Geography of Karnataka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
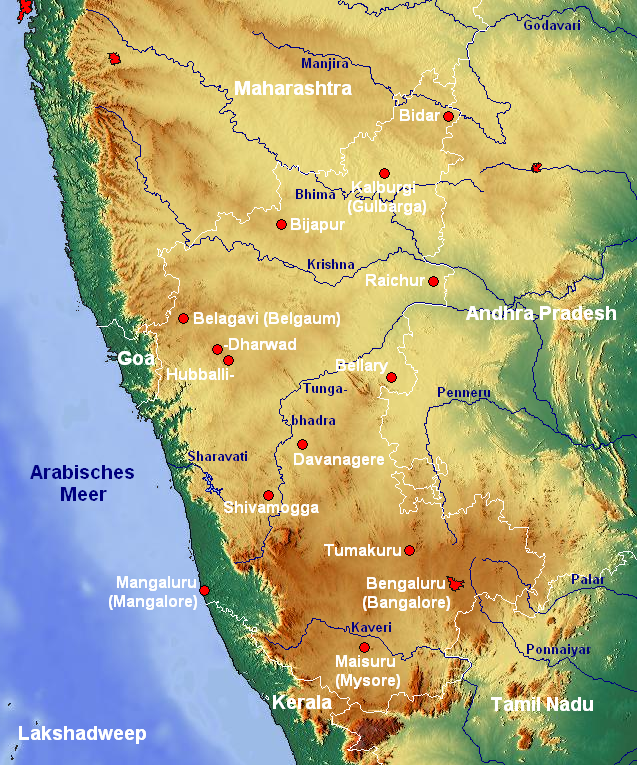 The
The
Ruby Press & Co
. New Delhi. (2013). {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Karnataka
 The
The India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n State of Karnataka is located between 11°30' North and 18°30' North latitudes and between 74° East and 78°30' East longitude.It is situated on a tableland where the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut ...
converge into the complex, in the western part of the Deccan Peninsular region of India. The State is bounded by Maharashtra and Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
States in the north and northwest; by the Lakshadweep Sea in the west; by Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
in the south-west and Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
in the south and south-east, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
in the south-east and east and Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
in the north-east. Karnataka extends to about from north to south and about from east to west.
Karnataka is situated in the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
and is bordered by the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
to the west, Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
to the southeast and east, Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
to the east, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
to the south and southeast, and Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
to the southwest. It is situated at the angle where the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut ...
of South India converge into the Nilgiri hills
The Nilgiri Mountains form part of the Western Ghats in northwestern Tamil Nadu, Southern Karnataka, and eastern Kerala in India. They are located at the trijunction of three states and connect the Western Ghats with the Eastern Ghats. At le ...
. The highest point in Karnataka is the Mullayanagiri
Mullayyanagiri is the highest peak in Karnataka, India. Mullayyanagiri is located in the Chandra Dhrona Hill Ranges of the Western Ghats of Chikkamagaluru Taluk. With a height of , it is the highest peak in Karnataka and also the 23rd highest p ...
hill in Chikkamagaluru district which has an altitude of above sea level.
Physiography
The state is divisible in to three distinct geomorphic zones: * The coastal plains, called theKaravali
Kanara, also known as Karavali is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka.
The region comprises three civil districts, ...
area lies between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea. The Karavali are lowlands, with moderate to high rainfall levels. This strip is around in length and wide.
* The Western Ghats, called Malenadu
Malnad (; Malēnādu) is a region in the state of Karnataka in India. Malenadu covers the western and eastern slopes of the Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountain range, and is roughly 100 kilometers in width.
Malnadis a region of Karnataka ...
, is a mountain range running parallel to the Arabian Sea trending NNW-SSE, rising to about average height with some peaks over above sea leavel. The mountain rage is around wide and with moderate to high rainfall levels.
* The Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
, called Bayalu Seeme
Bayaluseeme or Bayalu Seeme is the area lying to the east of Malenadu, a region of Karnataka state in India. The area is largely open plain, with few hillocks. It includes the districts of Bangalore, Bagalkot, Bijapur, Chitradurga, Davanagere, ...
, comprising the main inland region of the state, with an average elevation of above sea level. The plateau is relatively dry and verging on the semi-arid. The plateau is scattered with narrow ridges, and hills of schistose rock and granitic boulders.
Karnataka has one of the highest average elevations of Indian states, at . The highest recorded temperature was 45.6 °C (114.08 °F) at Raichuru on 23 May 1928. The lowest recorded temperature was 2.8 °C (37.04 °F) at Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
on 16 December 1918.
Area and population
Karnataka has a total land area of 191,791 km² and accounts for 5.83% of the total area of the country (measured at 3,288,000 km²). This puts it in seventh place in terms of size. With a population of 6,11,30,704, it occupies eighth place in terms of population. The population density which stands at 319 persons per km² is lower than the all-India average of 382.Mineral resource
Karnataka is rich in mineral wealth which is distributed fairly evenly across the state. Karnataka's Geological Survey department started in 1880 is one of the oldest in the country. Rich deposits of asbestos, bauxite, chromite, dolomite, gold, iron ore, kaolin, limestone, magnesite, Manganese, ochre, quartz, and silica sand are found in the state. Karnataka is also a major producer of felsite, molding sand (63%), and fuchsite quartzite (57%) in the country. Karnataka has two major centers of gold mining in the state Kolar and Raichur. These mines produce about 3000 kg of gold per annum which accounts for almost 84% of the country's production. Karnataka has very rich deposits of high-grade iron and manganese ores to the tune of 1,000 million tonnes. Most of the iron ores are concentrated around the Ballari-Hosapete region. Karnataka with a granite rock spread of over 4200 km² is also famous for its Ornamental Granites with different hues.Geology
According to Radhakrishnan and Vaidyanadhan (1997), there are four main types of geological formations in Karnataka:Detailed description of the geology of Karnataka is provided by * ''TheArchean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth during the Arc ...
complex made up of Dharwad
Dharwad (), also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the north western part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merge ...
schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes ...
s and granitic gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures a ...
es'': These cover around 60% of the area of the state and consist of gneisses, granites and charnockite rocks. Some of the minerals found in this region are dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is ch ...
, quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tec ...
, pyroxenite
Pyroxenite is an ultramafic igneous rock consisting essentially of minerals of the pyroxene group, such as augite, diopside, hypersthene, bronzite or enstatite. Pyroxenites are classified into clinopyroxenites, orthopyroxenites, and the we ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
and iron ores and metabasalt
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flak ...
.
* ''The Proterozoic non-fossiliferous sedimentary formations of the Kaladgi and Bhima series'': The Kaladgi series has horizontal rocks consists of sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, metabasalt
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flak ...
, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, trapstone that run for in the districts of Belagavi, Raichuru, Dharwad
Dharwad (), also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the north western part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merge ...
and Vijayapura
Vijayapur is a town in Devanahalli taluk and Bangalore Rural district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Vijayapura's old name is Vadigenahalli. Local villagers still refer Vijayapura as Vadigenahalli.
Geography
Vijayapura is located at . It has ...
districts. The Bhima series that is present on either side of the Bhima River
The Bhima River (also known as Chandrabhaga River) is a major river in Western India and South India. It flows southeast for through Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana states, before entering the Krishna River. After the first sixty-five k ...
consists of rocks containing sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
and shale and this is present in the Kalaburagi
Kalaburagi, formerly known as Gulbarga, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kalaburagi district and is the largest city in the region of North Karnataka (Kalyana-Karnataka). Kalaburagi is 6 ...
and Vijayapura
Vijayapur is a town in Devanahalli taluk and Bangalore Rural district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Vijayapura's old name is Vadigenahalli. Local villagers still refer Vijayapura as Vadigenahalli.
Geography
Vijayapura is located at . It has ...
districts.
* ''The Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
trappean and intertrappean deposits'': This is a part of the Deccan traps which were formed by the accumulation of basaltic lava. This is made up of greyish to black augite-basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
.
* ''The tertiary and recent laterites and alluvial deposits'': Laterite capping are found over the Deccan Traps and were formed after the cessation of volcanic activity in the early tertiary period. These are found in many districts in the Deccan plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
and also in the coast.
Soil types
Eleven groups of soil orders are found in Karnataka.Entisol
Entisols are soils defined in USDA soil taxonomy that do not show any profile development other than an A horizon. An entisol has no diagnostic horizons, and most are basically unaltered from their parent material, which can be unconsolidated sedi ...
s, Inceptisols
Inceptisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. They form quickly through alteration of parent material. They are more developed than Entisols. They have no accumulation of clays, iron oxide, aluminium oxide or organic matter. They have an ...
, Mollisol
Mollisol is a soil type which has deep, high organic matter, nutrient-enriched surface soil ( a horizon), typically between 60 and 80 cm in depth. This fertile surface horizon, called a mollic epipedon, is the defining diagnostic feature of ...
s, Spodosol
In soil science, podzols are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathland, which is often a construct of huma ...
s, Alfisol
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron ( ...
s, Ultisol
Ultisols, commonly known as red clay soils, are one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continu ...
s, Oxisol
Oxisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy, best known for their occurrence in tropical rain forest within 25 degrees north and south of the Equator. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), they belong mainly to the ferralsols, ...
s, Aridisol
Arid soils (or desert soils) are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Aridisols (from the Latin ''aridus'', for "dry", and ''solum'') form in an arid or semi-arid climate. Aridisols dominate the deserts and xeric shrublands, which occupy about one ...
s, Vertisol
A vertisol, or vertosol, is a soil type in which there is a high content of expansive clay minerals, many of them known as montmorillonite, that form deep cracks in drier seasons or years. In a phenomenon known as argillipedoturbation, alternate ...
s, Andisol
In USDA soil taxonomy, Andisols are soils formed in volcanic ash and defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite. In the World Reference Base for Soil ...
s and Histosol
In both the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) and the USDA soil taxonomy, a Histosol is a soil consisting primarily of organic materials. They are defined as having or more of organic soil material in the upper . Organic soil materia ...
s. Depending on the agricultural capability of the soil, the soil types are divided into six types., Red, lateritic (lateritic soil is found in bidar and kolar district), black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
, alluvio-colluvial, forest and coastal soils.
The common types of soil groups found in Karnataka are:
* Red soils: Red gravelly loam soil, Red loam soil, Red gravelly clay soil, Red clay soil
* Black soil: gravelly soil, loose, black soil , basalt deposits
* Lateritic soil
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
s: Lateritic gravelly soil, Lateritic soil
* Black soils: Deep black soil, Medium deep black soil, Shallow black soil
* Alluvio-Colluvial Soils: Non-saline, saline and sodic
* Forest soil: Brown forest soil
* Coastal soil: Coastal laterite soil, Coastal alluvial soil
Water Resources
With a surface water potential of about , Karnataka accounts for about six percent of the country's surface water resources. Around 60% of this is provided by the west flowing rivers while the remaining comes from the east flowing rivers. There are seven river basins in all formed by theGodavari
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
, Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri (hill), Karnataka, Brahmagiri range in th ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, the west-flowing rivers, Penna, Ponniyar, and Palar
Palar is a river of southern India. It rises in the Nandi Hills in Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka state, and flows in Karnataka, in Andhra Pradesh and in Tamil Nadu before reaching its confluence into the Bay of Bengal at Vayalur ab ...
.
Waterfalls in Karnataka
* Kalhatti Falls * Anashi Falls *Chakra River
The Chakra River is a river flowing through Kundapur and Gungolli in western India. It joins with the Souparnika River, Varahi River and Kubja River known as Panchagangavali river and merges into the Arabian Sea.
The Chakra nagar is a small town ...
* Vibhooti Falls
* Onake Abbi Falls
* Hanumangundi Falls
Hanumana Gundi Falls, also known as Suthanabbe Falls or Soothanabbi Falls is located in the hilly surroundings of the Kudremukh National Park in the Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India.
Hanumanagundi Falls is located between Karkala an ...
* Chelavara Falls
* Kadra Falls
* Gootlu Falls
* Hidlumane Falls
* Godchinamalaki Falls
Godachinmalki Falls in Godachinamalaki village is a waterfall located on Markandeya river in Belgaum district, Gokak Taluk, Karnataka, India. It is 15 kilometers away from Gokak and 40 kilometers from Belgaum. It is located in a deep green va ...
* Abbey Falls
Abbey Falls (also spelled Abbi Falls and Abbe Falls) ( kn, ಅಬ್ಬೆ ಜಲಪಾತ ) is a waterfall in Kodagu, in the Western Ghats of Karnataka, India. It is located 8 km from the Madikeri, 122 km from Mysore, 144 km ...
* Bandaje Falls
Bandaje falls, also known as Bandaje Arbi falls is a waterfall located in the Kudremukha section of the Western Ghats in the Belthangady taluk of Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka. The waterfalls can be reached only by undertaking trekking i ...
* Barkana Falls
The Barkana Falls, formed by Seetha River, is a water falls located near Agumbe in Shimoga district of state of Karnataka, India and the water falls is among the ten highest waterfalls in India. This water fall region is filled with water only d ...
* Chunchanakatte Falls
Chunchanakatte Falls is a waterfall on the Kaveri River, near the village of Chunchanakatte in saligrama taluk of Mysore district, Karnataka, India. Water cascades from a height of about 20 meters. It is in the Western Ghats. Here the river fa ...
* Devaragundi Falls
* Gokak Falls
The Gokak Falls is a waterfall located on the Ghataprabha River in Belagavi district of Karnataka, India. The waterfall is six and a half kilometers away from Gokak town.
About Gokak Water Falls
After a long winding course, the Ghataprabh ...
* Hebbe Falls
* Irupu Falls
The Irupu Falls (also Iruppu Falls) are located in the Brahmagiri Range in the Kodagu district of Karnataka, India, bordering the Wayanad district of Kerala. It is a fresh water cascade and is situated at a distance of 48 km from V ...
* Jaladurga Falls
* Jog Falls
Jog Falls is a waterfall on the Sharavati river located in the Western Ghats running between Uttara Kannada and Shimoga districts of Karnataka, India. It is the third highest plunge waterfall in India. It is a segmented waterfall which depend ...
* Kalhatti Falls
* Kunchikal Falls
Kunchikal Falls is a waterfall in India located in the Nidagodu village near Masthikatte in the Shimoga district of state Karnataka. Kunchikal falls cascades down rocky boulders and the total height of the falls is 183 meters (600 feet) accord ...
* Magod Falls
Magod Falls is a group of waterfalls in Karnataka, India, where the river Bedti falls from a height of nearly in two steps.
The falls are located about from the town of Yellapur and from Sirsi, in the district of Uttara Kannada, and are e ...
* Mallalli Falls
* Muthyalamaduvu Falls
* Sathodi Falls
Sathoddi Falls is a waterfall in Uttara Kannada District Located from Yellapur
Yellapura is a town in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India.It is a major trading centre for Arecanut, which is the primary crop grown in the villa ...
* Shivanasamudra Falls
Shivanasamudra Falls is a waterfall on the border of Malavalli taluk, Mandya district and Kollegala taluk, Chamarajanagara district of the state of Karnataka, India. It is situated along the river Kaveri, which forms here the boundary to the ...
* Shivagange Falls
* Sirimane Falls
* Vajrapoha Falls
Vajrapoha Falls (also Vajrapoya waterfalls), a waterfall in the Belgaum district of Karnataka in India, is situated about in the mountainous forest in south west direction from the village of Jamboti. Between the village of Gavali and Chapoli ...
* Varapoha Falls
* Unchalli Falls
East flowing rivers
30 East-flowing rivers. * Amarja *Arkavathy River
The Arkavati is an important mountain river in Karnataka, India, originating at Nandi Hills of Chikkaballapura district. It is a tributary of the Kaveri, which it joins at 34 km south of Kanakapura, Ramanagara District called Sangama in ...
* Agrani River
* Bhadra River
The Bhadra River (Kannada: ಭದ್ರಾ ನದಿ) is a river in Karnataka state in southern India.
The Bhadra originates at Gangamoola near Kudremukha, Western Ghats range, and flows east across the southern part of Deccan Plateau, joined ...
* Chakra River
The Chakra River is a river flowing through Kundapur and Gungolli in western India. It joins with the Souparnika River, Varahi River and Kubja River known as Panchagangavali river and merges into the Arabian Sea.
The Chakra nagar is a small town ...
* Dandavathi
* Doni River
The Doni river (Karnataka) (Kannada: ದೋಣಿ) flows eastwards from the area around Sangli in Maharashtra near Karnataka border and Most of its course is within North Karnataka in the districts of Belgaum, Bijapur and Kalaburagi. It joins the K ...
* Ghataprabha River
The Ghataprabha river is an important right-bank tributary of the Krishna River and flows eastward for a distance of 283 kilometers before its confluence with the Krishna River at Chikksangam. The river basin is 8,829 square kilometers wide and ...
* Hemavati River
The Hemavati is a river in southern India near Karnataka and an important tributary of the Kaveri.
Origin and course
The source of the Hemavati River lies in the Western Ghats(Javali village) at an elevation of about . Located in Mudigere t ...
* Hiranyakeshi River
The Hiranyakeshi river is a left-bank tributary of the Ghataprabha River originating in the western ghats in the Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra.
Etymology
The river derives its name from the Shri Hiranyakeshi temple. Located inside the ...
* Honnuhole River
* Kabini River
The Kabini River is one of the major tributaries of the river Cauvery in southern India. It originates near Kavilumpara in Kozhikode district of Kerala state by the confluence of the Panamaram River and the Mananthavady River. It flows eastw ...
* Kaveri River
* Kagina River
* Kedaka River
The Kedaka River is a river flowing through Kundapur and Gangolli in western India. It joins with the Souparnika River, Varahi River, Chakra River, and Kubja River and merges into the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ � ...
* Krishna River
* Kubja River
The Kubja River is a river flowing through Kundapur and Gungulli in western India. It joins with the Souparnika River, Varahi River, Chakra River, and Kedaka River and merges into the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ...
* Lakshmana Tirtha River
* Malaprabha River
The Malaprabha River (Kannada ಮಲಪ್ರಭಾ ನದಿ) is a tributary of the Krishna River and flows through the state of Karnataka in India. It rises in the Western Ghats at an elevation of in the state's Belgaum district. The rive ...
* Palar River
Palar is a river of southern India. It rises in the Nandi Hills in Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka state, and flows in Karnataka, in Andhra Pradesh and in Tamil Nadu before reaching its confluence into the Bay of Bengal at Vayalur ab ...
* Panchagangavalli River
* Penner River
Penna (also known as Pinakini, Pennar, Penner, Penneru (Telugu), Pennai (Tamil)) is a river of southern India. This is a unique river in world where after originating from Nandi hills, it flows as two different streams, one in North and South ...
* Ponnaiyar River
The South Pennar River (also known as ''Dakshina Pinakini'' in Kannada and ''Thenpennai or Ponnaiyar'' or ''Pennaiyar'' in Tamil) is a river in India. Bangalore, Hosur, Tiruvannamalai, and Cuddalore are the important cities on the banks of ...
* Shimsha
Shimsha is a river that flows in the state of Karnataka, India. It is one of the tributaries of the river Kaveri, which is one of the major rivers of South India. The river originates in the southern part of the Devarayanadurga hill in the Tu ...
* South Pennar River
* Tunga River
The Tunga River (alternatively spelled Thunga) is a river in Karnataka state, southern India. The river is born in the Western Ghats on a hill known as ''Varaha Parvata'' at a place called '' Gangamoola''. From here, the river flows through two ...
* Tungabhadra River
* Varada
The Varada River (Verada River) is a river in central Karnataka, India. It is a tributary of the Tungabhadra River.
Geography
The Varada river originates near Vardamoola in Sagara of Karnataka. It flows through the Western Ghats and ent ...
* Vedavathi River
* Vrishabhavathi River
The Vrishabhavathi River is a minor river, a tributary of the Arkavathy, that flows through the south of the Indian city of Bangalore. The river was once so pristine that the water from it was used for drinking and used by the famous Gali Anjan ...
West flowing rivers
12 West-flowing rivers, providing 60% of state's inland water resources. *Gangavalli River
Gangavalli River is one of the many small rivers that originates and flows entirely within the western part of state of Karnataka in India. The National Highway 17 (India) continues on the Hosur Bridge the bridge built over Gangavali River and ...
* Aghanashini River
The Aghanashini River (also historically the River Merjee) is a river located in India about 18 miles south east of Anjediva Island. The village of Aghanashini is to be found at the mouth of the river. The river Aghanashini originates at 'Shank ...
* Kali River
* Kumaradhara River
* Mahadayi River
* Shambhavi River
* Varahi River
Varahi River originate and flows through Western Ghats in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is also known as Halady or Haladi river in downstream areas. It joins the Arabian sea after flowing through places like Halady, Basrur, Kundapura and ...
* Souparnika River
Souparnika River or Sowparnika nadi is a river flowing through Kundapur taluk in Karnataka, India. It joins with the Varahi River, Kedaka River, Chakra River, and Kubja River known as Panchagangavali river and merges into the Arabian Sea
...
* Sharavathi River
Sharavati is a river which originates and flows entirely within the state of Karnataka in India. It is one of the few westward flowing rivers of India and a major part of the river basin lies in the Western Ghats. The famous Jog Falls, located ...
* Netravati River
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one ...
* Gurupura River
* Seetha river
Reservoirs
*Lal Bahadur Shastri Sagara, Alamatti. * Basava Sagar Reservoir. *Navilu theertha Reservoir. *Ghataprabha Reservoir. *Dhupdal Reservoir. *Tungabhadra dam
The Tungabhadra Dam, also known as Pampa Sagar, is a water reservoir constructed across the Tungabhadra River in the city of Hosapete Bellary district, Karnataka, India. It is a multipurpose dam serving irrigation, electricity generation, floo ...
, Hosapete
Hospet also known as Vijayanagara is the largest city and district headquarters of the Vijayanagara district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River and is 13 km from Hampi. The present day Ha ...
.
*Linganamakki
The Linganamakki Dam (Kannada : ಲಿಂಗನಮಕ್ಕಿ ಜಲಾಶಯ) was constructed by the Karnataka State Government in 1964. Located in the Kargal village of Sagara taluk, the dam has a length of stretching across the Sharavat ...
.
*Bhadra Dam
The Bhadra Dam or Lakkavalli Dam, which has created the Bhadra Reservoir, is located on the Bhadra River a tributary of Tungabhadra River. Bhadra Dam is located in the border of Bhadravathi and Tarikere, in the western part of Karnataka in I ...
.
*Krishna Raja Sagara
Krishna Raja Sagara, also popularly known as KRS, is a lake and the dam that creates it. They are close to the settlement of Krishna Raja Sagara in the Indian State of Karnataka. The gravity dam made of ''surki'' mortar is below the confluence o ...
.
*Tippagondanahalli Reservoir
Thippagondanahalli Reservoir, also known as T G Halli Dam or Chamarajasagara, is located at the confluence of the Arkavathy and Kumudavathi rivers, west of Bangalore, India. It is used by the Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board as a m ...
.
* Harangi dam.
* Hemavathi Reservoir.
*Karanja Reservoir, Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
.
* Kabini Reservoir(Kapila Jalashaya) H.D kote
* Suvarnavathi Reservoir
Lakes
* Lakes in Bengaluru * Mysuru City lakes * Shanthi Sagara,Davanagere
Davanagere is a city in the centre of the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the seventh largest city in the state, and the administrative headquarters of eponymous Davangere district. Hitherto being a cotton hub and hence popularly known ...
* Unkal lake, Hubballi
Hubli, officially known as Hubballi, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. The twin cities Hubli–Dharwad form the second largest city in the state by area and population and the largest city in North Karnataka. Hubli is in Dharwad distr ...
*Belagavi Fort Lake
*Heggeri Lake, Haveri
Haveri is a city in Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Haveri district. Haveri is famous for its cardamom garlands and Byadagi red chillies. Around 25 km away, there is a place called Bada, which is the birthplace o ...
* Hagari Jalashaya , Malavi
* Sharanabasava Lake , Kalaburagi
Climate
Karnataka has the following four seasons in the year: * The winter season from January to February * The summer season from March to May * The monsoon season from June to September * The post-monsoon season from October to December. The post-monsoon (period of retreating) and winter seasons are generally pleasant over the entire state. The months April and May are hot, very dry and generally uncomfortable. Weather tends to be oppressive during June due to high humidity and temperature. The next three months (July, August and September) are somewhat comfortable due to reduced day temperature although the humidity continue to be very high. The highest recorded temperature was at Raichuru on 23 May 1928. The lowest recorded temperature was C atBidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
on 16 December 1918.
Karnataka is divided into three meteorological zones:
* ''Coastal Karnataka'': This zone comprises the districts of Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada is a district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Uttara Kannada District is a major coastal district of Karnataka, and currently holding the title of the largest district in Karnataka. It is bordered by the state of Goa and Bel ...
, Udupi
Udupi (alternate spelling Udipi; also known as Odipu) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Udupi is situated about north of the educational, commercial and industrial hub of Mangalore and about west of state capital Bangalore by road.
...
and Dakshina Kannada. It is a region of heavy rainfall and receives an average rainfall of per annum.Average Rainfall of the zones in Karnataka are mentioned by far in excess of rest of state.
* ''North Interior Karnataka'': This zone comprises the districts of Belagavi, Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
, Vijayapura
Vijayapur is a town in Devanahalli taluk and Bangalore Rural district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Vijayapura's old name is Vadigenahalli. Local villagers still refer Vijayapura as Vadigenahalli.
Geography
Vijayapura is located at . It has ...
, Bagalkote
Bagalakote, is a city in the state of Karnataka, India, which is also the headquarters of Bagalakote district. It is situated on branch of River Ghataprabha about 481 km (299 mi) northwest of state capital Bengaluru, 410 km ( ...
, Haveri
Haveri is a city in Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Haveri district. Haveri is famous for its cardamom garlands and Byadagi red chillies. Around 25 km away, there is a place called Bada, which is the birthplace o ...
, Gadaga, Dharwad
Dharwad (), also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the north western part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merge ...
, Kalaburagi
Kalaburagi, formerly known as Gulbarga, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kalaburagi district and is the largest city in the region of North Karnataka (Kalyana-Karnataka). Kalaburagi is 6 ...
, Koppala, Ballari, Raichuru, Yadagiri and Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Bell ...
. This is an arid zone and receives only of average rainfall per annum.
* ''South Interior Karnataka'': The rest of the districts of Bengaluru Urban
Bangalore Urban district is the most densely populated district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is surrounded by the Bangalore Rural district on the east and north, the Ramanagara district on the west and the Krishnagiri district of Tami ...
, Bengaluru Rural, Ramanagara
Ramanagara is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is also the headquarters of Ramanagara district. It is approximately 50 kilometres from Bangalore. There are buses and trains as public transportations which approximately takes 90 minute ...
, Kolar
Kolar or Kolara is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Kolar district. The city is known for its milk production and gold mines. It is also known for Someshwara temple and Kolaramma temple.
History
The Wes ...
, Chikkaballapura
Chikkaballapur is the district headquarters of the newly created Chikkaballapur district in the state of Karnataka, India, which is carved out from Kolar district. It is located within 3 km of Muddenahalli (the birthplace of eminent enginee ...
, Mandya
Mandya is a city in the state of Karnataka. It is the headquarter of Mandya district and is located from Mysore and from Bangalore.
Sugar factories contribute to the major economic output. It is also called Sugar city (which in Kannada mean ...
, Mysuru
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, Chamarajanagara
Chamarajanagar or Chamarajanagara is a town in the southern part of Karnataka, India. Named after Chamaraja Wodeyar IX, the erstwhile king of Mysore, previously known as 'Arikottara'. Chamarajanagara is the headquarters of Chamarajanagar distr ...
, Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
, Tumakuru
Tumkur, officially renamed as Tumakuru, is a city located in the southern part of Indian state of Karnataka. Tumkur is situated at a distance of northwest of Bangalore, the state capital along NH 48 and NH 73. It is the headquarters of the ...
, Hassana, Chitradurga
Chitradurga is a city and the headquarters of Chitradurga district, which is located on the valley of the Vedavati river in the central part of the Indian state of Karnataka. Chitradurga is a place with historical significance which is locate ...
, Davanagere
Davanagere is a city in the centre of the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the seventh largest city in the state, and the administrative headquarters of eponymous Davangere district. Hitherto being a cotton hub and hence popularly known ...
, Chikkamagaluru and Shivamogga
Shimoga, officially known as Shivamogga, is a city and the district headquarters of Shimoga district in the central part of the state of Karnataka, India. The city lies on the banks of the Tunga River. Being the gateway for the hilly region o ...
. This zone receives of average rainfall per annum.
Rainfall
Thesouthwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscill ...
accounts for almost 80% of the rainfall that the state receives. The annual rainfall across the state ranges from low to copious . The districts of Vijapura, Raichuru, Ballari, Yadagiri and Southern half of Kalaburagi experience the lowest rainfall ranging from 50 to while the west coastal region and Malenadu
Malnad (; Malēnādu) is a region in the state of Karnataka in India. Malenadu covers the western and eastern slopes of the Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountain range, and is roughly 100 kilometers in width.
Malnadis a region of Karnataka ...
enjoy the highest rainfall.
The following were the top 5 places that peaked in rainfall statistics 010-2017
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
Forests
About 38724 km² (or 20% of Karnataka's geographic) are covered by forests. The forests are classified as reserved (28,611 km²) protected (3,932 km²), unclosed (5,748 km²), village (124 km²) and private (309 km²) forests. The percentage of forests area to Geographical area in the State is less than the all-India average of about 23%, and 33% prescribed in the National Forest Policy. The area under protected forests in the neighboring States is as follows: Andhra Pradesh 62,000 km² (9% of the total area of the country), Maharashtra 54,000 km² (8%), Tamil Nadu 22,000 km² (3%) and Kerala 11,000 km² (2%). Karnataka is known for its valuable timbers from the evergreen forests in the Western Ghat region, notably Teak and Rosewood, the richly ornate panels of which adorn the beautiful chambers of the Two Houses of Karnataka Legislature.References
Further reading
* ''Ground Water Quality in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Karnataka''. Dr. Oinam Jayalakshmi Devi & Dr. S.L. BelagaliRuby Press & Co
. New Delhi. (2013). {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Karnataka