Graph of a function on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In 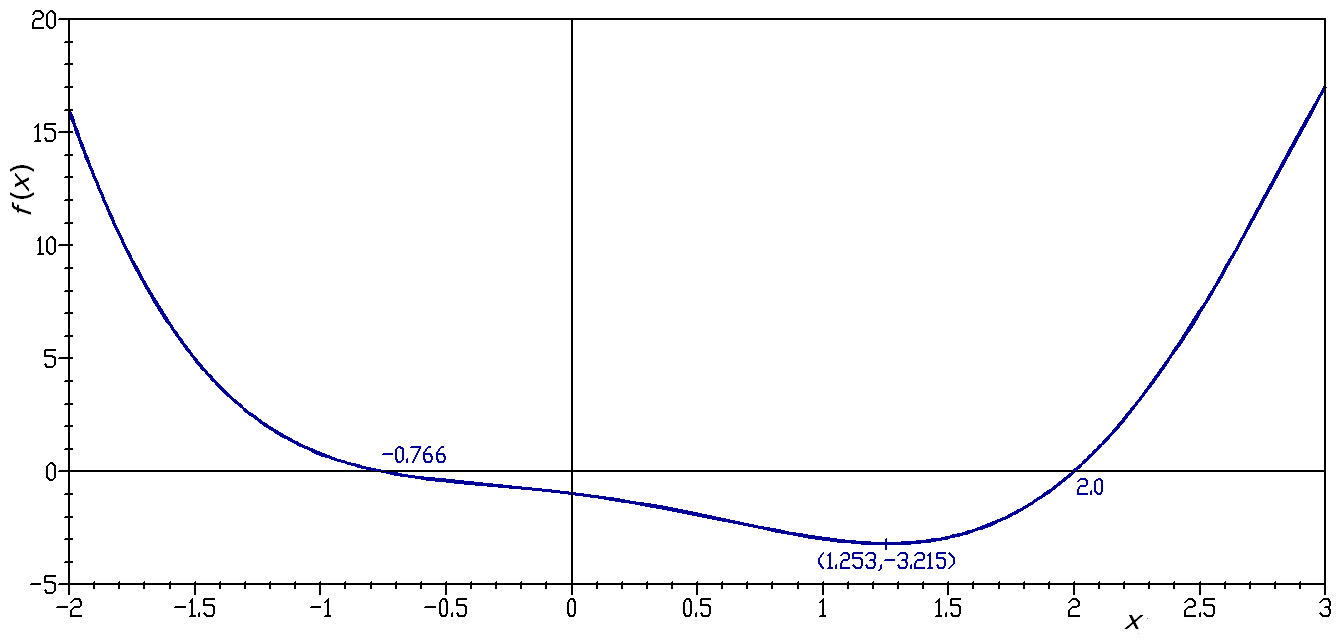
 The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the range can be recovered as .
The codomain , however, cannot be determined from the graph alone.
The graph of the cubic polynomial on the real line
is
If this set is plotted on a Cartesian plane, the result is a curve (see figure).
The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the range can be recovered as .
The codomain , however, cannot be determined from the graph alone.
The graph of the cubic polynomial on the real line
is
If this set is plotted on a Cartesian plane, the result is a curve (see figure).
 The graph of the
The graph of the
Function Graph
" From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. {{Visualization Charts Functions and mappings Numerical function drawing
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, the graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs , where In the common case where and are real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every ...
s, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates of points in two-dimensional space and thus form a subset of this plane.
In the case of functions of two variables, that is functions whose domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
** Domain of definition of a partial function
** Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* ...
consists of pairs the graph usually refers to the set of ordered triples where instead of the pairs as in the definition above. This set is a subset of three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informa ...
; for a continuous real-valued function of two real variables, it is a surface.
In science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
, technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
, finance, and other areas, graphs are tools used for many purposes. In the simplest case one variable is plotted as a function of another, typically using rectangular axes; see '' Plot (graphics)'' for details.
A graph of a function is a special case of a relation.
In the modern foundations of mathematics, and, typically, in set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory, as a branch of mathematics, is mostly concern ...
, a function is actually equal to its graph. However, it is often useful to see functions as mappings, which consist not only of the relation between input and output, but also which set is the domain, and which set is the codomain. For example, to say that a function is onto (surjective
In mathematics, a surjective function (also known as surjection, or onto function) is a function that every element can be mapped from element so that . In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element o ...
) or not the codomain should be taken into account. The graph of a function on its own doesn't determine the codomain. It is common to use both terms ''function'' and ''graph of a function'' since even if considered the same object, they indicate viewing it from a different perspective.
Definition
Given a mapping in other words a function together with its domain and codomain the graph of the mapping is the set which is a subset of . In the abstract definition of a function, is actually equal to One can observe that, if, then the graph is a subset of (strictly speaking it is but one can embed it with the natural isomorphism).Examples
Functions of one variable
 The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the range can be recovered as .
The codomain , however, cannot be determined from the graph alone.
The graph of the cubic polynomial on the real line
is
If this set is plotted on a Cartesian plane, the result is a curve (see figure).
The graph of the function defined by
is the subset of the set
From the graph, the domain is recovered as the set of first component of each pair in the graph .
Similarly, the range can be recovered as .
The codomain , however, cannot be determined from the graph alone.
The graph of the cubic polynomial on the real line
is
If this set is plotted on a Cartesian plane, the result is a curve (see figure).
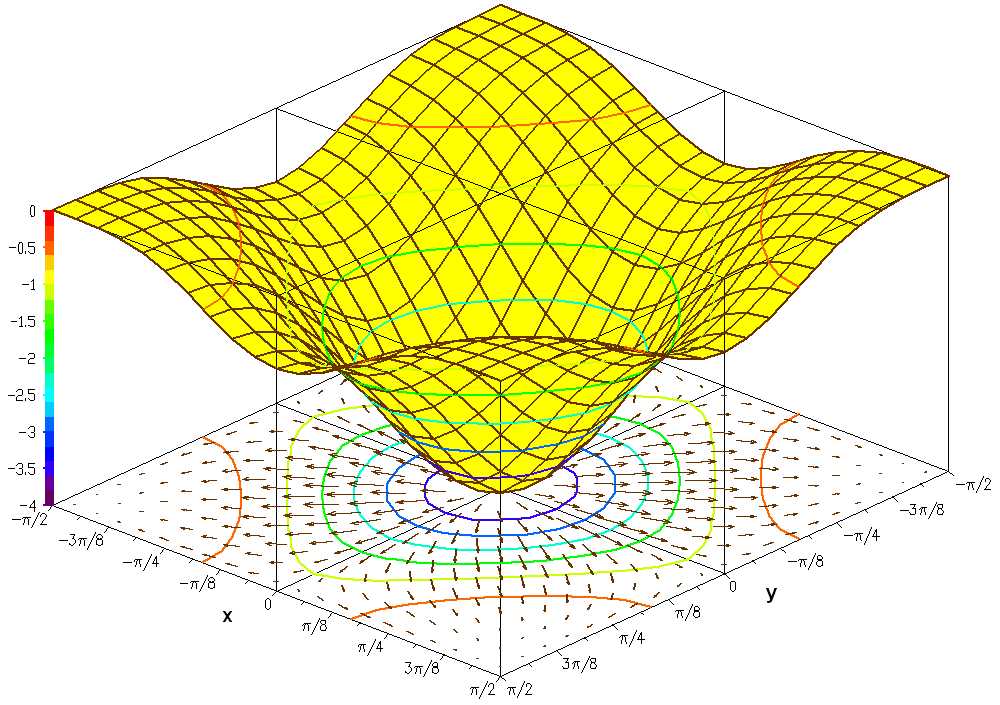
Functions of two variables
trigonometric function
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in a ...
is
If this set is plotted on a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, the result is a surface (see figure).
Oftentimes it is helpful to show with the graph, the gradient of the function and several level curves. The level curves can be mapped on the function surface or can be projected on the bottom plane. The second figure shows such a drawing of the graph of the function:
See also
* Asymptote * Chart * Concave function * Convex function * Contour plot * Critical point *Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
* Epigraph
* Normal to a graph
* Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is use ...
* Stationary point
* Tetraview A tetraview is an attempt to graph a complex function of a complex variable, by a method invented by Davide P. Cervone.
A graph of a real function of a real variable is the set of ordered pairs (x,y) such that y = f(x). This is the ordinary two ...
* Vertical translation
* y-intercept
References
*External links
* Weisstein, Eric W.Function Graph
" From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. {{Visualization Charts Functions and mappings Numerical function drawing