Genetic engineering on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Genetic engineering is a process that alters the genetic structure of an organism by either removing or introducing DNA, or modifying existing genetic material in situ. Unlike traditional
Genetic engineering is a process that alters the genetic structure of an organism by either removing or introducing DNA, or modifying existing genetic material in situ. Unlike traditional
Economic Impacts of Genetically Modified Crops on the Agri-Food Sector; p. 42 Glossary – Term and Definitions
The European Commission Directorate-General for Agriculture, "Genetic engineering: The manipulation of an organism's genetic endowment by introducing or eliminating specific genes through modern molecular biology techniques. A broad definition of genetic engineering also includes selective breeding and other means of artificial selection.", Retrieved 5 November 2012 Genetic engineering does not normally include traditional breeding,
 In 1972, Paul Berg created the first
In 1972, Paul Berg created the first
GM crops: A bitter harvest?
/ref> when a strawberry field and a potato field in California were sprayed with it. Both test fields were attacked by activist groups the night before the tests occurred: "The world's first trial site attracted the world's first field trasher". The first field trials of genetically engineered plants occurred in France and the US in 1986, tobacco plants were engineered to be resistant to herbicides. The People's Republic of China was the first country to commercialise transgenic plants, introducing a virus-resistant tobacco in 1992. In 1994
 Creating a GMO is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert into the organism. This is driven by what the aim is for the resultant organism and is built on earlier research. Genetic screens can be carried out to determine potential genes and further tests then used to identify the best candidates. The development of microarrays, transcriptomics and genome sequencing has made it much easier to find suitable genes. Luck also plays its part; the Roundup Ready gene was discovered after scientists noticed a bacterium thriving in the presence of the herbicide.
Creating a GMO is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert into the organism. This is driven by what the aim is for the resultant organism and is built on earlier research. Genetic screens can be carried out to determine potential genes and further tests then used to identify the best candidates. The development of microarrays, transcriptomics and genome sequencing has made it much easier to find suitable genes. Luck also plays its part; the Roundup Ready gene was discovered after scientists noticed a bacterium thriving in the presence of the herbicide.
 There are a number of techniques used to insert genetic material into the host genome. Some bacteria can naturally take up foreign DNA. This ability can be induced in other bacteria via stress (e.g. thermal or electric shock), which increases the cell membrane's permeability to DNA; up-taken DNA can either integrate with the genome or exist as extrachromosomal DNA. DNA is generally inserted into animal cells using microinjection, where it can be injected through the cell's nuclear envelope directly into the
There are a number of techniques used to insert genetic material into the host genome. Some bacteria can naturally take up foreign DNA. This ability can be induced in other bacteria via stress (e.g. thermal or electric shock), which increases the cell membrane's permeability to DNA; up-taken DNA can either integrate with the genome or exist as extrachromosomal DNA. DNA is generally inserted into animal cells using microinjection, where it can be injected through the cell's nuclear envelope directly into the  Further testing using PCR,
Further testing using PCR,
BBC News – Gene therapy: Glybera approved by European Commission
Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved on 15 December 2012. In 2015 a virus was used to insert a healthy gene into the skin cells of a boy suffering from a rare skin disease, epidermolysis bullosa, in order to grow, and then graft healthy skin onto 80 percent of the boy's body which was affected by the illness. Germline gene therapy would result in any change being inheritable, which has raised concerns within the scientific community. In 2015, CRISPR was used to edit the DNA of non-viable

 Genetic engineering is an important tool for
Genetic engineering is an important tool for
 Organisms can have their cells transformed with a gene coding for a useful protein, such as an enzyme, so that they will overexpress the desired protein. Mass quantities of the protein can then be manufactured by growing the transformed organism in
Organisms can have their cells transformed with a gene coding for a useful protein, such as an enzyme, so that they will overexpress the desired protein. Mass quantities of the protein can then be manufactured by growing the transformed organism in
 One of the best-known and Genetically modified food controversies, controversial applications of genetic engineering is the creation and use of
One of the best-known and Genetically modified food controversies, controversial applications of genetic engineering is the creation and use of
"Plant gene replacement results in the world's only blue rose"
blue roses, and GloFish, glowing fish have also been produced through genetic engineering.
/ref> The European Union by contrast has possibly the most stringent GMO regulations in the world. All GMOs, along with irradiated food, are considered "new food" and subject to extensive, case-by-case, science-based food evaluation by the European Food Safety Authority. The criteria for authorisation fall in four broad categories: "safety", "freedom of choice", "labelling", and "traceability".GMO Compass: The European Regulatory System.
Retrieved 28 July 2012. The level of regulation in other countries that cultivate GMOs lie in between Europe and the United States. One of the key issues concerning regulators is whether GM products should be labeled. The European Commission says that mandatory labeling and traceability are needed to allow for informed choice, avoid potential false advertising and facilitate the withdrawal of products if adverse effects on health or the environment are discovered. The American Medical Association and the American Association for the Advancement of ScienceAmerican Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), Board of Directors (2012)
Statement by the AAAS Board of Directors On Labeling of Genetically Modified Foods
and associate
Press release: Legally Mandating GM Food Labels Could Mislead and Falsely Alarm Consumers
say that absent scientific evidence of harm even voluntary labeling is Fear, uncertainty and doubt, misleading and will falsely alarm consumers. Labeling of GMO products in the marketplace is required in 64 countries. Labeling can be mandatory up to a threshold GM content level (which varies between countries) or voluntary. In Canada and the US labeling of GM food is voluntary, while in Europe all food (including processed food) or Compound feed, feed which contains greater than 0.9% of approved GMOs must be labelled.
GMO Safety - Information about research projects on the biological safety of genetically modified plants.
GMO-compass, news on GMO en EU
{{Authority control Genetic engineering, 1950s neologisms 1972 introductions Emerging technologies Biological engineering Biotechnology Molecular biology Engineering disciplines
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s using technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be f ...
methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s, the process can be used to remove, or " knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
.
An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (GM) and the resulting entity is a genetically modified organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, wit ...
(GMO). The first GMO was a bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
generated by Herbert Boyer
Herbert Wayne "Herb" Boyer (born July 10, 1936) is an American biotechnologist, researcher and entrepreneur in biotechnology. Along with Stanley N. Cohen and Paul Berg he discovered a method to coax bacteria into producing foreign proteins, the ...
and Stanley Cohen in 1973. Rudolf Jaenisch created the first GM animal when he inserted foreign DNA into a mouse in 1974. The first company to focus on genetic engineering, Genentech, was founded in 1976 and started the production of human proteins. Genetically engineered human insulin was produced in 1978 and insulin-producing bacteria were commercialised in 1982. Genetically modified food has been sold since 1994, with the release of the Flavr Savr tomato. The Flavr Savr was engineered to have a longer shelf life, but most current GM crops are modified to increase resistance to insects and herbicides. GloFish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was sold in the United States in December 2003. In 2016 salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
modified with a growth hormone were sold.
Genetic engineering has been applied in numerous fields including research, medicine, industrial biotechnology and agriculture. In research, GMOs are used to study gene function and expression through loss of function, gain of function, tracking and expression experiments. By knocking out genes responsible for certain conditions it is possible to create animal model organisms of human diseases. As well as producing hormones, vaccines and other drugs, genetic engineering has the potential to cure genetic diseases through gene therapy
Gene therapy is a Medicine, medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying ...
. The same techniques that are used to produce drugs can also have industrial applications such as producing enzymes for laundry detergent, cheeses and other products.
The rise of commercialised genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
has provided economic benefit to farmers in many different countries, but has also been the source of most of the controversy surrounding the technology. This has been present since its early use; the first field trials were destroyed by anti-GM activists. Although there is a scientific consensus that currently available food derived from GM crops poses no greater risk to human health than conventional food, critics consider GM food safety a leading concern. Gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
, impact on non-target organisms, control of the food supply and intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
rights have also been raised as potential issues. These concerns have led to the development of a regulatory framework, which started in 1975. It has led to an international treaty, the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety
The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity is an international agreement on biosafety as a supplement to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) effective since 2003. The Biosafety Protocol seeks to prot ...
, that was adopted in 2000. Individual countries have developed their own regulatory systems regarding GMOs, with the most marked differences occurring between the US and Europe.
Overview
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
and plant breeding, which involves doing multiple crosses and then selecting for the organism with the desired phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, developmental proc ...
, genetic engineering takes the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
directly from one organism and delivers it to the other. This is much faster, can be used to insert any genes from any organism (even ones from different domains) and prevents other undesirable genes from also being added.
Genetic engineering could potentially fix severe genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s in humans by replacing the defective gene with a functioning one. It is an important tool in research that allows the function of specific genes to be studied. Drugs, vaccines and other products have been harvested from organisms engineered to produce them. Crops have been developed that aid food security
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World ...
by increasing yield, nutritional value and tolerance to environmental stresses.
The DNA can be introduced directly into the host organism or into a cell that is then fused or hybridised with the host. This relies on recombinant nucleic acid techniques to form new combinations of heritable genetic material followed by the incorporation of that material either indirectly through a vector system or directly through micro-injection, macro-injection or micro-encapsulation.StafEconomic Impacts of Genetically Modified Crops on the Agri-Food Sector; p. 42 Glossary – Term and Definitions
The European Commission Directorate-General for Agriculture, "Genetic engineering: The manipulation of an organism's genetic endowment by introducing or eliminating specific genes through modern molecular biology techniques. A broad definition of genetic engineering also includes selective breeding and other means of artificial selection.", Retrieved 5 November 2012 Genetic engineering does not normally include traditional breeding,
in vitro fertilisation
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) ...
, induction of polyploidy, mutagenesis and cell fusion techniques that do not use recombinant nucleic acids or a genetically modified organism in the process. However, some broad definitions of genetic engineering include selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant ...
. Cloning and stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
research, although not considered genetic engineering, are closely related and genetic engineering can be used within them. Synthetic biology is an emerging discipline that takes genetic engineering a step further by introducing artificially synthesised material into an organism.
Plants, animals or microorganisms that have been changed through genetic engineering are termed genetically modified organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, wit ...
s or GMOs. If genetic material from another species is added to the host, the resulting organism is called transgenic. If genetic material from the same species or a species that can naturally breed with the host is used the resulting organism is called cisgenic
Cisgenesis is a product designation for a category of genetically engineered plants. A variety of classification schemes have been proposed that order genetically modified organisms based on the nature of introduced genotypical changes, rather tha ...
. If genetic engineering is used to remove genetic material from the target organism the resulting organism is termed a knockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, muay thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving strikin ...
organism. In Europe genetic modification is synonymous
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
with genetic engineering while within the United States of America and Canada genetic modification can also be used to refer to more conventional breeding methods.
History
Humans have altered the genomes of species for thousands of years throughselective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant ...
, or artificial selection as contrasted with natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. More recently, mutation breeding Mutation breeding, sometimes referred to as "variation breeding", is the process of exposing seeds to chemicals, radiation, or enzymes in order to generate mutants with desirable traits to be bred with other cultivars. Plants created using mutagene ...
has used exposure to chemicals or radiation to produce a high frequency of random mutations, for selective breeding purposes. Genetic engineering as the direct manipulation of DNA by humans outside breeding and mutations has only existed since the 1970s. The term "genetic engineering" was first coined by Jack Williamson
John Stewart Williamson (April 29, 1908 – November 10, 2006), who wrote as Jack Williamson, was an American science fiction writer, often called the "Dean of Science Fiction". He is also credited with one of the first uses of the term ''genet ...
in his science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
novel ''Dragon's Island'', published in 1951 – one year before DNA's role in heredity was confirmed by Alfred Hershey
Alfred Day Hershey (December 4, 1908 – May 22, 1997) was an American Nobel Prize–winning bacteriologist and geneticist.
He was born in Owosso, Michigan and received his B.S. in chemistry at Michigan State University in 1930 and his Ph.D. i ...
and Martha Chase
Martha Cowles Chase (November 30, 1927 – August 8, 2003), also known as Martha C. Epstein, was an American geneticist who in 1952, with Alfred Hershey, experimentally helped to confirm that DNA rather than protein is the genetic material ...
, and two years before James Watson and Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical stru ...
showed that the DNA molecule has a double-helix structure – though the general concept of direct genetic manipulation was explored in rudimentary form in Stanley G. Weinbaum
Stanley Grauman Weinbaum (April 4, 1902 – December 14, 1935) was an American science fiction writer. His first story, "A Martian Odyssey", was published to great acclaim in July 1934; the alien Tweel was arguably the first character to satisf ...
's 1936 science fiction story ''Proteus Island''.
 In 1972, Paul Berg created the first
In 1972, Paul Berg created the first recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be f ...
molecules by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with that of the lambda virus. In 1973 Herbert Boyer
Herbert Wayne "Herb" Boyer (born July 10, 1936) is an American biotechnologist, researcher and entrepreneur in biotechnology. Along with Stanley N. Cohen and Paul Berg he discovered a method to coax bacteria into producing foreign proteins, the ...
and Stanley Cohen created the first transgenic organism
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
by inserting antibiotic resistance genes into the plasmid of an ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' bacterium. A year later Rudolf Jaenisch created a transgenic mouse
A genetically modified mouse or genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) is a mouse (''Mus musculus'') that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or a ...
by introducing foreign DNA into its embryo, making it the world's first transgenic animal
Genetically modified animals are animals that have been genetically modified for a variety of purposes including producing drugs, enhancing yields, increasing resistance to disease, etc. The vast majority of genetically modified animals are at the ...
These achievements led to concerns in the scientific community about potential risks from genetic engineering, which were first discussed in depth at the Asilomar Conference in 1975. One of the main recommendations from this meeting was that government oversight of recombinant DNA research should be established until the technology was deemed safe.
In 1976 Genentech, the first genetic engineering company, was founded by Herbert Boyer and Robert Swanson and a year later the company produced a human protein ( somatostatin) in ''E. coli''. Genentech announced the production of genetically engineered human insulin in 1978. In 1980, the U.S. Supreme Court in the ''Diamond v. Chakrabarty
''Diamond v. Chakrabarty'', 447 U.S. 303 (1980), was a United States Supreme Court case dealing with whether living organisms can be patented. Writing for a five-justice majority, Chief Justice Warren E. Burger held that human-made bacteria could ...
'' case ruled that genetically altered life could be patented. The insulin produced by bacteria was approved for release by the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) in 1982.
In 1983, a biotech company, Advanced Genetic Sciences (AGS) applied for U.S. government authorisation to perform field tests with the ice-minus strain of ''Pseudomonas syringae
''Pseudomonas syringae'' is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from inte ...
'' to protect crops from frost, but environmental groups and protestors delayed the field tests for four years with legal challenges. In 1987, the ice-minus strain of ''P. syringae'' became the first genetically modified organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, wit ...
(GMO) to be released into the environmentBBC News 14 June 200GM crops: A bitter harvest?
/ref> when a strawberry field and a potato field in California were sprayed with it. Both test fields were attacked by activist groups the night before the tests occurred: "The world's first trial site attracted the world's first field trasher". The first field trials of genetically engineered plants occurred in France and the US in 1986, tobacco plants were engineered to be resistant to herbicides. The People's Republic of China was the first country to commercialise transgenic plants, introducing a virus-resistant tobacco in 1992. In 1994
Calgene
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in the ...
attained approval to commercially release the first genetically modified food, the Flavr Savr, a tomato engineered to have a longer shelf life. In 1994, the European Union approved tobacco engineered to be resistant to the herbicide bromoxynil, making it the first genetically engineered crop commercialised in Europe. In 1995, Bt potato was approved safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, after having been approved by the FDA, making it the first pesticide producing crop to be approved in the US. In 2009 11 transgenic crops were grown commercially in 25 countries, the largest of which by area grown were the US, Brazil, Argentina, India, Canada, China, Paraguay and South Africa.
In 2010, scientists at the J. Craig Venter Institute created the first synthetic genome and inserted it into an empty bacterial cell. The resulting bacterium, named Mycoplasma laboratorium, could replicate and produce proteins. Four years later this was taken a step further when a bacterium was developed that replicated a plasmid containing a unique base pair, creating the first organism engineered to use an expanded genetic alphabet. In 2012, Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier collaborated to develop the CRISPR/Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic ...
system, a technique which can be used to easily and specifically alter the genome of almost any organism.
Process
 Creating a GMO is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert into the organism. This is driven by what the aim is for the resultant organism and is built on earlier research. Genetic screens can be carried out to determine potential genes and further tests then used to identify the best candidates. The development of microarrays, transcriptomics and genome sequencing has made it much easier to find suitable genes. Luck also plays its part; the Roundup Ready gene was discovered after scientists noticed a bacterium thriving in the presence of the herbicide.
Creating a GMO is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert into the organism. This is driven by what the aim is for the resultant organism and is built on earlier research. Genetic screens can be carried out to determine potential genes and further tests then used to identify the best candidates. The development of microarrays, transcriptomics and genome sequencing has made it much easier to find suitable genes. Luck also plays its part; the Roundup Ready gene was discovered after scientists noticed a bacterium thriving in the presence of the herbicide.
Gene isolation and cloning
The next step is to isolate the candidate gene. The cell containing the gene is opened and the DNA is purified. The gene is separated by usingrestriction enzymes
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class ...
to cut the DNA into fragments or polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR) to amplify up the gene segment. These segments can then be extracted through gel electrophoresis. If the chosen gene or the donor organism's genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
has been well studied it may already be accessible from a genetic library. If the DNA sequence is known, but no copies of the gene are available, it can also be artificially synthesised. Once isolated the gene is ligated into a plasmid that is then inserted into a bacterium. The plasmid is replicated when the bacteria divide, ensuring unlimited copies of the gene are available. The RK2 plasmid is notable for its ability to replicate in a wide variety of single-celled organisms, which makes it suitable as a genetic engineering tool.
Before the gene is inserted into the target organism it must be combined with other genetic elements. These include a promoter and terminator region, which initiate and end transcription. A selectable marker A selectable marker is a gene introduced into a cell, especially a bacterium or to cells in culture, that confers a trait suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, an ...
gene is added, which in most cases confers antibiotic resistance, so researchers can easily determine which cells have been successfully transformed. The gene can also be modified at this stage for better expression or effectiveness. These manipulations are carried out using recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be f ...
techniques, such as restriction digests, ligations and molecular cloning.
Inserting DNA into the host genome
 There are a number of techniques used to insert genetic material into the host genome. Some bacteria can naturally take up foreign DNA. This ability can be induced in other bacteria via stress (e.g. thermal or electric shock), which increases the cell membrane's permeability to DNA; up-taken DNA can either integrate with the genome or exist as extrachromosomal DNA. DNA is generally inserted into animal cells using microinjection, where it can be injected through the cell's nuclear envelope directly into the
There are a number of techniques used to insert genetic material into the host genome. Some bacteria can naturally take up foreign DNA. This ability can be induced in other bacteria via stress (e.g. thermal or electric shock), which increases the cell membrane's permeability to DNA; up-taken DNA can either integrate with the genome or exist as extrachromosomal DNA. DNA is generally inserted into animal cells using microinjection, where it can be injected through the cell's nuclear envelope directly into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
, or through the use of viral vectors.
Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium
''Agrobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' is the most commonly studied species in this genus. ''Agrobacterium ...
'' for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In plants the DNA is often inserted using ''Agrobacterium''-mediated transformation, taking advantage of the ''Agrobacterium''s T-DNA
The transfer DNA (abbreviated T-DNA) is the transferred DNA of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of some species of bacteria such as ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and ''Agrobacterium rhizogenes(actually an Ri plasmid)''. The T-DNA is transferred fr ...
sequence that allows natural insertion of genetic material into plant cells. Other methods include biolistics, where particles of gold or tungsten are coated with DNA and then shot into young plant cells, and electroporation, which involves using an electric shock to make the cell membrane permeable to plasmid DNA.
As only a single cell is transformed with genetic material, the organism must be regenerated from that single cell. In plants this is accomplished through the use of tissue culture. In animals it is necessary to ensure that the inserted DNA is present in the embryonic stem cells. Bacteria consist of a single cell and reproduce clonally so regeneration is not necessary. Selectable markers A selectable marker is a gene introduced into a cell, especially a bacterium or to cells in culture, that confers a trait suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and ge ...
are used to easily differentiate transformed from untransformed cells. These markers are usually present in the transgenic organism, although a number of strategies have been developed that can remove the selectable marker from the mature transgenic plant.
 Further testing using PCR,
Further testing using PCR, Southern hybridization
A Southern blot is a method used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. Southern blotting combines transfer of electrophoresis-separated DNA fragments to a filter membrane and subsequent fragment detecti ...
, and DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. T ...
is conducted to confirm that an organism contains the new gene. These tests can also confirm the chromosomal location and copy number of the inserted gene. The presence of the gene does not guarantee it will be expressed at appropriate levels in the target tissue so methods that look for and measure the gene products (RNA and protein) are also used. These include northern hybridisation, quantitative RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chai ...
, Western blot, immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to spe ...
, ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presen ...
and phenotypic analysis.
The new genetic material can be inserted randomly within the host genome or targeted to a specific location. The technique of gene targeting
Gene targeting (also, replacement strategy based on homologous recombination) is a genetic technique that uses homologous recombination to modify an endogenous gene. The method can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene and modify ...
uses homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may ...
to make desired changes to a specific endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
gene. This tends to occur at a relatively low frequency in plants and animals and generally requires the use of selectable markers A selectable marker is a gene introduced into a cell, especially a bacterium or to cells in culture, that confers a trait suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and ge ...
. The frequency of gene targeting can be greatly enhanced through genome editing. Genome editing uses artificially engineered nucleases that create specific double-stranded breaks at desired locations in the genome, and use the cell's endogenous mechanisms to repair the induced break by the natural processes of homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may ...
and nonhomologous end-joining. There are four families of engineered nucleases: meganuclease Meganucleases are endodeoxyribonucleases characterized by a large recognition site (double-stranded DNA sequences of 12 to 40 base pairs); as a result this site generally occurs only once in any given genome. For example, the 18-base pair sequence ...
s, zinc finger nuclease
Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) are artificial restriction enzymes generated by fusing a zinc finger DNA-binding domain to a DNA-cleavage domain. Zinc finger domains can be engineered to target specific desired DNA sequences and this enables zin ...
s, transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), and the Cas9-guideRNA system (adapted from CRISPR). TALEN and CRISPR are the two most commonly used and each has its own advantages. TALENs have greater target specificity, while CRISPR is easier to design and more efficient. In addition to enhancing gene targeting, engineered nucleases can be used to introduce mutations at endogenous genes that generate a gene knockout.
Applications
Genetic engineering has applications in medicine, research, industry and agriculture and can be used on a wide range of plants, animals and microorganisms.Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, the first organisms to be genetically modified, can have plasmid DNA inserted containing new genes that code for medicines or enzymes that process food and other substrates. Plants have been modified for insect protection, herbicide resistance, virus resistance, enhanced nutrition, tolerance to environmental pressures and the production of edible vaccines. Most commercialised GMOs are insect resistant or herbicide tolerant crop plants. Genetically modified animals have been used for research, model animals and the production of agricultural or pharmaceutical products. The genetically modified animals include animals with genes knocked out, increased susceptibility to disease, hormones for extra growth and the ability to express proteins in their milk.
Medicine
Genetic engineering has many applications to medicine that include the manufacturing of drugs, creation ofmodel animals
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the working ...
that mimic human conditions and gene therapy
Gene therapy is a Medicine, medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying ...
. One of the earliest uses of genetic engineering was to mass-produce human insulin in bacteria. This application has now been applied to human growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
s, follicle stimulating hormones (for treating infertility), human albumin
Human serum albumin is the serum albumin found in human blood. It is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma; it constitutes about half of serum protein. It is produced in the liver. It is soluble in water, and it is monomeric.
Albumi ...
, monoclonal antibodies, antihemophilic factor
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. ...
s, vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s and many other drugs. Mouse hybridomas, cells fused together to create monoclonal antibodies, have been adapted through genetic engineering to create human monoclonal antibodies. Genetically engineered virus
A genetically modified virus is a virus that has been altered or generated using biotechnology methods, and remains capable of infection. Genetic modification involves the directed insertion, deletion, artificial synthesis or change of nucl ...
es are being developed that can still confer immunity, but lack the infectious sequences.
Genetic engineering is also used to create animal models of human diseases. Genetically modified mice are the most common genetically engineered animal model. They have been used to study and model cancer (the oncomouse), obesity, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, substance abuse, anxiety, aging and Parkinson disease. Potential cures can be tested against these mouse models.
Gene therapy is the genetic engineering of humans, generally by replacing defective genes with effective ones. Clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of healthcare science that determines the safety and effectiveness ( efficacy) of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treat ...
using somatic gene therapy has been conducted with several diseases, including X-linked SCID, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms beco ...
. In 2012, Alipogene tiparvovec became the first gene therapy treatment to be approved for clinical use.Gallagher, James. (2 November 2012BBC News – Gene therapy: Glybera approved by European Commission
Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved on 15 December 2012. In 2015 a virus was used to insert a healthy gene into the skin cells of a boy suffering from a rare skin disease, epidermolysis bullosa, in order to grow, and then graft healthy skin onto 80 percent of the boy's body which was affected by the illness. Germline gene therapy would result in any change being inheritable, which has raised concerns within the scientific community. In 2015, CRISPR was used to edit the DNA of non-viable
human embryos
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm c ...
, leading scientists of major world academies to call for a moratorium on inheritable human genome edits. There are also concerns that the technology could be used not just for treatment, but for enhancement, modification or alteration of a human beings' appearance, adaptability, intelligence, character or behavior. The distinction between cure and enhancement can also be difficult to establish. In November 2018, He Jiankui announced that he had edited the genomes of two human embryos, to attempt to disable the '' CCR5'' gene, which codes for a receptor that HIV uses to enter cells. The work was widely condemned as unethical, dangerous, and premature. Currently, germline modification is banned in 40 countries. Scientists that do this type of research will often let embryos grow for a few days without allowing it to develop into a baby.
Researchers are altering the genome of pigs to induce the growth of human organs, with the aim of increasing the success of pig to human organ transplantation. Scientists are creating "gene drives", changing the genomes of mosquitoes to make them immune to malaria, and then looking to spread the genetically altered mosquitoes throughout the mosquito population in the hopes of eliminating the disease.
Research

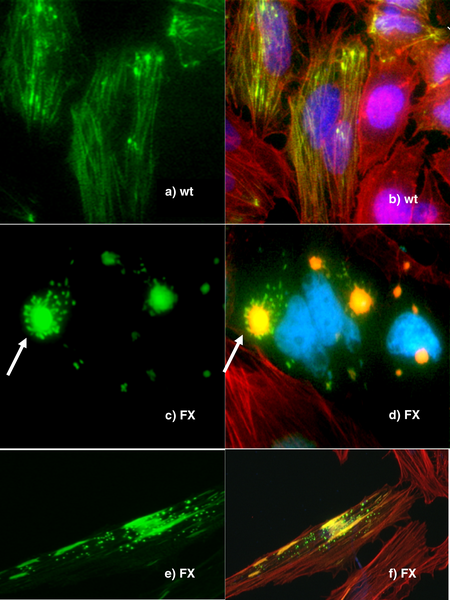
 Genetic engineering is an important tool for
Genetic engineering is an important tool for natural scientists
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeatabili ...
, with the creation of transgenic organisms one of the most important tools for analysis of gene function. Genes and other genetic information from a wide range of organisms can be inserted into bacteria for storage and modification, creating genetically modified bacteria in the process. Bacteria are cheap, easy to grow, clonal, multiply quickly, relatively easy to transform and can be stored at -80 °C almost indefinitely. Once a gene is isolated it can be stored inside the bacteria providing an unlimited supply for research.
Organisms are genetically engineered to discover the functions of certain genes. This could be the effect on the phenotype of the organism, where the gene is expressed or what other genes it interacts with. These experiments generally involve loss of function, gain of function, tracking and expression.
* Loss of function experiments, such as in a gene knockout experiment, in which an organism is engineered to lack the activity of one or more genes. In a simple knockout a copy of the desired gene has been altered to make it non-functional. Embryonic stem cells incorporate the altered gene, which replaces the already present functional copy. These stem cells are injected into blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called th ...
s, which are implanted into surrogate mothers. This allows the experimenter to analyse the defects caused by this mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
and thereby determine the role of particular genes. It is used especially frequently in developmental biology. When this is done by creating a library of genes with point mutations at every position in the area of interest, or even every position in the whole gene, this is called "scanning mutagenesis". The simplest method, and the first to be used, is "alanine scanning", where every position in turn is mutated to the unreactive amino acid alanine.
* Gain of function experiments, the logical counterpart of knockouts. These are sometimes performed in conjunction with knockout experiments to more finely establish the function of the desired gene. The process is much the same as that in knockout engineering, except that the construct is designed to increase the function of the gene, usually by providing extra copies of the gene or inducing synthesis of the protein more frequently. Gain of function is used to tell whether or not a protein is sufficient for a function, but does not always mean it is required, especially when dealing with genetic or functional redundancy.
* Tracking experiments, which seek to gain information about the localisation and interaction of the desired protein. One way to do this is to replace the wild-type gene with a 'fusion' gene, which is a juxtaposition of the wild-type gene with a reporting element such as green fluorescent protein (GFP) that will allow easy visualisation of the products of the genetic modification. While this is a useful technique, the manipulation can destroy the function of the gene, creating secondary effects and possibly calling into question the results of the experiment. More sophisticated techniques are now in development that can track protein products without mitigating their function, such as the addition of small sequences that will serve as binding motifs to monoclonal antibodies.
* Expression studies aim to discover where and when specific proteins are produced. In these experiments, the DNA sequence before the DNA that codes for a protein, known as a gene's promoter, is reintroduced into an organism with the protein coding region replaced by a reporter gene such as GFP or an enzyme that catalyses the production of a dye. Thus the time and place where a particular protein is produced can be observed. Expression studies can be taken a step further by altering the promoter to find which pieces are crucial for the proper expression of the gene and are actually bound by transcription factor proteins; this process is known as promoter bashing
Promoter bashing is a technique used in molecular biology to identify how certain regions of a DNA strand, commonly Promoter (biology), promoters, affect the Transcription (genetics), transcription of downstream genes. Under normal circumstances, ...
.
Industrial
bioreactor
A bioreactor refers to any manufactured device or system that supports a biologically active environment. In one case, a bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical process is carried out which involves organisms or biochemically active substance ...
equipment using industrial fermentation, and then purifying the protein. Some genes do not work well in bacteria, so yeast, insect cells or mammalian cells can also be used. These techniques are used to produce medicines such as insulin, human growth hormone, and vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s, supplements such as tryptophan, aid in the production of food (chymosin in cheese making) and fuels. Other applications with genetically engineered bacteria could involve making them perform tasks outside their natural cycle, such as making biofuels, cleaning up oil spills, carbon and other toxic waste and detecting arsenic in drinking water. Certain genetically modified microbes can also be used in biomining and bioremediation, due to their ability to extract heavy metals from their environment and incorporate them into compounds that are more easily recoverable.
In materials science, a genetically modified virus has been used in a research laboratory as a scaffold for assembling a more environmentally friendly lithium-ion battery. Bacteria have also been engineered to function as sensors by expressing a fluorescent protein under certain environmental conditions.
Agriculture
 One of the best-known and Genetically modified food controversies, controversial applications of genetic engineering is the creation and use of
One of the best-known and Genetically modified food controversies, controversial applications of genetic engineering is the creation and use of genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
or genetically modified livestock to produce genetically modified food. Crops have been developed to increase production, increase tolerance to abiotic stresses, alter the composition of the food, or to produce novel products.
The first crops to be released commercially on a large scale provided protection from insect pests or tolerance to herbicides. Fungal and virus resistant crops have also been developed or are in development. This makes the insect and weed management of crops easier and can indirectly increase crop yield. GM crops that directly improve yield by accelerating growth or making the plant more hardy (by improving salt, cold or drought tolerance) are also under development. In 2016 AquAdvantage salmon, Salmon have been genetically modified with growth hormones to reach normal adult size much faster.
GMOs have been developed that modify the quality of produce by increasing the nutritional value or providing more industrially useful qualities or quantities. The Amflora potato produces a more industrially useful blend of starches. Genetically modified soybean, Soybeans and Genetically modified canola, canola have been genetically modified to produce more healthy oils. The first commercialised GM food was a Flavr Savr, tomato that had delayed ripening, increasing its shelf life.
Plants and animals have been engineered to produce materials they do not normally make. Pharming (genetics), Pharming uses crops and animals as bioreactors to produce vaccines, drug intermediates, or the drugs themselves; the useful product is purified from the harvest and then used in the standard pharmaceutical production process. Cows and goats have been engineered to express drugs and other proteins in their milk, and in 2009 the FDA approved a drug produced in goat milk.
Other applications
Genetic engineering has potential applications in conservation and natural area management. Gene transfer through viral vectors has been proposed as a means of controlling invasive species as well as vaccinating threatened fauna from disease. Transgenic trees have been suggested as a way to confer resistance to pathogens in wild populations. With the increasing risks of maladaptation in organisms as a result of climate change and other perturbations, facilitated adaptation through gene tweaking could be one solution to reducing extinction risks. Applications of genetic engineering in conservation are thus far mostly theoretical and have yet to be put into practice. Genetic engineering is also being used to create microbial art. Some bacteria have been genetically engineered to create black and white photographs. Novelty items such as lavender-colored Dianthus caryophyllus#Colors, carnations,Phys.Org website. 4 April 200"Plant gene replacement results in the world's only blue rose"
blue roses, and GloFish, glowing fish have also been produced through genetic engineering.
Regulation
The regulation of genetic engineering concerns the approaches taken by governments to assess and manage the risks associated with the development and release of GMOs. The development of a regulatory framework began in 1975, at Asilomar Conference Grounds, Asilomar, California. The Asilomar conference on recombinant DNA, Asilomar meeting recommended a set of voluntary guidelines regarding the use of recombinant technology. As the technology improved the US established a committee at the Office of Science and Technology Policy, Office of Science and Technology, which assigned regulatory approval of GM food to the USDA, FDA and EPA. TheCartagena Protocol on Biosafety
The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity is an international agreement on biosafety as a supplement to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) effective since 2003. The Biosafety Protocol seeks to prot ...
, an international treaty that governs the transfer, handling, and use of GMOs, was adopted on 29 January 2000. One hundred and fifty-seven countries are members of the Protocol, and many use it as a reference point for their own regulations.
The legal and regulatory status of GM foods varies by country, with some nations banning or restricting them, and others permitting them with widely differing degrees of regulation. Some countries allow the import of GM food with authorisation, but either do not allow its cultivation (Russia, Norway, Israel) or have provisions for cultivation even though no GM products are yet produced (Japan, South Korea). Most countries that do not allow GMO cultivation do permit research. Some of the most marked differences occur between the US and Europe. The US policy focuses on the product (not the process), only looks at verifiable scientific risks and uses the concept of substantial equivalence.Emily Marden, Risk and Regulation: U.S. Regulatory Policy on Genetically Modified Food and Agriculture, 44 B.C.L. Rev. 733 (200/ref> The European Union by contrast has possibly the most stringent GMO regulations in the world. All GMOs, along with irradiated food, are considered "new food" and subject to extensive, case-by-case, science-based food evaluation by the European Food Safety Authority. The criteria for authorisation fall in four broad categories: "safety", "freedom of choice", "labelling", and "traceability".GMO Compass: The European Regulatory System.
Retrieved 28 July 2012. The level of regulation in other countries that cultivate GMOs lie in between Europe and the United States. One of the key issues concerning regulators is whether GM products should be labeled. The European Commission says that mandatory labeling and traceability are needed to allow for informed choice, avoid potential false advertising and facilitate the withdrawal of products if adverse effects on health or the environment are discovered. The American Medical Association and the American Association for the Advancement of ScienceAmerican Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), Board of Directors (2012)
Statement by the AAAS Board of Directors On Labeling of Genetically Modified Foods
and associate
Press release: Legally Mandating GM Food Labels Could Mislead and Falsely Alarm Consumers
say that absent scientific evidence of harm even voluntary labeling is Fear, uncertainty and doubt, misleading and will falsely alarm consumers. Labeling of GMO products in the marketplace is required in 64 countries. Labeling can be mandatory up to a threshold GM content level (which varies between countries) or voluntary. In Canada and the US labeling of GM food is voluntary, while in Europe all food (including processed food) or Compound feed, feed which contains greater than 0.9% of approved GMOs must be labelled.
Controversy
Critics have objected to the use of genetic engineering on several grounds, including ethical, ecological and economic concerns. Many of these concerns involve GM crops and whether food produced from them is safe and what impact growing them will have on the environment. These controversies have led to litigation, international trade disputes, and protests, and to restrictive regulation of commercial products in some countries. Accusations that scientists are "Playing God (ethics), playing God" and other Religious views on genetically modified foods, religious issues have been ascribed to the technology from the beginning. Other ethical issues raised include the Biological patent, patenting of life, the use ofintellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
rights, the level of labeling on products, control of the food supply and the objectivity of the regulatory process. Although doubts have been raised, economically most studies have found growing GM crops to be beneficial to farmers.
Gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
between GM crops and compatible plants, along with increased use of selective herbicides, can increase the risk of "superweeds" developing. Other environmental concerns involve potential impacts on non-target organisms, including soil microbes, and an increase in secondary and resistant insect pests. Many of the environmental impacts regarding GM crops may take many years to be understood and are also evident in conventional agriculture practices. With the commercialisation of genetically modified fish there are concerns over what the environmental consequences will be if they escape.
There are three main concerns over the safety of genetically modified food: whether they may provoke an allergic reaction; whether the genes could transfer from the food into human cells; and whether the genes not approved for human consumption could Outcrossing, outcross to other crops. There is a scientific consensus that currently available food derived from GM crops poses no greater risk to human health than conventional food, but that each GM food needs to be tested on a case-by-case basis before introduction. Nonetheless, members of the public are less likely than scientists to perceive GM foods as safe.
In popular culture
Genetic engineering features in manyscience fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
stories. Frank Herbert's novel ''The White Plague'' describes the deliberate use of genetic engineering to create a pathogen which specifically kills women. Another of Herbert's creations, the ''Dune (franchise), Dune'' series of novels, uses genetic engineering to create the powerful Tleilaxu. Few films have informed audiences about genetic engineering, with the exception of the 1978 ''The Boys from Brazil (film), The Boys from Brazil'' and the 1993 ''Jurassic Park (film), Jurassic Park'', both of which make use of a lesson, a demonstration, and a clip of scientific film. Genetic engineering methods are weakly represented in film; Michael Clark, writing for the Wellcome Trust, calls the portrayal of genetic engineering and biotechnology "seriously distorted" in films such as ''The 6th Day''. In Clark's view, the biotechnology is typically "given fantastic but visually arresting forms" while the science is either relegated to the background or fictionalised to suit a young audience.
In the 2007 video game, ''BioShock'', genetic engineering plays an important role in the central storyline and universe. The game takes place in the fictional underwater dystopia Rapture (BioShock), Rapture, in which its inhabitants possess genetic superhuman abilities after injecting themselves with “plasmids”, a serum which grants such powers. Also in the city of Rapture are “Little Sisters”, little girls who are generically engineered, as well as a side-plot in which a cabaret singer sells her foetus to genetic scientists who implant false memories into the newborn and genetically engineer it to grow into an adult.
See also
* Biological engineering * Modifications (genetics) * RNA editing#Therapeutic mRNA Editing * Mutagenesis (molecular biology technique)References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
GMO Safety - Information about research projects on the biological safety of genetically modified plants.
GMO-compass, news on GMO en EU
{{Authority control Genetic engineering, 1950s neologisms 1972 introductions Emerging technologies Biological engineering Biotechnology Molecular biology Engineering disciplines