a district in the northwest of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The administrative headquarters are based in the city Heidelberg, which is a district-free city. As of 2019, the district is the most populous in Baden-Würt ...
rural district surrounds it and has its seat in the town, although the town is not a part of the district. Heidelberg is a part of the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region, often referred to as the Rhein-Neckar Triangle.
This region consists of the southern part of the State of Hessen, the southern part of the State of Rhineland-Palatinate (''Vorderpfalz''), the administrative districts of Mannheim and Heidelberg, and the municipalities of the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis
The Rhein-Neckar-Kreis is a district in the northwest of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The administrative headquarters are based in the city Heidelberg, which is a district-free city. As of 2019, the district is the most populous in Baden-Würt ...
. The Rhein-Neckar Triangle became a European metropolitan area in 2005.
Heidelberg consists of 15 districts distributed in six sectors of the town. In the central area are Altstadt (the Old Town), Bergheim and Weststadt; in the north, Neuenheim and Handschuhsheim; in the east, Ziegelhausen and Schlierbach; in the south, Südstadt, Rohrbach, Emmertsgrund, and Boxberg; in the southwest, Kirchheim; in the west, Pfaffengrund, Wieblingen, and a new district, named ''Bahnstadt'', is built on land in Weststadt and Wieblingen. The new district will have approximately 5,000–6,000 residents and employment for 7,000. Further, new residential space for 10,000–15,000 residents was made available in Patrick Henry Village following the departure of the US Armed Forces.
Neighbouring communes
The following towns andcommune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
s border the city of Heidelberg, beginning in the west and in a clockwise direction: Edingen-Neckarhausen, Dossenheim
Dossenheim () is a municipality in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis (district) in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
It is located on Bergstraße and Bertha Benz Memorial Route.
Geography
Location
Dossenheim lies 5 kilometers north of Heidelberg along the B ...
, Schriesheim
Schriesheim ( South Franconian: ''Schriese'') is a town located in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is part of the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis and the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region.
Geography
Schriesheim lies on the Bergstraße, at the western edg ...
, Wilhelmsfeld
Wilhelmsfeld is a municipality in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis of Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Geography
Wilhelmsfeld is a state-certified climatic health resort in the hills of the southern Odenwald, between 260 and 533m above sea-level. The surrou ...
, Schönau, Neckargemünd
Neckargemünd ( pfl, Neggergmin) is a town in Germany, in the district of Rhein-Neckar-Kreis, state of Baden-Württemberg. It lies on the Neckar, 10 km upriver from Heidelberg at the confluence with the river Elsenz. This confluence of the ...
, Bammental
Bammental is a municipality in Rhein-Neckar Kreis of Baden-Württemberg.
Geography
Bammental is about 9 km southeast of Heidelberg and 13 km northwest of Sinsheim in the Elsenz valley, between Mauer and Neckargemünd. The borough of ...
, Gaiberg, Leimen, Sandhausen, Oftersheim
Oftersheim is a municipality in the district of Rhein-Neckar-Kreis, in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern par ...
, Plankstadt
Plankstadt () is a municipality in the district of Rhein-Neckar-Kreis, in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern ...
, Eppelheim
Eppelheim () is a city in northern Baden-Württemberg bordering Heidelberg. It belongs to the district Rhein-Neckar-Kreis.
Geography
Location and neighboring communities
Eppelheim is situated in the valley of the Upper Rhine southwest of the h ...
(all part of the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis
The Rhein-Neckar-Kreis is a district in the northwest of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The administrative headquarters are based in the city Heidelberg, which is a district-free city. As of 2019, the district is the most populous in Baden-Würt ...
) and Mannheim.
Climate
Heidelberg has a humid subtropical climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''), defined by the protected valley between the Pfälzerwald and the Odenwald. The almost year round warm temperatures are usually determined by Atlantic air masses in the winter and increased influence from the western Mediterranean in summer. This results in drier summers and wetter, cloudier winters on average. In contrast to the nearbyUpper Rhine Plain
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben ( German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the ...
, Heidelberg's position in the valley leads to more frequent easterly winds than average. The hillsides of the Odenwald favour clouding and precipitation.
Spring starts early and is one of the warmest in Europe besides the Mediterranean Coast. Especially April has a tendency to be also very dry, while the rising temperatures in May can create some thunderstorms with higher precipitation levels. Nights start cold and usually stay fresh throughout almost the whole spring, while day temperatures can already become hot from April on (30°C/86°F and higher).
Summers are long, hot and mostly dry. Day temperatures are around 28-30 on average, but will often rise beyond 35°C (95°F) in midsummer. A few single evening thunderstorms are usually the only measurable precipitation. With almost 300 sunshine hours on average, July is also the sunniest month of the year. Nights can stay pleasant, although the rate of nights with lows up to 26°C (78°F) are increasing significantly in the recent years.
Autumn starts very warm or even hot in September and cools down to typical winter temperatures for the region until the end of November. Precipitation levels are increasing and, due to the decreasing sunlight, the region gets affected by fog more frequently from the second part of October on. On the other hand, day temperatures will mostly stay around or above 20°C (68°F) until at least mid October (“Altweibersommer”). Nights cool down significantly during the month, but will usually remain above 10°C (50°F) until the second half of October.
Winters are mostly mild, though light night frosts do occur in the coldest months. Snow is a rare event and precipitation normally falls as rain. Besides that, winters are the wettest time of the year with frequent western winds blowing from the Atlantic. Storms (“Orkane”) can create severe damage and the Neckar is often affected by floods.
According to the German Meteorological Service
The () or DWD for short, is the German Meteorological Service, based in Offenbach am Main, Germany, which monitors weather and meteorological conditions over Germany and provides weather services for the general public and for nautical, aviat ...
, Heidelberg was the warmest place in Germany in 2009. With around 2,100 hours of sunshine it is also one of the sunniest of the country.
History


Early history
Between 600,000 and 200,000 years ago, " Heidelberg Man" died at nearbyMauer
Mauer is the German word for ''wall''. It may also refer to:
Places
*Mauer, Vienna, a former village of Lower Austria that has been part of Vienna since 1938
* Mauer bei Amstetten, a village in the municipality of Amstetten, in Lower Austria
* M ...
. His jaw bone was discovered in 1907. Scientific dating determined his remains as the earliest evidence of human life in Europe. In the 5th century BC, a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
fortress of refuge and place of worship were built on the ''Heiligenberg'', or "Holy Mountain". Both places can still be identified. In 40 AD, a fort was built and occupied by the 24th Roman cohort and the 2nd Cyrenaican cohort (CCG XXIIII and CCH II CYR). The late Roman Emperor Valentinian I, in 369 AD, built new and maintained older ''castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
'' (permanent camps) and a signal tower on the bank of the Neckar. They built a wooden bridge based on stone pillars across it. The camp protected the first civilian settlements and was eventually captured by Germanic tribes. The local administrative center in Roman times was the nearby city of Lopodunum, today known as Ladenburg
Ladenburg is a town in northwestern Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It lies on the right bank of the river Neckar, northwest of Heidelberg and east of Mannheim.
The town's history goes back to the Celtic and Roman Ages, when it was called Lop ...
.
Middle Ages
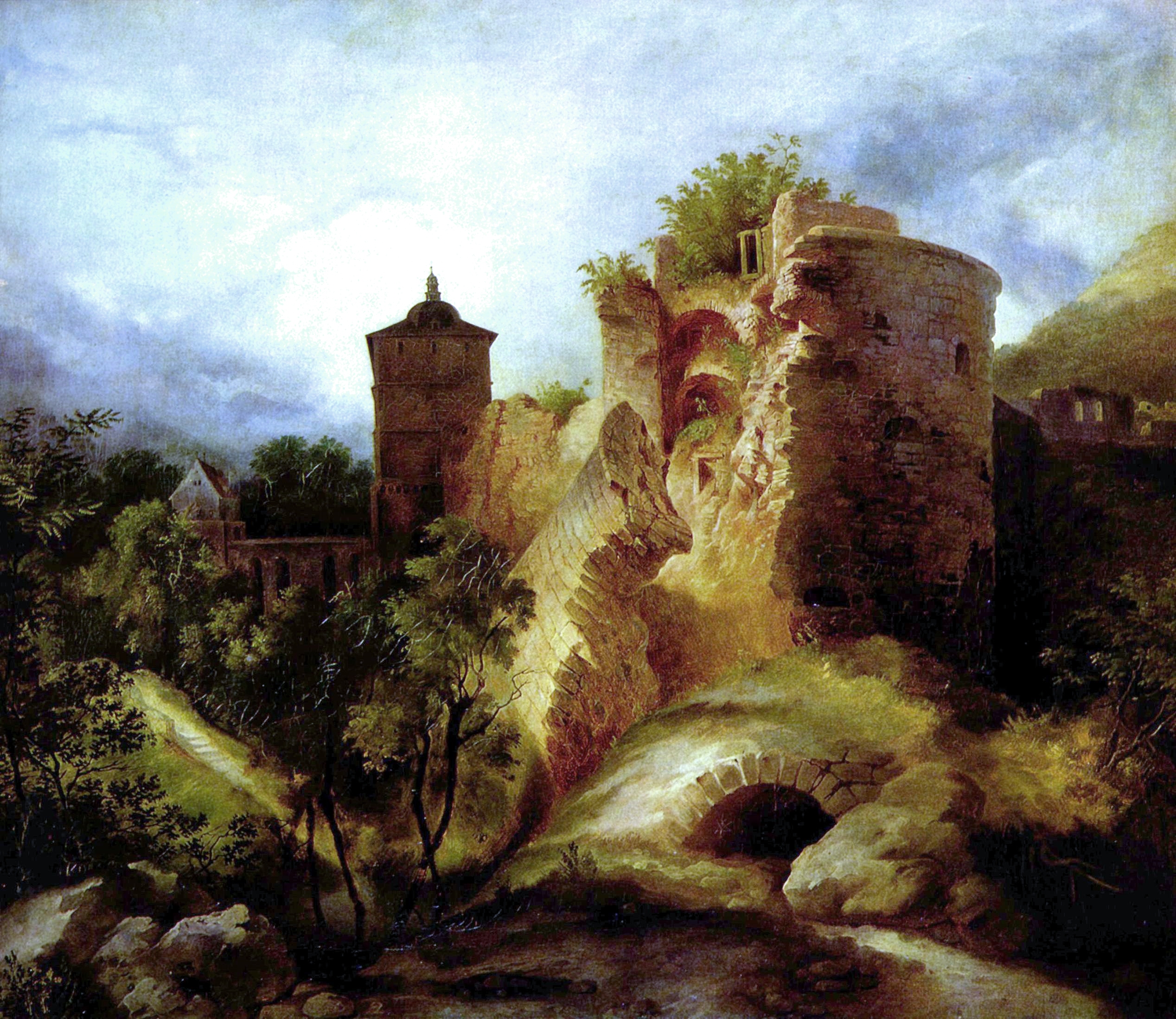 Modern Heidelberg can trace its beginnings to the fifth century. The village ''Bergheim'' ("Mountain Home") is first mentioned for that period in documents dated to 769 AD. ''Bergheim'' now lies in the middle of modern Heidelberg. The people gradually converted to Christianity. In 870 AD, the
Modern Heidelberg can trace its beginnings to the fifth century. The village ''Bergheim'' ("Mountain Home") is first mentioned for that period in documents dated to 769 AD. ''Bergheim'' now lies in the middle of modern Heidelberg. The people gradually converted to Christianity. In 870 AD, the monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
of St. Michael
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also ...
was founded on the Heiligenberg
Heiligenberg is a municipality and a village in the Bodensee district in Baden-Württemberg, about seven kilometres north of Salem, in Germany.
Location and climate
Heiligenberg (literally: the Holy Mountain or the Mountain of Saints) is loca ...
inside the double rampart of the Celtic fortress. Around 1130, the Neuburg Monastery was founded in the Neckar valley. At the same time, the bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
of Worms Worms may refer to:
*Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs
Places
*Worms, Germany
Worms () is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had ...
extended its influence into the valley, founding Schönau Abbey
Schönau Abbey (''Kloster Schönau'') in Schönau in the Odenwald, in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis in Baden-Württemberg, was a Cistercian monastery founded in 1142 from Eberbach Abbey. The present settlement of Schönau grew up round the monastery.
...
in 1142. Modern Heidelberg can trace its roots to this 12th-century monastery. The first reference to Heidelberg can be found in a document in Schönau Abbey
Schönau Abbey (''Kloster Schönau'') in Schönau in the Odenwald, in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis in Baden-Württemberg, was a Cistercian monastery founded in 1142 from Eberbach Abbey. The present settlement of Schönau grew up round the monastery.
...
dated to 1196. This is considered to be the town's founding date. In 1156, Heidelberg castle and its neighboring settlement were taken over by the house of Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynas ...
. Conrad of Hohenstaufen
Conrad of Hohenstaufen ( – 8 November 1195) was the first hereditary Count Palatine of the Rhine.
His parents were Frederick II of Swabia (1090–1147), Duke of Swabia, and his second wife Agnes of Saarbrücken, daughter of Frederick, Cou ...
became Count Palatine of the Rhine
The counts palatine of Lotharingia /counts palatine of the Rhine /electors of the Palatinate (german: Kurfürst von der Pfalz) ruled some part of Rhine area in the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire from 915 to 1803. The title was a kind ...
(german: link=no, Pfalzgraf bei Rhein). In 1195, the Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
passed to the House of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meus ...
through marriage. In 1214, Ludwig I, Duke of Bavaria acquired the Palatinate, as a consequence of which the castle came under his control. By 1303, another castle had been constructed for defense. In 1356, the Counts Palatine were granted far-reaching rights in the Golden Bull
A golden bull or chrysobull was a decree issued by Byzantine Emperors and later by monarchs in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, most notably by the Holy Roman Emperors. The term was originally coined for the golden seal (a ''bull ...
, in addition to becoming Electors. In 1386, Heidelberg University was founded by Rupert I, Elector Palatine
Rupert I "the Red", Elector Palatine (; 9 June 1309, Wolfratshausen – 16 February 1390, Neustadt an der Weinstraße) was Count Palatine of the Rhine from 1353 to 1356, and Elector Palatine from 10 January 1356 to 16 February 1390.
He was th ...
.
Modern history
Heidelberg University played a leading part in MedievalScholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translat ...
, Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
, the German Reformation
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, and in the subsequent conflict between Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
and Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
during the 15th and 16th centuries. In April 1518, a few months after proclaiming his ''Ninety-five Theses
The ''Ninety-five Theses'' or ''Disputation on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences''-The title comes from the 1517 Basel pamphlet printing. The first printings of the ''Theses'' use an incipit rather than a title which summarizes the content ...
'', Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
was received in Heidelberg, to defend them.
Heidelberg's library, founded in 1421, is the oldest existing public library
A public library is a library that is accessible by the general public and is usually funded from public sources, such as taxes. It is operated by librarians and library paraprofessionals, who are also civil servants.
There are five fundamen ...
in Germany.
In 1537, the castle located higher up the mountain was destroyed by a gunpowder explosion. The duke's palace was built at the site of the lower castle.

Elector Frederick III
Frederick III of Simmern, the Pious, Elector Palatine of the Rhine (14 February 1515 – 16 October 1576) was a ruler from the house of Wittelsbach, branch Palatinate-Simmern- Sponheim. He was a son of John II of Simmern and inherited the Pa ...
, sovereign of the Electoral Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine of ...
from 1559 to 1576, commissioned the composition of a new Catechism
A catechism (; from grc, κατηχέω, "to teach orally") is a summary or exposition of doctrine and serves as a learning introduction to the Sacraments traditionally used in catechesis, or Christian religious teaching of children and adul ...
for his territory. While the catechism's introduction credits the "entire theological faculty here" (at the University of Heidelberg
}
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, ...
) and "all the superintendents and prominent servants of the church" for the composition of the Catechism, Zacharius Ursinus is commonly regarded as the catechism's principal author. Caspar Olevianus
Caspar Olevian (or Kaspar Olevianus; 10 August 1536 – 15 March 1587) was a significant German Reformed theologian during the Protestant Reformation and along with Zacharius Ursinus was said to be co-author of the Heidelberg Catechism. That the ...
(1536–1587) was formerly asserted as a co-author of the document, though this theory has been largely discarded by modern scholarship. Johann Sylvan, Adam Neuser
Adam Neuser (c. 153012 October 1576) was a Protestant pastor of Heidelberg who held Antitrinitarian views.
Neuser was born in Gunzenhausen and was a popular pastor and theologian in Heidelberg in the 1560s, serving at the ''Peterskirche'' and ...
, Johannes Willing, Thomas Erastus
Thomas Erastus (original surname Lüber, Lieber, or Liebler; 7 September 152431 December 1583) was a Swiss physician and Calvinist theologian. He wrote 100 theses (later reduced to 75) in which he argued that the sins committed by Christians sh ...
, Michael Diller, Johannes Brunner, Tilemann Mumius, Petrus Macheropoeus, Johannes Eisenmenger, Immanuel Tremellius
Immanuel Tremellius ( it, Giovanni Emmanuele Tremellio; 1510 – 9 October 1580) was an Italian Jewish convert to Christianity. He was known as a leading Hebraist and Bible translator.
Life
He was born at Ferrara and educated at the University o ...
and Pierre Boquin
Pierre Boquin (also known as Bouquin, Boucquin, or Petrus Boquinus; post 1518 –1582 in Lausanne) was a French Reformed Theologian who played a critical role in the Reformation of the Electoral Palatinate.
Origins and early career
Pier ...
are all likely to have contributed to the Catechism in some way. Frederick himself wrote the preface to the Catechism and closely oversaw its composition and publication. Frederick, who was officially Lutheran but had strong Reformed leanings, wanted to even out the religious situation of his highly Lutheran territory within the primarily Catholic Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. The Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
had just concluded with its conclusions and decrees against the Protestant faiths, and the Peace of Augsburg had only granted toleration for Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
within the empire where the ruler was Lutheran. One of the aims of the catechism was to counteract the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
as well as Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
and "strict" Gnesio-Lutherans
Gnesio-Lutherans (from Greek γνήσιος nesios genuine, authentic) is a modern name for a theological party in the Lutheran churches, in opposition to the Philippists after the death of Martin Luther and before the Formula of Concord. In t ...
like Tilemann Heshusius
Tilemann Heshusius (also ''Hesshus, Heßhusen, Hess Husen, Heshusen'') (3 November 1527 in Wesel — 25 September 1588 in Helmstedt) was a Gnesio-Lutheran theologian and Protestant reformer.
Life
Heshusius came from an influential family in W ...
and Matthias Flacius
Matthias Flacius Illyricus (Latin; hr, Matija Vlačić Ilirik) or Francovich ( hr, Franković) (3 March 1520 – 11 March 1575) was a Lutheran reformer from Istria, present-day Croatia. He was notable as a theologian, sometimes dissenting strong ...
, who were resisting Frederick's Reformed influences, particularly on the matter of Eucharist (the Lord's Supper
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
). The Catechism-based each of its statements on biblical proof-texts, and Frederick himself would defend it as biblical, not reformed, at the 1566 Diet of Augsburg
The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sessi ...
when he was called to answer to charges of violating the Peace of Augsburg. This was the Heidelberg Catechism
The Heidelberg Catechism (1563), one of the Three Forms of Unity, is a Protestant confessional document taking the form of a series of questions and answers, for use in teaching Calvinist Christian doctrine. It was published in 1563 in Heidelberg ...
, officially called the ″Catechism, or Christian Instruction, according to the Usages of the Churches and Schools of the Electoral Palatinate.″

 In November 1619, the Royal
In November 1619, the Royal Crown of Bohemia
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of Bo ...
was offered to the Elector, Frederick V Frederick V or Friedrich V may refer to:
* Frederick V, Duke of Swabia (1164–1170)
*Frederick V, Count of Zollern (d.1289)
*Frederick V, Burgrave of Nuremberg (c. 1333–1398), German noble
*Frederick V of Austria (1415–1493), or Frederick III ...
. (He was married to Princess Elizabeth, eldest daughter of James VI and I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
of Scotland and England, respectively.) Frederick became known as the "Winter King", as he reigned for only one winter before the Imperial House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
regained Bohemia by force. His overthrow in 1621 marked the beginning of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
. In 1622, after a siege of two months, the armies of the Catholic League, commanded by Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly
Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly ( nl, Johan t'Serclaes Graaf van Tilly; german: Johann t'Serclaes Graf von Tilly; french: Jean t'Serclaes de Tilly ; February 1559 – 30 April 1632) was a field marshal who commanded the Catholic League's ...
, captured the town. Tilly gave the famous ''Bibliotheca Palatina
The Bibliotheca Palatina (" Palatinate library") of Heidelberg was the most important library of the German Renaissance, numbering approximately 5,000 printed books and 3,524 manuscripts. The Bibliotheca was a prominent prize captured during t ...
'' from the Church of the Holy Spirit to the Pope as a present. The Catholic and Bavarian House of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
gained control over the Palatinate and the title of Prince-Elector.

 In late 1634, after the Swedish army had conquered Heidelberg, imperial forces attempted to recapture the city. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by
In late 1634, after the Swedish army had conquered Heidelberg, imperial forces attempted to recapture the city. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by Urbain de Maillé-Brézé
Urbain de Maillé-Brézé () (1597 – 13 February 1650), was a 17th-century French soldier and diplomat, who was a Marshal of France, Ambassador to Sweden in 1632, and Viceroy of Catalonia 1641 to 1642.
His marriage to the younger sister ...
, who had fought in many battles and participated in the Siege of La Rochelle
The siege of La Rochelle (, or sometimes ) was a result of a war between the French royal forces of Louis XIII of France and the Huguenots of La Rochelle in 1627–28. The siege marked the height of the struggle between the Catholics and the Pr ...
(1627–1628), and Jacques-Nompar de Caumont, duc de La Force
Jacques-Nompar de Caumont, duc de La Force () (30 December 1558 – 10 May 1652) was a Marshal of France and Peer of France. He was the son of a Huguenot, Francois de Caumont, lord of Castelnau, and Philippe de Beaupoil. He survived the St. Barth ...
. They broke the siege and drove off the Imperial forces.
In 1648, at the end of the war, Frederick V's son Charles I Louis, Elector Palatine
Charles Louis, Elector Palatine (german: Karl I. Ludwig; 22 December 1617 – 28 August 1680), was the second son of Frederick V of the Palatinate, the "Winter King" of Bohemia, and of Elizabeth Stuart, Queen of Bohemia and sister of Charl ...
, was able to recover his titles and lands. To strengthen his dynasty, Charles I Louis arranged the marriage of his daughter Liselotte to Philip I, Duke of Orléans, brother of Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
, King of France. In 1685, after the death of Charles Louis' son, Elector Charles II, King Louis XIV laid claim to his sister-in-law's inheritance. The Germans rejected the claim, in part because of religious differences between local Protestants and the French Catholics, as the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
had divided the peoples of Europe. The War of the Grand Alliance
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
ensued. In 1689, French troops took the town and castle, bringing nearly total destruction to the area in 1693. As a result of the destruction due to repeated French invasions related to the War of the Palatinate Succession
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg mona ...
coupled with severe winters, thousands of German Calvinist Palatines emigrated in the early 18th century. They fled to other European cities and especially to London (where the refugees were called "the poor Palatines"). In sympathy for the Protestants, in 1709–1710, Queen Anne's government arranged transport for nearly 6,000 Palatines to New York. Others were transported to Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and to South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. They worked their passage and later settled in the English colonies there.
In 1720, after assigning a major church for exclusively Catholic use, religious conflicts with the mostly Protestant inhabitants of Heidelberg caused the Roman Catholic Prince-Elector Charles III Philip to transfer his court to nearby Mannheim. The court remained there until the Elector Charles Theodore became Elector of Bavaria
The following is a list of rulers during the history of Bavaria. Bavaria was ruled by several dukes and kings, partitioned and reunited, under several dynasties. Since 1949, Bavaria has been a democratic state in the Federal Republic of Germ ...
in 1777 and established his court in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
. In 1742, Elector Charles Theodore began rebuilding the Palace. In 1764, a lightning bolt destroyed other palace buildings during reconstruction, causing the work to be discontinued.
1803 to 1933
Heidelberg fell to theGrand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subs ...
in 1803. Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Baden
Charles Frederick (22 November 1728 – 10 June 1811) was Margrave, Elector and later Grand Duke of Baden (initially only Margrave of Baden-Durlach) from 1738 until his death.
Biography
Born at Karlsruhe, he was the son of Hereditary Prince Fred ...
, re-founded the university, named "Ruperto-Carola" after its two founders. Notable scholars soon earned it a reputation as a "royal residence of the intellect". In the 18th century, the town was rebuilt in the Baroque style on the old medieval layout.
In 1810 the French revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
refugee Count Charles Graimberg began to preserve the palace ruins
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
and establish a historical collection. In 1815, the Emperor of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, the Emperor of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and the King of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
formed the "Holy Alliance
The Holy Alliance (german: Heilige Allianz; russian: Священный союз, ''Svyashchennyy soyuz''; also called the Grand Alliance) was a coalition linking the monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia. It was created after ...
" in Heidelberg. In 1848, the German National Assembly was held there. In 1849, during the Palatinate-Baden rebellion of the 1848 Revolutions
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in Europe ...
, Heidelberg was the headquarters of a revolutionary army. It was defeated by a Prussian army near Waghaeusel. The city was occupied by Prussian troops until 1850. Between 1920 and 1933, Heidelberg University became a center of notable physicians Czerny, Erb, and Krehl; and humanists Rohde, Weber, and Gandolf.
Nazism and the World War II-period
During the Nazi period (1933–1945), Heidelberg was a stronghold of theNSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
/Nazi party, (the National Socialist German Workers' Party) the strongest party in the elections before 1933 (the NSDAP obtained 30% at the communal elections of 1930). The NSDAP received 45.9% of the votes in the German federal election of March 1933 (the national average was 43.9%).
In 1934 and 1935 the ''Reichsarbeitsdienst'' (State Labor Service) and Heidelberg University students built the huge ''Thingstätte'' amphitheatre on the ''Heiligenberg'' north of the town, for Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
and SS events. A few months later, the inauguration of the huge Ehrenfriedhof memorial cemetery completed the second and last NSDAP project in Heidelberg. This cemetery is on the southern side of the old part of town, a little south of the Königstuhl hilltop, and faces west towards France. During World War II and after, Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
soldiers were buried there.
Kristallnacht
() or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (german: Novemberpogrome, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) paramilitary and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation fro ...
'' on November 9, 1938, Nazis burned down synagogues at two locations in the city. The next day, they started the systematic deportation of Jews, sending 150 to Dachau concentration camp
,
, commandant = List of commandants
, known for =
, location = Upper Bavaria, Southern Germany
, built by = Germany
, operated by = ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS)
, original use = Political prison
, construction ...
. On October 22, 1940, during the "Wagner Buerckel event", the Nazis deported 6000 local Jews, including 281 from Heidelberg, to Camp Gurs
Gurs internment camp was an internment camp and prisoner of war camp constructed in 1939 in Gurs, a site in southwestern France, not far from Pau. The camp was originally set up by the French government after the fall of Catalonia at the ...
concentration camp in France. Within a few months, as many as 1000 of them (201 from Heidelberg) died of hunger and disease. Among the deportees from Heidelberg, the poet Alfred Mombert
Alfred Mombert (6 February 1872, in Karlsruhe – 8 April 1942, in Winterthur) was a German poet.
Biography
Mombert was the son of the Jewish-German merchant Eduard Mombert and his wife Helene Gombertz. The economist Paul Mombert was ...
(1872–1942) left the concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simpl ...
in April 1941 thanks to the Swiss poet Hans Reinhart but died shortly thereafter due to illness he contracted while held prisoner. From 1942, the deportees who had survived internment in Gurs were deported to Eastern Europe, where most of them were murdered.
On March 29, 1945, German troops left the city after destroying three arches of the old bridge, Heidelberg's treasured river crossing. They also destroyed the more modern bridge downstream. The U.S. Army ( 63rd Infantry, 7th Army) entered the town on March 30, 1945. The civilian population surrendered without resistance.
Heidelberg, unlike most German cities and towns, was spared from Allied bombing raids during the war. A popular belief is that Heidelberg escaped bombing because the U.S. Army wanted to use the city as a garrison after the war, but, as Heidelberg was neither an industrial center nor a transport hub, it did not present a tactical or strategic target. Other notable university towns, such as Tübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in three ...
and Göttingen
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the capital of the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911.
General information
The ori ...
, were spared bombing as well. Allied air raids focused extensively on the nearby industrial cities of Mannheim and Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it ...
.
The U.S. Army may have chosen Heidelberg as a garrison base because of its excellent infrastructure, including the Heidelberg–Mannheim Autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track' ...
(motorway), which connected to the Mannheim–Darmstadt–Frankfurt Autobahn, and the U.S. Army installations in Mannheim and Frankfurt. The intact rail infrastructure was more important in the late 1940s and early 1950s when most heavy loads were still carried by train, not by truck. Heidelberg had the untouched Wehrmacht barracks, the "Grossdeutschland Kaserne" which the US Army occupied soon after, renaming it the Campbell Barracks
Campbell Barracks, in Heidelberg, Germany, was home to Headquarters, United States Army Europe (USAREUR) from 1948 to 2013. It was also home to Headquarters, V Corps and Headquarters, Allied Force Command Heidelberg.
History
As part of the Ger ...
.
History after 1945
In 1945, the university was reopened relatively quickly on the initiative of a small group of professors, among whom were the anti-Nazi economistAlfred Weber
Alfred Weber (; 30 July 1868 – 2 May 1958) was a German economist, geographer, sociologist and theoretician of culture whose work was influential in the development of modern economic geography.
Life
Alfred Weber, younger brother of the ...
and the philosopher Karl Jaspers
Karl Theodor Jaspers (, ; 23 February 1883 – 26 February 1969) was a German-Swiss psychiatrist and philosopher who had a strong influence on modern theology, psychiatry, and philosophy. After being trained in and practicing psychiatry, Jaspe ...
. The surgeon Karl Heinrich Bauer was nominated rector.
On 9 December 1945, US Army General George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
was involved in a car accident in the adjacent city of Mannheim and died in the Heidelberg US Army hospital on December 21, 1945. His funeral ceremony was held at the Heidelberg-Weststadt ''Christuskirche'' (Christ Church), and he was buried in the 3rd Army cemetery in Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
.
During the post-war military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
, the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
used the ''Thingstätte
A ''Thingspiel'' (plural ''Thingspiele'') was a kind of multi-disciplinary outdoor theatre performance which enjoyed brief popularity in pre-war Nazi Germany during the 1930s. A Thingplatz or Thingstätte was a specially-constructed outdoor am ...
'' for cultural and religious events. Civilian use started in the early to mid-1980s for occasional concerts and other cultural events. Today, the celebrations on ''Hexennacht'' ("Witches' Night"), also called Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
), the night of April 30, are a regular "underground" fixture at the ''Thingstätte''. Thousands of mostly young people congregate there to drum, to breathe fire, and to juggle. The event has gained fame throughout the region, as well as a certain notoriety due to the amount of litter left behind. Officially, this event is forbidden due to security concerns. The City declares it will fence the Thingstätte and prosecute any trespassers.
In 2022, a mass shooting occurred in the university, killing a woman and injuring three other people. The gunman then committed suicide.
Population
fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were ...
of 1.1 children per woman in the ''Stadtkreis'' (county), Heidelberg had the lowest fertility rate in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
in 2008.
Politics
Since 2006, the ''Oberbürgermeister'' (lord mayor) of Heidelberg has been the independent Eckart Würzner. From 1990 to 2006, the mayor was Beate Weber ( SPD). The council consists of 48 volunteer members with the mayor as chairman. The council is directly elected for a term of five years. The task of the council is to decide all the affairs of the city, with the mayor presiding. The council controls the city administration and oversees the enforcement of its decisions. Heidelberg has always been a stronghold of the Greens. For the municipal elections in 2009, they split into the Green Alternative List and Alliance 90/The Greens and each ran their own lists. Together they gained 10 seats to become the strongest force for the first time. In September 2011, two members of the GAL Group joined the Alliance 90/The Greens, so that together with the members of , they formed the largest group in the council. For elections to theBundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Comm ...
, part of the Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German: ') is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students ...
constituency
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other poli ...
.
Cityscape
The old town


 The "old town" (german: link=no, Altstadt), on the south bank of the Neckar, is long and narrow. It is dominated by the ruins of Heidelberg Castle, 80 metres above the Neckar on the steep wooded slopes of the Königstuhl (''King's chair or throne'') hill.
*The Main Street (''Hauptstrasse''), a mile-long pedestrian street, running the length of the old town.
*The old stone bridge was erected 1786–1788. A medieval bridge gate is on the side of the old town, and was originally part of the town wall. Baroque tower helmets were added as part of the erection of the stone bridge in 1788.
*The Church of the Holy Spirit (''Heiliggeistkirche''), a late Gothic church in the marketplace of the old town.
*The Karls‘ gate (''Karlstor'') is a triumphal arch in honour of the Prince Elector Karl Theodor, located at Heidelberg's east side. It was built 1775–1781 and designed by Nicolas de Pigage.
*The house ''Zum Ritter Sankt Georg'' (Knight St. George) is one of the few buildings to survive the War of Succession. Standing across from the Church of the Holy Spirit, it was built in the style of the late
The "old town" (german: link=no, Altstadt), on the south bank of the Neckar, is long and narrow. It is dominated by the ruins of Heidelberg Castle, 80 metres above the Neckar on the steep wooded slopes of the Königstuhl (''King's chair or throne'') hill.
*The Main Street (''Hauptstrasse''), a mile-long pedestrian street, running the length of the old town.
*The old stone bridge was erected 1786–1788. A medieval bridge gate is on the side of the old town, and was originally part of the town wall. Baroque tower helmets were added as part of the erection of the stone bridge in 1788.
*The Church of the Holy Spirit (''Heiliggeistkirche''), a late Gothic church in the marketplace of the old town.
*The Karls‘ gate (''Karlstor'') is a triumphal arch in honour of the Prince Elector Karl Theodor, located at Heidelberg's east side. It was built 1775–1781 and designed by Nicolas de Pigage.
*The house ''Zum Ritter Sankt Georg'' (Knight St. George) is one of the few buildings to survive the War of Succession. Standing across from the Church of the Holy Spirit, it was built in the style of the late Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
. It is named after the sculpture at the top.
*The ''Marstall'' (Stables), a 16th-century building on the Neckar that has served several purposes through its history. It is now a cafeteria for the university.
Heidelberg Castle


 The castle is a mix of styles from
The castle is a mix of styles from Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
to Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
. Prince Elector Ruprecht III (1398–1410) erected the first building in the inner courtyard as a royal residence. The building was divided into a ground floor made of stone and framework upper levels. Another royal building is located opposite the Ruprecht Building: the Fountain Hall. Prince Elector Philipp (1476–1508) is said to have arranged the transfer of the hall's columns from a decayed palace of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
from Ingelheim
Ingelheim (), officially Ingelheim am Rhein ( en, Ingelheim upon Rhine), is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's west bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat ...
to Heidelberg.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Prince Electors added two palace buildings and turned the fortress into a castle. The two dominant buildings at the eastern and northern side of the courtyard were erected during the rule of Ottheinrich (1556–1559) and Friedrich IV (1583–1610). Under Friedrich V (1613–1619), the main building of the west side was erected, the so-called "English Building".
The castle and its garden were destroyed several times during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
and the Palatine War of Succession. As Prince Elector Karl Theodor tried to restore the castle, lightning struck in 1764, and ended all attempts at rebuilding. Later on, the castle was misused as a quarry; stones from the castle were taken to build new houses in Heidelberg. This was stopped in 1800 by Count Charles de Graimberg, who then began the process of preserving the castle.
Although the interior is in Gothic style, the King's Hall was not built until 1934. Today, the hall is used for festivities, e.g. dinner banquets, balls and theatre performances. During the Heidelberg Castle Festival in the summer, the courtyard is the site of open air musicals, operas, theatre performances, and classical concerts performed by the Heidelberg Philharmonics.
The castle is surrounded by a park, where the famous poet Johann von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as treat ...
once walked. The Heidelberger Bergbahn
The Heidelberg Mountain Railway (german: Heidelberger Bergbahn) is a two-section funicular railway in the city of Heidelberg, Germany. The first section runs from a lower station at Kornmarkt in Heidelberg's Altstadt, via an intermediate stati ...
funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite ...
railway runs from Kornmakt to the summit of the Königstuhl via the castle.
The castle looks over the entire city of Heidelberg and the Neckar Valley.
Philosophers' Walk
On the northern side of the Neckar is located the Heiligenberg (''Saints' Mountain''), along the side of which runs the Philosophers' Walk (german: link=no, Philosophenweg), with scenic views of the old town and castle. Traditionally, Heidelberg's philosophers and university professors would walk and talk along the pathway. Farther up the mountain lie the ruined 11th-century Monastery of St. Michael, the smaller Monastery of St. Stephen, a Nazi-era amphitheater, the so-called Pagan's hole and the remains of an earthenCeltic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
from the 4th century BC.
Heidelberg churches
There are many historical churches in Heidelberg and its surroundings. The Church of the Holy Spirit has been shared over the centuries since theProtestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
by both Catholics and Protestants. It is one of the few buildings to survive the many wars during the past centuries. It was rebuilt after the French set fire to it in 1709 during the War of the Palatinian Succession. The church has remains of the tombs and epitaphs of the past Palatinate electors. This Church stands in the ''Marktplatz'' next to the seat of local government. In 1720, Karl III Philip, Elector Palatine came into conflict with the town's Protestants as a result of giving the Church of the Holy Spirit exclusively to the Catholics for their use. It had previously been split by a partition and used by both congregations. Due to pressure by the mostly Protestant powers of Prussia, Holland, and Sweden, Prince Karl III Philip gave way and repartitioned the church for joint use. In 1936 the separating wall was removed. The church is now exclusively used by Protestants. Furthermore, there is the Catholic Church of the Jesuits. Its construction began in 1712. It was completed with the addition of a bell tower from 1866 to 1872. The church is also home to the Museum für sakrale Kunst und Liturgie (Museum of Ecclesiastical
{{Short pages monitor), such as


 * Ernst Albrecht (1930–2014), politician (CDU), Minister-president of Lower Saxony, father of
* Ernst Albrecht (1930–2014), politician (CDU), Minister-president of Lower Saxony, father of
Official site of Heidelberg
a small English section is available
Audio Tour in the Castle of Heidelberg
U.S. Army Garrison Heidelberg homepage
Heidelberg American High School
The official site of Heidelberg American High School {{Authority control Cities in Baden-Württemberg Karlsruhe (region) Baden Odenwald Holocaust locations in Germany Populated places on the Neckar basin Populated riverside places in Germany
Joseph von Eichendorff
Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff (10 March 178826 November 1857) was a German poet, novelist, playwright, literary critic, translator, and anthologist. Eichendorff was one of the major writers and critics of Romanticism.Cf. J. A. Cuddon: ' ...
, Johann Joseph von Görres
Johann, typically a male given name, is the German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin form of the Greek name ''Iōánnēs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew name ''Yochanan'' () in turn from its extended form (), meaning " Yahweh is Graciou ...
, Ludwig Achim von Arnim
Carl Joachim Friedrich Ludwig von Arnim (26 January 1781 – 21 January 1831), better known as Achim von Arnim, was a German poet, novelist, and together with Clemens Brentano and Joseph von Eichendorff, a leading figure of German Romanticism.
...
, and Clemens Brentano
Clemens Wenzeslaus Brentano (also Klemens; pseudonym: Clemens Maria Brentano ; ; 9 September 1778 – 28 July 1842) was a German poet and novelist, and a major figure of German Romanticism. He was the uncle, via his brother Christian, of Franz ...
. A relic of Romanticism is the Philosophers' Walk (german: link=no, Philosophenweg), a scenic walking path on the nearby Heiligenberg, overlooking Heidelberg.
The ''Romantik'' epoch of German philosophy and literature, was described as a movement against classical and realistic theories of literature, a contrast to the rationality of the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
. It elevated medievalism and elements of art and narrative perceived to be from the medieval period. It also emphasized folk art, nature and an epistemology based on nature, which included human activity conditioned by nature in the form of language, custom and usage.
Old Heidelberg
In 1901 Wilhelm Meyer-Förster wrote the play '' Old Heidelberg'' which was followed by a large number of film adaptations. It was the basis forSigmund Romberg
Sigmund Romberg (July 29, 1887 – November 9, 1951) was a Hungarian-born American composer. He is best known for his musicals and operettas, particularly '' The Student Prince'' (1924), '' The Desert Song'' (1926) and '' The New Moon'' (1928).
E ...
's 1924 operetta ''The Student Prince
''The Student Prince'' is an operetta in four acts with music by Sigmund Romberg and book and lyrics by Dorothy Donnelly. It is based on Wilhelm Meyer-Förster's play '' Old Heidelberg''. The piece has a score with some of Romberg's most enduri ...
'' which was itself turned into a film of the same title.
I Lost My Heart in Heidelberg
The 1925 song "I Lost My Heart in Heidelberg" composed by Fred Raymond was a major hit and inspired a stage musical and two films. It remains the theme song of Heidelberg.Sport
Heidelberg is one of the centres ofRugby union in Germany
Rugby union in Germany is a minor but growing sport with 124 men's clubs and 5 women's clubs competing in 4 men's and 1 women's national leagues.
Governing body
The German Rugby Federation (german: Deutscher Rugby-Verband or DRV), founded in 19 ...
, along with Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
. In 2008–09, four out of nine clubs in the Rugby-Bundesliga were from Heidelberg, these being RG Heidelberg
The RG Heidelberg (''german: Rudergesellschaft Heidelberg'', literally "Heidelberg Rowing Club") is a German rugby union club from Heidelberg, currently playing in the Rugby-Bundesliga. Apart from rugby, the club also offers the sport of rowing. ...
, who play at the Fritz-Grunebaum-Sportpark
The Fritz-Grunebaum-Sportpark is a rugby union stadium in Heidelberg, Germany. It is the home ground of the RG Heidelberg and also frequently used for international games of the Germany national rugby union team.
In its 2008-2010 European Na ...
, SC Neuenheim
The SC Neuenheim is a German rugby union club from Heidelberg, currently playing in the Rugby-Bundesliga. Having won nine men's and twelve women's German championships as of 2013, the club is one of the most accomplished in Germany.
History
Fo ...
, Heidelberger RK
The Heidelberger Ruderklub (Heidelberger RK or HRK for short) is a German rowing club and rugby union club from Heidelberg, currently playing in the Rugby-Bundesliga.
The club is one of only two professional rugby clubs in Germany, the other be ...
and TSV Handschuhsheim
The TSV Handschuhsheim is a German rugby union club from Heidelberg, currently playing in the Rugby-Bundesliga. Apart from rugby, the club also offers other sports like association football, handball and tennis.
History
The club was formed in 1 ...
. Heidelberger TV
The Heidelberger TV is a German rugby union club from Heidelberg, currently playing in the Rugby-Bundesliga. Apart from rugby, the club also offers other sports like basketball, tennis and badminton.
The club has three German rugby union champ ...
has a rugby department.
Rugby League Deutschland
Rugby League Deutschland was the governing body for the sport of rugby league football in Germany. The Association was formed in 2007. It folded in March 2015, and was replaced by the Nationaler Rugby League Deutschland e.V. (NRLD).https://www. ...
has two teams based in Heidelberg, Heidelberg Sharks formed in 2005 and Rohrbach Hornets formed in 2007.
The city is also home to the USC Heidelberg
USC Heidelberg, for sponsorship reasons named MLP Academics Heidelberg, is a professional basketball club from Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The club's men's senior team currently plays in the German first division Basketball Bundeslig ...
, which won 9 German Basketball Championship
The Basketball Bundesliga (BBL) ( English language: ''Federal Basketball League''), for sponsorship reasons named easyCredit BBL, is the highest level league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 18 teams. A BBL seas ...
s and remains the second most successful team in the history of German professional basketball. Today, the club plays in Germany's second division ProA
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the ...
. It is primarily known for its youth department which developed several members of Germany's senior national basketball team
The Germany men's national basketball team (german: Deutsche Basketballnationalmannschaft or ''Die Mannschaft'') represents Germany in international basketball competition. The team is directed by the German Basketball Federation (''Deutscher ...
.
SG Heidelberg-Kirchheim
SG Heidelberg-Kirchheim is a German association football club from the Kirchheim district of the city of Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg. The club's greatest success has been promotion to the Oberliga Baden-Württemberg on three occasions, in ...
is the local football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
team.
The city hosted 1972 Summer Paralympics
The 1972 Summer Paralympics (german: Paralympische Sommerspiele 1972), the fourth edition of the Paralympic Games, were held in Heidelberg, West Germany, from 2 to 11 August 1972. The games ended 15 days before the 1972 Summer Olympics held in Mu ...
.
They also hosted the 2019 WU24 Championships from July 13 to July 20. It was the fifth edition of this world championship and marked the third time Germany has hosted an ultimate frisbee
Ultimate, originally known as ultimate Frisbee, is a non-contact team sport played with a frisbee Flying disc sports, flung by hand. Ultimate was developed in 1968 by AJ Gator in Maplewood, New Jersey. Although ultimate resembles many traditiona ...
tournament.
Further, Germany's oldest tennis club, which was founded in the year 1890, is located in Heidelberg.
Twin towns – sister cities
Heidelberg is twinned with: *Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
, France (1961)
* Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, United Kingdom (1965)
* Rehovot
Rehovot ( he, רְחוֹבוֹת ''Rəḥōvōt'', ar, رحوڤوت ''Reḥūfūt'') is a city in the Central District of Israel, about south of Tel Aviv. In it had a population of .
Etymology
Israel Belkind, founder of the Bilu movement, ...
, Israel (1983)
* Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budi ...
, Germany (1991)
* Simferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
, Ukraine (1991)
* Kumamoto
is the capital city of Kumamoto Prefecture on the island of Kyushu, Japan. , the city has an estimated population of 738,907 and a population density of 1,893 people per km2. The total area is 390.32 km2.
had a population of 1,461,000, ...
, Japan (1992)
* Palo Alto
Palo Alto (; Spanish for "tall stick") is a charter city in the northwestern corner of Santa Clara County, California, United States, in the San Francisco Bay Area, named after a coastal redwood tree known as El Palo Alto.
The city was es ...
, United States (2017)
* Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also Chinese postal romanization, romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the prov ...
, China (2017)
Friendly cities
Heidelberg also has friendly relations with: * Calamba, Philippines *Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German: ') is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students ...
, South Africa
* Jelenia Góra
Jelenia Góra (pron. ; Polish: ; german: Hirschberg im Riesengebirge; Exonym: ''Deer Mountain''; szl, Jelyniŏ Gōra) is a historic city in southwestern Poland, within the historical region of Lower Silesia. Jelenia Góra is situated in the Low ...
, Poland
* Mostar
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = Mostar (collage image).jpg
, image_caption = From top, left to right: A panoramic view of the heritage town site and the Neretva river from Lučki Bridge, Koski Mehmed Pasha ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
In popular culture
Popular movies, TV and games
* Heidelberg features in the 1968 film '' The Girl on a Motorcycle'', the university being the ultimate destination ofMarianne Faithfull
Marianne Evelyn Gabriel Faithfull (born 29 December 1946) is an English singer and actress. She achieved popularity in the 1960s with the release of her hit single " As Tears Go By" and became one of the lead female artists during the British I ...
's character.
* Heidelberg also features during a mission in the Electronic Arts
Electronic Arts Inc. (EA) is an American video game company headquartered in Redwood City, California. Founded in May 1982 by Apple employee Trip Hawkins, the company was a pioneer of the early home computer game industry and promoted the ...
strategy game ''Red Alert 3
''Command & Conquer: Red Alert 3'' is a real-time strategy video game developed by EA Los Angeles and published by Electronic Arts. It was released in October 2008 in the United States and Europe for Microsoft Windows. An Xbox 360 version was r ...
''.
* '' Morris from America'' takes places in Heidelberg.
* In the ''Watchmen
''Watchmen'' is an American comic book maxiseries by the British creative team of writer Alan Moore, artist Dave Gibbons and colorist John Higgins. It was published monthly by DC Comics in 1986 and 1987 before being collected in a single-vo ...
'' TV series which serves as alternate direct sequels to the original ''Watchmen'' graphic novel, Dr. Manhattan aka Jonathan "Jon" Osterman aka Calvin "Cal" Abar (né Jelani), is said to be born in Heidelberg, Germany and immigrates to the US along with his father.
* Heidelberg is also revealed to be the home town of Sergeant Schultz
The following is a list of characters from '' Hogan's Heroes'', an American sitcom television series which starred Bob Crane, Werner Klemperer and John Banner, and featured Robert Clary, Richard Dawson, Ivan Dixon, and Larry Hovis. It ran fo ...
on ''Hogan's Heroes
''Hogan's Heroes'' is an American television sitcom set in a Nazi German prisoner-of-war (POW) camp during World War II. It ran for 168 episodes (six seasons) from September 17, 1965, to April 4, 1971, on the CBS network, the longest broadcast ...
''.
Popular literature
* Heidelberg Castle forms the setting for the beginning ofMark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has pr ...
's story '' The Awful German Language''.
* Most of David Lodge's novel ''Out of the Shelter
''Out of the Shelter'' (1970) is a novel by British author David Lodge.
Plot
Timothy Young, at five, enjoys having to go to his neighbor's shelter during the Blitz, partly because he gets to sleep with his friend Jill. However, Jill and her m ...
'' takes place in Heidelberg in 1951 during the American occupation after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
* Heidelberg is the home of a professional Quidditch
Quidditch is a fictional sport invented by author J.K. Rowling for her fantasy book series ''Harry Potter''. It first appeared in the novel '' Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'' (1997). It is a dangerous but popular sport played by wi ...
team operating within the fictional Harry Potter universe
The Wizarding World (previously known as J. K. Rowling's Wizarding World) is a fantasy media franchise and shared fictional universe centred on the ''Harry Potter'' novel series by J. K. Rowling. A series of films have been in production sin ...
: the Heidelberg Harriers
Heidelberg (; Palatine German: ') is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of student ...
have been described as “fiercer than a dragon and twice as clever”.
* Heidelberg is the residence of fictional character Nina Fortner/Anna Liebert in the anime
is Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside of Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, in Japan and in Japane ...
/manga
Manga ( Japanese: 漫画 ) are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long prehistory in earlier Japanese art. The term ''manga'' is ...
series ''Monster
A monster is a type of fictional creature found in horror, fantasy, science fiction, folklore, mythology and religion. Monsters are very often depicted as dangerous and aggressive with a strange, grotesque appearance that causes terror and fe ...
'', by Naoki Urasawa
is a Japanese manga artist and musician. He has been drawing manga since he was four years old, and for most of his professional career has created two series simultaneously. The stories to many of these were co-written in collaboration with his ...
.
* Heidelberg also features in Somerset Maugham's ''Of Human Bondage
''Of Human Bondage'' is a 1915 novel by W. Somerset Maugham. The novel is generally agreed to be Maugham's masterpiece and to be strongly autobiographical in nature, although he stated, "This is a novel, not an autobiography; though much in i ...
'' and its film versions.
* Heidelberg also is he setting of some German crime novels, for example by Wolfgang Burger (protagonist: Detective Gerlach) or Carlo Schäfer (protagonist: Detective Theurer).
Notable people


 * Ernst Albrecht (1930–2014), politician (CDU), Minister-president of Lower Saxony, father of
* Ernst Albrecht (1930–2014), politician (CDU), Minister-president of Lower Saxony, father of Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula Gertrud von der Leyen (; Albrecht, born 8 October 1958) is a German politician who has been serving as the president of the European Commission since 2019. She served in the German federal government between 2005 and 2019, holding suc ...
* Jill Asemota
Jill is an English feminine given name, a short form of the name Jillian (Gillian), which in turn originates as a Middle English variant of Juliana, the feminine form of the name Julian.
People with the given name
* Jill Astbury, Australian re ...
, German-Nigerian model
* Bettina Belitz
Bettina Belitz (Heidelberg, September 21, 1973) is a German writer and journalist.
After studying history and literature, she worked for '' Die Rheinpfalz'' and other publications.
She has a son, and lives currently in Westerwald
The Westerw ...
(born 1973), writer and journalist
* Petar Beron (1799–1871), Bulgarian educator
* Arvid Boecker
Arvid Boecker (born 1964) in Wuppertal) is a German painter and curator. He is a representative of concrete art and focuses on color field painting.
Biography
Arvid Boecker studied from 1987 to 1989 at the University of Trier Art history, co ...
(born 1964) painter and curator
* Carl Bosch
Carl Bosch (; 27 August 1874 – 26 April 1940) was a German chemist and engineer and Nobel Laureate in Chemistry. He was a pioneer in the field of high-pressure industrial chemistry and founder of IG Farben, at one point the world's largest ...
(1874–1940) chemist and engineer and Nobel Laureate in Chemistry
* Jackson Browne
Clyde Jackson Browne (born October 9, 1948) is an American musician, singer, songwriter, and political activist who has sold over 18 million albums in the United States.
Emerging as a precocious teenage songwriter in mid-1960s Los Angeles, he h ...
(born 1948), singer-songwriter and musician born here
* Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (;
30 March 1811
– 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bu ...
(1811–1899), German chemist
* Hubert Burda
Hubert Burda (born 9 February 1940) is a German billionaire publisher. He is the owner, publisher and general partner of Hubert Burda Media, a global media company of more than 600 media products, including websites, print magazines and other br ...
(born 1940), journalist and publisher
* Marcel Cartier (born 1984 in Heidelberg), battlefield journalist, communist, expert of Kurdish politics, and hip-hop artist
* Antje Duvekot
Antje Duvekot ( ; born 1974) is a singer-songwriter and guitarist based in Somerville, Massachusetts. She holds three top songwriting awards including the Kerrville New Folk Competition's Best New Folk Award, Boston Music Award for Outstanding ...
(born 1976), singer-songwriter
* Friedrich Ebert
Friedrich Ebert (; 4 February 187128 February 1925) was a German politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) and the first president of Germany from 1919 until his death in office in 1925.
Ebert was elected leader of the SPD on t ...
(1871–1925), President of Germany 1919–1925
* Marc S. Ellenbogen (born 1963), Member of National Advisory Board, U.S. Democratic Party (2004-2010), nominated by President Barack Obama to be U.S. Ambassador
* Michael Fassbender
Michael Fassbender (born 2 April 1977) is an Irish actor. He is the recipient of various accolades, including a Screen Actors Guild Award, a Critics' Choice Movie Award, and nominations for two Academy Awards, four British Academy Film Award ...
(born 1977), German-Irish actor born here
* Frederick V Frederick V or Friedrich V may refer to:
* Frederick V, Duke of Swabia (1164–1170)
*Frederick V, Count of Zollern (d.1289)
*Frederick V, Burgrave of Nuremberg (c. 1333–1398), German noble
*Frederick V of Austria (1415–1493), or Frederick III ...
(1596–1632), Count Palatine and Elector of the Palatinate from 1610 to 1623 and King of Bohemia (as ''Frederick I'') from 1619 to 1620
* Bernhard Fries (1820–1879), painter
* Ernst Fries
Ernst Fries (22 June 1801, Heidelberg – 11 October 1833, Karlsruhe) was a German painter, draftsman, watercolourist, etcher, printmaker, and lithograph. Besides Karl Philipp Fohr and Carl Rottmann, he was the youngest of the so-called triumvir ...
(1801–1833), painter
* Hans-Georg Gadamer
Hans-Georg Gadamer (; ; February 11, 1900 – March 13, 2002) was a German philosopher of the continental tradition, best known for his 1960 '' magnum opus'', '' Truth and Method'' (''Wahrheit und Methode''), on hermeneutics.
Life
Family ...
(1900–2002), philosopher
* Ian Harding
Ian Michael Harding (born September 16, 1986) is an American actor. He is known for his role as Ezra Fitz in the Freeform mystery drama ''Pretty Little Liars'' from 2010 to 2017.
Early life
Harding was born in Heidelberg, West Germany, to an ...
(born 1986), actor
* Harald zur Hausen
Harald zur Hausen NAS EASA APS (; born 11 March 1936) is a German virologist and professor emeritus. He has done research on cervical cancer and discovered the role of papilloma viruses in cervical cancer, for which he received the Nobel ...
(born 1936), virologist, Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make o ...
* Nico Hofmann
Naftiran Intertrade Company Société à responsabilité limitée#In Switzerland, limited (NICO) is a Switzerland, Swiss-based subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). NICO is a general contractor for the oil and gas industry. NIOC bu ...
(born 1959), film director, film producer, screenwriter and businessman
* Dietmar Hopp
Dietmar Hopp (; born 26 April 1940) is a German software engineer and billionaire businessman. He was one of the founders of SAP SE in 1972 with other former IBM employees Hans Werner Hector, Klaus Tschira, Claus Wellenreuther and Hasso Platt ...
(born 1940), software entrepreneur SAP
* Muhammad Iqbal
Sir Muhammad Iqbal ( ur, ; 9 November 187721 April 1938), was a South Asian Muslim writer, philosopher, Quote: "In Persian, ... he published six volumes of mainly long poems between 1915 and 1936, ... more or less complete works on philos ...
(1877–1938), British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
n poet, philosopher
* Ernst Jünger
Ernst Jünger (; 29 March 1895 – 17 February 1998) was a German author, highly decorated soldier, philosopher, and entomologist who became publicly known for his World War I memoir '' Storm of Steel''.
The son of a successful businessman and ...
(1895–1998), German author, officer, botanist and entomologist, famous for his World War I memoir Storm of Steel
* Wolfgang Ketterle
Wolfgang Ketterle (; born 21 October 1957) is a German physicist and professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). His research has focused on experiments that trap and cool atoms to temperatures close to absolute ze ...
(born 1957), physicist, professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of th ...
, Nobel Laureate
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make o ...
* Paul Kirchhof
Paul Kirchhof (born February 21, 1943 in Osnabrück) is a German jurist and tax law expert. He is also a professor of law, member of the Pontifical Academy of Social Sciences and, a former judge in the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany ( ...
(born 1943), former Judge in the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany
The Federal Constitutional Court (german: link=no, Bundesverfassungsgericht ; abbreviated: ) is the supreme constitutional court for the Federal Republic of Germany, established by the constitution or Basic Law () of Germany. Since its in ...
(''Bundesverfassungsgericht'')
* Hansi Flick (born 1965), football player and manager of the Germany national football team
The Germany national football team (german: link=no, Deutsche Fußballnationalmannschaft) represents Germany in men's international football and played its first match in 1908. The team is governed by the German Football Association (''Deuts ...
* Hans Kroh
__NOTOC__
Hans Kroh (13 May 1907 – 18 July 1967) was a German paratroop general in the Wehrmacht and Bundeswehr and a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords of Nazi Germany.
Kroh started his military care ...
(1907–1967), German officer in Wehrmacht and Bundeswehr
* Karl A. Lamers
Karl A. Lamers (born 12 February 1951, in Duisburg) is a German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who served as a member of the German Parliament from 1994 until 2021. From 2010 to 2012 he was the President of the NATO Parliame ...
(born 1951), politician, former President of the NATO Parliamentary Assembly
Founded in 1955, the NATO Parliamentary Assembly (NATO PA) serves as the consultative interparliamentary organisation for the North Atlantic Alliance. Its current President is Gerald E. Connolly from the United States, elected in 2019. Its curre ...
* Ananda Mahidol
Ananda Mahidol ( th, พระบาทสมเด็จพระปรเมนทรมหาอานันทมหิดล; ; 20 September 1925 – 9 June 1946), posthumous reigning title Phra Athamaramathibodin ( th, พระอั� ...
(1925–1946), King of Thailand
* Helene Mayer
Helene Julie Mayer (20 December 1910 – 10 October 1953) was a German-born fencer who won the gold medal at the 1928 Olympics in Amsterdam, and the silver medal at the 1936 Olympics in Berlin. She competed for Nazi Germany in Berlin, despite ...
(1910–1953), German and American Olympic champion fencer
* Malaika Mihambo
Malaika Mihambo (; born 3 February 1994) is a German athlete and the current Olympic and world champion in long jump.
Career
Mihambo's athletic career began around 2009, when at the age of 15 she became the German under-16 champion with the hep ...
(born 1994), Olympic champion in long jump (2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global social and economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, worldwide lockdowns and the largest economic recession since the Great Depression in t ...
) and twice world champion (2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
and 2022
File:2022 collage V1.png, Clockwise, from top left: Road junction at Yamato-Saidaiji Station several hours after the assassination of Shinzo Abe; Anti-government protest in Sri Lanka in front of the Presidential Secretariat; The global monkeypo ...
)
* Heinrich Neal Heinrich Neal (September 11, 1870 – 1940) was a German Kapellmeister at Heidelberg,"History of Lowell and its people, Volume 2" By Frederick William Coburn, p.532 born to the artist David Dalhoff Neal and Marie Ainmiller, and brother to dramati ...
(1870–1940), composer, directed the Heidelberg Conservatory of Music
* Nelson Piquet Jr.
Nelson Angelo Tamsma Piquet Souto Maior (born July 25, 1985), also known as Nelson Piquet Junior or Nelsinho Piquet, is a Brazilian stock car racing driver and former Formula One and Formula E driver where he was champion in the 2014–15 seaso ...
(born 1985), Brazilian race car driver and former Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
driver born here
* Vasil Radoslavov (1854–1929), Bulgarian Prime Minister
* José Rizal
José Protasio Rizal Mercado y Alonso Realonda (, ; June 19, 1861 – December 30, 1896) was a Filipino nationalist, writer and polymath active at the end of the Spanish colonial period of the Philippines. He is considered the national h ...
(1861–1896), national hero of the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
* Khalid Robinson (born 1998), American singer
* Christiane Schmidtmer (1939–2003), Hollywood actress and model
* Bernd Schmitt
Bernd Herbert Schmitt is a professor of international business in the marketing department at Columbia Business School, Columbia University in New York. He is known for his research, books, speaking and consulting on customer experience, customer ...
(born 1957), marketing professor at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
* Klaus Schütz
Klaus Schütz (17 September 1926
– 29 November 2012) was a German politician, who ...
(1926–2012), politician (SPD)
* – 29 November 2012) was a German politician, who ...
Elisabeth Seitz
Elisabeth Seitz (born 4 November 1993) is a German artistic gymnast. She is the 2022 European champion and the 2018 World bronze medalist on the uneven bars. She is one of the only female gymnasts in history to compete the Def (full-twisting G ...
(born 1993), Olympic gymnast
* Silvia Renate Sommerlath
Silvia () is a female given name of Latin origin, with a male equivalent Silvio and English-language cognate Sylvia. The name originates from the Latin word for forest, ''Silva'', and its meaning is "spirit of the wood"; the mythological god of ...
(born 1943), Queen of Sweden
The monarchy of Sweden is the monarchical head of state of Sweden,See the Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 5. which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system.Parliamentary system: see the Instrume ...
* Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as the Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of World War II. A close ally of Adolf Hitler, h ...
(1905–1981), German architect and Third Reich minister
* Ferdinand Thomas (1913–1944), resistance fighter
* Ashley Wagner
Ashley Elisabeth Wagner (born May 16, 1991) is an American former figure skater. She is the 2016 World silver medalist, a 2014 Olympic bronze medalist in the team event, the 2012 Four Continents champion, a three-time Grand Prix Final medali ...
(born 1991), American figure skater
* Karl Philipp von Wrede Karl may refer to:
People
* Karl (given name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Karl der Große, commonly known in English as Charlemagne
* Karl Marx, German philosopher and political writer
* Karl of Austria, last Austri ...
(1767–1838), Bavarian field marshal
* Jon Osterman (1929–2019), fictional character from the book Watchmen
''Watchmen'' is an American comic book maxiseries by the British creative team of writer Alan Moore, artist Dave Gibbons and colorist John Higgins. It was published monthly by DC Comics in 1986 and 1987 before being collected in a single-vo ...
and its HBO sequel series
* Paul Ripke
Paul Ripke (born February 10, 1981) is a German fashion and sports photographer and music video director prolific for his photographs and videos of athletes, celebrities, models, and other cultural figures.
Early life
Ripke was born in Heidelberg ...
(born 1981), photographer
* Nico Bastian (born 1990), racing driver
See also
*Heidelberg Center for American Studies
The University of Heidelberg's Heidelberg Center for American Studies (HCA) is a higher education and research center. It was founded in 2004, making it the newest institute of Germany's oldest university. The Heidelberg Center for American Studies ...
* Heidelberg University
* Schiller International University
Schiller International University (SIU) is a private for-profit university with its main campus and administrative headquarters in Tampa, Florida. It is named after the German playwright and philosopher Friedrich Schiller.
It has campuses on tw ...
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
* *Official site of Heidelberg
a small English section is available
Audio Tour in the Castle of Heidelberg
U.S. Army Garrison Heidelberg homepage
Heidelberg American High School
The official site of Heidelberg American High School {{Authority control Cities in Baden-Württemberg Karlsruhe (region) Baden Odenwald Holocaust locations in Germany Populated places on the Neckar basin Populated riverside places in Germany