Geography of India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


Cratons of India
lyellcollection.org. The Indian Craton can be divided into five major cratons as such: * Aravalli Craton (Marwar-Mewar Craton or Western Indian Craton): Covers
 The Himalayas in India extend from the Indian-administered region of
The Himalayas in India extend from the Indian-administered region of
 ** Satpura Range, lies south of Vindhya range and east of Aravali range, begins in eastern Gujarat near the Arabian Sea coast and runs east across
** Satpura Range, lies south of Vindhya range and east of Aravali range, begins in eastern Gujarat near the Arabian Sea coast and runs east across 
 * Ghats
** Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountains run along the western edge of India's
* Ghats
** Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountains run along the western edge of India's
 The Indo-Gangetic plains, also known as the ''Great Plains'' are large
The Indo-Gangetic plains, also known as the ''Great Plains'' are large
 The Thar Desert (also known as ''the deserts'') is by some calculations the world's seventh largest desert, by some others the tenth. It forms a significant portion of western India and covers an area of . The desert continues into Pakistan as the
The Thar Desert (also known as ''the deserts'') is by some calculations the world's seventh largest desert, by some others the tenth. It forms a significant portion of western India and covers an area of . The desert continues into Pakistan as the
 The Eastern Coastal Plain is a wide stretch of land lying between the
The Eastern Coastal Plain is a wide stretch of land lying between the
 The
The
Encyclopædia Britannica The Chambal, another tributary of the Ganges, via the Yamuna, originates from the Vindhya-Satpura watershed. The river flows eastward. Westward-flowing rivers from this watershed are the Narmada and Tapi, which drain into the Arabian Sea in Gujarat. The river network that flows from east to west constitutes 10% of the total outflow. (The Western Ghats are the source of all Deccan rivers, which include the through
(The Western Ghats are the source of all Deccan rivers, which include the through
 India's
India's
 Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic subtypes, ranging from arid desert in the west,
Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic subtypes, ranging from arid desert in the west,
 India's geological features are classified based on their era of formation. The
India's geological features are classified based on their era of formation. The
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north (the mainland) to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. India Yearbook, p. 1 It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of . Total area excludes disputed territories not under Indian control. India measures from north to south and from east to west. It has a land frontier of and a coastline of .
On the south, India projects into and is bounded by the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
—in particular, by the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
on the west, the Lakshadweep Sea
The Laccadive Sea or Lakshadweep Sea is a body of water bordering India (including its Lakshadweep islands), the Maldives, and Sri Lanka. It is located to the southwest of Karnataka, to the west of Kerala and to the south of Tamil Nadu. This war ...
to the southwest, the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
on the east, and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
proper to the south. The Palk Strait
The Palk Strait ( ta, பாக்கு நீரிணை ''Pākku Nīriṇai'', si, පෝක් සමුද්ර සන්ධිය ''Pok Samudra Sandhiya'') is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Jaffna Distri ...
and Gulf of Mannar
The Gulf of Mannar ( ) is a large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean with an average depth of .
separate India from Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
to its immediate southeast, and the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
are some to the south of India's Lakshadweep Islands across the Eight Degree Channel. India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
, some southeast of the mainland, share maritime borders with Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
. The southernmost tip of the Indian mainland (8°4′38″N, 77°31′56″E) is just south of Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
, while the southernmost point in India is Indira Point on Great Nicobar Island. The northernmost point which is under Indian administration is Indira Col, Siachen Glacier. India's territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potent ...
extend into the sea to a distance of from the coast baseline. India has the 18th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of .
The northern frontiers of India are defined largely by the Himalayan mountain range
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
, where the country borders China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
, and Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
. Its western border with Pakistan lies in the Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
and Western Himalayan ranges, Punjab Plains, the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
and the Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch (alternately spelled as Kuchchh) is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located in Gujarat (primarily the Kutch district), India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into ...
salt marshes. In the far northeast, the Chin Hills
The Chin Hills are a range of mountains in Chin State, northwestern Burma (Myanmar), that extends northward into India's Manipur state.
Geography
The highest peak in the Chin Hills is Khonu Msung, or Mount Victoria, in southern Chin State, w ...
and Kachin Hills, deeply forested mountainous regions, separate India from Burma. On the east, its border with Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
is largely defined by the Khasi Hills
The Khasi Hills () is a low mountain formation on the Shillong Plateau in Meghalaya state of India. The Khasi Hills are part of the Garo-Khasi-Jaintia range and connects with the Purvanchal Range and larger Patkai Range further east. Khasi Hil ...
and Mizo Hills
The Lushai (Pron: ˌlʊˈʃaɪ) Hills (or Mizo Hills) are a mountain range in Mizoram and Manipur, India. The range is part of the Patkai range system and its highest point is 2,157 m high Phawngpui, also known as 'Blue Mountain'.
Flora and fau ...
, and the watershed region of the Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
.
The Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
is the longest river originating in India. The Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
–Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
system occupies most of northern, central, and eastern India, while the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
occupies most of southern India. Kangchenjunga, in the Indian state of Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, is the highest point in India at and the world's third highest peak. The climate across India ranges from equatorial in the far south, to alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
and tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
in the upper regions of the Himalayas. Geologically, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
lies on the Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began ...
, the northern part of the Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and the surrounding ocean and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and the adjacent waters. It was formed by the fusion of the Indian an ...
.
Geological development
India is situated entirely on theIndian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began ...
, a major tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
that was formed when it split off from the ancient continent Gondwanaland (ancient landmass, consisting of the southern part of the supercontinent of Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
). The Indo-Australian plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and the surrounding ocean and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and the adjacent waters. It was formed by the fusion of the Indian an ...
is subdivided into the Indian and Australian plates. About 90 million years ago, during the late Cretaceous Period, the Indian Plate began moving north at about 15 cm/year (6 in/yr). About 50 to 55 million years ago, in the Eocene Epoch of the Cenozoic Era
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configu ...
, the plate collided with Asia after covering a distance of , having moved faster than any other known plate. In 2007, German geologists determined that the Indian Plate was able to move so quickly because it is only half as thick as the other plates which formerly constituted Gondwanaland. The collision with the Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent an ...
along the modern border between India and Nepal formed the orogenic belt
An orogenic belt, or orogen, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological processes collec ...
that created the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
and the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
. , the Indian Plate is moving northeast at 5 cm/yr (2 in/yr), while the Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent an ...
is moving north at only 2 cm/yr (0.8 in/yr). India is thus referred to as the "fastest continent". This is causing the Eurasian Plate to deform, and the Indian Plate to compress at a rate of 4 cm/yr (1.6 in/yr).
Political geography
India is divided into 28 States (further subdivided intodistricts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
) and 8 union territories including the National capital territory (i.e., Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
).
India's borders run a total length of .
Its borders with Pakistan and Bangladesh were delineated according to the Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab Province and Bengal Presidency of British India. It was named after Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissi ...
, which was created in 1947 during Partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
. Its western border with Pakistan extends up to , dividing the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
and running along the boundaries of the Thar Desert and the Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch (alternately spelled as Kuchchh) is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located in Gujarat (primarily the Kutch district), India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into ...
. This border runs along the Indian states and union territories of Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
, Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
, and Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. Both nations delineated a Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but serv ...
(LoC) to serve as the informal boundary between the Indian and Pakistan-administered areas of the Kashmir region
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
. India claims the whole of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, which includes areas now administered by Pakistan and China, which according to India are illegally occupied areas.
India's border with Bangladesh runs . West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and J ...
, Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ...
and Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo", the self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo language means "lan ...
are the states which share the border with Bangladesh. Before 2015, there were 92 enclaves of Bangladesh on Indian soil and 106 enclaves of India were on Bangladeshi soil. These enclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
were eventually exchanged in order to simplify the border. After the exchange, India lost roughly 40 km2 (10,000 acres) to Bangladesh.
The Line of Actual Control
The Line of Actual Control (LAC), in the context of the Sino-Indian border dispute, is a notional demarcation lineAnanth KrishnanLine of Actual Control , India-China: the line of actual contest, 13 June 2020: "In contrast, the alignment of ...
(LAC) is the effective border between India and the People's Republic of China. It traverses 4,057 km along the Indian states and union territories of Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several pea ...
, Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
and Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares ...
. The border with Burma (Myanmar) extends up to along the eastern borders of India
The Republic of India shares borders with several sovereign countries; it shares land borders with China, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Bangladesh and Pakistan share both land borders as well as maritime borders, while Sri L ...
's northeastern states viz. Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares ...
, Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
, Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ...
and Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo", the self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo language means "lan ...
. Located amidst the Himalayan range, India's border with Bhutan runs . Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
and Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares ...
are the states which share the border with Bhutan. The border with Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
runs along the foothills of the Himalayas in northern India. Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
are the states which share the border with Nepal. The Siliguri Corridor
The Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken's Neck, is a stretch of land around the city of Siliguri in West Bengal, India. at the narrowest section, this geo-political and geo-economical corridor connects the eight states of northeast I ...
, narrowed sharply by the borders of Bhutan, Nepal and Bangladesh, connects peninsular India with the northeastern states.
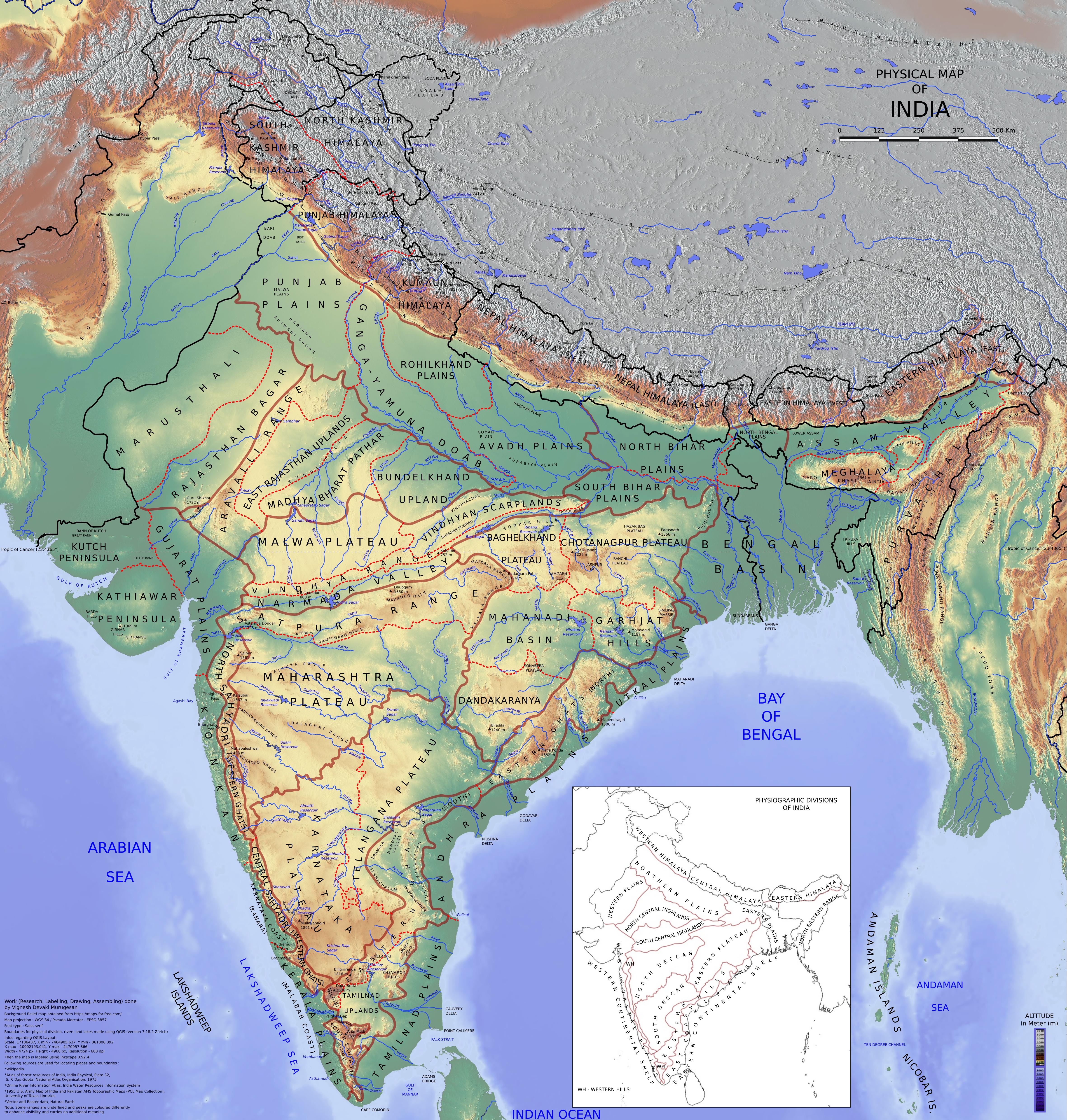
Physiographic regions

Cratons


Craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s are a specific kind of continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' be ...
made up of a top layer called platform and an older layer called basement
A basement or cellar is one or more Storey, floors of a building that are completely or partly below the storey, ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, ...
. A shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of ...
is the part of a craton where basement rock crops out of the ground, and it is relatively the older and more stable section, unaffected by plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
.Cratons of IndiaCratons of India
lyellcollection.org. The Indian Craton can be divided into five major cratons as such: * Aravalli Craton (Marwar-Mewar Craton or Western Indian Craton): Covers
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
as well as western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
. It comprises Mewar Craton in the east and Marwar Craton in the west. It is limited by the ''Great Boundary Fault'' in the east, sandy Thar Desert in the Thar desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
in the west, Indo-ganetic alluvium in the north, Son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some curren ...
- Narmada-Tapti
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujara ...
in the south. It mainly has quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tec ...
, marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
, pelite
A pelite ( Greek: ''pelos'', "clay") or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, ...
, greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke (German ''grauwacke'', signifying a grey, earthy rock) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or lit ...
and extinct volcanos exposed in Aravalli-Delhi Orogen
The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions.Mishra, D.C.; Kumar, M. Ravi. Proterozoic orogen ...
. Malani Igneous Suite is the largest in India and third largest igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
suite in the world.
* Bundelkand Craton, covers 26,00 km2 in the Bundelkhand
Bundelkhand (, ) is a geographical and cultural region and a proposed state and also a mountain range in central & North India. The hilly region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion l ...
region of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
and Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
and forms the basis of the Malwa Plateau. It is limited by the Aravalli in the west, Narmada river and Satpura range in the south, and Indo-Gantetic alluvium in the north. It is similar to the Aravali Craton, which used to be a single craton before being divided into two with the evolution of Hindoli
Hindoli is a small town in the Bundi district of Rajasthan, India. Situated in the lap of the Arawalli Hills, the town is a trade center for many small villages.
Police Station of Hindoli is honored as "Adarsh Police Thana" for maintaining low ...
and Mahakoshal belts at the margins of two cratons.
* Dharwar Craton
The Dharwar Craton is an Archean continental crust craton formed between 3.6-2.5 billion years ago ( Ga), which is located in southern India and considered as the oldest part of the Indian peninsula.
Studies in the 2010s suggest that the craton c ...
(Karnataka Craton), 3.4 - 2.6 Ga, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
- greenstone terrain covers the state of Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
and parts of eastern and southern Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
state, and forms the basis of the southern end of the Deccan Plateau. In 1886 it was divided into two tectonic blocks, namely Eastern Dharwar Craton (EDC) and Western Dharwar Craton (WDC).
* Singhbhum Craton, 4,000 km2 area which primarily covers Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
as well as parts of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
, northern Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, northern Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 35 ...
and eastern Maharashtra. It is limited by the Chhota Nagpur Plateau to the north, Eastern Ghats to the southeast, Bastar Craton to southwest and alluvium plain to the east.
* Bastar Craton (Bastar-Bhandara Craton), primarily covers Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
and forms the basis of the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. It is a remnant of 3.4-3.0 Ga old TTG gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures a ...
es of five types. It is subdivided into Kotri-Dongagarh Orogen and the Rest of Bastar Craton. It is limited by three rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
s, Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
rift in southwest, Narmada rift in northwest and Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay ...
rift in northeast.
Regions
India can be divided into six physiographic regions. They are: * Northern Mountains:Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
* Peninsular Plateau: contains mountain ranges ( Aravalli, Vindhayachal and Satpura
The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and ...
ranges), ghats (Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats) and plateaues (Malwa Plateau, Chhota Nagpur Plateau, Southern Garanulite terrain, Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
and Kutch Kathiawar plateau).
*Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
or The Northern Plains
*Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
* Coastal Plains: Eastern Ghat folds and Western Ghats folds
* Islands- The Andaman and Nicobar islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
and the Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
islands.
The Himalayas
An arc of mountains consisting of the Himalayas,Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
, and Patkai
The Pat-kai (Pron:pʌtˌkaɪ) or Patkai Bum ( Burmese: ''Kumon Taungdan'') are a series of mountains in the Indo-Myanmar border falling in the north-eastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Upper Burma region of Myanmar. The ...
ranges define the northern frontiers of the Indian subcontinent. These were formed by the ongoing tectonic plates collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates. The mountains in these ranges include some of the world's tallest mountains which act as a barrier to cold polar winds. They also facilitate the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds which in turn influence the climate in India. Rivers originating in these mountains flow through the fertile Indo–Gangetic plains. These mountains form the boundary between two biogeographic realm
A biogeographic realm or ecozone is the broadest biogeographic division of Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms. They are subdivided into bioregions, which are further subdivided into ecoregions. ...
s: the temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
Palearctic realm
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Si ...
that covers most of Eurasia, and the tropical and subtropical Indomalayan realm
The Indomalayan realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms. It extends across most of South and Southeast Asia and into the southern parts of East Asia.
Also called the Oriental realm by biogeographers, Indomalaya spreads all over the Ind ...
which includes South Asia, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and Indonesia.
 The Himalayas in India extend from the Indian-administered region of
The Himalayas in India extend from the Indian-administered region of Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
in the north to the state of Arunachal Pradesh in the east. Several Himalayan peaks in India rise above , including Kanchenjunga
Kangchenjunga, also spelled Kanchenjunga, Kanchanjanghā (), and Khangchendzonga, is the third highest mountain in the world. Its summit lies at in a section of the Himalayas, the ''Kangchenjunga Himal'', which is bounded in the west by the ...
() on the Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
–Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
border, and Nanda Devi () in the Garhwal Himalayas
The Garhwal Himalayas are mountain ranges located in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Geology
This range is also a part of Himalaya Sivalik Hills, the outer most hills of the Himalaya located in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Major peaks ...
of Uttarakhand. The snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
ranges between in Sikkim to around in Ladakh. The Himalayas act as a barrier to the frigid katabatic winds flowing down from Central Asia. Thus, northern India is kept warm or only mildly cooled during winter; in summer, the same phenomenon makes India relatively hot.
* The Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
range runs through Ladakh. The range is about in length and the most heavily glaciated
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
part of the world outside of the polar regions. The Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about , just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Kara ...
at ranks as the world's second longest glacier outside the polar regions.Measurements are from recent imagery, generally supplemented with Russian 1:200,000 scale topographic mapping as well as Jerzy Wala, ''Orographical Sketch Map: Karakoram: Sheets 1 & 2'', Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, Zurich, 1990. The southern boundary of the Karakoram is formed by the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
and Shyok
The Shyok River is a tributary of the Indus River that flows through northern Ladakh and enters Gilgit–Baltistan, spanning some .
The Shyok River originates at the Rimo Glacier, one of the tongues of Siachen Glacier. Its alignment is very ...
rivers, which separate the range from the northwestern end of the Himalayas.
*The Patkai
The Pat-kai (Pron:pʌtˌkaɪ) or Patkai Bum ( Burmese: ''Kumon Taungdan'') are a series of mountains in the Indo-Myanmar border falling in the north-eastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Upper Burma region of Myanmar. The ...
, or Purvanchal, are situated near India's eastern border with Burma. They were created by the same tectonic processes which led to the formation of the Himalayas. The physical features of the Patkai mountains are conical peaks, steep slopes and deep valleys. The Patkai ranges are not as rugged or tall as the Himalayas. There are three hill ranges that come under the Patkai: the Patkai–Bum, the Garo–Khasi
Khasi may refer to:
* Khasi people, an ethnic group of Meghalaya, India
* Khasi language, a major Austroasiatic language spoken in Meghalaya, India
* Khāṣi language, an Indo-Aryan language of Jammu and Kashmir, India
See also
* Khasi Hills
* ...
– Jaintia and the Lushai hills
The Lushai (Pron: ˌlʊˈʃaɪ) Hills (or Mizo Hills) are a mountain range in Mizoram and Manipur, India. The range is part of the Patkai range system and its highest point is 2,157 m high Phawngpui, also known as 'Blue Mountain'.
Flora and fa ...
. The Garo–Khasi range lies in Meghalaya. Mawsynram
Mawsynram () is a town in the East Khasi Hills district of Meghalaya state in Northeastern India, 69 kilometres from Shillong, the state capital. Mawsynram receives the highest rainfall in India. It is reportedly the wettest place on Earth, wi ...
, a village near Cherrapunji
Cherrapunji () or Sohra is a subdivisional town (Proposed District) East Khasi Hills district in the Indian state of Meghalaya. It is the traditional capital of ka ''hima'' Sohra (Khasi tribal kingdom).
Sohra has often been credited as being t ...
lying on the windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
side of these hills, has the distinction of being the wettest place in the world, receiving the highest annual rainfall.
The Peninsular Plateau
The main features of Indian Craton are: * Mountain ranges (clockwise from top-left) ** Aravali Range is the oldest mountain range in India, running across Rajasthan from northeast to southwest direction, extending approximately . The northern end of the range continues as isolated hills and rocky ridges intoHaryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
, ending near Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
. The highest peak in this range is Guru Shikhar at Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at abov ...
, rising to , lying near the border with Gujarat. The Aravali Range is the eroded stub of an ancient fold mountain
Fold mountains are formed by the effects of folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust. Before the development of the theory of plate tectonics and before the internal architecture of thrust belts became well understood, the te ...
system. The range rose in a Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
event called the Aravali–Delhi orogen. The range joins two of the ancient segments that make up the Indian craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
, the Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a particular area. English tra ...
segment to the northwest of the range, and the Bundelkhand segment to the southeast.
** Vindhya
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
range, lies north of Satpura range and east of Aravali range, runs across most of central India, extending . The average elevation of these hills is from and rarely goes above . They are believed to have been formed by the wastes created by the weathering of the ancient Aravali mountains. Geographically, it separates Northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a r ...
India from Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
India. The western end of the range lies in eastern Gujarat, near its border with Madhya Pradesh, and runs east and north, almost meeting the Ganges at Mirzapur
Mirzapur () is a city in Uttar Pradesh, India, 827 km from Delhi and 733 km from Kolkata, almost 91 km from Prayagraj (formally known as Allahabad) and 61 km from Varanasi. It is known for its carpets and brassware industries, and the folk ...
.  ** Satpura Range, lies south of Vindhya range and east of Aravali range, begins in eastern Gujarat near the Arabian Sea coast and runs east across
** Satpura Range, lies south of Vindhya range and east of Aravali range, begins in eastern Gujarat near the Arabian Sea coast and runs east across Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
. It extends with many peaks rising above . It is triangular in shape, with its apex at Ratnapuri and the two sides being parallel to the Tapti
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujara ...
and Narmada rivers. It runs parallel to the Vindhya Range, which lies to the north, and these two east–west ranges divide the Indo–Gangetic plain from the Deccan Plateau located north of River Narmada.
* Plateaus (clockwise from top-left)
**Malwa Plateau
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also sy ...
is spread across Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat. The average elevation of the Malwa plateau is 500 metres, and the landscape generally slopes towards the north. Most of the region is drained by the Chambal River
The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central and Northern India, and thus forms part of the greater Gangetic drainage system. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan t ...
and its tributaries; the western part is drained by the upper reaches of the Mahi River.
** Chhota Nagpur Plateau is situated in eastern India, covering much of Jharkhand and adjacent parts of Odisha, Bihar and Chhattisgarh. Its total area is approximately and is made up of three smaller plateaus—the Ranchi, Hazaribagh, and Kodarma plateaus. The Ranchi plateau is the largest, with an average elevation of . Much of the plateau is forested, covered by the Chhota Nagpur dry deciduous forests. Vast reserves of metal ores and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
have been found in the Chota Nagpur plateau. The Kathiawar
Kathiawar () is a peninsula, near the far north of India's west coast, of about bordering the Arabian Sea. It is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest and by the Gulf of Khambhat (Gulf of Cambay) in the east. In the northeast, i ...
peninsula in western Gujarat is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch and the Gulf of Khambat. The natural vegetation in most of the peninsula is xeric scrub, part of the Northwestern thorn scrub forests
The Northwestern thorn scrub forests, presently known as Aravalli west thorn scrub forests, is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of Pakistan and Northern India, stretching along the border lowlands and hills between the two countries. Once covered in ...
ecoregion.
** Southern Garanulite terrain: Covers South India especially Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
excluding western and eastern ghats.
** Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
, also called Deccan Trapps, is a large triangular plateau, bounded by the Vindhyas to the north and flanked by the Eastern and Western Ghats. The Deccan covers a total area of 1.9 million km2 (735,000-mile2). It is mostly flat, with elevations ranging from . The average elevation of the plateau is above sea level. The surface slopes from in the west to in the east. It slopes gently from west to east and gives rise to several peninsular rivers such as the Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, the Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is on ...
, the Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu d ...
and the Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay ...
which drain into the Bay of Bengal. This region is mostly semi-arid as it lies on the leeward side of both Ghats. Much of the Deccan is covered by thorn scrub forest scattered with small regions of deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
broadleaf forest. Climate in the Deccan ranges from hot summers to mild winters.
** Kutch Kathiawar plateau is located in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
state.
 * Ghats
** Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountains run along the western edge of India's
* Ghats
** Western Ghats or Sahyadri mountains run along the western edge of India's Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
and separate it from a narrow coastal plain along the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
. The range runs approximately from south of the Tapti River
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujara ...
near the Gujarat–Maharashtra border and across Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu to the southern tip of the Deccan peninsula. The average elevation is around . Anai Mudi
Anamudi is a mountain located in Ernakulam district and Idukki district of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the highest peak in the Western Ghats and in South India, at an elevation of and a topographic prominence of . The name Anamudi li ...
in the Anaimalai Hills in Kerala is the highest peak in the Western Ghats.
** Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and ...
are a discontinuous range of mountains, which have been eroded and quadrisected by the four major rivers of southern India, the Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is on ...
, and Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu d ...
. These mountains extend from West Bengal to Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, along the coast and parallel to the Bay of Bengal. Though not as tall as the Western Ghats, some of its peaks are over in height. The Nilgiri hills in Tamil Nadu lies at the junction of the Eastern and Western Ghats. Arma Konda
Arma Konda or Sitamma Konda, is a mountain peak in the northern part of the Eastern Ghats and located in Godavari River basin. It is located in the Madugula Konda sub-range north of Paderu village in Andhra Pradesh, India.
Highest point in An ...
() in Andhra Pradesh is the tallest peak in Eastern Ghats.
Indo-Gangetic plain
alluvial plain
An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smal ...
s dominated by three main rivers, the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
, and Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
. They run parallel to the Himalayas, from Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
in the west to Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
in the east, and drain most of northern and eastern India. The plains encompass an area of . The major rivers in this region are the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra along with their main tributaries—Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
, Chambal, Gomti, Ghaghara
Ghaghara, also called Karnali, is a perennial trans-boundary river originating on the Tibetan Plateau near Lake Manasarovar. The Karnali cuts through the Himalayas in Nepal and joins the Sharda River at Brahmaghat in India. Together they f ...
, Kosi
KOSI (101.1 FM) is a commercial radio station in Denver, Colorado. KOSI is owned by Salt Lake City–based Bonneville International and airs an adult contemporary music format. Its studios and offices are located on East Orchard Road in Green ...
, Sutlej
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the In ...
, Ravi, Beas
Beas is a riverfront town in the Amritsar district of the Indian state of Punjab. Beas lies on the banks of the Beas River. Beas town is mostly located in revenue boundary of Budha Theh with parts in villages Dholo Nangal and Wazir Bhullar. ...
, Chenab
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul ...
, and Tista—as well as the rivers of the Ganges Delta, such as the Meghna.
The great plains are sometimes classified into four divisions:
* The Bhabar
Bhabar or Bhabhar ( Kumaoni: bhābar) is a region south of the Lower Himalayas and the Sivalik Hills in Kumaon, India, containing some of the largest cities of Kumaon, Haldwani and Ramnagar, both in Nainital District. It is the alluvial apron ...
belt is adjacent to the foothills of the Himalayas and consists of boulders and pebbles which have been carried down by streams. As the porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measur ...
of this belt is very high, the streams flow underground. The Bhabar is generally narrow with its width varying between .
* The Tarai belt lies south of the adjacent Bhabar region and is composed of newer alluvium. The underground streams reappear in this region. The region is excessively moist and thickly forested. It also receives heavy rainfall throughout the year and is populated with a variety of wildlife.
* The Bangar belt consists of older alluvium and forms the alluvial terrace of the flood plains. In the Gangetic plains, it has a low upland covered by laterite deposits.
* The Khadar belt lies in lowland areas after the Bangar belt. It is made up of fresh newer alluvium which is deposited by the rivers flowing down the plain.
The Indo-Gangetic belt is the world's most extensive expanse of uninterrupted alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. ...
formed by the deposition of silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
by the numerous rivers. The plains are flat making it conducive for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
through canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface f ...
s. The area is also rich in ground water
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
sources. The plains are one of the world's most intensely farmed areas. The main crops grown are rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, which are grown in rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
. Other important crops grown in the region include maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
and cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
. The Indo-Gangetic plains rank among the world's most densely populated areas.
Thar Desert
 The Thar Desert (also known as ''the deserts'') is by some calculations the world's seventh largest desert, by some others the tenth. It forms a significant portion of western India and covers an area of . The desert continues into Pakistan as the
The Thar Desert (also known as ''the deserts'') is by some calculations the world's seventh largest desert, by some others the tenth. It forms a significant portion of western India and covers an area of . The desert continues into Pakistan as the Cholistan Desert
The Cholistan Desert ( ur, ; Punjabi: ), also locally known as Rohi (), is a desert in the southern part of Punjab, Pakistan that forms part of the Greater Thar Desert, which extends to Sindh province and the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is on ...
. Most of the Thar Desert is situated in Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
, covering 61% of its geographic area.
About 10 percent of this region consists of sand dunes, and the remaining 90 percent consist of craggy rock forms, compacted salt-lake bottoms, and interdunal and fixed dune areas. Annual temperatures can range from in the winter to over during the summer. Most of the rainfall received in this region is associated with the short July–September southwest monsoon that brings of precipitation. Water is scarce and occurs at great depths, ranging from below the ground level. Rainfall is precarious and erratic, ranging from below in the extreme west to eastward. The only river in this region is Luni. The soils of the arid region are generally sandy to sandy-loam in texture. The consistency and depth vary as per the topographical features. The low-lying loams are heavier may have a hard pan of clay, calcium carbonate or gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
.
In western India, the Kutch region in Gujarat and Koyna in Maharashtra are classified as a Zone IV region (high risk) for earthquakes. The Kutch city of Bhuj
Bhuj () is a Municipality and District Headquarters of Kutch District in the state of Gujarat, India.
Etymology
According to legend, Kutch was ruled by the Nāga chieftains in the past. Sagai, a queen of Sheshapattana, who was married to Kin ...
was the epicentre of the 2001 Gujarat earthquake
The 2001 Gujarat earthquake, also known as the Bhuj earthquake, occurred on 26 January, India's 52nd Republic Day, at . The epicentre was about 9 km south-southwest of the village of Chobari in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District of Gujarat ...
, which claimed the lives of more than 1,337 people and injured 166,836 while destroying or damaging near a million homes. The 1993 Latur earthquake in Maharashtra killed 7,928 people and injured 30,000. Other areas have a moderate to low risk of an earthquake occurring.
Coastal plains and ghats
Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and ...
and the oceanic boundary of India. It stretches from Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
in the south to West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
in the east. The Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay ...
, Godavari, Kaveri, and Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is on ...
rivers drain these plains. The temperature in the coastal regions often exceeds , and is coupled with high levels of humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
. The region receives both the northeast monsoon and southwest monsoon rains. The southwest monsoon splits into two branches, the Bay of Bengal branch and the Arabian Sea branch. The Bay of Bengal branch moves northwards crossing northeast India in early June. The Arabian Sea branch moves northwards and discharges much of its rain on the windward side of Western Ghats. Annual rainfall in this region averages between . The width of the plains varies between . The plains are divided into six regions—the Mahanadi delta, the southern Andhra Pradesh plain, the Krishna-Godavari deltas, the Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
coast, the Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an ...
, and sandy coastal.
The Western Coastal Plain is a narrow strip of land sandwiched between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea, ranging from in width. It extends from Gujarat in the north and extends through Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala. Numerous rivers and backwaters inundate the region. Mostly originating in the Western Ghats, the rivers are fast-flowing, usually perennial, and empty into estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
. Major rivers flowing into the sea are the Tapti, Narmada, Mandovi and Zuari
The Zuari River ''Zuvari,'' pronounced )
is the largest river in the state of Goa, India. It is a tidal river which originates at Hemad-Barshem in the Western Ghats. The Zuari is also referred to as the Aghanashani in the interior regions. It ...
. Vegetation is mostly deciduous, but the Malabar Coast moist forests constitute a unique ecoregion. The Western Coastal Plain can be divided into two parts, the Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
and the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing ...
.
Islands
TheLakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
are India's two major island formations and are classified as union territories.
The Lakshadweep Islands lie off the coast of Kerala in the Arabian sea with an area of . They consist of twelve atolls, three reefs, and five submerged banks, with a total of about 35 islands and islets.
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located between 6° and 14° north latitude and 92° and 94° east longitude. They consist of 572 islands, lying in the Bay of Bengal near the Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
coast running in a north–south axis for approximately 910 km. They are located from Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
(Calcutta) and from Cape Negrais in Burma. The territory consists of two island groups, the Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between t ...
and the Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of the Indian ...
. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands consist of 572 islands which run in a north–south axis for around 910 km. The Andaman group has 325 islands which cover an area of 6,170 km2 (2,382 sq mi) while the Nicobar group has only 247 islands with an area of 1,765 km2 (681 sq mi). India's only active volcano, Barren Island is situated here. It last erupted in 2017. The Narcondum is a dormant volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
and there is a mud volcano
A mud volcano or mud dome is a landform created by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. Several geological processes may cause the formation of mud volcanoes. Mud volcanoes are not true igneous volcanoes as they do not produce ...
at Baratang. Indira Point, India's southernmost land point, is situated in the Nicobar islands at 6°45’10″N and 93°49’36″E, and lies just from the Indonesian island of Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, to the southeast. The highest point is Mount Thullier at .
Other significant islands in India include Diu, a former Portuguese colony; Majuli
Mājuli or Majuli () is a river island in the Brahmaputra River, Assam and in 2016 it became the first island to be made a district in India. It had an area of at the beginning of the 20th century, but having lost significantly to erosion it c ...
, a river island of the Brahmaputra; Elephanta in Bombay Harbour
Mumbai Harbour (also English language, English; Bombay Harbour or Front Bay, Marathi language, Marathi''Mumba'ī bandar''), is a natural deep-water harbour in the southern portion of the Ulhas River estuary. The narrower, northern part of the es ...
; and Sriharikota
Sriharikota is a Barrier island off the Bay of Bengal coast located in the Shar Project settlement of Tirupati district in Andhra Pradesh, India. It houses the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, one of the two satellite launch centres in India (the ...
, a barrier island
Barrier islands are coastal landforms and a type of dune system that are exceptionally flat or lumpy areas of sand that form by wave and tidal action parallel to the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a ...
in Andhra Pradesh. Salsette Island
Salsette Island is an island in Konkan division of the state of Maharashtra on India's west coast. Administratively known as Greater Mumbai, the city district of Mumbai, Mumbai Suburban District, Mira Bhayander and a portion of Thane lie wi ...
is India's most populous island on which the city of Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
(Bombay) is located. Forty-two islands in the Gulf of Kutch constitute the Marine National Park.
Natural resources
Ecological resources
Water bodies
India has around 14,500 km of inland navigable waterways. There are twelve rivers which are classified as major rivers, with the total catchment area exceeding . All major rivers of India originate from one of the three main watersheds: * The Himalaya and the Karakoram ranges * Vindhya and Satpura range in central India * Sahyadri or Western Ghats in western India The Himalayan river networks are snow-fed and have a perennial supply throughout the year. The other two river systems are dependent on the monsoons and shrink into rivulets during the dry season. The Himalayan rivers that flow westward intoPunjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
are the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, Jhelum
Jhelum (Punjabi and ur, ) is a city on the east bank of the Jhelum River, which is located in the district of Jhelum in the north of Punjab province, Pakistan. It is the 44th largest city of Pakistan by population. Jhelum is known for p ...
, Chenab
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul ...
, Ravi, Beas
Beas is a riverfront town in the Amritsar district of the Indian state of Punjab. Beas lies on the banks of the Beas River. Beas town is mostly located in revenue boundary of Budha Theh with parts in villages Dholo Nangal and Wazir Bhullar. ...
, and Sutlej
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the In ...
.
 The
The Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
-Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
- Meghana system has the largest catchment area of about . The Ganges Basin
The Ganges Basin is a part of the Ganges-Brahmaputra- Meghna (GBM) basin draining 1,999,000 square kilometres in Tibet, Nepal, India and Bangladesh. To the north, the Himalaya or lower parallel ranges beyond form the Ganges-Brahmaputra divide. ...
alone has a catchment of about . The Ganges originates from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand. It flows southeast, draining into the Bay of Bengal. (The Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
and Gomti rivers also arise in the western Himalayas and join the Ganges in the plains. The Brahmaputra originates in Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, where it is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River
The Yarlung Tsangpo, also called Yarlung Zangbo () is the upper stream of the Brahmaputra River located in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is the longest river of Tibet and the fifth longest in China. The upper section is also called D ...
) (or "Tsangpo"). It enters India in the far-eastern state of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares ...
, then flows west through Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
. The Brahmaputra merges with the Ganges in Bangladesh, where it is known as the Jamuna River.Brahmaputra RiverEncyclopædia Britannica The Chambal, another tributary of the Ganges, via the Yamuna, originates from the Vindhya-Satpura watershed. The river flows eastward. Westward-flowing rivers from this watershed are the Narmada and Tapi, which drain into the Arabian Sea in Gujarat. The river network that flows from east to west constitutes 10% of the total outflow.
 (The Western Ghats are the source of all Deccan rivers, which include the through
(The Western Ghats are the source of all Deccan rivers, which include the through Godavari River
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
, Krishna River and Kaveri River
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu d ...
, all draining into the Bay of Bengal. These rivers constitute 20% of India's total outflow).
The heavy southwest monsoon rains cause the Brahmaputra and other rivers to distend their banks, often flooding surrounding areas. Though they provide rice paddy farmers with a largely dependable source of natural irrigation and fertilisation, such floods have killed thousands of people and tend to cause displacements of people in such areas.
Major gulfs include the Gulf of Cambay, Gulf of Kutch
The Gulf of Kutch is located between the peninsula regions of Kutch and Saurashtra, bounded in the state of Gujarat that borders Pakistan. It opens towards the Arabian Sea facing the Osman Gulf.
It is about 50 km wide at the entrance bef ...
, and the Gulf of Mannar
The Gulf of Mannar ( ) is a large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean with an average depth of .
. Straits include the Palk Strait
The Palk Strait ( ta, பாக்கு நீரிணை ''Pākku Nīriṇai'', si, පෝක් සමුද්ර සන්ධිය ''Pok Samudra Sandhiya'') is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Jaffna Distri ...
, which separates India from Sri Lanka; the Ten Degree Channel
The Ten Degree Channel is a channel that separates the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands from each other in the Bay of Bengal. The two sets of islands together form the Indian Union Territory (UT) of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. This channel i ...
, which separates the Andamans from the Nicobar Islands; and the Eight Degree Channel, which separates the Laccadive and Amindivi Islands from the Minicoy Island to the south. Important capes include the Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
(formerly called Cape Comorin), the southern tip of mainland India; Indira Point, the southernmost point in India (on Great Nicobar
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra.
History
The Nicobar Island has been well known to Indian mariners since the time of the seafaring Cholas https://www.britannica.com/place/Nicob ...
Island); Rama's Bridge, and Point Calimere. The Arabian Sea lies to the west of India, the Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean lie to the east and south, respectively. Smaller seas include the Laccadive Sea
The Laccadive Sea or Lakshadweep Sea is a body of water bordering India (including its Lakshadweep islands), the Maldives, and Sri Lanka. It is located to the southwest of Karnataka, to the west of Kerala and to the south of Tamil Nadu. This war ...
and the Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated fro ...
. There are four coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of Colony (biology), colonies of coral polyp (zoology), polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, wh ...
s in India, located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Gulf of Mannar, Lakshadweep, and the Gulf of Kutch. Important lakes include Sambhar Lake, the country's largest saltwater lake in Rajasthan, Vembanad Lake
Vembanad is the longest lake in India, as well as the largest lake in the state of Kerala. The lake has an area of 230 square kilometers and a maximum length of 96.5 km. Spanning several districts in the state of Kerala, it is known as Ve ...
in Kerala, Kolleru Lake
Kolleru Lake is one of the largest freshwater lakes in India located in state of Andhra Pradesh and forms the largest shallow freshwater lake in Asia (with 245 km2 of lake area and 302 km2 of total Ramsar designated wetland), 15 kilometers aw ...
in Andhra Pradesh, Loktak Lake
, image =
, caption = Different scenes of the Loktak lake of Manipur
, alt = View of Loktak Lake and Phumdis
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Manipur
, coords ...
in Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ...
, Dal Lake
Dal is a lake in Srinagar, the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is an urban lake, the second largest lake in Jammu and Kashmir, and the most visited place in Srinagar by tourists and locals. It is integral to tourism and recreation in t ...
in Kashmir, Chilka Lake (lagoon lake) in Odisha, and Sasthamkotta Lake
Sasthamcotta Lake or Sasthamkotta Lake, also categorized as a wetland, is the largest fresh water lake in Kerala, a state of India on the south of the West Coast. The lake is named after the ancient Sastha temple (a pilgrimage centre) located ...
in Kerala.
Wetlands
 India's
India's wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (Anoxic waters, anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in t ...
ecosystem is widely distributed from the cold and arid located in the Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir, and those with the wet and humid climate of peninsular India. Most of the wetlands are directly or indirectly linked to river networks. The Indian government has identified a total of 71 wetlands for conservation and are part of sanctuaries and national parks. India Yearbook, p. 306 Mangrove forests are present all along the Indian coastline in sheltered estuaries, creeks, backwaters, salt marshes and mudflats. The mangrove area covers a total of , India Yearbook, p. 309 which comprises 7% of the world's total mangrove cover. Prominent mangrove covers are located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Sundarbans
Sundarbans (pronounced ) is a mangrove area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Padma, Brahmaputra and Meghna Rivers in the Bay of Bengal. It spans the area from the Baleswar River in Bangladesh's division of Khulna to the Hooghly R ...
delta, the Gulf of Kutch
The Gulf of Kutch is located between the peninsula regions of Kutch and Saurashtra, bounded in the state of Gujarat that borders Pakistan. It opens towards the Arabian Sea facing the Osman Gulf.
It is about 50 km wide at the entrance bef ...
and the deltas of the Mahanadi, Godavari and Krishna rivers. Parts of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Kerala also have large mangrove covers.
The Sundarbans delta is home to the largest mangrove forest in the world. It lies at the mouth of the Ganges and spreads across areas of Bangladesh and West Bengal. The Sundarbans is a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, but is identified separately as the Sundarbans (Bangladesh) and the Sundarbans National Park (India). The Sundarbans are intersected by a complex network of tidal waterways, mudflats and small islands of salt-tolerant mangrove forests. The area is known for its diverse fauna, being home to a large variety of species of birds, spotted deer, crocodiles and snakes. Its most famous inhabitant is the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
. It is estimated that there are now 400 Bengal tigers and about 30,000 spotted deer in the area.
The Rann of Kutch is a marshy region located in northwestern Gujarat and the bordering Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
province of Pakistan. It occupies a total area of . The region was originally a part of the Arabian Sea. Geologic forces such as earthquakes resulted in the damming up of the region, turning it into a large saltwater lagoon. This area gradually filled with silt thus turning it into a seasonal salt marsh. During the monsoons, the area turn into a shallow marsh, often flooding to knee-depth. After the monsoons, the region turns dry and becomes parched.
Economic resources
Renewable water resources
India's total renewable water resources are estimated at 1,907.8 km3 a year. Its annual supply of usable and replenshable groundwater amounts to 350 billion cubic metres. Only 35% of groundwater resources are being utilised. About 44 million tonnes of cargo is moved annually through the country's major rivers and waterways. Groundwater supplies 40% of water in India's irrigation canals. 56% of the land is arable and used for agriculture. Black soils are moisture-retentive and are preferred for dry farming and growing cotton, linseed, etc. Forest soils are used for tea and coffee plantations. Red soils have a wide diffusion of iron content.Mineral oil
Most of India's estimated in oil reserves are located in the Mumbai High, upper Assam, Cambay, the Krishna-Godavari and Cauvery basins. India possesses about seventeen trillion cubic feet ofnatural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
in Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and Odisha. Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
is mined in Andhra Pradesh. India has 400 medium-to-high enthalpy thermal springs for producing geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pr ...
in seven "provinces"—the Himalayas, Sohana, Cambay, the Narmada-Tapti delta, the Godavari delta and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (specifically the volcanic Barren Island.)
Minerals and ores
India is the world's biggest producer of mica blocks and mica splittings. India ranks second amongst the world's largest producers of barite and chromite. The Pleistocene system is rich in minerals. India is the third-largest coal producer in the world and ranks fourth in the production ofiron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the ...
. It is the fifth-largest producer of bauxite, second largest of crude steel as of February 2018 replacing Japan, the seventh-largest of manganese ore and the eighth-largest of aluminium. India has significant sources of titanium ore, diamonds and limestone. India possesses 24% of the world's known and economically viable thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
, which is mined along shores of Kerala. Gold had been mined in the now-defunct Kolar Gold Fields
Kolar Gold Fields (K.G.F.) is a mining region in K.G.F. taluk (township), Kolar district, Karnataka, India. It is headquartered in Robertsonpet, where employees of Bharat Gold Mines Limited (BGML) and BEML Limited (formerly Bharat Earth Mov ...
in Karnataka.
Climate
alpine tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets ...
and glaciers in the north, and humid tropical regions supporting rainforests in the southwest and the island territories. The nation has four seasons: winter (January–February), summer (March–May), a monsoon (rainy) season (June–September) and a post-monsoon period (October–December).
The Himalayas act as a barrier to the frigid katabatic winds flowing down from Central Asia. Thus, northern India is kept warm or only mildly cooled during winter; in summer, the same phenomenon makes India relatively hot. Although the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towa ...
—the boundary between the tropics and subtropics—passes through the middle of India, the whole country is considered to be tropical.
Summer lasts between March and June in most parts of India. Temperatures can exceed during the day. The coastal regions exceed coupled with high levels of humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
. In the Thar desert area temperatures can exceed . The rain-bearing monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
clouds are attracted to the low-pressure system created by the Thar Desert. The southwest monsoon splits into two arms, the Bay of Bengal arm and the Arabian Sea arm. The Bay of Bengal arm moves northwards crossing northeast India in early June. The Arabian Sea arm moves northwards and deposits much of its rain on the windward side of Western Ghats. Winters in peninsula India see mild to warm days and cool nights. Further north the temperature is cooler. Temperatures in some parts of the Indian plains sometimes fall below freezing. Most of northern India is plagued by fog during this season. The highest temperature recorded in India was in Phalodi, Rajasthan. . And the lowest was in Dras, Jammu and Kashmir.
Geology
Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
formations of Cudappah and Vindhyan systems are spread out over the eastern and southern states. A small part of this period is spread over western and central India. The Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
formations from the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian and Devonian system are found in the Western Himalaya region in Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. The Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flo ...
formation is seen over most of the northern Deccan; they are believed to be the result of sub-aerial In natural science, subaerial (literally "under the air"), has been used since 1833,Subaerial
in the Merriam ...
volcanic activity. The Trap soil is black in colour and conducive to agriculture. The Carboniferous system, Permian System and Triassic systems are seen in the western Himalayas. The Jurassic system is seen in the western Himalayas and Rajasthan.
in the Merriam ...
Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
imprints are seen in parts of Manipur, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and along the Himalayan belt. The Cretaceous system is seen in central India in the Vindhyas and part of the Indo-Gangetic plains. The Gondwana system is seen in the Narmada River area in the Vindhyas and Satpuras. The Eocene system is seen in the western Himalayas and Assam. Oligocene formations are seen in Kutch and Assam. The Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
system is found over central India. The Andaman and Nicobar Island are thought to have been formed in this era by volcanoes. The Himalayas were formed by the convergence and deformation of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian Plates. Their continued convergence raises the height of the Himalayas by one centimetre each year.
Soils in India can be classified into eight categories: alluvial, black, red, laterite, forest, arid and desert, saline and alkaline and peaty and organic soils. Alluvial soil constitute the largest soil group in India, constituting 80% of the total land surface. It is derived from the deposition of silt carried by rivers and are found in the Great Northern plains from Punjab to the Assam valley. Alluvial soil are generally fertile but they lack nitrogen and tend to be phosphoric. National Disaster Management Authority says that 60% of Indian landmass is prone to earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s and 8% susceptible to cyclone risks.
Black soil are well developed in the Deccan lava region of Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh. These contain high percentage of clay and are moisture retentive. Red soils are found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka plateau, Andhra plateau, Chota Nagpur plateau and the Aravallis. These are deficient in nitrogen, phosphorus and humus. Laterite soils are formed in tropical regions with heavy rainfall. Heavy rainfall results in leaching out all soluble material of top layer of soil. These are generally found in Western ghats, Eastern ghats and hilly areas of northeastern states that receive heavy rainfall. Forest soils occur on the slopes of mountains and hills in Himalayas, Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats. These generally consist of large amounts of dead leaves and other organic matter called humus.
See also
*Borders of India
The Republic of India shares borders with several sovereign countries; it shares land borders with China, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Bangladesh and Pakistan share both land borders as well as maritime borders, while Sri L ...
* Climate change in India
* Disputed territories of India
* List of extreme points of India
The extreme points of India include the coordinates that are further north, south, east or west than any other location in India; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point claimed by India is in territory disp ...
* Exclusive economic zone of India
* List of disputed territories of India
* Outline of India
* Lists of villages in India
References
Bibliography
*Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * {{Geography of Asia Articles containing video clips de:Indien#Geographie und Landesnatur