Germania superior on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an
53.12
,
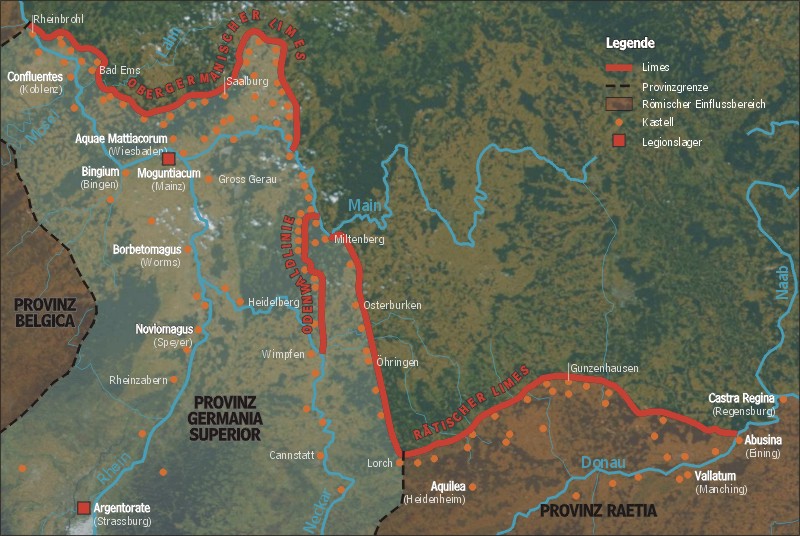
 The plan governing the development of the limes was relatively simple. From a strategic point of view, the
The plan governing the development of the limes was relatively simple. From a strategic point of view, the
The Fleets and Roman Border Policy
LIMES GERMANIAE SUPERIORIS Germany.
{{Authority control Germany in the Roman era Ancient Switzerland 80s establishments in the Roman Empire States and territories established in the 80s States and territories disestablished in the 5th century 470s disestablishments in the Roman Empire 475 disestablishments Former states and territories of Rhineland-Palatinate
 Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province
An imperial province was a Roman province during the Principate where the Roman Emperor had the sole right to appoint the governor (''legatus Augusti pro praetore''). These provinces were often the strategically located border provinces.
The pro ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon
Besançon (, , , ; archaic german: Bisanz; la, Vesontio) is the prefecture of the department of Doubs in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. The city is located in Eastern France, close to the Jura Mountains and the border with Switzer ...
('' Vesontio''), Strasbourg (''Argentoratum
Argentoratum or Argentorate was the ancient name of the city of Strasbourg. The name was first mentioned in 12 BC, when it was a Roman military outpost established by Nero Claudius Drusus. From 90 AD the Legio VIII Augusta was permanently stati ...
''), Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden () is a city in central western Germany and the capital of the state of Hesse. , it had 290,955 inhabitants, plus approximately 21,000 United States citizens (mostly associated with the United States Army). The Wiesbaden urban area ...
('' Aquae Mattiacae''), and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
(''Mogontiacum
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Main ...
''). It comprised the Middle Rhine
Between Bingen and Bonn, Germany, the river Rhine flows as the Middle Rhine (german: Mittelrhein) through the Rhine Gorge, a formation created by erosion, which happened at about the same rate as an uplift in the region, leaving the river a ...
, bordering on the ''Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier'') is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubd ...
'', and on the Alpine province of Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Germania Superior (along with Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agripp ...
) was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD.
Origin
Initial Roman involvement
The terms, "Upper Germania" and "Lower Germania" do not appear in the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; en, Commentaries on the Gallic War, italic=yes), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' ( en, Gallic War, italic=yes), is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it C ...
'' of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
, yet he writes about reports that the people who lived in those regions were referred to as "Germani" locally, a term used for a tribe that the Romans called the Germani cisrhenani
The ''Germani cisrhenani'' (Latin '' cis- rhenanus'' "on this side of the Rhine", referring to the Roman or western side), or "Left bank ''Germani''", were a group of Germanic peoples who lived west of the Lower Rhine at the time of the Gallic W ...
, and that the name Germania seems to have been adopted to designate other indigenous tribes in the area. Lower Germania was occupied by the Belgae. Upper Germania was occupied by Gaulish tribes including the Helvetii, Sequani
The Sequani were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the upper river basin of the Arar river (Saône), the valley of the Doubs and the Jura Mountains during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as ''Sequanos'' by Caesar (mi ...
, Leuci
The Leucī (Gaulish: ''Leucoi'', 'the bright, lightning ones') were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the southern part of the modern Lorraine region during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as ''Leucos'' (acc.) by Caesar (m ...
, and Treveri
The Trēverī ( Gaulish: *''Trēueroi'') were a Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fri ...
, and, on the north bank of the middle Rhine, the remnant of the Germanic troops that had attempted to take Vesontio under Ariovistus, but who were defeated by Caesar in 58 BC.
The Romans did not abandon this region at any time after then. During a 5-year period in the initial years of his reign (28–23 BC), as Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
tells us53.12
,
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
assumed direct governorship of the major senatorial provinces on grounds that they were in danger of insurrection and he alone commanded the troops required to restore security. They were to be restored to the Senate in ten years under proconsuls elected by the Senate.
Among these independent provinces was Upper Germania. Apparently it had become a province in the last years of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
. Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
also mentions it as the province of Germania Superior in his ''Annales
Annals are a concise form of historical writing which record events chronologically, year by year. The equivalent word in Latin and French is ''annales'', which is used untranslated in English in various contexts.
List of works with titles contai ...
'' (3.41, 4.73, 13.53). Cassius Dio viewed the Germanic tribes as Celts, an impression given perhaps by Belgica, the name assigned to lower Germania at the time. Dio does not mention the border, but he views upper Germany as extending to the source of the Rhine. It is not clear if he was aware of the Upper Rhine in Switzerland, upstream from Lake Constance. Today the section of the Rhine running through upper Germania is called the middle Rhine.
Limit of the empire

Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
had planned to incorporate all of central Germania in one province, Germania Magna. This plan was frustrated by the Germanic tribesmen at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctilius ...
. Augustus decided to limit the empire at the Rhine-Danube border. Thereafter continual conflict prevailed along it, forcing the Romans to conduct punitive expeditions and fortify Germania Superior.
By 12 BC, major bases existed at Xanten
Xanten (, Low Rhenish: ''Santen'') is a town in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the district of Wesel.
Xanten is known for the Archaeological Park, one of the largest archaeological open air museums in the wo ...
(Castra Vetera) and Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
(Mogontiacum), from which Drusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
operated. A system of forts gradually developed around these bases. In 69–70, all the Roman fortications along the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
were destroyed by Germanic insurrections and civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
between the legions. At the conclusion of this violent but brief social storm they were rebuilt more extensively than before, with a road connecting Mainz and Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ...
(Augusta Vindelicorum).
Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
went to war against the Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
in 83–85, who were north of Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
(in Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
named after them). At this time the first line, or continuous fortified border, was constructed. It consisted of a cleared zone of observation, a palisade where practicable, wooden watchtowers and forts at the road crossings. The system reached maximum extent by 90. A Roman road went through the Odenwald and a network of secondary roads connected all the forts and towers.
Defensive strategy
Agri Decumates
The ''Agri Decumates'' or ''Decumates Agri'' ("Decumatian Fields") were a region of the Roman Empire's provinces of Germania Superior and Raetia, covering the Black Forest, Swabian Jura, and Franconian Jura areas between the Rhine, Main, and Da ...
, or region between the Rhine and Danube, offers a bulge in the line between the Celts and the Germanics, which the Germanics had tried to exploit under Ariovistus. The bulge divided the densely populated Celtic settlements along the entire river system in two. Invading forces could move up under cover of the Black Forest. Roman defensive works therefore cut across the base of the bulge, denying the protected corridor and shortening the line.
The key point was the shoulder of the bulge at Mogontiacum (Mainz) where the ''masse de manoevre'' or strategic reserves were located. The forts through the forest were relatively lightly defended and on that account were always being burned by the Alamanni. They gave advance notice, however. On being notified, the legions would strike out in preventative and punitive expeditions from Mainz or Strasburg, or Augsburg on the other side.
The entire system could only succeed if heavy troop concentrations were kept at Mainz. Fixed defenses alone are not much of a defense, in either ancient or modern times. Other forces are required for attack. At best the fixed defenses serve to warn or delay until a counterattack can be launched. For more complete details on the development of the limes, or frontier, see under ''Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier'') is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubd ...
''.
In the subsequent peaceful years, the limes lost its temporary character. Vici, or communities, developed around the forts. By 150, the towers and the bases had been rebuilt in stone. The soldiers now lived in good stone barracks within walls decorated by frescoes. Germanic civilization had changed as well. Where Caesar had described burning the wretched brush hovels of the Suebi who had come to fight for Ariovistus, the Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
and the Alamanni now lived in comfortable Romanized villages around the limes.
Germania Superior was reestablished as an Imperial Roman province in 90, taking large amounts of territory from Gallia Lugdunensis
Gallia Lugdunensis (French: ''Gaule Lyonnaise'') was a province of the Roman Empire in what is now the modern country of France, part of the Celtic territory of Gaul formerly known as Celtica. It is named after its capital Lugdunum (today's Lyon) ...
. One of its first and most famous governors was the future Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, who ruled the province from 96 until his accession in 98. The Helvetii settlement area became part of the province of ''Germania Superior''.
End of the province
Post 400, as Rome slowly was losing control over its northernmost provinces over a period of 50 years, the southern (Swiss) parts of Germania Superior were incorporated into the Provincia Maxima Sequanorum before they became part of Burgundy in the early 5th century. The northern parts became part of Alemannia.Governors of Germania Superior
*Gaius Silius
Gaius Silius (died AD 24) was a Roman senator who achieved successes as a general over German barbarians following the disaster of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. For this achievement he was appointed consul in AD 13 with Lucius Munatius Pla ...
AD 14–16
* Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Gaetulicus 29–39
* Servius Sulpicius Galba, 39–41, later emperor in 69.
* Publius Pomponius Secundus
Publius Pomponius Secundus was a distinguished statesman and poet in the reigns of Tiberius, Caligula, and Claudius. He was suffect consul for the '' nundinium'' of January to June 44, succeeding the ordinary consul Gaius Sallustius Crispus Passi ...
50-54
* Hordeonius Flaccus c. 69Unless otherwise noted, governors from 69 to 112 are taken from
* Gaius Dillius Vocula Gaius Dillius Vocula (died 70 AD) was a Roman commander of the Legio XXII Primigenia during the Batavian revolt. Defending Castra Vetera, he was murdered by rebellious Roman troops.
An inscription found at Rome, commissioned by his wife Helvia Pr ...
69–70
* Appius Annius Gallus 70–72
* Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Clemens 72–75
* Quintus Corellius Rufus 79–83
* Lucius Antonius Saturninus 87–89
* Gaius Octavius Tidius Tossianus Lucius Javolenus Priscus
Gaius Octavius Tidius Tossianus Lucius Javolenus Priscus was a Roman senator and jurist who flourished during the Flavian dynasty. Many of his judgments are quoted in the ''Digest''. Priscus served as suffect consul for the '' nundinium'' (perio ...
89–92
*Sextus Lusianus Proculus
Sextus is an ancient Roman ''praenomen'' or "first name". Its standard abbreviation is Sex., and the feminine form would be Sexta. It is one of the numeral ''praenomina'', like Quintus ("fifth") and Decimus ("tenth"), and means "sixth". Although i ...
93–96
* Marcus Ulpius Traianus 96–97; better known as Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
* Lucius Julius Ursus Servianus 97/98
* ''Ignotus'' 110–112
* Kan s Junius Niger116–118Unless otherwise noted, governors from 116 to 135 are taken from
* Gaius Quinctius Certus Poblicius Marcellus
Gaius Quinctius Certus Poblicius Marcellus was a Roman senator active in the first quarter of the second century AD. He was suffect consul for the '' nundinium'' of May to June AD 120, with Titus Rutilius Propinquus as his colleague. The more co ...
''Between'' 121 and 128
* ..us Celer 128/129-130/131
* Tiberius Claudius Quartinus Tiberius Claudius Quartinus was a Roman senator active during the first half of the second century AD. Originally of the equestrian class, Quartinus was suffect consul during 130 as the colleague of Cassius Agrippa. Quartinus is known primarily ...
133/134-134/135
* Titus Caesernius Statianus c. 149 - c. 152Unless otherwise noted, governors from 149 to 180 are taken from
* Gaius Popilius Carus Pedo
Gaius Popilius Carus Pedo was a Roman senator who held several offices in the emperor's service during the second century. He was suffect consul in succession to Tiberius Licinius Cassius Cassianus as colleague of Sextus Cocceius Severianus Honor ...
c. 152 - c. 155
* Lucius Dasumius Tullius Tuscus c. 155 - c. 158
* Gaius Aufidius Victorinus
Gaius Aufidius Victorinus was a Roman senator and general of the second century. A friend of the Emperor Marcus Aurelius and the son-in-law of the advocate and orator Marcus Cornelius Fronto, he was twice consul and governor of several Roman provin ...
c. 162 - c. 166
* Lucius Victorinus Flavius Caelianus c. 166 - c. 169
* Caerellius Priscus, name uncertain; possibly c. 174 - c. 177
* Publius Cornelius Anullinus
Publius Cornelius Anullinus (or, occasionally, Anulinus) was one of the generals of the Roman emperor Septimius Severus. He was from the city of Iliberis (Granada, or identified by modern scholars as likely being in or near Albayzín), and, while ...
c. 177 - c. 180
* Marcus Helvius Clemens Dextrianus ''From'' 187
* Gaius Caesonius Macer Rufinianus c. 200 - c. 203
* Titus Statilius Barbarus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mi ...
c. 203
* Quintus Aiacius Modestus Crescentianus c. 206 - 209
* ..Avitius ''Attested'' 28 March 213
* Quintus Junius ..Quintianus ''Attested'' October 213
* Claudius Aelius Pollio c. 218
* Maximus Attianus ''Attested'' 28 March 229
* Sextus Catius Clementinus Priscillianus
Sextus Catius Clementinus Priscillianus (fl. 3rd century AD) was a Roman military officer and senator who was appointed consul in AD 230.
Biography
Catius Clementinus was a member of the third century '' gens Catia'', and it has been speculated t ...
c. 231
''Civitates''
*Ladenburg
Ladenburg is a town in northwestern Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It lies on the right bank of the river Neckar, northwest of Heidelberg and east of Mannheim.
The town's history goes back to the Celtic and Roman Ages, when it was called Lopo ...
(''Lopodunum'') = Civitas Ulpia Sueborum Nicretum;
* Wimpfen = Civitas Alisinensium;
* Stuttgart-Bad Cannstatt
Bad Cannstatt, also called Cannstatt (until July 23, 1933) or Kannstadt (until 1900), is one of the outer stadtbezirke, or city boroughs, of Stuttgart in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Bad Cannstatt is the oldest and most populous of Stuttgart's bo ...
* Rottenburg (''Sumelocenna'') = Civitas Sumelocennensis;
* Rottweil (''Arae Flaviae'')
*Baden-Baden
Baden-Baden () is a spa town in the state of Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, at the north-western border of the Black Forest mountain range on the small river Oos, ten kilometres (six miles) east of the Rhine, the border with Fra ...
(''Aquae'') = Civitas Aquensis;
*Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
(''Mogontiacum'') = Civitas Aresacium;
*Worms Worms may refer to:
*Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs
Places
*Worms, Germany
Worms () is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had ...
(''Borbetomagus'') = Civitas Vangionum;
*Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ''Speier'', French: ''Spire,'' historical English: ''Spires''; pfl, Schbaija) is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the river Rhine, Speyer li ...
(''Noviomagus'') = Civitas Nemetum;
*Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden () is a city in central western Germany and the capital of the state of Hesse. , it had 290,955 inhabitants, plus approximately 21,000 United States citizens (mostly associated with the United States Army). The Wiesbaden urban area ...
(''Mattiacorum'') = Civitas Mattiacorum;
* Heddernheim (''Nida'') = Civitas Taunensium;
*Dieburg
Dieburg () is a small town in southern Hesse, Germany. It was formerly the seat of the district ("Kreis") of Dieburg, but is now part of the district of Darmstadt-Dieburg.
History
The town of Dieburg was first named in 1492 in the tax books of the ...
= Civitas Auderiensium
See also
*List of Germanic peoples
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginn ...
* Heremus Helvetiorum
Notes
References
Further reading
*Valerie M. Hope: ''Constructing Identity: The Roman Funerary Monuments of Aquelia, Mainz and Nimes''; British Archaeological Reports (16. Juli 2001)External links
The Fleets and Roman Border Policy
LIMES GERMANIAE SUPERIORIS Germany.
{{Authority control Germany in the Roman era Ancient Switzerland 80s establishments in the Roman Empire States and territories established in the 80s States and territories disestablished in the 5th century 470s disestablishments in the Roman Empire 475 disestablishments Former states and territories of Rhineland-Palatinate