Hassan I of Morocco on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mawlay'' Hassan bin Mohammed ( ar, الحسن بن محمد, translit=al-Ḥassan bin Muḥammad), known as Hassan I ( ar, الحسن الأول, translit=al-Ḥassan al-Awwal), born in 1836 in Fes and died on 9 June 1894 in Tadla, was a sultan of
 Son of the sultan Muhammad IV, Mawlay (Moulay) Hassan was proclaimed sultan of Morocco on the death of his father in 1873. His first action was to crush an urban revolt in the capital Fes in 1874, which he had to besiege for a few months. The tanners rose up in protest "raging like lions and tigers" through the streets of Fes, pillaging the house of Muhammad Bennis, the Minister of Finance, turning Fes into a battleground. Mawlay Hassan I, who was on campaign sent letters calling for the pacification of the city. Shortly after, the hated tax collectors were withdrawn, and the rebellion halted. The tax collectors soon reappeared, leading to the rebellion commencing again more violently. The local Fes militiamen took up positions in minarets of Fes al-Bali and fired down on the army, but the two sides later negotiated peace and the rebellion was definitely terminated. Of strong Arab culture, he did not know any foreign language, although Mawlay Hassan I was a conservative ruler, he realised the need for modernization and the reform policy of his father.
He strived to maintain the cohesion of his kingdom through political, military, and religious action, in the face of European threats on its periphery, and internal rebellions, He initiated reforms. He strived to ensure the loyalty of the great chiefs of the south. He did not hesitate to appoint local Caids like Sheikh Ma al-'Aynayn who gave him the Bay'a, the pledge of allegiance in Islamic Sharia law. He tried to modernize his army, and lead several expeditions to assert his authority, such as to the Sus in 1882 and 1886, to the
Son of the sultan Muhammad IV, Mawlay (Moulay) Hassan was proclaimed sultan of Morocco on the death of his father in 1873. His first action was to crush an urban revolt in the capital Fes in 1874, which he had to besiege for a few months. The tanners rose up in protest "raging like lions and tigers" through the streets of Fes, pillaging the house of Muhammad Bennis, the Minister of Finance, turning Fes into a battleground. Mawlay Hassan I, who was on campaign sent letters calling for the pacification of the city. Shortly after, the hated tax collectors were withdrawn, and the rebellion halted. The tax collectors soon reappeared, leading to the rebellion commencing again more violently. The local Fes militiamen took up positions in minarets of Fes al-Bali and fired down on the army, but the two sides later negotiated peace and the rebellion was definitely terminated. Of strong Arab culture, he did not know any foreign language, although Mawlay Hassan I was a conservative ruler, he realised the need for modernization and the reform policy of his father.
He strived to maintain the cohesion of his kingdom through political, military, and religious action, in the face of European threats on its periphery, and internal rebellions, He initiated reforms. He strived to ensure the loyalty of the great chiefs of the south. He did not hesitate to appoint local Caids like Sheikh Ma al-'Aynayn who gave him the Bay'a, the pledge of allegiance in Islamic Sharia law. He tried to modernize his army, and lead several expeditions to assert his authority, such as to the Sus in 1882 and 1886, to the
 Hassan I appointed Mouha Zayani as Caid of the Zayanes in Khenifra in 1877. Mouha Zayani was to be an important figure in the 20th century colonial war against
Hassan I appointed Mouha Zayani as Caid of the Zayanes in Khenifra in 1877. Mouha Zayani was to be an important figure in the 20th century colonial war against
History of Morocco
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hassan 01 Of Morocco 'Alawi dynasty Sultans of Morocco 1836 births 1894 deaths Moroccan people of Arab descent 19th-century Arabs People from Fez, Morocco People from Marrakesh 19th-century Moroccan people 19th-century monarchs in Africa
Morocco
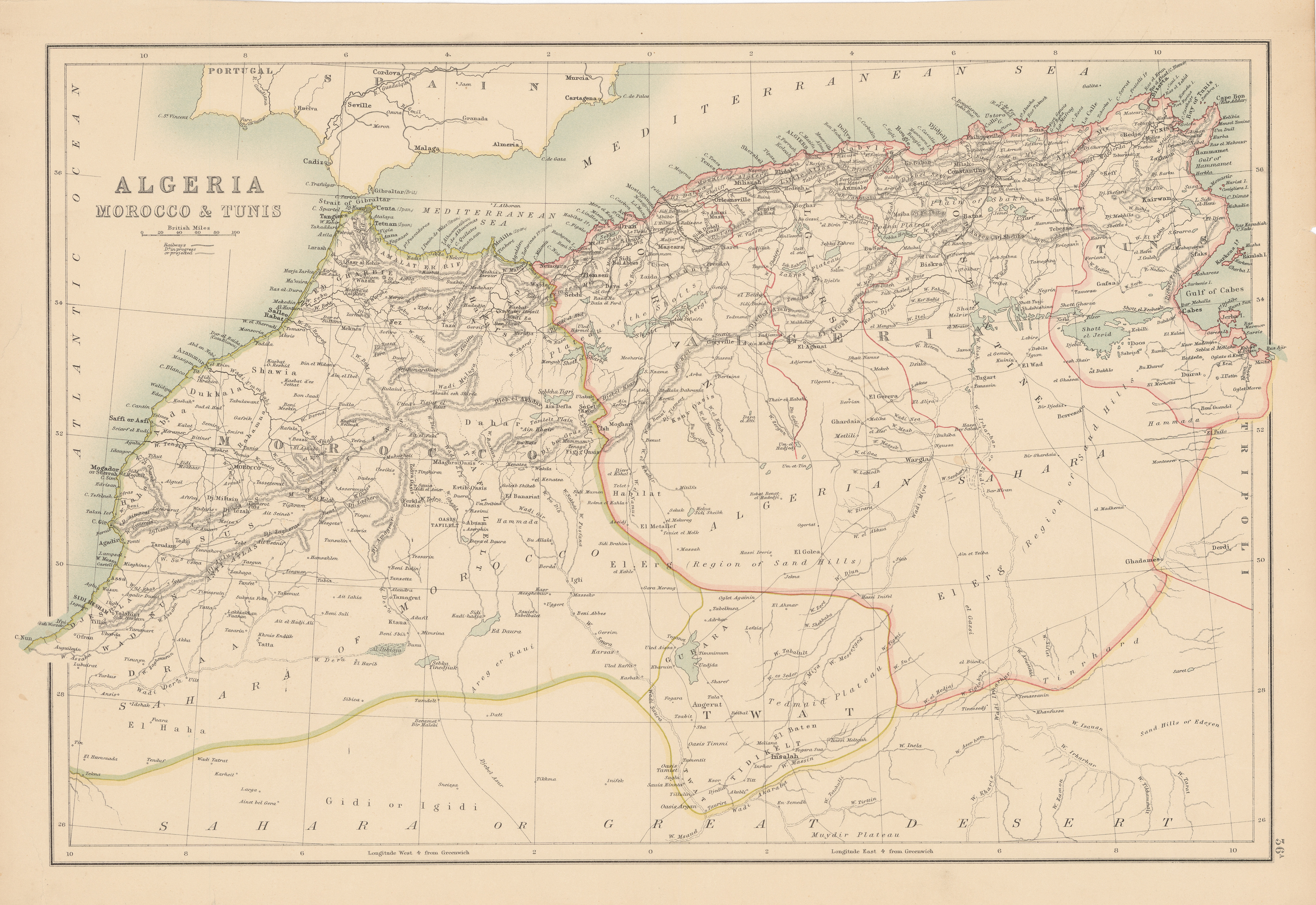
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
from 12 September 1873 to 7 June 1894, as a ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty
The Alawi dynasty ( ar, سلالة العلويين الفيلاليين, translit=sulālat al-ʿalawiyyīn al-fīlāliyyīn) – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Moroccan royal family and reigning d ...
. He was proclaimed sultan after the death of his father Mawlay Muhammad bin Abd al-Rahman. Mawlay Hassan was among the most successful sultans. He increased the power of the makhzen
Makhzen (Arabic: , Berber: ''Lmexzen'') is the governing institution in Morocco and in pre-1957 Tunisia, centered on the monarch and consisting of royal notables, top-ranking military personnel, landowners, security service bosses, civil servants ...
in Morocco and at a time when so much of the rest of Africa was falling under foreign control, he brought in military and administrative reforms to strengthen the regime within its own territory, and he carried out an active military and diplomatic program on the periphery. He died on 9 June 1894 and was succeeded by his son Abd al-Aziz
Abd al-Aziz ( ar, عبد العزيز, DMG: ''ʽAbd al-ʽAzīz''), frequently also transliterated Abdul-Aziz, is a male Arabic Muslim given name and, in modern usage, surname. It is built from the words '' ʽAbd'', the Arabic definite article an ...
.
Reign
Early reign and rebellion in Fes
 Son of the sultan Muhammad IV, Mawlay (Moulay) Hassan was proclaimed sultan of Morocco on the death of his father in 1873. His first action was to crush an urban revolt in the capital Fes in 1874, which he had to besiege for a few months. The tanners rose up in protest "raging like lions and tigers" through the streets of Fes, pillaging the house of Muhammad Bennis, the Minister of Finance, turning Fes into a battleground. Mawlay Hassan I, who was on campaign sent letters calling for the pacification of the city. Shortly after, the hated tax collectors were withdrawn, and the rebellion halted. The tax collectors soon reappeared, leading to the rebellion commencing again more violently. The local Fes militiamen took up positions in minarets of Fes al-Bali and fired down on the army, but the two sides later negotiated peace and the rebellion was definitely terminated. Of strong Arab culture, he did not know any foreign language, although Mawlay Hassan I was a conservative ruler, he realised the need for modernization and the reform policy of his father.
He strived to maintain the cohesion of his kingdom through political, military, and religious action, in the face of European threats on its periphery, and internal rebellions, He initiated reforms. He strived to ensure the loyalty of the great chiefs of the south. He did not hesitate to appoint local Caids like Sheikh Ma al-'Aynayn who gave him the Bay'a, the pledge of allegiance in Islamic Sharia law. He tried to modernize his army, and lead several expeditions to assert his authority, such as to the Sus in 1882 and 1886, to the
Son of the sultan Muhammad IV, Mawlay (Moulay) Hassan was proclaimed sultan of Morocco on the death of his father in 1873. His first action was to crush an urban revolt in the capital Fes in 1874, which he had to besiege for a few months. The tanners rose up in protest "raging like lions and tigers" through the streets of Fes, pillaging the house of Muhammad Bennis, the Minister of Finance, turning Fes into a battleground. Mawlay Hassan I, who was on campaign sent letters calling for the pacification of the city. Shortly after, the hated tax collectors were withdrawn, and the rebellion halted. The tax collectors soon reappeared, leading to the rebellion commencing again more violently. The local Fes militiamen took up positions in minarets of Fes al-Bali and fired down on the army, but the two sides later negotiated peace and the rebellion was definitely terminated. Of strong Arab culture, he did not know any foreign language, although Mawlay Hassan I was a conservative ruler, he realised the need for modernization and the reform policy of his father.
He strived to maintain the cohesion of his kingdom through political, military, and religious action, in the face of European threats on its periphery, and internal rebellions, He initiated reforms. He strived to ensure the loyalty of the great chiefs of the south. He did not hesitate to appoint local Caids like Sheikh Ma al-'Aynayn who gave him the Bay'a, the pledge of allegiance in Islamic Sharia law. He tried to modernize his army, and lead several expeditions to assert his authority, such as to the Sus in 1882 and 1886, to the Rif
The Rif or Riff (, ), also called Rif Mountains, is a geographic region in northern Morocco. This mountainous and fertile area is bordered by Cape Spartel and Tangier to the west, by Berkane and the Moulouya River to the east, by the Mediterrane ...
in 1887, and to Tafilalt in 1893.
Relations with Europe
Sultan Hassan I managed to maintain the independence of Morocco while neighbouring states fell under European influence, such asTunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
which was conquered by France in 1881 and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
which was occupied by Britain in 1882.
Both Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
hoped for a weak Makhzen
Makhzen (Arabic: , Berber: ''Lmexzen'') is the governing institution in Morocco and in pre-1957 Tunisia, centered on the monarch and consisting of royal notables, top-ranking military personnel, landowners, security service bosses, civil servants ...
government of Morocco, while the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
hoped for the opposite, a reformed Moroccan state which could stand on its own. Aware of this, Mawlay Hassan called for an international conference on the issue, and the Treaty of Madrid was signed on 3 July 1880 to limit the practice, an important event of Mawlay Hassan's reign. Instead of reducing foreign interference, the Makhzen had to grant concessions such as granting foreigners rights to own land in the countryside, something which Great Britain was pushing for all along. This was followed by French incursions into the region of Tuat
Tuat, or Touat, is a natural region of desert in central Algeria that contains a string of small oases. In the past, the oases were important for caravans crossing the Sahara.
Geography
Tuat lies to the south of the Grand Erg Occidental, to ...
in the south, which was considered Moroccan territory. This treaty effectively gave international approval and protection for lands which had been captured by foreign powers. This set the stage for the French Protectorate in Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco (french: Protectorat français au Maroc; ar, الحماية الفرنسية في المغرب), also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco between 1912 to 1956. The prote ...
beginning in 1912.
Since 1879, the British occupied Tarfaya
Tarfaya ( ar, طرفاية - ''Ṭarfāya''; ber, ⵟⵔⴼⴰⵢⴰ) is a coastal Moroccan town, located at the level of Cape Juby, in western Morocco, on the Atlantic coast. It is located about 890 km southwest of the capital Rabat, and ...
and built a fortification there in 1882 known as Port Victoria. It was not until 1886 that the sultan sent a military expedition there, damaging the fort and forcing Donald MacKenzie to leave. The sultan's expedition to Sus in 1886 was followed a year later by the Spanish occupation of Dakhla on the Saharan coast. Mawlay Hassan responded by appointing a khalifa (governor) over the Sahara, Ma al-'Aynayn.
Military reform
Mawlay Hassan I continued to expand the military reforms started by his father Muhammad IV. The new and reformed 'Askar al-Nizami introduced by sultanAbd al-Rahman
Abd al-Rahman ( ar, عبد الرحمن, translit=ʿAbd al-Raḥmān or occasionally ; DMG ''ʿAbd ar-Raḥman''; also Abdul Rahman) is a male Arabic Muslim given name, and in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' Abd'', '' ...
in 1845 after the Battle of Isly
The Battle of Isly () was fought on August 14, 1844 between France and Morocco, near the . French forces under Marshal Thomas Robert Bugeaud routed a much larger, but poorly organized, Moroccan force, mainly fighters from the tribes of , but als ...
was expanded by Mawlay Hassan I to the size of 25,000 men and 1,000 artillery. The sultan also enhanced the Moroccan coastal defences with batteries of large caliber cannon, and in 1888 built an arms factory in Fes known as Dar al-Makina, however production in it was little and costly. To train the reformed Moroccan army, Mawlay Hassan I sent students to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, but in 1876, the sultan hired Harry MacLean, a British officer based in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, who designed a military uniform in Arab-style, and learned to speak excellent Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
.
Every year from spring to fall, Mawlay Hassan I was on campaign, and lead expeditions to all parts of the kingdom. One of Mawlay Hassan's campaigns was dealing with the Darqawa
The Darqawiyya or Darqawi Sufi order is a revivalist branch of the Shadhiliyah brotherhood which originated in Morocco. The Darqawa comprised the followers of Sheikh Muhammad al-Arabi al-Darqawi (1760–1823) of Morocco. The movement, which becam ...
uprising near Figuig
Figuig or Figig ( ar, فجيج; Figuig Berber: Ifeyyey) is an oasis town in eastern Morocco near the Atlas Mountains, on the border with Algeria.
The town is built around an oasis of date palms, called ''Tazdayt'', meaning "palm tree" in the ...
in the fall of 1887, which was quickly suppressed. Particularly well known is the journey Hassan I undertook in 1893. He went from Fes (leaving on 29 June) to Marrakech
Marrakesh or Marrakech ( or ; ar, مراكش, murrākuš, ; ber, ⵎⵕⵕⴰⴽⵛ, translit=mṛṛakc}) is the fourth largest city in the Kingdom of Morocco. It is one of the four Imperial cities of Morocco and is the capital of the Marrakes ...
, passing through the Tafilalt, the sand dunes of Erg Chebbi, the valley of the Dades with the majestic gorges of the Todra, Warzazat, the Kasbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, قَـصَـبَـة, qaṣaba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term ''alca ...
of Aït Benhaddou
Aït Benhaddou (; ar, آيت بن حدّو) is a historic ''ighrem'' or ''ksar'' (fortified village) along the former caravan route between the Sahara and Marrakesh in Morocco. It is considered a great example of Moroccan earthen clay architect ...
, the high passage along Telouet
Telouet Kasbah (Berber: ⵉⵖⵔⵎ ⵏ ⵜⵍⵡⴰⵜ; ar, قصبة تلوات; french: Casbah de Télouet) is a Kasbah along the former route of the caravans from the Sahara over the Atlas Mountains to Marrakech. The kasbah was the seat of the ...
, the Tichka pass (2260 m) in the high Atlas, Guelmim port of the Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the ...
. The voyage took six months and succeeded in its objective of reuniting and pacifying the tribes of several regions. The Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp ...
cannon he gave on this occasion to the caid of Telouet
Telouet Kasbah (Berber: ⵉⵖⵔⵎ ⵏ ⵜⵍⵡⴰⵜ; ar, قصبة تلوات; french: Casbah de Télouet) is a Kasbah along the former route of the caravans from the Sahara over the Atlas Mountains to Marrakech. The kasbah was the seat of the ...
(member of the now famous Glaoua family) is still on display in the center of Warzazat. In 1881 he founded Tiznit
Tiznit or Tiznet ( ar, تزنيت, Tiznīt; ber, ⵜⵉⵣⵏⵉⵜ, Tiznit) is a town in the west coast of the Moroccan region of Souss-Massa, founded in 1881 by the Sultan Hassan I. It is the capital of Tiznit Province and recorded a populat ...
. Hassan I appointed Mouha Zayani as Caid of the Zayanes in Khenifra in 1877. Mouha Zayani was to be an important figure in the 20th century colonial war against
Hassan I appointed Mouha Zayani as Caid of the Zayanes in Khenifra in 1877. Mouha Zayani was to be an important figure in the 20th century colonial war against France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. In 1887 he appointed sheikh Ma al-'Aynayn as his caid in Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the ...
. Ma al-'Aynayn too played an important role in the struggle for independence of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
.
Death
On 9 June 1894, Mawlay Hassan I died from illness near Wadi al-Ubayd in the region of Tadla. Since the army was still in enemy territory, his chamberlain and Grand Wazir Ahmad bin Musa kept the death a secret, ordering the ministers to not reveal the news. The sultan's body was taken toRabat
Rabat (, also , ; ar, الرِّبَاط, er-Ribât; ber, ⵕⵕⴱⴰⵟ, ṛṛbaṭ) is the capital city of Morocco and the country's seventh largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan populatio ...
and buried in Dar al-Makhzen there. Mawlay Hassan was succeeded by his son Abd al-Aziz
Abd al-Aziz ( ar, عبد العزيز, DMG: ''ʽAbd al-ʽAzīz''), frequently also transliterated Abdul-Aziz, is a male Arabic Muslim given name and, in modern usage, surname. It is built from the words '' ʽAbd'', the Arabic definite article an ...
, sixteen years old at the time, and ruled under the regency of his father's former Grand Wazir, Ahmad bin Musa, until his death from heart failure in 1900.
See also
*'Alawi dynasty
The Alawi dynasty ( ar, سلالة العلويين الفيلاليين, translit=sulālat al-ʿalawiyyīn al-fīlāliyyīn) – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Moroccan royal family and reigning d ...
* List of Sultans of Morocco
* History of Morocco
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as wel ...
* Hassan I Dam
The Hassan I Dam is an embankment dam located northeast of Demnate on the Lakhdar River in Azilal Province, Morocco. Completed in 1986, the dam provides water for the irrigation of over of farmland. The dam's hydroelectric power plant also genera ...
* Hassan I Airport
References
External links
History of Morocco
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hassan 01 Of Morocco 'Alawi dynasty Sultans of Morocco 1836 births 1894 deaths Moroccan people of Arab descent 19th-century Arabs People from Fez, Morocco People from Marrakesh 19th-century Moroccan people 19th-century monarchs in Africa