Halide minerals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Halide minerals are those 
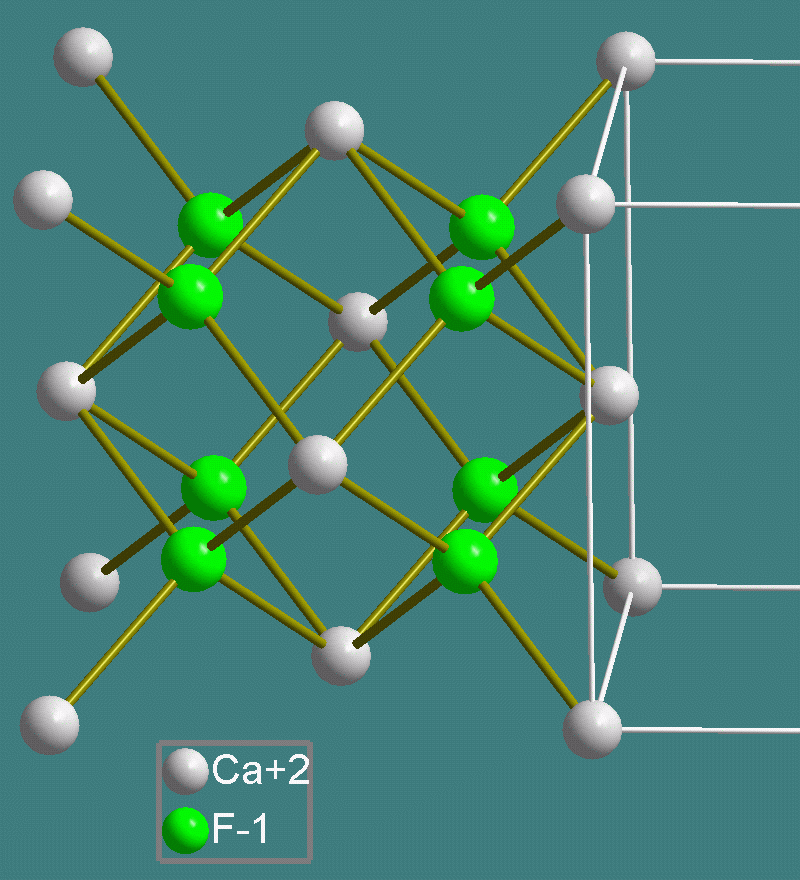 Examples include the following:
* Atacamite
*
Examples include the following:
* Atacamite
*Handbook of Mineralogy - Cryptohalite
. * Dietzeite * Eglestonite * Embolite AgCl+AgBr * Eriochalcite * Fluorite *
## x'': Nickel–Strunz mineral/group number; ''x'' an add-on letter
 * 03.A Simple halides, without H2O
** 03.AA M:X = 1:1, 2:3, 3:5, etc.: Panichiite; 05 Nantokite, 05
* 03.A Simple halides, without H2O
** 03.AA M:X = 1:1, 2:3, 3:5, etc.: Panichiite; 05 Nantokite, 05
Handbook of Mineralogy
{{Strunz *
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s with a dominant halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a flu ...
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
(, , and ). Complex halide minerals may also have polyatomic anions.

Avogadrite
Avogadrite ((K,Cs)BF4) is a potassium-caesium tetrafluoroborate in the halide class. Avogadrite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group ''Pnma'') with cell parameters ''a'' 8.66 Å, ''b'' 5.48 Å and ''c'' Å 7.03.
History
The miner ...
(K,Cs)BF
* Bararite (β)
* Bischofite
* Brüggenite
* Calomel
*Carnallite
Carnallite (also carnalite) is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula KMgCl3·6(H2O). It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rar ...
*Carnallite
Carnallite (also carnalite) is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula KMgCl3·6(H2O). It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rar ...
* Cerargyrite/Horn silver
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
AgCl
*Chlorargyrite
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
AgCl, bromargyrite
Bromyrite or bromargyrite is a natural mineral form of silver bromide found mainly in Mexico and Chile. Hardness is 1.5 to 2. Related are chlorargyrite and iodyrite.
It was first described in 1859 for an occurrence in Plateros, Zacatecas, Mex ...
AgBr, and iodargyrite AgI
* Cryolite
* Cryptohalite (a). * Dietzeite * Eglestonite * Embolite AgCl+AgBr * Eriochalcite * Fluorite *
Halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
NaCl
* Lautarite
*Marshite
Marshite (CuI) is a naturally occurring isometric halide mineral with occasional silver (Ag) substitution for copper (Cu).Prior, G.T. (1902“The identity of kilbrickenite with geocronite: And analyses of miersite, marshite, and copper-pyrites” ...
CuI
* Miersite AgI
* Nantokite CuCl
* Sal Ammoniac
*Sylvite
Sylvite, or sylvine, is potassium chloride (KCl) in natural mineral form. It forms crystals in the isometric system very similar to normal rock salt, halite ( NaCl). The two are, in fact, isomorphous. Sylvite is colorless to white with shades o ...
KCl
* Terlinguaite
* Tolbachite
*Villiaumite
Villiaumite is a rare halide mineral composed of sodium fluoride, Na F. It is very soluble in water and some specimens fluoresce under long and short wave ultraviolet light. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and is usually red, pink, or orange in col ...
NaF
*Yttrocerite
Yttrocerite is a variety of the mineral fluorite with a chemical formula Ca F2+( Y, Ce) F3. It is bluish red with isometric crystals and is named for the yttrium and cerium it contains. It has a Mohs hardness of 4–5. It has been found in Swede ...
(Ca,Y,Ce)F2
* Yttrofluorite (Ca,Y)F2
Many of these minerals are water-soluble and are often found in arid areas in crusts and other deposits as are various borates, nitrates, iodates, bromates and the like. Others, such as the fluorite group, are not water-soluble. As a collective whole, simple halide minerals (containing fluorine through iodine, alkali metals, alkaline Earth metals, in addition to other metals/cations) occur abundantly at the surface of the Earth in a variety of geologic settings. More complex minerals as shown below are also found.Sorrel, Charles A., ''Rocks & Minerals'' (originally ''Minerals of the World''), Chapter "Halides", pp. 118–127, 1973, St Martin's Press: NYC · Racine, WI, .
Commercially significant halide minerals
Two commercially important halide minerals are halite and fluorite. The former is a major source of sodium chloride, in parallel with sodium chloride extracted from sea water or brine wells. Fluorite is a major source ofhydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock ...
, complementing the supply obtained as a byproduct of the production of fertilizer. Carnallite and bischofite are important sources of magnesium. Natural cryolite was historically required for the production of aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
, however, currently most cryolite used is produced synthetically.
Many of the halide minerals occur in marine evaporite deposits. Other geologic occurrences include arid environments such as deserts. The Atacama Desert has large quantities of halide minerals as well as chlorates, iodates, oxyhalides, nitrates, borates and other water-soluble minerals. Not only do those minerals occur in subsurface geologic deposits, they also form crusts on the Earth's surface due to the low rainfall (the Atacama is the world's driest desert as well as one of the oldest at 25 million years of age).
Nickel–Strunz Classification -03- Halides
IMA-CNMNC proposes a new hierarchical scheme (Mills et al., 2009). This list uses the Classification of Nickel–Strunz (mindat.org
Mindat.org is a non-commercial online database, claiming to be the largest mineral database and mineralogical reference website on the Internet. It is used by professional mineralogists, geologists, and amateur mineral collectors alike.
The ...
, 10 ed, pending publication).
;Abbreviations:
* ''REE'': rare-earth element (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)
* ''PGE'': platinum-group element (Ru, Rh, Pd, Os, Ir, Pt)
* ''*'' : discredited (IMA/CNMNC status)
* ''?'' : questionable/doubtful (IMA/CNMNC status)
Regarding 03.C Aluminofluorides, 06 Borates, 08 Vanadates (04.H V ,6/sup> Vanadates), 09 Silicates:
* ''neso-'': insular (from Greek , "island")
* ''soro-'': grouped (from Greek , "heap, pile, mound")
* ''cyclo-'': ringed (from Greek , "circle")
* ''ino-'': chained (from Greek , "fibre", rom Ancient Greek
* ''phyllo-'': sheeted (from Greek , "leaf")
* ''tecto-'': of three-dimensional framework (from Greek , "of building")
;Nickel–Strunz code scheme ''NN.XY.##x'':
* ''NN'': Nickel–Strunz mineral class number
* ''X'': Nickel–Strunz mineral division letter
* ''Y'': Nickel–Strunz mineral family letter
* ''Class: halides
 * 03.A Simple halides, without H2O
** 03.AA M:X = 1:1, 2:3, 3:5, etc.: Panichiite; 05 Nantokite, 05
* 03.A Simple halides, without H2O
** 03.AA M:X = 1:1, 2:3, 3:5, etc.: Panichiite; 05 Nantokite, 05 Marshite
Marshite (CuI) is a naturally occurring isometric halide mineral with occasional silver (Ag) substitution for copper (Cu).Prior, G.T. (1902“The identity of kilbrickenite with geocronite: And analyses of miersite, marshite, and copper-pyrites” ...
, 05 Miersite; 10 Iodargyrite, 10 Tocornalite; 15 Bromargyrite
Bromyrite or bromargyrite is a natural mineral form of silver bromide found mainly in Mexico and Chile. Hardness is 1.5 to 2. Related are chlorargyrite and iodyrite.
It was first described in 1859 for an occurrence in Plateros, Zacatecas, Mex ...
, 15 Embolite*, 15 Chlorargyrite
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
; 20 Carobbiite
Carobbiite, chemical formula KF (potassium fluoride), is a rare, soft (Mohs 2 - 2.5), colourless cubic mineral. It is found at Monte Somma, Somma-Vesuvius Complex, Province of Naples, Campania, Italy. It was discovered in 1956 by Italian geologi ...
, 20 Griceite, 20 Halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
, 20 Sylvite
Sylvite, or sylvine, is potassium chloride (KCl) in natural mineral form. It forms crystals in the isometric system very similar to normal rock salt, halite ( NaCl). The two are, in fact, isomorphous. Sylvite is colorless to white with shades o ...
, 20 Villiaumite
Villiaumite is a rare halide mineral composed of sodium fluoride, Na F. It is very soluble in water and some specimens fluoresce under long and short wave ultraviolet light. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and is usually red, pink, or orange in col ...
; 25 Sal ammoniac, 25 Lafossaite; 30 Calomel, 30 Kuzminite, 30 Moschelite; 35 Neighborite
Neighborite is a mineral composed of a double fluoride salt of sodium and magnesium. It was initially recognized as pink and brown masses of round grains in the Green River Formation South of Ouray, Utah. Originally found in dark dolomitic oil sha ...
; 40 Chlorocalcite
Chlorocalcite is a rare potassium calcium chloride evaporite mineral with formula: KCaCl3. It is found in active volcanic fumaroles.
It was first described in 1872 for an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius and given the name for its calcium content pr ...
, 45 Kolarite, 50 Radhakrishnaite; 55 Hephaistosite, 55 Challacolloite
Challacolloite, KPb2Cl5, is a rare halide mineral. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (with space group ''P21/c'') and occurs as white fumarolic encrustations on lava. It occurs as intergrowths with cotunnite.
It was first described from a ...
** 03.AB M:X = 1:2: 05 Tolbachite, 10 Coccinite
Coccinite is a rare mercury iodide mineral with chemical formula of HgI2, mercury(II) iodide.
It was first discovered in Casas Viejas, Mexico; it has also been reported from Broken Hill, New South Wales, and from a uranium mine in Thuringia and ol ...
, 15 Sellaite; 20 Chloromagnesite*, 20 Lawrencite, 20 Scacchite; 25 Frankdicksonite, 25 Fluorite; 30 Tveitite-(Y); 35 Gagarinite-(Y); 35 Zajacite-(Ce)
Gagarinite-(Ce) previously zajacite-(Ce) is a rare radioactive fluoride mineral with formula Na( REE''x'' Ca1−''x'')(REE''y''Ca1−''y'') F6. REE refers to rare-earth elements, mostly those belonging to the lanthanide series. It crystallizes in ...
** 03.AC M:X = 1:3: 05 Zharchikhite, 10 Molysite; 15 Fluocerite
Fluocerite, also known as tysonite, is a mineral consisting of cerium and lanthanum fluorides, with the chemical formula . The end members are classified as two different mineral types depending on the cation, fluocerite-(Ce) and fluocerite-(La), ...
-(Ce), 15 Fluocerite-(La), 20 Gananite
* 03.B Simple Halides, with H2O
** 03.BA M:X = 1:1 and 2:3: 05 Hydrohalite
Hydrohalite is a mineral that occurs in saturated halite brines at cold temperatures (below 0.1 °C). It was first described in 1847 in Dürrnberg, Austria. It exists in cold weather.
Hydrohalite has a high nucleation energy, and solutions ...
, 10 Carnallite
Carnallite (also carnalite) is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula KMgCl3·6(H2O). It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rar ...
** 03.BB M:X = 1:2: 05 Eriochalcite, 10 Rokuhnite, 15 Bischofite, 20 Nickelbischofite, 25 Sinjarite, 30 Antarcticite, 35 Tachyhydrite
Tachyhydrite is an unstable mineral, a hydrous chloride of calcium and magnesium with formula: Ca Mg2 Cl6·12 H2O. It is a rare component of marine evaporite salt deposits. Upon exposure to moist air it rapidly deliquesces and dissolves.
It fo ...
** 03.BC M:X = 1:3: 05 Chloraluminite
** 03.BD Simple Halides with H2O and additional OH: 05 Cadwaladerite, 10 Lesukite, 15 Korshunovskite, 20 Nepskoeite, 25 Koenenite
* 03.C Complex Halides
** 03.C: Steropesite, IMA2008-032, IMA2008-039
** 03.CA Borofluorides: 05 Ferruccite; 10 Avogadrite
Avogadrite ((K,Cs)BF4) is a potassium-caesium tetrafluoroborate in the halide class. Avogadrite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group ''Pnma'') with cell parameters ''a'' 8.66 Å, ''b'' 5.48 Å and ''c'' Å 7.03.
History
The miner ...
, 10 Barberiite
** 03.CB Neso-aluminofluorides: 05 Cryolithionite; 15 Cryolite, 15 Elpasolite, 15 Simmonsite; 20 Colquiriite, 25 Weberite, 30 Karasugite, 35 Usovite; 40 Pachnolite, 40 Thomsenolite; 45 Carlhintzeite, 50 Yaroslavite
** 03.CC Soro-aluminofluorides: 05 Gearksutite; 10 Acuminite
Acuminite is a rare halide mineral with chemical formula: Sr Al F4( OH)·( H2O). Its name comes from the Latin word ''acumen'', meaning "spear point". Its Mohs scale rating is 3.5.
Acumenite has only been described from its type locality of t ...
, 10 Tikhonenkovite; 15 Artroeite; 20 Calcjarlite, 20 Jarlite, 20 Jorgensenite
** 03.CD Ino-aluminofluorides: 05 Rosenbergite, 10 Prosopite
** 03.CE Phyllo-aluminofluorides: 05 Chiolite
** 03.CF Tekto-aluminofluorides: 05 Ralstonite, 10 Boldyrevite?, 15 Bogvadite
** 03.CG Aluminofluorides with CO3, SO4, PO4: 05 Stenonite; 10 Chukhrovite-(Nd), 10 Chukhrovite-(Ce), 10 Chukhrovite-(Y), 10 Meniaylovite; 15 Creedite, 20 Boggildite, 25 Thermessaite
** 03.CH: 05 Malladrite, 10 Bararite; 15 Cryptohalite, 15 Hieratite; 20 Demartinite, 25 Knasibfite
** 03.CJ With MX6 complexes; M = Fe, Mn, Cu: 05 Chlormanganokalite, 05 Rinneite; 10 Erythrosiderite, 10 Kremersite; 15 Mitscherlichite
Potassium tetrachloridocuprate(II) is a salt (chemistry), salt with chemical formula , also written as ()2·[]2−.
The compound is often found as the dihydrate ·2, which is a brilliant greenish blue crystalline solid. This form also occurs natu ...
, 20 Douglasite, 30 Zirklerite
* 03.D Oxyhalides, Hydroxyhalides and Related Double Halides
** 03.DA With Cu, etc., without Pb: 05 Melanothallite; 10a Atacamite, 10a Kempite, 10a Hibbingite, 10b Botallackite, 10b Clinoatacamite, 10b Belloite, 10c Gillardite, 10c Kapellasite, 10c Haydeeite, 10c Paratacamite
Paratacamite is a mineral in the halide minerals category. Its chemical formula is . Its name is derived from its association with atacamite.
It is found in Chile, Botallack Mine in Cornwall, Broken Hill, Australia, and in Italy in Capo Calamita o ...
, 10c Herbertsmithite
Herbertsmithite is a mineral with chemical structure Zn Cu3( OH)6 Cl2. It is named after the mineralogist Herbert Smith (1872–1953) and was first found in 1972 in Chile. It is polymorphous with kapellasite and closely related to paratacami ...
; 15 Claringbullite, 20 Simonkolleite
Zinc chloride hydroxide monohydrate is a zinc hydroxy compound with chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound ...
; 25 Buttgenbachite, 25 Connellite; 30 Abhurite, 35 Ponomarevite; 40 Calumetite, 40 Anthonyite; 45 Khaidarkanite, 50 Bobkingite, 55 Avdoninite, 60 Droninoite
** 03.DB With Pb, Cu, etc.: 05 Diaboleite, 10 Pseudoboleite, 15 Boleite, 20 Cumengite, 25 Bideauxite, 30 Chloroxiphite
Chloroxiphite is a rare olive green to pistacio green lead copper halide mineral with formula: Pb3CuO2Cl2(OH)2.
It was first discovered in 1923 in the Mendip Hills, Somerset, England associated with mendipite. Like mendipite it is an oxychloride ...
, 35 Hematophanite; 40 Asisite, 40 Parkinsonite; 45 Murdochite, 50 Yedlinite
** 03.DC With Pb (As, Sb, Bi), without Cu: 05 Laurionite, 05 Paralaurionite; 10 Fiedlerite, 15 Penfieldite, 20 Laurelite; 25 Zhangpeishanite, 25 Matlockite, 25 Rorisite, 25 Daubreeite, 25 Bismoclite
Bismoclite is a bismuth oxohalide mineral with formula BiOCl. It is the naturally occurring form of bismuth oxychloride. The name was derived from its chemical constituents. It is a secondary bismuth mineral first thought to be composed of bismuth ...
, 25 Zavaritskite; 30 Nadorite, 30 Perite; 35 Aravaipaite, 37 Calcioaravaipaite, 40 Thorikosite, 45 Mereheadite, 50 Blixite, 55 Pinalite
Pinalite is a rare lead tungstate–chloride mineral with formula: Pb3WO5Cl2.
Pinalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. The orthorhombic system is described as having three crystallographic axes of unequal lengths, normally ref ...
, 60 Symesite; 65 Ecdemite, 65 Heliophyllite; 70 Mendipite
Mendipite is a rare mineral that was named in 1939 for the locality where it is found, the Mendip Hills in Somerset, England. It is an oxyhalide of lead with formula Pb3Cl2O2.
Crystal structure
Most references assert that mendipite crystallise ...
, 75 Damaraite, 80 Onoratoite, 85 Cotunnite
Cotunnite is the natural mineral form of lead(II) chloride with formula PbCl2.
It was first described in 1825 from an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius, Naples Province, Campania, Italy. It was named for Domenico Cotugno (Cotunnius) (1736–1822), I ...
, 90 Pseudocotunnite, 95 Barstowite
** 03.DD With Hg: 05 Eglestonite, 05 Kadyrelite; 10 Poyarkovite, 15 Hanawaltite, 20 Terlinguaite, 25 Pinchite; 30 Mosesite, 30 Gianellaite; 35 Kleinite, 40 Tedhadleyite, 45 Vasilyevite, 50 Aurivilliusite, 55 Terlinguacreekite, 60 Kelyanite, 65 Comancheite
** 03.DE With Rare-Earth Elements: 05 Haleniusite-(La)
* 03.X Unclassified Strunz Halogenides
** 03.XX Unknown: 00 Hydrophilite?, 00 Hydromolysite?, 00 Yttrocerite
Yttrocerite is a variety of the mineral fluorite with a chemical formula Ca F2+( Y, Ce) F3. It is bluish red with isometric crystals and is named for the yttrium and cerium it contains. It has a Mohs hardness of 4–5. It has been found in Swede ...
*, 00 Lorettoite?, 00 IMA2009-014, 00 IMA2009-015
References
* * *External links
Handbook of Mineralogy
{{Strunz *