Geography of Trinidad and Tobago on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
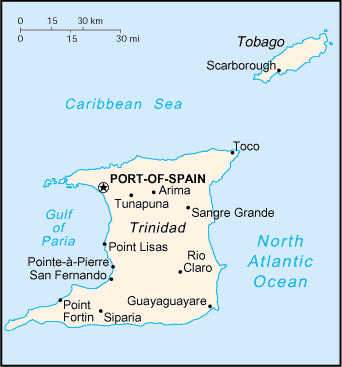
 Trinidad is split into 14 regional corporations and municipalities, consisting of 9 regions and 5 municipalities, which have a limited level of autonomy. The various councils are made up of a mixture of elected and appointed members. Elections are due to be held every three years with the last elections held in 2019. The island of Tobago is administered by the
Trinidad is split into 14 regional corporations and municipalities, consisting of 9 regions and 5 municipalities, which have a limited level of autonomy. The various councils are made up of a mixture of elected and appointed members. Elections are due to be held every three years with the last elections held in 2019. The island of Tobago is administered by the
 The country lies in the tropics, enjoying a generally pleasant maritime tropical climate influenced by the northeast trade winds. In Trinidad the annual mean temperature is , and the average maximum temperature is . The highest temperature ever was 37.8 degrees Celsius. The lowest (coldest felt) temperature recorded in Trinidad was in January 1964. The humidity is high, particularly during the rainy season, when it averages 85 to 87%. The island receives an average of of rainfall per year, usually concentrated in the months of June through December, when brief, intense showers frequently occur. Precipitation is highest in the Northern Range, which may receive as much as . During the dry season, drought plagues the island's central interior. Tobago's climate is similar to Trinidad's but slightly cooler. Its rainy season extends from June to December; the annual rainfall is . The islands lie outside the hurricane belt; despite this, Hurricane Flora damaged Tobago in 1963. The hurricane killed 18 people on Tobago and caused $30:million in crop and property damages (1963 USD).
The country lies in the tropics, enjoying a generally pleasant maritime tropical climate influenced by the northeast trade winds. In Trinidad the annual mean temperature is , and the average maximum temperature is . The highest temperature ever was 37.8 degrees Celsius. The lowest (coldest felt) temperature recorded in Trinidad was in January 1964. The humidity is high, particularly during the rainy season, when it averages 85 to 87%. The island receives an average of of rainfall per year, usually concentrated in the months of June through December, when brief, intense showers frequently occur. Precipitation is highest in the Northern Range, which may receive as much as . During the dry season, drought plagues the island's central interior. Tobago's climate is similar to Trinidad's but slightly cooler. Its rainy season extends from June to December; the annual rainfall is . The islands lie outside the hurricane belt; despite this, Hurricane Flora damaged Tobago in 1963. The hurricane killed 18 people on Tobago and caused $30:million in crop and property damages (1963 USD).

 Area:
Area:
''total:'' 5,128 km2
''land:'' 5,128 km2
''water:'' negligible Coastline: 362 km Maritime claims:
''contiguous zone:''
''continental shelf:'' or to the outer edge of the
''exclusive economic zone:''
''territorial sea:'' Terrain: mostly plains with some hills and low mountains Extreme points: Northernmost point: Marble Island,
''arable land:'' 4.9%
''permanent crops:'' 4.3% ''permanent pasture:'' 1.4% ''forest:'' 44%
''other:'' 45.4% (2018 est.) Irrigated land: 70 km2 (2012) Total renewable water resources: 3.84 billion m³ (2017)

Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
is an archipelagic republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
in the southern Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
between the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
and the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, northeast of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. They are southeasterly islands of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
, Monos
Monos is an island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is one of the "Bocas Islands", which lie in the ''Bocas del Dragón'' (''Dragons' Mouth'') between Trinidad and Venezuela. It is so named as the island was once home to noisy red ho ...
, Huevos, Gaspar Grande
Gaspar Grande or Gasparee is an island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago named for Gaspar de Percín. The island is in area and lies west of Port of Spain. It is one of the "Bocas Islands", which lie in the '' Bocas del Dragón'' (''Dragon's ...
(or Gasparee), Little Tobago
Little Tobago (or Bird of Paradise Island) is a small island off the northeastern coast of Tobago, and part of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago.
The island supports dry forest. It is an important breeding site for seabirds such as red-bille ...
, and St. Giles Island. Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
is off the northeast coast of Venezuela and south of the Grenadines
The Grenadines is a chain of small islands that lie on a line between the larger islands of Saint Vincent and Grenada in the Lesser Antilles. Nine are inhabited and open to the public (or ten, if the offshore island of Young Island is counted): ...
. The island measures in area (comprising 93.0% of the country's total area) with an average length of and an average width of . The island appears rectangular in shape with three projecting peninsular corners. Tobago is northeast of Trinidad and measures about in area, or 5.8% of the country's area, in length and at its greatest width. The island is cigar-shaped in appearance, with a northeast–southwest alignment.
Physical geography
Trinidad is traversed by three distinct mountain ranges that are a continuation of the Venezuelan coastal cordillera. TheNorthern Range
The Northern Range is the range of tall hills across north Trinidad, the major island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. The hills range from the Chaguaramas peninsula on the west coast to Toco in the east. The Northern Range covers approx ...
, an outlier of the Andes Mountains of Venezuela, consists of rugged hills that parallel the coast. This range rises into two peaks. The highest, El Cerro del Aripo
El Cerro del Aripo, at , is the highest point in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is part of the Aripo Massif and is located in the Northern Range on the island of Trinidad, northeast of the town of Arima.
El Cerro del Aripo lies on the b ...
, is high; the other, El Tucuche
El Tucuche (936 m) is the second highest peak in Trinidad's Northern Range and is noted for its interesting pyramidal shape. It is fabled in Amerindian lore as a sacred mountain. There are Amerindian petroglyphs on a rock outcrop below the mounta ...
, reaches . The Central Range Central Range, Central Mountains, or Central Mountain Range may refer to several ranges of mountains, including:
* Central Range, New Guinea
* Central Range, Taiwan
* Central Range, Trinidad and Tobago
* Central Range, Venezuela
See also
* Cent ...
extends diagonally across the island and is a low-lying range with swampy areas rising to rolling hills; its maximum elevation is . The Caroni Plain, composed of alluvial sediment, extends southward, separating the Northern Range and Central Range. The Southern Range consists of a broken line of hills with a maximum elevation of .
There are numerous rivers and streams on the island of Trinidad; the most significant are the Ortoire River
The Ortoire River is a river in Trinidad and Tobago. It forms the boundary between Nariva County and Mayaro County in east Trinidad.
At over in length, it is one of Trinidad's longest rivers and is navigable by very small crafts for at least ...
, long, which extends eastward into the Atlantic, and the -long Caroni River, reaching westward into the Gulf of Paria. Most of the soils of Trinidad are fertile, with the exception of the sandy and unstable terrain found in the southern part of the island.
Tobago is mountainous and dominated by the Main Ridge, which is long with elevations up to 550 meters. There are deep, fertile valleys running north and south of the Main Ridge. The southwestern tip of the island has a coral platform. Although Tobago is volcanic in origin, there are no active volcanoes. Forestation covers 43% of the island. There are numerous rivers and streams, but flooding and erosion are less severe than in Trinidad. The coastline is indented with numerous bays, beaches, and narrow coastal plains.
Tobago has several small satellite islands. The largest of these, Little Tobago, is starfish shaped, hilly, and .
Because it was once part of continental South America, Trinidad has an assortment of tropical vegetation and wildlife considerably more varied than that of most Caribbean islands. Tobago has a generally similar but less varied assortment.
Geology
Geologically
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Eart ...
, the islands are not part of the Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc
The Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc is a volcanic arc that forms the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Plate. It is part of a subduction zone, also known as the Lesser Antilles subduction zone, where the oceanic crust of the North American Plate is ...
. Rather, Trinidad was once part of the South American mainland and is situated on its continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, and Tobago is part of a sunken island arc chain related to the Pacific-derived Caribbean Plate. The islands are separated from the continent of South America by the Gulf of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries ...
; Bocas del Dragón
The Bocas del Dragón (Dragon's Mouths) is the name of the series of straits separating the Gulf of Paria from the Caribbean Sea. There are four Bocas, from west to east:
* The Boca Grande or Grand Boca separates Chacachacare from the Paria Penins ...
, a -wide northern passage; and Serpent's Mouth
The Columbus Channel or Serpent's Mouth ( es, Boca de la Serpiente), is a strait lying between Icacos Point in southwest Trinidad and Tobago and the north coast of Venezuela. It leads from the Atlantic Ocean to the Gulf of Paria
The Gulf of Pari ...
, a -wide southern passage.
The Northern Range consists mainly of Upper Jurassic and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
s. The Northern Lowlands (East–West Corridor
The East–West Corridor is the built-up area of north Trinidad stretching from the capital, Port of Spain, east to Arima. The term was coined by economist and political philosopher Lloyd Best, after gleaning the works of a technocrat named ...
and Caroni Plains) consist of younger shallow marine clastic sediment
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks ...
s. South of this, the Central Range Central Range, Central Mountains, or Central Mountain Range may refer to several ranges of mountains, including:
* Central Range, New Guinea
* Central Range, Taiwan
* Central Range, Trinidad and Tobago
* Central Range, Venezuela
See also
* Cent ...
fold and thrust belt
A fold and thrust belt (FTB) is a series of mountainous foothills adjacent to an orogenic belt, which forms due to contractional tectonics. Fold and thrust belts commonly form in the forelands adjacent to major orogens as deformation propagates ou ...
consists of Cretaceous and Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s, with Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
formations along the southern and eastern flanks. The Naparima Plains and the Nariva Swamp
The Nariva Swamp is the largest freshwater wetland in Trinidad and Tobago and has been designated a ''Wetland of International Importance'' under the Ramsar Convention. The swamp is located on the east coast of Trinidad, immediately inland from ...
form the southern shoulder of this uplift.
The Southern Lowlands consist of Miocene and Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58anticlinal Anticlinal may refer to:
*Anticline, in structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core.
*Anticlinal, in stereochemistry, a torsion angle between 90° to 150°, and –90° to –150°; see Alkane_st ...
uplift. It consists of several chains of hills, most famous being the Trinity Hills The Trinity Hills are a range of hills in southeastern Trinidad. According to legend, it is after these hills that Christopher Columbus named the island of Trinidad. Columbus had promised to name the next land he discovered after the ''Holy Trinit ...
. The rocks consist of sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
s, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
s, siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ...
s and clays formed in the Miocene and uplifted in the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. Oil sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and wate ...
and mud volcano
A mud volcano or mud dome is a landform created by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. Several geological processes may cause the formation of mud volcanoes. Mud volcanoes are not true igneous volcanoes as they do not produce lava ...
es are especially common in this area.
Political geography
Tobago House of Assembly
The Tobago House of Assembly (THA) is a unicameral devolved legislative body responsible for the island of Tobago within the unitary state of Trinidad and Tobago. The THA was re-established in 1980
.
Climate
Tropical Storm Alma
Tropical Storm Alma of the 2008 Pacific hurricane season was the easternmost forming Pacific tropical cyclone on record. It formed within the monsoon trough just off the coast of Costa Rica on May 29. Initially forecast to remain a weak tropic ...
hit Trinidad in 1974, causing damage before reaching full strength. Wind gusts reached 91 mph (147 km/h) at the Savonette gas field during the storm.
Statistics
 Area:
Area:''total:'' 5,128 km2
''land:'' 5,128 km2
''water:'' negligible Coastline: 362 km Maritime claims:
''contiguous zone:''
''continental shelf:'' or to the outer edge of the
continental margin
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
''exclusive economic zone:''
''territorial sea:'' Terrain: mostly plains with some hills and low mountains Extreme points: Northernmost point: Marble Island,
Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
Southernmost point: Icacos, Siparia region
Siparia is a region of Trinidad and Tobago in the southwestern portion of the island. The Region of Siparia is a Regional Corporation, which handles local government functions. The Siparia Regional Corporation is headquartered in Siparia. Other ...
, Trinidad Island
Westernmost point: Icacos, Siparia region
Siparia is a region of Trinidad and Tobago in the southwestern portion of the island. The Region of Siparia is a Regional Corporation, which handles local government functions. The Siparia Regional Corporation is headquartered in Siparia. Other ...
, Trinidad Island
Easternmost point: Easternmost tip of Little Tobago
Little Tobago (or Bird of Paradise Island) is a small island off the northeastern coast of Tobago, and part of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago.
The island supports dry forest. It is an important breeding site for seabirds such as red-bille ...
, Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
Lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
Highest point: El Cerro del Aripo
El Cerro del Aripo, at , is the highest point in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is part of the Aripo Massif and is located in the Northern Range on the island of Trinidad, northeast of the town of Arima.
El Cerro del Aripo lies on the b ...
, Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
940 m
Natural resources:
petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
Land use:
''arable land:'' 4.9%
''permanent crops:'' 4.3% ''permanent pasture:'' 1.4% ''forest:'' 44%
''other:'' 45.4% (2018 est.) Irrigated land: 70 km2 (2012) Total renewable water resources: 3.84 billion m³ (2017)
See also
*Trinidad and Tobago dry forests
Trinidad and Tobago dry forests are tropical dry forests located primarily in western and southern parts of the island of Trinidad, in southern parts of the island of Tobago and on smaller offshore islands including Chacachacare, Monos, Huevos, ...
* Biota of Trinidad and Tobago
* List of rivers of Trinidad and Tobago
This is a list of rivers of Trinidad and Tobago.
Trinidad
*Caroni River
*Lalland River
*Oropouche River
*Salybia River
*Mathura River
*Maracas River
*Shark River
*Caura River
*Valencia River
*Caparo River
*Marchine River (Affluentto the Lalland ...
* List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago
This is a list of islands of Trinidad and Tobago. Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic republic in the southern Caribbean.
Major islands
* Trinidad
* Tobago
Bocas Islands
The Bocas Islands lie between Trinidad and Venezuela, in the Bocas de ...
References