Geography of North Korea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

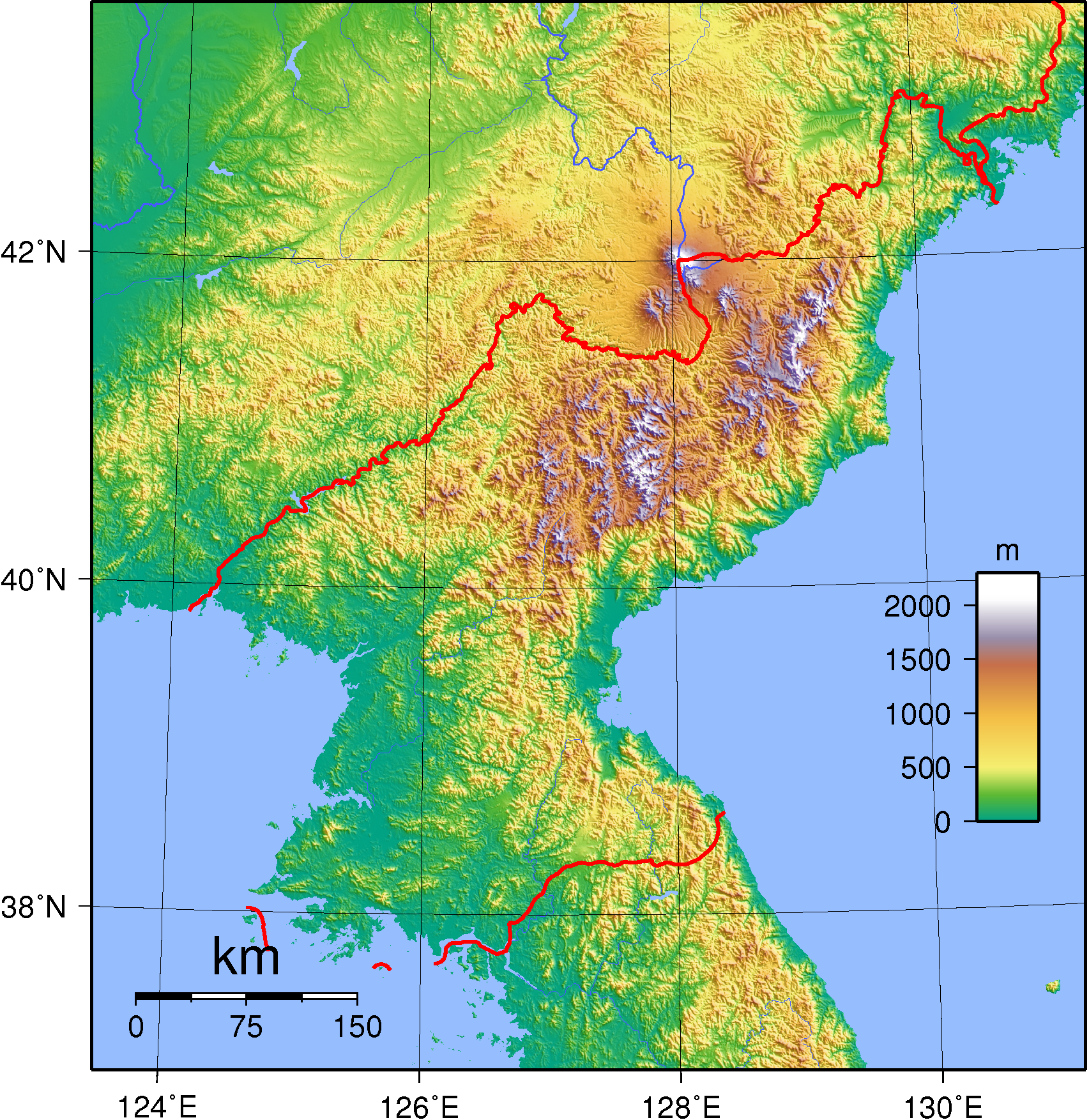 The terrain consists mostly of
The terrain consists mostly of
 North Korea has a combination of a continental climate and an oceanic climate, with four distinct seasons. Most of North Korea is classified as being of a
North Korea has a combination of a continental climate and an oceanic climate, with four distinct seasons. Most of North Korea is classified as being of a
 The environment of North Korea is diverse, encompassing alpine, forest, farmland, freshwater, and
The environment of North Korea is diverse, encompassing alpine, forest, farmland, freshwater, and
 North Korea has an area of 120,538 km², of which 120,408 km² is land and 130 km² is water. It has of land boundaries; of these, are with China, are with South Korea, and are with Russia.
The Korean Peninsula extends about southward from the northeast Asian continental landmass. The coastline of
North Korea has an area of 120,538 km², of which 120,408 km² is land and 130 km² is water. It has of land boundaries; of these, are with China, are with South Korea, and are with Russia.
The Korean Peninsula extends about southward from the northeast Asian continental landmass. The coastline of
North Korea Uncovered
(North Korea Google Earth), a comprehensive mapping of North Korea on Google Earth {{Asia topic, Climate of * bn:উত্তর কোরিয়া#ভূগোল

North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
is located in East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
in the Northern half of Korea, partially on the Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
. It borders three countries: China along the Yalu (Amnok) River, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
along the Tumen River
The Tumen River, also known as the Tuman River or Duman River (), is a long river that serves as part of the boundary between China, North Korea and Russia, rising on the slopes of Mount Paektu and flowing into the Sea of Japan. The river ha ...
, and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
to the south.
Topography and drainage
 The terrain consists mostly of
The terrain consists mostly of hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not a ...
s and mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually highe ...
s separated by deep, narrow valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
s. The coastal plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s are wide in the west and discontinuous in the east.
Early Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an visitors to Korea remarked that the country resembled "a sea in a heavy gale" because of the many successive mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s that crisscross the peninsula. Some 80 percent of North Korea's land area is composed of mountains and uplands, with all of the peninsula's mountains with elevations of or more located in North Korea. The great majority of the population lives in the plains and lowlands.
Paektu Mountain
Paektu Mountain (), also known as Baekdu Mountain and in China as Changbai Mountain ( zh, s=长白山, t=長白山; Manchu: Golmin Šanggiyan Alin), is an active stratovolcano on the Chinese–North Korean border. At , it is the highest mo ...
, the highest point in North Korea at , is a volcanic mountain
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
near Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
with basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
with elevations between and above sea level. The Hamgyong Range, located in the extreme northeastern part of the peninsula, has many high peaks, including Kwanmobong at approximately .
Other major ranges include the Rangrim Mountains, which are located in the north-central part of North Korea and run in a north-south direction, making communication between the eastern and western parts of the country rather difficult; and the Kangnam Range, which runs along the North Korea–China border. Kumgangsan
Mount Kumgang () or the Kumgang Mountains is a mountain massif, with a peak, in Kangwon-do, North Korea. It is located on the east coast of the country, in Mount Kumgang Tourist Region, formerly part of Kangwŏn Province, and is part of ...
, or Diamond Mountain, (approximately ) in the Thaebaek Range, which extends into South Korea, is famous for its scenic beauty.
For the most part, the plains are small. The most extensive are the Pyongyang
Pyongyang (, , ) is the capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is known as the "Capital of the Revolution". Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. According to the 2008 populat ...
and Chaeryong
Chaeryŏng County is a county in South Hwanghae province, North Korea.
Geography
Located on the Chaeryŏng River, the county is bordered to the west by Anak and Sinch'ŏn, to the south by Sinwŏn, and to the east by Ŭnp'a, Pongsan and Sariw� ...
plains, each covering about 500 km2. Because the mountains on the east coast drop abruptly to the sea, the plains are even smaller there than on the west coast.
The mountain ranges in the northern and eastern parts of North Korea form the watershed for most of its rivers, which run in a westerly direction and empty into the Yellow Sea and Korea Bay. The longest is the Amnok River, which is navigable for 678 km of its . The Tuman River, one of the few major rivers to flow into the Sea of Japan, is the second longest at but is navigable for only because of the mountainous topography.
The third longest river, the Taedong River
The Taedong River (Chosŏn'gŭl: ) is a large river in North Korea. The river rises in the Rangrim Mountains of the country's north where it then flows southwest into Korea Bay at Namp'o.Suh, Dae-Sook (1987) "North Korea in 1986: Strengthenin ...
, flows through Pyongyang and is navigable for 245 of its 397 km. Lakes tend to be small because of the lack of glacial activity and the stability of the Earth's crust in the region. Unlike neighboring Japan or northern China, North Korea experiences few severe earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s. The country has a number of natural spas and hot springs, which number 124 according to one North Korean source.
Climate
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
within the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
scheme, with warm summers and cold, dry winters. In summer, there is a short rainy season called ''changma''.
Long winters bring bitter cold and clear weather interspersed with snowstorms as a result of northern and northwestern winds that blow from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
. The daily average high and low temperatures for Pyongyang in January are . On average, it snows thirty-seven days during the winter. Winter can be particularly harsh in the northern, mountainous regions.
Summer tends to be short, hot, humid, and rainy because of the southern and southeastern monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
winds that bring moist air from the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. Spring and autumn are transitional seasons marked by mild temperatures and variable winds and bring the most pleasant weather. The daily average high and low temperatures for Pyongyang
Pyongyang (, , ) is the capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is known as the "Capital of the Revolution". Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. According to the 2008 populat ...
in August are .
On average, approximately 60% of all precipitation occurs from June to September. Natural hazards include late spring droughts which are often followed by severe flooding. Typhoons affect the peninsula on an average of at least once every summer or early autumn. The drought that started in June 2015, according to the Korean Central News Agency
The Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) is the state news agency of North Korea. The agency portrays the views of the North Korean government for both domestic and foreign consumption. It was established on December 5, 1946 and now features onli ...
, has been the worst seen in 100 years.
Examples
Climate change
Environment
 The environment of North Korea is diverse, encompassing alpine, forest, farmland, freshwater, and
The environment of North Korea is diverse, encompassing alpine, forest, farmland, freshwater, and marine ecosystems
Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the su ...
.
In recent years, the environment has been reported to be in a state of "crisis", "catastrophe", or "collapse".
Cultivation, logging, and natural disasters have all put pressure on North Korea's forests. During the economic crisis of the 1990s, deforestation accelerated, as people turned to the woodlands to provide firewood and food. This in turn has led to soil erosion, soil depletion, and increased risk of flooding. In response, the government has promoted a tree planting program. Based on satellite imagery, it was estimated in 2013 that 40% of forest cover had been lost since 1985. A forest restoration policy was adopted in 2012.
Boundaries, coastline, and islands
 North Korea has an area of 120,538 km², of which 120,408 km² is land and 130 km² is water. It has of land boundaries; of these, are with China, are with South Korea, and are with Russia.
The Korean Peninsula extends about southward from the northeast Asian continental landmass. The coastline of
North Korea has an area of 120,538 km², of which 120,408 km² is land and 130 km² is water. It has of land boundaries; of these, are with China, are with South Korea, and are with Russia.
The Korean Peninsula extends about southward from the northeast Asian continental landmass. The coastline of Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
is highly irregular, and North Korea accounts for of this, roughly one-third. Some 3579 island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
s lie adjacent to the Korean Peninsula, mostly along the south and west coasts.
The southern stretch of its east coast forms the northern side of the East Korea Bay
__NOTOC__
The East Korea Bay ( ko, 동조선만, 동한만), also formerly known in English as Broughton Bay, is a bight in the east coast of North Korea and an extension of the Sea of Japan, located between the provinces of South Hamgyong and ...
. At the headland Musu Dan
Musu Point or Musu Dan ( ko, , , "Cape of the Dancing Water" or "Waters") is a North Korean headland in the middle of the country's eastern coast along the Sea of Japan. It forms the eastern side of North Hamgyong's Hwadae County and the north ...
, this ends and the coast turns sharply northward.
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 1,483km² of tidal flats in North Korea, making it the 21st ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.
Maritime claims
TheNorth Korean government
In the North Korean government, the Cabinet is the administrative and executive body. The North Korean government consists of three branches: administrative, legislative, and judicial. However, they are not independent of each other, but al ...
claims territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potent ...
extending from shore. It also claims an exclusive economic zone from shore. In addition, a maritime military boundary that lies offshore in the Sea of Japan and offshore in the Yellow Sea demarcates the waters and airspace into which foreign ships and planes are prohibited from entering without permission.
Waters of the Yellow Sea are demarcated between North Korea and South Korea by the disputed Northern Limit Line
The Northern Limit Line or North Limit Line (NLL) – 북방한계선 (in ROK) – is a disputed maritime demarcation line in the Yellow (West) Sea between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) on the north, and the Republic of Ko ...
drawn by the United Nations Command
United Nations Command (UNC or UN Command) is the multinational military force established to support the Republic of Korea (South Korea) during and after the Korean War. It was the first international unified command in history, and the first a ...
in early 1950s and not officially recognized by North Korea. Disputes between North and South Korean naval vessels have occurred in this area. A total of five disputes were noteworthy enough to have been reported in the news (three in 2009 and two in 2010).
Resources and land use
Natural resources includecoal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
, magnesite, iron ore, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, pyrites
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue ...
, salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
, fluorspar and hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
.
Land use
Irrigated land
*14,600 km² (2003)Total renewable water resources
*778.15 km3 (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
*total: 8.66 km3/yr (10%/13%/76%) *per capita: 360.6 m3/yr (2005)See also
* Administrative divisions of North Korea * Geography of South Korea * '' North Korea Uncovered'' Lists: * List of cities in North Korea *List of islands of North Korea
The following is a list of major islands in North Korea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, arranged by province. For a list of islands in South Korea, the Republic of Korea, see: List of islands of South Korea
This article is about th ...
* List of lakes in Korea
* List of national parks of Korea
* List of rivers of Korea
The Korean peninsula is mainly mountainous along its east coast, so most of its river water flows west, emptying into the Yellow Sea. Some of these rivers flow through lakes en route to the coast, but these are all artificial reservoirs, as ther ...
* List of mountains in Korea
The following is a list of mountains in Korea:
List of mountains in North Korea Pyeongyang
* Taesongsan (대성산; ) –
Chagang Province
* Namsan (남산; ) –
* Obongsan (오봉산; ) –
North Pyongan Province
* Myohyangsan (묘향 ...
References
Works cited
*Further reading
*Dormels, Rainer. North Korea's Cities: Industrial facilities, internal structures and typification. Jimoondang, 2014.External links
North Korea Uncovered
(North Korea Google Earth), a comprehensive mapping of North Korea on Google Earth {{Asia topic, Climate of * bn:উত্তর কোরিয়া#ভূগোল