Geography of Guadeloupe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


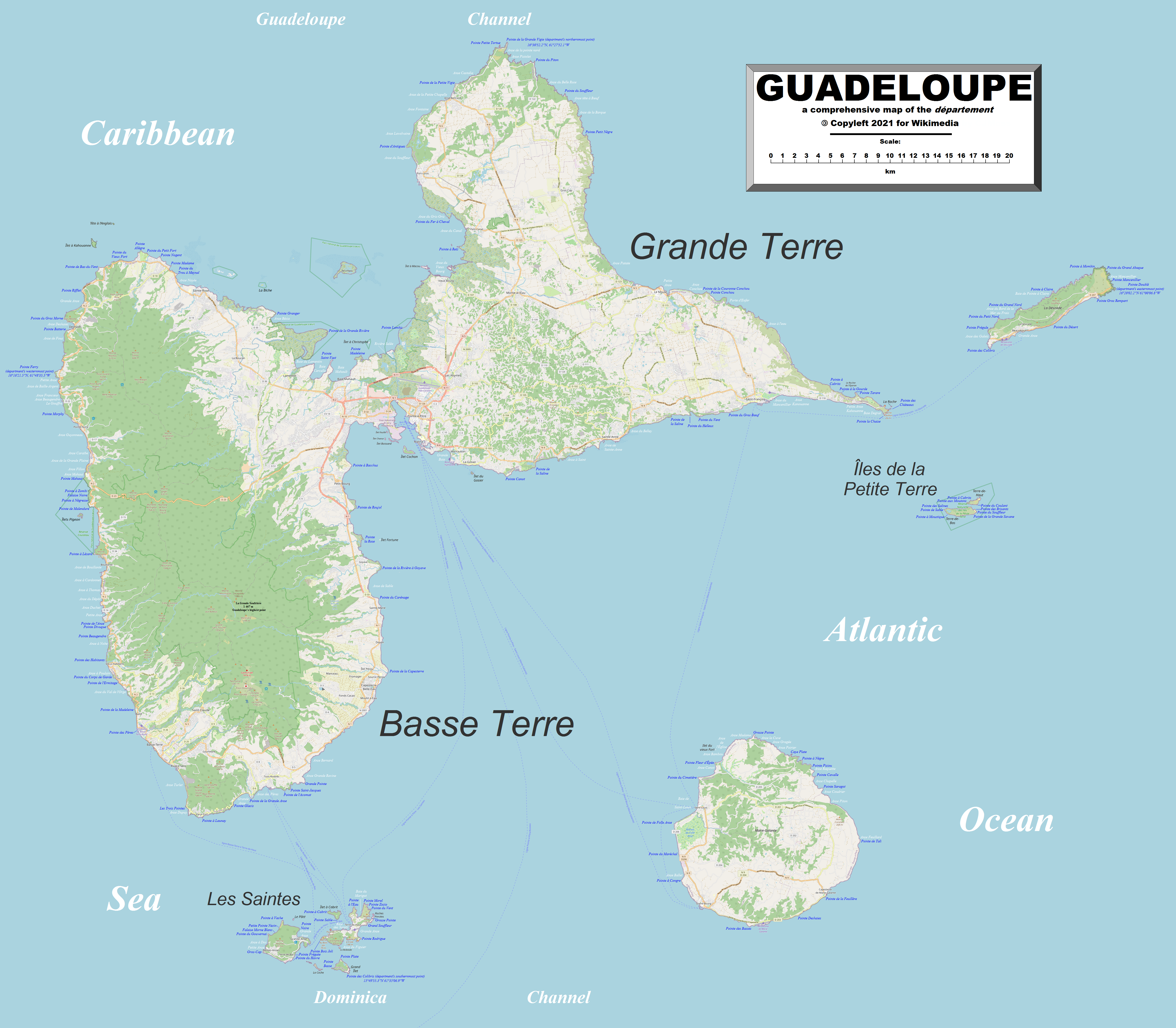 Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as
Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as


 Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as
Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s and rocks situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
meets the western Atlantic Ocean. It is located in the Leeward Islands in the northern part of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
, a partly volcanic island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
. To the north lie Antigua and Barbuda and the British Overseas Territory of Montserrat, with Dominica lying to the south.
The two main islands are Basse-Terre (west) and Grande-Terre (east), which form a butterfly shape as viewed from above, the two 'wings' of which are separated by the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin, and Petit Cul-de-Sac Marin. More than half of Guadeloupe's land surface consists of the 847.8 km2 Basse-Terre. The island is mountainous, containing such peaks as Mount Sans Toucher (4,442 feet; 1,354 metres) and Grande Découverte (4,143 feet; 1,263 metres), culminating in the active volcano La Grande Soufrière
La Grande Soufrière ( en, "big sulfur outlet"), is an active stratovolcano on the French island of Basse-Terre, in Guadeloupe. It is the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles, rising 1,467 m high.
The last magmatic eruption was in 1 ...
, the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
with an elevation of . In contrast Grande-Terre is mostly flat, with rocky coasts to the north, irregular hills at the centre, mangrove at the southwest, and white sand beaches sheltered by coral reefs
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
along the southern shore. This is where the main tourist resorts are found.
Marie-Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 ...
is the third-largest island, followed by La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France.
History
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian p ...
, a north-east slanted limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
plateau, the highest point of which is . To the south lies the Îles de Petite-Terre, which are two islands (Terre de Haut and Terre de Bas) totalling 2 km2.
Les Saintes is an archipelago of eight islands of which two, Terre-de-Bas
Terre-de-Bas (; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Tèdéba) is a commune in the French overseas department and region of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. Terre-de-Bas is made up of Terre-de-Bas Island and several uninhabited islands and islets ...
and Terre-de-Haut
Terre-de-Haut (; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Tèdého) is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe, including Terre-de-Haut Island and a few other small uninhabited islands of the archipelago (''les Roches Percées''; ''Îlet ...
are inhabited. The landscape is similar to that of Basse-Terre, with volcanic hills and irregular shoreline with deep bays.
There are numerous other smaller islands, most notably Tête à l'Anglais, Îlet à Kahouanne, Îlet à Fajou, Îlet Macou, Îlet aux Foux, Îlets de Carénage, La Biche, Îlet Crabière, Îlets à Goyaves, Îlet à Cochons, Îlet à Boissard, Îlet à Chasse and Îlet du Gosier.
Geology
Basse-Terre is a volcanic island. The Lesser Antilles are at the outer edge of theCaribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America.
Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders ...
, and Guadeloupe is part of the outer arc of the Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc
The Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc is a volcanic arc that forms the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Plate. It is part of a subduction zone, also known as the Lesser Antilles subduction zone, where the oceanic crust of the North American Plate i ...
. Many of the islands were formed as a result of the subduction of oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic ...
of the Atlantic Plate under the Caribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America.
Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders ...
in the Lesser Antilles subduction zone
The Lesser Antilles subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary on the seafloor along the eastern margin of the Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc. In this subduction zone, oceanic crust of the South American Plate is being subducted under the Cari ...
. This process is ongoing and is responsible for volcanic and earthquake activity in the region. Guadeloupe was formed from multiple volcanoes, of which only La Grande Soufrière is not extinct. Its last eruption was in 1976, and led to the evacuation of the southern part of Basse-Terre. 73,600 people were displaced throughout three and a half months following the eruption.
K–Ar dating
Potassium–argon dating, abbreviated K–Ar dating, is a radiometric dating method used in geochronology and archaeology. It is based on measurement of the product of the radioactive decay of an isotope of potassium (K) into argon (Ar). Potassium ...
indicates that the three northern massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a ...
s on Basse-Terre Island
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the tw ...
are 2.79 million years old. Sections of volcanoes collapsed and eroded within the last 650,000 years, after which the Sans Toucher volcano grew in the collapsed area. Volcanoes in the north of Basse-Terre Island mainly produced andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predo ...
and basaltic andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central Amer ...
. There are several beaches of dark or "black" sand.
La Désirade, east of the main islands, has a basement from the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
, overlaid with thick limestones
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when t ...
from the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Quaternary periods.
Grande-Terre and Marie-Galante have basements probably composed of volcanic units of

 With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as mahogany,
With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as mahogany, 
 The Guadalupe National Park was created on 20 February 1989. In 1992, under the auspices of
The Guadalupe National Park was created on 20 February 1989. In 1992, under the auspices of
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
to Oligocene, but there are no visible outcrops. On Grande-Terre, the overlying carbonate platform
A carbonate platform is a sedimentary body which possesses topographic relief, and is composed of autochthonic calcareous deposits. Platform growth is mediated by sessile organisms whose skeletons build up the reef or by organisms (usually micr ...
is 120 metres thick.
Climate
The islands are part of the Leeward Islands, so called because they are downwind of the prevailingtrade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
s, which blow out of the northeast. This was significant in the days of sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
s. Grande-Terre is so named because it is on the eastern, or windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
side, exposed to the Atlantic winds. Basse-Terre is so named because it is on the leeward south-west side and sheltered from the winds. Guadeloupe has a tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
tempered by maritime influences and the Trade Winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
. There are two seasons, the dry season called "Lent" from January to June, and the wet season called "winter", from July to December.

Tropical cyclones and storm surges
Located in a very exposed region, Guadeloupe and its dependencies have to face many cyclones. The deadliest hurricane to hit Guadeloupe was the Pointe-à-Pitre hurricane of 1776, which killed at least 6,000 people. On 16 September 1989, Hurricane Hugo caused severe damage to the islands of the archipelago and left a deep mark on the memory of the local inhabitants. In 1995, three hurricanes (Iris, Luis and Marilyn) hit the archipelago in less than three weeks. Some of the deadliest hurricanes that have hit Guadeloupe are the following: In the 20th century: 12 September 1928: 1928 Okeechobee hurricane; 11 August 1956: Hurricane Betsy; 22 August 1964:Hurricane Cleo
Hurricane Cleo was the strongest tropical cyclone of the 1964 Atlantic hurricane season. It was the third named storm, first hurricane, and first major hurricane of the season. Cleo was one of the longest-lived storms of the season. This compa ...
; 27 September 1966: Hurricane Inez
Hurricane Inez was a powerful major hurricane that affected the Caribbean, Bahamas, Florida, and Mexico in 1966. It was the first storm on record to affect all of those areas. It originated from a tropical wave over Africa, and became a tropical ...
; 16–17 September 1989: Hurricane Hugo; 14–15 September 1995: Hurricane Marilyn
Hurricane Marilyn was the most powerful hurricane to strike the Virgin Islands since Hurricane Hugo of 1989, and the third such tropical cyclone in roughly a two-week time span to strike or impact the Leeward Islands, the others being Hurricane ...
.
In the 21st century: 6 September 2017: Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two ...
; 18–19 September 2017: Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Category 5 hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the worst natural disaster in recorded history to affect ...
.
Wildlife
Flora
 With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as mahogany,
With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as mahogany, ironwood
Ironwood is a common name for many woods or plants that have a reputation for hardness, or specifically a wood density that is heavier than water (approximately 1000 kg/m3, or 62 pounds per cubic foot), although usage of the name ironwood in E ...
and chestnut trees. Mangrove swamps line the Salée River. Much of the forest on Grande-Terre has been cleared, with only a few small patches remaining.
Between 300 and 1,000 m of altitude, the rainforest that covers a large part of the island of Basse-Terre develops. There we find the white gum tree, the acomat-boucan or chestnut tree, the marbri or bois-bandé or the oleander; shrubs and herbaceous plants such as the mountain palm, the balisier or ferns; many epiphytes: bromeliads
The Bromeliaceae (the bromeliads) are a family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, ...
, philodendrons, orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
and lianas
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a t ...
. Above 1,000 m, the humid savannah develops, composed of mosses, lichens, sphagnum or more vigorous plants such as mountain mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
, high altitude violet or mountain thyme.
The dry forest
Dry or dryness most often refers to:
* Lack of rainfall, which may refer to
**Arid regions
**Drought
* Dry or dry area, relating to legal prohibition of selling, serving, or imbibing alcoholic beverages
* Dry humor, deadpan
* Dryness (medical)
* ...
occupies a large part of the islands of Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, Les Saintes, La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France.
History
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian p ...
and also develops on the leeward coast of Basse-Terre. The coastal forest is more difficult to develop because of the nature of the soil (sandy, rocky), salinity, sunshine and wind and is the environment where the sea grape, the mancenilla (a very toxic tree whose trunk is marked with a red line), the icaquier or the Coconut tree grow. On the cliffs
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on co ...
and in the Arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
zones are found cacti such as the cactus-cigar (Cereus), the prickly pear, the chestnut cactus, the "Tête à l'anglais" cactus and the aloes.
The Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
forest that borders some of Guadalupe's coasts is structured in three levels, from the closest to the sea to the farthest. On the first level are the red mangroves; on the second, about ten metres from the sea, the black mangroves form the shrubby mangrove; on the third level the white mangroves form the tall mangrove. Behind the mangrove, where the tide and salt do not penetrate, a swamp forest sometimes develops, unique in Guadeloupe. The representative species of this environment is the Mangrove-medaille.
Fauna
Few terrestrial mammals, aside from bats andraccoons
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of . ...
, are native to the islands. The introduced Javan mongoose
The Javan mongoose (''Urva javanica'') is a mongoose species native to Southeast Asia.
Taxonomy
''Ichneumon javanicus'' was the scientific name proposed by Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire in 1818. It was later classified in the genus ''Herpestes' ...
is also present on Guadeloupe. Bird species include the endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
purple-throated carib
The purple-throated carib (''Eulampis jugularis'') is a species of hummingbird in the subfamily Polytminae. It is resident on most of the islands of the Lesser Antilles and has occurred as a vagrant both further north and south.HBW and BirdLif ...
and the Guadeloupe woodpecker. The waters of the islands support a rich variety of marine life.
However, by studying 43,000 bone remains from six islands in the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
, 50 to 70% of snakes and lizards on the Guadeloupe Islands became extinct after European colonists arrived, who had brought with them mammals such as cats, mongooses, rats, and raccoons, which might have preyed upon the native reptiles.
Environmental preservation
In recent decades, Guadeloupe's natural environments have been affected by hunting and fishing, forest retreat, urbanization and suburbanization. They also suffer from the development of intensive crops (banana andsugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
, in particular), which reached their peak in the years 1955–75. This has led to the following situation: seagrass beds and reefs
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes—deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock out ...
have degraded by up to 50% around the large islands; mangroves and mantids
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species '' Mantis religiosa''; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many referen ...
have almost disappeared in Marie-Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 ...
, Les Saintes and La Désirade; the salinity of the fresh water table has increased due to "the intensity of use of the layer"; and pollution of agricultural origin (pesticides and nitrogenous compounds).
In addition, the ChlEauTerre study, unveiled in March 2018, concludes that 37 different anthropogenic molecules (more than half of which come from residues of now-banned pesticides, such as chlordecone) were found in "79% of the watersheds analyzed in Grande-Terre and 84% in Basse-Terre." A report by the Guadeloupe Water Office notes that in 2019 there is a "generalized degradation
Degradation may refer to:
Science
* Degradation (geology), lowering of a fluvial surface by erosion
* Degradation (telecommunications), of an electronic signal
* Biodegradation of organic substances by living organisms
* Environmental degradatio ...
of water bodies."
Despite everything, there is a will to preserve these environments whose vegetation and landscape are preserved in some parts of the islands and constitute a sensitive asset for tourism. These areas are partially protected and classified as ZNIEFF, sometimes with nature reserve status, and several caves are home to protected chiropterans.
 The Guadalupe National Park was created on 20 February 1989. In 1992, under the auspices of
The Guadalupe National Park was created on 20 February 1989. In 1992, under the auspices of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, the Biosphere Reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
of the Guadeloupe Archipelago (''Réserve de biosphère de l'archipel de la Guadeloupe'') was created. As a result, on 8 December 1993, the marine site of Grand Cul-de-sac was listed as a wetland of international importance. The island thus became the overseas department with the most protected areas.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
The archipelago is crossed by numerous geological faults such as those of la Barre or la Cadoue, while in depth, in front of Moule andLa Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France.
History
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian p ...
begins the Désirade Fault, and between the north of Maria-Galante and the south of Grande-Terre begins the Maria Galante Fault. And it is because of these geological characteristics, the islands of the department of Guadeloupe are classified in zone III according to the seismic zoning of France and are subject to a specific risk prevention plan.
The 1843 earthquake in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
is, to this day, the most violent earthquake known. It caused the death of more than a thousand people, as well as major damage in Pointe-à-Pitre.
On 21 November 2004, the islands of the department, in particular Les Saintes archipelago, were shaken by a violent earthquake that reached a magnitude of 6.3 on the Richter scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 ...
and caused the death of one person, as well as extensive material damage.
See also
*Caribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America.
Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders ...
References
{{reflist