Habsburg-Valois Wars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into
 Largely driven by the rivalry between the
Largely driven by the rivalry between the
 The war began when Ludovico Sforza, then Regent of Milan, encouraged Charles VIII of France to invade Italy, using the
The war began when Ludovico Sforza, then Regent of Milan, encouraged Charles VIII of France to invade Italy, using the
 The next phase of the conflict originated in the long-standing rivalry between Florence and the
The next phase of the conflict originated in the long-standing rivalry between Florence and the  Florence now asked for French assistance in retaking Pisa, a request Louis was in no hurry to fulfil since they had refused to support his capture of Milan. He was also initially occupied in defeating efforts to regain his duchy by Ludovico, who was captured at Novaro in April 1500 and spent the rest of his life in a French prison. However, Louis needed to maintain good relations with Florence, whose territory he would have to cross in order to conquer Naples, and on 29 June 1500 a combined Franco-Florentine army appeared outside Pisa. Once again, the French artillery quickly opened a gap in the walls but several assaults were repulsed and the siege was abandoned on 11 July.
With Milan firmly in his control, Louis returned to France and left the Florentines to blockade Pisa, which eventually surrendered in 1509. Anxious to begin the conquest of Naples, on 11 November he signed the
Florence now asked for French assistance in retaking Pisa, a request Louis was in no hurry to fulfil since they had refused to support his capture of Milan. He was also initially occupied in defeating efforts to regain his duchy by Ludovico, who was captured at Novaro in April 1500 and spent the rest of his life in a French prison. However, Louis needed to maintain good relations with Florence, whose territory he would have to cross in order to conquer Naples, and on 29 June 1500 a combined Franco-Florentine army appeared outside Pisa. Once again, the French artillery quickly opened a gap in the walls but several assaults were repulsed and the siege was abandoned on 11 July.
With Milan firmly in his control, Louis returned to France and left the Florentines to blockade Pisa, which eventually surrendered in 1509. Anxious to begin the conquest of Naples, on 11 November he signed the
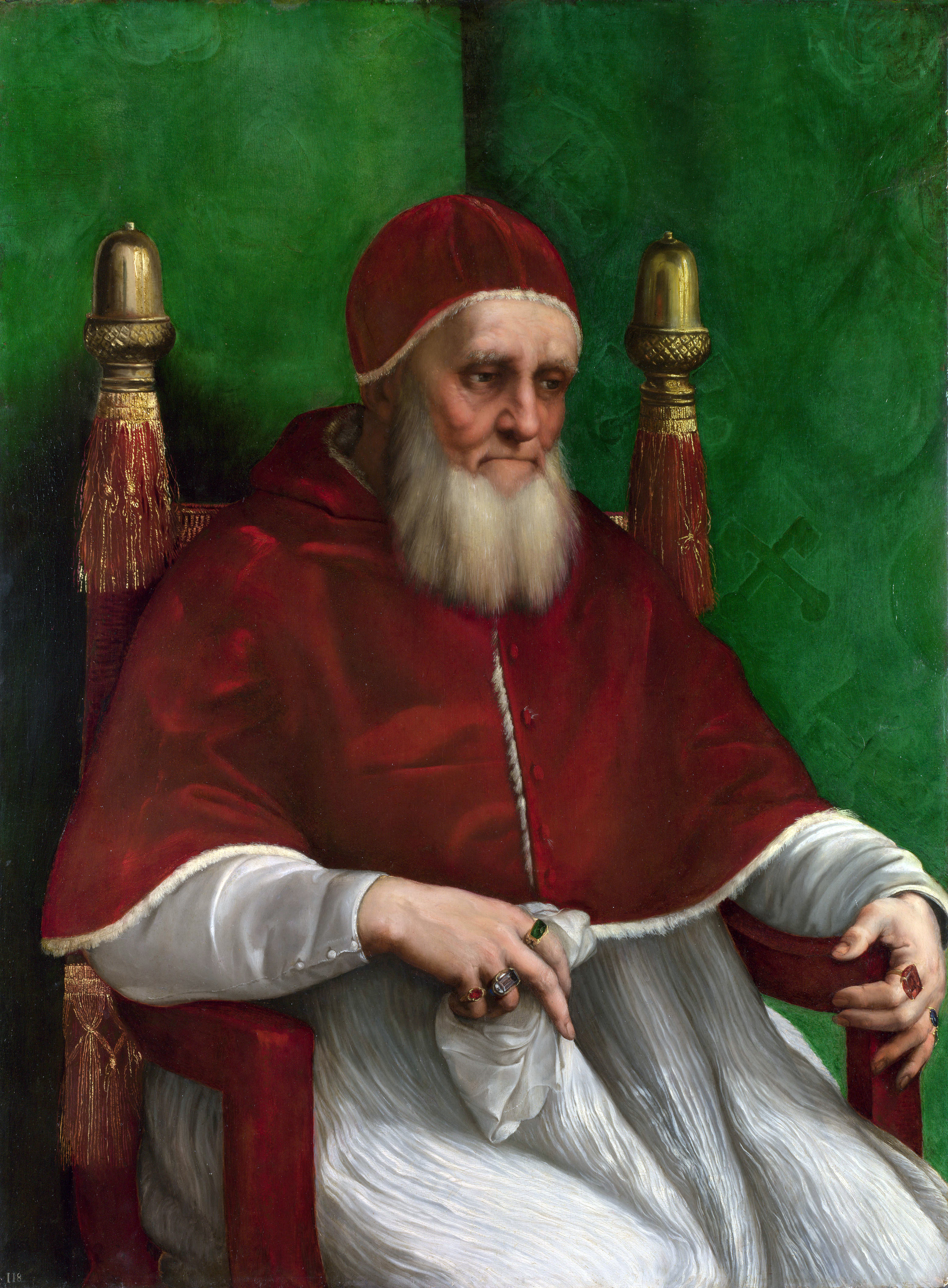 On 18 October 1503, Pius III was replaced by
On 18 October 1503, Pius III was replaced by
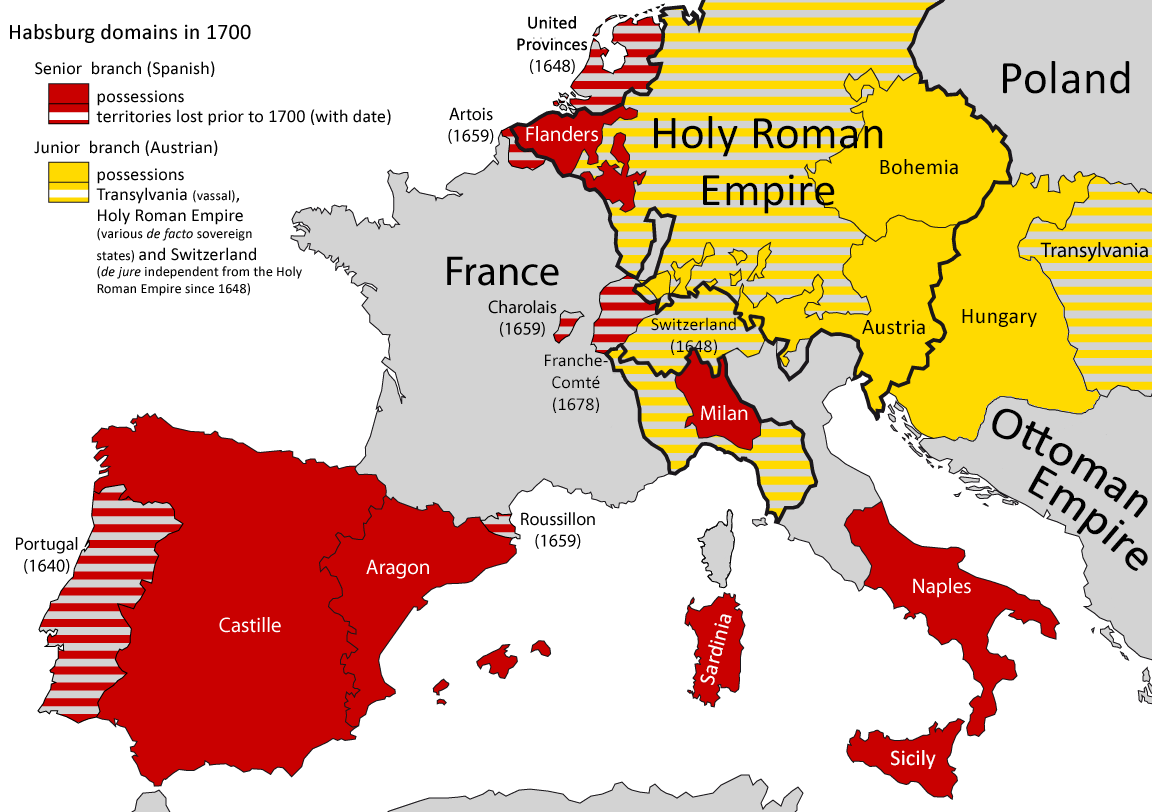 Following the death of Maximilian in January 1519, the
Following the death of Maximilian in January 1519, the
 Under the Treaty of Cambrai, Francesco Sforza was reinstated as Duke of Milan; since he had no children, it also stated Charles V would inherit the duchy on his death, which occurred on 1 November 1535. Francis refused to accept this, arguing Milan was rightfully his along with Genoa and Asti, and once again prepared for war. In April 1536, pro-Valois elements in Asti expelled the Imperial garrison and a French army under Philippe de Chabot occupied Turin, although they failed to take Milan.
In response, a Spanish army invaded
Under the Treaty of Cambrai, Francesco Sforza was reinstated as Duke of Milan; since he had no children, it also stated Charles V would inherit the duchy on his death, which occurred on 1 November 1535. Francis refused to accept this, arguing Milan was rightfully his along with Genoa and Asti, and once again prepared for war. In April 1536, pro-Valois elements in Asti expelled the Imperial garrison and a French army under Philippe de Chabot occupied Turin, although they failed to take Milan.
In response, a Spanish army invaded
 The 1538 truce failed to resolve underlying tensions between Francis, who still claimed Milan, and Charles, who insisted he comply with the treaties of Madrid and Cambrai. Their relationship collapsed in 1540 when Charles made his son Philip II of Spain, Philip Duke of Milan, thus precluding any possibility it would revert to France. In 1541, Charles made a disastrous attack on Ottoman port of Algiers expedition (1541), Algiers, which severely weakened his military and led Suleiman to reactivate his French alliance. With Ottoman support, on 12 July 1542 Francis once again declared war on the Holy Roman Empire, initiating the Italian War of 1542–46.
In August, French armies attacked Siege of Perpignan (1542), Perpignan on the Spanish border, as well as Artois, Flanders and Duchy of Luxemburg, Luxemburg, a Valois possession prior to 1477. Imperial resistance proved far more formidable than expected, with most of these attacks easily repulsed and in 1543 Henry VIII allied with Charles and agreed to support his offensive in Flanders. Neither side made much progress, and although a combined Franco-Ottoman fleet under Hayreddin Barbarossa captured Nice on 22 August and besieged the citadel, the onset of winter and presence of a Spanish fleet forced them to withdraw. A joint attack by Christian and Islamic troops on a Christian town was regarded as shocking, especially when Francis allowed Barbarossa to use the French port of
The 1538 truce failed to resolve underlying tensions between Francis, who still claimed Milan, and Charles, who insisted he comply with the treaties of Madrid and Cambrai. Their relationship collapsed in 1540 when Charles made his son Philip II of Spain, Philip Duke of Milan, thus precluding any possibility it would revert to France. In 1541, Charles made a disastrous attack on Ottoman port of Algiers expedition (1541), Algiers, which severely weakened his military and led Suleiman to reactivate his French alliance. With Ottoman support, on 12 July 1542 Francis once again declared war on the Holy Roman Empire, initiating the Italian War of 1542–46.
In August, French armies attacked Siege of Perpignan (1542), Perpignan on the Spanish border, as well as Artois, Flanders and Duchy of Luxemburg, Luxemburg, a Valois possession prior to 1477. Imperial resistance proved far more formidable than expected, with most of these attacks easily repulsed and in 1543 Henry VIII allied with Charles and agreed to support his offensive in Flanders. Neither side made much progress, and although a combined Franco-Ottoman fleet under Hayreddin Barbarossa captured Nice on 22 August and besieged the citadel, the onset of winter and presence of a Spanish fleet forced them to withdraw. A joint attack by Christian and Islamic troops on a Christian town was regarded as shocking, especially when Francis allowed Barbarossa to use the French port of
 The European balance of power changed significantly during the Italian Wars. The affirmation of French power in Italy around 1494 brought Austria and Spain to join an anti-French league that formed the "Habsburg ring" around France (Low Countries, Aragon, Castile, Empire) via dynastic marriages that eventually led to the large inheritance of Charles V. On the other hand, the last Italian war ended with the division of the Habsburg Empire between the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs following the abdication of Charles V. Philip II of Spain was heir of the kingdoms held by Charles V in Spain, southern Italy, and South America. Ferdinand I was the successor of Charles V in the Holy Roman Empire extending from Germany to northern Italy and became ''suo jure'' king of the Habsburg monarchy. The Habsburg Netherlands and the Duchy of Milan were left in personal union to the king of Spain while continuing to be part of the Holy Roman Empire.
The division of the empire of Charles V, along with the expansion of the French state over the Pas-de-Calais and the
The European balance of power changed significantly during the Italian Wars. The affirmation of French power in Italy around 1494 brought Austria and Spain to join an anti-French league that formed the "Habsburg ring" around France (Low Countries, Aragon, Castile, Empire) via dynastic marriages that eventually led to the large inheritance of Charles V. On the other hand, the last Italian war ended with the division of the Habsburg Empire between the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs following the abdication of Charles V. Philip II of Spain was heir of the kingdoms held by Charles V in Spain, southern Italy, and South America. Ferdinand I was the successor of Charles V in the Holy Roman Empire extending from Germany to northern Italy and became ''suo jure'' king of the Habsburg monarchy. The Habsburg Netherlands and the Duchy of Milan were left in personal union to the king of Spain while continuing to be part of the Holy Roman Empire.
The division of the empire of Charles V, along with the expansion of the French state over the Pas-de-Calais and the Legacies of the Italian Wars
/ref> The most significant Italian power left was the Papacy in central Italy, as it maintained major baroque, cultural and political influence during the Catholic Reformation. The Council of Trent, suspended during the war, was reconvened by the terms of the peace treaties and came to an end in 1563.
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. The primary belligerents were the Valois kings of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, and their Habsburg opponents in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. They were supported by various Italian states
Italy, up until the Italian unification in 1861, was a conglomeration of city-states, republics, and other independent entities. The following is a list of the various Italian states during that period. Following the fall of the Western Roman Em ...
at different stages of the war, with limited involvement from England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
The Italic League
The Italic League or Most Holy League was an international agreement concluded in Venice on 30 August 1454, between the Papal States, the Republic of Venice, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, and the Kingdom of Naples, following the T ...
established in 1454 achieved a balance of power in Italy, but fell apart after the death of its chief architect, Lorenzo de' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (; 1 January 1449 – 8 April 1492) was an Italian statesman, banker, ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic and the most powerful and enthusiastic patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Also known as Lorenzo ...
, in 1492. Combined with the ambition of Ludovico Sforza, its collapse allowed Charles VIII of France to invade Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
in 1494, which drew in Spain and the Holy Roman Empire. Despite being forced to withdraw in 1495, Charles showed the Italian states were wealthy, but vulnerable due to political divisions, making parts of Italy a battleground in the struggle for European domination between France and the Habsburgs.
Fought with considerable brutality, the wars took place against the background of religious turmoil caused by the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, particularly in France and the Holy Roman Empire. They are seen as a turning point in the evolution from medieval to modern warfare, with the use of the arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
or handgun becoming common, along with significant technological improvements in siege artillery. Literate commanders and modern printing methods also make them one of the first conflicts with a significant number of contemporary accounts, including those of Francesco Guicciardini
Francesco Guicciardini (; 6 March 1483 – 22 May 1540) was an Italian historian and statesman. A friend and critic of Niccolò Machiavelli, he is considered one of the major political writers of the Italian Renaissance. In his masterpiece, ''Th ...
, Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
and Blaise de Montluc
Blaise de Monluc, also known as Blaise de Lasseran-Massencôme, seigneur de Monluc, (24 July 1577) was a professional soldier whose career began in 1521 and reached the rank of marshal of France in 1574. Written between 1570 and 1576, an account o ...
.
After 1503, most of the fighting was initiated by French invasions of Lombardy and Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, but although able to hold territory for periods of time, they could not do so permanently. By 1557, both France and the Empire were confronted by internal divisions over religion, while Spain faced a potential revolt in the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the H ...
. The Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis (1559) largely expelled France from northern Italy, gaining in exchange Calais and the Three Bishoprics
The Three Bishoprics (french: les Trois-Évêchés ) constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the ...
; it established Spain as the dominant power in the south, controlling Naples and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, as well as Milan in the north.
Background
 Largely driven by the rivalry between the
Largely driven by the rivalry between the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
and Duchy of Milan, the long-running Wars in Lombardy
The Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy and ...
had finally been ended by the 1454 Treaty of Lodi
The Treaty of Lodi, or Peace of Lodi, was a peace agreement between Milan, Naples and Florence that was signed on 9 April 1454 at Lodi in Lombardy, on the banks of the Adda. It put an end to the Wars in Lombardy between expansive Milan, under ...
. Followed shortly thereafter by a non-aggression pact known as the Italic League
The Italic League or Most Holy League was an international agreement concluded in Venice on 30 August 1454, between the Papal States, the Republic of Venice, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, and the Kingdom of Naples, following the T ...
, it led to a forty year period of stability and economic expansion, marred only by the 1479 to 1481 Pazzi conspiracy and 1482 to 1484 War of Ferrara
The War of Ferrara (also known as the Salt War, Italian: ''Guerra del Sale'') was fought in 1482–1484 between Ercole I d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, and the Papal forces mustered by Ercole's personal nemesis, Pope Sixtus IV and his Venetian allies. ...
. The League's main supporter was the Florentine ruler Lorenzo de' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (; 1 January 1449 – 8 April 1492) was an Italian statesman, banker, ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic and the most powerful and enthusiastic patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Also known as Lorenzo ...
, who also pursued a policy of excluding France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
from the Italian peninsula.
Lorenzo's death in April 1492 severely weakened the League at a time when France was seeking to expand in Italy. This originated when Louis XI of France inherited the County of Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
from his cousin Charles IV of Anjou
Charles IV, Duke of Anjou, also Charles of Maine, Count of Le Maine and Guise (1446 – 10 December 1481) was the son of the Angevin prince Charles of Le Maine, Count of Maine and Isabelle of Luxembourg.
He succeeded his father as Count of Maine ...
in 1481, along with the Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
**Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
* House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
claim to the Kingdom of Naples. His son Charles VIII succeeded him in 1483 and formally incorporated Provence into France in 1486; its ports of Marseilles and Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
provided direct access to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
and thus the ability to pursue his territorial ambitions.
In the run-up to the First Italian War
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number 1 (number), one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, D ...
, Charles sought to secure the neutrality of other European rulers through a series of treaties. These included the November 1492 Peace of Étaples
The Peace of Étaples was signed on 3 November 1492 in Étaples between Charles VIII of France and Henry VII of England. Charles agreed to end his support for the Yorkist Pretender Perkin Warbeck, in return for being recognised as ruler of the D ...
with Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henry's mother, Margaret Beauf ...
and the March 1493 Treaty of Barcelona with Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death. He was never crowned by the pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself E ...
.
Italian War of 1494–1498
 The war began when Ludovico Sforza, then Regent of Milan, encouraged Charles VIII of France to invade Italy, using the
The war began when Ludovico Sforza, then Regent of Milan, encouraged Charles VIII of France to invade Italy, using the Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
**Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
* House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
claim to the throne of Naples as a pretext. This in turn was driven by the intense rivalry between Ludovico's wife, Beatrice d'Este
Beatrice d'Este (29 June 1475 – 3 January 1497), was Duchess of Bari and Milan by marriage to Ludovico Sforza (known as "il Moro"). She was one of the most important personalities of the time and, despite her short life, she was a major playe ...
, and that of his nephew Gian Galeazzo Sforza
Gian Galeazzo Sforza (20 June 1469 – 21 October 1494), also known as Giovan Galeazzo Sforza, was the sixth Duke of Milan.
Early life
Born in Abbiategrasso, he was only seven years old when in 1476 his father, Galeazzo Maria Sforza, was assa ...
, son of Isabella of Aragon. Despite being the hereditary Duke of Milan, Gian Galeazzo had been sidelined by his uncle in 1481 and exiled to Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
. Both women wanted to ensure their children inherited the Duchy and when Isabella's father became Alfonso II of Naples
Alfonso II (4 November 1448 – 18 December 1495) was Duke of Calabria and ruled as King of Naples from 25 January 1494 to 23 January 1495. He was a soldier and a patron of Renaissance architecture and the arts.
Heir to his father Fer ...
in January 1494, she asked for his help in securing their rights. In September Charles invaded the peninsula, which he justified by claiming he wanted to use Naples as a base for a crusade against the Ottoman Turks.
In October, Ludovico formally became Duke of Milan following the death of Gian Galeazzo, who was popularly supposed to have been poisoned by his uncle, and the French marched through Italy virtually unopposed, entering Pisa on 8 November, Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilan ...
on 17th, and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
on 31 December. Charles was backed by Girolamo Savonarola
Girolamo Savonarola, OP (, , ; 21 September 1452 – 23 May 1498) or Jerome Savonarola was an Italian Dominican friar from Ferrara and preacher active in Renaissance Florence. He was known for his prophecies of civic glory, the destruction of ...
, who used the opportunity to established a short-lived theocracy in Florence, while Pope Alexander VI allowed his army free passage through the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
.
In February 1495, the French reached Monte San Giovanni Campano
Monte San Giovanni Campano is a ''comune'' (municipality) of about 12,800 inhabitants in the province of Frosinone in the Italian region Lazio, located about southeast of Rome and about east of Frosinone. Monte San Giovanni Campano is in the Lat ...
in the Kingdom of Naples and despatched envoys to negotiate terms with its Neapolitan garrison, who murdered them and sent their mutilated bodies back to the French lines. On 9 February, the enraged besiegers breached the walls of the castle with artillery fire, then stormed it, killing everyone inside. Known as the "Sack of Naples", widespread outrage within Italy allied with concern over the power of France led to the formation of the League of Venice on March 31, 1495, an anti-French alliance composed of Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
, Milan, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
.
Later joined by Florence, following the overthrow of Savonarola, the Papal States and Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the Eur ...
, this coalition cut off Charles and his army from their bases in France. Charles' cousin, Louis d'Orleans, now tried to take advantage of Ludovico's change of sides to conquer Milan, which he claimed through his grandmother, Valentina Visconti. On 11 June, he captured Novara
Novara (, Novarese: ) is the capital city of the province of Novara in the Piedmont region in northwest Italy, to the west of Milan. With 101,916 inhabitants (on 1 January 2021), it is the second most populous city in Piedmont after Turin. It i ...
when the garrison defected, and reached Vigevano
Vigevano (; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Avgevan) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Pavia, Lombardy in northern Italy. A historic art town, it is also renowned for shoemaking and is one of the main centres of Lomellina, a rice-growing a ...
, forty kilometres from Milan. At this crucial point, Ludovico was incapacitated either by a stroke or nervous breakdown, while his unpaid soldiers were on the verge of mutiny. In his absence, his wife Beatrice d'Este took personal control of the Duchy and the siege of Novara, with Louis eventually forced to surrender in return for his freedom.
Having replaced Ferdinand II of Naples
Ferdinando Trastámara d'Aragona, of the branch of Naples, known to contemporaries especially with the name of Ferrandino (Naples, 26 June 1467 - Naples, 7 October 1496). Acclaimed "the first among all the Kings and Lords of the World" and univer ...
with a pro-French government, Charles turned north and on 6 July was intercepted by the League outside Fornovo di Taro. In the resulting Battle of Fornovo, the French forced their opponents back across the Taro river
The Taro (Latin ''Tarus'') is a river in Emilia-Romagna, in northern Italy. It is a tributary of the Po and is long. It flows almost entirely in the province of Parma, west of the city Parma. The Taro flows into the Po near Gramignazzo, a fraz ...
and continued onto Asti, leaving most of their supplies behind. Both sides claimed victory but the general consensus favoured the French, since the League suffered heavier casualties and failed to halt their retreat, the reason for fighting in the first place. In the south, despite some initial reverses, by September 1495 Ferdinand II had regained control of his kingdom. Although the French invasion achieved little, it showed the Italian states were rich and comparatively weak, making future intervention attractive to outside powers. Charles himself died on 7 April 1498, and was succeeded by the former Duke of Orleans, who became Louis XII.
Italian Wars of 1499–1504
 The next phase of the conflict originated in the long-standing rivalry between Florence and the
The next phase of the conflict originated in the long-standing rivalry between Florence and the Republic of Pisa
The Republic of Pisa ( it, Repubblica di Pisa) was an independent state centered on the Tuscan city of Pisa, which existed from the 11th to the 15th century. It rose to become an economic powerhouse, a commercial center whose merchants dominated ...
, which had been annexed by Florence in 1406 but took advantage of the French invasion to regain its independence in 1494. Despite Charles' retreat in 1495, Pisa continued to receive support from Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, Venice and Milan, all of whom were suspicious of Florentine power. In order to strengthen his own position, Ludovico once again invited an external power to settle an internal Italian affair, in this case Emperor Maximilian I
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death. He was never crowned by the pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself Ele ...
. In doing so, Maximilian hoped to bolster the League of Venice, which he viewed as an essential barrier to French intervention, but Florence was convinced he favoured Pisa and refused to accept mediation. To enforce a settlement, in July 1496 Maximilian besieged the Florentine city of Livorno, but withdrew in September due to shortages of men and supplies.
Following the death of Charles VIII in April 1498, Louis XII began planning another attempt on Milan, while also pursuing his predecessor's claim to the Kingdom of Naples. Aware of the hostility caused by French ambitions in Italy, in July 1498 he renewed the 1492 Peace of Étaples
The Peace of Étaples was signed on 3 November 1492 in Étaples between Charles VIII of France and Henry VII of England. Charles agreed to end his support for the Yorkist Pretender Perkin Warbeck, in return for being recognised as ruler of the D ...
with England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and signed a treaty confirming French borders with Burgundy. This was followed in August by the Treaty of Marcoussis
Marcoussis () is a commune in the southern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris.
Marcoussis is the location of the CNR (National Centre of Rugby) where the French national rugby union team prepare for internationa ...
with Ferdinand II of Aragon; although it did not address outstanding territorial disputes between the two countries, it agreed "have all enemies in common except the Pope." On 9 February 1499, Louis signed the Treaty of Blois, a military alliance with Venice against Ludovico.
With these agreements finalised, a French army of 27,000 under the Milanese exile Gian Giacomo Trivulzio invaded Lombardy, and in August besieged Rocca d'Arazzo, a fortified town in the western part of the Duchy of Milan. The French siege artillery breached the walls in less than five hours and after the town capitulated, Louis ordered the execution of its garrison and senior members of the civil administration. Other Milanese strongholds surrendered rather than face the same fate, while Ludovico, whose wife Beatrice had died in 1497, fled the duchy with his children and took refuge with Maximilian. On 6 October 1499, Louis made a triumphant entry into Milan.
 Florence now asked for French assistance in retaking Pisa, a request Louis was in no hurry to fulfil since they had refused to support his capture of Milan. He was also initially occupied in defeating efforts to regain his duchy by Ludovico, who was captured at Novaro in April 1500 and spent the rest of his life in a French prison. However, Louis needed to maintain good relations with Florence, whose territory he would have to cross in order to conquer Naples, and on 29 June 1500 a combined Franco-Florentine army appeared outside Pisa. Once again, the French artillery quickly opened a gap in the walls but several assaults were repulsed and the siege was abandoned on 11 July.
With Milan firmly in his control, Louis returned to France and left the Florentines to blockade Pisa, which eventually surrendered in 1509. Anxious to begin the conquest of Naples, on 11 November he signed the
Florence now asked for French assistance in retaking Pisa, a request Louis was in no hurry to fulfil since they had refused to support his capture of Milan. He was also initially occupied in defeating efforts to regain his duchy by Ludovico, who was captured at Novaro in April 1500 and spent the rest of his life in a French prison. However, Louis needed to maintain good relations with Florence, whose territory he would have to cross in order to conquer Naples, and on 29 June 1500 a combined Franco-Florentine army appeared outside Pisa. Once again, the French artillery quickly opened a gap in the walls but several assaults were repulsed and the siege was abandoned on 11 July.
With Milan firmly in his control, Louis returned to France and left the Florentines to blockade Pisa, which eventually surrendered in 1509. Anxious to begin the conquest of Naples, on 11 November he signed the Treaty of Granada
The Treaty of Granada, also known as the Capitulation of Granada or simply the Capitulations, was signed and ratified on November 25, 1491, between Boabdil, the sultan of Granada, and Ferdinand and Isabella, the King and Queen of Castile, Leó ...
with Ferdinand II of Aragon, an agreement to divide the kingdom between the two. Since Ferdinand had supported the expulsion of the French from Naples in 1495, Louis hoped these concessions would allow him to acquire the bulk of the kingdom without an expensive war. His action was criticised by contemporaries like Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
and modern historians, who argue the 1499 Treaty of Marcoussis already gave Louis everything he needed, while inviting Spain into Naples could only work to his detriment.
In July 1501, the French army reached Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrus ...
; strongly defended by forces loyal to Frederick of Naples
Frederick (April 19, 1452 – November 9, 1504), sometimes called Frederick IV or Frederick of Aragon, was the last King of Naples from the Neapolitan branch of the House of Trastámara, ruling from 1496 to 1501. He was the second son of Ferdinan ...
, it surrendered on 24 July after a short siege but was then sacked. In addition to the extensive material destruction, many women were subjected to mass rape and estimates of the dead ranged from 2,000 to 4,000, actions that caused consternation throughout Italy. Resistance crumbled as other towns tried to avoid the same fate and on 12 October Louis appointed the Duke of Nemours Duke of Nemours was a title in the Peerage of France. The name refers to Nemours in the Île-de-France region of north-central France.
History
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Lordship of Nemours, in the Gatinais, France, was a possession of t ...
his viceroy in Naples. However, the Treaty of Granada had left the ownership of key Neapolitan territories undecided and disputes over these quickly poisoned relationships between the two powers. This led to war in late 1502, which ended with the French being expelled from Naples once again after defeats at Cerignola
Cerignola (; nap, label= Cerignolano, Ceregnòule ) is a town and ''comune'' of Apulia, Italy, in the province of Foggia, southeast from the town of Foggia. It has the third-largest land area of any ''comune'' in Italy, at , after Rome and Ra ...
on 28 April 1503, and Garigliano
The Garigliano () is a river in central Italy.
It forms at the confluence of the rivers Gari (also known as the Rapido) and Liri. Garigliano is actually a deformation of "Gari-Lirano" (which in Italian means something like "Gari from the Liri") ...
on 29 December.
War of the League of Cambrai
 On 18 October 1503, Pius III was replaced by
On 18 October 1503, Pius III was replaced by Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or th ...
, who as ruler of the Papal States was concerned by Venetian power in northern Italy. This fear was shared by his home town of Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, which also resented its expulsion from the Po Valley, and Maximilian, whose acquisition of Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gori ...
in 1500 was threatened by Venetian possession of neighbouring Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
. Milan, controlled by Louis XII, was a long-standing opponent of Venice, while Ferdinand II, now king of Naples, wished to regain control of Venetian ports on the southern Adriatic coast. Along with the Duchy of Ferrara
The Duchy of Ferrara ( la, Ducatus Ferrariensis; it, Ducato di Ferrara; egl, Ducà ad Frara) was a state in what is now northern Italy. It consisted of about 1,100 km2 south of the lower Po River, stretching to the valley of the lower Reno ...
, Julius united these disparate interests into the anti-Venetian League of Cambrai
League or The League may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Leagues'' (band), an American rock band
* ''The League'', an American sitcom broadcast on FX and FXX about fantasy football
Sports
* Sports league
* Rugby league, full contact footba ...
, signed on 10 December 1508.
Although the French largely destroyed a Venetian army at Agnadello on 14 May 1509, Maximilian failed to capture Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
and withdrew from Italy. Now seeing the power of Louis XII as the greater threat, in February 1510 Pope Julius made peace with Venice, followed in March by an agreement with the Swiss Cantons
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss C ...
to supply him with 6,000 mercenaries. After a year of fighting in which Louis XII occupied large parts of the Papal States, in October 1511 Julius formed the anti-French Holy League, which included Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
, Maximilian and Spain.
A French army defeated the Spanish at Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the ca ...
on 11 April 1512, but their leader Gaston de Foix was killed, while the Swiss recaptured Milan and restored Ludovico's son Massimiliano Sforza as duke. The members of the League then fell out over dividing the spoils and the death of Pope Julius on 20 February 1513 left it without effective leadership. In March, Venice and France formed an alliance, but from June to September 1513 the League won victories at Novara
Novara (, Novarese: ) is the capital city of the province of Novara in the Piedmont region in northwest Italy, to the west of Milan. With 101,916 inhabitants (on 1 January 2021), it is the second most populous city in Piedmont after Turin. It i ...
and La Motta
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
in Lombardy, Guinegate in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
and Flodden
The Battle of Flodden, Flodden Field, or occasionally Branxton, (Brainston Moor) was a battle fought on 9 September 1513 during the War of the League of Cambrai between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland, resulting in an English ...
in England. Despite this, fighting continued in Italy, with neither side able to gain a decisive advantage.
On 1 January 1515, Louis XII died and was succeeded by his son-in-law, Francis I, who took up his predecessor's cause and routed the Swiss at Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was the last major engagement of the War of the League of Cambrai and took place on 13–14 September 1515, near the town now called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan. It pitted the French army, composed of the b ...
on 13-14 September 1515. Combined with the unpopularity of Massiliano Sforza, victory allowed Francis to retake Milan and the Holy League collapsed as both Spain and Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X ( it, Leone X; born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, 11 December 14751 December 1521) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 March 1513 to his death in December 1521.
Born into the prominent political an ...
saw little benefit in fighting on. In the treaty of Noyon
Noyon (; pcd, Noéyon; la, Noviomagus Veromanduorum, Noviomagus of the Veromandui, then ) is a commune in the Oise department, northern France.
Geography
Noyon lies on the river Oise, about northeast of Paris. The Oise Canal and the Cana ...
, signed on 13 August 1516, Charles I of Spain
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fro ...
acknowledged Francis as Duke of Milan, while Francis "passed" his claim to Naples onto Charles. Left isolated, in December Maximilian signed the Treaty of Brussels, which confirmed French possession of Milan.
Italian War of 1521–1526
 Following the death of Maximilian in January 1519, the
Following the death of Maximilian in January 1519, the German Princes
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
elected Charles I of Spain as Emperor Charles V on 28 June. This brought Spain, the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and the Holy Roman Empire under one ruler, and meant France was surrounded by the so-called "Habsburg ring". Francis I had also been a candidate for the Imperial throne, adding a personal dimension to his rivalry with Charles that became one of the fundamental conflicts of the sixteenth century.
Planning an offensive against Habsburg possessions in Navarre and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, Francis first secured his position in Italy by agreeing a new alliance with Venice. As Leo X had backed his candidacy for Emperor, he also counted on Papal support but Leo sided with Charles in return for his help against Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
and his proposed reforms to the Catholic church. In November 1521, an Imperial-Papal army under Prospero Colonna
Prospero Colonna (1452–1523), sometimes referred to as Prosper Colonna, was an Italian condottiero in the service of the Papal States, the Holy Roman Empire, and the Kingdom of Spain during the Italian Wars.
Biography
A member of the ancient ...
and the Marquis of Pescara captured Milan and restored Francesco Sforza as duke. After Leo died in December, Adrian VI
Pope Adrian VI ( la, Hadrianus VI; it, Adriano VI; nl, Adrianus/Adriaan VI), born Adriaan Florensz Boeyens (2 March 1459 – 14 September 1523), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 January 1522 until his d ...
was elected Pope on 9 January 1522, while a French attempt to retake Milan was ended by defeat at Bicocca on 27 April.
In May 1522, England joined the Imperial alliance and declared war on France. Venice left the war in July 1523, while Adrian died in November and was succeeded by Clement VII
Pope Clement VII ( la, Clemens VII; it, Clemente VII; born Giulio de' Medici; 26 May 1478 – 25 September 1534) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 November 1523 to his death on 25 September 1534. Deemed "the ...
, who tried to negotiate an end to the fighting without success. Although France had lost ground in Lombardy and been invaded by English, Imperial and Spanish armies, her opponents had differing objectives and failed to co-ordinate their attacks. Since Papal policy was to prevent either France or the Empire from becoming too powerful, in late 1524 Clement secretly allied himself with Francis, enabling him to mount another offensive against Milan. On 24 February 1525, the French army suffered a devastating defeat at Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
, in which Francis was captured and imprisoned in Spain.
This led to frantic diplomatic manoeuvres to secure his release, including a French mission to Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
, asking for Ottoman assistance. Although Suleiman avoided involvement on this occasion, it was the beginning of a long-standing, if often unacknowledged, Franco-Turkish relationship. Francis was eventually released in March 1526 after signing the Treaty of Madrid, in which he renounced French claims to Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht'') ...
, Milan and Burgundy.
War of the League of Cognac
Once Francis was free, his Council renounced the Treaty of Madrid, claiming conditions extorted under duress could not be considered binding. Concerned that Imperial power now posed a threat to Papal independence, on 22 May 1526 Clement VII formed theLeague of Cognac
The War of the League of Cognac (1526–30) was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V—primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain—and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Rep ...
, whose members included France, the Papal States, Venice, Florence and Milan. Many of the Imperial troops were close to mutiny having not been paid for months and the Duke of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino was an independent duchy in early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1625.
It was bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the east ...
, commander of the League army, hoped to take advantage of this confusion. However, he delayed taking the offensive awaiting additional Swiss reinforcements.
Although the League gained an easy victory on 24 June when the Venetians occupied Lodi, this delay allowed Charles to gather fresh troops and support a Milanese revolt in July against Francesco Sforza, who was once again forced into exile. In September, Charles financed an attack on Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
by the Colonna family, who competed with the rival Orsinis for control of the city, and Clement was forced to pay them to withdraw. Seeking to recapture Milan, Francis invaded Lombardy at the beginning of 1527, with an army financed by Henry VIII, who hoped thereby to win Papal support for divorcing his first wife, Katherine of Aragon
Catherine of Aragon (also spelt as Katherine, ; 16 December 1485 – 7 January 1536) was Queen of England as the first wife of King Henry VIII from their marriage on 11 June 1509 until their annulment on 23 May 1533. She was previously P ...
.
In May, Imperial troops, many of whom were followers of Martin Luther, sacked Rome and besieged Clement in the Castel Sant'Angelo, while Urbino and the League army sat outside and failed to intervene. Although the French marched south to relieve Rome, they were too late to prevent Clement making peace with Charles V in November. Meanwhile Venice, the largest and most powerful of the Italian states and which also possessed the most effective army, now refused to contribute any more troops to the League. Weakened by its losses in 1509 to 1517 and with its maritime possessions increasingly threatened by the Ottomans, under Andrea Gritti
Andrea Gritti (17 April 1455 – 28 December 1538) was the Doge of the Venetian Republic from 1523 to 1538, following a distinguished diplomatic and military career. He started out as a successful merchant in Constantinople and transitioned into t ...
the Republic tried to remain neutral and after 1529 avoided participation in the fighting.
Supported by a Genoese fleet, in April 1528 a French expeditionary force besieged Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
before disease forced them to withdraw in August. Both sides were now anxious to end the war and after another French defeat at Landriano
Landriano is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about southeast of Milan and about northeast of Pavia.
Landriano borders the following municipalities: Bascapè, Carpiano, Siziano, Torrev ...
on 21 June 1529, Francis agreed the Treaty of Cambrai
The Treaty of Cambrai is also known as the Paz de las Damas or Paix des Dames (Ladies' Peace). On August 3, 1529, this agreement ended a war between the French king Francis I and the Spanish Habsburg emperor Charles V. The treaty temporarily ...
with Charles in August. Known as the "Peace of the Ladies" because it was negotiated by Francis's mother, Louise of Savoy
Louise of Savoy (11 September 1476 – 22 September 1531) was a French noble and regent, Duchess ''suo jure'' of Auvergne and Bourbon, Duchess of Nemours, and the mother of King Francis I. She was politically active and served as the regent of F ...
, and Charles's aunt Margaret, Francis recognised Charles as ruler of Milan, Naples, Flanders and Artois. Venice also made peace, leaving only Florence, which had expelled their Medici
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mu ...
rulers in 1527. At Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label=Emilian language, Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 1 ...
in the summer of 1529, Charles V was named King of Italy
King of Italy ( it, links=no, Re d'Italia; la, links=no, Rex Italiae) was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a barbarian military leader ...
; he agreed to restore the Medici on behalf of Pope Clement, who was himself a Medici, and after a lengthy Siege of Florence (1529–1530), siege, Florence surrendered in August 1530.
Prior to 1530, interference by foreign powers in Italy was viewed as a short term problem, since they could not sustain it over time; for example, French conquests of Naples in 1494 and 1501 and Milan in 1499 and 1515 were quickly reversed. On the other hand, Venice was generally viewed by other states as the greatest threat because it was an ''Italian'' power. Many assumed the primacy established at Bologna by Charles V in Italy would also soon pass but instead it was the start of a long period of Imperial dominance. One factor was Venice's withdrawal from Italian affairs after 1530 in favour of protecting its maritime empire from Ottoman expansion.
Italian War of 1536–1538
 Under the Treaty of Cambrai, Francesco Sforza was reinstated as Duke of Milan; since he had no children, it also stated Charles V would inherit the duchy on his death, which occurred on 1 November 1535. Francis refused to accept this, arguing Milan was rightfully his along with Genoa and Asti, and once again prepared for war. In April 1536, pro-Valois elements in Asti expelled the Imperial garrison and a French army under Philippe de Chabot occupied Turin, although they failed to take Milan.
In response, a Spanish army invaded
Under the Treaty of Cambrai, Francesco Sforza was reinstated as Duke of Milan; since he had no children, it also stated Charles V would inherit the duchy on his death, which occurred on 1 November 1535. Francis refused to accept this, arguing Milan was rightfully his along with Genoa and Asti, and once again prepared for war. In April 1536, pro-Valois elements in Asti expelled the Imperial garrison and a French army under Philippe de Chabot occupied Turin, although they failed to take Milan.
In response, a Spanish army invaded Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
and captured Aix-en-Provence, Aix on 13 August 1536, before withdrawing, a fruitless expedition that diverted resources from Italy, where the situation had become more serious. The 1536 Franco-Ottoman alliance, a comprehensive treaty covering a wide range of commercial and diplomatic issues, also agreed to a joint assault on Genoa, with French land forces supported by an Ottoman fleet.
Finding the garrison of Genoa had recently been reinforced while a planned internal uprising failed to materialise, the French instead occupied the towns of Pinerolo, Chieri and Carmagnola in Piedmont. Fighting continued in Flanders and northern Italy throughout 1537, while the Ottoman fleet raided the coastal areas around Naples, raising fears of invasion throughout Italy. Pope Paul III, who had replaced Clement in 1534, grew increasingly anxious to end the war and brought the two sides together at Nice in May 1538. The Truce of Nice, signed on 18 June, agreed a ten year halt in hostilities and left France in possession of most of Duchy of Savoy, Savoy, Piedmont and Artois.
Italian War of 1542–1546
 The 1538 truce failed to resolve underlying tensions between Francis, who still claimed Milan, and Charles, who insisted he comply with the treaties of Madrid and Cambrai. Their relationship collapsed in 1540 when Charles made his son Philip II of Spain, Philip Duke of Milan, thus precluding any possibility it would revert to France. In 1541, Charles made a disastrous attack on Ottoman port of Algiers expedition (1541), Algiers, which severely weakened his military and led Suleiman to reactivate his French alliance. With Ottoman support, on 12 July 1542 Francis once again declared war on the Holy Roman Empire, initiating the Italian War of 1542–46.
In August, French armies attacked Siege of Perpignan (1542), Perpignan on the Spanish border, as well as Artois, Flanders and Duchy of Luxemburg, Luxemburg, a Valois possession prior to 1477. Imperial resistance proved far more formidable than expected, with most of these attacks easily repulsed and in 1543 Henry VIII allied with Charles and agreed to support his offensive in Flanders. Neither side made much progress, and although a combined Franco-Ottoman fleet under Hayreddin Barbarossa captured Nice on 22 August and besieged the citadel, the onset of winter and presence of a Spanish fleet forced them to withdraw. A joint attack by Christian and Islamic troops on a Christian town was regarded as shocking, especially when Francis allowed Barbarossa to use the French port of
The 1538 truce failed to resolve underlying tensions between Francis, who still claimed Milan, and Charles, who insisted he comply with the treaties of Madrid and Cambrai. Their relationship collapsed in 1540 when Charles made his son Philip II of Spain, Philip Duke of Milan, thus precluding any possibility it would revert to France. In 1541, Charles made a disastrous attack on Ottoman port of Algiers expedition (1541), Algiers, which severely weakened his military and led Suleiman to reactivate his French alliance. With Ottoman support, on 12 July 1542 Francis once again declared war on the Holy Roman Empire, initiating the Italian War of 1542–46.
In August, French armies attacked Siege of Perpignan (1542), Perpignan on the Spanish border, as well as Artois, Flanders and Duchy of Luxemburg, Luxemburg, a Valois possession prior to 1477. Imperial resistance proved far more formidable than expected, with most of these attacks easily repulsed and in 1543 Henry VIII allied with Charles and agreed to support his offensive in Flanders. Neither side made much progress, and although a combined Franco-Ottoman fleet under Hayreddin Barbarossa captured Nice on 22 August and besieged the citadel, the onset of winter and presence of a Spanish fleet forced them to withdraw. A joint attack by Christian and Islamic troops on a Christian town was regarded as shocking, especially when Francis allowed Barbarossa to use the French port of Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
as a winter base.
On 14 April 1544, a French army commanded by Francis, Count of Enghien, defeated the Imperials at Battle of Ceresole, Ceresole, a victory of limited strategic value since they failed to make progress elsewhere in Lombardy. The Imperial position was further strengthened at Battle of Serravalle (1544), Serravalle in June, when Alfonso d'Avalos defeated a mercenary force led by the Florentine exile Piero Strozzi on their way to meet Enghien. An English army captured Sieges of Boulogne (1544–1546), Boulogne on 10 September, while Imperial forces advanced to within of Paris. However, with his treasury exhausted and concerned by Ottoman naval strength in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
, on 14 September Charles agreed the Treaty of Crépy with Francis, which essentially restored the position to that prevailing in 1542. The agreement excluded Henry VIII, whose war with France continued until the two countries made peace in 1546 and confirmed his possession of Boulogne.
Italian War of 1551–1559
Francis died on 31 March 1547 and was succeeded by his son, Henry II of France. He continued attempts to restore the French position in Italy, encouraged by Italian exiles and his cousin Francis, Duke of Guise, who claimed the throne of Naples through his grandfather René II, Duke of Lorraine. Henry first strengthened his diplomatic position by reactivating the Franco-Ottoman alliance and supporting their capture of Siege of Tripoli (1551), Tripoli in August 1551. Despite his devout personal Catholicism and persecution of Huguenot "heretics" at home, in January 1552 he signed the Treaty of Chambord with several Protestantism, Protestant princes within the Empire, which gave him control of theThree Bishoprics
The Three Bishoprics (french: les Trois-Évêchés ) constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the ...
of Ancient Diocese of Toul, Toul, Bishopric of Verdun, Verdun, and Bishopric of Metz, Metz.
Following the outbreak of the Second Schmalkaldic War in March 1552, French troops occupied the Three Bishoprics and invaded Duchy of Lorraine, Lorraine. In 1553, a Franco-Ottoman force captured the Genoese island of Invasion of Corsica (1553), Corsica, while supported by Henry's wife, Catherine de' Medici, French-backed Tuscan exiles seized control of Siena. This brought Henry into conflict with the ruler of Florence, Cosimo I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, Cosimo de' Medici, who defeated a French army at Battle of Marciano, Marciano on 2 August 1554; although Siena held out until April 1555, it was absorbed by Florence and in 1569 became part of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany.
In July 1554, Philip II of Spain became king of England through his marriage to Mary I of England, Mary I, and in November he also received the kingdoms of Naples and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
from his father, who reconfirmed him as Duke of Milan. In January 1556, Charles formally abdicated as Emperor and split his possessions; the Holy Roman Empire went to his brother Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I, while Spain, its overseas territories and the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the H ...
were assigned to Philip. Over the next century, Naples and Lombardy became a major source of men and money for the Spanish Army of Flanders during the 1568 to 1648 Eighty Years' War.
England entered the war in June 1557 and the focus shifted to Flanders, where a Spanish army defeated the French at Battle of St. Quentin (1557), St. Quentin on 10 August. Despite this, in January 1558 the French took Siege of Calais (1558), Calais; held by the English since 1347, its loss severely diminished their future ability to intervene directly in mainland Europe. They also captured Siege of Thionville (1558), Thionville in June but peace negotiations had already begun, with Henry absorbed by the internal conflict that led to the French Wars of Religion in 1562. The Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis (1559), Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis on 3 April 1559 brought the Italian wars to an end. Corsica was returned to Genoa, while Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy, re-established the Savoyard state in northern Italy as an independent entity. France retained Calais and the Three Bishoprics, while other provisions essentially returned the position to that prevailing in 1551. Finally, Henry II and Philip II agreed to ask Pope Pius IV to recognise Ferdinand as Emperor, and reconvene the Council of Trent.
Aftermath
 The European balance of power changed significantly during the Italian Wars. The affirmation of French power in Italy around 1494 brought Austria and Spain to join an anti-French league that formed the "Habsburg ring" around France (Low Countries, Aragon, Castile, Empire) via dynastic marriages that eventually led to the large inheritance of Charles V. On the other hand, the last Italian war ended with the division of the Habsburg Empire between the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs following the abdication of Charles V. Philip II of Spain was heir of the kingdoms held by Charles V in Spain, southern Italy, and South America. Ferdinand I was the successor of Charles V in the Holy Roman Empire extending from Germany to northern Italy and became ''suo jure'' king of the Habsburg monarchy. The Habsburg Netherlands and the Duchy of Milan were left in personal union to the king of Spain while continuing to be part of the Holy Roman Empire.
The division of the empire of Charles V, along with the expansion of the French state over the Pas-de-Calais and the
The European balance of power changed significantly during the Italian Wars. The affirmation of French power in Italy around 1494 brought Austria and Spain to join an anti-French league that formed the "Habsburg ring" around France (Low Countries, Aragon, Castile, Empire) via dynastic marriages that eventually led to the large inheritance of Charles V. On the other hand, the last Italian war ended with the division of the Habsburg Empire between the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs following the abdication of Charles V. Philip II of Spain was heir of the kingdoms held by Charles V in Spain, southern Italy, and South America. Ferdinand I was the successor of Charles V in the Holy Roman Empire extending from Germany to northern Italy and became ''suo jure'' king of the Habsburg monarchy. The Habsburg Netherlands and the Duchy of Milan were left in personal union to the king of Spain while continuing to be part of the Holy Roman Empire.
The division of the empire of Charles V, along with the expansion of the French state over the Pas-de-Calais and the Three Bishoprics
The Three Bishoprics (french: les Trois-Évêchés ) constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the ...
, was a positive result for France. However, the Habsburgs had gained a position of primacy in Europe and Italy at the expense of the French Valois. In fact, in order to achieve this defensive objective, France was forced to end opposition to Habsburg power and abandon its claims in Italy. Henry II also restored the Savoyard state to Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy, Emmanuel Philibert, who settled in Piedmont, and Corsica to the Republic of Genoa. For this reason, the conclusion of the Italian Wars for France is considered to be a mixed result.
At the end of the wars, Italy was largely divided between viceroyalties of the Spanish Habsburgs in the south and Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), formal fiefs of the Austrian Habsburgs in the north./ref> The most significant Italian power left was the Papacy in central Italy, as it maintained major baroque, cultural and political influence during the Catholic Reformation. The Council of Trent, suspended during the war, was reconvened by the terms of the peace treaties and came to an end in 1563.
Interpretations
As in the case of France, the Habsburg result is also variously interpreted. Many historians in the 20th century, including Garrett Mattingly, Eric Cochrane and Manuel F. Alvarez, identified the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis as the beginning of Spanish hegemony in Italy. According to that view, the partition of the Habsburg empire at the abdication of Charles V left the position of the Holy Roman Empire in Italy weakened in favour of Spain so that the peace was mostly a victory of the latter. However, in 21st-century historiography there is a reconsideration of the topic. Christine Shaw in her revised ''Italian Wars (1494-1559)'', Micheal J. Levin in ''Agents of Empire'', and William Reger in ''Limits of Empire'', reject the concept of a Spanish hegemony on the ground that too many limits prevented Spain's dominance in the peninsula, and maintain that other powers also held major influence in Italy after 1559. According to Christine Shaw, it was the dual protection of Spain and the Holy Roman Empire that was established in Italy after Cateau-Cambrésis. Among Italian historians, a similar view was held by Salvatore Puglisi (in ''le prime strette dell'Austria in Italia''), who understood the result of the wars as the beginning of both Austrian and Spanish Habsburg power in Italy. According to Angelantonio Spagnoletti in his ''Principi Italiani e Spagna nell'età barocca'', echoing Benedetto Croce in his works on Baroque Italy, the Papacy and Spain emerged as the two main forces in the peninsula after Cateau-Cambrésis. According to their view, the position of the Papacy was strengthened by the conclusion of the council of Trent and the beginning of the counter-reformation. Peter J. Wilson writes that three overlapping and competing feudal networks, Imperial, Spanish, and Papal, were affirmed in Italy as a result of the end of the wars. Terms such as "refeudalization" (''rifeudalizzazione'') have also been used by Italian authors to describe the political and socio-economic situation of Italy after 1559. In the long-term, Habsburg primacy in Italy continued to exist, but it varied significantly due to the change of dynasties in Austria and Spain. Following the European wars of succession, the Habsburg-Lorraine of Austria gained direct or indirect control of the fiefs of Imperial Italy, whereas the south passed to a cadet branch of the Spanish Bourbons. France would return in Italy to confront Habsburg power, first under Louis XIV, and later under Napoleon, but only the unification of Italy will permanently remove foreign powers from the peninsula. Charles Tilly has characterized the Italian Wars as a key part in Coercion, Capital, and European States, AD 990–1992, his theory of state formation, as the wars demonstrated the value of large armies and superior military technology. In ''Coercion, Capital, and European States, AD 990–1992'', Tilly argues that a "comprehensive European state system" can be reasonably dated to the Italian Wars.Military
The Italian Wars represented a revolution in military technology and tactics, some historians suggesting they form the dividing point between modern and medieval battlefields. Contemporary historian Francesco Guicciardini wrote of the initial 1494 French invasion that "...sudden and violent wars broke out, ending with the conquest of a state in less time than it used to take to occupy a villa. The siege and taking of a city became extremely rapid and achieved not in months but in days and hours". Infantry underwent profound developments during the Italian Wars, evolving from a primary pike- and halberd-wielding force to a more flexible arrangement ofarquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
iers, pikemen, and other troops. While landsknechts and Swiss mercenaries continued to dominate during the early part of the wars, the Italian War of 1521 demonstrated the power of massed firearms in pike and shot formations.
A 1503 skirmish between French and Spanish forces first demonstrated the utility of arquebuses in battle. The Spanish general, Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, Gonzalo de Córdoba, faked a retreat, luring a contingent of French men-at-arms between two groups of his arquebusiers. As the French army stepped between the marksmen, volleys of bullets battered them on both flanks. Before the French could attack the vulnerable arquebusiers, a Spanish cavalry charge broke the French forces and forced their retreat. While the French army escaped, the Spanish inflicted severe casualties.
So successful was the employment of firearms in the Italian Wars that Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
, often characterized as an enemy of the use of the arquebus, wrote in his treatise on ''The Art of War (Machiavelli), The Art of War'' that all citizens in a city should know how to fire a gun.
Veterans turned conquistadors
Many ''conquistadors'', such as Hernán Cortés, had considered Italy before opting to serve in New Spain, Spanish America, while large numbers of veterans from Naples and southern Italy later emigrated there, either as colonists or soldiers. Experience in Italy was often considered a prerequisite for military employment, although the chronicler Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés claimed those who did so must have "failed to become rich,...gambled the riches away or [somehow] lost them" and suggested conditions in the Americas were far tougher. Francisco Sebastián, an Italian veteran who accompanied Hernando de Soto on his expedition into North America, agreed with this assessment, largely because "no plunder of value could be obtained" from the inhabitants. Italian veterans included Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar, who conquered Governorate of Cuba, Cuba in 1511, Francisco de Carvajal and Pedro de Valdivia, both of whom fought atPavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
in 1526. Carvajal and Valdivia served with the Pizarro brothers in Peru during their conflict with Spanish rival Diego de Almagro in 1538. Carvajal remained with the Pizarros while Valdivia began the conquest of Chile and ignited the Arauco War. The two men fought on opposite sides in the 1548 Battle of Jaquijahuana; Carvajal was executed after being taken prisoner, while Valdivia died in 1553 at Battle of Tucapel, Tucapel.
Cavalry
Heavy cavalry, the final evolution of the fully armoured medieval knight, remained significant players on the battlefields of the Italian Wars. Largely due to their excellent horses, French Gendarme (historical), gendarmes were generally successful against heavy mounted troops from other states, but were very vulnerable to pikemen. The Spanish used heavy cavalry and light cavalry, or ''Jinetes'', for skirmishing.Artillery
Artillery, particularly field artillery, became an indispensable part of any first-rate army during the wars. When Charles VII invaded in 1494, he brought with him the first truly mobile siege train of culverins and bombard (weapon), bombards. It included various innovations, such as mounting the guns on wheeled carriages, drawn by horses rather than oxen as was the custom, which allowed them to be deployed against an enemy stronghold on arrival. This mobility stemmed from their lightness, achieved by employing the methods used to cast bronze church bells. Perhaps the most important improvement was the creation of the iron cannonball, rather than the stone balls that often shattered on impact. The combination meant Charles could level in an hour castles that had resisted sieges for months or even years.Historiography
The Italian Wars are one of the first major conflicts for which extensive contemporary accounts from people involved in the wars are available, owing largely to the presence of literate, and often extremely-well educated, commanders. The Printing#impact of German movable type printing press, invention of modern printing, still less than one century old, undoubtedly played a large role in the memorialization of the conflict as well. Major historians of the period includeFrancesco Guicciardini
Francesco Guicciardini (; 6 March 1483 – 22 May 1540) was an Italian historian and statesman. A friend and critic of Niccolò Machiavelli, he is considered one of the major political writers of the Italian Renaissance. In his masterpiece, ''Th ...
and Paolo Sarpi.
Nomenclature
The naming of the component conflicts within the Italian Wars has never been standardized and varies among historians of the period. Some wars may be split or combined differently, causing ordinal numbering systems to be inconsistent among different sources. The wars may be referred to by their dates or by the monarchs fighting them. Usually, the Italian Wars are grouped into three major phases: 1494-1516; 1521-1530; and 1535-1559.Contemporary accounts
A major contemporary account for the early portion of the Italian Wars is Francesco Guicciardini's ''Storia d'Italia'' (''History of Italy''), written during the conflict and advantaged by the access that Guicciardini had to papal affairs.Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Konstam, Angus. ''Pavia 1525: The Climax of the Italian Wars''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 1996. . * * * * * * * * * * John Julius Norwich, Norwich, John Julius. ''A History of Venice''. New York: Vintage Books, 1989. . * Charles Oman, Oman, Charles. ''A History of the Art of War in the Sixteenth Century''. London: Methuen & Co., 1937. * * * Phillips, Charles and Alan Axelrod. ''Encyclopedia of Wars''. 3 vols. New York: Facts on File, 2005. . * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Le Gall, Jean-Marie, ''Les guerres d'Italie (1494–1559): une lecture religieuse.'' Geneva: Droz, 2017. * Max Boot, Boot, Max. ''War Made New: Technology, Warfare, and the Course of History: 1500 to Today.'' New York: Gotham Books, 2006. . * Martin Du Bellay, Du Bellay, Martin, Sieur de Langey. ''Mémoires de Martin et Guillaume du Bellay.'' Edited by V. L. Bourrilly and F. Vindry. 4 volumes. Paris: Société de l'histoire de France, 1908–19. * Paolo Giovio, Giovio, Paolo. ''Pauli Iovii Opera.'' Volume 3, part 1, ''Historiarum sui temporis.'' Edited by D. Visconti. Rome: Libreria dello Stato, 1957. * Lot, Ferdinand. ''Recherches sur les effectifs des armées françaises des guerres d'Italie aux guerres de religion, 1494–1562.'' Paris: École Pratique des Hautes Études, 1962. * Blaise de Lasseran-Massencôme, seigneur de Montluc, Monluc, Blaise de. ''Commentaires.'' Edited by P. Courteault. 3 volumes. Paris: 1911–25. Translated by Charles Cotton as ''The Commentaries of Messire Blaize de Montluc'' (London: A. Clark, 1674). * Blaise de Lasseran-Massencôme, seigneur de Montluc, Monluc, Blaise de. ''Military Memoirs: Blaise de Monluc, The Habsburg-Valois Wars, and the French Wars of Religion.'' Edited by Ian Roy. London: Longmans, 1971. * Gaspard de Saulx, sieur de Tavannes, Saulx, Gaspard de, Seigneur de Tavanes. ''Mémoires de très noble et très illustre Gaspard de Saulx, seigneur de Tavanes, Mareschal de France, admiral des mers de Levant, Gouverneur de Provence, conseiller du Roy, et capitaine de cent hommes d'armes.'' Château de Lugny: Fourny, 1653. {{authority control Italian Wars, Wars involving the states and peoples of Europe 15th century in France 16th century in France 15th century in Italy 16th century in Italy 15th-century military history of France 16th-century military history of France