Gyeongbu Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Gyeongbu Line (''Gyeongbuseon'') is a
 In 1894–1895, the
In 1894–1895, the
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
line in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
and is considered to be the most important and one of the oldest ones in the country. It was constructed in 1905, connecting Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
with Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea ...
via Suwon
Suwon (, ) is the capital and largest city of Gyeonggi-do, South Korea's most populous province which surrounds Seoul, the national capital. Suwon lies about south of Seoul. It is traditionally known as "The City of Filial Piety". With a popul ...
, Daejeon, and Daegu
Daegu (, , literally 'large hill', 대구광역시), formerly spelled Taegu and officially known as the Daegu Metropolitan City, is a city in South Korea.
It is the third-largest urban agglomeration in South Korea after Seoul and Busan; it is ...
. It is by far the most heavily travelled rail line in South Korea.
All types of high-speed, express, local, and freight trains provide frequent service along its entire length.
History
 In 1894–1895, the
In 1894–1895, the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
and Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
fought the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
for influence over Korea. Following the war, Japan competed with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
's railway expansion in Northeast Asia, which led it to seek the right from the Korean Empire
The Korean Empire () was a Korean monarchical state proclaimed in October 1897 by Emperor Gojong of the Joseon dynasty. The empire stood until Japan's annexation of Korea in August 1910.
During the Korean Empire, Emperor Gojong oversaw the Gwan ...
to build a railway from Busan to Keijō. This railway line was intended by Japan to solidify its strategic positions against Russia, which it would later go to war. Surveying began in 1896, and in spite of local protests, the Korean Empire gave Japan the right to build the line in 1898. Construction of the railway started on August 20, 1901, with a ceremony at Eitōho-ku, Keijō. Construction was supervised by Japanese, with local Koreans commandeered into forced labor and paid with coupons.
Japan also sought to gain control of the Keigi Railway project that was to continue tracks further north, recognizing the trunk route as a means to keep Korea under its influence. After the outbreak of the Russo-Japanese War, Japan ignored Korea's declaration of neutrality and transported troops to Incheon
Incheon (; ; or Inch'ŏn; literally "kind river"), formerly Jemulpo or Chemulp'o (제물포) until the period after 1910, officially the Incheon Metropolitan City (인천광역시, 仁川廣域市), is a city located in northwestern South Kore ...
. Japan also forced the Korean government to sign an agreement that ceded its control of the railway. Japanese military bases were established in connection with the railway, the biggest of them next to Ryūzan Station in Keijō.
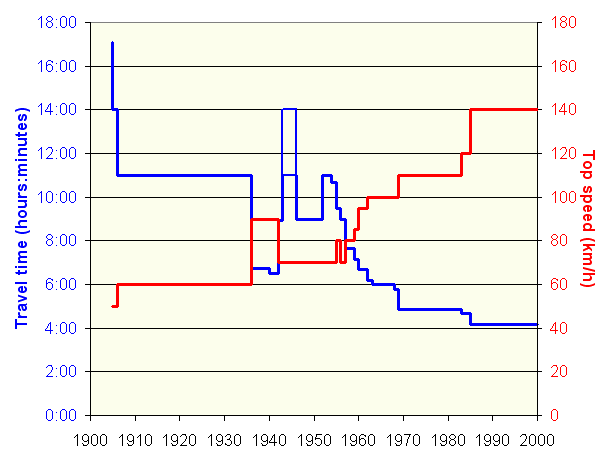
The Gyeongbu Line was publicly inaugurated on January 1, 1905 as the . The first trains travelled the line in 17 hours 4 minutes. By April 1906, travel time was reduced to 11 hours, while top speed was . The line developed into the backbone of transport in Korea under Japanese rule
Between 1910 and 1945, Korea was ruled as a part of the Empire of Japan. Joseon Korea had come into the Japanese sphere of influence with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876; a complex coalition of the Meiji government, military, and business off ...
. Following the Japanese invasion of Manchuria, from April 1, 1933, the line was traversed by direct trains from Busan to Andong (today Dandong
Dandong (), formerly known as Andong, is a coastal prefecture-level city in southeastern Liaoning province, in the northeastern region of People's Republic of China.
It is the largest Chinese border city, facing Sinuiju, North Korea across th ...
) across the border. From December 1, 1936, the ''Akatsuki'' luxury express trains ran on the line with a maximum speed of , and achieved the shortest pre-war travel time of 6 hours 30 minutes in the timetable valid from November 1, 1940.
Travel times increased greatly while the line was used for transport in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Following World War II, the Seoul–Busan express train re-established on May 20, 1946, was named ''Chosun Liberator''. During the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
, the line transported troops and refugees. The line remained the backbone of transport in South Korea after the war, when diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving whee ...
s and the cross-country Mugunghwa-ho train class was introduced. Following the 1961 coup, the Supreme Council for National Reconstruction started South Korea's first five-year plan, which included a construction program to complete the railway network, to foster economic growth. On the Gyeongbu Line, the effort was advertised with a new class of express trains named ''Jaegeon-ho'', (Reconstruction train) introduced on May 15, 1962. These trains reduced travel times below the best pre-WWII travel times for the first time, connecting Seoul and Busan in 6 hours 10 minutes at a top speed of .
From the 1960s, road construction began to make road transport more attractive and faster. Although top speed rose to and the Seoul–Busan travel time along the Gyeongbu Line was reduced to 4 hours 50 minutes by June 10, 1969, on the parallel Gyeongbu Expressway
The Gyeongbu Expressway ( ko, 경부고속도로; ''Gyeongbu Gosokdoro'') ( Asian Highway Network ) is the second oldest and most heavily travelled expressway in South Korea, connecting Seoul to Suwon, Daejeon, Gumi, Daegu, Gyeongju, Ulsan ...
, completed in 1970, travel time was only 4 hours to 4 hours 30 minutes. Korean National Railroad
The Korea Railroad Corporation ( Korean: 한국철도공사, Hanja: ), branded as KORAIL (코레일, officially changed to in November 2019), is the national railway operator in South Korea. Currently, KORAIL is a public corporation, manag ...
responded by introducing the Saemaul-ho
The Saemaeul-ho, formerly known as the Saemaul-ho and Saemaul Express, is a class of train operated by Korail, the national railroad of South Korea, since February 8, 1969. Before the introduction of the KTX express trains, the Saemaeul-ho was ...
class of elevated-comfort express trains on August 15, 1974. with the introduction of new streamlined diesel locomotives and then diesel multiple unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also ...
s in Saemaul-ho service, top speed was raised to and travel time was reduced to 4 hours 10 minutes with the timetable valid from November 16, 1985.
Upgrade
The Gyeongbu Line was extensively upgraded in parallel with the development of theSeoul Metropolitan Subway
The Seoul Metropolitan Subway is a metropolitan railway system consisting of 23 rapid transit, light metro, commuter rail and people mover lines located in northwest South Korea. The system serves most of the Seoul Metropolitan Area inc ...
urban rapid transit system and the Korea Train Express
Korea Train eXpress (), often known as KTX (), is South Korea's high-speed rail system, operated by Korail. Construction began on the high-speed line from Seoul to Busan in 1992. KTX services were launched on April 1, 2004.
From Seoul Station the ...
(KTX) high-speed rail system from the 1970s.
The Gyeongbu Line is six-tracked from Seoul to Guro, four-tracked from Guro to Cheonan, and double-tracked from Cheonan all the way to Busan. The entire line is electrified.
Relationship with the KTX project
TheSeoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
-Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea ...
axis is Korea's main traffic corridor. In 1995, it housed 73.3% of Korea's population, and conducted 70% of the freight traffic and 66% of the passenger traffic. With both the Gyeongbu Expressway
The Gyeongbu Expressway ( ko, 경부고속도로; ''Gyeongbu Gosokdoro'') ( Asian Highway Network ) is the second oldest and most heavily travelled expressway in South Korea, connecting Seoul to Suwon, Daejeon, Gumi, Daegu, Gyeongju, Ulsan ...
and Korail
The Korea Railroad Corporation ( Korean: 한국철도공사, Hanja: ), branded as KORAIL (코레일, officially changed to in November 2019), is the national railway operator in South Korea. Currently, KORAIL is a public corporation, manag ...
's Gyeongbu Line congested, the government saw the need to develop railways. The first proposals for a second Seoul-Busan railway line originated from a study prepared between 1972 and 1974 by experts of France's SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffic ...
and Japan Railway Technical Service (JARTS) on a request from the IBRD. A more detailed 1978-1981 study by KAIST, focusing on the needs of freight transport, also came to the conclusion that the necessary capacity for freight transport on the existing Gyeongbu Line could best be released by separating off long-distance passenger traffic on a parallel high speed passenger railway, which was then taken up in Korea's next Five Year Plan.
Following the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998– ...
, the government decided to finish the Gyeongbu High Speed Railway (Gyeongbu HSR) in two phases, and upgrade and electrify the conventional Gyeongbu Line for KTX services on the sections paralleling the parts of the high-speed line not completed in the first phase.
Plans foresaw the development of the Gyeongbu Line into a high-capacity freight corridor after the completion of the second phase of the Gyeongbu HSR. At the time of the opening of the Daegu–Busan section of the high-speed line on November 1, 2010, capacity available for freight trains on the conventional line was expected to increase by a factor of 7.7, while the capacity for passenger transport in the entire corridor increased by a factor of 3.4.
Electrification
The line was electrified in stages from 1974 to 2006: For KTX trains and new electric locomotives, top speed was also raised to up to 150 km/h.Services
The Gyeongbu Line is the major route out ofSeoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
and Yongsan stations and, in addition to regular departures for Busan, trains travel along the Gyeongbu Line en route to Janghang, Gwangju
Gwangju () is South Korea's sixth-largest metropolis. It is a designated metropolitan city under the direct control of the central government's Home Minister. The city was also the capital of South Jeolla Province until the provincial offic ...
, Mokpo, Suncheon
Suncheon () (''Suncheon-si'') is a city in South Jeolla Province, South Korea. It is a scenic agricultural and industrial city of around 250,000 people near Suncheon Bay. It is located in the southeastern corner of Jeollanam-do, just over an hou ...
, Yeosu, Pohang
Pohang () is a city in the province of North Gyeongsang, South Korea, and a main seaport in the Daegu-Gyeongbuk region. The built-up area of Pohang is located on the alluvium of the mouth of the Hyeongsan River. The city is divided into t ...
, Ulsan
Ulsan (), officially the Ulsan Metropolitan City is South Korea's seventh-largest metropolitan city and the eighth-largest city overall, with a population of over 1.1 million inhabitants. It is located in the south-east of the country, neighboring ...
, Haeundae, Masan, and Jinju
Jinju () is a city in South Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. It was the location of the first (1592) and second (1593) Sieges of Jinju by Japanese forces during the Imjin War. The Republic of Korea Air Force Education and Training Command is ...
. Trains for Jecheon
Jecheon () is a city in North Chungcheong Province, South Korea. The city is a major railway junction or a transportation mecca, served by the Jungang, Chungbuk and Taebaek Lines. Jecheon has scenic surroundings and several tourist spots like ...
, Andong
Andong () is a city in South Korea, and the capital of North Gyeongsang Province. It is the largest city in the northern part of the province with a population of 167,821 as of October 2010. The Nakdong River flows through the city. Andong is a ...
, and Yeongju
Yeongju () is a city in the far north region of North Gyeongsang province in South Korea, covering 668.84 km2 with a population of 113,930 people according to the 2008 census. The city borders Bonghwa county to the east, Danyang county of Nort ...
also operate along sections of the Gyeongbu Line.
On the section between Seoul Station, Guro (where roughly half of the trains leave the Gyeongbu Line to head out to Incheon
Incheon (; ; or Inch'ŏn; literally "kind river"), formerly Jemulpo or Chemulp'o (제물포) until the period after 1910, officially the Incheon Metropolitan City (인천광역시, 仁川廣域市), is a city located in northwestern South Kore ...
via the Gyeongin Line
The Gyeongin Line (Gyeonginseon) is a railway mainline in South Korea, currently connecting Guro station in Seoul and Incheon. Commuter services along the line through operates into Seoul Subway Line 1.
History
The Gyeongin Line was the f ...
), Suwon, and Byeongjeom, Seoul Subway Line 1
Seoul Metropolitan Subway Line 1 of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway is a rapid transit and commuter rail line which links central Seoul, South Korea to Soyosan Station in the northeast, Incheon in the southwest, and Sinchang (Soonchunhyang U ...
provides frequent commuter services.
The Gyeongbu Line is served along its entire length by frequent intercity Saemaul-ho
The Saemaeul-ho, formerly known as the Saemaul-ho and Saemaul Express, is a class of train operated by Korail, the national railroad of South Korea, since February 8, 1969. Before the introduction of the KTX express trains, the Saemaeul-ho was ...
and cross-country Mugunghwa-ho trains. Some trains run along the entire length of the line, others only on some sections, including trains diverging to the connected lines. As of October 2010, direct Saemaul day trains connect Seoul to Busan in a minimum 4 hours 50 minutes, and Mughungwa trains in a minimum 5 hours 28 minutes.
KTX
Korail launched KTX high-speed services with the opening of the first phase of the Gyeongbu HSR on April 1, 2004. The Seoul–Busan travel distance was shortened to 408.5 km, the shortest travel time was 2 hours 40 minutes. All KTX services use the conventional Gyeongbu Line between Seoul and the start of the Siheung Interconnection at a junction afterGeumcheon-gu Office station
Geumcheon-gu Office Station, formerly known as Siheung Station, is a station on the Line 1 of the Seoul Subway, as well as the Gyeongbu Line. Commuter rail trains on Line 1 travel southwards from here to Anyang, Suwon, Pyeongtaek and Cheonan Stat ...
, until the Siheung Interconnection diverges in a tunnel towards the present start of the Gyeongbu HSR. The terminal for most Gyeongbu KTX services is Seoul Station, for most Honam KTX services, Yongsan station. In addition, some trains continue beyond Seoul Station for 14.9 km along the Gyeongui Line to terminate at Haengsin station, next to which KTX trains have a depot. An additional stop at Yeongdeungpo station was proposed in 2004, however, the plans were dropped in face of opposition from locals living around Gwangmyeong station along the Gyeongbu HSR, who feared that Yeongdeungpo would draw away passengers from the new station and force its closing. However, the November 1, 2010, timetable change made Yeongdeungpo a KTX stop, for newly introduced trains that also use the Gyeongbu Line on the entire Seoul–Daejeon section, to serve Suwon
Suwon (, ) is the capital and largest city of Gyeonggi-do, South Korea's most populous province which surrounds Seoul, the national capital. Suwon lies about south of Seoul. It is traditionally known as "The City of Filial Piety". With a popul ...
.
From its opening, the Gyeongbu KTX service also returned to the Gyeongbu Line for two short sections crossing Daejeon and Daegu, where local disputes about the high-speed line alignment across urban areas held up construction; and all the way from Daegu to Busan. Consequently, all but two of the stations of the Gyeongbu KTX service were on the conventional Gyeongbu Line: after the two stations on the high-speed line, Gwangmyeong and Cheonan-Asan, stops were at Daejeon, Dongdaegu (East Daegu), Miryang, Gupo and Busan. Some Gyeongbu KTX services maintained service on this relation after the November 1, 2010, opening of the second phase of the Gyeongbu HSR, with the daily number of halts in Miryang and Gupo increased. Korail met local demands by introducing additional KTX services between Seoul and Dongdaegu in June 2007, which used the conventional Gyeongbu Line between Daejeon and Dongdaegu to serve Gimcheon and Gumi. However, these services were discontinued with the opening of the Gimcheon–Gumi station on the high-speed line.
The section between Daegu and Samnangjin, the junction with the Gyeongjeon Line, is also used by the Gyeongjeon KTX services, which connect Seoul to Masan on the Gyeongjeon Line since December 15, 2010, and will be extended to Jinju by 2012. Stops along the Gyeongbu Line will be at Dongdaegu and Miryang.
Evolution of long-distance passenger traffic
Between Seoul and Cheonan, the Mugunghwa and Saemaul express trains on the Gyeongbu Line gave rail around a fifth of the modal share before the launch of KTX services. Due to the short distance and the location of the KTX station outside the city, the conventional line could retain most of its passengers, and the increase in the total modal share of rail was modest. On the medium-distance relation from Seoul to Daejeon, KTX gained market share mostly at the expense of normal express services on the Gyeongbu Line, which decreased by half in the first year, while the total share of rail increased to a third. On the long-distance relations from Seoul to Daegu and Busan, the total share of rail increased from around two-fifths to a market dominating three-fifths, with the bulk of that traffic taken by the KTX. For intercity passenger traffic on the conventional Gyeongbu Line, that translates to a sharp drop on the Daejeon-Daegu section (bypassed by KTX trains) and a sharp increase on the Daegu-Busan section.Station list
See also
*Korail
The Korea Railroad Corporation ( Korean: 한국철도공사, Hanja: ), branded as KORAIL (코레일, officially changed to in November 2019), is the national railway operator in South Korea. Currently, KORAIL is a public corporation, manag ...
References
External links
{{Gyeongbu Line Railway lines in South Korea Railway lines opened in 1905 Korail lines 1905 establishments in Korea