Haakon VII of Norway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Haakon VII (; born Prince Carl of Denmark; 3 August 187221 September 1957) was the
 Prince Carl was born on 3 August 1872 at his parents' country residence, Charlottenlund Palace north of
Prince Carl was born on 3 August 1872 at his parents' country residence, Charlottenlund Palace north of
 Prince Carl was raised with his siblings in the royal household in Copenhagen, and grew up between his parents' residence in
Prince Carl was raised with his siblings in the royal household in Copenhagen, and grew up between his parents' residence in
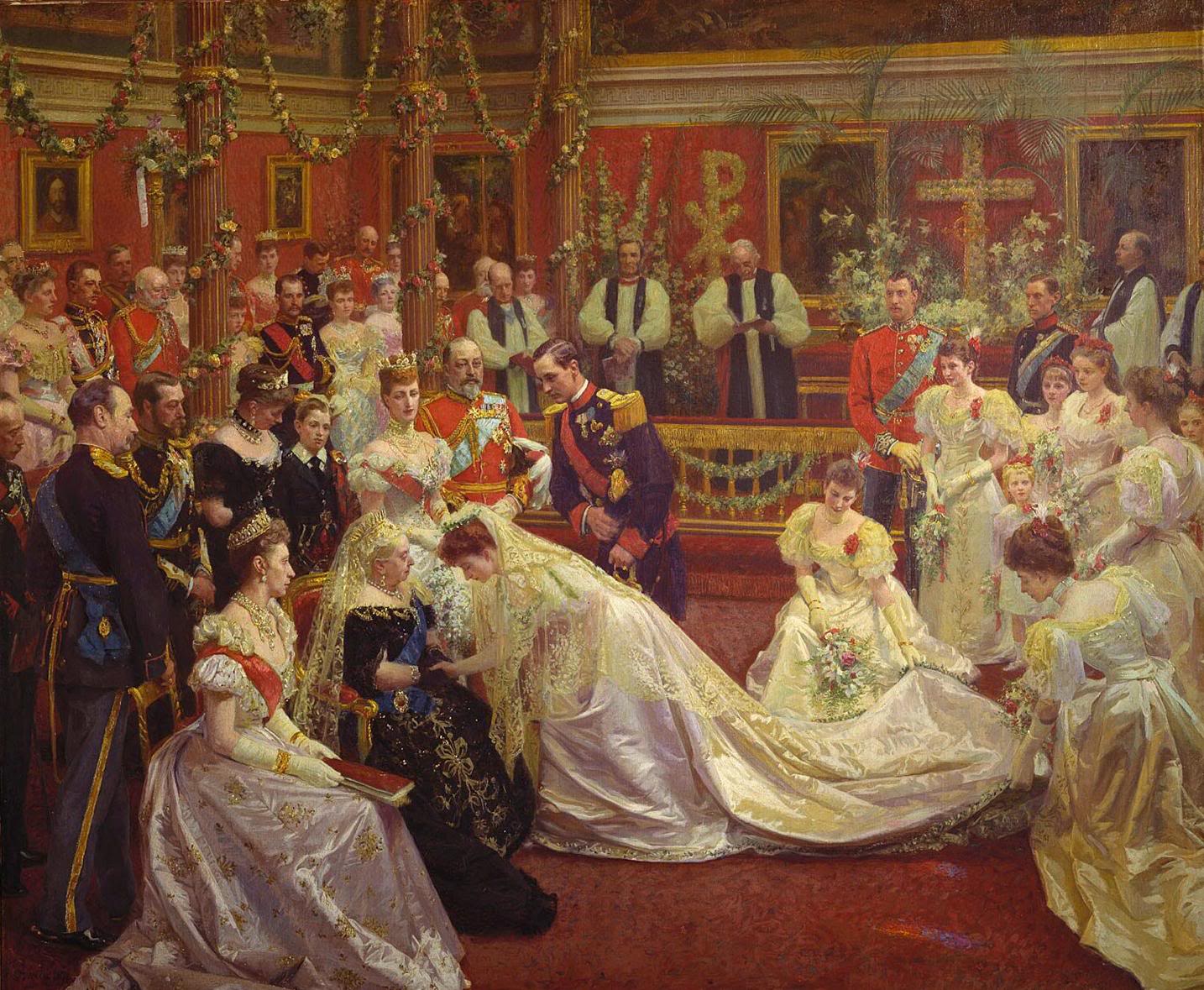 On 22 July 1896, in the Private Chapel of Buckingham Palace, Prince Carl married his first cousin Princess Maud of Wales. Princess Maud was the youngest daughter of the Prince of Wales, the future King
On 22 July 1896, in the Private Chapel of Buckingham Palace, Prince Carl married his first cousin Princess Maud of Wales. Princess Maud was the youngest daughter of the Prince of Wales, the future King
 On the morning of 20 November, a large crowd gathered outside King Haakon and Queen Maud's residence in Bernstorff's Palace in Copenhagen. The attendees greeted the royal couple as they appeared in the window and started singing '' Ja, vi elsker dette landet''. Later the same day, King Christian IX of Denmark received a delegation from the Storting in an audience in Christian VII's Palace at
On the morning of 20 November, a large crowd gathered outside King Haakon and Queen Maud's residence in Bernstorff's Palace in Copenhagen. The attendees greeted the royal couple as they appeared in the window and started singing '' Ja, vi elsker dette landet''. Later the same day, King Christian IX of Denmark received a delegation from the Storting in an audience in Christian VII's Palace at
 On 22 June 1906, King Haakon and Queen Maud were solemnly crowned and anointed in the Nidaros Cathedral in
On 22 June 1906, King Haakon and Queen Maud were solemnly crowned and anointed in the Nidaros Cathedral in
 King Haakon gained much sympathy from the Norwegian people. He travelled extensively through Norway. As king, Haakon endeavored to redefine the role of the monarchy in egalitarian Norway and to find a balance between the informal Norwegian way of life and the monarchy's need for formal representation. Although the Constitution of Norway vests the King with considerable executive powers, in practice nearly all major governmental decisions were made by the Government (the Council of State) in his name. Haakon confined himself to non-partisan roles without interfering in politics, a practice continued by his son and grandson. However, his long rule gave him considerable
King Haakon gained much sympathy from the Norwegian people. He travelled extensively through Norway. As king, Haakon endeavored to redefine the role of the monarchy in egalitarian Norway and to find a balance between the informal Norwegian way of life and the monarchy's need for formal representation. Although the Constitution of Norway vests the King with considerable executive powers, in practice nearly all major governmental decisions were made by the Government (the Council of State) in his name. Haakon confined himself to non-partisan roles without interfering in politics, a practice continued by his son and grandson. However, his long rule gave him considerable  In 1927, the Labour Party became the largest party in parliament and early the following year Norway's first Labour Party government rose to power. The Labour Party was considered to be "revolutionary" by many and the deputy prime minister at the time advised against appointing Christopher Hornsrud as Prime Minister. Haakon, however, refused to abandon parliamentary convention and asked Hornsrud to form a new government. In response to some of his detractors he stated, "I am also the King of the Communists" ( no, "Jeg er også kommunistenes konge").
Crown Prince Olav married his cousin Princess Märtha of Sweden on 21 March 1929. She was the daughter of Haakon's sister
In 1927, the Labour Party became the largest party in parliament and early the following year Norway's first Labour Party government rose to power. The Labour Party was considered to be "revolutionary" by many and the deputy prime minister at the time advised against appointing Christopher Hornsrud as Prime Minister. Haakon, however, refused to abandon parliamentary convention and asked Hornsrud to form a new government. In response to some of his detractors he stated, "I am also the King of the Communists" ( no, "Jeg er også kommunistenes konge").
Crown Prince Olav married his cousin Princess Märtha of Sweden on 21 March 1929. She was the daughter of Haakon's sister
 The following morning, 11 April 1940, in an attempt to wipe out Norway's unyielding king and government, bombers attacked Nybergsund, destroying the small town where the Government was staying. Neutral Sweden was only away, but the Swedish government decided it would "detain and incarcerate" King Haakon if he crossed their border (which Haakon never forgave). The Norwegian king and his ministers took refuge in the snow-covered woods and escaped harm, continuing farther north through the mountains toward Molde on Norway's west coast. As the British forces in the area lost ground under Luftwaffe bombardment, the King and his party were taken aboard the British cruiser HMS ''Glasgow'' at Molde and conveyed a further north to
The following morning, 11 April 1940, in an attempt to wipe out Norway's unyielding king and government, bombers attacked Nybergsund, destroying the small town where the Government was staying. Neutral Sweden was only away, but the Swedish government decided it would "detain and incarcerate" King Haakon if he crossed their border (which Haakon never forgave). The Norwegian king and his ministers took refuge in the snow-covered woods and escaped harm, continuing farther north through the mountains toward Molde on Norway's west coast. As the British forces in the area lost ground under Luftwaffe bombardment, the King and his party were taken aboard the British cruiser HMS ''Glasgow'' at Molde and conveyed a further north to
 Initially, King Haakon and Crown Prince Olav were guests at Buckingham Palace, but at the start of the London Blitz in September 1940, they moved to Bowdown House in Berkshire. The construction of the adjacent RAF Greenham Common airfield in March 1942 prompted another move to
Initially, King Haakon and Crown Prince Olav were guests at Buckingham Palace, but at the start of the London Blitz in September 1940, they moved to Bowdown House in Berkshire. The construction of the adjacent RAF Greenham Common airfield in March 1942 prompted another move to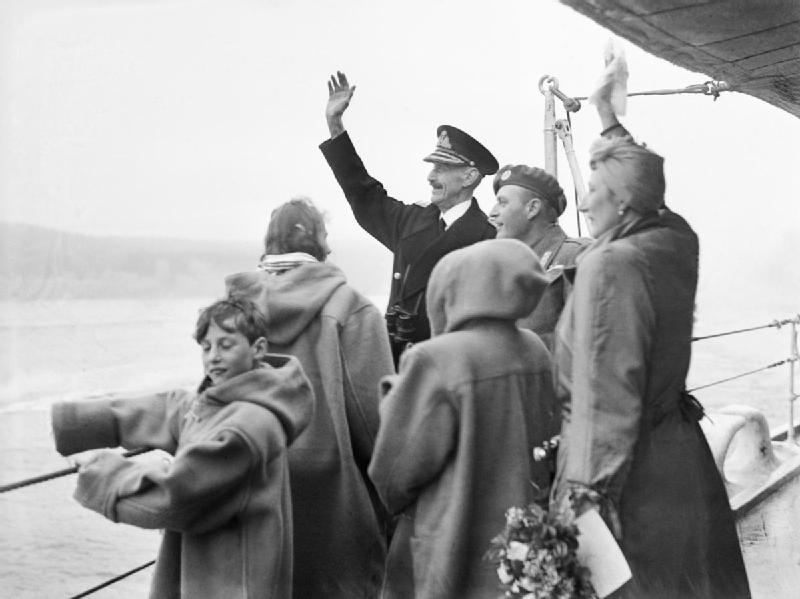  Meanwhile, Hitler had appointed
Meanwhile, Hitler had appointed
 After his return, Haakon did not continue the political role that he had played during the war, and limited himself to his constitutional duties as head of state. In the late summer of 1945 he went on an extensive tour of Norway to examine the war damage and to give consolation to the population. Because of his role during the war and his personal integrity, Haakon VII was considered the highest moral authority in the country and enjoyed great esteem in all classes of the population.
In 1947, the Norwegian people, by public subscription, purchased the royal yacht ''Norge'' for the King.
In 1952, he attended the funeral of his wife's nephew King
After his return, Haakon did not continue the political role that he had played during the war, and limited himself to his constitutional duties as head of state. In the late summer of 1945 he went on an extensive tour of Norway to examine the war damage and to give consolation to the population. Because of his role during the war and his personal integrity, Haakon VII was considered the highest moral authority in the country and enjoyed great esteem in all classes of the population.
In 1947, the Norwegian people, by public subscription, purchased the royal yacht ''Norge'' for the King.
In 1952, he attended the funeral of his wife's nephew King
 Haakon died at the Royal Palace in Oslo on 21 September 1957. He was 85 years old. At his death, Olav succeeded him as Olav V. Haakon was buried on 1 October 1957 alongside his wife in the white sarcophagus in the Royal Mausoleum at Akershus Fortress. He was the last surviving son of King Frederick VIII of Denmark.
Haakon died at the Royal Palace in Oslo on 21 September 1957. He was 85 years old. At his death, Olav succeeded him as Olav V. Haakon was buried on 1 October 1957 alongside his wife in the white sarcophagus in the Royal Mausoleum at Akershus Fortress. He was the last surviving son of King Frederick VIII of Denmark.
(Norwegian) Retrieved 5 October 2007. * : **
Official Website of the Royal House of Norway
* ttp://www.kongernessamling.dk/en/amalienborg/person/carl-haakon-vii/ Prince Carl (Haakon VII)at the website of the
The Royal Norwegian Order of St Olav − H.M. King Haakon VII the former Grand Master of the Order
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Haakon 07 Of Norway 1872 births 1957 deaths 20th-century Norwegian monarchs Norwegian monarchs Danish princes House of Glücksburg (Norway) House of Glücksburg (Denmark) Norwegian people of World War II Governments in exile during World War II Protestant monarchs 19th-century Danish naval officers 20th-century Danish naval officers Presidents of the Organising Committees for the Olympic Games Recipients of the War Cross with Sword (Norway) Holmenkollen medalists Grand Commanders of the Order of the Dannebrog Recipients of the Cross of Honour of the Order of the Dannebrog Grand Crosses of the Order of the White Lion Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur Recipients of the Croix de Guerre 1939–1945 (France) Extra Knights Companion of the Garter Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order Bailiffs Grand Cross of the Order of St John Recipients of the War Cross (Greece) Grand Crosses of the Order of the Sun of Peru 3 3 3 Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 1st class Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Russia) Recipients of the Order of Saint Stanislaus (Russian) Knights of the Golden Fleece of Spain Grand Crosses with Diamonds of the Order of the Sun of Peru Burials at the Royal Mausoleum (Norway) Sons of kings Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland)
King of Norway
The Norwegian monarch is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty kingd ...
from November 1905 until his death in September 1957.
Originally a Danish prince, he was born in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
as the son of the future Frederick VIII of Denmark and Louise of Sweden. Prince Carl was educated at the Royal Danish Naval Academy and served in the Royal Danish Navy. After the 1905 dissolution of the union between Sweden and Norway, Prince Carl was offered the Norwegian crown. Following a November plebiscite, he accepted the offer and was formally elected King of Norway by the Storting
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years ...
. He took the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
name ''Haakon'' and ascended to the throne as Haakon VII, becoming the first independent Norwegian monarch since 1387.
As king, Haakon gained much sympathy from the Norwegian people. Although the Constitution of Norway vests the King with considerable executive powers, in practice Haakon confined himself to non-partisan roles without interfering in politics, a practice continued by his son and grandson.
Norway was invaded by Nazi Germany in April 1940. Haakon rejected German demands to legitimise the Quisling regime's puppet government, and refused to abdicate after going into exile in Great Britain. As such, he played a pivotal role in uniting the Norwegian nation in its resistance to the invasion and the subsequent five-year-long occupation during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. He returned to Norway in June 1945 after the defeat of Germany.
He became King of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
when his grandfather Christian IX
Christian IX (8 April 181829 January 1906) was King of Denmark from 1863 until his death in 1906. From 1863 to 1864, he was concurrently Duke of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg.
A younger son of Frederick William, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein ...
was still reigning in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, and before his father and elder brother became kings of Denmark. During his reign he saw his father Frederick VIII, his elder brother Christian X
Christian X ( da, Christian Carl Frederik Albert Alexander Vilhelm; 26 September 1870 – 20 April 1947) was King of Denmark from 1912 to his death in 1947, and the only King of Iceland as Kristján X, in the form of a personal union rather ...
, and his nephew Frederick IX ascend the throne of Denmark, in 1906, 1912 (also of Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
from 1918 to 1944), and 1947 respectively. Haakon died at the age of 85 in September 1957, after having reigned for nearly 52 years. He was succeeded by his only son, who ascended to the throne as Olav V.
Early life
Birth and family
 Prince Carl was born on 3 August 1872 at his parents' country residence, Charlottenlund Palace north of
Prince Carl was born on 3 August 1872 at his parents' country residence, Charlottenlund Palace north of Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, during the reign of his paternal grandfather, King Christian IX. He was the second son of Crown Prince Frederick of Denmark (the future King Frederick VIII), and his wife Louise of Sweden. His father was the eldest son of King Christian IX and Louise of Hesse-Kassel, and his mother was the only daughter of King Charles XV of Sweden (who was also king of Norway as Charles IV), and Louise of the Netherlands
Louise of the Netherlands (Wilhelmina Frederika Alexandrine Anna Louise; 5 August 1828 – 30 March 1871) was Queen of Sweden and Norway from 8 July 1859 until her death in 1871 as the wife of King Charles XV & IV.
Youth
Princess Louise was bo ...
. At birth, he was third in the succession to the Danish throne after his father and older brother, but without any real prospect of inheriting the throne. The young prince was baptised at Charlottenlund Palace on 7 September 1872 by the Bishop of Zealand, Hans Lassen Martensen
Hans Lassen Martensen (19 August 1808 – 3 February 1884) was a Danish bishop and academic. He was a professor at the University of Copenhagen and Bishop of the Diocese of Zealand.
Early life
Martensen was born in a middle-class Lutheran f ...
. He was baptised with the names ''Christian Frederik Carl Georg Valdemar Axel'', and was known as Prince Carl (namesake of his maternal grandfather the King of Sweden-Norway).
Prince Carl belonged to the Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg (often shortened to Glücksburg) branch of the House of Oldenburg. The House of Oldenburg had been the Danish royal family since 1448; between 1536 and 1814 it also ruled Norway, which was then part of the Kingdom of Denmark-Norway. The house was originally from northern Germany, where the Glücksburg (Lyksborg) branch held their small fief. The family had links with Norway beginning from the 15th century. Several of his paternal ancestors had been kings of Norway in union with Denmark and at times Sweden. They included Christian I of Norway, Frederick I, Christian III, Frederick II, Christian IV, as well as Frederick III of Norway who integrated Norway into the Oldenburg state with Denmark, Schleswig and Holstein. His subsequent paternal ancestors had been dukes in Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
. Christian Frederick
Christian VIII (18 September 1786 – 20 January 1848) was King of Denmark from 1839 to 1848 and, as Christian Frederick, King of Norway in 1814.
Christian Frederick was the eldest son of Hereditary Prince Frederick, a younger son of King Frederic ...
, who was King of Norway briefly in 1814, the first king of the Norwegian 1814 constitution and struggle for independence, was his great-granduncle.
Childhood and education
 Prince Carl was raised with his siblings in the royal household in Copenhagen, and grew up between his parents' residence in
Prince Carl was raised with his siblings in the royal household in Copenhagen, and grew up between his parents' residence in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, the Frederick VIII's Palace, an 18th-century palace which forms part of the Amalienborg Palace complex in central Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, and their country residence, Charlottenlund Palace, located by the coastline of the Øresund strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean chan ...
north of the city. In contrast to the usual practise of the period, where royal children were brought up by governesses, the children were raised by Crown Princess Louise herself. Under the supervision of their mother, the children of the Crown Princess received a rather strict Christian-dominated upbringing, which was characterized by severity, the fulfillment of duties, care and order.
As a younger son of the Crown Prince, there was little expectation that Carl would become king. He was third in line to the throne, after his father and elder brother, Prince Christian and spent his early life in the shadow of his elder brother. Carl was less than two years younger than Christian, and the two princes were educated together and had a joint confirmation at Christiansborg Palace Chapel in 1887.
After his confirmation, as was customary for princes at that time, Prince Carl was expected to start a military education. It was decided that he, in accordance with his own wishes, should enter the Royal Danish Navy. He was educated at the Royal Danish Naval Academy from 1889 to 1893, graduating as a second lieutenant. In 1894 he was promoted to the rank of first lieutenant and remained in service with the Royal Danish Navy until 1905.
Marriage
 On 22 July 1896, in the Private Chapel of Buckingham Palace, Prince Carl married his first cousin Princess Maud of Wales. Princess Maud was the youngest daughter of the Prince of Wales, the future King
On 22 July 1896, in the Private Chapel of Buckingham Palace, Prince Carl married his first cousin Princess Maud of Wales. Princess Maud was the youngest daughter of the Prince of Wales, the future King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second chil ...
of the United Kingdom, and his wife, Princess Alexandra of Denmark, eldest daughter of King Christian IX and Queen Louise. The wedding was attended by the bride's grandmother, the 77-year-old Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
.
After the wedding, the couple settled in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, where Prince Carl continued his career as a naval officer. The bride's father gave them Appleton House on the Sandringham Estate as a country residence for his daughter's frequent visits to England. It was there that the couple's only child, Prince Alexander Prince Alexander may refer to:
* Alexander, a character from the ''King's Quest'' series of video games
* Alexander Cambridge, 1st Earl of Athlone, born as Prince Alexander of Teck
* Alexander Karađorđević, Prince of Serbia (r. 1842–1858)
* Ale ...
, the future Crown Prince Olav (and eventually King Olav V of Norway
Olav V (; born Prince Alexander of Denmark; 2 July 1903 – 17 January 1991) was the King of Norway from 1957 until his death in 1991.
Olav was the only child of King Haakon VII of Norway and Maud of Wales. He became heir apparent to the Nor ...
), was born on 2 July 1903.
Accession to the Norwegian throne
Background and election
After the Union between Sweden and Norway was dissolved in 1905, a committee of the Norwegian government identified several princes of European royal houses as candidates for the Norwegian crown. Although Norway had legally had the status of an independent state since 1814, it had not had its own king since 1387. Gradually, Prince Carl became the leading candidate, largely because he was descended from independent Norwegian kings. He also had a son, providing an heir-apparent to the throne, and the fact that his wife, Princess Maud, was a member of the British Royal Family was viewed by many as an advantage to the newly independent Norwegian nation. The democratically minded Carl, aware that Norway was still debating whether to remain a kingdom or to switch instead to a republican system of government, was flattered by the Norwegian government's overtures, but he made his acceptance of the offer conditional on the holding of a referendum to show whether monarchy was the choice of the Norwegian people. After thereferendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
overwhelmingly confirmed by a 79 percent majority (259,563 votes for and 69,264 against) that Norwegians desired to retain a monarchy, Prince Carl was formally offered the throne of Norway by the Storting
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years ...
(parliament) and was elected on 18 November 1905. When Carl accepted the offer that same evening (after the approval of his grandfather Christian IX of Denmark), he immediately endeared himself to his adopted country by taking the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
name of Haakon, a name which had not been used by kings of Norway for over 500 years. In so doing, he succeeded his maternal great-uncle, Oscar II of Sweden, who had abdicated the Norwegian throne in October following the agreement between Sweden and Norway on the terms of the separation of the union.
 On the morning of 20 November, a large crowd gathered outside King Haakon and Queen Maud's residence in Bernstorff's Palace in Copenhagen. The attendees greeted the royal couple as they appeared in the window and started singing '' Ja, vi elsker dette landet''. Later the same day, King Christian IX of Denmark received a delegation from the Storting in an audience in Christian VII's Palace at
On the morning of 20 November, a large crowd gathered outside King Haakon and Queen Maud's residence in Bernstorff's Palace in Copenhagen. The attendees greeted the royal couple as they appeared in the window and started singing '' Ja, vi elsker dette landet''. Later the same day, King Christian IX of Denmark received a delegation from the Storting in an audience in Christian VII's Palace at Amalienborg
Amalienborg () is the official residence for the Danish royal family, and is located in Copenhagen, Denmark. Queen Magrethe ll lives here in winter and autumn. It consists of four identical classical palace façades with rococo interiors ar ...
. The delegation conveyed the message that the king's grandson had been elected King of Norway, while Christian IX expressed his consent to the election of Prince Carl. The head of the delegation, the President of the Storting Carl Berner, conveyed a greeting and congratulations from the Norwegian people, and expressed the people's wishes for a happy cooperation. The king replied:
Mr. President of the Storthing, gentlemen. The first greeting from the Representatives of the Norwegian People, who in their unanimous Storthing decision on 18 November has elected me their King, has touched me deeply. The people have thereby shown me a confidence which I know how to appreciate, and which I hope will still grow stronger as it gets to know my wife and me. As it will be known to you, gentlemen, it was at my request that the newly concluded referendum took place. I wanted to be sure that it was a people and not a party that wanted me to be king, as my task above all should be to unite, not divide. My life I will devote to the good of Norway, and it is the fervent wish of my wife and I that the people who have chosen us will unite to cooperate and strive towards this great goal, and with full confidence I can then take as my motto: ALL FOR NORWAY.
Arrival in Norway
On 23 November, the new royal family of Norway left Copenhagen on the Danish royal yacht, thepaddle steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses wer ...
''Dannebrog'' and sailed into the Oslofjord
The Oslofjord (, ; en, Oslo Fjord) is an inlet in the south-east of Norway, stretching from an imaginary line between the and lighthouses and down to in the south to Oslo in the north. It is part of the Skagerrak strait, connecting the N ...
. At Oscarsborg Fortress, they boarded the Norwegian naval ship . After a three-day journey, they arrived in Kristiania
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population o ...
(now Oslo) early on the morning of 25 November 1905 where the king was received at the harbour by the Prime Minister of Norway Christian Michelsen
Peter Christian Hersleb Kjerschow Michelsen (15 March 1857 – 29 June 1925), better known as Christian Michelsen, was a Norwegian shipping magnate and statesman. He was the first prime minister of independent Norway and Norway's 9th prime mini ...
. On the deck of the Heimdal, the Prime Minister gave the following speech to the king:
For almost 600 years, the Norwegian people have not had their own king. Never has he been completely our own. Always have we had to share him with others. Never has he had his home with us. But where the home is, there will also be the fatherland. Today it is different. Today, Norway's young king comes to build his future home in Norway's capital. Named by a free people as a free man to lead his country, he will be completely our own. Once again, the Norwegians' king will be the strong, unifying mark for all national deeds in the new, independent Norway ...Two days later, on 27 November, Haakon VII took his constitutional oath before parliament as Norway's first independent king in 518 years. However, Norway counts 18 November, the day of his election, as the formal beginning of his reign.
Coronation
 On 22 June 1906, King Haakon and Queen Maud were solemnly crowned and anointed in the Nidaros Cathedral in
On 22 June 1906, King Haakon and Queen Maud were solemnly crowned and anointed in the Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, an ...
by the Bishop of Trondheim Vilhelm Andreas Wexelsen. The coronation was in keeping with the constitutional mandate, but many Norwegian statesmen had come to regard coronation rites as "undemocratic and archaic". The coronation clause was deleted from Norway's constitution in 1908, and although coronations are not expressly banned under current Norwegian legislation, this became the last coronation of a Norwegian monarch. In the period before and after the coronation, the king and Queen made an extensive coronation journey through Norway.
The King and Queen moved into the Royal Palace in Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
. Haakon became the first monarch to use the palace permanently and the palace was therefore refurbished for two years before he, Queen Maud and Crown Prince Olav could move in. After the coronation, King Haakon and Queen Maud also received the estate '' Kongesæteren'' at Voksenkollen in Oslo as a gift from the Norwegian people.
Early reign
 King Haakon gained much sympathy from the Norwegian people. He travelled extensively through Norway. As king, Haakon endeavored to redefine the role of the monarchy in egalitarian Norway and to find a balance between the informal Norwegian way of life and the monarchy's need for formal representation. Although the Constitution of Norway vests the King with considerable executive powers, in practice nearly all major governmental decisions were made by the Government (the Council of State) in his name. Haakon confined himself to non-partisan roles without interfering in politics, a practice continued by his son and grandson. However, his long rule gave him considerable
King Haakon gained much sympathy from the Norwegian people. He travelled extensively through Norway. As king, Haakon endeavored to redefine the role of the monarchy in egalitarian Norway and to find a balance between the informal Norwegian way of life and the monarchy's need for formal representation. Although the Constitution of Norway vests the King with considerable executive powers, in practice nearly all major governmental decisions were made by the Government (the Council of State) in his name. Haakon confined himself to non-partisan roles without interfering in politics, a practice continued by his son and grandson. However, his long rule gave him considerable moral authority Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive, laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change, the princi ...
as a symbol of the country's unity. The Norwegian explorer and Nobel Prize laureate Fridtjof Nansen became a friend of the Royal Family.
 In 1927, the Labour Party became the largest party in parliament and early the following year Norway's first Labour Party government rose to power. The Labour Party was considered to be "revolutionary" by many and the deputy prime minister at the time advised against appointing Christopher Hornsrud as Prime Minister. Haakon, however, refused to abandon parliamentary convention and asked Hornsrud to form a new government. In response to some of his detractors he stated, "I am also the King of the Communists" ( no, "Jeg er også kommunistenes konge").
Crown Prince Olav married his cousin Princess Märtha of Sweden on 21 March 1929. She was the daughter of Haakon's sister
In 1927, the Labour Party became the largest party in parliament and early the following year Norway's first Labour Party government rose to power. The Labour Party was considered to be "revolutionary" by many and the deputy prime minister at the time advised against appointing Christopher Hornsrud as Prime Minister. Haakon, however, refused to abandon parliamentary convention and asked Hornsrud to form a new government. In response to some of his detractors he stated, "I am also the King of the Communists" ( no, "Jeg er også kommunistenes konge").
Crown Prince Olav married his cousin Princess Märtha of Sweden on 21 March 1929. She was the daughter of Haakon's sister Ingeborg
Ingeborg is a Germanic feminine given name, mostly used in Germany, Denmark, Sweden and Norway, derived from Old Norse ''Ingiborg, Ingibjǫrg'', combining the theonym ''Ing'' with the element ''borg'' "stronghold, protection". Ingebjørg is the N ...
and Prince Carl, Duke of Västergötland. Olav and Märtha had three children: Ragnhild (1930–2012), Astrid (born 1932) and Harald (born 1937), who was to become king in 1991.
Queen Maud died unexpectedly while visiting the United Kingdom on 20 November 1938. In 1939, King Haakon toured southeast Montana and parts of the proposed secessionist state of Absaroka, with supporters of the succession movement claiming this event as formal recognition of their state.
Resistance during World War II
The German invasion
Norway was invaded by the naval and air forces ofNazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
during the early hours of 9 April 1940. The German naval detachment sent to capture Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
was opposed by Oscarsborg Fortress. The fortress fired at the invaders, sinking the heavy cruiser '' Blücher'' and damaging the heavy cruiser '' Lützow'', with heavy German losses that included many of the armed forces, Gestapo agents, and administrative personnel who were to have occupied the Norwegian capital. This led to the withdrawal of the rest of the German flotilla, preventing the invaders' planned dawn occupation of Oslo. The German delay in occupying Oslo, along with swift action by the President of the Storting, C. J. Hambro
Carl Joachim Hambro (5 January 1885 – 15 December 1964) was a Norwegian journalist, author and leading politician representing the Conservative Party. A ten-term member of the Parliament of Norway, Hambro served as President of the Parliament ...
, created the opportunity for the Norwegian Royal Family, the cabinet, and most of the 150 members of the Storting (parliament) to make a hasty departure from the capital by special train.
The Storting first convened at Hamar
Hamar is a town in Hamar Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. Hamar is the administrative centre of Hamar Municipality. It is located in the traditional region of Hedmarken. The town is located on the shores of Mjøsa, Norway's largest lak ...
the same afternoon, but with the rapid advance of German troops, the group moved on to Elverum. The assembled Storting unanimously enacted a resolution, the so-called Elverum Authorization, granting the cabinet full powers to protect the country until such time as the Storting could meet again.
The next day, Curt Bräuer, the German Ambassador to Norway, demanded a meeting with Haakon. The German diplomat called on Haakon to accept Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
's demands to end all resistance and appoint Vidkun Quisling as prime minister. Quisling, the leader of Norway's fascist party, the Nasjonal Samling, had declared himself prime minister hours earlier in Oslo as head of what would be a German puppet government; had Haakon formally appointed him, it would effectively have given legal sanction to the invasion. Bräuer suggested that Haakon follow the example of the Danish government and his brother, Christian X
Christian X ( da, Christian Carl Frederik Albert Alexander Vilhelm; 26 September 1870 – 20 April 1947) was King of Denmark from 1912 to his death in 1947, and the only King of Iceland as Kristján X, in the form of a personal union rather ...
, which had surrendered almost immediately after the previous day's invasion, and threatened Norway with harsh reprisals if it did not surrender. Haakon told Bräuer that he could not make the decision himself, but could only act on the advice of the Government.
In a meeting in Nybergsund, the King reported the German ultimatum to the cabinet sitting as a council of state. Haakon told the cabinet:
I am deeply affected by the responsibility laid on me if the German demand is rejected. The responsibility for the calamities that will befall people and country is indeed so grave that I dread to take it. It rests with the government to decide, but my position is clear. For my part I cannot accept the German demands. It would conflict with all that I have considered to be my duty as King of Norway since I came to this country nearly thirty-five years ago.Haakon went on to say that he could not appoint Quisling as prime minister, since he knew neither the people nor the Storting had confidence in him. However, if the cabinet felt otherwise, the King said he would abdicate so as not to stand in the way of the Government's decision.
Nils Hjelmtveit
Nils Hjelmtveit (21 July 1892–30 October 1985) was a Norwegian educator and politician for the Labour Party. He was mayor of Stokken, MP from 1925 to 1930, Minister of Education and Church Affairs from 1935 to 1945 and County Governor ...
, Minister of Church and Education, later wrote:
This made a great impression on us all. More clearly than ever before, we could see the man behind the words; the king who had drawn a line for himself and his task, a line from which he could not deviate. We had through the five years n governmentlearned to respect and appreciate our king, and now, through his words, he came to us as a great man, just and forceful; a leader in these fatal times to our country.Inspired by Haakon's stand, the Government unanimously advised him not to appoint any government headed by Quisling. Within hours, it telephoned its refusal to Bräuer. That night,
NRK
NRK, an abbreviation of the Norwegian ''Norsk Rikskringkasting AS'', generally expressed in English as the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation, is the Norwegian government-owned radio and television public broadcasting company, and the largest ...
broadcast the government's rejection of the German demands to the Norwegian people. In that same broadcast, the Government announced that it would resist the German invasion as long as possible, and expressed their confidence that Norwegians would lend their support to the cause.
After Norway was eventually invaded, Quisling, "transformed he countryinto a one-party fascist state and recruited 6,000 Norwegians to fight alongside the Germans on the Russian front". A very small percentage of the population supported Quisling and many joined the Norwegian resistance movement
The Norwegian resistance ( Norwegian: ''Motstandsbevegelsen'') to the occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany began after Operation Weserübung in 1940 and ended in 1945. It took several forms:
*Asserting the legitimacy of the exiled governme ...
. After the war, Quisling would be tried for treason, found guilty and executed.
Norwegian campaign
 The following morning, 11 April 1940, in an attempt to wipe out Norway's unyielding king and government, bombers attacked Nybergsund, destroying the small town where the Government was staying. Neutral Sweden was only away, but the Swedish government decided it would "detain and incarcerate" King Haakon if he crossed their border (which Haakon never forgave). The Norwegian king and his ministers took refuge in the snow-covered woods and escaped harm, continuing farther north through the mountains toward Molde on Norway's west coast. As the British forces in the area lost ground under Luftwaffe bombardment, the King and his party were taken aboard the British cruiser HMS ''Glasgow'' at Molde and conveyed a further north to
The following morning, 11 April 1940, in an attempt to wipe out Norway's unyielding king and government, bombers attacked Nybergsund, destroying the small town where the Government was staying. Neutral Sweden was only away, but the Swedish government decided it would "detain and incarcerate" King Haakon if he crossed their border (which Haakon never forgave). The Norwegian king and his ministers took refuge in the snow-covered woods and escaped harm, continuing farther north through the mountains toward Molde on Norway's west coast. As the British forces in the area lost ground under Luftwaffe bombardment, the King and his party were taken aboard the British cruiser HMS ''Glasgow'' at Molde and conveyed a further north to Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
, where a provisional capital was established on 1 May. Haakon and Crown Prince Olav took up residence in a forest cabin in Målselvdalen
Målselvdalen is the largest valley in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The river Målselva runs through the valley, ending at the Målselvfjorden (an arm off the main Malangen fjord). The long valley runs to the north, along with the river, ...
valley in inner Troms County, where they would stay until evacuation to the United Kingdom.
The Allies had a fairly secure hold over northern Norway until late May. The situation was dramatically altered, however, by their deteriorating situation in the Battle of France. With the Germans rapidly overrunning France, the Allied high command decided that the forces in northern Norway should be withdrawn. The Royal Family and Norwegian Government were evacuated from Tromsø on 7 June aboard HMS ''Devonshire'' with a total of 461 passengers. This evacuation became extremely costly for the Royal Navy when the German warships ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' attacked and sank the nearby aircraft carrier HMS ''Glorious'' with its escorting destroyers HMS ''Acasta'' and HMS ''Ardent''. ''Devonshire'' did not rebroadcast the enemy sighting report made by ''Glorious'' as it could not disclose its position by breaking radio silence. No other British ship received the sighting report, and 1,519 British officers and men and three warships were lost. ''Devonshire'' arrived safely in London and King Haakon and his Cabinet set up a Norwegian government in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile ...
in the British capital.
Government in exile
Foliejon Park
Foliejon Park is a manorialism, manorial country house in the civil parish of Winkfield in the England, English county of Berkshire. The building has been listed as Listed building, Grade II since 7 December 1966 and was the temporary residence o ...
in Winkfield, near Windsor, in Berkshire, where they remained until the liberation of Norway. The King's official residence was the Norwegian Legation at 10 Palace Green, Kensington, which became the seat of the Norwegian government in exile. Here Haakon attended weekly Cabinet meetings and worked on the speeches which were regularly broadcast by radio to Norway by the BBC World Service
The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC, with funding from the British Government through the Foreign Secretary's office. It is the world's largest external broadcaster in terms of reception a ...
. These broadcasts helped to cement Haakon's position as an important national symbol to the Norwegian resistance. Many broadcasts were made from Saint Olav's Norwegian Church in Rotherhithe, where the Royal Family were regular worshippers.
 Meanwhile, Hitler had appointed
Meanwhile, Hitler had appointed Josef Terboven
Josef Terboven (23 May 1898 – 8 May 1945) was a Nazi Party official and politician who was the long-serving '' Gauleiter'' of Gau Essen and the ''Reichskommissar'' for Norway during the German occupation.
Early life
Terboven was born in E ...
as ' for Norway. On Hitler's orders, Terboven attempted to coerce the Storting
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years ...
to depose the King; the Storting declined, citing constitutional principles. A subsequent ultimatum was made by the Germans, threatening to intern all Norwegians of military age in German concentration camps. With this threat looming, the Storting's representatives in Oslo wrote to their monarch on 27 June, asking him to abdicate. The King declined, politely replying that the Storting was acting under duress. The King gave his answer on 3 July, and proclaimed it on BBC radio on 8 July.
After one further German attempt in September to force the Storting to depose Haakon failed, Terboven finally decreed that the Royal Family had "forfeited their right to return" and dissolved the democratic political parties.
During Norway's five years under German control, many Norwegians surreptitiously wore clothing or jewellery made from coins bearing Haakon's "H7" monogram as symbols of resistance to the German occupation
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 ...
and of solidarity with their exiled King and Government, just as many people in Denmark wore his brother's monogram on a pin. The King's monogram was also painted and otherwise reproduced on various surfaces as a show of resistance to the occupation.
After the end of the war, Haakon and the Norwegian royal family returned to Norway aboard the cruiser , arriving with the First Cruiser Squadron to cheering crowds in Oslo on 7 June 1945, exactly five years after they had been evacuated from Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
. Crown Prince Olav had returned a few weeks earlier, on 13 May 1945.
Post-war years
 After his return, Haakon did not continue the political role that he had played during the war, and limited himself to his constitutional duties as head of state. In the late summer of 1945 he went on an extensive tour of Norway to examine the war damage and to give consolation to the population. Because of his role during the war and his personal integrity, Haakon VII was considered the highest moral authority in the country and enjoyed great esteem in all classes of the population.
In 1947, the Norwegian people, by public subscription, purchased the royal yacht ''Norge'' for the King.
In 1952, he attended the funeral of his wife's nephew King
After his return, Haakon did not continue the political role that he had played during the war, and limited himself to his constitutional duties as head of state. In the late summer of 1945 he went on an extensive tour of Norway to examine the war damage and to give consolation to the population. Because of his role during the war and his personal integrity, Haakon VII was considered the highest moral authority in the country and enjoyed great esteem in all classes of the population.
In 1947, the Norwegian people, by public subscription, purchased the royal yacht ''Norge'' for the King.
In 1952, he attended the funeral of his wife's nephew King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of I ...
and openly wept.
The King's granddaughter, Princess Ragnhild, married businessman Erling Lorentzen (of the Lorentzen family
:''Lorentzen is a common surname in Denmark and Norway. This article refers to the family related to the Norwegian royal family.''
Lorentzen or Bie-Lorentzen is a Norwegian family of Danish origin. Several members have been noted as shipping magna ...
) on 15 May 1953, being the first member of the new Norwegian royal family to marry a commoner.
Haakon lived to see two of his great-grandchildren born; Haakon Lorentzen (b. 23 August 1954) and Ingeborg Lorentzen (b. 3 February 1957).
Crown Princess Märtha died of cancer on 5 April 1954.
King Haakon VII fell in his bathroom at the Bygdøy Royal Estate
Bygdøy Royal Estate ( no, Bygdøy kongsgård), also known as the ''Bygdø Royal Farm'', is a Kongsgård estate and manor house that occupies a large part of the northwestern part of the Bygdøy peninsula in Oslo, Norway. It is the official summer ...
(''Bygdøy kongsgård'') in July 1955. This fall, which occurred just a month before his eighty-third birthday, resulted in a fracture to the thighbone
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
and, although there were few other complications resulting from the fall, the King was left using a wheelchair. The once-active King was said to have been depressed by his resulting helplessness and began to lose his customary involvement and interest in current events. With Haakon's loss of mobility, and as his health deteriorated further in the summer of 1957, Crown Prince Olav appeared on behalf of his father on ceremonial occasions and took a more active role in state affairs.
Death and succession
 Haakon died at the Royal Palace in Oslo on 21 September 1957. He was 85 years old. At his death, Olav succeeded him as Olav V. Haakon was buried on 1 October 1957 alongside his wife in the white sarcophagus in the Royal Mausoleum at Akershus Fortress. He was the last surviving son of King Frederick VIII of Denmark.
Haakon died at the Royal Palace in Oslo on 21 September 1957. He was 85 years old. At his death, Olav succeeded him as Olav V. Haakon was buried on 1 October 1957 alongside his wife in the white sarcophagus in the Royal Mausoleum at Akershus Fortress. He was the last surviving son of King Frederick VIII of Denmark.
Legacy
Haakon VII is regarded by many as one of the greatest Norwegian leaders of the pre-war period, managing to hold his young and fragile country together in unstable political conditions. He was ranked highly in the Norwegian of the Century poll in 2005.Honours
TheKing Haakon VII Sea
King Haakon VII Sea ( no, King Haakon VII Hav) is a proposed name for part of the Southern Ocean on the coast of East Antarctica.
Geography
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), often recognized as the authority for worldwide wa ...
in East Antarctica is named in the king's honour as well as the entire plateau surrounding the South Pole was named ''King Haakon VII Vidde
A number of Antarctic features were named after Norwegian royal family members. This is due to either the name being bestowed by Roald Amundsen when he reached the South Pole as the first person ever in 1911, or due to Norwegian feats of explorati ...
'' by Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Amundsen beg ...
when he in 1911 became the first human to reach the South Pole. See Polheim
Polheim ("Home at the Pole") was Roald Amundsen's name for his camp (the first ever) at the South Pole. He arrived there on December 14, 1911, along with four other members of his expedition: Helmer Hanssen, Olav Bjaaland, Oscar Wisting, and Sve ...
.
In 1914 Haakon County
Haakon County is a county in the U.S. state of South Dakota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,872. Its county seat is Philip.
History
The county was created in 1914 and organized in 1915, and was formed from the original countie ...
in the American state of South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large po ...
was named in his honour.
Two Royal Norwegian Navy
The Royal Norwegian Navy ( no, Sjøforsvaret, , Sea defence) is the branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces responsible for naval operations of Norway. , the Royal Norwegian Navy consists of approximately 3,700 personnel (9,450 in mobilized state, ...
ships—'' King Haakon VII'', an escort ship in commission from 1942 to 1951, and '' Haakon VII'', a training ship in commission from 1958 to 1974—have been named after King Haakon VII.
For his struggles against the Nazi regime and his effort to revive the Holmenkollen ski festival following World War II, King Haakon VII earned the Holmenkollen medal in 1955 (Shared with Hallgeir Brenden, Veikko Hakulinen
Veikko Johannes Hakulinen (4 January 1925 – 24 October 2003) was a Finnish cross-country skier, triple champion in both the Olympics and World Championships. He also competed in biathlon, orienteering, ski-orienteering, cross-country running, a ...
, and Sverre Stenersen
Sverre Stenersen (18 June 1926 – 17 December 2005) was a Norwegian Nordic combined skier who dominated the event throughout the 1950s. His biggest triumphs were winning individual gold medals at the 1954 World Championships and 1956 Olympics. ...
), one of only 11 people not famous for Nordic skiing to receive this honour. (The others are Norway's Stein Eriksen, Borghild Niskin
Borghild Niskin (19 February 1924 – 18 January 2013) is a Nordic country located on ...) are the others.) She also finished fifth in the alpine combined event at the Alpine World Skiing Championships in 1956.
References
External links
*
...
, Inger Bjørnbakken
Inger Bjørnbakken (28 December 1933 – 13 February 2021) was a Norwegian alpine skier.
Career
She was born in Bærum and represented the club Bærums SK.
She finished tied for sixth place (with fellow Norwegian Astrid Sandvik) in the women' ...
, Astrid Sandvik
Astrid Sandvik (born 1 October 1939) is a Norwegian Alpine skier who finished tied for sixth place (with fellow Norwegian and 1958 Holmenkollen medalist Inger Bjørnbakken) in the women's slalom at the 1956 Winter Olympics in Cortina d'Ampezzo ...
, King Olav V (his son), Erik Håker, Jacob Vaage
Jakob Vaage (9 February 1905 – 29 January 1994) was a Norwegian educator, author and historian. He served as secretary of the Association for the Promotion of Skiing and curator of the Holmenkollen Ski Museum.
Biography
Vaage was born in Aker ...
, King Harald V (his paternal grandson), and Queen Sonja (his paternal granddaughter-in-law), and Sweden's Ingemar Stenmark
Jan Ingemar Stenmark (; born 18 March 1956) is a Swedish former World Cup alpine ski racer. He is regarded as one of the most prominent Swedish athletes ever, and as the greatest slalom and giant slalom specialist of all time. He competed fo ...
).
His father-in-law King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
appointed him Honorary Lieutenant in the British Fleet shortly after succeeding in February 1901. His father King Frederick VIII appointed him Admiral of the Royal Danish Navy on 20 November 1905.
;NationalRoyal House of Norway web page on King Haakon VII's decorations(Norwegian) Retrieved 5 October 2007. * : **
Knight of the Elephant
The Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) is a Danish order of chivalry and is Denmark's highest-ranked honour. It has origins in the 15th century, but has officially existed since 1693, and since the establishment of constitutional ...
, ''3 August 1890''
** Cross of Honour of the Order of the Dannebrog
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a s ...
, ''3 August 1890''
** Grand Commander of the Dannebrog, ''28 July 1912''
** King Christian X's Freedom Medal
** Commemorative Medal for King Christian IX and Queen Louise's Golden Wedding anniversary
** Commemorative Medal for King Christian IX's 100th birthday
** Commemorative Medal for King Frederik VIII's 100th birthday
* :
** War Cross with Sword
** Gold Medal for Outstanding Civic Achievement
** Grand Master of the Order of St. Olav
The Royal Norwegian Order of Saint Olav ( no, Den Kongelige Norske Sankt Olavs Orden; or ''Sanct Olafs Orden'', the old Norwegian name) is a Norwegian order of chivalry instituted by King Oscar I on 21 August 1847. It is named after King Olav II ...
, ''18 November 1905''
;Foreign
In popular culture
Haakon was portrayed byJakob Cedergren
Jakob Cedergren (born 10 January 1973) is a Swedish-born Danish actor. He has appeared in more than 40 films and television shows since 1998. He starred in the film '' Dark Horse'', which was screened in the Un Certain Regard section at the 2005 ...
in the 2009 NRK
NRK, an abbreviation of the Norwegian ''Norsk Rikskringkasting AS'', generally expressed in English as the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation, is the Norwegian government-owned radio and television public broadcasting company, and the largest ...
drama series '' Harry & Charles'', a series that focused on the events leading up to the election of King Haakon in 1905. Jesper Christensen portrayed the King in the 2016 film '' The King's Choice'' (''Kongens nei'') which was based on the events surrounding the German invasion of Norway and the King's decision to resist. The film won widespread critical acclaim, and was Norway's submission for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film at the 89th Academy Awards. The film made the shortlist of nine finalists in December 2016. Haakon was portrayed by Søren Pilmark
Søren Louis Pilmark (born 16 October 1955) is a Danish actor. Pilmark has worked as a film and theatrical actor, a director, and as an author.
Career Theater
Pilmark graduated from the School of Acting at Aarhus Theater in 1977, where he ...
in the 2020 NRK drama series Atlantic Crossing
''Atlantic Crossing'' is the sixth studio album by English singer-songwriter Rod Stewart, released on 15 August 1975. It peaked at number one in the UK (his fifth solo album to do so), and number nine on the ''Billboard'' Top Pop Albums chart ...
, a series regarding Crown Princess Märtha's handling of the royal family exile from 1939 to 1945.
Ancestry
See also
* List of state visits made by Haakon VII of Norway * List of covers of Time magazine (1920s), (1930s)References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * *External links
Official Website of the Royal House of Norway
* ttp://www.kongernessamling.dk/en/amalienborg/person/carl-haakon-vii/ Prince Carl (Haakon VII)at the website of the
Royal Danish Collection
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
at Amalienborg Palace
The Royal Norwegian Order of St Olav − H.M. King Haakon VII the former Grand Master of the Order
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Haakon 07 Of Norway 1872 births 1957 deaths 20th-century Norwegian monarchs Norwegian monarchs Danish princes House of Glücksburg (Norway) House of Glücksburg (Denmark) Norwegian people of World War II Governments in exile during World War II Protestant monarchs 19th-century Danish naval officers 20th-century Danish naval officers Presidents of the Organising Committees for the Olympic Games Recipients of the War Cross with Sword (Norway) Holmenkollen medalists Grand Commanders of the Order of the Dannebrog Recipients of the Cross of Honour of the Order of the Dannebrog Grand Crosses of the Order of the White Lion Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur Recipients of the Croix de Guerre 1939–1945 (France) Extra Knights Companion of the Garter Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order Bailiffs Grand Cross of the Order of St John Recipients of the War Cross (Greece) Grand Crosses of the Order of the Sun of Peru 3 3 3 Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 1st class Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Russia) Recipients of the Order of Saint Stanislaus (Russian) Knights of the Golden Fleece of Spain Grand Crosses with Diamonds of the Order of the Sun of Peru Burials at the Royal Mausoleum (Norway) Sons of kings Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland)