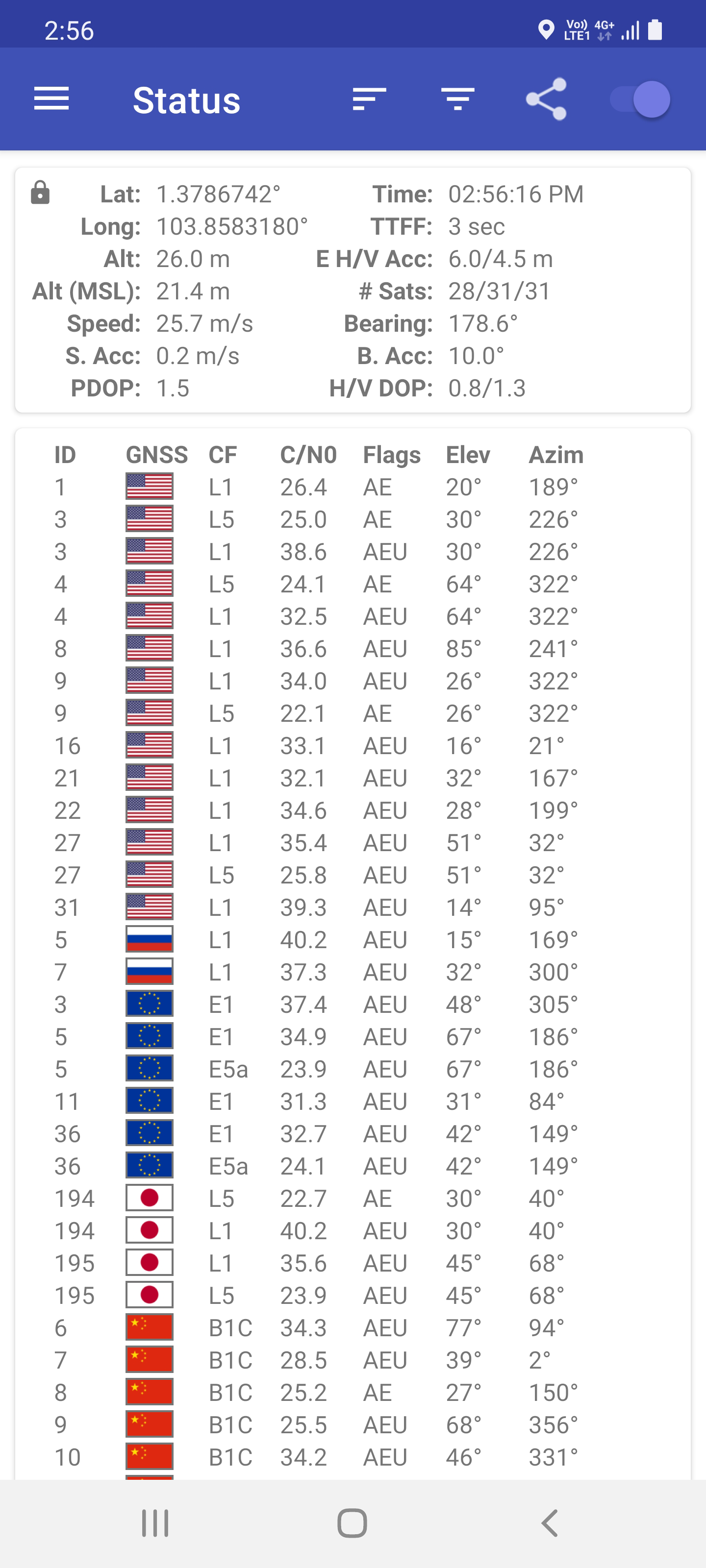
Global Navigation Satellite System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses
 Ground based radio navigation is decades old. The
Ground based radio navigation is decades old. The
 The original motivation for satellite navigation was for military applications. Satellite navigation allows precision in the delivery of weapons to targets, greatly increasing their lethality whilst reducing inadvertent casualties from mis-directed weapons. (See
The original motivation for satellite navigation was for military applications. Satellite navigation allows precision in the delivery of weapons to targets, greatly increasing their lethality whilst reducing inadvertent casualties from mis-directed weapons. (See
ESA information on EGNOS
Global Navigation Satellite System Fundamentals
* ttp://www.ion.org/meetings/#gnss Institute of Navigation (ION) GNSS Meetings
The International GNSS Service (IGS)
International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Society Inc (IGNSS)
International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) International GNSS Service (IGS)
US National Executive Committee for Space-Based Positioning, Navigation, and Timing
US National Geodetic Survey
Orbits for the Global Positioning System satellites in the Global Navigation Satellite System
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) GNSS Implementation Team
( Java applet) Simulation and graphical depiction of the motion of space vehicles, including DOP computation.
GPS, GNSS, Geodesy and Navigation Concepts in depth
{{DEFAULTSORT:Satellite Navigation American inventions Aircraft instruments Avionics Geodesy Maritime communication Navigation
 A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
s to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning
Geopositioning, also known as geotracking, geolocalization, geolocating, geolocation, or geoposition fixing, is the process of determining or estimating the geographic position of an object.
Geopositioning yields a set of geographic coordinates ...
. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
, latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
, and altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
/elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signal
A time signal is a visible, audible, mechanical, or electronic signal used as a reference to determine the time of day.
Church bells or voices announcing hours of prayer gave way to automatically operated chimes on public clocks; however, a ...
s transmitted along a line of sight by radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent systems as well. Satnav systems operate independently of any telephonic or internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the positioning information generated.
A satellite navigation system with global coverage may be termed a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). , the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
' Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
(GPS), Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is ...
), China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
's Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
are fully operational GNSSs. Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) is a (US) GPS satellite-based augmentation system to enhance the accuracy of GPS, with satellite navigation independent of GPS scheduled for 2023. The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) plans to expand to a global version in the long term.
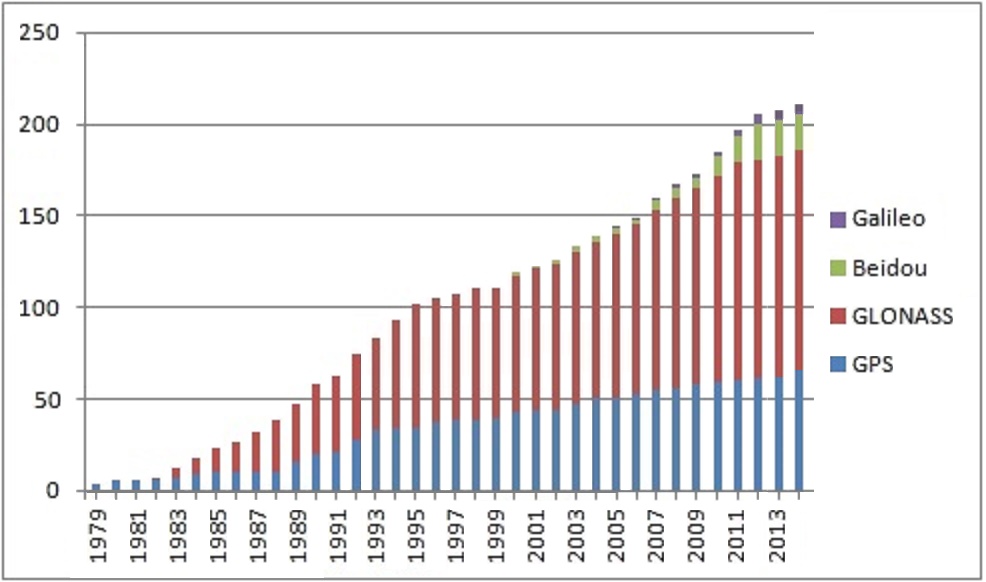
Global coverage for each system is generally achieved by a satellite constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global coverage, such that at any time everywhere on Earth at least one s ...
of 18–30 medium Earth orbit
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between above sea level.
(MEO) satellites spread between several orbital planes
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) a ...
. The actual systems vary, but all use orbital inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...
s of >50° and orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting pla ...
s of roughly twelve hours (at an altitude of about ).
Classification
GNSS systems that provide enhanced accuracy and integrity monitoring usable for civil navigation are classified as follows: * GNSS-1 is the first generation system and is the combination of existing satellite navigation systems (GPS and GLONASS), with Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) or Ground Based Augmentation Systems (GBAS). In the United States, the satellite-based component is the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS); in Europe, it is the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS); and in Japan, it is the Multi-Functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS). Ground-based augmentation is provided by systems like the Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS). * GNSS-2 is the second generation of systems that independently provide a full civilian satellite navigation system, exemplified by the European Galileo positioning system. These systems will provide the accuracy and integrity monitoring necessary for civil navigation; including aircraft. Initially, this system consisted of only Upper L Band frequency sets (L1 for GPS, E1 for Galileo,and
or AND may refer to:
Logic, grammar, and computing
* Conjunction (grammar), connecting two words, phrases, or clauses
* Logical conjunction in mathematical logic, notated as "∧", "⋅", "&", or simple juxtaposition
* Bitwise AND, a boolea ...
G1 for GLONASS). In recent years, GNSS systems have begun activating lLower L-Band frequency sets (L2 and L5 for GPS, E5a and E5b for Galileo, and
or AND may refer to:
Logic, grammar, and computing
* Conjunction (grammar), connecting two words, phrases, or clauses
* Logical conjunction in mathematical logic, notated as "∧", "⋅", "&", or simple juxtaposition
* Bitwise AND, a boolea ...
G3 for GLONASS) for civilian use; they feature higher aggregate accuracy and fewer problems with signal reflection. As of late 2018, a few consumer-grade GNSS devices are being sold that leverage both. They are typically called "Dual band GNSS" or "Dual band GPS" devices.
By their roles in the navigation system, systems can be classified as:
* There are four core satellite navigation systems, currently GPS (United States), GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is ...
(Russian Federation), Beidou
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS; ) is a Chinese satellite navigation system. It consists of two separate satellite constellations. The first BeiDou system, officially called the BeiDou Satellite Navigation Experimental System a ...
(China) and Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
(European Union).
* Global Satellite-Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) such as OmniSTAR OmniSTAR is a satellite-based augmentation system ( SBAS) service provider. OmniSTAR correction signals are proprietary, and a subscription must be bought from the OmniSTAR corporation to receive a subscription authorization. OmniSTAR uses geostat ...
and StarFire.
* Regional SBAS including WAAS (US), EGNOS (EU), MSAS (Japan), GAGAN Gagan may refer to:
Given name
* Gagan Bhagat, Indian politician and member of the Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly
* Gagan Biyani, Indian American serial entrepreneur, marketer, and journalist
*Gagan Singh Bhandari, Nepalese General
*Gagan B ...
(India) and SDCM (Russia).
* Regional Satellite Navigation Systems such as India's NAVIC
The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), with an operational name of NavIC (acronym for 'Navigation with Indian Constellation; also, 'sailor' or 'navigator' in Indian languages), is an autonomous regional satellite navigation ...
, and Japan's QZSS.
* Continental scale Ground Based Augmentation Systems (GBAS) for example the Australian GRAS and the joint US Coast Guard, Canadian Coast Guard, US Army Corps of Engineers and US Department of Transportation National Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to .
DGPSs ...
(DGPS) service.
* Regional scale GBAS such as CORS networks.
* Local GBAS typified by a single GPS reference station operating Real Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections.
As many of the global GNSS systems (and augmentation systems) use similar frequencies and signals around L1, many "Multi-GNSS" receivers capable of using multiple systems have been produced. While some systems strive to interoperate with GPS as well as possible by providing the same clock, others do not.
History
DECCA Decca may refer to:
Music
* Decca Records or Decca Music Group, a record label
* Decca Gold, a classical music record label owned by Universal Music Group
* Decca Broadway, a musical theater record label
* Decca Studios, a recording facility in We ...
, LORAN
LORAN, short for long range navigation, was a hyperbolic radio navigation system developed in the United States during World War II. It was similar to the UK's Gee system but operated at lower frequencies in order to provide an improved range ...
, GEE and Omega
Omega (; capital: Ω, lowercase: ω; Ancient Greek ὦ, later ὦ μέγα, Modern Greek ωμέγα) is the twenty-fourth and final letter in the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system/ isopsephy ( gematria), it has a value of 800. The ...
systems used terrestrial longwave radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ...
s which broadcast a radio pulse from a known "master" location, followed by a pulse repeated from a number of "slave" stations. The delay between the reception of the master signal and the slave signals allowed the receiver to deduce the distance to each of the slaves, providing a fix.
The first satellite navigation system was Transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
, a system deployed by the US military in the 1960s. Transit's operation was based on the Doppler effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who ...
: the satellites travelled on well-known paths and broadcast their signals on a well-known radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the up ...
. The received frequency will differ slightly from the broadcast frequency because of the movement of the satellite with respect to the receiver. By monitoring this frequency shift over a short time interval, the receiver can determine its location to one side or the other of the satellite, and several such measurements combined with a precise knowledge of the satellite's orbit can fix a particular position. Satellite orbital position errors are caused by radio-wave refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
, gravity field changes (as the Earth's gravitational field is not uniform), and other phenomena. A team, led by Harold L Jury of Pan Am Aerospace Division in Florida from 1970-1973, found solutions and/or corrections for many error sources. Using real-time data and recursive estimation, the systematic and residual errors were narrowed down to accuracy sufficient for navigation.
Principles
Part of an orbiting satellite's broadcast includes its precise orbital data. Originally, the US Naval Observatory (USNO) continuously observed the precise orbits of these satellites. As a satellite's orbit deviated, the USNO sent the updated information to the satellite. Subsequent broadcasts from an updated satellite would contain its most recentephemeris
In astronomy and celestial navigation, an ephemeris (pl. ephemerides; ) is a book with tables that gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky, i.e., the position (and possibly ...
.
Modern systems are more direct. The satellite broadcasts a signal that contains orbital data (from which the position of the satellite can be calculated) and the precise time the signal was transmitted. Orbital data include a rough almanac
An almanac (also spelled ''almanack'' and ''almanach'') is an annual publication listing a set of current information about one or multiple subjects. It includes information like weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, tide tables, and othe ...
for all satellites to aid in finding them, and a precise ephemeris for this satellite. The orbital ephemeris
In astronomy and celestial navigation, an ephemeris (pl. ephemerides; ) is a book with tables that gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky, i.e., the position (and possibly ...
is transmitted in a data message that is superimposed on a code that serves as a timing reference. The satellite uses an atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
to maintain synchronization of all the satellites in the constellation. The receiver compares the time of broadcast encoded in the transmission of three (at sea level) or four (which allows an altitude calculation also) different satellites, measuring the time-of-flight to each satellite. Several such measurements can be made at the same time to different satellites, allowing a continual fix to be generated in real time using an adapted version of trilateration: see GNSS positioning calculation for details.
Each distance measurement, regardless of the system being used, places the receiver on a spherical shell at the measured distance from the broadcaster. By taking several such measurements and then looking for a point where they meet, a fix is generated. However, in the case of fast-moving receivers, the position of the signal moves as signals are received from several satellites. In addition, the radio signals slow slightly as they pass through the ionosphere, and this slowing varies with the receiver's angle to the satellite, because that changes the distance through the ionosphere. The basic computation thus attempts to find the shortest directed line tangent to four oblate spherical shells centred on four satellites. Satellite navigation receivers reduce errors by using combinations of signals from multiple satellites and multiple correlators, and then using techniques such as Kalman filtering to combine the noisy, partial, and constantly changing data into a single estimate for position, time, and velocity.
Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for d ...
's theory of general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
is applied to GPS time correction, the net result is that time on a GPS satellite clock advances faster than a clock on the ground by about 38 microseconds per day.
Applications
 The original motivation for satellite navigation was for military applications. Satellite navigation allows precision in the delivery of weapons to targets, greatly increasing their lethality whilst reducing inadvertent casualties from mis-directed weapons. (See
The original motivation for satellite navigation was for military applications. Satellite navigation allows precision in the delivery of weapons to targets, greatly increasing their lethality whilst reducing inadvertent casualties from mis-directed weapons. (See Guided bomb
A guided bomb (also known as a smart bomb, guided bomb unit, or GBU) is a precision-guided munition designed to achieve a smaller circular error probable (CEP).
The creation of precision-guided munitions resulted in the retroactive renaming of ...
). Satellite navigation also allows forces to be directed and to locate themselves more easily, reducing the fog of war
The fog of war (german: links=no, Nebel des Krieges) is the uncertainty in situational awareness experienced by participants in military operations. The term seeks to capture the uncertainty regarding one's own capability, adversary capability, ...
.
Now a global navigation satellite system, such as Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
, is used to determine users location and the location of other people or objects at any given moment. The range of application of satellite navigation in the future is enormous, including both the public and private sectors across numerous market segments such as science, transport, agriculture etc.
The ability to supply satellite navigation signals is also the ability to deny their availability. The operator of a satellite navigation system potentially has the ability to degrade or eliminate satellite navigation services over any territory it desires.
Global navigation satellite systems
In order of first launch year:
GPS
First launch year: 1978 The United States' Global Positioning System (GPS) consists of up to 32medium Earth orbit
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between above sea level.
satellites in six different orbital planes. The exact number of satellites varies as older satellites are retired and replaced. Operational since 1978 and globally available since 1994, GPS is the world's most utilized satellite navigation system.
GLONASS
First launch year: 1982 The formerlySoviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, and now Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n, ''Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema'', (GLObal NAvigation Satellite System or GLONASS), is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides a civilian radionavigation-satellite service and is also used by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. GLONASS has full global coverage since 1995 and with 24 active satellites.
BeiDou
First launch year: 2000 BeiDou started as the now-decommissioned Beidou-1, an Asia-Pacific local network on the geostationary orbits. The second generation of the system BeiDou-2 became operational in China in December 2011. The BeiDou-3 system is proposed to consist of 30 MEO satellites and five geostationary satellites (IGSO). A 16-satellite regional version (covering Asia and Pacific area) was completed by December 2012. Global service was completed by December 2018. On 23 June 2020, the BDS-3 constellation deployment is fully completed after the last satellite was successfully launched at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center.Galileo
First launch year: 2011 TheEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
and European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ...
agreed in March 2002 to introduce their own alternative to GPS, called the Galileo positioning system. Galileo became operational on 15 December 2016 (global Early Operational Capability, EOC). At an estimated cost of €10 billion, the system of 30 MEO satellites was originally scheduled to be operational in 2010. The original year to become operational was 2014. The first experimental satellite was launched on 28 December 2005. Galileo is expected to be compatible with the modernized GPS system. The receivers will be able to combine the signals from both Galileo and GPS satellites to greatly increase the accuracy. The full Galileo constellation consists of 24 active satellites, the last of which was launched in December 2021. The main modulation used in Galileo Open Service signal is the Composite Binary Offset Carrier
The Composite Binary Offset Carrier (CBOC) modulation is a particular implementation of the Multiplexed Binary Offset Carrier modulation and it is nowadays used by Galileo satellite signals. It is formed by addition or subtraction of two weight ...
(CBOC) modulation.
Regional navigation satellite systems
NavIC
The NavIC or NAVigation with Indian Constellation is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system developed byIndian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman o ...
(ISRO). The government approved the project in May 2006, and consists of a constellation of 7 navigational satellites. 3 of the satellites are placed in the Geostationary orbit (GEO) and the remaining 4 in the Geosynchronous orbit (GSO) to have a larger signal footprint and lower number of satellites to map the region. It is intended to provide an all-weather absolute position accuracy of better than throughout India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and within a region extending approximately around it. An Extended Service Area lies between the primary service area and a rectangle area enclosed by the 30th parallel south
The 30th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 30 degrees south of the Earth's equator. It stands one-third of the way between the equator and the South Pole and crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, Australia, the Pacific Ocean, South Am ...
to the 50th parallel north
The 50th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 50 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the sun is visible for 16 hours, 22 ...
and the 30th meridian east to the 130th meridian east, 1,500–6,000 km beyond borders. A goal of complete Indian control has been stated, with the space segment
The space segment of an artificial satellite system is one of its three operational components (the others being the user and ground segments). It comprises the satellite or satellite constellation and the uplink and downlink satellite links.
Th ...
, ground segment
A ground segment consists of all the ground-based elements of a space system used by operators and support personnel, as opposed to the space segment and user segment. The ground segment enables management of a spacecraft, and distribution of pay ...
and user receivers all being built in India.
The constellation was in orbit as of 2018, and the system was available for public use in early 2018. NavIC provides two levels of service, the "standard positioning service", which will be open for civilian use, and a "restricted service" (an encrypted one) for authorized users (including military). There are plans to expand NavIC system by increasing constellation size from 7 to 11.
QZSS
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) is a four-satellite regional time transfer system and enhancement for GPS coveringJapan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
and the Asia-Oceania regions. QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of January 12, 2018, and were started in November 2018. The first satellite was launched in September 2010. An independent satellite navigation system (from GPS) with 7 satellites is planned for 2023.
Comparison of systems
Sources: Using multiple GNSS systems for user positioning increases the number of visible satellites, improves precise point positioning (PPP) and shortens the average convergence time. The signal-in-space ranging error (SISRE) in November 2019 were 1.6 cm for Galileo, 2.3 cm for GPS, 5.2 cm for GLONASS and 5.5 cm for BeiDou when using real-time corrections for satellite orbits and clocks.The average SISREs of the BDS-3 MEO, IGSO, and GEO satellites were 0.52 m, 0.90 m and 1.15 m, respectively. Compared to the four major global satellite navigation systems consisting of MEO satellites, the SISRE of the BDS-3 MEO satellites was slightly inferior to 0.4 m of Galileo, slightly superior to 0.59 m of GPS, and remarkably superior to 2.33 m of GLONASS. The SISRE of BDS-3 IGSO was 0.90 m, which was on par with the 0.92 m of QZSS IGSO. However, as the BDS-3 GEO satellites were newly launched and not completely functioning in orbit, their average SISRE was marginally worse than the 0.91 m of the QZSS GEO satellites.Augmentation
GNSS augmentation is a method of improving a navigation system's attributes, such as accuracy, reliability, and availability, through the integration of external information into the calculation process, for example, the Wide Area Augmentation System, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service, the Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System,Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to .
DGPSs ...
, GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation (GAGAN) and inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors ( accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity ...
s.
Related techniques
DORIS
Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) is a French precision navigation system. Unlike other GNSS systems, it is based on static emitting stations around the world, the receivers being on satellites, in order to precisely determine their orbital position. The system may be used also for mobile receivers on land with more limited usage and coverage. Used with traditional GNSS systems, it pushes the accuracy of positions to centimetric precision (and to millimetric precision for altimetric application and also allows monitoring very tiny seasonal changes of Earth rotation and deformations), in order to build a much more precise geodesic reference system.LEO satellites
The two current operationallow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
(LEO) satellite phone
A satellite telephone, satellite phone or satphone is a type of mobile phone that connects to other phones or the telephone network by radio through orbiting satellites instead of terrestrial cell sites, as cellphones do. The advantage of a sa ...
networks are able to track transceiver units with accuracy of a few kilometres using doppler shift calculations from the satellite. The coordinates are sent back to the transceiver unit where they can be read using AT command
AT or at may refer to:
Geography Austria
* Austria (ISO 2-letter country code)
* .at, Internet country code top-level domain
United States
* Atchison County, Kansas (county code)
* The Appalachian Trail (A.T.), a 2,180+ mile long mountaino ...
s or a graphical user interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, ins ...
. This can also be used by the gateway to enforce restrictions on geographically bound calling plans.
International regulation
TheInternational Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU) defines a radionavigation-satellite service (RNSS) as "a radiodetermination-satellite service used for the purpose of radionavigation. This service may also include feeder links necessary for its operation".
RNSS is regarded as a safety-of-life service and an essential part of navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation ...
which must be protected from interferences.
Classification
ITU Radio Regulations (article 1) classifies radiocommunication services as: * Radiodetermination service (article 1.40) * Radiodetermination-satellite service (article 1.41) * Radionavigation service (article 1.42) **Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43) **Maritime radionavigation service
Maritime radionavigation service (short: MRNS) is – according to ''Article 1.44'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.44, defin ...
(article 1.44)
***Maritime radionavigation-satellite service
Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (short: MRNSS) is – according to ''Article 1.45'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article ...
(article 1.45)
**Aeronautical radionavigation service
Aeronautical radionavigation service (short: ARNS) is – according to ''Article 1.46'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as "''A radionavigation service intended for the benefit and for the ...
(article 1.46)
***Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite service Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite (short: ARNSS) is – according to ''Article 1.47'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.47, ...
(article 1.47)
; Examples of RNSS use
*Augmentation system GNSS augmentation
* Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast
* BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)
*GALILEO
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
, European GNSS
*Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
(GPS), with Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to .
DGPSs ...
(DGPS)
*GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is ...
*NAVIC
The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), with an operational name of NavIC (acronym for 'Navigation with Indian Constellation; also, 'sailor' or 'navigator' in Indian languages), is an autonomous regional satellite navigation ...
* Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
Frequency allocation
The allocation of radio frequencies is provided according to ''Article 5'' of the ITU Radio Regulations (edition 2012).''ITU Radio Regulations, CHAPTER II – Frequencies, ARTICLE 5 Frequency allocations, Section IV – Table of Frequency Allocations'' To improve harmonisation in spectrum utilisation, most service allocations are incorporated in national Tables of Frequency Allocations and Utilisations within the responsibility of the appropriate national administration. Allocations are: * primary: indicated by writing in capital letters * secondary: indicated by small letters * exclusive or shared utilization: within the responsibility of administrations.See also
* Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics * Geoinformatics * GNSS positioning calculation * GNSS reflectometry *GPS spoofing
In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage.
Internet Spoofing and ...
* GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation
*List of emerging technologies
This is a list of emerging technologies, in-development technical innovations with significant potential in their applications. The criteria for this list is that the technology must:
# Exist in some way; purely hypothetical technologies ca ...
*Pseudolite
Pseudolite is a contraction of the term "pseudo-satellite," used to refer to something that is not a satellite which performs a function commonly in the domain of satellites. Pseudolites are most often small transceivers that are used to create ...
* Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring
*Software GNSS Receiver
A software GNSS receiver is a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver that has been designed and implemented using software-defined radio.
A GNSS receiver, in general, is an electronic device that receives and digitally processes the ...
*Space Integrated GPS/INS Space Integrated GPS/INS (SIGI) is a strapdown Inertial Navigation Unit (INU) developed and built by Honeywell International to control and stabilize spacecraft during flight.
SIGI has integrated global positioning and inertial navigation techno ...
(SIGI)
*United Kingdom Global Navigation Satellite System
The United Kingdom Global Navigation Satellite System (UK GNSS) was a United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA) research programme which, between May 2018 and September 2020, developed outline proposals for a United Kingdom (UK) owned and operated conve ...
*UNSW School of Surveying and Geospatial Engineering
The UNSW School of Surveying and Geospatial Engineering (SAGE), part of the UNSW Faculty of Engineering, was founded in 1970 and disestablished in 2013.
The School has undergraduate and postgraduate programs in Surveying and in GeoInformation ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Office for Outer Space Affairs of the United Nations (2010), ''Report on Current and Planned Global and Regional Navigation Satellite Systems and Satellite-based Augmentation Systems''External links
Information on specific GNSS systems
ESA information on EGNOS
Global Navigation Satellite System Fundamentals
Organizations related to GNSS
* ttp://www.ion.org/meetings/#gnss Institute of Navigation (ION) GNSS Meetings
The International GNSS Service (IGS)
International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Society Inc (IGNSS)
International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) International GNSS Service (IGS)
US National Executive Committee for Space-Based Positioning, Navigation, and Timing
US National Geodetic Survey
Orbits for the Global Positioning System satellites in the Global Navigation Satellite System
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) GNSS Implementation Team
Supportive or illustrative sites
( Java applet) Simulation and graphical depiction of the motion of space vehicles, including DOP computation.
GPS, GNSS, Geodesy and Navigation Concepts in depth
{{DEFAULTSORT:Satellite Navigation American inventions Aircraft instruments Avionics Geodesy Maritime communication Navigation