Governor-General of Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The governor general of Canada (french: gouverneure générale du Canada) is the federal viceregal representative of the . The is
/ref> and in 1927 the first official international visit by a governor general was made. Finally, in 1947, King
 The position of governor general is mandated by both the ''
The position of governor general is mandated by both the ''
 Although required by the tenets of
Although required by the tenets of
 Canada shares the person of the sovereign equally with 14 other countries in the
Canada shares the person of the sovereign equally with 14 other countries in the
 The governor general, as the representative of the Canadian sovereign, carries out the parliamentary duties of the sovereign in their absence, such as summoning Parliament, reading the
The governor general, as the representative of the Canadian sovereign, carries out the parliamentary duties of the sovereign in their absence, such as summoning Parliament, reading the
 The governor general is also tasked with fostering national unity and pride. Queen Elizabeth II stated in 1959 to then Governor General Vincent Massey "maintain ngthe right relationship between the Crown and the people of Canada sthe most important function among the many duties of the appointment which you have held with such distinction." One way in which this is carried out is travelling the country and meeting with Canadians from all regions and
The governor general is also tasked with fostering national unity and pride. Queen Elizabeth II stated in 1959 to then Governor General Vincent Massey "maintain ngthe right relationship between the Crown and the people of Canada sthe most important function among the many duties of the appointment which you have held with such distinction." One way in which this is carried out is travelling the country and meeting with Canadians from all regions and
 Prior to 1952, all governors general of Canada were members of the
Prior to 1952, all governors general of Canada were members of the
 With the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, France relinquished most of its North American territories, including Canada, to
With the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, France relinquished most of its North American territories, including Canada, to
 The Rebellions of 1837 brought about great changes to the role of the governor general, prompting, as they did, the British government to grant
The Rebellions of 1837 brought about great changes to the role of the governor general, prompting, as they did, the British government to grant
 In 1926, Liberal prime minister
In 1926, Liberal prime minister
 It was in 1952, a mere five days before King George VI's death, that Vincent Massey became the first Canadian-born person to be appointed as a governor general in Canada since the Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal was made Governor General of New France on 1 January 1755, as well as the first not to be elevated to the
It was in 1952, a mere five days before King George VI's death, that Vincent Massey became the first Canadian-born person to be appointed as a governor general in Canada since the Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal was made Governor General of New France on 1 January 1755, as well as the first not to be elevated to the  The Cabinet in June 1978 proposed the constitutional amendment Bill C-60, that, amongst other changes, vested executive authority directly in the governor general and renamed the position as ''First Canadian'', but the proposal was thwarted by the provincial premiers. When the constitution was patriated four years later, the new amending formula for the documents outlined that any changes to the Crown, including the Office of the Governor General, would require the consent of all the provincial legislatures plus the federal parliament. By 1984, Canada's first female governor general— Jeanne Sauvé—was appointed. While it was she who created the Canadian Heraldic Authority, as permitted by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth II, and who championed youth and world peace, Sauvé proved to be a controversial vicereine, closing to the public the grounds of the Queen's residence and self-aggrandizingly breaching protocol on a number of occasions.
The Cabinet in June 1978 proposed the constitutional amendment Bill C-60, that, amongst other changes, vested executive authority directly in the governor general and renamed the position as ''First Canadian'', but the proposal was thwarted by the provincial premiers. When the constitution was patriated four years later, the new amending formula for the documents outlined that any changes to the Crown, including the Office of the Governor General, would require the consent of all the provincial legislatures plus the federal parliament. By 1984, Canada's first female governor general— Jeanne Sauvé—was appointed. While it was she who created the Canadian Heraldic Authority, as permitted by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth II, and who championed youth and world peace, Sauvé proved to be a controversial vicereine, closing to the public the grounds of the Queen's residence and self-aggrandizingly breaching protocol on a number of occasions.
 It was with the Queen's appointment of
It was with the Queen's appointment of  Prime Minister
Prime Minister
Proclamation Constituting the Office of Governor General and Commander-in-Chief of Canada
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Governor General Of Canada Canada and the Commonwealth of Nations Government of Canada Westminster system Monarchy in Canada 1867 establishments in Canada
head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
and the 14 other Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s, but resides in oldest and most populous realm, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
. The , on the advice
Advice (noun) or advise (verb) may refer to:
* Advice (opinion), an opinion or recommendation offered as a guide to action, conduct
* Advice (constitutional law) a frequently binding instruction issued to a constitutional office-holder
* Advice (p ...
of Canadian prime minister, appoints a governor general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
to carry on the Government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown-i ...
in the 's name, performing most of constitutional and ceremonial duties. The commission is for an indefinite period—known as serving ''at Majesty's pleasure
AT or at may refer to:
Geography Austria
* Austria (ISO 2-letter country code)
* .at, Internet country code top-level domain
United States
* Atchison County, Kansas (county code)
* The Appalachian Trail (A.T.), a 2,180+ mile long mountaino ...
''—though five years is the usual length of time. Since 1959, it has also been traditional to alternate between francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
and anglophone
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language ...
officeholders—although many recent governors general have been bilingual.
The office began in the 17th century, when the French crown appointed governors of the colony of Canada. Following the British conquest of the colony, the British monarch appointed governors of the Province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen ...
(later the Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for the provinces of Lower Canada and Upper Canada, two historical British colonies in present-day Canada. The two colonies were formed in 1791, when the British Parliament passed the '' Constitutional Act'', ...
) from 1763 onward. Consequently, the office is, along with the Crown, the oldest continuous institution in Canada. The present version of the office emerged with Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominio ...
and the passing of the '' British North America Act, 1867'', which defines the role of the governor general as "carrying on the Government of Canada on behalf and in the Name of the King, by whatever Title he is designated". Although the post initially still represented the Government of the United Kingdom
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
(that is, the monarch in his British council), the office was gradually Canadianized until, with the passage of the Statute of Westminster in 1931
The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown.
Passed on 11 December 1931, the statute increased the sovereignty of ...
and the establishment of a separate and uniquely Canadian monarchy, the governor general became the direct personal representative of the independently and uniquely Canadian sovereign, the monarch in his Canadian council. Throughout this process of gradually increasing Canadian independence, the role of governor general took on additional responsibilities. For example, in 1904, the ''Militia Act'' granted permission for the governor general to use the title of '' Commander-in-Chief of the Canadian militia'', while command-in-chief remained vested in the sovereign,''Constitution Act, 1867'', s. 15./ref> and in 1927 the first official international visit by a governor general was made. Finally, in 1947, King
George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of I ...
issued letters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, tit ...
allowing the viceroy to carry out almost all powers on behalf of the monarch. As a result, the day-to-day duties of the monarch are carried out by the governor general, although, as a matter of law, the governor general is not in the same constitutional position as the sovereign; the office itself does not independently possess any powers of the royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
. In accordance with the '' Constitution Act, 1982'', any constitutional amendment that affects the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
, including the office of Governor General, requires the unanimous consent of each provincial legislature as well as the Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada (french: Parlement du Canada) is the federal legislature of Canada, seated at Parliament Hill in Ottawa, and is composed of three parts: the King, the Senate, and the House of Commons. By constitutional convention, ...
.
The 30th and current governor general is Mary Simon
Mary Jeannie May Simon (in Inuktitut syllabics: ᒥᐊᓕ ᓴᐃᒪᓐ, iu, script=Latn, Ningiukudluk; born August 21, 1947) is a Canadian civil servant, diplomat, and former broadcaster who has served as the 30th governor general of Canada ...
, who was sworn in on 26 July 2021. An Inuk leader from Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; iu, ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the ...
in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
, Simon is the first Indigenous person to hold the office. She was nominated on 6 July 2021 to replace Julie Payette
Julie Payette (; born October 20, 1963) is a Canadian engineer, scientist and former astronaut who served from 2017 to 2021 as Governor General of Canada, the 29th since Canadian Confederation.
Payette holds engineering degrees from McGill ...
, who had resigned in January; Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
, the chief justice of Canada, had served as Administrator of the Government of Canada in the interim.
Spelling of the title
The letters patent constituting the office, and official publications of theGovernment of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown-i ...
, spell the title ''governor general'', without a hyphen
The hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words and to separate syllables of a single word. The use of hyphens is called hyphenation. ''Son-in-law'' is an example of a hyphenated word. The hyphen is sometimes confused with dashes ( figure ...
, unlike the spelling of the title in the other Commonwealth realms
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonweal ...
, which do include a hyphen as part of their titles. The hyphenated form, 'Governor-General of Canada', is sometimes used unofficially.
As ''governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
'' is the noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Living creatures (including people, alive, ...
in the title, it is plural
The plural (sometimes list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical number, grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the ...
ized thus, ''governors general'', rather than ''governor generals''.
Appointment
 The position of governor general is mandated by both the ''
The position of governor general is mandated by both the ''Constitution Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (french: Loi constitutionnelle de 1867),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 186 ...
'' (formerly known as the ''British North America Act, 1867'') and the letters patent issued in 1947 by King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of I ...
. As such, on the recommendation of the Canadian prime minister, the Canadian monarch appoints the governor general by commission issued under the royal sign-manual and Great Seal of Canada
The Great Seal of Canada (french: Grand Sceau du Canada) is a governmental seal used for purposes of state in Canada, being set on letters patent, proclamations and commissions, both to representatives of the monarch and for the appointment of ...
. That individual is, from then until being sworn in, referred to as the ''governor general-designate''.
Besides the administration of the oaths of office, there is no set formula for the swearing-in of a governor general-designate. Though there may therefore be variations to the following, the appointee will generally travel to Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
, there receiving an official welcome and taking up residence at 7 Rideau Gate
7 Rideau Gate is the Canadian government's official state guest house for very important dignitaries, such as visiting heads of government or other high-level officials. The house is located in Ottawa, Ontario, near other official residences such ...
, and will begin preparations for their upcoming role, meeting with various high-level officials to ensure a smooth transition between governors general. The sovereign will also hold an audience
An audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature (in which they are called "readers"), theatre, music (in which they are called "listeners"), video games (in which they are called "players"), o ...
with the appointee and will at that time induct both the governor general-designate and their spouse into the Order of Canada
The Order of Canada (french: Ordre du Canada; abbreviated as OC) is a Canadian state order and the second-highest honour for merit in the system of orders, decorations, and medals of Canada, after the Order of Merit.
To coincide with the cen ...
as Companions, as well as appointing the former as a Commander of both the Order of Military Merit and the Order of Merit of the Police Forces
The Order of Merit of the Police Forces (french: Ordre du mérite des corps policiers) is an honour for merit that is, within the Canadian system of honours, the only such fellowship reserved for only members of Canada's various police forces. C ...
(should either person not have already received either of those honours).
The incumbent will generally serve for at least five years, though this is only a developed convention, and the governor general acts at Majesty's pleasure
AT or at may refer to:
Geography Austria
* Austria (ISO 2-letter country code)
* .at, Internet country code top-level domain
United States
* Atchison County, Kansas (county code)
* The Appalachian Trail (A.T.), a 2,180+ mile long mountaino ...
(or the ''Royal Pleasure''). The prime minister may therefore recommend to the that the viceroy remain in service for a longer period of time, sometimes upwards of more than seven years. A governor general may also resign, and two have died in office. In such a circumstance, or if the governor general leaves the country for longer than one month, the chief justice of Canada (or, if that position is vacant or unavailable, the senior puisne justice of the Supreme Court) serves as the administrator of the Government of Canada and exercises all powers of the governor general.
Selection
In a speech on the subject ofConfederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical iss ...
, made in 1866 to the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada
The Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada was the lower house of the legislature for the Province of Canada, which consisted of the former provinces of Lower Canada, then known as Canada East and later the province of Quebec, and Upper ...
, John A. Macdonald said of the planned governor: "We place no restriction on Her Majesty's prerogative in the selection of her representative ... The sovereign has unrestricted freedom of choice ... We leave that to Her Majesty in all confidence." However, between 1867 and 1931, governors general were appointed by the monarch on the advice of the British Cabinet. Thereafter, in accordance with the Statute of Westminster 1931
The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown.
Passed on 11 December 1931, the statute increased the sovereignty of the ...
, the appointment was made by the sovereign with the direction of their Canadian ministers only. Until 1952, all governors general were also either peers or sons of peers, and were born beyond Canada's borders. These viceroys spent a relatively limited time in Canada, but their travel schedules were so extensive that they could "learn more about Canada in five years than many Canadians in a lifetime". Still, though all Canadian nationals were as equally British subject
The term "British subject" has several different meanings depending on the time period. Before 1949, it referred to almost all subjects of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Dominions, and colonies, but excluding protectorates ...
s as their British counterparts prior to the implementation of the ''Canadian Citizenship Act
The ''Canadian Citizenship Act'' (french: Loi sur la citoyenneté canadienne) was a statute passed by the Parliament of Canada in 1946 which created the legal status of Canadian citizenship. The Act defined who were Canadian citizens, separa ...
'' in 1947, the idea of Canadian-born persons being appointed governor general was raised as early as 1919, when, at the Paris Peace Conference, Sir Robert Borden
Sir Robert Laird Borden (June 26, 1854 – June 10, 1937) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known for his leadership of Canada during World War I.
Borde ...
, prime minister of Canada, consulted with Louis Botha
Louis Botha (; 27 September 1862 – 27 August 1919) was a South African politician who was the first prime minister of the Union of South Africa – the forerunner of the modern South African state. A Boer war hero during the Second Boer Wa ...
, prime minister of South Africa
The prime minister of South Africa ( af, Eerste Minister van Suid-Afrika) was the head of government in South Africa between 1910 and 1984.
History of the office
The position of Prime Minister was established in 1910, when the Union of Sout ...
, and the two agreed that the viceregal appointees should be long-term residents of their respective dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s. Calls for just such an individual to be made viceroy came again in the late 1930s, but it was not until Vincent Massey's appointment by King George VI in 1952 that the position was filled by a Canadian-born individual. Massey stated of this that "a Canadian s governor general
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''.
Histor ...
makes it far easier to look on the Crown as our own and on the Sovereign as Queen of Canada." This practice continued until 1999, when Queen Elizabeth II commissioned as her representative Adrienne Clarkson
Adrienne Louise Clarkson (; ; born February 10, 1939) is a Hong Kong-born Canadian journalist who served from 1999 to 2005 as Governor General of Canada, the 26th since Canadian Confederation.
Clarkson arrived in Canada with her family in 19 ...
, a Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
-born refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
to Canada. Moreover, the practice of alternating between francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
and anglophone
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language ...
Canadians was instituted with the appointment of Georges Vanier
Georges-Philias Vanier (23 April 1888 – 5 March 1967) was a Canadian military officer and diplomat who served as governor general of Canada, the first Quebecer and second Canadian-born person to hold the position.
Vanier was born an ...
, a francophone who succeeded the anglophone Massey. All persons whose names are put forward to the for approval must first undergo background check
A background check is a process a person or company uses to verify that an individual is who they claim to be, and this provides an opportunity to check and confirm the validity of someone's criminal record, education, employment history, and oth ...
s by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal and national police service of Canada. As poli ...
and the Canadian Security Intelligence Service.
 Although required by the tenets of
Although required by the tenets of constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
to be nonpartisan
Nonpartisanism is a lack of affiliation with, and a lack of bias towards, a political party.
While an Oxford English Dictionary definition of ''partisan'' includes adherents of a party, cause, person, etc., in most cases, nonpartisan refers sp ...
while in office, governors general were often former politicians; a number held seats in the British House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
by virtue of their inclusion in the peerage. Appointments of former ministers of the Crown in the 1980s and 1990s were criticized by Peter H. Russell
Peter Howard Russell (born 1932) is a Canadian political scientist, serving as professor emeritus of political science at the University of Toronto, where he taught from 1958 to 1997. He was a member of the Toronto chapter of Alpha Delta Phi. He ...
, who stated in 2009: "much of headvantage of the monarchical system is lost in Canada when prime ministers recommend partisan colleagues to be appointed governor general and represent he
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
" Clarkson was the first governor general in Canadian history without either a political or military background, as well as the first Asian-Canadian and the second woman, following on Jeanne Sauvé. The third woman to hold this position was also the first Caribbean-Canadian governor general, Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian stateswoman and former journalist who served from 2005 to 2010 as governor general of Canada, the 27th since Canadian Confederation. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person ...
.
There have been, from time to time, proposals put forward for modifications to the selection process of the governor general. Most recently, the group Citizens for a Canadian Republic has advocated the election of the nominee to the , either by popular or parliamentary vote; a proposal echoed by Adrienne Clarkson, who called for the prime minister's choice to not only be vetted by a parliamentary committee, but also submit to a televised quiz on Canadiana
Canadiana is a term used to describe things (e.g., books, historical documents, and artifacts), ideas, or activities that concern or are distinctive of Canada, its people, and/or its culture, especially works of literature and other cultural pro ...
. Constitutional scholars, editorial boards, and the Monarchist League of Canada
The Monarchist League of Canada (french: Ligue monarchiste du Canada) is a Canadian nonprofit monarchist advocacy organization.
have argued against any such constitutional tinkering with the viceregal appointment process, stating that the position being "not elected is an asset, not a handicap", and that an election would politicize the office, thereby undermining the impartiality necessary to the proper functioning of the governor general.
A new approach was used in 2010 for the selection of David Johnston as governor general-designate. For the task, Prime Minister Stephen Harper
Stephen Joseph Harper (born April 30, 1959) is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. Harper is the first and only prime minister to come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, ...
convened a special search group — the Governor General Consultation Committee—was instructed to find a non-partisan candidate who would respect the monarchical aspects of the viceregal office and conducted extensive consultations with more than 200 people across the country. In 2012, the committee was made permanent and renamed as the Advisory Committee on Vice-Regal Appointments The Advisory Committee on Vice-Regal Appointments was established on 4 November 2012 to assist the government of Canada (the Crown- in-Council) with the appointment of the Governor General of Canada, provincial lieutenant governors, and territoria ...
, with a modified membership and its scope broadened to include the appointment of provincial lieutenant governors and territorial commissioners
A commissioner (commonly abbreviated as Comm'r) is, in principle, a member of a commission or an individual who has been given a commission (official charge or authority to do something).
In practice, the title of commissioner has evolved to in ...
(though the latter are not personal representatives of the monarch). However, Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since ...
did not make use of a selection committee when he recommended Julie Payette
Julie Payette (; born October 20, 1963) is a Canadian engineer, scientist and former astronaut who served from 2017 to 2021 as Governor General of Canada, the 29th since Canadian Confederation.
Payette holds engineering degrees from McGill ...
as Johnston's successor in 2017.
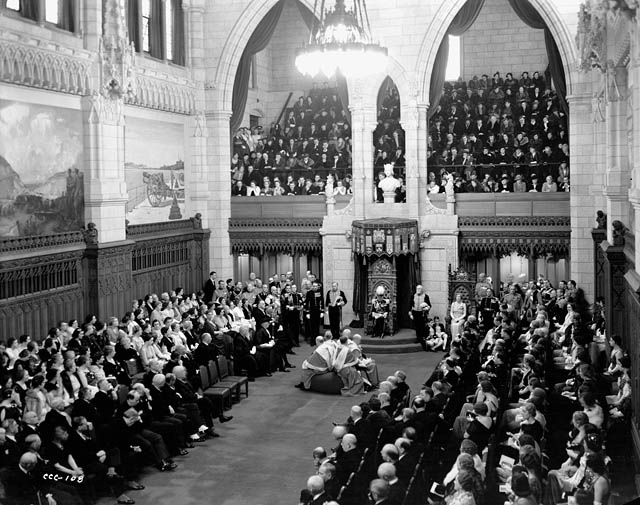
Swearing-in ceremony
The swearing-in ceremony begins with the arrival at 7 Rideau Gate of one of the ministers of the Crown, who then accompanies the governor general-designate toParliament Hill
Parliament Hill (french: Colline du Parlement, colloquially known as The Hill, is an area of Crown land on the southern banks of the Ottawa River in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Its Gothic revival suite of buildings, and their archit ...
, where a Canadian Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force.
...
guard of honour
A guard of honour ( GB), also honor guard ( US), also ceremonial guard, is a group of people, usually military in nature, appointed to receive or guard a head of state or other dignitaries, the fallen in war, or to attend at state ceremonials, ...
(consisting of the Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
Guard, Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
Guard, and Flag Party of the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack subma ...
) awaits to give a general salute
A salute is usually a formal hand gesture or other action used to display respect in military situations. Salutes are primarily associated with the military and law enforcement, but many civilian organizations, such as Girl Guides, Boy Sco ...
. From there, the party is led by the 's parliamentary messenger—the usher of the Black Rod
Black Rod (officially known as the Lady Usher of the Black Rod or, if male, the Gentleman Usher of the Black Rod) is an official in the parliaments of several Commonwealth countries. The position originates in the House of Lords of the Parliam ...
—to the Senate chamber, wherein all justices of the Supreme Court, senators, members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
, and other guests are assembled. The 's commission for the governor general-designate is then read aloud by the secretary to the governor general and the required oaths are administered to the appointee by either the chief justice or one of the puisne justices of the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
; the three oaths are: the Oath of Allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. Fo ...
, the Oath of Office as Governor General and Commander-in-Chief, and the Oath as Keeper of the Great Seal of Canada. With the affixing of their signature to these three solemn promises, the individual is officially the governor general, and at that moment the flag of the governor general of Canada
The flag of the governor general of Canada is a flag used as a symbol to mark the presence of the governor general of Canada. Such a flag has been used by governors general since just after Canadian Confederation and the design has altered over dec ...
is raised on the Peace Tower
The Peace Tower (french: link=no, Tour de la Paix) is a focal bell and clock tower sitting on the central axis of the Centre Block of the Canadian parliament buildings in Ottawa, Ontario. The present incarnation replaced the Victoria Tower af ...
, the Viceregal Salute is played by the Central Band of the Canadian Forces, and a 21-gun salute
A 21-gun salute is the most commonly recognized of the customary gun salutes that are performed by the firing of cannons or artillery as a military honor. As naval customs evolved, 21 guns came to be fired for heads of state, or in exception ...
is conducted by the Royal Regiment of Canadian Artillery. The governor general is seated on the throne while a prayer is read, and then receives the Great Seal of Canada (which is passed to the registrar general
General Register Office or General Registry Office (GRO) is the name given to the civil registry in the United Kingdom, many other Commonwealth nations and Ireland. The GRO is the government agency responsible for the recording of vital recor ...
for protection), as well as the chains of both the chancellor of the Order of Canada and of the Order of Military Merit. The governor general will then give a speech, outlining whichever cause or causes they will champion during their time as viceroy.
Role
 Canada shares the person of the sovereign equally with 14 other countries in the
Canada shares the person of the sovereign equally with 14 other countries in the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
and that individual, in the monarch's capacity as the Canadian sovereign, has 10 other legal personas within the Canadian federation
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total ...
. As the sovereign works and resides predominantly outside of Canada's borders, the governor general's primary task is to perform federal constitutional duties on behalf of the monarch. As such, the governor general carries on "the Government of Canada on behalf and in the name of the Sovereign".
The governor general acts within the principles of parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
and responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
as a guarantor of continuous and stable governance and as a nonpartisan
Nonpartisanism is a lack of affiliation with, and a lack of bias towards, a political party.
While an Oxford English Dictionary definition of ''partisan'' includes adherents of a party, cause, person, etc., in most cases, nonpartisan refers sp ...
safeguard against the abuse of power. For the most part, however, the powers of the Crown are exercised on a day-to-day basis by elected and appointed individuals, leaving the governor general to perform the various ceremonial duties the sovereign otherwise carries out when in the country; at such a moment, the governor general removes him or herself from public, though the presence of the monarch does not affect the governor general's ability to perform governmental roles.
Past governor general the Marquess of Lorne said of the job: "It is no easy thing to be a governor general of Canada. You must have the patience of a saint, the smile of a cherub
A cherub (; plural cherubim; he, כְּרוּב ''kərūḇ'', pl. ''kərūḇīm'', likely borrowed from a derived form of akk, 𒅗𒊏𒁍 ''karabu'' "to bless" such as ''karibu'', "one who blesses", a name for the lamassu) is one of the ...
, the generosity of an Indian prince, and the back of a camel", and the Earl of Dufferin stated that the governor general is "A representative of all that is august, stable, and sedate in the government, the history, and the traditions of the country; incapable of partizanship, and lifted far above the atmosphere of faction; without adherents to reward or opponents to oust from office; docile to the suggestions of his Ministers, and yet securing to the people the certainty of being able to get rid of an Administration or Parliament the moment either had forfeited their confidence."
Constitutional role
Allexecutive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive di ...
, legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known ...
, and judicial power in and over Canada is vested in the monarch. The governor general is permitted to exercise most of this power, including the royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
, in the sovereign's name; some as outlined in the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', and some through various letters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, tit ...
issued over the decades, particularly those from 1947 that constitute the Office of Governor General of Canada. The 1947 letters patent state: "And We do hereby authorize and empower Our Governor General, with the advice of Our Privy Council for Canada or of any members thereof or individually, as the case requires, to exercise all powers and authorities lawfully belonging to Us in respect of Canada." The office itself does not, however, independently possess any powers of the royal prerogative, only exercising the Crown's powers with its permission; a fact the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' left unchanged. Among other duties, the monarch retains the sole right to appoint the governor general. It is also stipulated that the governor general may appoint deputies—usually Supreme Court justices and the secretary to the governor general—who can perform some of the viceroy's constitutional duties in the governor general's absence, and the chief justice of the Supreme Court (or a puisne justice in the chief justice's absence) will act as the administrator of the government upon the death or removal, as well as the incapacitation, or absence of the governor general for more than one month.
It is the governor general who is required by the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', to appoint for life persons to the 's Privy Council for Canada
's may refer to:
* 's, an ending used to form the possessive of English nouns and noun phrases
* 's, a contraction of the English words ''is'' and ''has''
* 's, a form of the English plural ending, written after single letters and in some other i ...
, who are all theoretically tasked with tendering to the monarch and viceroy guidance on the exercise of the royal prerogative. Convention dictates, though, that the governor general must draw from the Privy Council an individual to become the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
—in almost all cases the member of Parliament who commands the confidence of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. The prime minister then advises the governor general to appoint other members of parliament to a committee of the privy council known as the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
, and it is in practice only from this group of ministers of the Crown that the and governor general will take advice
Advice (noun) or advise (verb) may refer to:
* Advice (opinion), an opinion or recommendation offered as a guide to action, conduct
* Advice (constitutional law) a frequently binding instruction issued to a constitutional office-holder
* Advice (p ...
on the use of executive power; an arrangement called the '' -in-Council'' or, more specifically, the ''Governor-in-Council''. In this capacity, the governor general will issue royal proclamation
A proclamation (Lat. ''proclamare'', to make public by announcement) is an official declaration issued by a person of authority to make certain announcements known. Proclamations are currently used within the governing framework of some nations ...
s and sign orders in council
An Order-in-Council is a type of legislation in many countries, especially the Commonwealth realms. In the United Kingdom this legislation is formally made in the name of the monarch by and with the advice and consent of the Privy Council (''King ...
. The Governor-in-Council is also specifically tasked by the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', to appoint in the 's name the lieutenant governors of the provinces (with the Advisory Committee on Vice-Regal Appointments The Advisory Committee on Vice-Regal Appointments was established on 4 November 2012 to assist the government of Canada (the Crown- in-Council) with the appointment of the Governor General of Canada, provincial lieutenant governors, and territoria ...
and the premiers of the provinces concerned playing an advisory role), senators, the speaker of the Senate, and superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
, district and county court judges in each province, except those of the Courts of Probate in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
. The advice given by the Cabinet is, in order to ensure the stability of government, by political convention typically binding; both the and viceroy, however, may in exceptional circumstances invoke the reserve powers, which remain the Crown's final check against a ministry's abuse of power.
 The governor general, as the representative of the Canadian sovereign, carries out the parliamentary duties of the sovereign in their absence, such as summoning Parliament, reading the
The governor general, as the representative of the Canadian sovereign, carries out the parliamentary duties of the sovereign in their absence, such as summoning Parliament, reading the speech from the throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining t ...
, and proroguing and dissolving Parliament. The governor general also grants royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
in the 's name; legally, the governor general has three options: grant royal assent (making the bill a law), withhold royal assent (vetoing the bill), or reserve the bill for the signification of the 's pleasure (allowing the sovereign to personally grant or withhold assent). If the governor general withholds the 's assent, the sovereign may within two years disallow
''Disallow'' is the third album by High Rise, released on May 25, 1996, through P.S.F. Records.
Track listing
Personnel
;High Rise
*Asahito Nanjo – vocals, bass guitar, engineering
*Munehiro Narita – guitar
*Pill � ...
the bill, thereby annulling the law in question. No modern Canadian viceroy has denied royal assent to a bill. Provincial viceroys, however, are able to reserve royal assent to provincial bills for the governor general, which was last invoked in 1961 by the lieutenant governor of Saskatchewan
The lieutenant governor of Saskatchewan () is the viceregal representative in Saskatchewan of the , who operates distinctly within the province but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada, as well as the other Common ...
.
Ceremonial role
With most constitutional functions lent to Cabinet, the governor general acts in a primarily ceremonial fashion. The governor general will host members ofCanada's royal family
The monarchy of Canada is Canada's form of government embodied by the Canadian sovereign and head of state. It is at the core of Canada's constitutional federal structure and Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. The monarchy is the found ...
, as well as foreign royalty and heads of state, and will represent the and country abroad on state visits to other nations, though the monarch's permission is necessary, via the prime minister, for the viceroy to leave Canada. Also as part of international relations, the governor general issues letters of credence and of recall for Canadian ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or s ...
s and high commissioners
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift ...
and receives the same from foreign ambassadors and other Commonwealth countries' high commissioners appointed to Canada.
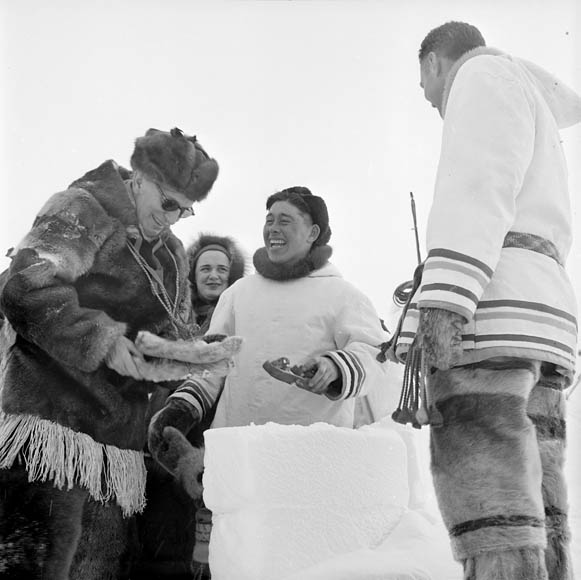
 The governor general is also tasked with fostering national unity and pride. Queen Elizabeth II stated in 1959 to then Governor General Vincent Massey "maintain ngthe right relationship between the Crown and the people of Canada sthe most important function among the many duties of the appointment which you have held with such distinction." One way in which this is carried out is travelling the country and meeting with Canadians from all regions and
The governor general is also tasked with fostering national unity and pride. Queen Elizabeth II stated in 1959 to then Governor General Vincent Massey "maintain ngthe right relationship between the Crown and the people of Canada sthe most important function among the many duties of the appointment which you have held with such distinction." One way in which this is carried out is travelling the country and meeting with Canadians from all regions and ethnic groups in Canada
According to the 2021 Canadian census, over 450 "ethnic or cultural origins" were self-reported by Canadians. The major panethnic origin groups in Canada are: European (), North American (), Asian (), North American Indigenous (), African ...
, continuing the tradition begun in 1869 by Governor General the Lord Lisgar. The governor general will also induct individuals into the various national orders and present national medals and decorations. Similarly, the viceroy administers and distributes the Governor General's Awards, and will also give out awards associated with private organizations, some of which are named for past governors general. During a federal election, the governor general will curtail these public duties, so as not to appear as though they are involving themselves in political affairs.
Although the constitution of Canada states that the "Command-in-Chief of the Land and Naval Militia, and of all Naval and Military Forces, of and in Canada, is hereby declared to continue and be vested in the Queen," the governor general acts in place as Commander-in-Chief of the Canadian Forces
The commander-in-chief of the Canadian Armed Forces (french: Commandant en chef des Forces armées canadiennes) exercises supreme command and control over Canada's military, the Canadian Armed Forces. Constitutionally, the command-in-chief is ves ...
and is permitted through the 1947 Letters Patent to use the title ''Commander-in-Chief in and over Canada''. The position technically involves issuing commands for Canadian troops, airmen, and sailors, but is predominantly a ceremonial role in which the viceroy will visit Canadian Forces base
A Canadian Forces base or CFB (french: links=no, base des Forces canadiennes, BFC) is a military installation of the Canadian Armed Forces. For a facility to qualify as a Canadian Forces base, it must station one or more major units (e.g., army r ...
s across Canada and abroad to take part in military ceremonies, see troops off to and return from active duty, and encourage excellence and morale amongst the forces. The governor general also serves as honorary Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge ...
of three household regiments: the Governor General's Horse Guards, Governor General's Foot Guards
The Governor General's Foot Guards (GGFG) is the senior reserve infantry regiment in the Canadian Army. Located in Ottawa at the Cartier Square Drill Hall, the regiment is a Primary Reserve infantry unit, and the members are part-time soldiers. ...
and Canadian Grenadier Guards. This ceremonial position is directly under that of Colonel-in-Chief, which is held by the . Since 1910, the governor general was also always made the chief scout for Canada, which was renamed ''Chief Scout of Canada'' after 1946 and again in 2011 as '' Patron Scout''.
Residences and household
Rideau Hall
Rideau Hall (officially Government House) is the official residence in Ottawa of both the Canadian monarch and their representative, the governor general of Canada. It stands in Canada's capital on a estate at 1 Sussex Drive, with the main bu ...
, located in Ottawa, is the official residence of the Canadian monarch and of the governor general and is thus the location of the viceregal household and the Chancellery of Honours. For a part of each year since 1872, governors general have also resided at the Citadel () in Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
. A governor general's wife is known as the of Rideau Hall, though there is no equivalent term for a governor general's husband.
The viceregal household aids the governor general in the execution of the royal constitutional and ceremonial duties and is managed by the Office of the Secretary to the Governor General. The Chancellery of Honours depends from the and is thus also located at Rideau Hall and administered by the governor general. As such, the viceroy's secretary ''ex officio'' holds the position of Herald Chancellor of Canada
The Herald Chancellor (''Chancelier d'armes'' in French) is an officer at the Canadian Heraldic Authority. The office is always filled by the Secretary to the Governor General. The Herald Chancellor is responsible for the administration of the e ...
, overseeing the Canadian Heraldic Authority—the mechanism of the Canadian honours system by which armorial bearings are granted to Canadians by the governor general in the name of the sovereign. These organized offices and support systems include aides-de-camp, press officers, financial managers, speech writers, trip organizers, event planners, protocol officers, chefs and other kitchen employees, waiters, and various cleaning staff, as well as visitors' centre staff and tour guides at both official residences. In this official and bureaucratic capacity, the entire household is often referred to as '' Government House'' and its departments are funded through the normal federal budgetary process, as is the governor general's salary of CAD$288,900, which has been taxed since 2013. Additional costs are incurred from separate ministries and organizations such as the National Capital Commission
The National Capital Commission (NCC; french: Commission de la capitale nationale, CCN) is the Crown corporation responsible for development, urban planning, and conservation in Canada's Capital Region (Ottawa, Ontario and Gatineau, Quebec), i ...
, the Department of National Defence Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philippin ...
, and the Royal Canadian Mounted Police.
The governor general's air transportation is assigned to 412 Transport Squadron of the Royal Canadian Air Force. The squadron uses Bombardier Challenger 600 VIP jets to transport the governor general to locations within and outside of Canada.
Symbols and protocol
As the personal representative of the monarch, the governor general follows only the sovereign in the Canadian order of precedence, preceding even other members of the Royal Family. Though the federal viceroy is considered ''primus inter pares
''Primus inter pares'' is a Latin phrase meaning first among equals. It is typically used as an honorary title for someone who is formally equal to other members of their group but is accorded unofficial respect, traditionally owing to their se ...
'' amongst provincial counterparts, the governor general also outranks the lieutenant governors in the federal sphere; at provincial functions, however, the relevant lieutenant governor, as the 's representative in the province, precedes the governor general. The incumbent governor general and their spouse are also the only people in Canada, other than serving Canadian ambassadors and high commissioners, entitled to the use of the style
Style is a manner of doing or presenting things and may refer to:
* Architectural style, the features that make a building or structure historically identifiable
* Design, the process of creating something
* Fashion, a prevailing mode of clothing ...
''His'' or ''Her Excellency
Excellency is an honorific style given to certain high-level officers of a sovereign state, officials of an international organization, or members of an aristocracy. Once entitled to the title "Excellency", the holder usually retains the r ...
'' and the governor general is granted the additional honorific of ''the Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The ter ...
'' for their time in office and for life afterwards.
 Prior to 1952, all governors general of Canada were members of the
Prior to 1952, all governors general of Canada were members of the peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Be ...
or heir apparent to a peerage. Typically, individuals appointed as federal viceroy were already a peer, either by inheriting the title, such as the Duke of Devonshire, or by prior elevation by the sovereign in their own right, as was the case with the Viscount Alexander of Tunis. None were life peer
In the United Kingdom, life peers are appointed members of the peerage whose titles cannot be inherited, in contrast to hereditary peers. In modern times, life peerages, always created at the rank of baron, are created under the Life Peerages ...
s, the '' Life Peerages Act 1958'' postdating the beginning of the tradition of appointing Canadian citizens as governor general. John Buchan
John Buchan, 1st Baron Tweedsmuir (; 26 August 1875 – 11 February 1940) was a Scottish novelist, historian, and Unionist politician who served as Governor General of Canada, the 15th since Canadian Confederation.
After a brief legal career ...
was, in preparation for his appointment as governor general, made the Baron Tweedsmuir of Elsfield in the County of Oxford by King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother ...
, six months before Buchan was sworn in as viceroy. The leader of His Majesty's Loyal Opposition at the time, William Lyon Mackenzie King
William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A L ...
, felt Buchan should serve as governor general as a commoner; however, King George V insisted he be represented by a peer. With the appointment of Vincent Massey as governor general in 1952, governors general ceased to be members of the peerage; successive governments since that date have held to the non-binding and defeated (in 1934) principles of the 1919 Nickle Resolution The Canadian titles debate originated with the presentation to the House of Commons of Canada of the Nickle Resolution in 1917. This resolution marked the earliest attempt to establish a Government of Canada policy requesting the sovereign, in the ...
.
Under the orders' constitutions, the governor general serves as Chancellor and Principal Companion of the Order of Canada
The Order of Canada (french: Ordre du Canada; abbreviated as OC) is a Canadian state order and the second-highest honour for merit in the system of orders, decorations, and medals of Canada, after the Order of Merit.
To coincide with the cen ...
, Chancellor of the Order of Military Merit, and Chancellor of the Order of Merit of the Police Forces
The Order of Merit of the Police Forces (french: Ordre du mérite des corps policiers) is an honour for merit that is, within the Canadian system of honours, the only such fellowship reserved for only members of Canada's various police forces. C ...
. The governor general also upon installation automatically becomes a Knight or Dame of Justice and the Prior and Chief Officer in Canada of the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem
The Order of St John, short for Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem (french: l'ordre très vénérable de l'Hôpital de Saint-Jean de Jérusalem) and also known as St John International, is a British royal order of c ...
. As acting commander-in-chief, the governor general is further routinely granted the Canadian Forces Decoration
The Canadian Forces' Decoration (post-nominal letters "CD") is a Canadian award bestowed upon members of the Canadian Armed Forces who have completed twelve years of military service, with certain conditions. By convention, it is also given to t ...
by the chief of the Defence Staff on behalf of the monarch. All of these honours are retained following an incumbent's departure from office, with the individual remaining in the highest categories of the orders, and they may also be further distinguished with induction into other orders or the receipt of other awards.
The Viceregal Salute — composed of the first six bars of the Royal Anthem ("God Save the
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
") followed by the first and last four bars of the national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europea ...
("O Canada
"O Canada" (french: Ô Canada, italic=no) is the national anthem of Canada. The song was originally commissioned by Lieutenant Governor of Quebec Théodore Robitaille for the 1880 Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day ceremony; Calixa Lavallée composed the ...
") — is the salute
A salute is usually a formal hand gesture or other action used to display respect in military situations. Salutes are primarily associated with the military and law enforcement, but many civilian organizations, such as Girl Guides, Boy Sco ...
used to greet the governor general upon arrival and departure from most official events. To mark the viceroy's presence at any building, ship, airplane, or car in Canada, the governor general's flag is employed. The present form was adopted on 23 February 1981 and, in the federal jurisdiction, takes precedence over all other flags except for the 's personal Canadian standard. When the governor general undertakes a state visit, however, the national flag
A national flag is a flag that represents and symbolizes a given nation. It is flown by the government of that nation, but usually can also be flown by its citizens. A national flag is typically designed with specific meanings for its colours a ...
is generally employed to mark governor general's presence. This flag is also, along with all flags on Canadian Forces property, flown at half-mast upon the death of an incumbent or former governor general.
The crest of the Royal Arms of Canada is employed as the badge of the governor general, appearing on the viceroy's flag and on other objects associated with the person or the office. This is the fourth such incarnation of the governor general's mark since confederation.
History
French and British colonies
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
colonization of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
began in the 1580s and Aymar de Chaste
Aymar de Chaste (1514–1603) was a Catholic French admiral during the Franco-Spanish Wars between 1582 and 1598.
A gentleman of the King's Chamber, François Aymar (or Aimar) de Cleremont de Chaste served as governor of Dieppe and Arques-la-Bata ...
was appointed in 1602 by King Henry IV as Viceroy of Canada. The explorer Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; Fichier OrigineFor a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a Fr ...
became the first unofficial Governor of New France The governor of New France was the viceroy of the King of France in North America. A French nobleman, he was appointed to govern the colonies of New France, which included Canada, Acadia and Louisiana. The residence of the Governor was at the C ...
in the early 17th century, serving until Charles Huault de Montmagny
Charles Jacques Huault de Montmagny (c. 1583 to 1599 – 4 July 1657) was governor of New France from 1636 to 1648. He was the first person to bear the title of Governor of New France and succeeded Samuel de Champlain, who governed the colony ...
was in 1636 formally appointed to the post by King Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown. ...
. The French Company of One Hundred Associates
The Company of One Hundred Associates ( French: formally the Compagnie de la Nouvelle-France, or colloquially the Compagnie des Cent-Associés or Compagnie du Canada), or Company of New France, was a French trading and colonization company ch ...
then administered New France until King Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ver ...
took control of the colony and appointed Augustin de Saffray de Mésy
Augustin de Saffray de Mésy (1598–1665) was the first Governor General of New France in 1663 after Louis XIV took over the administration of New France from the Compagnie des Cent-Associés.
Very little is known of de Mésy, but he serve ...
as the first governor general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
in 1663, after whom 12 more people served in the post.
 With the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, France relinquished most of its North American territories, including Canada, to
With the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, France relinquished most of its North American territories, including Canada, to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
. King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great B ...
then issued in that same year a royal proclamation establishing, amongst other regulations, the Office of the Governor of Quebec to preside over the new Province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen ...
. Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
remained completely separate colonies, each with their own governor, until the cabinet of William Pitt adopted in the 1780s the idea that they, along with Quebec and Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, should have as their respective governors a single individual styled as ''Governor-in-Chief''. The post was created in 1786, with The Lord Dorchester as its first occupant. However, the governor-in-chief directly governed only Quebec. It was not until the splitting in 1791 of the Province of Quebec, to accommodate the influx of United Empire Loyalist
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America ...
s fleeing the American revolutionary war
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, that the king's representative, with a change in title to ''Governor General'', directly governed Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec ...
, while the other three colonies were each administered by a lieutenant governor in his stead.
Following the 1783 recognition of the independence of the thirteen continental colonies that became the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
and the transfer of East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
and West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former S ...
to Spain, the remaining British colonies of North America, including the archipelago of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, were partly integrated as British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
. During the American War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It ...
, Lieutenant-General Sir George Prevost was ''Captain-General and Governor-in-Chief in and over the Provinces of Upper-Canada, Lower-Canada, Nova-Scotia, and New~Brunswick, and their several Dependencies, Vice-Admiral of the same, Lieutenant-General and Commander of all His Majesty’s Forces in the said Provinces of Lower Canada and Upper-Canada, Nova-Scotia and New-Brunswick, and their several Dependencies, and in the islands of Newfoundland, Prince Edward, Cape Breton and the Bermudas, &c. &c. &c.'' Beneath Prevost, the staff of the British Army in ''the Provinces of Nova-Scotia, New-Brunswick, and their Dependencies, including the Islands of Newfoundland, Cape Breton, Prince Edward and Bermuda'' were under the Command of Lieutenant-General Sir John Coape Sherbrooke
General Sir John Coape Sherbrooke, (29 April 1764 – 14 February 1830) was a British soldier and colonial administrator. After serving in the British army in Nova Scotia, the Netherlands, India, the Mediterranean (including Sicily), and Spa ...
. Below Sherbrooke, the Bermuda Garrison was under the immediate control of the lieutenant-governor of Bermuda
The Governor of Bermuda (fully the ''Governor and Commander-in-Chief of the Somers Isles (alias the Islands of Bermuda)'') is the representative of the British monarch in the British overseas territory of Bermuda.
For the purposes of this ar ...
, Major-General George Horsford). Although the civil government of Bermuda would soon be separated, again, its naval establishment, military garrison, and the established Church of England in Bermuda would long remain linked (the headquarters of the Royal Navy's North America and West Indies Station
The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956. The North American Station was separate from the Jamaica Station until 1830 when the ...
would alternate between Halifax, Nova Scotia, and Bermuda until the 1820s, after which it remained at Bermuda year round until the station was abolished in 1956; the Royal Navy having handed over Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax to the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack subma ...
in 1907. The governor and commander-in-chief of Bermuda and the garrison of Bermuda remained subsidiary to the British Army commander-in-chief at Halifax until the British Army handed military defence over to the Canadian militia and withdrew from the Maritimes in 1870, following the Confederation of Canada. Bermuda and Newfoundland, both left out of the Confederation, remained under the bishop of Newfoundland
The Anglican Diocese of Newfoundland was, from its creation in 1839 until 1879, the Diocese of Newfoundland and Bermuda, with the Cathedral of St. John the Baptist at St. John's, Newfoundland, and a chapel-of-ease named ''Trinity Church'' in the ...
and Bermuda until 1919, when the bishop of Bermuda
The Bishop of Bermuda is an episcopal title given to the ordinary of the Anglican Church of Bermuda, one of six extra-provincial Anglican churches within the Church of England overseen by the Archbishop of Canterbury. The present Bishop is Nick ...
became a separate office from the bishop of Newfoundland.
Responsible government
 The Rebellions of 1837 brought about great changes to the role of the governor general, prompting, as they did, the British government to grant
The Rebellions of 1837 brought about great changes to the role of the governor general, prompting, as they did, the British government to grant responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
to the Canadian provinces. As a result, the viceroys became largely nominal heads, while the democratically elected legislatures and the premiers they supported exercised the authority belonging to the Crown; a concept first put to the test when, in 1849, Governor-General of the Province of Canada
The Governor General of the Province of Canada was the viceregal post of the pre-Confederation Province of Canada that existed from 1840 to Canadian Confederation in 1867.
The post replaced the Governor General of New France and later Governor Gen ...
and Lieutenant-Governor of Canada East
Canada East (french: links=no, Canada-Est) was the northeastern portion of the United Province of Canada. Lord Durham's Report investigating the causes of the Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions recommended merging those two colonies. The ne ...
the Earl of Elgin granted Royal Assent to the Rebellion Losses Bill, despite his personal misgivings towards the legislation.
This arrangement continued after the reunification in 1840 of Upper and Lower Canada into the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
, and the establishment of the Dominion of Canada in 1867. The governor general carried out in Canada all the parliamentary and ceremonial functions of a constitutional monarch—amongst other things, granting Royal Assent, issuing Orders-in-Council, and taking advice from the Canadian Privy Council. However, the governor still remained not a viceroy, in the true sense of the word, being still a representative of and liaison to the British government—the Queen in her British council of ministers—who answered to the secretary of state for the colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the British Cabinet minister in charge of managing the United Kingdom's various colonial dependencies.
History
The position was first created in 1768 to deal with the increas ...
in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and who, as a British observer of Canadian politics, held well into the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
a suite of offices in the East Block of Parliament Hill
Parliament Hill (french: Colline du Parlement, colloquially known as The Hill, is an area of Crown land on the southern banks of the Ottawa River in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Its Gothic revival suite of buildings, and their archit ...
. But, the new position of Canadian high commissioner to the United Kingdom
The High Commission of Canada in the United Kingdom (french: Haut-commissariat du Canada au Royaume-Uni) is the diplomatic mission of Canada to the United Kingdom. It is housed at Canada House on Trafalgar Square in central London, with an addi ...
, created in 1880, began to take over the governor general's role as a link between the Canadian and British governments, leaving the viceroy increasingly as a personal representative of the monarch. As such, the governor general had to retain a sense of political neutrality; a skill that was put to the test when the Marquess of Lorne disagreed with his Canadian prime minister, John A. Macdonald, over the dismissal of Lieutenant Governor of Quebec
The lieutenant governor of Quebec (; French (masculine): ''Lieutenant-gouverneur du Québec'', or (feminine): ''Lieutenante-gouverneure du Québec'') is the viceregal representative in Quebec of the , who operates distinctly within the province ...
Luc Letellier de St-Just. On the advice of the colonial secretary, and to avoid conflict with the cabinet of Canada, the Marquess did eventually concede, and released St-Just from duty. The governor general was then in May 1891 called upon to resolve the Dominion's first cabinet crisis, wherein Prime Minister Macdonald died, leaving the Lord Stanley of Preston to select a new prime minister.
As early as 1880, the viceregal family and court attracted minor ridicule from the Queen's subjects: in July of that year, someone under the pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name ( orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individu ...
''Captain Mac'' included in a pamphlet called ''Canada: from the Lakes to the Gulf'', a coarse satire of an investiture ceremony at Rideau Hall, in which a retired inn-keeper and his wife undergo the rigorous protocol of the royal household and sprawl on the floor before the Duke of Argyll
Duke of Argyll ( gd, Diùc Earraghàidheil) is a title created in the peerage of Scotland in 1701 and in the peerage of the United Kingdom in 1892. The earls, marquesses, and dukes of Argyll were for several centuries among the most powerfu ...
so as to be granted the knighthood for which they had "paid in cold, hard cash". Later, prior to the arrival of Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn
Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (Arthur William Patrick Albert; 1 May 185016 January 1942), was the seventh child and third son of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He served as G ...
(the uncle of King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Qu ...
), to take up the post of governor general, there was a "feeble undercurrent of criticism" centring on worries about a rigid court at Rideau Hall; worries that turned out to be unfounded as the royal couple was actually more relaxed than their predecessors.
Emerging nationality to an independent kingdom
During theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, into which Canada was drawn due to its association with the United Kingdom, the governor general's role turned from one of cultural patron and state ceremony to one of military inspector and morale booster. Starting in 1914, Governor General Prince Arthur donned his Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
's uniform and put his efforts into raising contingents, inspecting army camps, and seeing troops off before their voyage to Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. These actions, however, led to conflict with the prime minister at the time, Robert Borden
Sir Robert Laird Borden (June 26, 1854 – June 10, 1937) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known for his leadership of Canada during World War I.
Borde ...
; though the latter placed blame on Military Secretary Edward Stanton, he also opined that the Duke "laboured under the handicap of his position as a member of the Royal Family and never realized his limitations as Governor General". Prince Arthur's successor, the Duke of Devonshire
Duke of Devonshire is a title in the Peerage of England held by members of the Cavendish family. This (now the senior) branch of the Cavendish family has been one of the wealthiest British aristocratic families since the 16th century and ha ...
, faced the Conscription Crisis of 1917
The Conscription Crisis of 1917 (french: Crise de la conscription de 1917) was a political and military crisis in Canada during World War I. It was mainly caused by disagreement on whether men should be conscripted to fight in the war, but also b ...
and held discussions with his Canadian prime minister, as well as members of the Official Opposition, on the matter. Once the government implemented conscription, Devonshire, after consulting on the pulse of the nation with Sir Wilfrid Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, ( ; ; November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime mini ...
, Vincent Massey, Henri Bourassa
Joseph-Napoléon-Henri Bourassa (; September 1, 1868 – August 31, 1952) was a French Canadian political leader and publisher. In 1899, Bourassa was outspoken against the British government's request for Canada to send a militia to fight for ...
, Archbishop of Montreal
The Archdiocese of Montréal ( la, Archdioecesis Marianopolitana) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Canada. A metropolitan see, its archepiscopal see is the Montreal, Quebec. It includes Montreal ...
Paul Bruchési
Louis Joseph Napoléon Paul Bruchési (October 29, 1855 – September 20, 1939) was a Canadian prelate, the second Archbishop of Montreal. In 1910 he directed the 21st International Eucharistic Congress held in Montreal.
Life
Louis-Joseph-Pa ...
, Duncan Campbell Scott, Vilhjalmur Stefansson, and Stephen Leacock, made efforts to conciliate Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
, though he had little real success.
Canada's national sentiment had gained fortitude through the country's sacrifices on the battlefields of the First World War and, by war's end, the interference of the British government in Canadian affairs was causing ever-increasing discontent amongst Canadian officials; in 1918, the ''Toronto Star
The ''Toronto Star'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet daily newspaper. The newspaper is the country's largest daily newspaper by circulation. It is owned by Toronto Star Newspapers Limited, a subsidiary of Torstar Corporation and par ...
'' was even advocating the end of the office. The governor general's role was also changing to focus less on the larger Empire and more on uniquely Canadian affairs, including the undertaking of official international visits on behalf of Canada, the first being that of the Marquess of Willingdon to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, where he was accorded by President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a Republican lawyer from New England who climbed up the ladder of Ma ...
the full honours of representative of a head of state. It would be another decade, however, before the King-Byng Affair: another catalyst for change in the relationship between Canada—indeed, all the dominions—and the United Kingdom, and thus the purpose of the governor general.
 In 1926, Liberal prime minister
In 1926, Liberal prime minister William Lyon Mackenzie King
William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A L ...
, facing a non-confidence vote in the House of Commons over a scandal in his party, requested that Governor General Lord Byng dissolve parliament and call an election. Byng, however, refused his Canadian prime minister's advice, citing both the facts that King held the minority of seats in the house and that a general election had been held only months earlier; he thus called on Arthur Meighen
Arthur Meighen (; June 16, 1874 – August 5, 1960) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the ninth prime minister of Canada from 1920 to 1921 and from June to September 1926. He led the Conservative Party from 1920 to 1926 and fr ...
to form a government. Within a week however, Meighen's Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
government lost its own non-confidence vote, forcing the Governor General to dissolve parliament and call elections that saw Mackenzie King returned to power. King then went on to the Imperial Conference that same year and there pushed for reorganizations that resulted in the Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
, which declared formally the practical reality that had existed for some years: namely, that the Dominions were fully autonomous and equal in status to the United Kingdom. These new developments were codified in the Statute of Westminster, through the enactment of which on 11 December 1931, Canada, along with the Union of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Tr ...
and the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
, immediately obtained formal legislative independence from the UK. In addition, the Balfour Declaration also held that the governor general would cease to act as the representative of the British government. Accordingly, in 1928, the United Kingdom appointed its first High Commissioner to Canada thus effectively ending the governor general's diplomatic role as the British government's envoy.
The governor general thus became solely the representative of the monarch within Canadian jurisdiction, ceasing completely to be an agent of the British Cabinet, and as such would be appointed by the monarch granting his royal sign-manual under the Great Seal of Canada
The Great Seal of Canada (french: Grand Sceau du Canada) is a governmental seal used for purposes of state in Canada, being set on letters patent, proclamations and commissions, both to representatives of the monarch and for the appointment of ...
only on the advice of his Canadian prime minister.
The Canadian Cabinet's first recommendation under this new system was still, however, a British subject
The term "British subject" has several different meanings depending on the time period. Before 1949, it referred to almost all subjects of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Dominions, and colonies, but excluding protectorates ...
born outside of Canada: Lord Tweedsmuir
John Buchan, 1st Baron Tweedsmuir (; 26 August 1875 – 11 February 1940) was a Scottish novelist, historian, and Unionist politician who served as Governor General of Canada, the 15th since Canadian Confederation.
After a brief legal career ...
. His birthplace aside, though, the professional author took further than any of his predecessors the idea of a distinct Canadian identity, travelling the length and breadth of the country, including, for the first time for a governor general, the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
regions. Not all Canadians, however, shared Tweedsmuir's views; the Baron raised the ire of imperialists when he said in Montreal in 1937: "a Canadian's first loyalty is not to the British Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
, but to Canada and Canada's King", a statement the ''Montreal Gazette
The ''Montreal Gazette'', formerly titled ''The Gazette'', is the only English-language daily newspaper published in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Three other daily English-language newspapers shuttered at various times during the second half of t ...
'' dubbed as "disloyal". During Tweedsmuir's time as viceroy, which started in 1935, calls began to emerge for a Canadian-born individual to be appointed as governor general; but Tweedsmuir died suddenly in office in 1940, while Canada was in the midst of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, and Prime Minister Mackenzie King did not feel it was the right time to search for a suitable Canadian. The Earl of Athlone was instead appointed by King George VI, Athlone's nephew, to be his viceroy for the duration of the war.
Quebec nationalism and constitutional patriation
 It was in 1952, a mere five days before King George VI's death, that Vincent Massey became the first Canadian-born person to be appointed as a governor general in Canada since the Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal was made Governor General of New France on 1 January 1755, as well as the first not to be elevated to the
It was in 1952, a mere five days before King George VI's death, that Vincent Massey became the first Canadian-born person to be appointed as a governor general in Canada since the Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal was made Governor General of New France on 1 January 1755, as well as the first not to be elevated to the peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Be ...
since Sir Edmund Walker Head in 1854. There was some trepidation about this departure from tradition and Massey was intended to be a compromise: he was known to embody loyalty, dignity, and formality, as expected from a viceroy. As his viceregal tenure neared an end, it was thought that Massey, an anglophone
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language ...
, should be followed by a francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
Canadian; and so, in spite of his Liberal Party attachments, Georges Vanier
Georges-Philias Vanier (23 April 1888 – 5 March 1967) was a Canadian military officer and diplomat who served as governor general of Canada, the first Quebecer and second Canadian-born person to hold the position.
Vanier was born an ...
was chosen by Conservative prime minister John Diefenbaker as the next governor general. Vanier was subsequently appointed by Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
in person at a meeting of her Canadian Cabinet, thus initiating the convention of alternating between individuals from Canada's two main linguistic groups. This move did not, however, placate those who were fostering the new Quebec nationalist movement, for whom the monarchy and other federal institutions were a target for attack. Though Vanier was a native of Quebec and fostered biculturalism, he was not immune to the barbs of the province's sovereigntists and, when he attended '' la Fête St-Jean-Baptiste'' in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
in 1964, a group of separatists held placards reading ''"'"'' ("Vanier sold out") and ''"'"'' ("Vanier Queen's jester").
In light of this regional nationalism and a resultant change in attitudes towards Canadian identity, images and the role of the monarchy were cautiously downplayed, and Vanier's successor, Roland Michener, was the last viceroy to practice many of the office's ancient traditions, such as the wearing of court uniform
Court uniform and dress were required to be worn by those in attendance at the royal court in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Specifically, ''court uniform'' was worn by those holding particular offices associated with the government, the C ...
by the governor general, the requirement of court dress
Court dress comprises the style of clothes and other attire prescribed for members of courts of law. Depending on the country and jurisdiction's traditions, members of the court ( judges, magistrates, and so on) may wear formal robes, gowns ...
for state occasions, and expecting women to curtsey
A curtsy (also spelled curtsey or incorrectly as courtsey) is a traditional gendered gesture of greeting, in which a girl or woman bends her knees while bowing her head. In Western culture it is the feminine equivalent of bowing by males. Miss Ma ...
before the governor general. At the same time, he initiated new practices for the viceroy, including regular conferences with the lieutenant governors and the undertaking of state visits. He presided over Canada's centennial celebrations and the coincidental Expo 67
The 1967 International and Universal Exposition, commonly known as Expo 67, was a general exhibition from April 27 to October 29, 1967. It was a category One World's Fair held in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is considered to be one of the most su ...
, to which French president Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Governm ...
was invited. Michener was with de Gaulle when he made his infamous ''"'"'' speech in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
and was cheered wildly by the gathered crowd while they booed and jeered Michener. With the additional recognition of the monarchy as a Canadian institution, the establishment of a distinct Canadian honours system
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
, an increase of state visits coming with Canada's growing role on the world stage, and the more prevalent use of television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
to visually broadcast ceremonial state affairs, the governor general became more publicly active in national life.
 The Cabinet in June 1978 proposed the constitutional amendment Bill C-60, that, amongst other changes, vested executive authority directly in the governor general and renamed the position as ''First Canadian'', but the proposal was thwarted by the provincial premiers. When the constitution was patriated four years later, the new amending formula for the documents outlined that any changes to the Crown, including the Office of the Governor General, would require the consent of all the provincial legislatures plus the federal parliament. By 1984, Canada's first female governor general— Jeanne Sauvé—was appointed. While it was she who created the Canadian Heraldic Authority, as permitted by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth II, and who championed youth and world peace, Sauvé proved to be a controversial vicereine, closing to the public the grounds of the Queen's residence and self-aggrandizingly breaching protocol on a number of occasions.
The Cabinet in June 1978 proposed the constitutional amendment Bill C-60, that, amongst other changes, vested executive authority directly in the governor general and renamed the position as ''First Canadian'', but the proposal was thwarted by the provincial premiers. When the constitution was patriated four years later, the new amending formula for the documents outlined that any changes to the Crown, including the Office of the Governor General, would require the consent of all the provincial legislatures plus the federal parliament. By 1984, Canada's first female governor general— Jeanne Sauvé—was appointed. While it was she who created the Canadian Heraldic Authority, as permitted by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth II, and who championed youth and world peace, Sauvé proved to be a controversial vicereine, closing to the public the grounds of the Queen's residence and self-aggrandizingly breaching protocol on a number of occasions.
Withering and renaissance
Sarah, Duchess of York
Sarah, Duchess of York (born Sarah Margaret Ferguson; 15 October 1959), also known by the nickname Fergie, is a member of the British royal family. She is the former wife of Prince Andrew, Duke of York, the younger brother of King Charles III ...
, said in 2009 that sometime during her marriage to Prince Andrew, Duke of York
Prince Andrew, Duke of York, (Andrew Albert Christian Edward; born 19 February 1960) is a member of the British royal family. He is the younger brother of King Charles III and the third child and second son of Queen Elizabeth II and Princ ...
, her husband was offered the position of governor general of Canada, and she speculated in hindsight that their agreement to refuse the commission may have been a contributing factor in their eventual break-up. Instead, Sauvé's tenure as governor general was book-ended by a series of appointments—Edward Schreyer
Edward Richard Schreyer (born December 21, 1935) is a Canadian politician, diplomat, and statesman who served as Governor General of Canada, the 22nd since Canadian Confederation.
Schreyer was born and educated in Manitoba, and was first electe ...
, Ray Hnatyshyn, and Roméo LeBlanc
Roméo-Adrien LeBlanc (December 18, 1927June 24, 2009) was a Canadian journalist, politician and statesman who served as Governor General of Canada, the 25th since Canadian Confederation.
LeBlanc was born and educated in New Brunswick, and also ...
—that have been generally regarded as mere patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
postings for former politicians and friends of the incumbent prime minister at the time, and despite the duties they carried out, their combined time in the viceregal office is generally viewed as unremarkable at best, and damaging to the office at worst. As David Smith described it: "Notwithstanding the personal qualities of the appointees, which have often been extraordinary, the Canadian governor general has become a hermetic head of state—ignored by press, politicians and public." It was theorized by Peter Boyce that this was due, in part, to widespread misunderstanding about the governor general's role coupled with a lack of public presence compared to the media coverage dedicated to the increasingly presidentialized prime minister.
 It was with the Queen's appointment of
It was with the Queen's appointment of Adrienne Clarkson
Adrienne Louise Clarkson (; ; born February 10, 1939) is a Hong Kong-born Canadian journalist who served from 1999 to 2005 as Governor General of Canada, the 26th since Canadian Confederation.
Clarkson arrived in Canada with her family in 19 ...
, on the advice of then Prime Minister Jean Chrétien
Joseph Jacques Jean Chrétien (; born January 11, 1934) is a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 20th prime minister of Canada from 1993 to 2003.
Born and raised in Shawinigan, Shawinigan Falls, Quebec, Chrétien is a law gradua ...
, that a shift in the office took place. Clarkson was the first Canadian viceroy to have not previously held any political or military position—coming as she did from a background of television journalism with the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (french: Société Radio-Canada), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a federal Crown corporation that receives funding from the governmen ...
—was the first since 1952 to have been born outside of Canada, the first from a visible minority
A visible minority () is defined by the Government of Canada as "persons, other than aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour". The term is used primarily as a demographic category by Statistics Canada, in connect ...
(she is of Chinese ancestry), and, by her being accompanied to Rideau Hall by her husband, author and philosopher John Ralston Saul
John Ralston Saul (born June 19, 1947) is a Canadian writer, political philosopher, and public intellectual. Saul is most widely known for his writings on the nature of individualism, citizenship and the Public good (economics), public good; t ...
, the official appointment brought an unofficial pair to the viceregal placement, in that the governor general would not be the only person actively exploring Canadian theory and culture. Clarkson managed to bring the viceregal office back into the collective consciousness of Canadians, winning praise for touring the country more than any of her predecessors, her inspiring speeches, and her dedication to the military in her role as the Commander-in-Chief's representative. This did not come without a cost, however, as the attention also drew widespread criticism of the governor general's increased spending on state affairs, for which the office was symbolically rebuked by parliament when it voted in favour of cutting by 10% the viceregal budget it had earlier supported, as well as for fostering the notion, through various demonstrations, that the governor general was ultimately the Canadian head of state above the Queen herself, an approach that was said by Jack Granatstein to have caused "a fury" with the Queen on one occasion in 2004. This attitude was not unique to Clarkson, though; it had been observed that, for some decades, staff at Rideau Hall and various government departments in Ottawa had been pushing to present the governor general as head of state, part of a wider Liberal policy on the monarchy that had been in effect at least since the proposed constitutional changes in the 1970s, if not the 1964 Truncheon Saturday riot in Quebec City. Indeed, international observers opined that the viceroys had been, over the years, making deliberate attempts to distance themselves from the sovereign, for fear of being too closely associated with any "Britishness" the monarch embodied.
 Prime Minister
Prime Minister Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
The son ...
followed Chrétien's example and, for Clarkson's successor, put forward to the Queen the name of Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian stateswoman and former journalist who served from 2005 to 2010 as governor general of Canada, the 27th since Canadian Confederation. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person ...
, who was, like Clarkson, a woman, a refugee, a member of a visible minority, a CBC career journalist, and married to an intellectual husband who worked in the arts. Her appointment initially sparked accusations that she was a supporter of Quebec sovereignty, and it was observed that she had on a few occasions trodden into political matters, as well as continuing to foster the notion that the governor general had replaced the Queen as head of state, thereby "unbalancing ... the federalist symmetry". But Jean ultimately won plaudits, particularly for her solidarity with the Canadian Forces and the Indigenous peoples in Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and '' Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider th ...
, as well as her role in the parliamentary dispute that took place between December 2008 and January 2009.
With the appointment of academic David Johnston, former principal of McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter granted by King George IV,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill Univer ...
and subsequently president of the University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
, there was a signalled emphasis for the governor general to vigorously promote learning and innovation. Johnston stated in his inaugural address: "e want to be
E, or e, is the fifth letter and the second vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''e'' (pronounced ); plu ...
a society that innovates, embraces its talent and uses the knowledge of each of its citizens to improve the human condition for all." There was also a recognition of Johnston's expertise in constitutional law
Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a state, namely, the executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as the basic rights of citizens and, in fe ...
, following the controversial prorogations of Parliament in 2008 and 2009, which initiated some debate about the governor general's role as the representative of Canada's head of state.
Activities post-retirement
Retired governors general usually either withdraw from public life or go on to hold other public offices. Edward Schreyer, for instance, was appointedCanadian High Commissioner to Australia
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source o ...
upon his departure from the viceregal role in 1984, and Michaëlle Jean became the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
special envoy
Diplomatic rank is a system of professional and social rank used in the world of diplomacy and international relations. A diplomat's rank determines many ceremonial details, such as the order of precedence at official processions, table seating ...
to Haiti and, later, the secretary-general of La Francophonie
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
. Schreyer also become the first former governor general to run for elected office in Canada when he unsuccessfully vied for a seat in the House of Commons as a New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party (NDP; french: Nouveau Parti démocratique, NPD) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* ...
candidate. Prior to 1952, several former viceroys returned to political careers in the United Kingdom, sitting with party affiliations in the House of Lords and, in some cases, taking a position in the British Cabinet. The Marquess of Lorne was elected a Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
in the United Kingdom in 1895, and remained so until he became the Duke of Argyll and took his seat in the House of Lords. Others were made governors in other countries or territories: the Viscount Monck was appointed Lord Lieutenant of Dublin
This is a list of those who have held the post of Lord Lieutenant of County Dublin.
There were lieutenants of counties in Ireland until the reign of James II, when they were renamed governors. The office of Lord Lieutenant was recreated on 23 ...
, the Earl of Aberdeen was appointed Lord Lieutenant of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (), or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the King ...
, and the Earl of Dufferin, the Marquess of Lansdowne, The Earl of Minto, and The Earl of Willingdon all subsequently served as Viceroy of India
The Governor-General of India (1773–1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 19 ...
.
An outgoing governor general may leave an eponymous award as a legacy, such as the Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup (french: La Coupe Stanley) is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, an ...
, the Clarkson Cup
The Clarkson Cup (french: La Coupe Clarkson) is a women's ice hockey trophy, which from 2009 to 2019 was awarded to the winner of the Canadian Women's Hockey Championship (CWHL champion). With the folding of the Canadian Women's Hockey League (C ...
, the Vanier Cup
The Vanier Cup (french: Coupe Vanier) is the championship of Canadian university football. It is organized by U Sports football and is currently played between the winners of the Uteck Bowl and the Mitchell Bowl. It is named after Georges Vanier ...
, or the Grey Cup
The Grey Cup (french: Coupe Grey) is both the championship game of the Canadian Football League (CFL) and the trophy awarded to the victorious team playing in the namesake championship of professional Canadian football. The game is contested be ...
. They may found an institution, as Georges Vanier did with the Vanier Institute of the Family and Adrienne Clarkson with the Institute for Canadian Citizenship. Three former governors general have released memoirs: the Lord Tweedsmuir (''Memory Hold-the-Door''), Vincent Massey (''What's Past is Prologue''), and Adrienne Clarkson (''Heart Matters'').
Remuneration
As of 2021, former governors general are entitled to a lifetime pension of nearly $150,000 and also to claim an additional $206,000 in expenses each year.Living former governors general of Canada
, there are five living former governors general of Canada. The most recently deceased former governor general,Roméo LeBlanc
Roméo-Adrien LeBlanc (December 18, 1927June 24, 2009) was a Canadian journalist, politician and statesman who served as Governor General of Canada, the 25th since Canadian Confederation.
LeBlanc was born and educated in New Brunswick, and also ...
(1995–2000), died on 24 June 2009.
See also
* Governor General's Awards * List of governors general of Canada * Armorial of the Governors General of Canada * List of awards presented by the Governor General of Canada *Royal Canadian Air Force VIP aircraft
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) maintains specialised aircraft to transport Canada's monarch, governor general, members of the Royal Family, prime minister, senior members of the Government of Canada, and other dignitaries. A small fleet of d ...
* The Canadian Crown and the Canadian Armed Forces
The relationship between the Canadian Crown and the Canadian Armed Forces is both constitutional and ceremonial with the King of Canada being the Commander-in-Chief of the Canadian Forces and with the King and other members of the Canadian Roya ...
* Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
*Proclamation Constituting the Office of Governor General and Commander-in-Chief of Canada
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Governor General Of Canada Canada and the Commonwealth of Nations Government of Canada Westminster system Monarchy in Canada 1867 establishments in Canada