Geography of Iraqi Kurdistan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan ( ku, باشووری کوردستان, Başûrê Kurdistanê) refers to the
Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan ( ku, باشووری کوردستان, Başûrê Kurdistanê) refers to the
 The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an
The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an


 Iraqi Kurdistan is largely mountainous, with the highest point being a 3,611 m (11,847 ft) point known locally as Cheekha Dar ("black tent"). Mountains in Iraqi Kurdistan include the
Iraqi Kurdistan is largely mountainous, with the highest point being a 3,611 m (11,847 ft) point known locally as Cheekha Dar ("black tent"). Mountains in Iraqi Kurdistan include the
 Due to its latitude and altitude, Iraqi Kurdistan is cooler and much wetter than the rest of Iraq. Most areas in the region fall within the
Due to its latitude and altitude, Iraqi Kurdistan is cooler and much wetter than the rest of Iraq. Most areas in the region fall within the
 The region was conquered by
The region was conquered by 
 During World War I, the British and French divided
During World War I, the British and French divided  In 1922, Britain restored Shaikh Mahmud Barzanji to power, hoping that he would organize the Kurds to act as a buffer against the
In 1922, Britain restored Shaikh Mahmud Barzanji to power, hoping that he would organize the Kurds to act as a buffer against the
 After the
After the  By February 1961, Barzani had successfully defeated the pro-government forces and consolidated his position as leader of the Kurds. At this point, Barzani ordered his forces to occupy and expel government officials from all Kurdish territory. This was not received well in Baghdad, and the Third Kurdish Teachers Congress was cancelled and Qasim even denied that "Kurds" constituted an own nation. Qasim began to prepare for a military offensive against the north to return government control of the region. Meanwhile, in June 1961, the KDP issued a detailed ultimatum to Qasim outlining Kurdish grievances, demanding that the Kurdish language would become an official language in Kurdish majority regions. Qasim ignored the Kurdish demands and continued his planning for war.
It was not until September 10, when an Iraqi army column was ambushed by a group of Kurds, that the Kurdish revolt truly began. In response to the attack, Qasim lashed out and ordered the
By February 1961, Barzani had successfully defeated the pro-government forces and consolidated his position as leader of the Kurds. At this point, Barzani ordered his forces to occupy and expel government officials from all Kurdish territory. This was not received well in Baghdad, and the Third Kurdish Teachers Congress was cancelled and Qasim even denied that "Kurds" constituted an own nation. Qasim began to prepare for a military offensive against the north to return government control of the region. Meanwhile, in June 1961, the KDP issued a detailed ultimatum to Qasim outlining Kurdish grievances, demanding that the Kurdish language would become an official language in Kurdish majority regions. Qasim ignored the Kurdish demands and continued his planning for war.
It was not until September 10, when an Iraqi army column was ambushed by a group of Kurds, that the Kurdish revolt truly began. In response to the attack, Qasim lashed out and ordered the
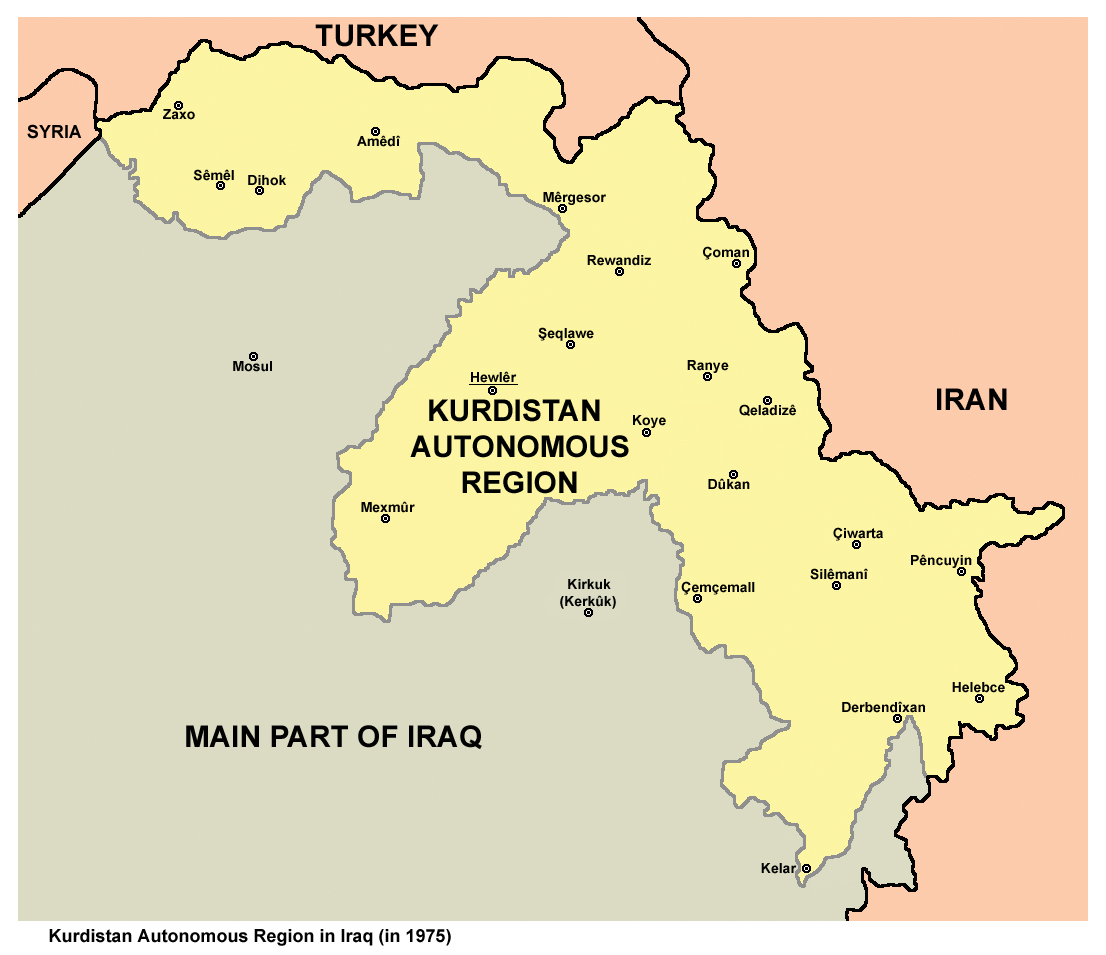 In 1973, the US made a secret agreement with the Shah of Iran to begin covertly funding Kurdish rebels against Baghdad through the
In 1973, the US made a secret agreement with the Shah of Iran to begin covertly funding Kurdish rebels against Baghdad through the
 During the
During the
 Tensions between Iraqi Kurdistan and the central Iraqi government mounted through 2011–2012 on the issues of power sharing, oil production and territorial control. In April 2012, the president of Iraq's semi-autonomous northern Kurdish region demanded that officials agree to their demands or face the prospect of secession from Baghdad by September 2012.
In September 2012, the Iraqi government ordered the KRG to transfer its powers over the Peshmerga to the central government. Relations became further strained by the formation of a new command center (Tigris Operation Command) for Iraqi forces to operate in a disputed area over which both Baghdad and the
Tensions between Iraqi Kurdistan and the central Iraqi government mounted through 2011–2012 on the issues of power sharing, oil production and territorial control. In April 2012, the president of Iraq's semi-autonomous northern Kurdish region demanded that officials agree to their demands or face the prospect of secession from Baghdad by September 2012.
In September 2012, the Iraqi government ordered the KRG to transfer its powers over the Peshmerga to the central government. Relations became further strained by the formation of a new command center (Tigris Operation Command) for Iraqi forces to operate in a disputed area over which both Baghdad and the
The Kurdish Institute of Paris
– Provides news, bulletins, articles and conference information on the situation in Iraqi Kurdistan.
Iraqi Kurdistan timeline
Kurdistan's Politicized Society Confronts a Sultanistic System (Carnegie Paper)
The Kurds of Iraq
* * – Kurdistan Investment Research
Kurds in the Contemporary Middle East
{{Authority control Kurds in Iraq Geography of Iraq Geography of Kurdistan Kurdistan Politics of Iraq Subdivisions of Iraq Kurdistan independence movement Upper Mesopotamia Separatism in Iraq Levant Eastern Mediterranean
Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
-populated part of northern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
. It is considered one of the four parts of "Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages ...
" in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, which also includes parts of southeastern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
(Northern Kurdistan
Turkish Kurdistan or Northern Kurdistan () refers to the southeastern part of Turkey, where Kurds form the predominant ethnic group. The Kurdish Institute of Paris estimates that there are 20 million Kurds living in Turkey, the majority of t ...
), northern Syria (Western Kurdistan
Syrian Kurdistan is a Kurdish-inhabited area in northern Syria surrounding three noncontiguous enclaves along the Turkish and Iraqi borders: Afrin in the northwest, Kobani in the north, and Jazira in the northeast.
Syrian Kurdistan is often ...
), and northwestern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(Eastern Kurdistan
Iranian Kurdistan or Eastern Kurdistan ( ku, ڕۆژھەڵاتی کوردستان, translit=Rojhilatê Kurdistanê) is an unofficial name for the parts of northwestern Iran with either a majority or sizable population of Kurds. Geographically, it ...
). Much of the geographical and cultural region of Iraqi Kurdistan is part of the Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region ( ku, هەرێمی کوردستان, translit=Herêmî Kurdistan; ar, إقليم كردستان), abbr. KRI, is an autonomous region in Iraq comprising the four Kurdish-majority governorates of Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Duhok ...
(KRI), an autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
recognized by the Constitution of Iraq. As with the rest of Kurdistan, and unlike most of the rest of Iraq, the region is inland and mountainous.
Etymology
 The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an
The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
term for region. The literal translation
Literal translation, direct translation or word-for-word translation, is a translation of a text done by translating each word separately, without looking at how the words are used together in a phrase or sentence.
In translation theory, anoth ...
for Kurdistan is "Region of Kurds".
The name was also formerly spelled ''Curdistan''. One of the ancient names of Kurdistan is '' Corduene''.A.D. Lee, ''The Role of Hostages in Roman Diplomacy with Sasanian Persia'', Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte, Vol. 40, No. 3 (1991), pp. 366–374 (see p.371)
Geography


 Iraqi Kurdistan is largely mountainous, with the highest point being a 3,611 m (11,847 ft) point known locally as Cheekha Dar ("black tent"). Mountains in Iraqi Kurdistan include the
Iraqi Kurdistan is largely mountainous, with the highest point being a 3,611 m (11,847 ft) point known locally as Cheekha Dar ("black tent"). Mountains in Iraqi Kurdistan include the Zagros
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
, Sinjar Mountains, Hamrin Mountains
The Hamrin Mountains ( ar, جبل حمرين, Jabāl Hamrīn, ku, چیای حەمرین, Çiyayê Hemrîn or Çiyayên Hemrîn) are a small mountain ridge in northeast Iraq. The westernmost ripple of the greater Zagros mountains, the Hamrin moun ...
, Mount Nisir and Qandil mountains. There are many rivers running through the region, which is distinguished by its fertile lands, plentiful water, and picturesque nature. The Great Zab and the Little Zab flow east–west in the region. The Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
river enters Iraqi Kurdistan from Turkish Kurdistan.
The mountainous nature of Iraqi Kurdistan, the difference of temperatures in its various parts, and its numerous bodies of water make it a land of agriculture and tourism. The largest lake in the region is Lake Dukan. There are also several smaller lakes, such as Darbandikhan Lake and Duhok Lake. The western and southern parts of Iraqi Kurdistan are not as mountainous as the east. Instead, it is rolling hills and plains
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands.
In ...
vegetated by sclerophyll
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaves, short internodes (the distance between leaves along the stem) and leaf orientation which is parallel or oblique to direct ...
scrubland.
Climate
 Due to its latitude and altitude, Iraqi Kurdistan is cooler and much wetter than the rest of Iraq. Most areas in the region fall within the
Due to its latitude and altitude, Iraqi Kurdistan is cooler and much wetter than the rest of Iraq. Most areas in the region fall within the Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
zone (''Csa''), with areas to the southwest being semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
(''BSh'').
Average summer temperatures range from in the cooler northernmost areas to blistering in the southwest, with lows around to . Winters, however, are dramatically cooler than the rest of Iraq, with highs averaging between and and with lows hovering around in some areas and freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
in others, dipping to and on average.
Among other cities in the climate table below, Soran, Shaqlawa and Halabja
Halabja ( ku, هەڵەبجە, Helebce, ) is a city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq and the capital of Halabja Governorate, located about northeast of Baghdad and from the Iranian border.
The city lies at the base of what is often referred to ...
also experience lows which average below in winter. Duhok has the hottest summers in the region, with highs averaging around . Annual rainfall differs across Iraqi Kurdistan, with some places seeing rainfall as low as in Erbil to as high as in places like Amadiya. Most of the rain falls in winter and spring, and is usually heavy. Summer and early autumn are virtually dry, and spring is fairly tepid. Iraqi Kurdistan sees snowfall occasionally in the winter, and frost is common. There is a seasonal lag
Seasonal lag is the phenomenon whereby the date of maximum average air temperature at a geographical location on a planet is delayed until some time after the date of maximum insolation (i.e. the summer solstice). This also applies to the minim ...
in some places in summer, with temperatures peaking around August and September.
Economy
The provinces of Duhok, Erbil and Sulaymanyah are rich in agricultural lands. Wheat and other cereals are grown there. Most of the areas are rainfed, but there are also some smallerirrigation systems
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been develop ...
in place. Tourism is another branch which draws the attention of the KRI, which achieved the declaration of Erbil as the Tourism Capital by the Arab Council of Tourism in 2014.
History
Pre-Islamic period
In prehistoric times, the region was home to aNeanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
culture such as has been found at the Shanidar Cave
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
It is known for the ...
. The region was host to the Jarmo culture circa 7000 BCE. The earliest neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
site in Kurdistan is at Tell Hassuna, the centre of the ''Hassuna culture'', circa 6000 BCE.
In Early and Middle Bronze Age the region was geographically known as Subartu
The land of Subartu (Akkadian ''Šubartum/Subartum/ina Šú-ba-ri'', Assyrian '' mât Šubarri'') or Subar (Sumerian Su-bir4/Subar/Šubur, Ugaritic 𐎘𐎁𐎗 ṯbr) is mentioned in Bronze Age literature. The name also appears as ''Subari'' in ...
and was inhabited by the Hurrian speaking Subarians along with Gutians
The Guti () or Quti, also known by the derived exonyms Gutians or Guteans, were a nomadic people of West Asia, around the Zagros Mountains (Modern Iran) during ancient times. Their homeland was known as Gutium ( Sumerian: ,''Gu-tu-umki'' or ,'' ...
and Lullubi
Lullubi, Lulubi ( akk, 𒇻𒇻𒉈: ''Lu-lu-bi'', akk, 𒇻𒇻𒉈𒆠: ''Lu-lu-biki'' "Country of the Lullubi"), more commonly known as Lullu, were a group of tribes during the 3rd millennium BC, from a region known as ''Lulubum'', now the Sha ...
. In 2200 BCE Naram-Sin of Akkad
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen ( akk, : '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine"), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC ...
conquered the region and it came under the rule of the Gutians in 2150 BCE. The main cities of the region attested in the inscriptions in this period are Mardaman, Azuhinum, Ninet (Nineveh), Arrapha
Arrapha or Arrapkha ( Akkadian: ''Arrapḫa''; ar, أررابخا ,عرفة) was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be on the site of the modern city of Kirkuk.
In 1948, ''Arrapha'' became the name of the residential ...
, Urbilum
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000.
Hu ...
, and Kurda Kurda was an ancient city-state and kingdom located in Northern Mesopotamia. Kurda emerged during the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia) and is attested in the administrative texts of this era as a city state and geographical territory in Upper Mes ...
.
In early 2nd millennium the region was ruled by the kingdom of Kurda except for two decades in 18th century BCE when it was conquered by the Amorite
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied la ...
Shamshi Adad and was incorporated into the Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia. In 1760s BCE the kingdom of Kurda faced an invasion by Elam and Eshnunna
Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Although situated in th ...
during the Babylonian-Elam war and the kingdom eventually sided with Mari and Babylon.
In 16th century BCE the Mitannians incorporated the region into their Hurrian empire. Following the destruction of the Mitannian Empire by the Hittites, between 14th-13th century BCE the region gradually came under the rule of the Assyrians. Tukulti-Ninurta I in 13rd century BCE finally conquered the whole region and appointed one of his commanders as the governor of the villages and towns of Kurda. Kurda was reduced to a province centering around modern Sinjar. Erbil's name was Akkadianized to Arba-ilu and during the Neo-Assyrian Empire the city was noted for its distinctive cult of Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
. The region was partially under the rule of Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
and the kingdom of Musasir in early 1st millennium BCE. Modern Rawandiz district was a religious center of the Urartians.
The Medes conquered the region in 7th century BCE. Later it came under the rule of the Achaemenids and remained as part of the satrapy of Media. When Xenophon passed through the region in 4th century BCE, it was inhabited by the Medes. In 332 BC the region fell to Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and was thereafter ruled by the Greek Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
Empire until the middle of the second century BCE when it fell to Mithridates I of Parthia. During the four centuries of the Parthian era (247 BCE to 226 AD) the region was ruled by semi-independent principalities of Barzan and Sharazur, and in 1st century it was partially under the rule of the Jewish kingdom of Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of N ...
. Between 3rd and 4th centuries the region was ruled by the House of Kayus until it was incorporated into the Sassanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
in 380 AD and it was renamed to Nodshēragān. The region was gradually converted to Christianity between 1st and 5th centuries and Erbil became the seat of the metropolitan of Hadhyab of the Church of the East and it was divided into several bishoprics namely Marga, Beth Garmai, Beth Qardu, Beth MahQard, Beth BihQard, Beth Nuhadra and Shahr-Qard. In Syriac the region was commonly called Beth Qardwaye.
Islamic period
 The region was conquered by
The region was conquered by Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
in the mid 7th century AD as the invading forces conquered the Sassanian Empire, the region fell to Muslims after they fought the Kurds in Mosul and Tikrit 'Utba ibn Farqad captured all the forts of the Kurds when he conquered Erbil in 641. The area became part of the Muslim Arab Rashidun, Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
, and later the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
Caliphates, before becoming part of various Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
, Turkic, and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalen ...
s. Following the disintegration of the Ak Koyunlu, all of its territories including what is modern-day Iraqi Kurdistan passed to the Iranian Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
in the earliest 16th century.
Between the 16th and 17th century the area nowadays known as Iraqi Kurdistan, (formerly ruled by three principalities of Baban
Baban () was a Kurdish principality existing from the 16th century to 1850, centered around Sulaymaniyah. The Baban principality played an active role in the Ottoman-Safavid conflict and gave significant military support to the Ottomans. They were ...
, Badinan, and Soran) was continuously passed back and forth between archrivals the Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
and the Ottomans, until the Ottomans managed to decisively seize power in the region starting from the mid 17th century through the Ottoman–Safavid War (1623–39) and the resulting Treaty of Zuhab.Roemer (1989), p. 285 In the early 18th century, it briefly passed to the Iranian Afsharids
Afsharid Iran ( fa, ایران افشاری), also referred as the Afsharid Empire was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, ruling Iran (Persia). The state was ruled by the Af ...
led by Nader Shah. Following Nader's death in 1747, Ottoman suzerainty was reimposed, and in 1831, direct Ottoman rule was established which lasted until World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, when the Ottomans were defeated by the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
.

Kurdish revolts under British control
 During World War I, the British and French divided
During World War I, the British and French divided Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
in the Sykes-Picot Agreement. The Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
(which did not enter into force), and the Treaty of Lausanne which superseded it, led to the advent of modern Western Asia and the modern Republic of Turkey. The League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
granted France mandates over Syria and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and granted the United Kingdom mandates over Palestine (which then consisted of two autonomous regions: Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
and Transjordan) and what was to become Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
. Parts of the Ottoman Empire on the Arabian Peninsula were eventually taken over by Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
.
 In 1922, Britain restored Shaikh Mahmud Barzanji to power, hoping that he would organize the Kurds to act as a buffer against the
In 1922, Britain restored Shaikh Mahmud Barzanji to power, hoping that he would organize the Kurds to act as a buffer against the Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, who had territorial claims over Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
and Kirkuk. However, defiant to the British, in 1922 Shaikh Mahmud declared a Kurdish Kingdom with himself as king. It took two years for the British to bring Kurdish areas into submission, while Shaikh Mahmud found refuge in an unknown location.
In 1930, following the announcement of the admission of Iraq to the League of Nations, Shaikh Mahmud started a third uprising which was suppressed with British air and ground forces.
By 1927, the Barzani clan had become vocal supporters of Kurdish rights in Iraq. In 1929, the Barzani demanded the formation of a Kurdish province in northern Iraq. Emboldened by these demands, in 1931 Kurdish notables petitioned the League of Nations to set up an independent Kurdish government. In late 1931, Ahmed Barzani initiated a Kurdish rebellion against Iraq, and though defeated within several months, the movement gained a major importance in the Kurdish struggle later on, creating the ground for such a notable Kurdish rebel as Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani ( ku, مەلا مستهفا بارزانی, Mistefa Barzanî; 14 March 1903 – 1 March 1979) also known as Mela Mustafa (Preacher Mustafa), was a Kurdish leader, general and one of the most prominent political figures in mod ...
.
During World War II, the power vacuum in Iraq was exploited by the Kurdish tribes and under the leadership of Mustafa Barzani a rebellion broke out in the north, effectively gaining control of Kurdish areas until 1945, when Iraqis could once again subdue the Kurds with British support. Under pressure from the Iraqi government and the British, the most influential leader of the clan, Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani ( ku, مەلا مستهفا بارزانی, Mistefa Barzanî; 14 March 1903 – 1 March 1979) also known as Mela Mustafa (Preacher Mustafa), was a Kurdish leader, general and one of the most prominent political figures in mod ...
was forced into exile in Iran in 1945. Later he moved to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
after the collapse of the Republic of Mahabad in 1946.
Barzani Revolt (1960–1970)
 After the
After the military coup
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
by Arab nationalists on the 14 July 1958, Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani ( ku, مەلا مستهفا بارزانی, Mistefa Barzanî; 14 March 1903 – 1 March 1979) also known as Mela Mustafa (Preacher Mustafa), was a Kurdish leader, general and one of the most prominent political figures in mod ...
was invited by Abdul Karim Qasim to return from exile, where he was greeted with a hero's welcome. As part of the deal arranged between Qasim and Barzani, Qasim had promised to give the Kurds regional autonomy in return for Barzani's support for his policies. The Provisional Constitution described Iraq being included in the Arab world but saw the Kurds as partners within an Iraqi statehood and the coat of arms included a Kurdish dagger besides the Arab sword. Meanwhile, during 1959–1960, Barzani became the head of the Kurdistan Democratic Party (KDP), which was granted legal status in 1960. By early 1960, it became apparent that Qasim would not follow through with his promise of regional autonomy. As a result, the KDP began to agitate for regional autonomy. In the face of growing Kurdish dissent, as well as Barzani's personal power, Qasim began to incite the Barzanis historical enemies, the ''Baradost'' and ''Zebari'' tribes, which led to intertribal warfare throughout 1960 and early 1961.
 By February 1961, Barzani had successfully defeated the pro-government forces and consolidated his position as leader of the Kurds. At this point, Barzani ordered his forces to occupy and expel government officials from all Kurdish territory. This was not received well in Baghdad, and the Third Kurdish Teachers Congress was cancelled and Qasim even denied that "Kurds" constituted an own nation. Qasim began to prepare for a military offensive against the north to return government control of the region. Meanwhile, in June 1961, the KDP issued a detailed ultimatum to Qasim outlining Kurdish grievances, demanding that the Kurdish language would become an official language in Kurdish majority regions. Qasim ignored the Kurdish demands and continued his planning for war.
It was not until September 10, when an Iraqi army column was ambushed by a group of Kurds, that the Kurdish revolt truly began. In response to the attack, Qasim lashed out and ordered the
By February 1961, Barzani had successfully defeated the pro-government forces and consolidated his position as leader of the Kurds. At this point, Barzani ordered his forces to occupy and expel government officials from all Kurdish territory. This was not received well in Baghdad, and the Third Kurdish Teachers Congress was cancelled and Qasim even denied that "Kurds" constituted an own nation. Qasim began to prepare for a military offensive against the north to return government control of the region. Meanwhile, in June 1961, the KDP issued a detailed ultimatum to Qasim outlining Kurdish grievances, demanding that the Kurdish language would become an official language in Kurdish majority regions. Qasim ignored the Kurdish demands and continued his planning for war.
It was not until September 10, when an Iraqi army column was ambushed by a group of Kurds, that the Kurdish revolt truly began. In response to the attack, Qasim lashed out and ordered the Iraqi Air Force
The Iraqi Air Force (IQAF or IrAF) ( ar, القوات الجوية العراقية, Al Quwwat al Jawwiyah al Iraqiyyah}) is the aerial warfare service branch of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It is responsible for the defense of Iraqi airspace as well ...
to indiscriminately bomb Kurdish villages, which ultimately served to rally the entire Kurdish population to Barzani's standard. Due to Qasim's profound distrust of the Iraqi Army, which he purposely failed to adequately arm (in fact, Qasim implemented a policy of ammunition rationing), Qasim's government was not able to subdue the insurrection. This stalemate irritated powerful factions within the military and is said to be one of the main reasons behind the Ba'athist coup against Qasim in February 1963. In November 1963, after considerable infighting amongst the civilian and military wings of the Ba'athists, they were ousted by Abdul Salam Arif in a coup. Then, after another failed offensive, Arif declared a ceasefire in February 1964 which provoked a split among Kurdish urban radicals on one hand and Peshmerga
The Peshmerga ( ku, پێشمەرگه, Pêşmerge, lit=those who face death) is the Kurdish military forces of the autonomous Kurdistan Region of Iraq. According to the Constitution of Iraq, the Peshmerga, along with their security subsidiaries, ...
(Freedom fighters) forces led by Barzani on the other.
Barzani agreed to the ceasefire and fired the radicals from the party. Following the unexpected death of Arif, whereupon he was replaced by his brother, Abdul Rahman Arif
Hajj ʿAbd al-Rahman Mohammed ʿArif al-Jumayli ( ar, عبد الرحمن محمد عارف الجميلي, ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ʿĀrif; 14 April 191624 August 2007) was a career soldier and the third president of Iraq from 16 April 1966 to 17 Ju ...
, the Iraqi government launched a last-ditch effort to defeat the Kurds. This campaign failed in May 1966, when Barzani forces thoroughly defeated the Iraqi Army at the Battle of Mount Handrin, near Rawandiz. At this battle, it was said that the Kurds slaughtered an entire brigade. Recognizing the futility of continuing this campaign, Rahamn Arif announced a 12-point peace program in June 1966, which was not implemented due to the overthrow of Rahman Arif in a 1968 coup by the Ba'ath Party.
The Ba'ath government started a campaign to end the Kurdish insurrection, which stalled in 1969. This can be partly attributed to the internal power struggle in Baghdad and also tensions with Iran. Moreover, the Soviet Union pressured the Iraqis to come to terms with Barzani. A peace plan was announced in March 1970 and provided for broader Kurdish autonomy. The plan also gave Kurds representation in government bodies, to be implemented in four years. Despite this, the Iraqi government embarked on an Arabization program in the oil rich regions of Kirkuk and Khanaqin in the same period.
In the following years, Baghdad government overcame its internal divisions and concluded a treaty of friendship with the Soviet Union in April 1972 and ended its isolation within the Arab world. On the other hand, Kurds remained dependent on the Iranian military support and could do little to strengthen their forces.
Second Kurdish Iraqi War Algiers Agreement
 In 1973, the US made a secret agreement with the Shah of Iran to begin covertly funding Kurdish rebels against Baghdad through the
In 1973, the US made a secret agreement with the Shah of Iran to begin covertly funding Kurdish rebels against Baghdad through the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
and in collaboration with the Mossad, both of which would be active in the country through the launch of the Iraqi invasion and into the present. By 1974, the Iraqi government retaliated with a new offensive against the Kurds and pushed them close to the border with Iran. Iraq informed Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
that it was willing to satisfy other Iranian demands in return for an end to its aid to the Kurds. With mediation by Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
n President Houari Boumediene Houari is a given name and surname. It may refer to:
Persons Given name
*Houari Boumédiène, also transcribed Boumediene, Boumedienne etc. (1932–1978), served as Chairman of the Revolutionary Council of Algeria from 19 June 1965 until 12 Decembe ...
, Iran and Iraq reached a comprehensive settlement in March 1975 known as the '' Algiers Pact''. The agreement left the Kurds helpless and Tehran cut supplies to the Kurdish movement. Barzani went to Iran with many of his supporters. Others surrendered ''en masse'' and the rebellion ended after a few days.
As a result, the Iraqi government extended its control over the northern region after 15 years and in order to secure its influence, started an Arabization program by moving Arabs to the vicinity of oil fields in northern Iraq, particularly those around Kirkuk, and other regions, which were populated by Turkmen, Kurds and Christians. The repressive measures carried out by the government against the Kurds after the Algiers agreement led to renewed clashes between the Iraqi Army and Kurdish guerrillas in 1977. In 1978 and 1979, 600 Kurdish villages were burned down and around 200,000 Kurds were deported to the other parts of the country.
Arabization campaign and PUK insurgency
The Ba'athist government of Iraq forcibly displaced and culturally Arabized minorities (Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ira ...
, Yezidis
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The maj ...
, Assyrians, Shabaks
Shabaks ( ar, الشبك; ku, شەبەک, translit=Şebek) are a group with a disputed ethnic origin. Some Shabaks identify themselves as a distinct ethnic group and others as ethnic Kurds. They live east of Mosul in Iraq. However their cultural t ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Turkmen, Mandeans), in line with settler colonialist policies, from the 1960s to the early 2000s, in order to shift the demographics of North Iraq towards Arab domination. The Baath party under Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein ( ; ar, صدام حسين, Ṣaddām Ḥusayn; 28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003. A leading member of the revolutio ...
engaged in active expulsion of minorities from the mid-1970s onwards.Eva Savelsberg, Siamend Hajo, Irene Dulz. ''Effectively Urbanized – Yezidis in the Collective Towns of Sheikhan and Sinjar''. Etudes rurales 2010/2 (n°186). In 1978 and 1979, 600 Kurdish villages were burned down and around 200,000 Kurds were deported to the other parts of the country.
The campaigns took place during the Iraqi–Kurdish conflict
The Iraqi–Kurdish conflict consists of a series of wars and rebellions by the Kurds against the central authority of Iraq during the 20th century, which began shortly after the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I and lasting until the ...
, being largely motivated by the Kurdish–Arab ethnic and political conflict. Arab settlement programs reached their peak during the late 1970s, in line with depopulation efforts of the Ba'athist regime. The Baathist policies motivating those events are sometimes referred to as "internal colonialism", described by Dr. Francis Kofi Abiew as a "Colonial 'Arabization program, including large-scale Kurdish deportations and forced Arab settlement in the region.
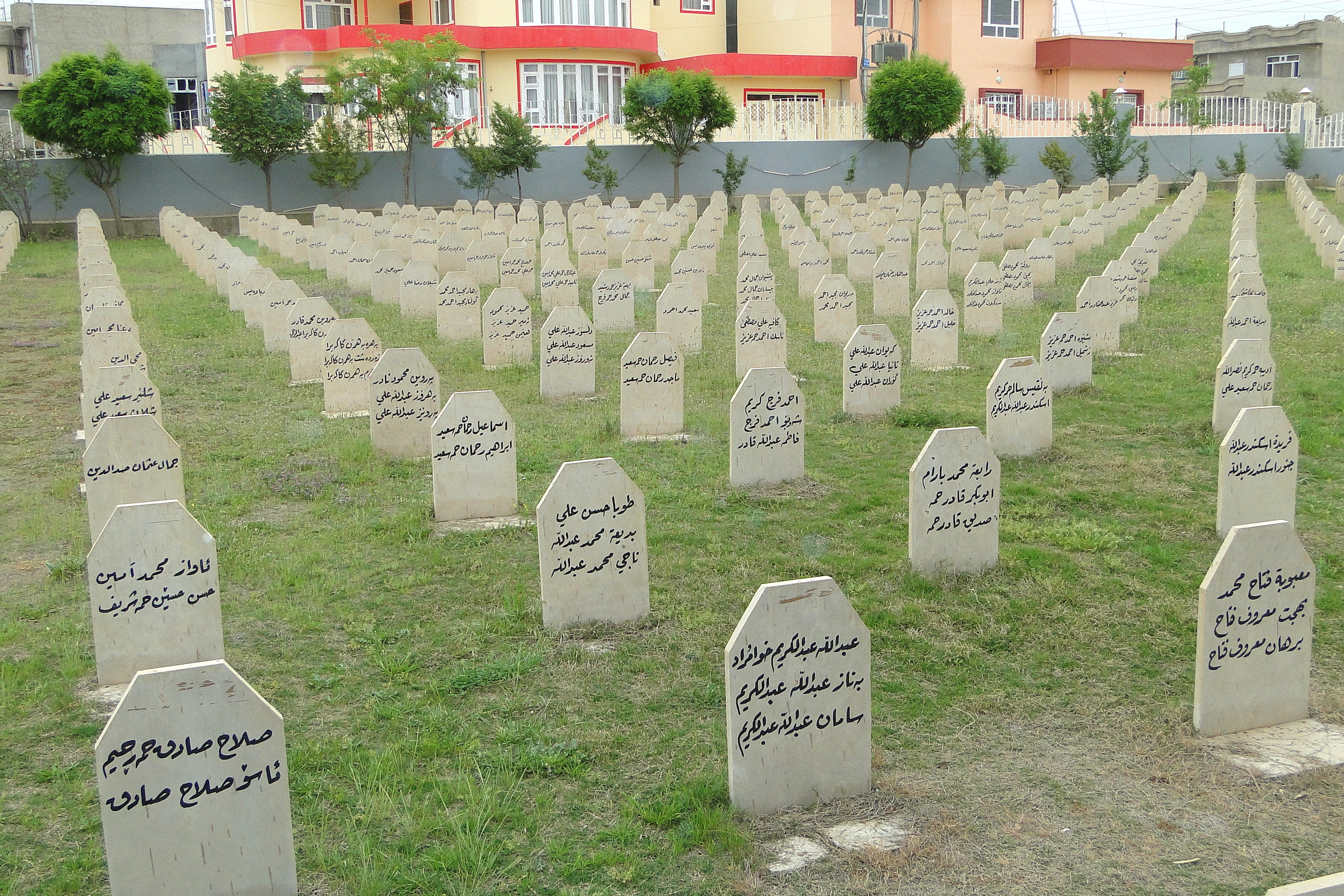
Iran–Iraq War and Anfal Campaign
 During the
During the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Ba'athist Iraq, Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations S ...
, the Iraqi government again implemented anti-Kurdish policies and a ''de facto'' civil war broke out. Iraq was widely condemned by the international community, but was never seriously punished for oppressive measures, including the use of chemical weapons
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be any chemical compound intended as a ...
against the Kurds, which resulted in thousands of deaths.
The Al-Anfal Campaign constituted a systematic genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Lat ...
of the Kurdish people in Iraq.
The second and more extensive and widespread wave began from March 29, 1987, until April 23, 1989, when the Iraqi army under the command of Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein ( ; ar, صدام حسين, Ṣaddām Ḥusayn; 28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003. A leading member of the revolutio ...
& Ali Hassan al-Majid
Ali Hassan Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti ( ar, علي حسن عبد المجيد التكريت, ʿAlī Ḥasan ʿAbd al-Majīd al-Tikrītī; 30 November 1941 – 25 January 2010), nicknamed Chemical Ali ( ar, علي الكيمياوي, ʿAlī al-Kīm ...
carried out a genocidal campaign against the Kurds, characterized by the following human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
violations: The widespread use of chemical weapons, the wholesale destruction of some 2,000 villages, and slaughter of around 50,000 rural Kurds, by the most conservative estimates. The large Kurdish town of Qala Dizeh (population 70,000) was completely destroyed by the Iraqi army. The campaign also included Arabization of Kirkuk, a program to drive Kurds and other ethnic groups out of the oil-rich city and replace them with Arab settlers from central and southern Iraq.
Autonomous period
After the Persian Gulf War
Even though autonomy had been agreed in 1970, the local population did not enjoy any democratic freedom, facing similar conditions to the rest of Iraq. Things began to change after the 1991 uprising againstSaddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein ( ; ar, صدام حسين, Ṣaddām Ḥusayn; 28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003. A leading member of the revolutio ...
at the end of the Persian Gulf War. The United Nations Security Council Resolution 688
United Nations Security Council Resolution 688, adopted on 5 April 1991, after receiving letters from the representatives of France, Iran, and Turkey and expressing its concern over political repression of the Iraqi people, including those in Ira ...
gave birth to a ''safe haven'' following international concern for the safety of Kurdish refugees. The U.S. and the Coalition established a No Fly Zone over a large part of northern Iraq (see Operation Provide Comfort
Operation Provide Comfort and Provide Comfort II were military operations initiated by the United States and other Coalition nations of the Persian Gulf War, starting in April 1991, to defend Kurdish refugees fleeing their homes in northern I ...
), however, it left out Sulaymaniyah, Kirkuk and other important Kurdish populated regions. Bloody clashes between Iraqi forces and Kurdish troops continued and, after an uneasy and shaky balance of power was reached, the Iraqi government fully withdrew its military and other personnel from the region in October 1991 allowing Iraqi Kurdistan to function de facto independently. The region was to be ruled by the two principal Kurdish parties; the Kurdish Democratic Party (KDP) and the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan (PUK). The region also has its own flag and national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europea ...
.
At the same time, Iraq imposed an economic blockade over the region, reducing its oil and food supplies. Elections held in June 1992 produced an inconclusive outcome, with the assembly divided almost equally between the two main parties and their allies. During this period, the Kurds were subjected to a double embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they m ...
: one imposed by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
on Iraq and one imposed by Saddam Hussein on their region. The severe economic hardships caused by the embargoes fueled tensions between the two dominant political parties, the KDP and the PUK, over control of trade routes and resources. Relations between the PUK and the KDP started to become dangerously strained from September 1993 after rounds of amalgamations occurred between parties.
After 1996, 13% of the Iraqi oil sales were allocated for Iraqi Kurdistan and this led to relative prosperity in the region. In return, the Kurds under KDP enabled Saddam to establish an oil smuggling route through territory controlled by the KDP, with the active involvement of senior Barzani family members. The taxation of this trade at the crossing point between Saddam's territory and Kurdish controlled territory and then into Turkey, along with associated service revenue, meant that whoever controlled Dohuk and Zakho
Zakho, also spelled Zaxo ( ku, زاخۆ, Zaxo, syr, ܙܵܟ݂ܘܿ, Zākhō, , ) is a city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, at the centre of the eponymous Zakho District of the Dohuk Governorate, located a few kilometers from the Iraq–Turkey b ...
had the potential to earn several million dollars a week. Direct United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
mediation led the two parties to a formal ceasefire in what was termed the ''Washington Agreement'' in September 1998. It is also argued that the Oil-for-Food Programme
The Oil-for-Food Programme (OIP), established by the United Nations in 1995 (under UN Security Council Resolution 986) was established to allow Iraq to sell oil on the world market in exchange for food, medicine, and other humanitarian needs f ...
from 1997 onward had an important effect on cessation of hostilities.
During and after US-led invasion
Iraqi Kurds played an important role in theIraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
. Kurdish parties joined forces against the Iraqi government during the war in Spring 2003. Kurdish military forces, known as Peshmerga
The Peshmerga ( ku, پێشمەرگه, Pêşmerge, lit=those who face death) is the Kurdish military forces of the autonomous Kurdistan Region of Iraq. According to the Constitution of Iraq, the Peshmerga, along with their security subsidiaries, ...
, played an important role in the overthrow of the Iraqi government; however, Kurds have been reluctant to send troops into Baghdad since then, preferring not to be dragged into the sectarian struggle that so dominates much of Iraq.
A new constitution of Iraq was established in 2005, defining Iraq as a federalist state consisting of Regions and Governorate's. The Kurdistan region includes the Governorate Erbil, Sulaymaniyah
Sulaymaniyah, also spelled as Slemani ( ku, سلێمانی, Silêmanî, ar, السليمانية, as-Sulaymāniyyah), is a city in the east of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, not far from the Iran–Iraq border. It is surrounded by the Azmar, G ...
and Duhok. It recognized both the Kurdistan Region and all laws passed by the KRG since 1992. There is provision for Governorates to create, join or leave Regions. However, as of late 2015, no new Regions have been formed, and the KRG remains the only regional government within Iraq.
PUK leader Jalal Talabani
Jalal Talabani ( ku, مام جەلال تاڵەبانی, translit=Celal Talebanî; ar, جلال طالباني ; 1933 – 3 October 2017) was an Iraqi Kurdish politician who served as the sixth president of Iraq from 2006 to 2014, as well as ...
was elected President of the new Iraqi administration, while KDP leader Masoud Barzani became President of the Kurdistan Regional Government.
Following US withdrawal
Kurdistan Regional Government
The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) ( ku, حکوومەتی هەرێمی کوردستان, ''Hikûmetî Herêmî Kurdistan'') is the official executive body of the autonomous Kurdistan Region of northern Iraq.
The cabinet is selected by the m ...
claim jurisdiction. On 16 November 2012 a military clash between the Iraqi forces and the Peshmerga resulted in one person killed. CNN reported that two people were killed (one of them an Iraqi soldier) and ten wounded in clashes at the Tuz Khurmato town.
As of 2014, Iraqi Kurdistan is in dispute with the Federal Iraqi government on the issues of territorial control, export of oil and budget distribution and is functioning largely outside Baghdad's control. With the escalation of the Iraqi crisis and fears of Iraq's collapse, Kurds have increasingly debated the issue of independence. During the 2014 Northern Iraq offensive, Iraqi Kurdistan seized the city of Kirkuk and the surrounding area, as well as most of the disputed territories in Northern Iraq. On 1 July 2014, Masoud Barzani announced that "Iraq's Kurds will hold an independence referendum within months." After previously opposing the independence for Iraqi Kurdistan, Turkey later gave signs that it could recognize an independent Kurdish state. On 11 July 2014, KRG forces seized control of the Bai Hassan and Kirkuk oilfields, prompting a condemnation from Baghdad and a threat of "dire consequences" if the oilfields were not relinquished back to Iraq's control.
In September, Kurdish leaders decided to postpone the referendum so as to focus on the fight against ISIL. In November, Ed Royce
Edward Randall Royce (born October 12, 1951) is an American politician who served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from California from 1993 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, Royce served as Chairman of the United ...
, Chairman of the Foreign Affairs Committee of the United States House of Representatives, introduced legislation to arm the Kurds directly, rather than continue working through the local governments.
In August 2014, the US began a campaign of airstrikes in Iraq, in part to protect Kurdish areas such as Erbil from the militants.
In February 2016, Kurdish president Barzani stated once again that "Now the time is ripe for the people of Kurdistan to decide their future through a referendum", supporting an independence referendum and citing similar referendums in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
. On March 23, Barzani officially declared that Iraqi Kurdistan will hold the referendum some time "before October" of that year. On April 2, 2017, the two governing parties released a joint statement announcing they would form a joint committee to prepare for a referendum to be held on 25 September.
The 2017 Kurdistan Region independence referendum
An independence referendum for the Kurdistan Region of Iraq was held on 25 September 2017, with preliminary results showing approximately 92.73 percent of votes cast in favour of independence. Despite reporting that the independence referendum ...
took place on September 25, with 92.73% voting in favor of independence. This triggered a military operation
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operations ma ...
in which the Iraqi government retook control of Kirkuk and surrounding areas, and forced the KRG to annul the referendum. Scholars have argued that the retaking of Kirkuk, a PUK stronghold, and the loss of other territory to Iraq, has actually consolidated the power of the Barzani family and the KDP, who remain in power.
Culture
Kurdish culture is a group of distinctive cultural traits practiced by Kurdish people. The Kurdish culture is a legacy from the various ancient peoples who shaped modern Kurds and their society, but primarily Iranian. Among their neighbours, the Kurdish culture is closest to Persian culture. For example, they celebrate Newroz as the new year day, which is celebrated on March 21. It is the first day of the month of ''Xakelêwe'' in Kurdish calendar and the first day of spring.References
External links
The Kurdish Institute of Paris
– Provides news, bulletins, articles and conference information on the situation in Iraqi Kurdistan.
Iraqi Kurdistan timeline
Kurdistan's Politicized Society Confronts a Sultanistic System (Carnegie Paper)
The Kurds of Iraq
* * – Kurdistan Investment Research
Kurds in the Contemporary Middle East
{{Authority control Kurds in Iraq Geography of Iraq Geography of Kurdistan Kurdistan Politics of Iraq Subdivisions of Iraq Kurdistan independence movement Upper Mesopotamia Separatism in Iraq Levant Eastern Mediterranean