HMS Agamemnon (1906) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HMS ''Agamemnon'' was one of two
 HMS ''Agamemnon'' was ordered in 1904 and was the first warship built by the William Beardmore and Company's Dalmuir Naval Construction Works. She was laid down on 15 May 1905 and launched on 23 June 1906 before the dockyards themselves were finished. Her completion was greatly delayed by labour troubles and by the diversion of the 12-inch (305 mm) guns intended for her to expedite completion of , and she was not finally completed until June 1908, six months before her sister ''Lord Nelson''.McBride, p. 72
''Agamemnon'' displaced at deep load as built, with a length of , a beam of and a draft of . She was powered by two inverted
HMS ''Agamemnon'' was ordered in 1904 and was the first warship built by the William Beardmore and Company's Dalmuir Naval Construction Works. She was laid down on 15 May 1905 and launched on 23 June 1906 before the dockyards themselves were finished. Her completion was greatly delayed by labour troubles and by the diversion of the 12-inch (305 mm) guns intended for her to expedite completion of , and she was not finally completed until June 1908, six months before her sister ''Lord Nelson''.McBride, p. 72
''Agamemnon'' displaced at deep load as built, with a length of , a beam of and a draft of . She was powered by two inverted  The ship was armed with four BL 12-inch Mk X guns arranged in two twin
The ship was armed with four BL 12-inch Mk X guns arranged in two twin
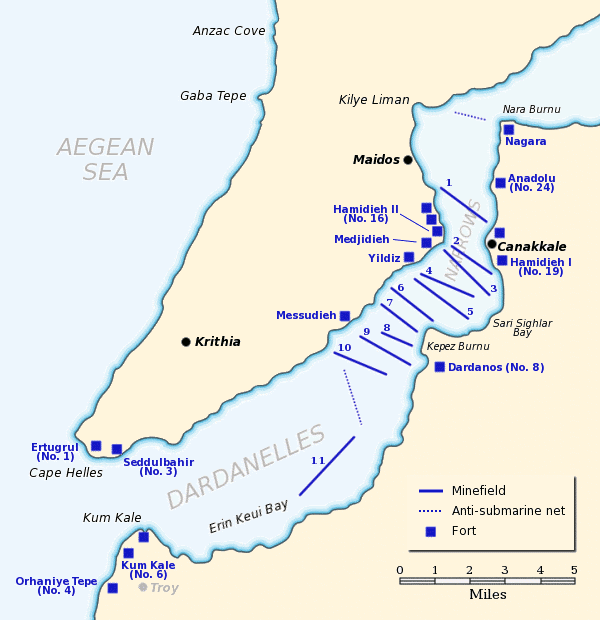 In February 1915, ''Agamemnon'' was ordered to participate in the Dardanelles Campaign. She departed Portland on 9 February, and joined the British Dardanelles Squadron at
In February 1915, ''Agamemnon'' was ordered to participate in the Dardanelles Campaign. She departed Portland on 9 February, and joined the British Dardanelles Squadron at  She supported the small amphibious landings of 4 March and participated in another bombardment on 6 March 1915. She came under heavy fire from Fort Hamidieh on 7 March, taking eight hits from large-calibre shells; one of them, allegedly a round, blew a large hole in her
She supported the small amphibious landings of 4 March and participated in another bombardment on 6 March 1915. She came under heavy fire from Fort Hamidieh on 7 March, taking eight hits from large-calibre shells; one of them, allegedly a round, blew a large hole in her
 Based on the earlier experience in Radio Control British drone weapons 'Agamemnon' was modified at
Based on the earlier experience in Radio Control British drone weapons 'Agamemnon' was modified at
Lord Nelson class battleships
{{DEFAULTSORT:Agamemnon (1906) Lord Nelson-class battleships Ships built on the River Clyde 1906 ships World War I battleships of the United Kingdom Maritime incidents in 1911
pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
battleship
A battleship is a large armour, armored warship with a main artillery battery, battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1 ...
s launched in 1906 and completed in 1908. She was the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
's second-to-last pre-dreadnought battleship to be built, followed by her sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a ...
, . She was assigned to the Channel Fleet
The Channel Fleet and originally known as the Channel Squadron was the Royal Navy formation of warships that defended the waters of the English Channel from 1854 to 1909 and 1914 to 1915.
History
Throughout the course of Royal Navy's history the ...
when the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
began in 1914. The ship was transferred to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
with ''Lord Nelson'' in early 1915 to participate in the Dardanelles Campaign. She made a number of bombardments against Turkish fortifications and in support of British troops. ''Agamemnon'' remained in the Mediterranean after the conclusion of that campaign to prevent the German battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
and light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to th ...
from breaking out into the Mediterranean. ''Agamemnon'' shot down the German Zeppelin ''LZ-55'' (''LZ-85'') during a bombing mission over Salonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
in 1916. On 30 October 1918, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
signed the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
on board the ship while she was anchored at Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...
in the northern Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi ( Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
. She was converted to a radio-controlled target ship
A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunit ...
following her return to the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
in March 1919 and began service in 1921. ''Agamemnon'' was replaced by at the end of 1926 and sold for scrap in January 1927, the last pre-dreadnought in service with the Royal Navy.
Construction and description
 HMS ''Agamemnon'' was ordered in 1904 and was the first warship built by the William Beardmore and Company's Dalmuir Naval Construction Works. She was laid down on 15 May 1905 and launched on 23 June 1906 before the dockyards themselves were finished. Her completion was greatly delayed by labour troubles and by the diversion of the 12-inch (305 mm) guns intended for her to expedite completion of , and she was not finally completed until June 1908, six months before her sister ''Lord Nelson''.McBride, p. 72
''Agamemnon'' displaced at deep load as built, with a length of , a beam of and a draft of . She was powered by two inverted
HMS ''Agamemnon'' was ordered in 1904 and was the first warship built by the William Beardmore and Company's Dalmuir Naval Construction Works. She was laid down on 15 May 1905 and launched on 23 June 1906 before the dockyards themselves were finished. Her completion was greatly delayed by labour troubles and by the diversion of the 12-inch (305 mm) guns intended for her to expedite completion of , and she was not finally completed until June 1908, six months before her sister ''Lord Nelson''.McBride, p. 72
''Agamemnon'' displaced at deep load as built, with a length of , a beam of and a draft of . She was powered by two inverted vertical triple expansion
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up he ...
four-cylinder steam engines, which developed a total of and gave a maximum speed of .
 The ship was armed with four BL 12-inch Mk X guns arranged in two twin
The ship was armed with four BL 12-inch Mk X guns arranged in two twin gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
s, one each fore and aft. Her secondary armament consisted of ten BL 9.2-inch Mk XI guns, in twin gun turrets on each corner of the superstructure, and a single gun turret between them, plus 24 QF 12-pounder 18 cwt guns. She also mounted five submerged torpedo tubes for which 23 torpedoes were stowed aboard.
''Agamemnon'' had an armour belt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practiti ...
at her waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indi ...
that was thick, as were the faces and sides of her gun turrets.
Service history
Pre-First World War
HMS ''Agamemnon'' commissioned on 25 June 1908 atChatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham (at its most extensive, in the early 20th century ...
for service in the Nore Division of the Home Fleet
The Home Fleet was a fleet of the Royal Navy that operated from the United Kingdom's territorial waters from 1902 with intervals until 1967. In 1967, it was merged with the Mediterranean Fleet creating the new Western Fleet.
Before the Firs ...
. On 11 February 1911, she grazed an uncharted rock in the harbour at Ferrol, Spain
Ferrol () is a city in the Province of A Coruña in Galicia, on the Atlantic coast in north-western Spain, in the vicinity of Strabo's Cape Nerium (modern day Cape Prior). According to the 2021 census, the city has a population of 64,785, ma ...
, and damaged her bottom.Burt, p. 298 She was temporarily attached in September 1913 to the 4th Battle Squadron
The 4th Battle Squadron was a squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships. The 4th Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Home Fleet (1912–14) and then the Grand Fleet after the outbreak of the First World War ...
.Gardiner and Gray, p. 10
First World War
After theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
began in August 1914, ''Agamemnon'' was assigned to the 5th Battle Squadron
The 5th Battle Squadron was a squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships. The 5th Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Second Fleet. During the First World War, the Home Fleet was renamed the Grand Fleet.
His ...
in the Channel Fleet
The Channel Fleet and originally known as the Channel Squadron was the Royal Navy formation of warships that defended the waters of the English Channel from 1854 to 1909 and 1914 to 1915.
History
Throughout the course of Royal Navy's history the ...
and was based at Portland. With other ships, she covered the safe transport of the British Expeditionary Force, under the command of Sir John French
Field Marshal John Denton Pinkstone French, 1st Earl of Ypres, (28 September 1852 – 22 May 1925), known as Sir John French from 1901 to 1916, and as The Viscount French between 1916 and 1922, was a senior British Army officer. Born in Kent ...
, to France. On 14 November, she transferred to Sheerness
Sheerness () is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby tow ...
to guard the English coast against the possibility of a German invasion. She returned to Portland on 30 December and was employed in the defence of the southern ports of England and patrols of the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
until February 1915.
Dardanelles campaign, 1915–16
 In February 1915, ''Agamemnon'' was ordered to participate in the Dardanelles Campaign. She departed Portland on 9 February, and joined the British Dardanelles Squadron at
In February 1915, ''Agamemnon'' was ordered to participate in the Dardanelles Campaign. She departed Portland on 9 February, and joined the British Dardanelles Squadron at Mudros
Moudros ( el, Μούδρος) is a town and a former municipality on the island of Lemnos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lemnos, of which it is a municipal unit. It covers the entire eas ...
10 days later. That was the second day of the opening bombardment of the Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, لِسانِ عُثمانى, Lisân-ı Osmânî, ; tr, Osmanlı Türkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extens ...
forts guarding the entrance to the Dardanelles, and the ship immediately joined the attack. She also took part in the subsequent bombardment of the inner forts later in February. ''Agamemnon'' was hit by seven shells in ten minutes on 25 February and was holed above the waterline, suffering three dead.
 She supported the small amphibious landings of 4 March and participated in another bombardment on 6 March 1915. She came under heavy fire from Fort Hamidieh on 7 March, taking eight hits from large-calibre shells; one of them, allegedly a round, blew a large hole in her
She supported the small amphibious landings of 4 March and participated in another bombardment on 6 March 1915. She came under heavy fire from Fort Hamidieh on 7 March, taking eight hits from large-calibre shells; one of them, allegedly a round, blew a large hole in her quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ...
and wrecked the wardroom and the gunroom
A gunroom is the junior officers' mess on a naval vessel. It was occupied by the officers below the rank of lieutenant. In the wooden sailing ships it was on the lower deck, and was originally the quarters of the gunner, but in its form as a mess ...
. She also took several hits by light shells that day, and, although she suffered damage to her superstructure, her fighting and steaming capabilities were not seriously impaired.
The ship also participated in the main attack on the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
forts on 18 March. This time, a howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
battery opened fire on ''Agamemnon'' and hit her 12 times in 25 minutes; five of the howitzer shells hit her armour and did no damage, but the seven that hit outside her armour protection did considerable structural damage and temporarily put one of her guns out of action.
On 25 April, ''Agamemnon'' supported the main landings as part of the 5th Squadron, and after that she patrolled to protect Allied minesweeping
Minesweeping is the practice of the removal of explosive naval mines, usually by a specially designed ship called a minesweeper using various measures to either capture or detonate the mines, but sometimes also with an aircraft made for that ...
and netlaying vessels operating in the Dardanelles. In action against Ottoman field batteries, she took two hits between 28 April and 30 April, and she provided fire support for Allied troops during a Turkish counterattack on 1 May. ''Agamemnon'' bombarded Ottoman artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
batteries on 6 May prior to the Second Battle of Krithia
The Second Battle of Krithia ( tr, İkinci Kirte Muharebesi) continued the Allies' attempts to advance on the Helles battlefield during the Battle of Gallipoli of the First World War. The village of Krithia and neighbouring hill of Achi Bab ...
.
''Agamemnon'' was withdrawn to Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
later in May to undergo a refit and returned to the Dardanelles in June. On 2 December, the ship joined the protected cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers re ...
and monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West ...
in bombarding the Kavak bridge, destroying several spans of it and interdicting Ottoman communications to the Gallipoli Peninsula.
Mediterranean operations, 1916–18
With the end of the Dardanelles Campaign in January 1916, British naval forces in the area were reorganized, and ''Agamemnon'' became part of theEastern Mediterranean Squadron
The Eastern Mediterranean Squadron later known as the British Aegean Squadron was a naval formation of the Mediterranean Fleet based at Mudros from 1914 to 1916. It then alternated between Mudros and Salonika from 1917 to 1919.
History
The Easter ...
, which was re-designated the 'Aegean Squadron' in August 1917. Under both names, the squadron was dispersed throughout the area to protect Allied-held islands, support the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
at Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, and guard against any attempted breakout from the Dardanelles by the German battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
and light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to th ...
. ''Agamemnon'' spent the remainder of the war based at Salonika and Mudros
Moudros ( el, Μούδρος) is a town and a former municipality on the island of Lemnos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lemnos, of which it is a municipal unit. It covers the entire eas ...
, alternating between the two bases with her sister ''Lord Nelson''; ''Agamemnon'' was based mostly at Mudros, ''Lord Nelson'' mostly at Salonika. While carrying out these duties, ''Agamemnon'' damaged the Imperial German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Navy Zeppelin ''LZ-55'' (''LZ-85'') on 5 May at Salonika with a shell from a 12-pounder and forced it to crash-land.
Of all the responsibilities given the two ships, the most important was to guard the Eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
against a breakout by ''Goeben'', but when ''Goeben'' and ''Breslau'' finally made their breakout attempt on 20 January 1918, ''Lord Nelson'' was away at Salonika and ''Agamemnon'' could not get steam up to depart Mudros in time to participate in the resulting Battle of Imbros
The Battle of Imbros was a naval action that took place during the First World War. The battle occurred on 20 January 1918 when an Ottoman squadron engaged a flotilla of the British Royal Navy off the island of Imbros in the Aegean Sea. A lac ...
. After both German ships struck mines, ''Breslau'' sank and ''Goeben'' returned to the Dardanelles before ''Agamemnon'' could arrive on the scene.
''Agamemnon'' underwent a refit at Malta in 1918. On 30 October, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
signed the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
on board ''Agamemnon'' while she was anchored at Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...
in the northern Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi ( Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
.
Post-war
''Agamemnon'' was part of the British squadron that went toConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in November 1918 following the armistice. She returned to the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
in March 1919, where she paid off at Chatham Dockyard and went into reserve on 20 March.
In September 1918, the Commander-in-Chief, Grand Fleet
The Grand Fleet was the main battlefleet of the Royal Navy during the First World War. It was established in August 1914 and disbanded in April 1919. Its main base was Scapa Flow in the Orkney Islands.
History
Formed in August 1914 from the F ...
, Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet ...
David Beatty, had called for a large target to be provided which would allow realistic gunnery practice for the battleships of the Grand Fleet, which had seen little action since the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet, under Vice ...
in 1916. Tests against armour plate in 1919 demonstrated that firing 15-inch (381-mm) guns at any pre-dreadnought would sink her quickly, but the use of a pre-dreadnought for target practice and tests by guns of 6-inch calibre (152-mm) or smaller seemed practical. At first, the pre-dreadnought was suggested for target duties, but ultimately ''Agamemnon'' became available and was selected instead.Burt, p. 295
 Based on the earlier experience in Radio Control British drone weapons 'Agamemnon' was modified at
Based on the earlier experience in Radio Control British drone weapons 'Agamemnon' was modified at Chatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham (at its most extensive, in the early 20th century ...
for use as a target ship
A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunit ...
between 6 December 1920 and 8 April 1921.Most sources say that ''Agamemnon'' served as a target ship
A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunit ...
from 1923 to 1926, and Burt, p. 298, says that she underwent conversion to a radio-controlled target ship from September 1922 to April 1923. However, Burt, p. 295, provides specifics about her conversion to a radio-controlled target ship in 1920–21, as well as specifics about her use as a target in 1921. It is possible that the conversion took place in 1920–1921 and is often confused with a 1922–23 refit. The ship was rewired for radio control and stripped; the 12-inch turrets remained aboard, but all of her guns and their equipment were removed, as were her torpedo equipment, flying deck, sea cabins, main derrick and boat equipment, lower conning tower, masts and yards, most of her crew amenities, and other unnecessary equipment. Unnecessary hatches, coamings, scuttles, and lifts were removed and plated over, and she was ballast
Ballast is material that is used to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within a boat, ship ...
ed differently than she had been as a battleship. It was not intended to sink her, so she was assigned a crew of 153 to maintain and operate her when she was not under fire.
''Agamemnon''s first target service took place before her modifications were completed. On 19 March 1921, she was exposed to a cloud of poisonous gas to determine the effect of gas on a battleship. It was found that gas could penetrate the ship via her various openings, but the ship had not been sealed against gas before the trial and no accurate results applicable to a commissioned battleship could be obtained. On 21 September, she was subjected to machine-gun fire by strafing aircraft. These trials showed that such strafing could harass a battleship, but could not impair her fighting or steaming capabilities, and helped to determine protection for bridge personnel.
''Agamemnon'' also was used to test the vulnerability of battleships to 6-inch (152-mm), 5.5-inch (140-mm), and 4.7-inch (120-mm) rounds fired at her by ships such as the battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
s and while she maneuvered under radio control. These tests showed that ships protected as well as ''Agamemnon'', such as the later dreadnoughts, would suffer damage to their upper works if struck by such shells, but would not have their steaming or fighting capability seriously impaired even by numerous smaller-caliber hits. Agamemnon was replaced in 1926 by HMS when this dreadnought battleship
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
was converted to Remote Radio Control.
Disposal
''Agamemnon'' was relieved as target ship by the dreadnought in December 1926. By then the last British pre-dreadnought battleship in existence, she was sold to J Cashmore of Newport, South Wales, on 24 January 1927 for scrap, and departedPortsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is ...
on 1 March to be broken up at Newport.
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * *External links
Lord Nelson class battleships
{{DEFAULTSORT:Agamemnon (1906) Lord Nelson-class battleships Ships built on the River Clyde 1906 ships World War I battleships of the United Kingdom Maritime incidents in 1911