Greater Bulgaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
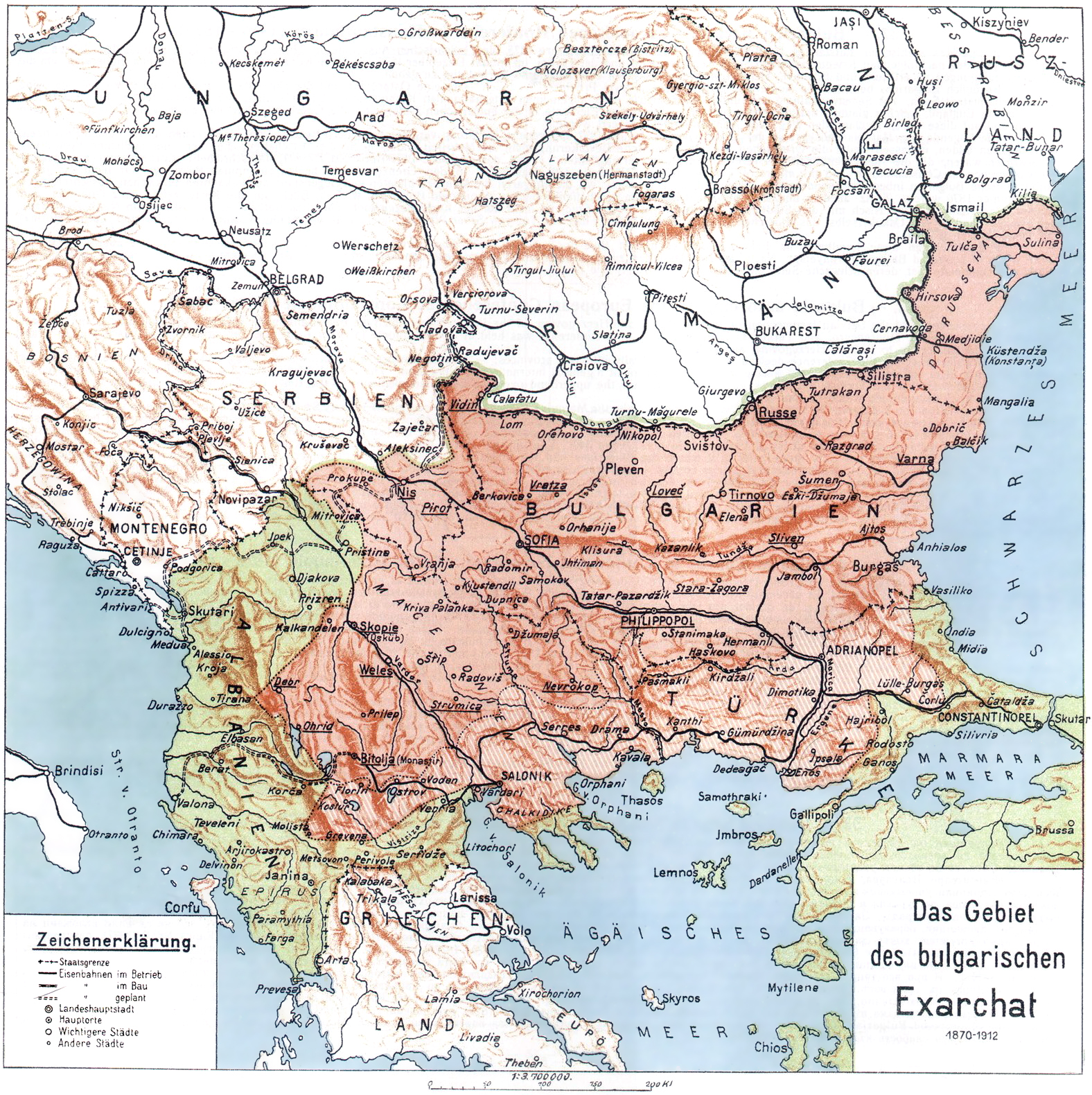

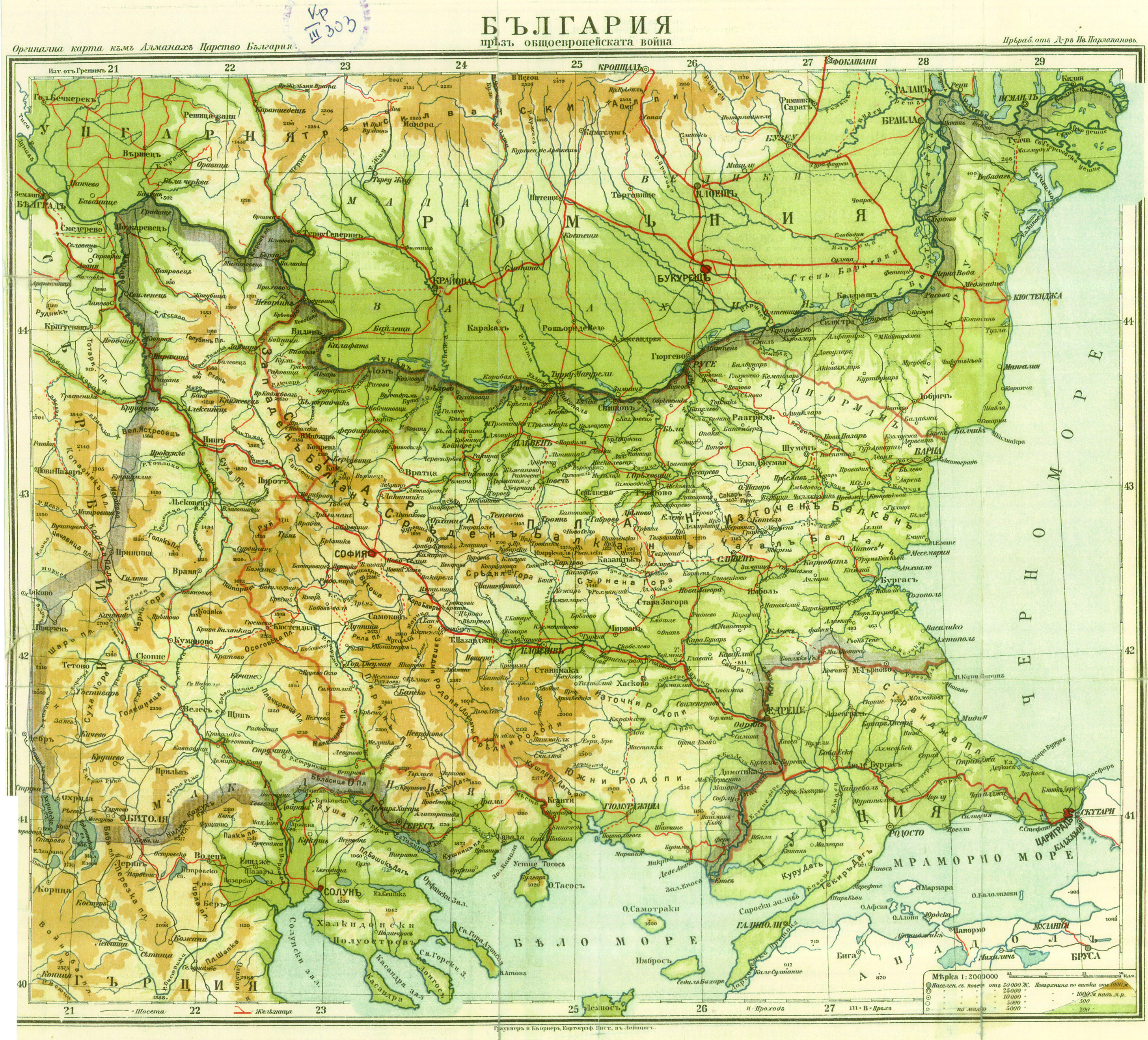 Bulgarian irredentism is a term to identify the territory associated with a historical national state and a modern Bulgarian irredentist
Bulgarian irredentism is a term to identify the territory associated with a historical national state and a modern Bulgarian irredentist
Yugoslav - Bulgarian Relations from 1955 to 1980
{{Pan-nationalist concepts Political history of Bulgaria Irredentism Bulgarian nationalism Bulgarian irredentism


 Bulgarian irredentism is a term to identify the territory associated with a historical national state and a modern Bulgarian irredentist
Bulgarian irredentism is a term to identify the territory associated with a historical national state and a modern Bulgarian irredentist nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
movement in the 19th and 20th centuries, which would include most of Macedonia, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
.
History
The larger proposed Bulgarian state was suggested under the Treaty of San Stefano in 1878. The issue of irredentism and nationalism gained greater prominence after the Treaty of San Stefano. It established a Principality of Bulgaria, with territory including most ofMoesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
- the plain between the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and the Balkan mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border bet ...
range (Stara Planina), the regions of Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, Pirot
Pirot ( sr-cyr, Пирот) is a city and the administrative center of the Pirot District in southeastern Serbia. According to 2011 census, the urban area of the city has a population of 38,785, while the population of the city administrative are ...
, and Vranje
Vranje ( sr-Cyrl, Врање, ) is a city in Southern Serbia and the administrative center of the Pčinja District. The municipality of Vranje has a population of 83,524 and its urban area has 60,485 inhabitants.
Vranje is the economical, poli ...
in the Morava Valley, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
- Northern Thrace
Northern Thrace or North Thrace ( bg, Северна Тракия, as opposed to Western Thrace and East Thrace to the south; tr, Kuzey Trakya; el, Βόρεια Θράκη), also called Bulgarian Thrace, constitutes the northern and largest pa ...
, parts of Eastern Thrace, and nearly all of Macedonia. This treaty laid grounds for much of the later claims for a Greater Bulgaria. However, the Treaty of San Stefano was a preliminary one, and the borders of the newly created Bulgaria were established in the Treaty of Berlin. It saw the previous territory divided in three – the Principality of Bulgaria
The Principality of Bulgaria ( bg, Княжество България, Knyazhestvo Balgariya) was a vassal state under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire. It was established by the Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
After the Russo-Turkish War end ...
, the autonomous province of Eastern Rumelia, and Macedonia, which remained under Ottoman control.
In the early 20th century, control over Macedonia was a key point of contention between Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, and Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
who fought both the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
of 1912–1913 and the Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies ...
of 1913. The area was further fought over during the Macedonian Campaign of World War I (1915–1918).
Just before entering World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Bulgaria had peacefully secured the return of Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja, South Dobruja or Quadrilateral ( Bulgarian: Южна Добруджа, ''Yuzhna Dobrudzha'' or simply Добруджа, ''Dobrudzha''; ro, Dobrogea de Sud, or ) is an area of northeastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silis ...
from Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
in the Treaty of Craiova. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, some of the territories in question were briefly added to Bulgaria by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, as a reward to Bulgaria, which had fought with Germany as one of the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
. It was granted territory in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, namely Eastern Macedonia and parts of Western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace ( el, �υτικήΘράκη, '' ytikíThráki'' ; tr, Batı Trakya; bg, Западна/Беломорска Тракия, ''Zapadna/Belomorska Trakiya''), also known as Greek Thrace, is a geographic and historica ...
, as well as Yugoslav Macedonia ( Vardar Macedonia).Bulgaria During the Second World War, Marshall Lee Miller, Stanford University Press, 1975, , p. 128. With the exception of the Southern Dobruja, these concessions were reversed with the Allied victory (i.e. at the Paris Peace Conference of 1947).
See also
* Balkan sprachbund * Bulgarian Crisis (1885–88) *Bulgarian Declaration of Independence
The ''de jure'' independence of Bulgaria ( bg, Независимост на България, ''Nezavisimost na Bǎlgariya'') from the Ottoman Empire was proclaimed on in the old capital of Tarnovo by Prince Ferdinand of Bulgaria, who afte ...
*Bulgarian Millet
Bulgarian Millet ( tr, Bulgar Milleti) was an ethno-religious and linguistic community within the Ottoman Empire from the mid-19th to early 20th century. The semi-official term ''Bulgarian millet'', was used by the Sultan for the first time in ...
*Bulgarian National Awakening
The Bulgarian National Awakening ( bg, Ранно възраждане) is the initial period of the Bulgarian National Revival in the history of Bulgaria, from the Treaty of Karlowitz to the Ottoman coups of 1807–08. During this historical per ...
* Bulgarian unification
* Greater Albania
* Greater Croatia
*Greater Moldova
Greater Moldova or Greater Moldavia ( ro, Moldova Mare; Moldovan Cyrillic: ) is an irredentist concept today used for the credence that the Republic of Moldova should be expanded with lands that used to belong to the Principality of Moldavia or ...
*Greater Romania
The term Greater Romania ( ro, România Mare) usually refers to the borders of the Kingdom of Romania in the interwar period, achieved after the Great Union. It also refers to a pan-nationalist idea.
As a concept, its main goal is the creatio ...
* Greater Serbia
*Hungarian irredentism
Hungarian irredentism or Greater Hungary ( hu, Nagy-Magyarország) are irredentist political ideas concerning redemption of territories of the historical Kingdom of Hungary. Targeting at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in ...
* Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising
* Kresna–Razlog uprising
* Megali Idea
* National awakening of Bulgaria
References
External links
Yugoslav - Bulgarian Relations from 1955 to 1980
{{Pan-nationalist concepts Political history of Bulgaria Irredentism Bulgarian nationalism Bulgarian irredentism