Greater Albania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Greater Albania is an
Greater Albania is an
 Many Kosovo Albanians were preoccupied with driving out the Serb community, particularly the post-1919 Serbian and Montenegrin colonists, often settled on confiscated Albanian property. Albanians saw Serbian and Yugoslav rule as foreign, and according to Ramet they felt that anything would be better than the chauvinism, corruption, administrative hegemonism and exploitation they had experienced under the Serbian authorities. Albanians collaborated broadly with the Axis occupiers, who had promised them a Greater Albania. Collapse of Yugoslav rule resulted in actions of revenge being undertaken by Albanians, some joining the local ''
Many Kosovo Albanians were preoccupied with driving out the Serb community, particularly the post-1919 Serbian and Montenegrin colonists, often settled on confiscated Albanian property. Albanians saw Serbian and Yugoslav rule as foreign, and according to Ramet they felt that anything would be better than the chauvinism, corruption, administrative hegemonism and exploitation they had experienced under the Serbian authorities. Albanians collaborated broadly with the Axis occupiers, who had promised them a Greater Albania. Collapse of Yugoslav rule resulted in actions of revenge being undertaken by Albanians, some joining the local ''
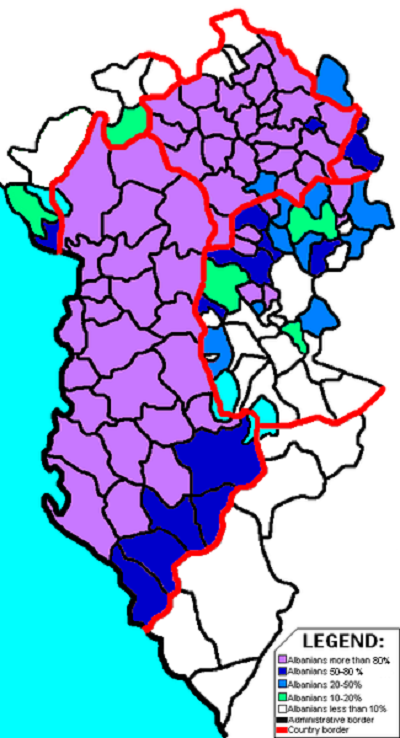
 Political parties advocating and willing to fight for a Greater Albania emerged in Albania during the 2000s. They were the National Liberation Front of Albanians (KKCMTSH) and Party of National Unity (PUK) that both merged in 2002 to form the United National Albanian Front (FBKSh) which acted as the political organisation for the
Political parties advocating and willing to fight for a Greater Albania emerged in Albania during the 2000s. They were the National Liberation Front of Albanians (KKCMTSH) and Party of National Unity (PUK) that both merged in 2002 to form the United National Albanian Front (FBKSh) which acted as the political organisation for the
Book 5 – Total population according to the Ethnic Affiliation, Mother Tongue and Religion
'', The State Statistical Office, Skopje, 2002, p. 62. Cities with Albanian majorities or large minorities include Tetovo (Tetova),
Albanian Canadian League Information Service (ACLIS)Perspective: Albania and Kosova by Van ChristoAlbania and Kosovo , What happened to Greater Albania?
''
 Greater Albania is an
Greater Albania is an irredentist
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent st ...
and nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
concept that seeks to unify the lands that many Albanians consider to form their national homeland. It is based on claims on the present-day or historical presence of Albanian populations in those areas. In addition to the existing Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
, the term incorporates claims to regions in the neighbouring states, the areas include Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
, the Preševo Valley
The Preševo Valley ( sr-cyrl, Прешевска долина, Preševska dolina, al, Lugina e Preshevës) is a geopolitical region in southern Serbia, along the border with Kosovo. The valley geographically includes municipalities of Bujanovac ...
of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
, territories in southern Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
, northwestern Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
(the Greek regional units of Thesprotia
Thesprotia (; el, Θεσπρωτία, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the ...
and Preveza
Preveza ( el, Πρέβεζα, ) is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula at the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is part of the region of Epiru ...
, referred by Albanians as Chameria, and other territories that were part of the Vilayet of Yanina during the Ottoman Empire),. and a western part of North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
.
The unification of an even larger area into a single territory under Albanian authority had been theoretically conceived by the League of Prizren
The League of Prizren ( sq, Besëlidhja e Prizrenit), officially the League for the Defense of the Rights of the Albanian Nation ( sq, Lidhja për mbrojtjen e të drejtave te kombit Shqiptar), was an Albanian political organization which was offi ...
, an organization of the 19th century whose goal was to unify the Albanian inhabited lands (and other regions, mostly from the regions of Macedonia and Epirus) into a single autonomous Albanian Vilayet
The Albanian Vilayet ( ota, ولايت ارناود, ''Vilâyet-i Arnavid'') was a projected ''vilayet'' of the Ottoman Empire in the western Balkan Peninsula, which was to include the four Ottoman vilayets with substantial ethnic Albanian popul ...
within the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, which was briefly achieved ''de jure'' in September 1912. The concept of a Greater Albania, as in greater than Albania within its 1913 borders, was implemented under the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
and Nazi German
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
occupation of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. The idea of unification has roots in the events of the Treaty of London in 1913, when roughly
30% of the predominantly Albanian territories and 35% of the population were left outside the new country's borders.."Roughly 30% of the predominantly Albanian territories and 35% of the population were left outside the new country's borders"
Terminology
''Greater Albania'' is a term used mainly by the Western scholars, politicians, etc. Albanian nationalists dislike the expression "Greater Albania" and prefer to use the term "Ethnic Albania". Ethnic Albania ( sq, Shqipëria Etnike) is a term used primarily byAlbanian nationalists
Albanian nationalism is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts generated by ethnic Albanians that were first formed in the 19th century during the Albanian National Awakening ( sq, Rilindja). Albanian nationalism is also associated w ...
to denote the territories claimed as the traditional homeland of ethnic Albanians, despite these lands also being inhabited by many non-Albanians. Those that use the second term refer to an area which is smaller than the four Ottoman vilayets, while still encompassing Albania, Kosovo, western North Macedonia, Albanian populated areas of Southern Serbia and parts of Northern Greece ( Chameria) that had a historic native Albanian population. Albanian nationalists ignore that within these regions there are also sizable numbers of non-Albanians.. Another term used by Albanians, is "Albanian national reunification" ( sq, Ribashkimi kombëtar shqiptar).
History
Under the Ottoman Empire
Prior to theBalkan wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and def ...
of the beginning of the 20th century, Albanians were subjects of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
.
The Albanian independence movement emerged in 1878 with the League of Prizren
The League of Prizren ( sq, Besëlidhja e Prizrenit), officially the League for the Defense of the Rights of the Albanian Nation ( sq, Lidhja për mbrojtjen e të drejtave te kombit Shqiptar), was an Albanian political organization which was offi ...
(a council based in Kosovo) whose goal was cultural and political autonomy for ethnic Albanians inside the framework of the Ottoman Empire. However, the Ottomans were not prepared to grant The League's demands. Ottoman opposition to the League's cultural goals eventually helped transform it into an Albanian national movement.
Albanian nationalism overall was a reaction to the gradual breakup of the Ottoman Empire and a response to Balkan and Christian national movements that posed a threat to an Albanian population that was mainly Muslim. Efforts were devoted to including vilayets with an Albanian population into a larger unitary Albanian autonomous province within the Ottoman state while Greater Albania was not considered a priority.. "These scholars did not have access to many primary sources to be able to construct the notion of the Illyrian origin of the Albanians yet, and Greater Albania was not a priority. The goal of the day was to persuade the Ottoman officials that Albanians were a nation and they deserved some autonomy with the Empire. In fact, Albanian historians and politicians were very moderate compared to their peers in neighbouring countries. Albanian nationalism during the late Ottoman era was not imbued with separatism that aimed to create an Albanian nation-state, though Albanian nationalists did envisage an independent Greater Albania.. Albanian nationalists were mainly focused on defending rights that were sociocultural, historic and linguistic within existing countries without being connected to a particular polity.."Nineteenth-century Albanianism was not by any means a separatist project based on the desire to break with the Ottoman Empire and to create a nationstate. In its essence Albanian nationalism was a reaction to the gradual disintegration of the Ottoman Empire and a response to the threats posed by Christian and Balkan national movements to a population that was predominantly Muslim. In this sense, its main goal was to gather all 'Albanian' vilayet's into an autonomous province inside the Ottoman Empire. In fact, given its focus on the defence of the language, history and culture of a population spread across various regions and states, from Italy to the Balkans, it was not associated with any specific type of polity, but rather with the protection of its rights within the existing states. This was due to the fact that, culturally, early Albanian nationalists belonged to a world in which they were at home, though poised between different languages, cultures, and at times even states.".
Balkan Wars and Albanian Independence (1912–1913)
The imminence of collapsing Ottoman rule through military defeat during the Balkan wars pushed Albanians represented byIsmail Qemali
Ismail Qemal bey Vlora, mostly known as Ismail Qemali (; 16 January 184426 January 1919), was an Albanian diplomat, politician, rilindas, statesman and the Founding Father of modern Albania, and one of the most famous Southern Albanian perso ...
to declare independence
"Declare Independence" is a song written and recorded by Icelandic singer Björk. The track was released as the third single from her sixth full-length studio album, '' Volta''. The single was released on 1 January 2008. Björk's dedication of t ...
(28 November 1912) in Vlorë
Vlorë ( , ; sq-definite, Vlora) is the third most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surrounded by the foo ...
from the Ottoman Empire. The main motivation for independence was to prevent Balkan Albanian inhabited lands from being annexed by Greece and Serbia... Italy and Austria-Hungary supported Albanian independence due to their concerns that Serbia with an Albanian coast would be a rival power in the Adriatic Sea and open to influence from its ally Russia......... Apart from geopolitical interests, some Great powers were reluctant to include more Ottoman Balkan Albanian inhabited lands into Albania due to concerns that it would be the only Muslim dominated state in Europe.. Russo-French proposals were for a truncated Albania based on central Albania with a mainly Muslim population, which was also supported by Serbia and Greece who considered that only Muslims could only be Albanians.. "Benckendorff, on the other hand, proposed only a truncated coastal strip to form a central Muslim dominated Albania, in accordance with the common view amongst Slavs, and also Greeks, that only Muslims could be considered Albanian (and not even Muslims necessarily)." As more Albanians became part of the Serbian and Greek states, Albanian scholars with nationalistic perspectives interpret the declaration of independence as a partial victory for the Albanian nationalist movement..
World War II
On 7 April 1939, Italy headed byBenito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
after prolonged interest and overarching sphere of influence during the interwar period invaded Albania.. Italian fascist regime members such as Count Galeazzo Ciano
Gian Galeazzo Ciano, 2nd Count of Cortellazzo and Buccari ( , ; 18 March 1903 – 11 January 1944) was an Italian diplomat and politician who served as Foreign Minister in the government of his father-in-law, Benito Mussolini, from 1936 until 1 ...
pursued Albanian irredentism with the view that it would earn Italians support among Albanians while also coinciding with Italian war aims of Balkan conquest.. The Italian annexation of Kosovo to Albania was considered a popular action by Albanians of both areas..
The Western part of North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
was also annexed by Italy to their protectorate of Albania... In newly acquired territories, non-Albanians had to attend Albanian schools that taught a curriculum containing nationalism alongside fascism and were made to adopt Albanian forms for their names and surnames. Members from the landowning elite, liberal nationalists opposed to communism with other sectors of society in Albania came to form the Balli Kombëtar
The Balli Kombëtar (literally ''National Front''), known as Balli, was an Albanian nationalist, collaborationist and anti-communist resistance movement during the Second World War. It was led by Ali Këlcyra and by Midhat Frashëri. The move ...
organisation and the collaborationist government under the Italians which all as nationalists sought to preserve Greater Albania....
 Many Kosovo Albanians were preoccupied with driving out the Serb community, particularly the post-1919 Serbian and Montenegrin colonists, often settled on confiscated Albanian property. Albanians saw Serbian and Yugoslav rule as foreign, and according to Ramet they felt that anything would be better than the chauvinism, corruption, administrative hegemonism and exploitation they had experienced under the Serbian authorities. Albanians collaborated broadly with the Axis occupiers, who had promised them a Greater Albania. Collapse of Yugoslav rule resulted in actions of revenge being undertaken by Albanians, some joining the local ''
Many Kosovo Albanians were preoccupied with driving out the Serb community, particularly the post-1919 Serbian and Montenegrin colonists, often settled on confiscated Albanian property. Albanians saw Serbian and Yugoslav rule as foreign, and according to Ramet they felt that anything would be better than the chauvinism, corruption, administrative hegemonism and exploitation they had experienced under the Serbian authorities. Albanians collaborated broadly with the Axis occupiers, who had promised them a Greater Albania. Collapse of Yugoslav rule resulted in actions of revenge being undertaken by Albanians, some joining the local ''Vulnetari
The Vulnetari ("volunteers") were a volunteer militia of Albanians from Kosovo set up in 1941 by Italian forces after the successful invasion of Yugoslavia. They served as an auxiliary force for civilian control and protection of villages.
Some ...
'' militia that burned Serbian settlements and killed Serbs while interwar Serbian and Montenegrin colonists were expelled into Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia.. The aim of these actions were to create a homogeneous Greater Albanian state.. Italian authorities in Kosovo allowed the use of the Albanian language in schools, university education and administration.. The same nationalist sentiments among Albanians which welcomed the addition of Kosovo and its Albanians within an enlarged state also worked against the Italians as foreign occupation became increasingly rejected in Albania.. An attempt to get Kosovan Albanians to join the resistance, a meeting in Bujan (1943–1944), northern Albania was convened between Balli Kombëtar members and Albanian communists that agreed to common struggle and maintenance of the newly expanded boundaries. The deal was opposed by Yugoslav partisans and later rescinded resulting in limited Kosovan Albanian recruits.. Some Balli Kombëtar members such as Shaban Polluzha
Shaban Mustafë Kastrati (1871 – 21 February 1945), known as Shaban Polluzha, was a Kosovo Albanian military leader active in Drenica during World War II. He was a collaborationist, serving in the Royal Albanian gendarmerie and as a commander ...
became partisans with the view that Kosovo would become part of Albania. With the end of the war, some of those Kosovan Albanians felt betrayed by the return of Yugoslav rule and for several years Albanian nationalists in Kosovo resisted both the partisans and later the new Yugoslav army.... Albanian nationalists viewed their inclusion within Yugoslavia as an occupation..
The Albanian Fascist Party became the ruling party of the Italian Protectorate of Albania in 1939 and the prime minister Shefqet Verlaci approved the possible administrative union of Albania and Italy, because he wanted the Italian support in order to get the union of Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
, Chameria and other "Albanian irredentism" into ''Greater Albania''. Indeed, this unification was realized after the Axis occupation of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
from spring 1941. The Albanian fascists claimed in May 1941 that nearly all the Albanian populated territories were united to Albania.. "It was under the Italian and German occupation of 1939–1944 that the project of Greater Albania... was conceived."
Between May 1941 and September 1943, Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
placed nearly all the land inhabited by ethnic Albanians under the jurisdiction of an Albanian quisling government. That included parts of the region of Kosovo, parts of Vardar Macedonia and some small border areas of Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
. In Chameria an Albanian high commissioner, Xhemil Dino, was appointed by the Italians, but the area remained under the control of the Italian military command in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
and so technically remained a region of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
.
When the Germans occupied the area and substituted the Italians, they maintained the borders created by Mussolini, but after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the Albanian borders were returned by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
to the pre-war status.
Yugoslav Wars
TheKosovo Liberation Army
The Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA; , UÇK) was an ethnic Albanian separatist militia that sought the separation of Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, ...
(KLA) was an ethnic-Albanian paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carr ...
organisation which sought the separation of Kosovo from Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
during the 1990s and the eventual creation of a ''Greater Albania'', encompassing Kosovo, Albania, and the ethnic Albanian minority of neighbouring Macedonia. The KLA found great moral and financial support among the Albanian diaspora.
KLA Commander Sylejman Selimi insisted:
By 1998 the KLA's operations had evolved into a significant armed insurrection. According to the report of the USCRI, the "Kosovo Liberation Army ... attacks aimed at trying to 'cleanse' Kosovo of its ethnic Serb population." The UNHCR
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrat ...
estimated the figure at 55,000 refugees who had fled to Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
and Central Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, централна Србија / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ужа Србија / uža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the nor ...
, most of whom were Kosovo Serbs
Kosovo Serbs are one of the ethnic groups of Kosovo. There are around 100,000 Kosovo Serbs as of 2014 and about half of them live in North Kosovo. Other Serb communities live in southern Kosovo. After Albanians, they form the largest ethnic com ...
..
Its campaign against Yugoslav security forces, police, government officers and ethnic Serb villages precipitated a major Yugoslav military crackdown which led to the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the war ...
of 1998–1999. Military intervention by Yugoslav security forces led by Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević (, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the president of Serbia within Yugoslavia from 1989 to 1997 (originally the Socialist Republic of Serbia, a constituent republic of ...
and Serb paramilitaries within Kosovo prompted an exodus of Kosovar Albanians and a refugee crisis that eventually caused NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
to intervene militarily in order to stop what was widely identified as an ongoing campaign of ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
.
The war ended with the Kumanovo Treaty
The Military Technical Agreement, also known as the Kumanovo Agreement, signed between the International Security Force ( KFOR) and the Governments of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republic of Serbia, was an accord concluded on 9 June ...
, with Yugoslav forces agreeing to withdraw from Kosovo to make way for an international presence. The Kosovo Liberation Army disbanded soon after this, with some of its members going on to fight for the UÇPMB in the Preševo Valley
The Preševo Valley ( sr-cyrl, Прешевска долина, Preševska dolina, al, Lugina e Preshevës) is a geopolitical region in southern Serbia, along the border with Kosovo. The valley geographically includes municipalities of Bujanovac ...
and others joining the National Liberation Army (NLA) and Albanian National Army
The Albanian National Army (ANA; sq, Armata Kombëtare Shqiptare, AKSh), is an Albanian paramilitary organization which operates in North Macedonia, Serbia and Kosovo. The group opposes the Ohrid Framework Agreement which ended the 2001 insurge ...
(ANA) during the armed ethnic conflict in Macedonia.
2000s–present

 Political parties advocating and willing to fight for a Greater Albania emerged in Albania during the 2000s. They were the National Liberation Front of Albanians (KKCMTSH) and Party of National Unity (PUK) that both merged in 2002 to form the United National Albanian Front (FBKSh) which acted as the political organisation for the
Political parties advocating and willing to fight for a Greater Albania emerged in Albania during the 2000s. They were the National Liberation Front of Albanians (KKCMTSH) and Party of National Unity (PUK) that both merged in 2002 to form the United National Albanian Front (FBKSh) which acted as the political organisation for the Albanian National Army
The Albanian National Army (ANA; sq, Armata Kombëtare Shqiptare, AKSh), is an Albanian paramilitary organization which operates in North Macedonia, Serbia and Kosovo. The group opposes the Ohrid Framework Agreement which ended the 2001 insurge ...
(AKSh) militant group and consisted of some disaffected KLA and NLA members. Regarded internationally as terrorist both have gone underground and its members have been involved in various violent incidents in Kosovo, Serbia and Macedonia during the 2000s.... In the early 2000s, the Liberation Army of Chameria (UCC) was a reported paramilitary formation that intended to be active in northern Greek region of Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
... Political parties active only in the political scene exist that have a nationalist outlook are the monarchist Legality Movement Party
The Legality Movement Party (; PLL) is a right-wing monarchist political party in Albania. It supports the return to power of the House of Zogu under Crown Prince Leka of the Albanians. In the 2001 parliamentary election it was part of the Uni ...
(PLL), the National Unity Party The National Unity Party, National United Party, Party of National Unity or National Unity Front may refer to:
* National United Party of Afghanistan (founded 2003)
* National Unity Party (Albania)
* National United Party (Armenia), defunct
* Nati ...
(PBKSh) alongside the Balli Kombëtar, a party to have passed the electoral threshold and enter parliament. These political parties, some of whom advocate for a Greater Albania have been mainly insignificant and remained at the margins of the Albanian political scene. The Kosovo question has limited appeal among Albanian voters who generally speaking are not interested in electing parties advocating redrawn borders creating a Greater Albania.. Centenary Albanian independence celebrations in 2012 generated nationalistic commentary among the political elite of whom prime-minister Sali Berisha
Sali Ram Berisha (; born 15 October 1944) is an Albanian conservative politician and former cardiologist who served as the second President of Albania from 1992 to 1997 and Prime Minister from 2005 to 2013.
He is also the current chairman of ...
referred to Albanian lands as extending to Preveza
Preveza ( el, Πρέβεζα, ) is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula at the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is part of the region of Epiru ...
, northern Greece and Preševo
Preševo ( sr-cyrl, Прешево; sq, Preshevë, ) is a town and municipality located in the Pčinja District of southern Serbia. It is the southernmost town in Central Serbia and largest in the geographical region of Preševo Valley.
Prešev ...
, southern Serbia angering Albania's neighbors.. In Kosovo, a prominent left wing nationalist movement turned political party Vetëvendosje
Lëvizja Vetëvendosje (, en, Self-determination Movement; LVV) is a centre-left to left-wing political party in Kosovo. It is orientated towards principles of social democracy, populism, and Albanian nationalism.
Vetëvendosje was founded in ...
(Self Determination) has emerged who advocates for closer Kosovo-Albania relations and pan-Albanian self determination in the Balkans... Another smaller nationalist party, the Balli Kombetar Kosovë (BKK) sees itself as an heir to the original Second World War organisation that supports Kosovan independence and pan-Albanian unification. Greater Albania remains mainly in the sphere of political rhetoric and overall Balkan Albanians view EU integration as the solution to combat crime, weak governance, civil society and bringing different Albanian populations together...
On 19 July 2020, singer of Albanian descent Dua Lipa
Dua Lipa ( , ; born ) is an English and Albanian singer and songwriter. Possessing a mezzo-soprano vocal range, she is known for her signature disco-pop sound. Lipa has received numerous accolades, including six Brit Awards, three Grammy A ...
faced backlash after she shared an image of a banner associated with supporters of extreme Albanian nationalism
Albanian nationalism is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts generated by ethnic Albanians that were first formed in the 19th century during the Albanian National Awakening ( sq, Rilindja). Albanian nationalism is also associated w ...
. The same banner had sparked controversy at the 2014 Serbia vs. Albania football game. The banner depicts the irredentist
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent st ...
map of Greater Albania, while the caption, " autochthonous". In response, Twitter
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...
users, many of them Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Montenegrin and Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguation ...
, accused the singer of ethno-nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politic ...
. Political scientist Florian Bieber
Florian Bieber (born 4 October 1973) is a Luxembourgian political scientist, historian and professor working on inter-ethnic relations, ethnic conflict and nationalism, focusing primarily on Balkans.
Education
In 1991–1992, he studied His ...
described Lipa's tweet as "stupid nationalism".
In Feb 2021, in an interview with Euronews
Euronews (styled on-air in lowercase as euronews) is a European television news network, headquartered in Lyon, France. The network began broadcasting on 1 January 1993 and covers world news from a European perspective.
The majority of Eurone ...
, Albin Kurti
Albin Kurti (; born 24 March 1975) is a Kosovar Albanian politician and activist, serving as the Prime Minister of Kosovo since 22 March 2021, having previously served in that role between February and June 2020.
He came to prominence in 1997 ...
, former Prime Minister of Kosovo
The prime minister of the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Kryeministri i Republikës së Kosovës, sr, Премијер Републике Косова, Premijer Republike Kosova) is the head of government of Kosovo.
The prime minister and the Gover ...
, said that he would personally vote to unify Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
and Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
.
Public opinion
According to the ''Gallup Balkan Monitor'' 2010 report, the idea of a Greater Albania was supported by the majority of Albanians in Albania (63%), Kosovo (81%) and the Republic of Macedonia (53%), although the same report noted that most Albanians thought this unlikely to happen. In a survey carried out byUnited Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
(UNDP), published in March 2007, only 2.5% of the Albanians in Kosovo thought unification with Albania is the best solution for Kosovo. Ninety-six percent said they wanted Kosovo to become independent within its present borders.
According to a 2019 poll by Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is a grantmaking network founded and chaired by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the world, with a st ...
that covered 2,504 respondents in both countries, 79.4% of Kosovar Albanian respondents were in favor of unification between Albania and Kosovo, compared to 82.9% of the respondents in Albania. When asked whether they would be willing to pay a tax for unification, 66.1% of respondents in Kosovo agreed, compared to 45.5% in Albania.
Political uses of the concept
The Albanian question in the Balkan peninsula is in part the consequence of the decisions made by Western powers in late 19th and early 20th century. TheTreaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-18 ...
and the 1878 Treaty of Berlin
The Treaty of Berlin (formally the Treaty between Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Great Britain and Ireland, Italy, Russia, and the Ottoman Empire for the Settlement of Affairs in the East) was signed on 13 July 1878. In the aftermath of the ...
assigned Albanian inhabited territories to other States, hence the reaction of the League of Prizren.. One theory posits that the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, and Austro-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern ...
wanted to maintain a brittle balance in Europe in the late 19th century.
The degree to which different groups are working towards and what efforts such groups are undertaking in order to achieve a Greater Albania is disputed. There seems no evidence that anything more than a few unrepresentative extremist groups are working towards this cause; the vast majority of Albanians want to live in peace with their neighbors. However, they also want the human rights of the Albanian ethnic populations in North Macedonia, Serbia, Greece to be respected. An excellent example is the friendly relationship between the Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
and the support towards the integration of the Albanian population in North Macedonia. There is Albanian representation in government, the national parliament, local government, and the business sector, and no evidence of systematic discrimination on an ethnic or religious basis against the Albanian (or indeed any other minority) population.
In 2000, the then-US Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
Madeleine Albright said that the international community would not tolerate any efforts towards the creation of a Greater Albania.
In 2004, the Vetëvendosje
Lëvizja Vetëvendosje (, en, Self-determination Movement; LVV) is a centre-left to left-wing political party in Kosovo. It is orientated towards principles of social democracy, populism, and Albanian nationalism.
Vetëvendosje was founded in ...
movement was formed in Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
, which opposes foreign involvement in Kosovan affairs and campaigns instead for the sovereignty the people, as part of the right of self-determination. Vetëvendosje obtained 12.66% of the votes in an election in December 2010, and the party manifesto calls for a referendum on union with Albania.
In 2012, the Red and Black Alliance
The Red and Black Alliance ( sq, Aleanca Kuq e Zi) is a nationalist political party in Albania. It was created by Kreshnik Spahiu, the former Deputy Head of the High Council of Justice of Albania. It has sometimes been described as ultra-nation ...
( sq, Aleanca Kuq e Zi) was established as a political party in Albania, the core of its program is national unification of all Albanians in their native lands.
In 2012, as part of the celebrations for 100th Anniversary of the Independence of Albania
The 100th Anniversary of the Independence of Albania was a yearlong celebration in 2012 when Albanians celebrated the 100th anniversary of establishing independent Albania, the first Albanian state in modern history.
Celebration
In Albania ...
, Prime Minister Sali Berisha spoke of "Albanian lands" stretching from Preveza
Preveza ( el, Πρέβεζα, ) is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula at the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is part of the region of Epiru ...
in Greece to Presevo in Serbia, and from the Macedonian capital of Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; r ...
to the Montenegrin capital of Podgorica
Podgorica (Cyrillic: Подгорица, ; lit. 'under the hill') is the capital and largest city of Montenegro. The city was formerly known as Titograd (Cyrillic: Титоград, ) between 1946 and 1992—in the period that Montenegro form ...
, angering Albania's neighbors. The comments were also inscribed on a parchment that will be displayed at a museum in the city of Vlore, where the country's independence from the Ottoman Empire was declared in 1912.
Use in other media
The concept is also often used, especially withIlirida
Ilirida ( sq, Ilirida; mk, Илирида, ''Ilirida'') or the Republic of Ilirida ( sq, Republika e Iliridës; mk, Република Илирида, ''Republika Ilirida'') is a proposed state in the western regions of North Macedonia (then ...
(the proposed western region of North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
), by nationalists in circles of Macedonian and Serbian politics in bids to rally support.
Areas
Kosovo
Kosovo has an overwhelmingly Albanian majority, estimated to be around 88%. The 2011 census stated a higher percentage Albanian people, but due to the exclusion of northern Kosovo, a Serb-dominated area, and a partial boycott by the Romani and Serb population in south Kosovo, those numbers are unreliable.Montenegro
The irredentist claims in Montenegro are in the border areas, including Kraja, Ulcinj,Tuzi
Tuzi ( cnr, Tuzi/Тузи, ; sq, Tuz or ''Tuzi'') is a small town in Montenegro and the seat of Tuzi Municipality, Montenegro. It is located along a main road between the city of Podgorica and the Albanian border crossing, just a few kilometers ...
(Malësia
Malësia e Madhe ("Great Highlands"), known simply as Malësia ( sq, Malësia, cnr, / ), is a historical and ethnographic region in northern Albania and eastern central Montenegro corresponding to the highlands of the geographical subdivision ...
), Plav and Gusinje, and Rožaje
Rožaje ( cnr, Рожаје, bs, Rožaje), ; sq, Rozhajë) is a town in northeastern Montenegro.
As of 2011, the city has a population of 9,567 inhabitants.
Surrounded by hills to its west and mountains to its east (notably Mount Hajla), the ...
(Sandžak
Sandžak (; sh, / , ; sq, Sanxhaku; ota, سنجاق, Sancak), also known as Sanjak, is a historical geo-political region in Serbia and Montenegro. The name Sandžak derives from the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, a former Ottoman administrative dis ...
). According to the 2011 census, the Albanian proportion in those municipalities are following: Ulcinj–14,076 (70%), Tuzi–2,383 (50%), Plav–(19%), Rožaje–188 (2%). The claim on the Sandžak area, where the Albanian community is small and the Bosniak community is the majority, is based on the Albanian state borders in World War II and presence in the late Ottoman period.
North Macedonia
The western part of North Macedonia is an area with a large ethnic Albanian minority. The Albanian population in North Macedonia make up 25% of the population, numbering 509,083 in the 2002 census.Macedonian Census (2002),Book 5 – Total population according to the Ethnic Affiliation, Mother Tongue and Religion
'', The State Statistical Office, Skopje, 2002, p. 62. Cities with Albanian majorities or large minorities include Tetovo (Tetova),
Gostivar
Gostivar ( mk, Гостивар , Albanian and Turkish: ''Gostivar''), is a city in North Macedonia, located in the upper Polog valley region. It is one of the largest municipalities in the country with a population of 81,042, and the town als ...
(Gostivari), Struga
Struga ( mk, Струга , sq, Strugë) is a town and popular tourist destination situated in the south-western region of North Macedonia, lying on the shore of Lake Ohrid. The town of Struga is the seat of Struga Municipality.
Name
The n ...
(Struga) and Debar
Debar ( mk, Дебaр ; Albanian: ''Dibër''/''Dibra'' or ''Dibra e Madhe;'' ) is a city in the western part of North Macedonia, near the border with Albania, off the road from Struga to Gostivar. It is the seat of Debar Municipality. Debar has ...
(Diber).
In the 1980s, Albanian irredentist organizations appeared in the SR Macedonia
The Socialist Republic of Macedonia ( mk, Социјалистичка Република Македонија, Socijalistička Republika Makedonija), or SR Macedonia, commonly referred to as Socialist Macedonia or Yugoslav Macedonia, was ...
, particularly Vinica, Kicevo, Tetovo and Gostivar. In 1992, Albanian activists in Struga proclaimed also the founding of the Republic of Ilirida
Ilirida ( sq, Ilirida; mk, Илирида, ''Ilirida'') or the Republic of Ilirida ( sq, Republika e Iliridës; mk, Република Илирида, ''Republika Ilirida'') is a proposed state in the western regions of North Macedonia (then ...
( sq, Republika e Iliridës). with the intention of autonomy or federalization inside Macedonia. The declaration had only a symbolic meaning and the idea of an autonomous State of Ilirida is not officially accepted by the ethnic Albanian politicians in North Macedonia..
Preševo Valley
The irredentist claims inCentral Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, централна Србија / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ужа Србија / uža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the nor ...
(excluding Kosovo) are in the southern Preševo Valley
The Preševo Valley ( sr-cyrl, Прешевска долина, Preševska dolina, al, Lugina e Preshevës) is a geopolitical region in southern Serbia, along the border with Kosovo. The valley geographically includes municipalities of Bujanovac ...
, including municipalities of Preševo
Preševo ( sr-cyrl, Прешево; sq, Preshevë, ) is a town and municipality located in the Pčinja District of southern Serbia. It is the southernmost town in Central Serbia and largest in the geographical region of Preševo Valley.
Prešev ...
( sq, Preshevë), Bujanovac
Bujanovac ( sr-cyr, Бујановац, ; sq, Bujanoc) is a town and municipality located in the Pčinja District of southern Serbia. Situated in the South Morava basin, it is located in the geographical area known as Preševo Valley. It is ...
( sq, Bujanoc) and partially Medveđa
Medveđa ( sr-cyr, Медвеђа, ; sq, Medvegja, ) is a town and municipality located in the Jablanica District of southern Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 2,848 inhabitants, while the municipality has 7,438 ...
( sq, Medvegjë), where there is an Albanian community. In 2001, the Albanians were estimated to have numbered 70,000 in the area. According to the 2002 census, the Albanian proportion in those municipalities were following: Preševo–31,098 (89%), Bujanovac–23,681 (55%), Medveđa–2,816 (26%).
Following the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the war ...
(1998–99), the Albanian separatist Liberation Army of Preševo, Medveđa and Bujanovac
The Liberation Army of Preševo, Medveđa and Bujanovac ( sq, Ushtria Çlirimtare e Preshevës, Medvegjës dhe Bujanocit, UÇPMB) was an Albanian militant group fighting for separation from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia for three municipalit ...
( sq, Ushtria Çlirimtare e Preshevës, Medvegjës dhe Bujanocit, UÇPMB), fought an insurgency against the Serbian government, aiming to seceding the Preševo Valley into Kosovo.
Greece
The irredentist claim in Greece are Chameria, parts ofEpirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
, the historical Vilayet of Janina.: "The Congress of Berlin in 1878 rejected the petition of the Prizren League to put the regions of Kosovo, Shkodra, Monastir and Janina into one political-administrative unit within the Ottoman Empire ...": "The Albanian propaganda spread very rapidly, and by 1910 they had reached the stage of claiming the unification of the four vilayets inhabited by Albanians, as a kind of autonomous 'Great Albania'.": " he League of Prizrenalso sought to set up the framework for a form of administrative autonomy within the Ottoman state for the four vilayets (provinces) with a sizeable Albanian population, Janina, Shkodër, Kosovo and Monastir (Bitola).": " he League of Prizrenfast adopted an expansive agenda, seeking to unify the four parts of Albania in the four vilayets (Kosovo, Shkoder, Monastir, Janina) into one political unit."
The coastal region of Thesprotia
Thesprotia (; el, Θεσπρωτία, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the ...
in northwestern Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
referred to by Albanians as ''Çamëria
Chameria ( sq, Çamëria; el, Τσαμουριά, ''Tsamouriá''; tr, Çamlık) is a term used today mostly by Albanians to refer to parts of the coastal region of Epirus in southern Albania and Greece, traditionally associated with the Albani ...
'' is sometimes included in Greater Albania.. According to the 1928 census held by the Greek state, there were around 20,000 Muslim Cams in Thesprotia prefecture
Thesprotia (; el, Θεσπρωτία, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the re ...
. They were forced to seek refuge in Albania at the end of World War II after a large part of them collaborated and committed a number of crimes together with the Nazis during the 1941–1944 period.. In the first post-war census (1951), only 123 Muslim Çams were left in the area. Descendants of the exiled Muslim Chams (they claim that they are now up to 170,000 now living in Albania) claim that up to 35,000 Muslim Çams were living in southern Epirus before World War II. Many of them are currently trying to pursue legal ways to claim compensation for the properties seized by Greece. For Greece the issue "does not exist".
International Crisis Group research
International Crisis Group
The International Crisis Group (ICG; also known as the Crisis Group) is a transnational non-profit, non-governmental organisation founded in 1995. It is a think tank, used by policymakers and academics, performing research and analysis on global ...
researched the issue of Pan-Albanianism and published a report titled "Pan-Albanianism: How Big a Threat to Balkan Stability?" on February 2004.
The International Crisis Group advised in the report the Albanian and Greek governments to endeavour and settle the longstanding issue of the Chams displaced from Greece in 1945, before it gets hijacked and exploited by extreme nationalists, and the Chams' legitimate grievances get lost in the struggle to further other national causes. Moreover, the ICG findings suggest that Albania is more interested in developing cultural and economic ties with Kosovo and maintaining separate statehood.
See also
*Albanian nationalism
Albanian nationalism is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts generated by ethnic Albanians that were first formed in the 19th century during the Albanian National Awakening ( sq, Rilindja). Albanian nationalism is also associated w ...
* Albanian National Awakening
The Albanian National Awakening ( sq, Rilindja or ), commonly known as the Albanian Renaissance or Albanian Revival, is a period throughout the 19th and 20th century of a cultural, political and social movement in the Albanian history where the ...
* Albanophobia
* History of Albania
The history of Albania forms a part of the history of Europe. During classical antiquity, Albania was home to several Illyrian tribes such as the Ardiaei, Albanoi, Amantini, Enchele, Taulantii and many others, but also Thracian and Gree ...
* History of the Balkans
The Balkans and parts of this area are alternatively situated in Southeast, Southern, Eastern Europe and Central Europe. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often turbulent history regarding centuries ...
* Kosovo independence precedent
On 17 February 2008, the majority of members of the Assembly of Kosovo, including Hashim Thaçi, and Fatmir Sejdiu (who were not members of the Assembly), not acting in the capacity of PISG, declared Kosovo an independent and sovereign state. ...
* League of Prizren
The League of Prizren ( sq, Besëlidhja e Prizrenit), officially the League for the Defense of the Rights of the Albanian Nation ( sq, Lidhja për mbrojtjen e të drejtave te kombit Shqiptar), was an Albanian political organization which was offi ...
* Unification of Albania and Kosovo
The unification of Albania and Kosovo is a political idea, revived after Kosovo declared independence in 2008. This idea has been connected to the irredentist concept of Greater Albania. As of the 2011 census, approximately 93% of Kosovars are ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Canak, Jovan M. ''Greater Albania: concepts and possibile icconsequences''. Belgrade: Institute of Geopolitical Studies, 1998. *Jaksic G. and Vuckovic V. ''Spoljna politika srbije za vlade''. Kneza Mihaila, Belgrade, 1963. *Dimitrios Triantaphyllou. ''The Albanian Factor''. ELIAMEP, Athens, 2000. *External links
Albanian Canadian League Information Service (ACLIS)
''
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'', 18 January 2007
{{Pan-nationalist concepts
Albanian separatism
Political history of Albania
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
Albanian nationalism
Political movements
Albania–Greece relations
Albania–Kosovo relations
Albania–Montenegro relations
Albania–North Macedonia relations
Albania–Serbia relations