Hampton Court on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hampton Court Palace is a Grade I listed royal palace in the

General; Ashford, East Bedfont with Hatton, Feltham, Hampton with Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton (1911), pp. 371–379. Retrieved 21 March 2009.) which contained his private rooms (''O on plan''). The Base Court contained forty-four lodgings reserved for guests, while the second court (today, Clock Court) contained the very best rooms the state apartments reserved for the King and his family.Thurley, p. 6. Henry VIII stayed in the state apartments as Wolsey's guest immediately after their completion in 1525. In building his palace, Wolsey was attempting to create a
In building his palace, Wolsey was attempting to create a  Wolsey was only to enjoy his palace for a few years. In 1528, knowing that his enemies and the King were engineering his downfall, he passed the palace to the King as a gift. Wolsey died two years later in 1530.
Within six months of coming into ownership, the King began his own rebuilding and expansion. Henry VIII's court consisted of over one thousand people, while the King owned over sixty houses and palaces. Few of these were large enough to hold the assembled court, and thus one of the first of the King's building works (in order to transform Hampton Court to a principal residence) was to build the vast kitchens. These were quadrupled in size in 1529, enabling the King to provide bouche of court for his entire court. The architecture of King Henry's new palace followed the design precedent set by Wolsey: perpendicular Gothic-inspired Tudor with restrained Renaissance ornament. This hybrid architecture was to remain almost unchanged for nearly a century, until
Wolsey was only to enjoy his palace for a few years. In 1528, knowing that his enemies and the King were engineering his downfall, he passed the palace to the King as a gift. Wolsey died two years later in 1530.
Within six months of coming into ownership, the King began his own rebuilding and expansion. Henry VIII's court consisted of over one thousand people, while the King owned over sixty houses and palaces. Few of these were large enough to hold the assembled court, and thus one of the first of the King's building works (in order to transform Hampton Court to a principal residence) was to build the vast kitchens. These were quadrupled in size in 1529, enabling the King to provide bouche of court for his entire court. The architecture of King Henry's new palace followed the design precedent set by Wolsey: perpendicular Gothic-inspired Tudor with restrained Renaissance ornament. This hybrid architecture was to remain almost unchanged for nearly a century, until  During the Tudor period, the palace was the scene of many historic events. In 1537, the King's much desired male heir, the future
During the Tudor period, the palace was the scene of many historic events. In 1537, the King's much desired male heir, the future
 On the death of Elizabeth I in 1603, the Tudor period came to an end. The Queen was succeeded by her first cousin-twice-removed,
On the death of Elizabeth I in 1603, the Tudor period came to an end. The Queen was succeeded by her first cousin-twice-removed,  The country's most eminent architect,
The country's most eminent architect,  During this work, half the Tudor palace was replaced and Henry VIII's staterooms and private apartments were both lost; the new wings around the Fountain Court contained new state apartments and private rooms, one set for the King and one for the Queen. Each suite of state rooms was accessed by a state staircase. The royal suites were of completely equal value in order to reflect William and Mary's unique status as joint sovereigns.Williams, p. 54. The King's Apartments face south over the Privy Garden, the Queen's east over the Fountain Garden. The suites are linked by a gallery running the length of the east façade, another reference to Versailles, where the King and Queen's apartments are linked by the
During this work, half the Tudor palace was replaced and Henry VIII's staterooms and private apartments were both lost; the new wings around the Fountain Court contained new state apartments and private rooms, one set for the King and one for the Queen. Each suite of state rooms was accessed by a state staircase. The royal suites were of completely equal value in order to reflect William and Mary's unique status as joint sovereigns.Williams, p. 54. The King's Apartments face south over the Privy Garden, the Queen's east over the Fountain Garden. The suites are linked by a gallery running the length of the east façade, another reference to Versailles, where the King and Queen's apartments are linked by the
 On 2 September 1952, the palace was given statutory protection by being Grade I listed. Other buildings and structures within the grounds are separately Grade I listed, including the early 16th-century tilt yard tower (the only surviving example of the five original towers);
On 2 September 1952, the palace was given statutory protection by being Grade I listed. Other buildings and structures within the grounds are separately Grade I listed, including the early 16th-century tilt yard tower (the only surviving example of the five original towers);

 The palace houses many works of art and furnishings from the
The palace houses many works of art and furnishings from the 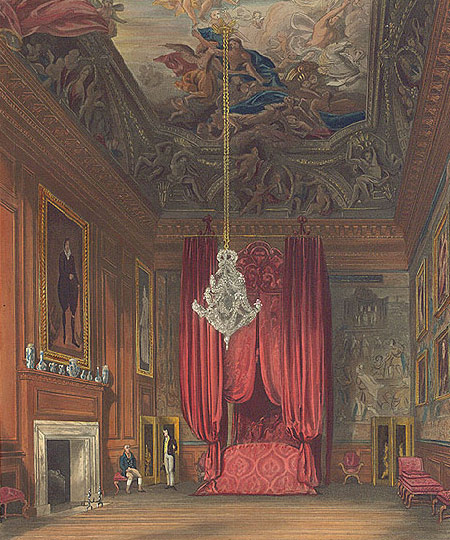 Much of the original furniture dates from the late 17th and early 18th centuries, including tables by
Much of the original furniture dates from the late 17th and early 18th centuries, including tables by
 The timber and plaster ceiling of the chapel is considered the "most important and magnificent in Britain", but is all that remains of the Tudor decoration, after redecoration supervised by Sir Christopher Wren. The altar is framed by a massive but plain oak reredos with garlands carved by
The timber and plaster ceiling of the chapel is considered the "most important and magnificent in Britain", but is all that remains of the Tudor decoration, after redecoration supervised by Sir Christopher Wren. The altar is framed by a massive but plain oak reredos with garlands carved by
 On the south side of the palace is the Privy Garden bounded by semi-circular wrought iron gates by
On the south side of the palace is the Privy Garden bounded by semi-circular wrought iron gates by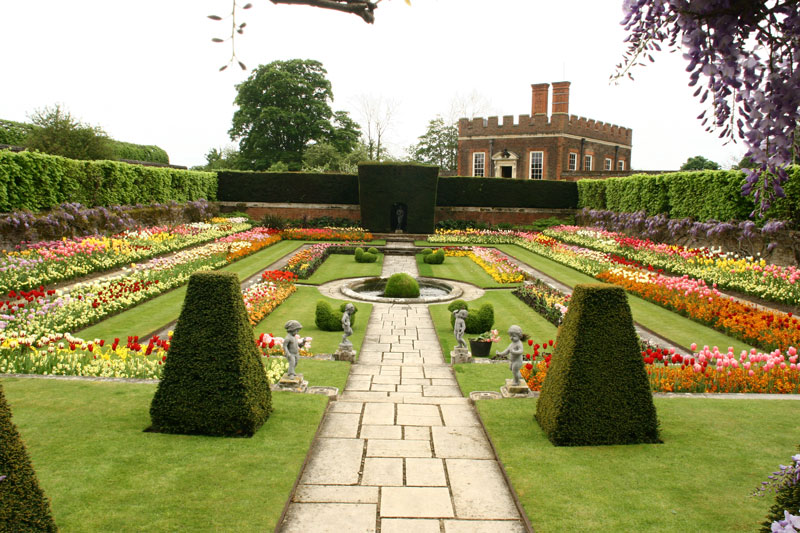  A well-known curiosity of the palace's grounds is
A well-known curiosity of the palace's grounds is
File:Garden in Hampton Court.jpg,
File:Hampton court garden (2016).jpg,
File:Rose Garden in Hampton Court.jpg,
 There are ten statues of heraldic animals, called the King's Beasts, that stand on the bridge over the moat leading to the great gatehouse. Unlike the
There are ten statues of heraldic animals, called the King's Beasts, that stand on the bridge over the moat leading to the great gatehouse. Unlike the
/ref> To decorate the garden eight small wooden King's Beasts were carved and painted in bright colours, each sitting atop a 6-foot-high painted wooden column. The heraldic beasts, carved by
 Inspired by Wren's work at Hampton Court, the American
Inspired by Wren's work at Hampton Court, the American
Historic photos of Hampton Court Palace''Hampton Court''
by
Hampton Court Palace entry from The DiCamillo Companion to British & Irish Country HousesGrace & Favour: A handbook of who lived where at Hampton Court 1750–1950 (pdf)
– there are full floor plans of the palace on pages 10–13
Aerial photo and map of the Palace - Google MapsAerial view of the maze - Google MapsThe Hampton Court Garden FestivalThe Royal Tennis Court at Hampton Court PalaceThe Choir of The Chapel Royal at Hampton Court PalaceOnline 3D Virtual Hampton Maze browser simulation
{{Authority control Buildings and structures on the River Thames Christopher Wren buildings in London Country houses in London Edward Blore buildings Episcopal palaces of archbishops of York Gardens in London Grade I listed buildings in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Grade I listed gates Grade I listed museum buildings Grade I listed parks and gardens in London Historic house museums in London Historic Royal Palaces History of Middlesex History of the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Houses in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Mazes in the United Kingdom Middlesex Museums in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Museums on the River Thames Nicholas Hawksmoor buildings Royal buildings in London Royal residences in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Royal residences in the United Kingdom Tudor royal palaces in England Venues of the 2012 Summer Olympics
London Borough of Richmond upon Thames
The London Borough of Richmond upon Thames () in southwest London forms part of Outer London and is the only London borough on both sides of the River Thames. It was created in 1965 when three smaller council areas amalgamated under the London ...
, southwest and upstream of central London on the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
. The building of the palace began in 1514 for Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the ...
, the chief minister of Henry VIII. In 1529, as Wolsey fell from favour, the cardinal gave the palace to the king to check his disgrace. The palace went on to become one of Henry's most favoured residences; soon after acquiring the property, he arranged for it to be enlarged so that it might more easily accommodate his sizeable retinue of courtiers. Along with St James' Palace, it is one of only two surviving palaces out of the many the king owned. The palace is currently in the possession of King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
and the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
.
In the following century, King William III
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the ...
's massive rebuilding and expansion work, which was intended to rival the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
, destroyed much of the Tudor palace.Dynes, p. 90. His work ceased in 1694, leaving the palace in two distinct contrasting architectural styles, domestic Tudor and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
. While the palace's styles are an accident of fate, a unity exists due to the use of pink bricks and a symmetrical, if vague, balancing of successive low wings.Dynes, p. 86. King George II was the last monarch to reside in the palace.
Today, the palace is open to the public and a major tourist attraction, easily reached by train from Waterloo station
Waterloo station (), also known as London Waterloo, is a central London terminus on the National Rail network in the United Kingdom, in the Waterloo area of the London Borough of Lambeth. It is connected to a London Underground station of t ...
in central London and served by Hampton Court railway station
Hampton Court railway station is a suburban terminus station at East Molesey, in the Borough of Elmbridge in the county of Surrey, 100 yards short of Hampton Court Bridge, the midpoint of which is a boundary of Greater London. The station is do ...
in East Molesey
Molesey is a district of two twin towns, East Molesey and West Molesey, in the Borough of Elmbridge, Surrey, England, and is situated on the south bank of the River Thames.
East and West Molesey share a high street, and there is a second retai ...
, in Transport for London's Zone 6. In addition, London Buses routes 111, 216, 411 and R68 stop outside the palace gates. The structure and grounds are cared for by an independent charity, Historic Royal Palaces
Historic Royal Palaces is an independent charity that manages some of the United Kingdom's unoccupied royal palaces.
These are:
* Tower of London
* Hampton Court Palace
* Kensington Palace (State Apartments and Orangery)
* The Banqueting Hous ...
, which receives no funding from the Government or the Crown. In addition, the palace displays many works of art from the Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
.
Apart from the palace itself and its gardens, other points of interest for visitors include the celebrated maze, the historic royal tennis
Real tennis – one of several games sometimes called "the sport of kings" – is the original racquet sport from which the modern game of tennis (also called "lawn tennis") is derived. It is also known as court tennis in the United Sta ...
court (see below), and the huge grape vine
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, ...
, the largest in the world . The palace's Home Park is the site of the annual Hampton Court Palace Festival
The Hampton Court Palace Festival (also promoted as the Hampton Court Palace Music Festival) is an annual musical event at Hampton Court Palace in London.
Established in 1993, the Festival is known for presenting artists across the music genres ...
and Hampton Court Garden Festival
The Hampton Court Garden Festival (formerly The Hampton Court Flower Show) is an annual British flower show, held in early July. The show is run by the Royal Horticultural Society (RHS) at Hampton Court Palace in the London Borough of Richmond u ...
.
History
Tudor times

Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the ...
, Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
, chief minister to and a favourite of Henry VIII, took over the site of Hampton Court Palace in 1514.Summerson, p. 12. It had previously been a property of the Order of St John of Jerusalem
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
. Over the following seven years, Wolsey spent lavishly (200,000 Crowns
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
) to build the finest palace in England at Hampton Court. Today, little of Wolsey's building work remains unchanged. The first courtyard, the Base Court, (''B on plan''), was his creation, as was the second, inner gatehouse (''C'') which leads to the Clock Court (''D'') (Wolsey's seal remains visible over the entrance arch of the clock towerSpelthorne Hundred: Hampton Court Palace: architectural description, ''A History of the County of Middlesex'', Volume 2General; Ashford, East Bedfont with Hatton, Feltham, Hampton with Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton (1911), pp. 371–379. Retrieved 21 March 2009.) which contained his private rooms (''O on plan''). The Base Court contained forty-four lodgings reserved for guests, while the second court (today, Clock Court) contained the very best rooms the state apartments reserved for the King and his family.Thurley, p. 6. Henry VIII stayed in the state apartments as Wolsey's guest immediately after their completion in 1525.
 In building his palace, Wolsey was attempting to create a
In building his palace, Wolsey was attempting to create a Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
cardinal's palace of a rectilinear symmetrical plan with grand apartments on a raised piano nobile
The ''piano nobile'' (Italian for "noble floor" or "noble level", also sometimes referred to by the corresponding French term, ''bel étage'') is the principal floor of a palazzo. This floor contains the main reception and bedrooms of the hou ...
, all rendered with classical detailing. The historian Jonathan Foyle
Jonathan Foyle is an architectural historian, broadcaster and advocate for heritage sites. He is also an artist.
Background
Foyle grew up in Market Deeping in Lincolnshire and attended The Deepings School. He has a Master of Arts from the ...
has suggested that it is likely that Wolsey had been inspired by Paolo Cortese's ''De Cardinalatu'', a manual for cardinals that included advice on palatial architecture, published in 1510. The architectural historian Sir John Summerson
Sir John Newenham Summerson (25 November 1904 – 10 November 1992) was one of the leading British architectural historians of the 20th century.
Early life
John Summerson was born at Barnstead, Coniscliffe Road, Darlington. His grandfather wo ...
asserts that the palace shows "the essence of Wolsey—the plain English churchman who nevertheless made his sovereign the arbiter of Europe and who built and furnished Hampton Court to show foreign embassies that Henry VIII's chief minister knew how to live as graciously as any cardinal in Rome."Summerson, p. 14. Whatever the concepts were, the architecture is an excellent and rare example of a thirty-year era when English architecture was in a harmonious transition from domestic Tudor, strongly influenced by perpendicular Gothic, to the Italian Renaissance classical style. Perpendicular Gothic owed nothing historically to the Renaissance style, yet harmonised well with it.Copplestone, p. 254. This blending of styles was realised by a small group of Italian craftsmen working at the English court in the second and third decades of the sixteenth century. They specialised in the adding of Renaissance ornament to otherwise straightforward Tudor buildings. It was one of these, Giovanni da Maiano
Giovanni da Maiano II (c. 1486 – c. 1542) was an Italian sculptor employed by Henry VIII of England and Cardinal Wolsey to decorate their palaces. Maiano, from which village Giovanni took his name, is near Fiesole and Florence. He was the so ...
, who was responsible for the set of eight relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
busts of Roman emperors which were set in the Tudor brickwork.
 Wolsey was only to enjoy his palace for a few years. In 1528, knowing that his enemies and the King were engineering his downfall, he passed the palace to the King as a gift. Wolsey died two years later in 1530.
Within six months of coming into ownership, the King began his own rebuilding and expansion. Henry VIII's court consisted of over one thousand people, while the King owned over sixty houses and palaces. Few of these were large enough to hold the assembled court, and thus one of the first of the King's building works (in order to transform Hampton Court to a principal residence) was to build the vast kitchens. These were quadrupled in size in 1529, enabling the King to provide bouche of court for his entire court. The architecture of King Henry's new palace followed the design precedent set by Wolsey: perpendicular Gothic-inspired Tudor with restrained Renaissance ornament. This hybrid architecture was to remain almost unchanged for nearly a century, until
Wolsey was only to enjoy his palace for a few years. In 1528, knowing that his enemies and the King were engineering his downfall, he passed the palace to the King as a gift. Wolsey died two years later in 1530.
Within six months of coming into ownership, the King began his own rebuilding and expansion. Henry VIII's court consisted of over one thousand people, while the King owned over sixty houses and palaces. Few of these were large enough to hold the assembled court, and thus one of the first of the King's building works (in order to transform Hampton Court to a principal residence) was to build the vast kitchens. These were quadrupled in size in 1529, enabling the King to provide bouche of court for his entire court. The architecture of King Henry's new palace followed the design precedent set by Wolsey: perpendicular Gothic-inspired Tudor with restrained Renaissance ornament. This hybrid architecture was to remain almost unchanged for nearly a century, until Inigo Jones
Inigo Jones (; 15 July 1573 – 21 June 1652) was the first significant architect in England and Wales in the early modern period, and the first to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings.
As the most notable archit ...
introduced strong classical influences from Italy to the London palaces of the first Stuart kings.
Between 1532 and 1535 Henry added the Great Hall (the last medieval great hall built for the English monarchy) and the Royal Tennis Court. The Great Hall has a carved hammerbeam roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "...the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams pr ...
. During Tudor times, this was the most important room of the palace; here, the King would dine in state seated at a table upon a raised dais
A dais or daïs ( or , American English also but sometimes considered nonstandard)dais
in the Random House Dictionary< ...
. The hall took five years to complete; so impatient was the King for completion that the masons were compelled to work throughout the night by candlelight.
The gatehouse to the second, inner court was adorned in 1540 with the Hampton Court astronomical clock, an early example of a pre- Copernican in the Random House Dictionary< ...
astronomical clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.
Definition ...
. Still functioning, the clock shows the time of day, the phases of the moon, the month, the quarter of the year, the date, the sun and star sign, and high water
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ca ...
at London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It r ...
. The latter information was of great importance to those visiting this Thames-side palace from London, as the preferred method of transport at the time was by barge, and at low water London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It r ...
created dangerous rapids. This gatehouse is also known today as Anne Boleyn
Anne Boleyn (; 1501 or 1507 – 19 May 1536) was Queen of England from 1533 to 1536, as the second wife of King Henry VIII. The circumstances of her marriage and of her execution by beheading for treason and other charges made her a key ...
's gate, after Henry's second wife. Work was still underway on Anne Boleyn's apartments above the gate when Boleyn was beheaded.
 During the Tudor period, the palace was the scene of many historic events. In 1537, the King's much desired male heir, the future
During the Tudor period, the palace was the scene of many historic events. In 1537, the King's much desired male heir, the future Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
, was born at the palace and the child's mother, Jane Seymour
Jane Seymour (c. 150824 October 1537) was List of English consorts, Queen of England as the third wife of King Henry VIII of England from their Wives of Henry VIII, marriage on 30 May 1536 until her death the next year. She became queen followi ...
, died there two weeks later.Thurley, p. 9. Four years afterwards, whilst attending Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
in the palace's chapel, the King was informed of the adultery of his fifth wife, Catherine Howard
Catherine Howard ( – 13 February 1542), also spelled Katheryn Howard, was Queen of England from 1540 until 1542 as the fifth wife of Henry VIII. She was the daughter of Lord Edmund Howard and Joyce Culpeper, a cousin to Anne Boleyn (the se ...
. She was then confined to her room for a few days before being sent to Syon House and then on to the Tower of London. Legend claims she briefly escaped her guards and ran through The Haunted Gallery to beg Henry for her life but she was recaptured.Thurley, p. 23.
King Henry died in January 1547 and was succeeded by his son Edward VI, and then by both his daughters in turn. It was to Hampton Court that Queen Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. Sh ...
(Henry's elder daughter) retreated with King Philip to spend her honeymoon, after their wedding at Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
.Williams, p. 52. Mary chose Hampton Court as the place for the birth of her first child, which turned out to be the first of two phantom pregnancies. Mary had initially wanted to give birth at Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original c ...
as it was a more secure location, and she was still fearful of rebellion. But Hampton Court was considerably larger and could accommodate the entire court and more besides. Mary stayed at the palace awaiting the birth of the "child" for over five months and only left because of the uninhabitable state of the palace with the court being kept in the one location for so long. Her court departed for the much smaller palace of Oatlands. Mary was succeeded by her half-sister, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
, and it was Elizabeth who had the eastern kitchen built; today, this is the palace's public tea room.
Stuart times
 On the death of Elizabeth I in 1603, the Tudor period came to an end. The Queen was succeeded by her first cousin-twice-removed,
On the death of Elizabeth I in 1603, the Tudor period came to an end. The Queen was succeeded by her first cousin-twice-removed, James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
*James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
*James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
*James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334–13 ...
of the House of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fi ...
.
Two entertainments for the Stuart court were staged in the Great Hall in January 1604, ''The Masque of Indian and China Knights
''The Masque of Indian and China Knights'' was performed at Hampton Court in Richmond, England on 1 January 1604. The masque was not published, and no text survives. It was described in a letter written by Dudley Carleton. The historian Leeds B ...
'' and ''The Vision of the Twelve Goddesses
''The Vision of the Twelve Goddesses'' was an early Jacobean-era masque, written by Samuel Daniel and performed in the Great Hall of Hampton Court Palace on the evening of Sunday, 8 January 1604. One of the earliest of the Stuart Court masqu ...
''. On 6 January, Scottish courtiers performed a sword dance
Sword dances are recorded throughout world history. There are various traditions of solo and mock-battle (Pyrrhic) sword dances from Africa, Asia and Europe.
General types of sword dance include:
*solo dancers around swords – such as t ...
for Anne of Denmark
Anne of Denmark (; 12 December 1574 – 2 March 1619) was the wife of King James VI and I; as such, she was Queen of Scotland
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional fo ...
. Their dance was compared to a Spanish ''matachin
Matachines (Spanish singular ''matachín''; sword dancers dressed in ritual attire called bouffon) are a carnivalesque dance troupe that emerged in Spain in the early 17th century inspired by similar European traditions such as the moresca. Th ...
''. Later in 1604, the palace was the site of King James' meeting with representatives of the English Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
, known as the Hampton Court Conference; while an agreement with the Puritans was not reached, the meeting led to James's commissioning of the King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an Bible translations into English, English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and publis ...
of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
.Thurley, p. 10.
King James was succeeded in 1625 by his son, the ill-fated Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
. Hampton Court was to become both his palace and his prison. It was also the setting for his honeymoon with his fifteen-year-old bride, Henrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria (french: link=no, Henriette Marie; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until Charles was executed on 30 January 1649. She was ...
in 1625. Following King Charles' execution in 1649, the palace became the property of the Commonwealth presided over by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
. Unlike some other former royal properties, the palace escaped relatively unscathed. While the government auctioned much of the contents, the building was ignored.
After the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
, King Charles II and his successor James II visited Hampton Court but largely preferred to reside elsewhere. By current French court standards, Hampton Court now appeared old-fashioned. It was in 1689, shortly after Louis XIV's court had moved permanently to Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
, that the palace's antiquated state was addressed. England had joint monarchs, William III and Mary II. Within months of their accession, they embarked on a massive rebuilding project at Hampton Court. The intention was to demolish the Tudor palace a section at a time while replacing it with a huge modern palace in the Baroque style retaining only Henry VIII's Great Hall.Summerson, p. 16.
 The country's most eminent architect,
The country's most eminent architect, Sir Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren PRS FRS (; – ) was one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history, as well as an anatomist, astronomer, geometer, and mathematician-physicist. He was accorded responsibility for rebuilding 52 churches ...
, was called upon to draw the plans, while the master of works was to be William Talman. The plan was for a vast palace constructed around two courtyards at right angles to each other. Wren's design for a domed palace bore resemblances to the work of Jules Hardouin Mansart
Jules Hardouin-Mansart (; 16 April 1646 – 11 May 1708) was a French Baroque architect and builder whose major work included the Place des Victoires (1684–1690); Place Vendôme (1690); the domed chapel of Les Invalides (1690), and the Grand ...
and Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau (1612 – 11 October 1670) was a French Baroque architect, who worked for Louis XIV of France. He was an architect that helped develop the French Classical style in the 17th Century.''Encyclopedia of World Biography''"Louis Le Vau", ...
, both architects employed by Louis XIV at Versailles. It has been suggested, though, that the plans were abandoned because the resemblance to Versailles was too subtle and not strong enough; at this time, it was impossible for any sovereign to visualise a palace that did not emulate Versailles' repetitive Baroque form. However, the resemblances are there: while the façades are not so long as those of Versailles, they have similar, seemingly unstoppable repetitive rhythms beneath a long flat skyline. The monotony is even repeated as the façade turns the corner from the east to the south fronts. However, Hampton Court, unlike Versailles, is given an extra dimension by the contrast between the pink brick and the pale Portland stone quoins, frames and banding.Dynes, p. 95. Further diversion is added by the circular and decorated windows of the second-floor mezzanine. This theme is repeated in the inner Fountain Court, but the rhythm is faster and the windows, unpedimented on the outer façades, are given pointed pediments in the courtyard; this has led the courtyard to be described as "Startling, as of simultaneous exposure to a great many eyes with raised eyebrows."Summerson, p. 19.
 During this work, half the Tudor palace was replaced and Henry VIII's staterooms and private apartments were both lost; the new wings around the Fountain Court contained new state apartments and private rooms, one set for the King and one for the Queen. Each suite of state rooms was accessed by a state staircase. The royal suites were of completely equal value in order to reflect William and Mary's unique status as joint sovereigns.Williams, p. 54. The King's Apartments face south over the Privy Garden, the Queen's east over the Fountain Garden. The suites are linked by a gallery running the length of the east façade, another reference to Versailles, where the King and Queen's apartments are linked by the
During this work, half the Tudor palace was replaced and Henry VIII's staterooms and private apartments were both lost; the new wings around the Fountain Court contained new state apartments and private rooms, one set for the King and one for the Queen. Each suite of state rooms was accessed by a state staircase. The royal suites were of completely equal value in order to reflect William and Mary's unique status as joint sovereigns.Williams, p. 54. The King's Apartments face south over the Privy Garden, the Queen's east over the Fountain Garden. The suites are linked by a gallery running the length of the east façade, another reference to Versailles, where the King and Queen's apartments are linked by the Galerie des Glaces
The Hall of Mirrors (french: Grande Galerie, Galerie des Glaces, Galerie de Louis XIV) is a grand Baroque style gallery and one of the most emblematic rooms in the royal Palace of Versailles near Paris, France. The grandiose ensemble of the h ...
. However, at Hampton Court, the linking gallery is of more modest proportions and decoration. The King's staircase was decorated with fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
s by Antonio Verrio and delicate ironwork by Jean Tijou
Jean Tijou () was a French Huguenot ironworker. He is known solely through his work in England, where he worked on several of the key English Baroque buildings. Very little is known of his biography. He arrived in England in c. 1689 and enjoyed ...
. Other artists commissioned to decorate the rooms included Grinling Gibbons
Grinling Gibbons (4 April 1648 – 3 August 1721) was an Anglo-Dutch sculptor and wood carver known for his work in England, including Windsor Castle and Hampton Court Palace, St Paul's Cathedral and other London churches, Petworth House and othe ...
, Sir James Thornhill
Sir James Thornhill (25 July 1675 or 1676 – 4 May 1734) was an English painter of historical subjects working in the Italian baroque tradition. He was responsible for some large-scale schemes of murals, including the "Painted Hall" at the ...
and Jacques Rousseau; furnishings were designed by Daniel Marot
Daniel Marot or Daniel Marot the Elder (1661–1752) was a French-born Dutch architect, furniture designer and engraver at the forefront of the classicizing Late Baroque Louis XIV style. He worked for a long time in England and the Dutch Republic ...
.
After the death of Queen Mary, King William lost interest in the renovations, and work ceased. However, it was in Hampton Court Park
Hampton Court Park, also known as Home Park, is a walled royal park managed by the Historic Royal Palaces.
in 1702 that he fell from his horse, later dying from his injuries at Kensington Palace. He was succeeded by his sister-in-law Queen Anne who continued the decoration and completion of the state apartments. On Queen Anne's death in 1714 the Stuart dynasty came to an end.
Queen Anne's successor was George I George I or 1 may refer to:
People
* Patriarch George I of Alexandria (fl. 621–631)
* George I of Constantinople (d. 686)
* George I of Antioch (d. 790)
* George I of Abkhazia (ruled 872/3–878/9)
* George I of Georgia (d. 1027)
* Yuri Dolgor ...
; he and his son George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089) ...
were the last monarchs to reside at Hampton Court. Under George I six rooms were completed in 1717 to the design of John Vanbrugh
Sir John Vanbrugh (; 24 January 1664 (baptised) – 26 March 1726) was an English architect, dramatist and herald, perhaps best known as the designer of Blenheim Palace and Castle Howard. He wrote two argumentative and outspoken Restora ...
.Thurley, Simon (2003). ''Hampton Court: A Social and Architectural History''. p. 255. Under George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089) ...
and his wife, Caroline of Ansbach, further refurbishment took place, with the architect William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, bu ...
employed to design new furnishings and decor including the Queen's Staircase, (1733)Thurley, Simon (2003). ''Hampton Court: A Social and Architectural History''. p. 279. and the Cumberland Suite (1737) for the Duke of Cumberland
Duke of Cumberland is a peerage title that was conferred upon junior members of the British Royal Family, named after the historic county of Cumberland.
History
The Earldom of Cumberland, created in 1525, became extinct in 1643. The dukedom ...
. Today, the Queen's Private Apartments are open to the public.
Later use
Since the reign of King George II, no monarch has resided at Hampton Court. In fact,George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
, from the moment of his accession, never set foot in the palace: he associated the state apartments with a humiliating scene when his grandfather had once struck him following an innocent remark. He did however have the Great Vine planted here in 1763 and had the top two storeys of the Great Gatehouse removed in 1773.
From the 1760s, the palace was used to house grace and favour
''Grace & Favour'' (American title: ''Are You Being Served? Again!'') is a British sitcom and a spin-off of '' Are You Being Served?'' that aired on BBC1 for two series from 1992 to 1993. It was written by ''Are You Being Served?'' creators and ...
residents. Many of the palace rooms were adapted to be rent-free apartments, with vacant ones allocated by the Lord Chamberlain
The Lord Chamberlain of the Household is the most senior officer of the Royal Household of the United Kingdom, supervising the departments which support and provide advice to the Sovereign of the United Kingdom while also acting as the main cha ...
to applicants to reward past services rendered to the Crown. From 1862 to his death in 1867, the scientist and pioneer of electricity Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
lived here. From the 1960s the number of new residents declined, with the last admitted in the 1980s. However existing residents could continue to live here. In 2005 three remained, with none by 2017.
In 1796, the Great Hall was restored and in 1838, during the reign of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
, the restoration was completed and the palace opened to the public. The heavy-handed restoration plan at this time reduced the Great Gatehouse (''A''), the palace's principal entrance, by two storeys and removed the lead cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, from ...
s adorning its four towers. Once opened, the palace soon became a major tourist attraction and, by 1881, over ten million visits had been recorded. Visitors arrived both by boat from London and via Hampton Court railway station
Hampton Court railway station is a suburban terminus station at East Molesey, in the Borough of Elmbridge in the county of Surrey, 100 yards short of Hampton Court Bridge, the midpoint of which is a boundary of Greater London. The station is do ...
, opened in February 1849.
 On 2 September 1952, the palace was given statutory protection by being Grade I listed. Other buildings and structures within the grounds are separately Grade I listed, including the early 16th-century tilt yard tower (the only surviving example of the five original towers);
On 2 September 1952, the palace was given statutory protection by being Grade I listed. Other buildings and structures within the grounds are separately Grade I listed, including the early 16th-century tilt yard tower (the only surviving example of the five original towers); Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren PRS FRS (; – ) was one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history, as well as an anatomist, astronomer, geometer, and mathematician-physicist. He was accorded responsibility for rebuilding 52 churches ...
's Lion gate built for Anne and George I; and the Tudor and 17th-century perimeter walls.
In 1986, the palace was damaged by a major fire, which spread to the King's Apartments. The fire claimed the life of Lady Daphne Gale, widow of General Sir Richard Gale, who resided in a grace and favour apartment. The fire led to a new programme of restoration work which was completed in 1990. The Royal School of Needlework
The Royal School of Needlework (RSN) is a hand embroidery school in the United Kingdom, founded in 1872 and based at Hampton Court Palace since 1987.
History
The RSN began as the School of Art Needlework in 1872, founded by Lady Victoria Welby ...
moved to premises within the palace from Princes Gate in Kensington
Kensington is a district in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in the West End of London, West of Central London.
The district's commercial heart is Kensington High Street, running on an east–west axis. The north-east is taken up b ...
1987, and the palace also houses the headquarters of Historic Royal Palaces
Historic Royal Palaces is an independent charity that manages some of the United Kingdom's unoccupied royal palaces.
These are:
* Tower of London
* Hampton Court Palace
* Kensington Palace (State Apartments and Orangery)
* The Banqueting Hous ...
, a charitable foundation
A foundation (also a charitable foundation) is a category of nonprofit organization or charitable trust that typically provides funding and support for other charitable organizations through grants, but may also engage directly in charitable act ...
.
21st century
The location was used for a performance of '' The Six Wives of Henry VIII'' by rock keyboardist Rick Wakeman in 2009. The palace was the venue for the Road Cycling Time Trial of the2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
and temporary structures for the event, including a set of thrones for time trialists in the medal positions, were installed in the grounds.
In 2015, Hampton Court celebrated the 500th anniversary of the groundbreaking of construction of the palace. The celebrations included daily dramatised historical scenes. The palace's construction began on 12 February 1515.
On 9 February the following year, Vincent Nichols
Vincent Gerard Nichols (born 8 November 1945) is an English cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church, Archbishop of Westminster and President of the Catholic Bishops' Conference of England and Wales. He previously served as Archbishop of Birm ...
, the Catholic archbishop of Westminster, celebrated vespers
Vespers is a service of evening prayer, one of the canonical hours in Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic (both Latin liturgical rites, Latin and Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern), Lutheranism, Lutheran, and Anglican ...
in the Chapel Royal. This was the first Catholic service held at the palace for 450 years, and the first since the Elizabethan Religious Settlement
The Elizabethan Religious Settlement is the name given to the religious and political arrangements made for England during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Implemented between 1559 and 1563, the settlement is considered the end of the ...
established Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
as the national denomination.
Contents

 The palace houses many works of art and furnishings from the
The palace houses many works of art and furnishings from the Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
, mainly dating from the two principal periods of the palace's construction, the early Tudor (Renaissance) and the late Stuart to the early Georgian period. In September 2015, the Royal Collection recorded 542 works (only those with images) as being located at Hampton Court, mostly paintings and furniture, but also ceramics and sculpture. The full current list can be obtained from their website. The single most important work is Mantegna's ''Triumphs of Caesar
The ''Triumphs of Caesar'' are a series of nine large paintings created by the Italian Renaissance artist Andrea Mantegna between 1484 and 1492 for the Gonzaga Ducal Palace, Mantua. They depict a triumphal military parade celebrating the victor ...
'' housed in the Lower Orangery. The palace once housed the Raphael Cartoons
The Raphael Cartoons are seven large cartoons for tapestries, belonging to the British Royal Collection but since 1865 on loan to the Victoria and Albert Museum in London, designed by the High Renaissance painter Raphael in 1515–16 and show ...
, now kept at the Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and nam ...
. Their former home, the Cartoon Gallery on the south side of the Fountain Court, was designed by Christopher Wren; copies were painted in the 1690s by a minor artist, Henry Cooke, are now displayed in their place. Also on display are important collections of ceramics, including numerous pieces of blue and white porcelain collected by Queen Mary II, both Chinese imports and Delftware
Delftware or Delft pottery, also known as Delft Blue ( nl, Delfts blauw) or as delf,
is a general term now used for Dutch tin-glazed earthenware, a form of faience. Most of it is blue and white pottery, and the city of Delft in the Netherland ...
.
 Much of the original furniture dates from the late 17th and early 18th centuries, including tables by
Much of the original furniture dates from the late 17th and early 18th centuries, including tables by Jean Pelletier
Jean Pelletier, (; February 21, 1935 – January 10, 2009) was a Canadian politician who served as the 37th mayor of Quebec City, Chief of Staff in the Prime Minister's Office, and chairman of Via Rail. He was a leading organizer of the Libe ...
, "India back" walnut chairs by Thomas Roberts and clocks and a barometer by Thomas Tompion
Thomas Tompion, FRS (1639–1713) was an English clockmaker, watchmaker and mechanician who is still regarded to this day as the "Father of English Clockmaking". Tompion's work includes some of the most historic and important clocks and watc ...
. Several state bed
A baldachin, or baldaquin (from it, baldacchino), is a canopy of state typically placed over an altar or throne. It had its beginnings as a cloth canopy, but in other cases it is a sturdy, permanent Architecture, architectural feature, particu ...
s are still in their original positions, as is the Throne Canopy in the King's Privy Chamber. This room contains a crystal chandelier of circa 1700, possibly the first such in the country.
The King's Guard Chamber contains a large quantity of arms: muskets, pistols, swords, daggers, powder horn
A powder horn is a container for gunpowder, and was generally created from cow, ox or buffalo horn (anatomy), horn. The term may also be used for any personal container for gunpowder, although powder flask is the strictly correct term.
Featur ...
s and pieces of armour arranged on the walls in decorative patterns. Bills exist for payment to a John Harris dated 1699 for an arrangement believed to be that still seen today.
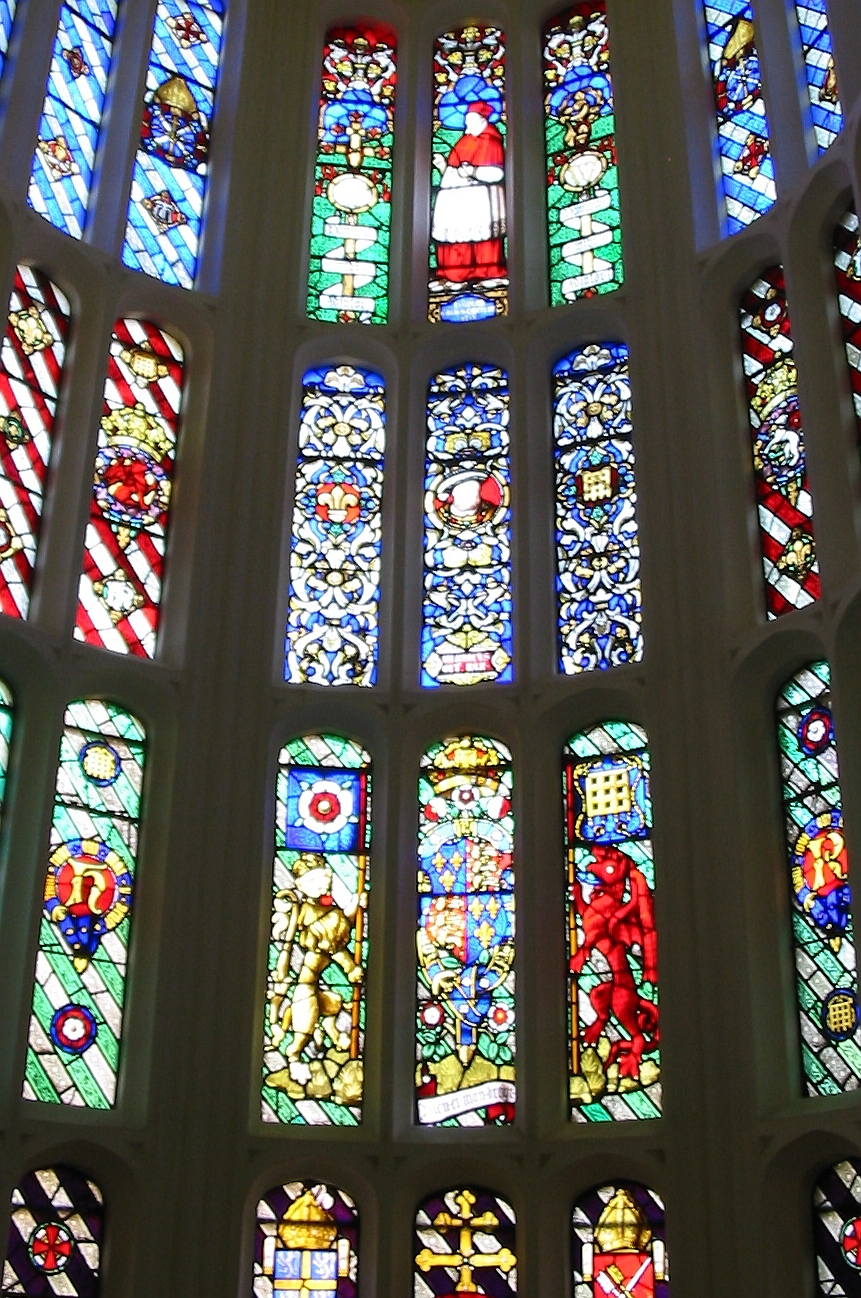
The Chapel
 The timber and plaster ceiling of the chapel is considered the "most important and magnificent in Britain", but is all that remains of the Tudor decoration, after redecoration supervised by Sir Christopher Wren. The altar is framed by a massive but plain oak reredos with garlands carved by
The timber and plaster ceiling of the chapel is considered the "most important and magnificent in Britain", but is all that remains of the Tudor decoration, after redecoration supervised by Sir Christopher Wren. The altar is framed by a massive but plain oak reredos with garlands carved by Grinling Gibbons
Grinling Gibbons (4 April 1648 – 3 August 1721) was an Anglo-Dutch sculptor and wood carver known for his work in England, including Windsor Castle and Hampton Court Palace, St Paul's Cathedral and other London churches, Petworth House and othe ...
during the reign of Queen Anne. Opposite the altar, at first-floor level, is the royal pew where the royal family would attend services apart from the general congregation seated below.
The clergy, musicians and other ecclesiastical officers employed by the monarch at Hampton Court, as in other English royal premises, are known collectively as the Chapel Royal
The Chapel Royal is an establishment in the Royal Household serving the spiritual needs of the sovereign and the British Royal Family. Historically it was a body of priests and singers that travelled with the monarch. The term is now also applie ...
; properly used the term does not refer to a building.
Grounds
The grounds as they appear today were laid out in grand style in the late 17th century. There are no authentic remains of Henry VIII's gardens, merely a smallknot garden
A knot garden is a garden of formal design in a square frame, consisting of a variety of aromatic plants and culinary herbs including germander, marjoram, thyme, southernwood
''Artemisia abrotanum'', the southernwood, lad's love, or southern ...
, planted in 1924, which hints at the gardens' 16th-century appearance.Thurley, p. 44. Today, the dominating feature of the grounds is the great landscaping scheme constructed for Sir Christopher Wren's intended new palace. From a water-bounded semicircular parterre
A ''parterre'' is a part of a formal garden constructed on a level substrate, consisting of symmetrical patterns, made up by plant beds, low hedges or coloured gravels, which are separated and connected by paths. Typically it was the part of ...
, the length of the east front, three avenues radiate in a crow's foot pattern. The central avenue, containing not a walk or a drive, but the great canal known as the Long Water, was excavated during the reign of Charles II, in 1662. The design, radical at the time, is another immediately recognizable influence from Versailles and was indeed laid out by pupils of André Le Nôtre, Louis XIV's landscape gardener.
 On the south side of the palace is the Privy Garden bounded by semi-circular wrought iron gates by
On the south side of the palace is the Privy Garden bounded by semi-circular wrought iron gates by Jean Tijou
Jean Tijou () was a French Huguenot ironworker. He is known solely through his work in England, where he worked on several of the key English Baroque buildings. Very little is known of his biography. He arrived in England in c. 1689 and enjoyed ...
. This garden, originally William III's private garden, was replanted in 1992 in period style with manicured hollies
The Hollies are a British pop rock band, formed in 1962. One of the leading British groups of the 1960s and into the mid-1970s, they are known for their distinctive three-part vocal harmony style. Allan Clarke and Graham Nash founded the band ...
and yews along a geometric system of paths.
On a raised site overlooking the Thames, is a small pavilion, the Banqueting House. This was built circa 1700, for informal meals and entertainments in the gardens rather than for the larger state dinners which would have taken place inside the palace itself. A nearby conservatory houses the "Great Vine", planted in 1769; by 1968 it had a trunk 81 inches thick and has a length of 100 feet. It still produces an annual crop of grapes.Thurley, p. 46.
The palace included apartments for the use of favoured royal friends. One such apartment is described as being in "The Pavilion and situated on the Home Park" of Hampton Court Palace. This privilege was first extended about 1817 by Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, to his friend, Lieut General James Moore, K.C., and his new bride, Cecilia Watson. George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
continued this arrangement following the death of Prince Edward on 23 January 1820. The Queen continued the arrangement for the widow of General Moore, following his death on 24 April 1838. This particular apartment was used for 21 years or more and spanned three different sponsors.
 A well-known curiosity of the palace's grounds is
A well-known curiosity of the palace's grounds is Hampton Court Maze
Hampton Court Maze is a hedge maze at Hampton Court Palace and the oldest surviving hedge maze in Britain.
Commissioned by King William III, the maze, which is about one-third of an acre, is planted in a trapezoid shape and was designed by ...
; planted in the 1690s by George London and Henry Wise for William III. It was originally planted with hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30–40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Origin of names
The common English name ''hornbeam ...
; it has been repaired latterly using many different types of hedge. (There is a 3D online browser simulation of the Hampton Court Maze
Hampton Court Maze is a hedge maze at Hampton Court Palace and the oldest surviving hedge maze in Britain.
Commissioned by King William III, the maze, which is about one-third of an acre, is planted in a trapezoid shape and was designed by ...
, see the External Links section.)
Inspired by narrow views of a Tudor garden that can be seen through doorways in a painting, ''The Family of Henry VIII'', hanging in the palace's Haunted Gallery, a new garden in the style of Henry VIII's 16th-century Privy Gardens, has been designed to celebrate the anniversary of that King's accession to the throne. Sited on the former Chapel Court Garden, it has been planted with flowers and herbs from the 16th century and is completed by gilded heraldic beasts and bold green and white painted fences. The garden's architect was Todd Longstaffe-Gowan.
The formal gardens and park are Grade I listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens
The Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in England provides a listing and classification system for historic parks and gardens similar to that used for listed buildings. The register is managed by Historic England ...
.
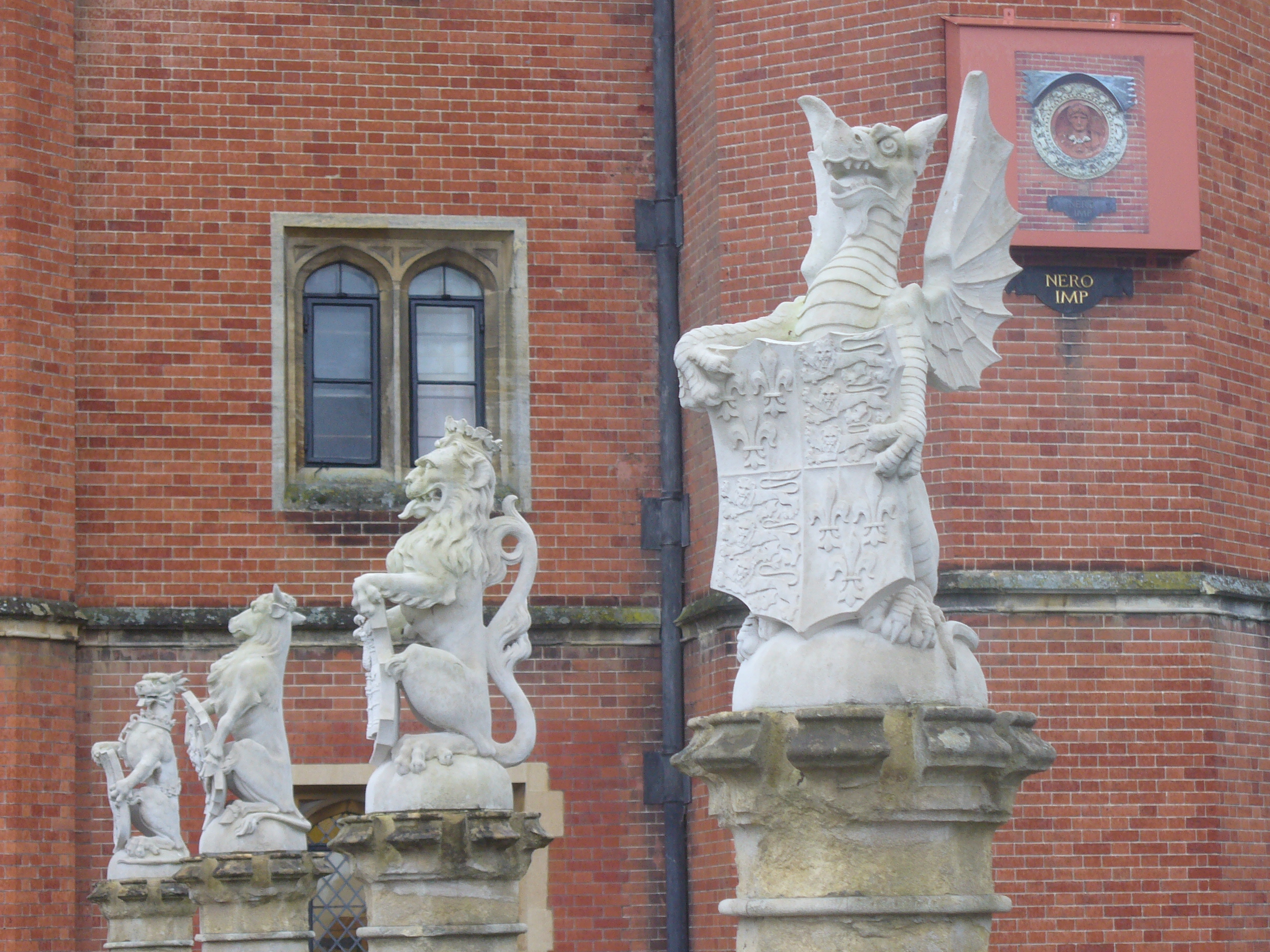
King's Beasts
 There are ten statues of heraldic animals, called the King's Beasts, that stand on the bridge over the moat leading to the great gatehouse. Unlike the
There are ten statues of heraldic animals, called the King's Beasts, that stand on the bridge over the moat leading to the great gatehouse. Unlike the Queen's Beasts
The Queen's Beasts are ten heraldic statues representing the genealogy of Queen Elizabeth II, depicted as the Royal supporters of England. They stood in front of the temporary western annexe to Westminster Abbey for the Queen's coronation in ...
in Kew Gardens
Kew Gardens is a botanical garden, botanic garden in southwest London that houses the "largest and most diverse botany, botanical and mycology, mycological collections in the world". Founded in 1840, from the exotic garden at Kew Park, its li ...
, these statues represent the ancestry of King Henry VIII and his third wife Jane Seymour. The animals are: the lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, the Seymour lion, the royal dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
, the black bull of Clarence Clarence may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Clarence County, New South Wales, a Cadastral division
* Clarence, New South Wales, a place near Lithgow
* Clarence River (New South Wales)
* Clarence Strait (Northern Territory)
* City of Clarence, a l ...
, the yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
of Beaufort, the white lion of Mortimer
Mortimer () is an English surname, and occasionally a given name.
Norman origins
The surname Mortimer has a Norman origin, deriving from the village of Mortemer, Seine-Maritime, Normandy. A Norman castle existed at Mortemer from an early point; ...
, the White Greyhound of Richmond, the Tudor dragon, the Seymour panther
Panther may refer to:
Large cats
*Pantherinae, the cat subfamily that contains the genera ''Panthera'' and ''Neofelis''
**'' Panthera'', the cat genus that contains tigers, lions, jaguars and leopards.
*** Jaguar (''Panthera onca''), found in So ...
, and the Seymour unicorn
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since antiquity as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn projecting from its forehead.
In European literature and art, the unicorn has for the last thousand years o ...
. The set of Queen's Beasts at the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II
The coronation of Elizabeth II took place on 2 June 1953 at Westminster Abbey in London. She acceded to the throne at the age of 25 upon the death of her father, George VI, on 6 February 1952, being proclaimed queen by her privy and executive ...
replaced the three Seymour items and one of the dragons by the gryphon of Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
, the horse of Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, the falcon of the Plantagenets
The House of Plantagenet () was a royal house which originated from the lands of Anjou in France. The family held the English throne from 1154 (with the accession of Henry II at the end of the Anarchy) to 1485, when Richard III died in batt ...
, and the unicorn of Scotland.
In 2009 to celebrate the 500th anniversary of the accession to the throne of King Henry VIII, a new "Tudor Garden" was created in Chapel Court, Hampton Court, designed by Todd Longstaffe-Gowan.Todd Longstaffe-Gowan/ref> To decorate the garden eight small wooden King's Beasts were carved and painted in bright colours, each sitting atop a 6-foot-high painted wooden column. The heraldic beasts, carved by
Ben Harms
Ben Harms (January 1955 – December 2021) was a German-born traditional woodcarver working in England. Some of his work can be seen at The Tower of London, Windsor Castle, Kensington Palace, Hampton Court and alongside the work of Grinling Gibbo ...
and Ray Gonzalez of G&H Studios, include the golden lion of England, the white greyhound of Richmond, the red dragon of Wales, and the white hart of Richard II, all carved from English oak. The historically correct colours were researched by Patrick Baty, paint/colour consultant at Hampton Court. The beasts are of a different design to those on the bridge, based on period drawings in the College of Arms
The College of Arms, or Heralds' College, is a royal corporation consisting of professional Officer of Arms, officers of arms, with jurisdiction over England, Wales, Northern Ireland and some Commonwealth realms. The heralds are appointed by the ...
.
Transport links
The palace is served byHampton Court railway station
Hampton Court railway station is a suburban terminus station at East Molesey, in the Borough of Elmbridge in the county of Surrey, 100 yards short of Hampton Court Bridge, the midpoint of which is a boundary of Greater London. The station is do ...
which is immediately to the south of Hampton Court Bridge
Hampton Court Bridge is a Grade II listed bridge that crosses the River Thames in England approximately north–south between Hampton, London and East Molesey, Surrey, carrying the A309. It is the upper of two road bridges on the reach ab ...
in East Molesey
Molesey is a district of two twin towns, East Molesey and West Molesey, in the Borough of Elmbridge, Surrey, England, and is situated on the south bank of the River Thames.
East and West Molesey share a high street, and there is a second retai ...
, and by London bus routes 111, 216, 411 and R68 from Kingston and Richmond.Cultural appearances and influence
Florham, USA
 Inspired by Wren's work at Hampton Court, the American
Inspired by Wren's work at Hampton Court, the American Vanderbilt family
The Vanderbilt family is an American family who gained prominence during the Gilded Age. Their success began with the shipping and railroad empires of Cornelius Vanderbilt, and the family expanded into various other areas of industry and philanthr ...
modelled their estate known as Florham
Florham is a former Vanderbilt estate that is located in Madison and Florham Park, New Jersey. It was built during the 1890s for Hamilton McKown Twombly and his wife, Florence Adele Vanderbilt, a member of the Vanderbilt family. Now part of th ...
, in Madison, New Jersey
Madison is a borough in Morris County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 16,937.
Located along the Morris & Essex Lines, it is noted for Madison's historic railroad station becoming one ...
, US after it. Florham was commissioned by Florence Adele Vanderbilt Twombly
Florence Adele Vanderbilt Twombly (January 8, 1854 – April 11, 1952) was an American socialite and heiress. She was a member of the prominent Vanderbilt family. She and her husband Hamilton McKown Twombly built Florham, a gilded age estate in M ...
and Hamilton McKown Twombly
Hamilton McKown Twombly Sr. (August 11, 1849 – January 11, 1910) was an American businessman.
Early life
Hamilton McKown Twombly Sr. was born on August 11, 1849 in Middlesex County, Massachusetts and grew up in Boston. His parents were Alexand ...
from McKim, Mead & White. It was built in 1893.
Film location
The palace has been used as a location for filming, including: '' A Man for All Seasons'' (1966); the HBO miniseries ''John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
'' (2008); ''To Kill a King
''To Kill a King'' is a 2003 English Civil War film directed by Mike Barker, and starring Tim Roth, Rupert Everett and Dougray Scott. It centres on the relationship between Oliver Cromwell and Thomas Fairfax in the post-war period from 1648 unt ...
'' (2003); ''The New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
'' (2005); '' Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides'' (2011) '' Sherlock Holmes: A Game of Shadows'' (2011); ''Holmes & Watson
''Holmes & Watson'' is a 2018 American-Canadian mystery-comedy film written and directed by Etan Cohen. The film stars Will Ferrell and John C. Reilly as the eponymous characters Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, respectively; with Rebecca Hall, R ...
'' (2018); ''The Favourite
''The Favourite'' is a 2018 Historical drama, period black comedy film co-produced and directed by Yorgos Lanthimos, from a screenplay by Deborah Davis (screenwriter), Deborah Davis and Tony McNamara (writer), Tony McNamara. Set in early 18th ...
'' (2018); Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
's ''Cinderella'' (2015); the ITV series ''Belgravia''; and the Hulu
Hulu () is an American subscription streaming service majority-owned by The Walt Disney Company, with Comcast's NBCUniversal holding a minority stake. It was launched on October 29, 2007 and it offers a library of films and television serie ...
tv series ''The Great
This is a list of people known as the Great, or the equivalent, in their own language. Other languages have their own suffixes, such as Persian ''e Bozorg'' and Urdu ''e Azam''.
In Persia, the title "the Great" at first seems to have been a co ...
'' (2021).
See also
*Coughton Court
Coughton Court () is an English Tudor country house, situated on the main road between Studley and Alcester in Warwickshire. It is a Grade I listed building.
The house has a long crenellated façade directly facing the main road, at the cen ...
in Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, and the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare at Stratford-upon-Avon an ...
* Het Loo Palace
Het Loo Palace ( nl, Paleis Het Loo , meaning "The Lea") is a palace in Apeldoorn, Netherlands, built by the House of Orange-Nassau.
History
The symmetrical Dutch Baroque building was designed by Jacob Roman and Johan van Swieten and was b ...
in the Netherlands
* List of works of art at Hampton Court Palace
* Treaty of Hampton Court (1562)
The Treaty of Hampton Court (also known as the Treaty of Richmond) was signed on 22 September 1562 between Queen Elizabeth and Huguenot leader Louis I de Bourbon, prince de Condé. The treaty was concluded by François de Beauvais, Seigneur de Br ...
, also known as the Treaty of Richmond, signed on 22 September 1562 between Queen Elizabeth and Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
leader Louis I de Bourbon, prince de Condé Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
* Hampton Court Maze
Hampton Court Maze is a hedge maze at Hampton Court Palace and the oldest surviving hedge maze in Britain.
Commissioned by King William III, the maze, which is about one-third of an acre, is planted in a trapezoid shape and was designed by ...
Notes
References
* * * * * Williams, Neville (1971). ''Royal Homes''.Lutterworth Press
The Lutterworth Press, one of the oldest independent British publishing houses, has traded since the late eighteenth century - initially as the Religious Tract Society (RTS). The Lutterworth imprint, named after the small English town of Lutte ...
. .
External links
*Historic photos of Hampton Court Palace
by
Walter Jerrold
Walter Copeland Jerrold (3 May 1865 – 27 October 1929) was an English writer, biographer and newspaper editor.
Early life
Jerrold was born in Liverpool, the son of Thomas Serle Jerrold and Jane Matilda Copeland (who were first cousins), and on ...
Hampton Court Palace entry from The DiCamillo Companion to British & Irish Country Houses
– there are full floor plans of the palace on pages 10–13
Aerial photo and map of the Palace - Google Maps
{{Authority control Buildings and structures on the River Thames Christopher Wren buildings in London Country houses in London Edward Blore buildings Episcopal palaces of archbishops of York Gardens in London Grade I listed buildings in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Grade I listed gates Grade I listed museum buildings Grade I listed parks and gardens in London Historic house museums in London Historic Royal Palaces History of Middlesex History of the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Houses in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Mazes in the United Kingdom Middlesex Museums in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Museums on the River Thames Nicholas Hawksmoor buildings Royal buildings in London Royal residences in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames Royal residences in the United Kingdom Tudor royal palaces in England Venues of the 2012 Summer Olympics