Galiza on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Galicia (; gl, Galicia or ; es, Galicia}; pt, Galiza) is an
 The name ''Galicia'' derives from the Latin toponym Callaecia, later ''
The name ''Galicia'' derives from the Latin toponym Callaecia, later ''
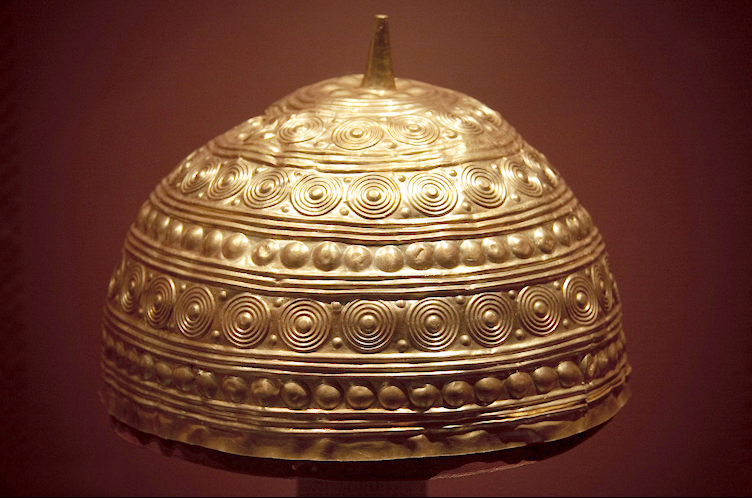 The oldest attestation of human presence in Galicia has been found in the Eirós Cave, in the municipality of
The oldest attestation of human presence in Galicia has been found in the Eirós Cave, in the municipality of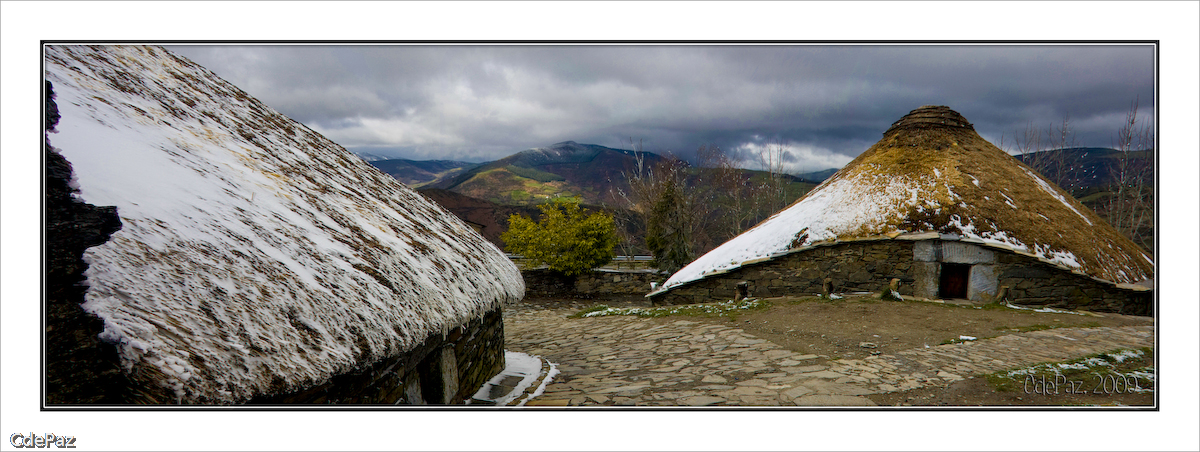  Dating from the end of the Megalithic era, and up to the Bronze Age, numerous stone carvings (petroglyphs) are found in open air. They usually represent cup and ring marks, labyrinths, deer, Bronze Age weapons, and riding and hunting scenes. Large numbers of these stone carvings can be found in the Rías Baixas regions, at places such as Tourón and Campo Lameiro.
The Castro culture ('Culture of the Castles') developed during the Iron Age, and flourished during the second half of the first millennium BC. It is usually considered a local evolution of the Atlantic Bronze Age, with later developments and influences overlapping into the Roman era. Geographically, it corresponds to the people the Romans called
Dating from the end of the Megalithic era, and up to the Bronze Age, numerous stone carvings (petroglyphs) are found in open air. They usually represent cup and ring marks, labyrinths, deer, Bronze Age weapons, and riding and hunting scenes. Large numbers of these stone carvings can be found in the Rías Baixas regions, at places such as Tourón and Campo Lameiro.
The Castro culture ('Culture of the Castles') developed during the Iron Age, and flourished during the second half of the first millennium BC. It is usually considered a local evolution of the Atlantic Bronze Age, with later developments and influences overlapping into the Roman era. Geographically, it corresponds to the people the Romans called  Gallaeci lived in ''hill fort#Portugal and Spain, castros''. These were usually annular forts, with one or more concentric earthen or stony walls, with a trench in front of each one. They were frequently located on hills, or in seashore cliffs and peninsulas. Some well known ''castros'' can be found on the seashore at: Fazouro, Santa Tegra, Baroña, and O Neixón; and inland at: San Cibrao de Lás hill fort, San Cibrao de Lás, Borneiro, Castromao, and Viladonga. Some other distinctive features, such as temples, baths, reservoirs, warrior statues, and decorative carvings have been found associated with this culture, together with rich gold and metalworking traditions.
The Roman legions first entered the area under Decimus Junius Brutus Callaicus, Decimus Junius Brutus in 137–136 BC, but the country was only incorporated into the
Gallaeci lived in ''hill fort#Portugal and Spain, castros''. These were usually annular forts, with one or more concentric earthen or stony walls, with a trench in front of each one. They were frequently located on hills, or in seashore cliffs and peninsulas. Some well known ''castros'' can be found on the seashore at: Fazouro, Santa Tegra, Baroña, and O Neixón; and inland at: San Cibrao de Lás hill fort, San Cibrao de Lás, Borneiro, Castromao, and Viladonga. Some other distinctive features, such as temples, baths, reservoirs, warrior statues, and decorative carvings have been found associated with this culture, together with rich gold and metalworking traditions.
The Roman legions first entered the area under Decimus Junius Brutus Callaicus, Decimus Junius Brutus in 137–136 BC, but the country was only incorporated into the
 In the early 5th century, the deep crisis suffered by the
In the early 5th century, the deep crisis suffered by the
 In the 9th century, the rise of the cult of the James, son of Zebedee, Apostle James in
In the 9th century, the rise of the cult of the James, son of Zebedee, Apostle James in  On the other hand, the lack of an effective royal justice system in the Kingdom led to the social conflict known as the ''Irmandiño, Guerras Irmandiñas'' ('Wars of the brotherhoods'), when leagues of peasants and burghers, with the support of several knights, noblemen, and under legal protection offered by the remote king, toppled many of the castles of the Kingdom and briefly drove the noblemen into Portugal and Castile. Soon after, in the late 15th century, in the dynastic conflict between Isabella I of Castile and Joanna La Beltraneja, part of the Galician aristocracy supported Joanna. After Isabella's victory, she initiated an administrative and political reform which the chronicler Zurita y Castro, Jeronimo, Jeronimo Zurita defined as "doma del Reino de Galicia": 'It was then when the taming of Galicia began, because not just the local lords and knights, but all the people of that nation were the ones against the others very bold and warlike'. These reforms, while establishing a local government and tribunal (the ''Real Audiencia del Reino de Galicia''), and bringing the nobleman under submission, also brought most Galician monasteries and institutions under Castilian control, in what has been criticized as a process of centralisation. At the same time the kings began to call the Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia, ''Xunta'' or ''Cortes'' of the Kingdom of Galicia, an assembly of deputies or representatives of the cities of the Kingdom, to ask for monetary and military contributions. This assembly soon developed into the voice and legal representation of the Kingdom, and the depositary of its will and laws.
On the other hand, the lack of an effective royal justice system in the Kingdom led to the social conflict known as the ''Irmandiño, Guerras Irmandiñas'' ('Wars of the brotherhoods'), when leagues of peasants and burghers, with the support of several knights, noblemen, and under legal protection offered by the remote king, toppled many of the castles of the Kingdom and briefly drove the noblemen into Portugal and Castile. Soon after, in the late 15th century, in the dynastic conflict between Isabella I of Castile and Joanna La Beltraneja, part of the Galician aristocracy supported Joanna. After Isabella's victory, she initiated an administrative and political reform which the chronicler Zurita y Castro, Jeronimo, Jeronimo Zurita defined as "doma del Reino de Galicia": 'It was then when the taming of Galicia began, because not just the local lords and knights, but all the people of that nation were the ones against the others very bold and warlike'. These reforms, while establishing a local government and tribunal (the ''Real Audiencia del Reino de Galicia''), and bringing the nobleman under submission, also brought most Galician monasteries and institutions under Castilian control, in what has been criticized as a process of centralisation. At the same time the kings began to call the Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia, ''Xunta'' or ''Cortes'' of the Kingdom of Galicia, an assembly of deputies or representatives of the cities of the Kingdom, to ask for monetary and military contributions. This assembly soon developed into the voice and legal representation of the Kingdom, and the depositary of its will and laws.
 The modern period of the Kingdom of Galicia began with the defeat of some of the most powerful Galician lords, such as Pedro Álvarez de Sotomayor, called Pedro Madruga, and Rodrigo Henriquez Osorio, at the hands of the Castilian armies sent to Galicia between the years 1480 and 1486. Isabella I of Castile, considered a usurper by many Galician nobles, defeated all armed resistance and definitively established the royal power of the Castilian monarchy. Fearing a general revolt, the monarchs ordered the banishing of the rest of the great lords like Pedro de Bolaño, Diego de Andrade, or Lope Sánchez de Moscoso, among others.
The modern period of the Kingdom of Galicia began with the defeat of some of the most powerful Galician lords, such as Pedro Álvarez de Sotomayor, called Pedro Madruga, and Rodrigo Henriquez Osorio, at the hands of the Castilian armies sent to Galicia between the years 1480 and 1486. Isabella I of Castile, considered a usurper by many Galician nobles, defeated all armed resistance and definitively established the royal power of the Castilian monarchy. Fearing a general revolt, the monarchs ordered the banishing of the rest of the great lords like Pedro de Bolaño, Diego de Andrade, or Lope Sánchez de Moscoso, among others.
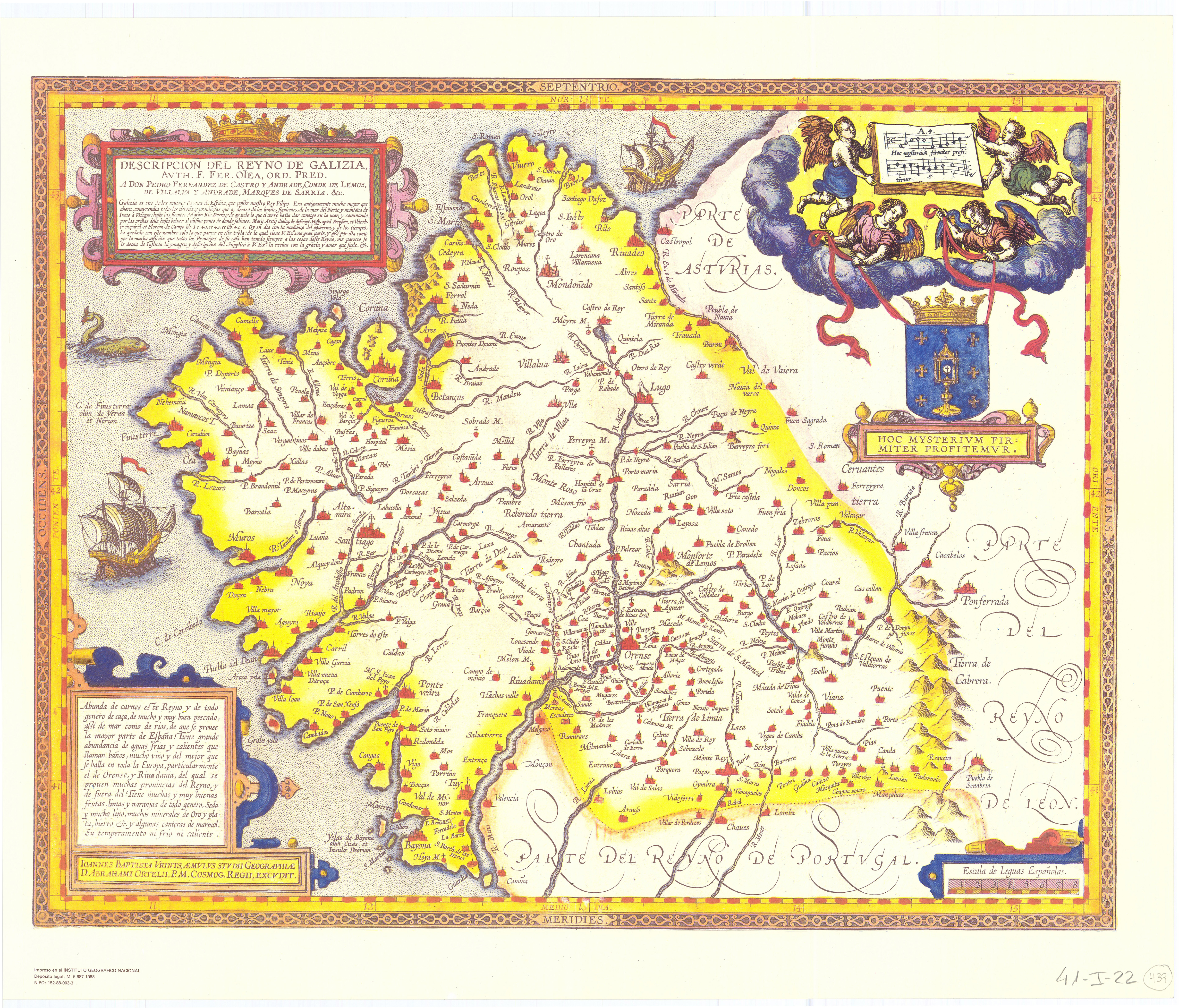 The establishment of the Santa Hermandad in 1480, and the
The establishment of the Santa Hermandad in 1480, and the  After the rupture of the wars with Portuguese Restoration War, Portugal and Reapers' War, Catalonia, the ''Junta'' changed its attitude, this time due to the exhaustion of Galicia, now involved not just in naval or oversea operations, but also in an exhausting war with the Portuguese, war which produced thousands of casualties and refugees and was heavily disturbing to the local economy and commerce. So, in the second half of the 17th century the ''Junta'' frequently denied or considerably reduced the initial petitions of the monarch, and though the tension didn't rise to the levels experienced in Portugal or Catalonia, there were frequent urban mutinies and some voices even asked for the secession of the Kingdom of Galicia.
After the rupture of the wars with Portuguese Restoration War, Portugal and Reapers' War, Catalonia, the ''Junta'' changed its attitude, this time due to the exhaustion of Galicia, now involved not just in naval or oversea operations, but also in an exhausting war with the Portuguese, war which produced thousands of casualties and refugees and was heavily disturbing to the local economy and commerce. So, in the second half of the 17th century the ''Junta'' frequently denied or considerably reduced the initial petitions of the monarch, and though the tension didn't rise to the levels experienced in Portugal or Catalonia, there were frequent urban mutinies and some voices even asked for the secession of the Kingdom of Galicia.
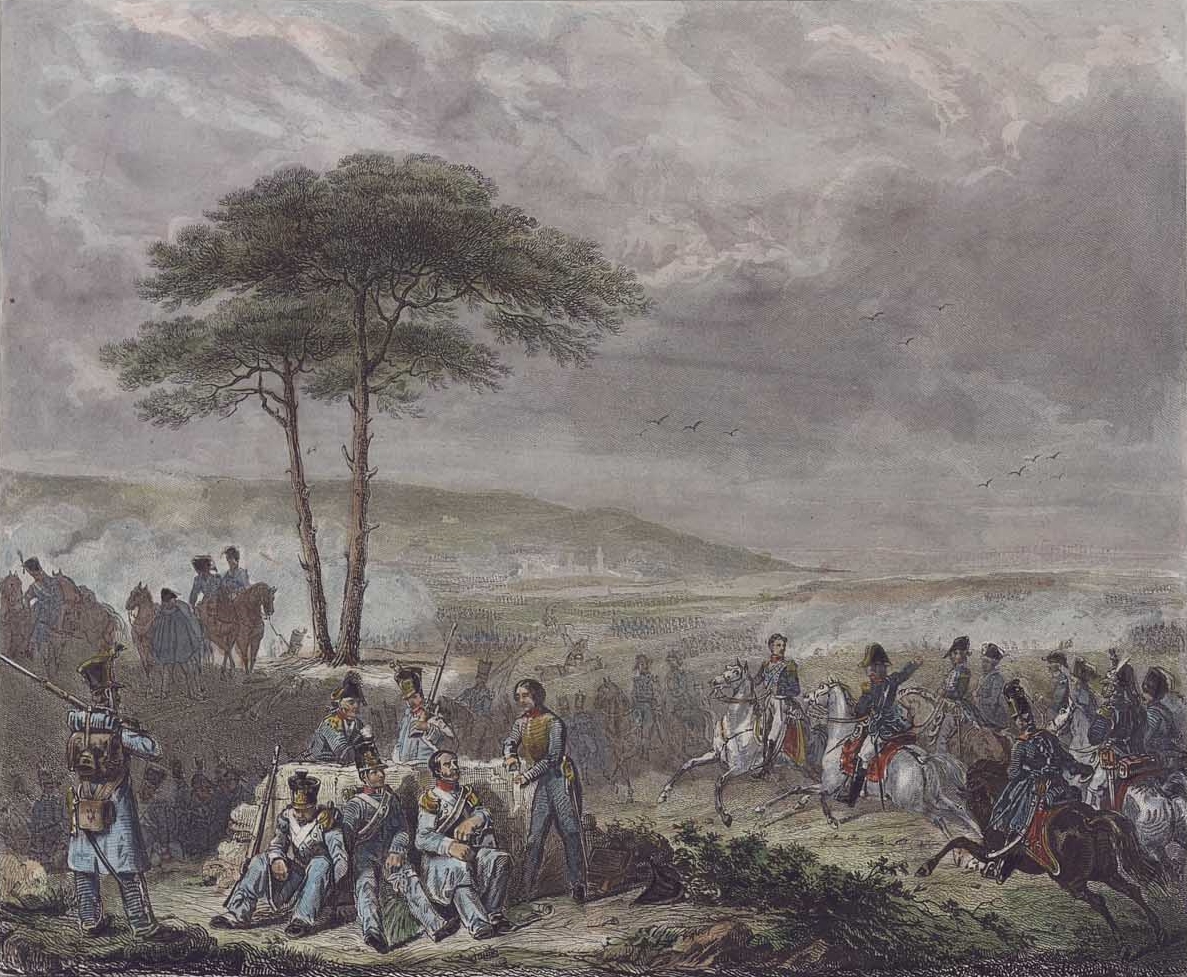 During the Peninsular War the successful uprising of the local people against the new French authorities, together with the support of the British Army, limited the occupation to six months in 1808–1809. During the pre-war period the Supreme Council of the Kingdom of Galicia (''Junta Suprema del Reino de Galicia''), auto-proclaimed interim sovereign in 1808, was the sole government of the country and mobilized near 40,000 men against the invaders.
The 1833 territorial division of Spain put a formal end to the Kingdom of Galicia, unifying Spain into a single centralized monarchy. Instead of seven provinces and a regional administration, Galicia was reorganized into the current four provinces. Although it was recognized as a "historical region", that status was strictly honorific. In reaction, Galician nationalism, nationalist and federalism, federalist movements arose.
During the Peninsular War the successful uprising of the local people against the new French authorities, together with the support of the British Army, limited the occupation to six months in 1808–1809. During the pre-war period the Supreme Council of the Kingdom of Galicia (''Junta Suprema del Reino de Galicia''), auto-proclaimed interim sovereign in 1808, was the sole government of the country and mobilized near 40,000 men against the invaders.
The 1833 territorial division of Spain put a formal end to the Kingdom of Galicia, unifying Spain into a single centralized monarchy. Instead of seven provinces and a regional administration, Galicia was reorganized into the current four provinces. Although it was recognized as a "historical region", that status was strictly honorific. In reaction, Galician nationalism, nationalist and federalism, federalist movements arose.
 The liberalism, liberal General Miguel Solís Cuetos led a Solís Uprising, separatist coup attempt in 1846 against the authoritarianism, authoritarian regime of Ramón María Narváez. Solís and his forces were defeated at the Battle of Cacheiras, 23 April 1846, and the survivors, including Solís himself, were shot. They have taken their place in Galician memory as the Martyrs of Carral or simply the Martyrs of Liberty.
Defeated on the military front, Galicians turned to culture. The ''Rexurdimento'' focused on the recovery of the Galician language as a vehicle of social and cultural expression. Among the writers associated with this movement are Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal.
In the early 20th century came another turn toward nationalist politics with ''Galician Solidarity, Solidaridad Gallega'' (1907–1912) modeled on ''Catalan Solidarity (1906), Solidaritat Catalana'' in Catalonia. Solidaridad Gallega failed, but in 1916 ''Irmandades da Fala'' (Brotherhood of the Language) developed first as a cultural association but soon as a full-blown nationalist movement. Vicente Risco and Ramón Otero Pedrayo were outstanding cultural figures of this movement, and the magazine ''Nós (Galicia), Nós'' ('Us'), founded in 1920, its most notable cultural institution, Lois Peña Novo the outstanding political figure.
The liberalism, liberal General Miguel Solís Cuetos led a Solís Uprising, separatist coup attempt in 1846 against the authoritarianism, authoritarian regime of Ramón María Narváez. Solís and his forces were defeated at the Battle of Cacheiras, 23 April 1846, and the survivors, including Solís himself, were shot. They have taken their place in Galician memory as the Martyrs of Carral or simply the Martyrs of Liberty.
Defeated on the military front, Galicians turned to culture. The ''Rexurdimento'' focused on the recovery of the Galician language as a vehicle of social and cultural expression. Among the writers associated with this movement are Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal.
In the early 20th century came another turn toward nationalist politics with ''Galician Solidarity, Solidaridad Gallega'' (1907–1912) modeled on ''Catalan Solidarity (1906), Solidaritat Catalana'' in Catalonia. Solidaridad Gallega failed, but in 1916 ''Irmandades da Fala'' (Brotherhood of the Language) developed first as a cultural association but soon as a full-blown nationalist movement. Vicente Risco and Ramón Otero Pedrayo were outstanding cultural figures of this movement, and the magazine ''Nós (Galicia), Nós'' ('Us'), founded in 1920, its most notable cultural institution, Lois Peña Novo the outstanding political figure.
 The Second Spanish Republic was declared in 1931. During the republic, the Partido Galeguista (1931), Partido Galeguista (PG) was the most important of a shifting collection of Galician nationalist parties. Following a referendum on a Galician Statute of Autonomy (1936), Galician Statute of Autonomy, Galicia was granted the status of an autonomous region.
Galicia was spared the worst of the fighting in that war: it was one of the areas where the initial coup attempt at the outset of the war was successful, and it remained in Nationalist hands (Franco's army) throughout the war. While there were no pitched battles, there was repression and death: all political parties were abolished, as were all labor unions and Galician nationalist organizations as the ''Seminario de Estudos Galegos''. Galicia's statute of autonomy was annulled (as were those of Catalonia and the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque provinces once those were conquered). According to Carlos Fernández Santander, at least 4,200 people were killed either extrajudicially or after summary trials, among them republicans, communists, Galician nationalists, socialists, and anarchists. Victims included the civil governors of all four Galician provinces; Juana Capdevielle, the wife of the governor of A Coruña; mayors such as Ánxel Casal of Santiago de Compostela, of the Partido Galeguista; prominent socialists such as Jaime Quintanilla in Ferrol and Emilio Martínez Garrido in
The Second Spanish Republic was declared in 1931. During the republic, the Partido Galeguista (1931), Partido Galeguista (PG) was the most important of a shifting collection of Galician nationalist parties. Following a referendum on a Galician Statute of Autonomy (1936), Galician Statute of Autonomy, Galicia was granted the status of an autonomous region.
Galicia was spared the worst of the fighting in that war: it was one of the areas where the initial coup attempt at the outset of the war was successful, and it remained in Nationalist hands (Franco's army) throughout the war. While there were no pitched battles, there was repression and death: all political parties were abolished, as were all labor unions and Galician nationalist organizations as the ''Seminario de Estudos Galegos''. Galicia's statute of autonomy was annulled (as were those of Catalonia and the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque provinces once those were conquered). According to Carlos Fernández Santander, at least 4,200 people were killed either extrajudicially or after summary trials, among them republicans, communists, Galician nationalists, socialists, and anarchists. Victims included the civil governors of all four Galician provinces; Juana Capdevielle, the wife of the governor of A Coruña; mayors such as Ánxel Casal of Santiago de Compostela, of the Partido Galeguista; prominent socialists such as Jaime Quintanilla in Ferrol and Emilio Martínez Garrido in  From 1990 to 2005, Manuel Fraga, former minister and ambassador in the Franco dictatorship, presided over the Galician autonomous government, the
From 1990 to 2005, Manuel Fraga, former minister and ambassador in the Franco dictatorship, presided over the Galician autonomous government, the
 Galicia has a surface area of .Galicia 08
Galicia has a surface area of .Galicia 08
Xunta de Galicia, Consellaría de Cultura e Deporte. Its northernmost point, at 43°47′N, is Estaca de Bares Point, Estaca de Bares (also the northernmost point of Spain); its southernmost, at 41°49′N, is on the Portuguese border in the Baixa Limia-Serra do Xurés Natural Park. The easternmost longitude is at 6°42′W on the border between the province of Ourense and the Castile and León, Castilian-Leonese province of Zamora) its westernmost at 9°18′W reached in two places: the A Nave Cape in Fisterra (also known as Finisterre), and Cape Touriñán, both in the province of A Coruña.
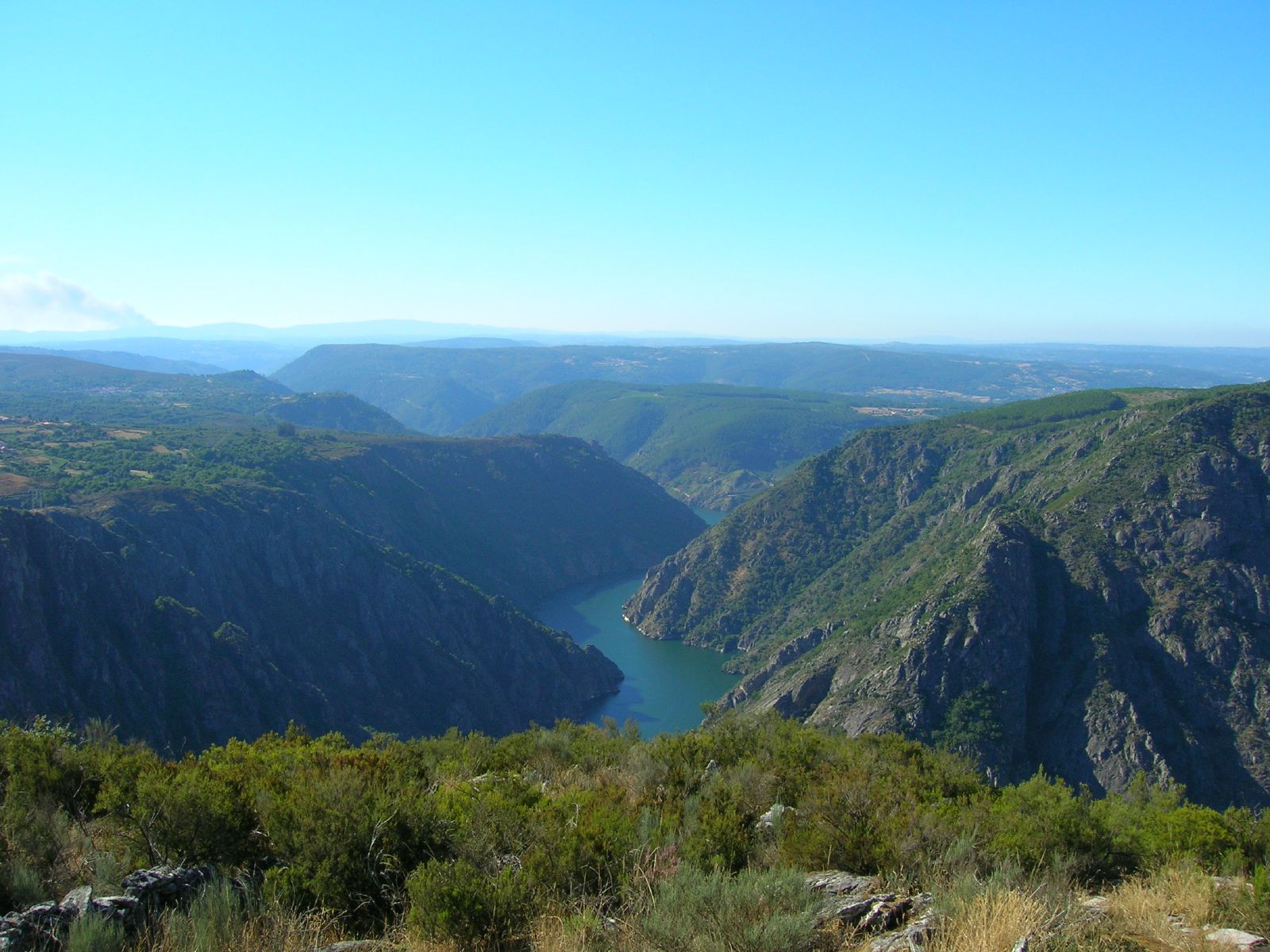
 The interior of Galicia is a hilly landscape, composed of relatively low mountain ranges, usually below high, without sharp peaks, rising to in the eastern mountains. There are many rivers, most (though not all) running down relatively gentle slopes in narrow river valleys, though at times their courses become far more rugged, as in the canyons of the Sil (river), Sil river, Galicia's second most important river after the Minho River, Miño.
The interior of Galicia is a hilly landscape, composed of relatively low mountain ranges, usually below high, without sharp peaks, rising to in the eastern mountains. There are many rivers, most (though not all) running down relatively gentle slopes in narrow river valleys, though at times their courses become far more rugged, as in the canyons of the Sil (river), Sil river, Galicia's second most important river after the Minho River, Miño.
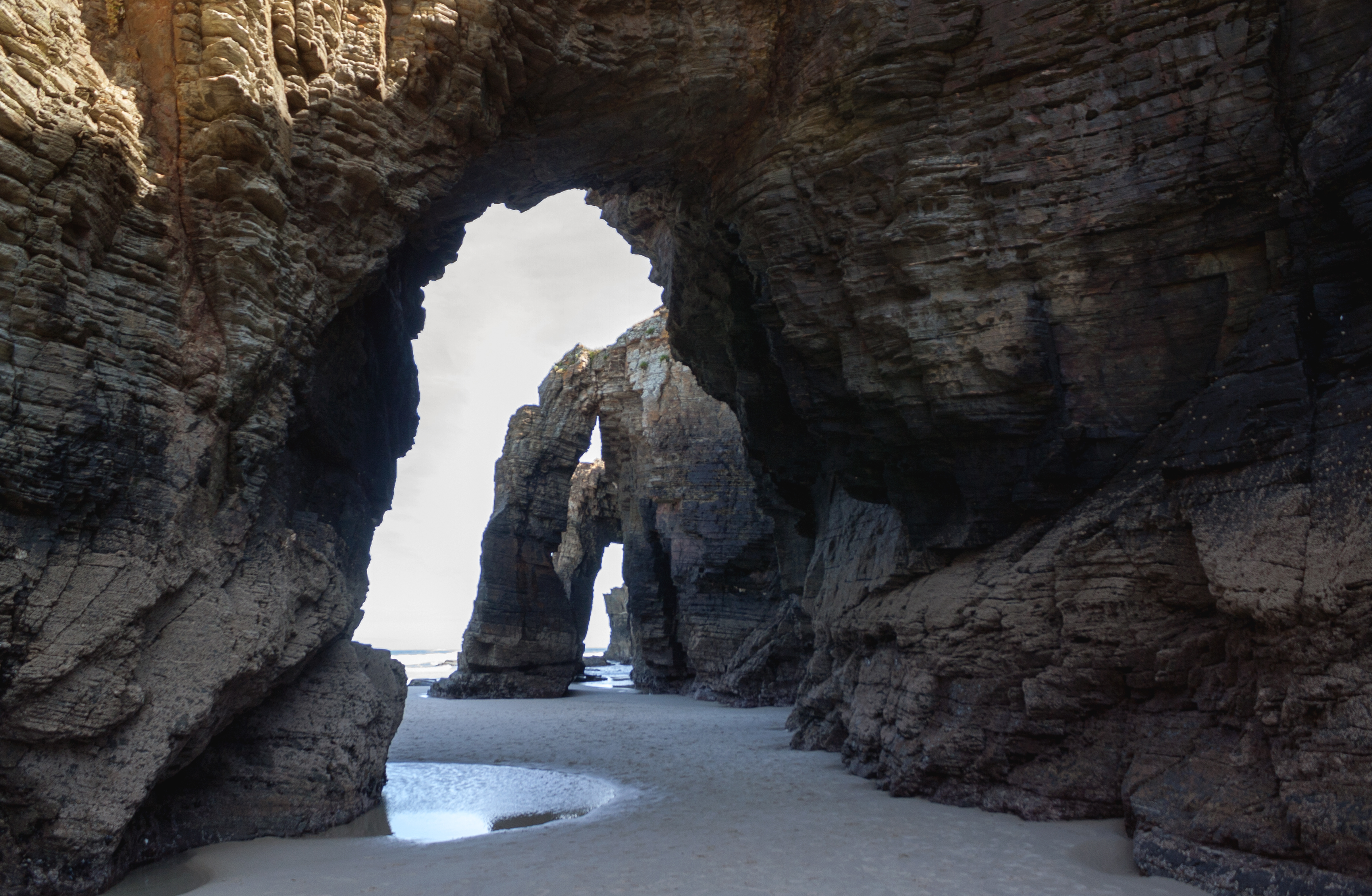
 Topographically, a remarkable feature of Galicia is the presence of many firth-like inlets along the coast, Estuary, estuaries that were drowned with rising sea levels after the Quaternary glaciation, ice age. These are called ''Ria, rías'' and are divided into the smaller ''Rías Altas'' ("High Rías"), and the larger ''
Topographically, a remarkable feature of Galicia is the presence of many firth-like inlets along the coast, Estuary, estuaries that were drowned with rising sea levels after the Quaternary glaciation, ice age. These are called ''Ria, rías'' and are divided into the smaller ''Rías Altas'' ("High Rías"), and the larger '' All along the Galician coast are various archipelagos near the mouths of the ''rías''. These archipelagos provide protected deepwater harbors and also provide habitat for seagoing birds. A 2007 inventory estimates that the Galician coast has 316 archipelagos, islets, and freestanding rocks. Among the most important of these are the archipelagos of Cíes Islands, Cíes, Ons, and
All along the Galician coast are various archipelagos near the mouths of the ''rías''. These archipelagos provide protected deepwater harbors and also provide habitat for seagoing birds. A 2007 inventory estimates that the Galician coast has 316 archipelagos, islets, and freestanding rocks. Among the most important of these are the archipelagos of Cíes Islands, Cíes, Ons, and  Galicia is quite mountainous, a fact which has contributed to isolate the rural areas, hampering communications, most notably in the inland. The main mountain range is the Macizo Galaico (Serra do Eixe, Serra da Lastra, Serra do Courel), also known as ''Macizo Galaico-Leonés'', located in the eastern parts, bordering with Castile and León. Noteworthy mountain ranges are O Xistral (northern province of Lugo, Lugo), the Serra dos Ancares (on the border with Province of León, León and
Galicia is quite mountainous, a fact which has contributed to isolate the rural areas, hampering communications, most notably in the inland. The main mountain range is the Macizo Galaico (Serra do Eixe, Serra da Lastra, Serra do Courel), also known as ''Macizo Galaico-Leonés'', located in the eastern parts, bordering with Castile and León. Noteworthy mountain ranges are O Xistral (northern province of Lugo, Lugo), the Serra dos Ancares (on the border with Province of León, León and
 Galicia is poetically known as the "country of the Rivers of Galicia, thousand rivers" ("o país dos mil ríos"). The largest and most important of these rivers is the Minho River, Miño, poetically known as ''O Pai Miño'' (Father Miño), which is long and discharges per second, with its affluent the Sil (river), Sil, which has created a spectacular canyon. Most of the rivers in the inland are tributaries of this river system, which drains some . Other rivers run directly into the
Galicia is poetically known as the "country of the Rivers of Galicia, thousand rivers" ("o país dos mil ríos"). The largest and most important of these rivers is the Minho River, Miño, poetically known as ''O Pai Miño'' (Father Miño), which is long and discharges per second, with its affluent the Sil (river), Sil, which has created a spectacular canyon. Most of the rivers in the inland are tributaries of this river system, which drains some . Other rivers run directly into the
 Galicia has preserved some of its dense forests. It is relatively unpolluted, and its landscapes composed of green hills, cliffs, and ''rias'' are generally different from what is commonly understood as Spanish landscape. Nevertheless, Galicia has some important environmental problems.
Deforestation and forest fires are a problem in many areas, as is the continual spread of the eucalyptus tree, a species imported from Australia, actively promoted by the paper industry since the mid-20th century. Galicia is one of the more forested areas of Spain, but the majority of Galicia's plantations, usually growing eucalyptus or pine, lack any formal management. Massive eucalyptus plantation, especially of ''Eucalyptus globulus'', began in the Francisco Franco era, largely on behalf of the paper company Empresa Nacional de Celulosas de España (ENCE) in
Galicia has preserved some of its dense forests. It is relatively unpolluted, and its landscapes composed of green hills, cliffs, and ''rias'' are generally different from what is commonly understood as Spanish landscape. Nevertheless, Galicia has some important environmental problems.
Deforestation and forest fires are a problem in many areas, as is the continual spread of the eucalyptus tree, a species imported from Australia, actively promoted by the paper industry since the mid-20th century. Galicia is one of the more forested areas of Spain, but the majority of Galicia's plantations, usually growing eucalyptus or pine, lack any formal management. Massive eucalyptus plantation, especially of ''Eucalyptus globulus'', began in the Francisco Franco era, largely on behalf of the paper company Empresa Nacional de Celulosas de España (ENCE) in
Prestige oil spill far worse than thought
''New Scientist'', August 27, 2003
 Galicia has more than 2,800 plant species and 31 endemic plant taxa. Plantations and mixed forests of eucalyptus predominate in the west and north; a few oak forests (variously known locally as ''fragas'' or ''devesas'') remain, particularly in the north-central part of the province of Lugo and the north of the province of A Coruña (Fragas do Eume). In the interior regions of the country, oak and bushland predominate.
Galicia has 262 inventoried species of vertebrates, including 12 species of freshwater fish, 15 amphibians, 24 reptiles, 152 birds, and 59 mammals.
Galicia has more than 2,800 plant species and 31 endemic plant taxa. Plantations and mixed forests of eucalyptus predominate in the west and north; a few oak forests (variously known locally as ''fragas'' or ''devesas'') remain, particularly in the north-central part of the province of Lugo and the north of the province of A Coruña (Fragas do Eume). In the interior regions of the country, oak and bushland predominate.
Galicia has 262 inventoried species of vertebrates, including 12 species of freshwater fish, 15 amphibians, 24 reptiles, 152 birds, and 59 mammals.
 The animals most often thought of as being "typical" of Galicia are the livestock raised there. The Galician horse is native to the region, as is the Galician Blond cow and the domestic fowl known as the ''galiña de Mos (Spain), Mos''. The last is an endangered species, although it is showing signs of a comeback since 2001.
Galicia is home to one of the largest populations of Iberian wolf, wolves in western Europe. Galicia's woodlands and mountains are also home to rabbits, hares, wild boars, and roe deer, all of which are popular with hunters. Several important bird migration routes pass through Galicia, and some of the community's relatively few environmentally protected areas are Special Protection Areas (such as on the Ría de Ribadeo) for these birds. From a domestic point of view, Galicia has been credited by the author Manuel Rivas as the "land of one million cows". Galician Blond and Holstein cattle coexist on meadows and farms.
The animals most often thought of as being "typical" of Galicia are the livestock raised there. The Galician horse is native to the region, as is the Galician Blond cow and the domestic fowl known as the ''galiña de Mos (Spain), Mos''. The last is an endangered species, although it is showing signs of a comeback since 2001.
Galicia is home to one of the largest populations of Iberian wolf, wolves in western Europe. Galicia's woodlands and mountains are also home to rabbits, hares, wild boars, and roe deer, all of which are popular with hunters. Several important bird migration routes pass through Galicia, and some of the community's relatively few environmentally protected areas are Special Protection Areas (such as on the Ría de Ribadeo) for these birds. From a domestic point of view, Galicia has been credited by the author Manuel Rivas as the "land of one million cows". Galician Blond and Holstein cattle coexist on meadows and farms.
 Being located on the Atlantic coastline, Galicia has a very mild climate for the latitude and the marine influence affects most of the province to various degrees. In comparison to similar latitudes on the other side of the Atlantic, winters are exceptionally mild, with consistent rainfall. At sea level snow is exceptional, with temperatures just occasionally dropping below freezing; on the other hand, snow regularly falls in the eastern mountains from November to May. Overall, the climate of Galicia is comparable to the Pacific Northwest; the warmest coastal station of Pontevedra has a yearly mean temperature of . Ourense located somewhat inland is only slightly warmer with . Lugo, to the north, is colder, with , similar to the of Portland, Oregon.
In coastal areas summers are tempered, with daily maximums averaging around in Vigo. Temperatures are further cooler in A Coruña, with a subdued normal. Temperatures are much higher in inland areas such as Ourense, where days above are regular.
Being located on the Atlantic coastline, Galicia has a very mild climate for the latitude and the marine influence affects most of the province to various degrees. In comparison to similar latitudes on the other side of the Atlantic, winters are exceptionally mild, with consistent rainfall. At sea level snow is exceptional, with temperatures just occasionally dropping below freezing; on the other hand, snow regularly falls in the eastern mountains from November to May. Overall, the climate of Galicia is comparable to the Pacific Northwest; the warmest coastal station of Pontevedra has a yearly mean temperature of . Ourense located somewhat inland is only slightly warmer with . Lugo, to the north, is colder, with , similar to the of Portland, Oregon.
In coastal areas summers are tempered, with daily maximums averaging around in Vigo. Temperatures are further cooler in A Coruña, with a subdued normal. Temperatures are much higher in inland areas such as Ourense, where days above are regular.
 The lands of Galicia are ascribed to two different areas in the Köppen climate classification: a south area (roughly, the province of Ourense and Province of Pontevedra, Pontevedra) with appreciable summer drought, classified as a Mediterranean climate, warm-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csb''), with mild temperatures and rainfall usual throughout the year; and the western and northern coastal regions, the provinces of province of Lugo, Lugo and province of A Coruña, A Coruña, which are characterized by their Oceanic climate (''Cfb''), with a more uniform precipitation distribution along the year, and milder summers. However, precipitation in southern coastal areas are often classified as oceanic since the averages remain significantly higher than a typical Mediterranean climate.
As an example,
The lands of Galicia are ascribed to two different areas in the Köppen climate classification: a south area (roughly, the province of Ourense and Province of Pontevedra, Pontevedra) with appreciable summer drought, classified as a Mediterranean climate, warm-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csb''), with mild temperatures and rainfall usual throughout the year; and the western and northern coastal regions, the provinces of province of Lugo, Lugo and province of A Coruña, A Coruña, which are characterized by their Oceanic climate (''Cfb''), with a more uniform precipitation distribution along the year, and milder summers. However, precipitation in southern coastal areas are often classified as oceanic since the averages remain significantly higher than a typical Mediterranean climate.
As an example,
 The Xunta de Galicia is a collective entity with executive and administrative power. It consists of the President of the Xunta of Galicia, President, a vice president, and twelve councillors. Administrative power is largely delegated to dependent bodies. The Xunta also coordinates the activities of the provincial councils ( gl, deputacións) located in
The Xunta de Galicia is a collective entity with executive and administrative power. It consists of the President of the Xunta of Galicia, President, a vice president, and twelve councillors. Administrative power is largely delegated to dependent bodies. The Xunta also coordinates the activities of the provincial councils ( gl, deputacións) located in
 The Parliament of Galicia, Galician Parliament consists of 75 deputies elected by universal suffrage, universal adult suffrage under a system of proportional representation. The franchise includes also Galicians who reside abroad. Elections occur every four years.
The last elections, held 12 July 2020, resulted in the following distribution of seats:
* People's Party of Galicia, Partido Popular de Galicia (PPdeG): 41 deputies (47.98% of popular vote)
* Galician Nationalist Bloc, Bloque Nacionalista Galego (BNG): 19 deputies (23.80% of popular vote)
* Socialists' Party of Galicia, Partido Socialista de Galicia (PSdeG-PSOE): 15 deputies (19.38% of popular vote)
The Parliament of Galicia, Galician Parliament consists of 75 deputies elected by universal suffrage, universal adult suffrage under a system of proportional representation. The franchise includes also Galicians who reside abroad. Elections occur every four years.
The last elections, held 12 July 2020, resulted in the following distribution of seats:
* People's Party of Galicia, Partido Popular de Galicia (PPdeG): 41 deputies (47.98% of popular vote)
* Galician Nationalist Bloc, Bloque Nacionalista Galego (BNG): 19 deputies (23.80% of popular vote)
* Socialists' Party of Galicia, Partido Socialista de Galicia (PSdeG-PSOE): 15 deputies (19.38% of popular vote)
 There are 314 municipalities ( gl, concellos) in Galicia, each of which is run by a mayor–council government known as a .
There is a further subdivision of local government known as an ; each has its own council () and mayor (). There are nine of these in Galicia: Arcos da Condesa, Bembrive, Camposancos, Chenlo, Morgadáns, Pazos de Reis, Queimadelos, Vilasobroso, Mondariz, Vilasobroso and Berán.
Galicia is also traditionally subdivided in some 3,700 civil Parish (administrative division), parishes, each one comprising one or more ''vilas'' (towns), ''aldeas'' (villages), ''lugares'' (hamlets) or ''barrios'' (neighbourhoods).
There are 314 municipalities ( gl, concellos) in Galicia, each of which is run by a mayor–council government known as a .
There is a further subdivision of local government known as an ; each has its own council () and mayor (). There are nine of these in Galicia: Arcos da Condesa, Bembrive, Camposancos, Chenlo, Morgadáns, Pazos de Reis, Queimadelos, Vilasobroso, Mondariz, Vilasobroso and Berán.
Galicia is also traditionally subdivided in some 3,700 civil Parish (administrative division), parishes, each one comprising one or more ''vilas'' (towns), ''aldeas'' (villages), ''lugares'' (hamlets) or ''barrios'' (neighbourhoods).
Location A Coruña (Province).svg, A Coruña
Location Lugo (Province).svg, Lugo
Location Ourense (Province).svg, Ourense
Location Pontevedra (Province).svg, Pontevedra
Galicia is further divided into 53 ''comarcas of Spain, comarcas'', 315 municipalities of Spain, municipalities (Municipalities in A Coruña, 93 in A Coruña, Municipalities in Lugo, 67 in Lugo, Municipalities in Ourense, 92 in Ourense, Municipalities in Pontevedra, 62 in Pontevedra) and 3,778 parroquia (Spain), parishes. Municipalities are divided into parishes, which may be further divided into ''aldeas'' ("hamlets") or ''lugares'' ("places"). This traditional breakdown into such small areas is unusual when compared to the rest of Spain. Roughly half of the named population entities of Spain are in Galicia, which occupies only 5.8 percent of the country's area. It is estimated that Galicia has over a million named places, over 40,000 of them being communities.
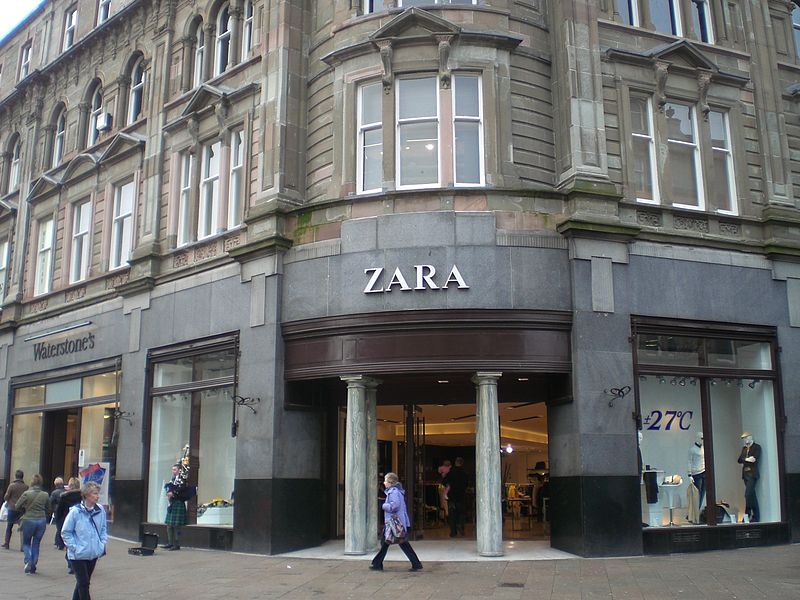 Textiles, fishing, livestock, forestry, and car manufacturing are the most dynamic sectors of the Galician economy.
The companies based in the province of Coruña generate 70% of the entrepreneurial output of Galicia. Arteixo, an industrial municipality in the A Coruña metropolitan area, is the headquarters of Inditex, the world's largest fashion retailer. Of their eight brands, Zara (retailer), Zara is the best-known; indeed, it is the best-known Spanish brand of any sort on an international basis. For 2007, Inditex had 9,435 million euros in sales for a net profit of 1,250 million euros. The company president, Amancio Ortega, is the richest person in Spain and indeed Europe with a net worth of 45 billion euros.
A major economic sector of Galicia is its fishing Industry; the main ports are port of A Coruña, A Coruña, Port of Marín and Ria de Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra, Port of Vigo, Vigo and Ferrol. Related to this fact, the European Fisheries Control Agency, which coordinates fishing controls in European Union waters, is based in Vigo.
Galicia is a land of economic contrast. While the western coast, with its major population centers and its fishing and manufacturing industries, is prosperous and increasing in population, the rural hinterland—the provinces of Ourense and Lugo—is economically dependent on traditional agriculture, based on small landholdings called ''minifundios''. However, the rise of tourism, sustainable forestry, and organic and traditional agriculture are bringing other possibilities to the Galician economy without compromising the preservation of the natural resources and the local culture.
Textiles, fishing, livestock, forestry, and car manufacturing are the most dynamic sectors of the Galician economy.
The companies based in the province of Coruña generate 70% of the entrepreneurial output of Galicia. Arteixo, an industrial municipality in the A Coruña metropolitan area, is the headquarters of Inditex, the world's largest fashion retailer. Of their eight brands, Zara (retailer), Zara is the best-known; indeed, it is the best-known Spanish brand of any sort on an international basis. For 2007, Inditex had 9,435 million euros in sales for a net profit of 1,250 million euros. The company president, Amancio Ortega, is the richest person in Spain and indeed Europe with a net worth of 45 billion euros.
A major economic sector of Galicia is its fishing Industry; the main ports are port of A Coruña, A Coruña, Port of Marín and Ria de Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra, Port of Vigo, Vigo and Ferrol. Related to this fact, the European Fisheries Control Agency, which coordinates fishing controls in European Union waters, is based in Vigo.
Galicia is a land of economic contrast. While the western coast, with its major population centers and its fishing and manufacturing industries, is prosperous and increasing in population, the rural hinterland—the provinces of Ourense and Lugo—is economically dependent on traditional agriculture, based on small landholdings called ''minifundios''. However, the rise of tourism, sustainable forestry, and organic and traditional agriculture are bringing other possibilities to the Galician economy without compromising the preservation of the natural resources and the local culture.
 Traditionally, Galicia depended mainly on agriculture and fishing. Nonetheless, today the tertiary sector of the economy (the service sector) is the largest, with 582,000 workers out of a regional total of 1,072,000 (as of 2002).
The secondary sector (manufacturing) includes shipbuilding in Vigo, Marín, Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra and Ferrol, textiles and granite work in A Coruña. A Coruña also manufactures automobiles. The French ''Centro de Vigo de PSA Peugeot Citroën'', founded in 1958, makes about 450,000 vehicles annually (455,430 in 2006); a Citroën C4 Picasso made in 2007 was their nine-millionth vehicle.Nueve millones de coches `made in´ Vigo
Traditionally, Galicia depended mainly on agriculture and fishing. Nonetheless, today the tertiary sector of the economy (the service sector) is the largest, with 582,000 workers out of a regional total of 1,072,000 (as of 2002).
The secondary sector (manufacturing) includes shipbuilding in Vigo, Marín, Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra and Ferrol, textiles and granite work in A Coruña. A Coruña also manufactures automobiles. The French ''Centro de Vigo de PSA Peugeot Citroën'', founded in 1958, makes about 450,000 vehicles annually (455,430 in 2006); a Citroën C4 Picasso made in 2007 was their nine-millionth vehicle.Nueve millones de coches `made in´ Vigo
, FaroDeVigo.es, 12 September 2007. Retrieved 9 November 2008. Other companies with a large number of workers and a significant asset turnover, turnover are San José, based in
 Galicia's main airport is Santiago de Compostela Airport. Having been used by 2,083,873 passengers in 2014, it connects the Galician capital with cities in Spain as well as several major European cities. There are two other domestic airports in Galicia: A Coruña Airport – Alvedro and Vigo-Peinador Airport.
The most important Galician fishing port is the Port of Vigo; It is one of the European's leading fishing ports, with an annual catch worth 1,500 million euros. In 2007 the port took in of fish and seafood, and about of other cargoes. Other important ports are
Galicia's main airport is Santiago de Compostela Airport. Having been used by 2,083,873 passengers in 2014, it connects the Galician capital with cities in Spain as well as several major European cities. There are two other domestic airports in Galicia: A Coruña Airport – Alvedro and Vigo-Peinador Airport.
The most important Galician fishing port is the Port of Vigo; It is one of the European's leading fishing ports, with an annual catch worth 1,500 million euros. In 2007 the port took in of fish and seafood, and about of other cargoes. Other important ports are  includes ''Highways in Spain, autopistas'' and ''autovías'' connecting the major cities, as well as national and secondary roads to the rest of the municipalities. The Autovía A-6 connects
includes ''Highways in Spain, autopistas'' and ''autovías'' connecting the major cities, as well as national and secondary roads to the rest of the municipalities. The Autovía A-6 connects
 Galicia's inhabitants are known as Galicians ( gl, galegos, es, gallegos). For well over a century Galicia has grown more slowly than the rest of Spain, due largely to a poorer economy compared with other regions of Spain and emigration to Latin America and to other parts of Spain. Sometimes Galicia has lost population in absolute terms. In 1857, Galicia had Spain's population density, densest population and constituted 11.5% of the national population. , only 6.1% of the Spanish population resided in the autonomous community. This is due to an exodus of Galician people since the 19th century, first to South America and later to Central Europe and the development of population centers and industry in other parts of Spain.
According to the 2006 census, Galicia has a fertility rate of 1.03 children per woman, compared to 1.38 nationally, and far below the figure of 2.1 that represents a stable populace. Lugo and Ourense provinces have the lowest fertility rates in Spain, 0.88 and 0.93, respectively.
In northern Galicia, the
Galicia's inhabitants are known as Galicians ( gl, galegos, es, gallegos). For well over a century Galicia has grown more slowly than the rest of Spain, due largely to a poorer economy compared with other regions of Spain and emigration to Latin America and to other parts of Spain. Sometimes Galicia has lost population in absolute terms. In 1857, Galicia had Spain's population density, densest population and constituted 11.5% of the national population. , only 6.1% of the Spanish population resided in the autonomous community. This is due to an exodus of Galician people since the 19th century, first to South America and later to Central Europe and the development of population centers and industry in other parts of Spain.
According to the 2006 census, Galicia has a fertility rate of 1.03 children per woman, compared to 1.38 nationally, and far below the figure of 2.1 that represents a stable populace. Lugo and Ourense provinces have the lowest fertility rates in Spain, 0.88 and 0.93, respectively.
In northern Galicia, the
Vista de la avenida de la Marina desde la parte de atrás de la Biblioteca Provincial de A Coruña.JPG,
The largest conurbations are:
* Pontevedra-Vigo 660,000
* A Coruña-Ferrol 640,000
 Galicia has two official languages: Galician (Galician: ''galego'') and Spanish (also known in Spain as ''Castellano'', i.e. ''"Castilian"''), both of them Romance languages. Galician originated regionally; the latter was associated with County of Castile, Castile. Galician is recognized in the Statute of Autonomy of Galicia as the ''lingua propia'' ("own language") of Galicia.
Galician is closely related to
Galicia has two official languages: Galician (Galician: ''galego'') and Spanish (also known in Spain as ''Castellano'', i.e. ''"Castilian"''), both of them Romance languages. Galician originated regionally; the latter was associated with County of Castile, Castile. Galician is recognized in the Statute of Autonomy of Galicia as the ''lingua propia'' ("own language") of Galicia.
Galician is closely related to
), Ethnologue. Retrieved 19 February 2010. Though considered to be independent languages in Galicia, the shared history between Galician and Portuguese has been widely acknowledged; in 2014, the Galician parliament approved Law 1/2014 on the promotion of Portuguese and links with the Lusophony. The official Galician language has been standardized by the Real Academia Galega based on literary tradition. Although there are local dialects, Galician media conform to this standard form, which is also used in primary, secondary, and university education. There are more than three million Galician speakers in the world. Galician ranks in the lower orders of the 150 most widely spoken languages on earth. For more than four centuries of Castilian domination, Spanish was the only official language in Galicia. Galician faded from day-to-day use in urban areas. Since the re-establishment of democracy in Spain—in particular since the passage and implementation of the ''Lei de Normalización Lingüística'' ("Law of Linguistic Normalization", Ley 3/1983, 15 June 1983)—the first generation of students in mass education has attended schools conducted in Galician. (Spanish is also taught.) Since the late 20th century and the establishment of Galicia's autonomy, the Galician language is resurgent. In the cities, it is generally used as a second language for most. According to a 2001 census, 99.16 percent of the population of Galicia understood the language, 91.04 percent spoke it, 68.65 percent could read it and 57.64 percent could write it.Plano Xeral de Normalización da lingua galega
, Xunta de Galicia. (In Galician.) p. 38. The first two numbers (understanding and speaking) were roughly the same as responses a decade earlier. But there were great gains in the percentage of the population who could read and write Galician: a decade earlier, only 49.3 percent of the population could read Galician, and 34.85 percent could write it. During the Francisco Franco, Franco era, the teaching of Galician was prohibited. Today older people may speak the language but have no written competence because of those years. Among the regional languages of Spain, Galician has the highest percentage of speakers in its population. The earliest known document in Galician-Portuguese dates from 1228. The ''Foro do bo burgo do Castro Caldelas'' was granted by Alfonso IX of León to the town of Burgo, in Castro Caldelas, after the model of the constitutions of the town of Allariz. A distinct Galician literature emerged during the Middle Ages: In the 13th century important contributions were made to the Romance canon in Galician-Portuguese, the most notable those by the troubadour Martín Codax, the priest Airas Nunes, King Dinis of Portugal, Denis of Portugal, and King Alfonso X of Castile, ''Alfonso O Sabio'' ("Alfonso the Wise"), the same monarch who began the process of standardization of the Spanish language. During this period, Galician-Portuguese was considered the language of love poetry in the Iberian Romance languages, Romance linguistic culture. The names and memories of Codax and other popular cultural figures are well preserved in modern Galicia.
 Christianity is the most widely practised religion in Galicia. It was introduced in Late Antiquity and was practiced alongside the native Celtic religion for a few centuries which, incidentally, was re-established as an officially recognised religion in 2015. Still, today about 77.7% of Galicians identify as Catholic. Most Christians adhere to Roman Catholicism, though only 32.1% of the population described themselves as active members. The Catholic Church in Galicia has had its primatial seat in
Christianity is the most widely practised religion in Galicia. It was introduced in Late Antiquity and was practiced alongside the native Celtic religion for a few centuries which, incidentally, was re-established as an officially recognised religion in 2015. Still, today about 77.7% of Galicians identify as Catholic. Most Christians adhere to Roman Catholicism, though only 32.1% of the population described themselves as active members. The Catholic Church in Galicia has had its primatial seat in
 Hundreds of ancient standing stone monuments like dolmens, menhirs, and megalithic Tumulus, tumuli were erected during the prehistoric period in Galicia. Amongst the best-known are the dolmens of Dombate, Corveira, Axeitos of Pedra da Arca, and menhirs like the Lapa de Gargñáns. From the Iron Age, Galicia has a rich heritage based mainly on a great number of hill forts, few of them excavated like Baroña, Sta. Tegra, San Cibrao de Lás and Formigueiros among others. With the introduction of Ancient Roman architecture, there was a development of basilicas, castra, city walls, cities, villas, Roman temples, Roman roads, and the Roman bridge of Ponte Vella. It was the Romans who founded some of the first cities in Galicia like Lugo and Ourense. Perhaps the best-known examples are the Roman Walls of Lugo and the Tower of Hercules in
Hundreds of ancient standing stone monuments like dolmens, menhirs, and megalithic Tumulus, tumuli were erected during the prehistoric period in Galicia. Amongst the best-known are the dolmens of Dombate, Corveira, Axeitos of Pedra da Arca, and menhirs like the Lapa de Gargñáns. From the Iron Age, Galicia has a rich heritage based mainly on a great number of hill forts, few of them excavated like Baroña, Sta. Tegra, San Cibrao de Lás and Formigueiros among others. With the introduction of Ancient Roman architecture, there was a development of basilicas, castra, city walls, cities, villas, Roman temples, Roman roads, and the Roman bridge of Ponte Vella. It was the Romans who founded some of the first cities in Galicia like Lugo and Ourense. Perhaps the best-known examples are the Roman Walls of Lugo and the Tower of Hercules in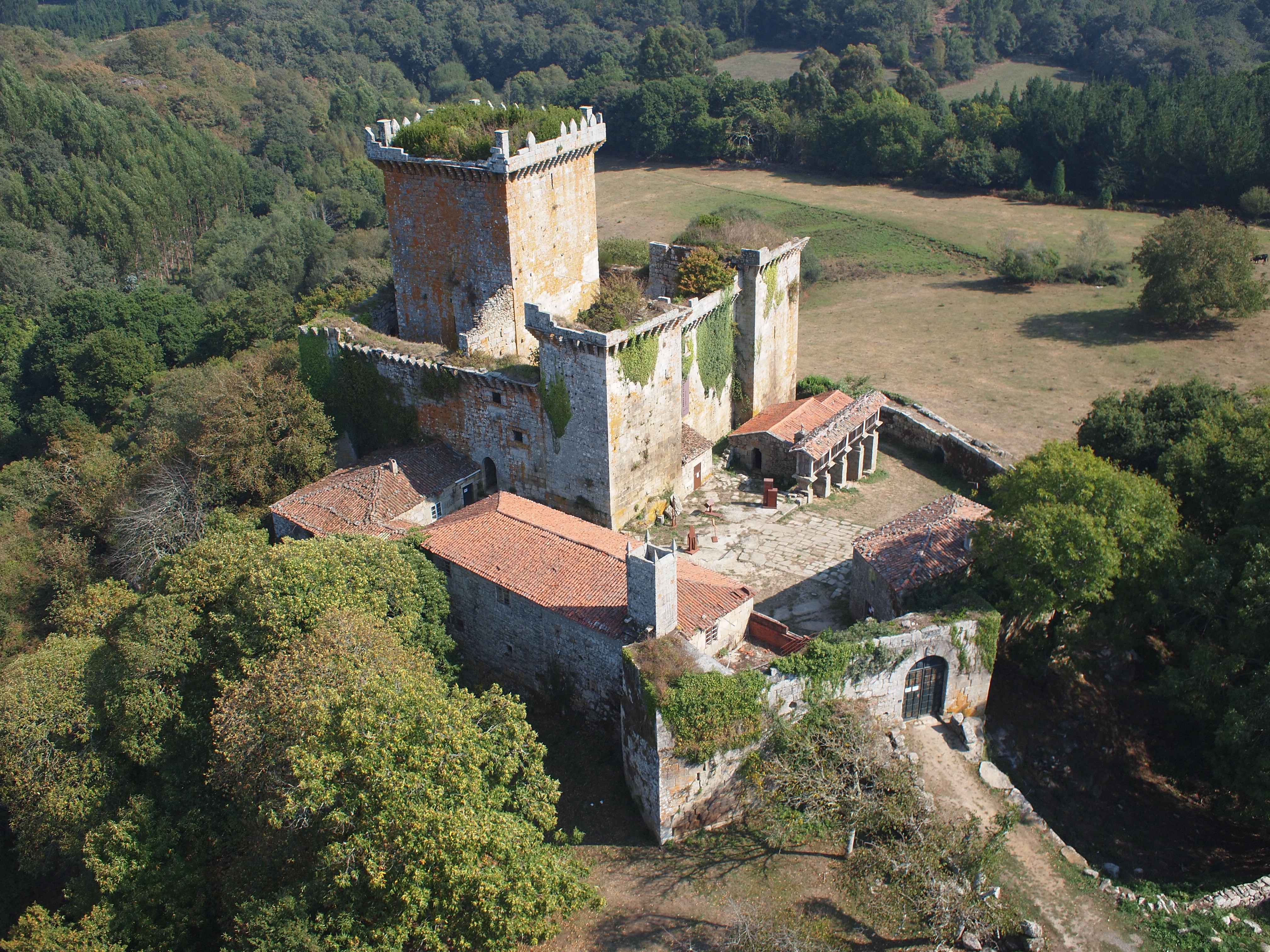  During the Middle Ages, many fortified castles were built by Galician feudal nobles to mark their powers against their rivals. Although most of them were demolished during the Irmandiño, Irmandiño Wars (1466–1469), some Galician castles that survived are Pambre, Castro Caldelas, Sobroso Castle, Sobroso, Castle of Soutomaior, Soutomaior and Monterrei. The ecclesiastical architecture was raised early in Galicia, and the first churches and monasteries as San Pedro de Rocas began to be built in the 5th and 6th centuries. However, the most famous medieval architecture in Galicia had been using Romanesque architecture like most of Western Europe. Some of the greatest examples of Romanesque churches in Galicia are the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, the Ourense Cathedral, Saint John of Caaveiro, Our Lady Mary of Cambre, and the Church of San Xoán, Portomarín, Church of San Xoán of Portomarín among others.
During the Middle Ages, many fortified castles were built by Galician feudal nobles to mark their powers against their rivals. Although most of them were demolished during the Irmandiño, Irmandiño Wars (1466–1469), some Galician castles that survived are Pambre, Castro Caldelas, Sobroso Castle, Sobroso, Castle of Soutomaior, Soutomaior and Monterrei. The ecclesiastical architecture was raised early in Galicia, and the first churches and monasteries as San Pedro de Rocas began to be built in the 5th and 6th centuries. However, the most famous medieval architecture in Galicia had been using Romanesque architecture like most of Western Europe. Some of the greatest examples of Romanesque churches in Galicia are the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, the Ourense Cathedral, Saint John of Caaveiro, Our Lady Mary of Cambre, and the Church of San Xoán, Portomarín, Church of San Xoán of Portomarín among others.
 Galician cuisine often uses fish and shellfish. The ''empanada'' is a meat or fish pie, with a bread-like base, top, and crust with the meat or fish filling usually being in a tomato sauce including onions and garlic. ''Caldo galego'' is a hearty soup whose main ingredients are potatoes and a local vegetable named Rapini, grelo (broccoli rabe). The latter is also employed in ''lacón con grelos'', a typical carnival dish, consisting of pork shoulder boiled with ''grelos'', potatoes, and chorizo. ''Centolla'' is the equivalent of king crab. It is prepared by being boiled alive, having its main body opened like a shell, and then having its innards mixed vigorously. Another popular dish is octopus, boiled (traditionally in a copper pot) and served on a wooden plate, cut into small pieces, and laced with olive oil, sea salt, and ''pimentón'' (Spanish paprika). This dish is called ''pulpo a la gallega'' or in Galician ''polbo á feira'', which roughly translates as 'fair-style octopus', most commonly translated as 'Galician-style octopus'. There are several regional varieties of cheese. The best-known one is the so-called ''tetilla cheese, tetilla'', named after its breast-like shape. Other highly regarded varieties include the San Simón cheese from Vilalba and the creamy cheese produced in the Arzúa-Ulloa area. A classical is ''filloas'', crêpe-like pancakes made with flour, broth or milk, and eggs. When cooked at a pig slaughter festival, they may also contain the animal's blood. A famous almond cake called ''Tarta de Santiago'' (St. James' cake) is a Galician sweet specialty mainly produced in Santiago de Compostela and all around Galicia.
Galician cuisine often uses fish and shellfish. The ''empanada'' is a meat or fish pie, with a bread-like base, top, and crust with the meat or fish filling usually being in a tomato sauce including onions and garlic. ''Caldo galego'' is a hearty soup whose main ingredients are potatoes and a local vegetable named Rapini, grelo (broccoli rabe). The latter is also employed in ''lacón con grelos'', a typical carnival dish, consisting of pork shoulder boiled with ''grelos'', potatoes, and chorizo. ''Centolla'' is the equivalent of king crab. It is prepared by being boiled alive, having its main body opened like a shell, and then having its innards mixed vigorously. Another popular dish is octopus, boiled (traditionally in a copper pot) and served on a wooden plate, cut into small pieces, and laced with olive oil, sea salt, and ''pimentón'' (Spanish paprika). This dish is called ''pulpo a la gallega'' or in Galician ''polbo á feira'', which roughly translates as 'fair-style octopus', most commonly translated as 'Galician-style octopus'. There are several regional varieties of cheese. The best-known one is the so-called ''tetilla cheese, tetilla'', named after its breast-like shape. Other highly regarded varieties include the San Simón cheese from Vilalba and the creamy cheese produced in the Arzúa-Ulloa area. A classical is ''filloas'', crêpe-like pancakes made with flour, broth or milk, and eggs. When cooked at a pig slaughter festival, they may also contain the animal's blood. A famous almond cake called ''Tarta de Santiago'' (St. James' cake) is a Galician sweet specialty mainly produced in Santiago de Compostela and all around Galicia.
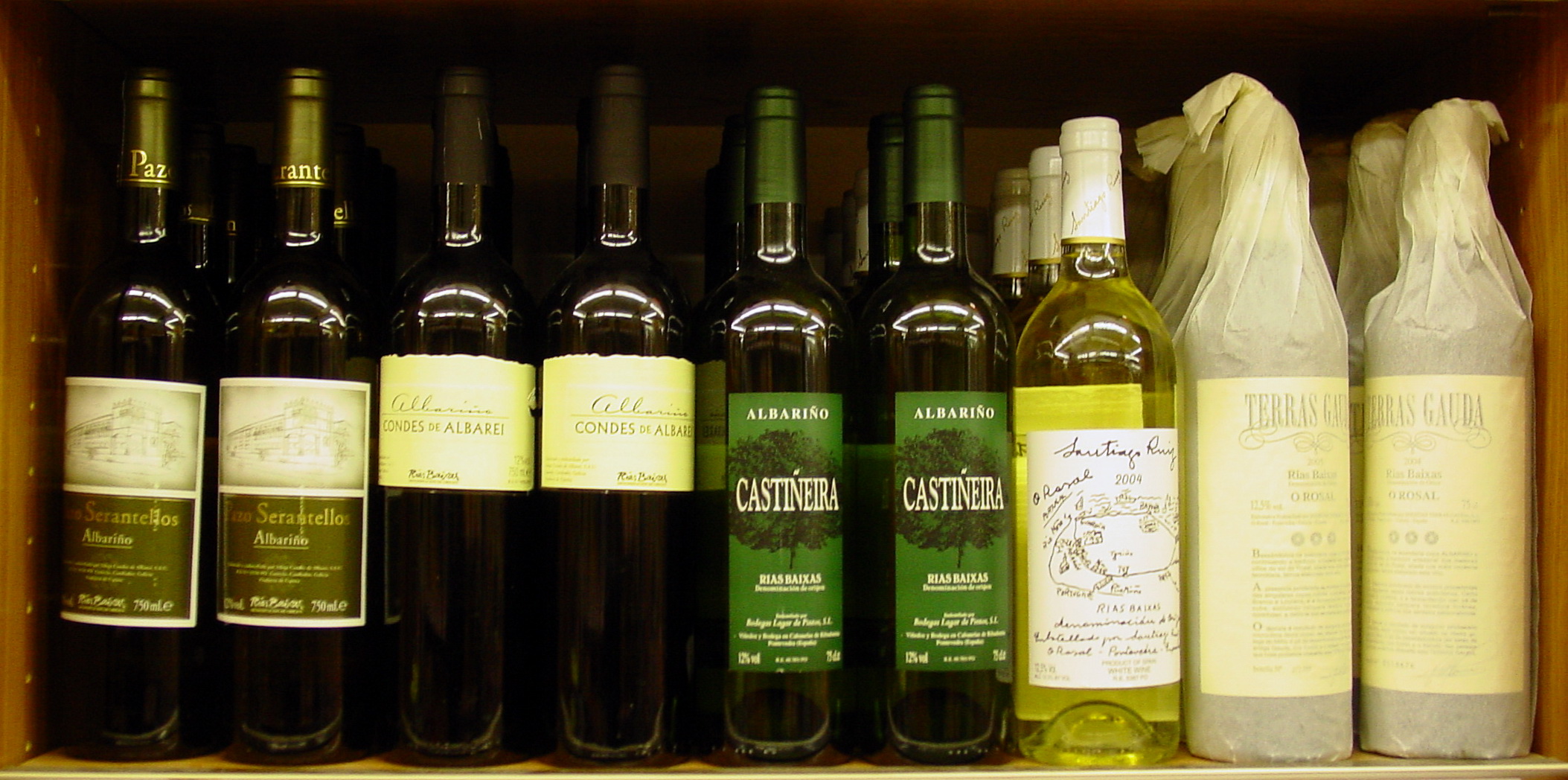 Galicia has 30 products with ''Denominación de origen, Denominación de orixe'' (D.O.), some of them with ''Denominación de Orixe Protexida'' (D.O.P.). D.O. and D.O.P. are part of a system of regulation of quality and geographical origin among Spain's finest producers. Galicia produces a number of high-quality Galician wines, including Albariño, Ribeiro (DO), Ribeiro, Ribeira Sacra, Monterrei and Valdeorras. The grape varieties used are local and rarely found outside Galicia and Northern Portugal. Just as notably from Galicia comes the spirit ''Augardente''—the name means burning water—often referred to as Orujo in Spain and internationally or as Orujo, caña in Galicia. This spirit is made from the distillation of the pomace of grapes.
Galicia has 30 products with ''Denominación de origen, Denominación de orixe'' (D.O.), some of them with ''Denominación de Orixe Protexida'' (D.O.P.). D.O. and D.O.P. are part of a system of regulation of quality and geographical origin among Spain's finest producers. Galicia produces a number of high-quality Galician wines, including Albariño, Ribeiro (DO), Ribeiro, Ribeira Sacra, Monterrei and Valdeorras. The grape varieties used are local and rarely found outside Galicia and Northern Portugal. Just as notably from Galicia comes the spirit ''Augardente''—the name means burning water—often referred to as Orujo in Spain and internationally or as Orujo, caña in Galicia. This spirit is made from the distillation of the pomace of grapes.
 The traditional music of Galicia and
The traditional music of Galicia and
 As a literary language it was revived again during the 18th and, most notably, the 19th-century (''Rexurdimento'' ''Resurgence'') with such writers as Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal. In the 20th century, before the Spanish Civil War the ''Irmandades da Fala'' ("Brotherhood of the Language") and ''Nós (Galicia), Grupo Nós'' included such writers as Vicente Risco, Ramón Cabanillas and Castelao. Public use of Galician was largely suppressed during the Franco dictatorship but has been resurgent since the restoration of democracy. Though written primarily in Castilian, several works by the Nobel laureate Camilo José Cela, notably ''Mazurka for Two Dead Men'', are set in the author's native Galicia and make frequent allusions to Galician folklore, customs, and language. Other notable Galician authors who wrote mostly in Spanish, but always around Galician subjects, are Valle-Inclán, Wenceslao Fernández Flórez, Emilia Pardo Bazán and Gonzalo Torrente Ballester. Contemporary writers in Galician include Xosé Luís Méndez Ferrín, Manuel Rivas, Chus Pato, and Suso de Toro.
As a literary language it was revived again during the 18th and, most notably, the 19th-century (''Rexurdimento'' ''Resurgence'') with such writers as Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal. In the 20th century, before the Spanish Civil War the ''Irmandades da Fala'' ("Brotherhood of the Language") and ''Nós (Galicia), Grupo Nós'' included such writers as Vicente Risco, Ramón Cabanillas and Castelao. Public use of Galician was largely suppressed during the Franco dictatorship but has been resurgent since the restoration of democracy. Though written primarily in Castilian, several works by the Nobel laureate Camilo José Cela, notably ''Mazurka for Two Dead Men'', are set in the author's native Galicia and make frequent allusions to Galician folklore, customs, and language. Other notable Galician authors who wrote mostly in Spanish, but always around Galician subjects, are Valle-Inclán, Wenceslao Fernández Flórez, Emilia Pardo Bazán and Gonzalo Torrente Ballester. Contemporary writers in Galician include Xosé Luís Méndez Ferrín, Manuel Rivas, Chus Pato, and Suso de Toro.
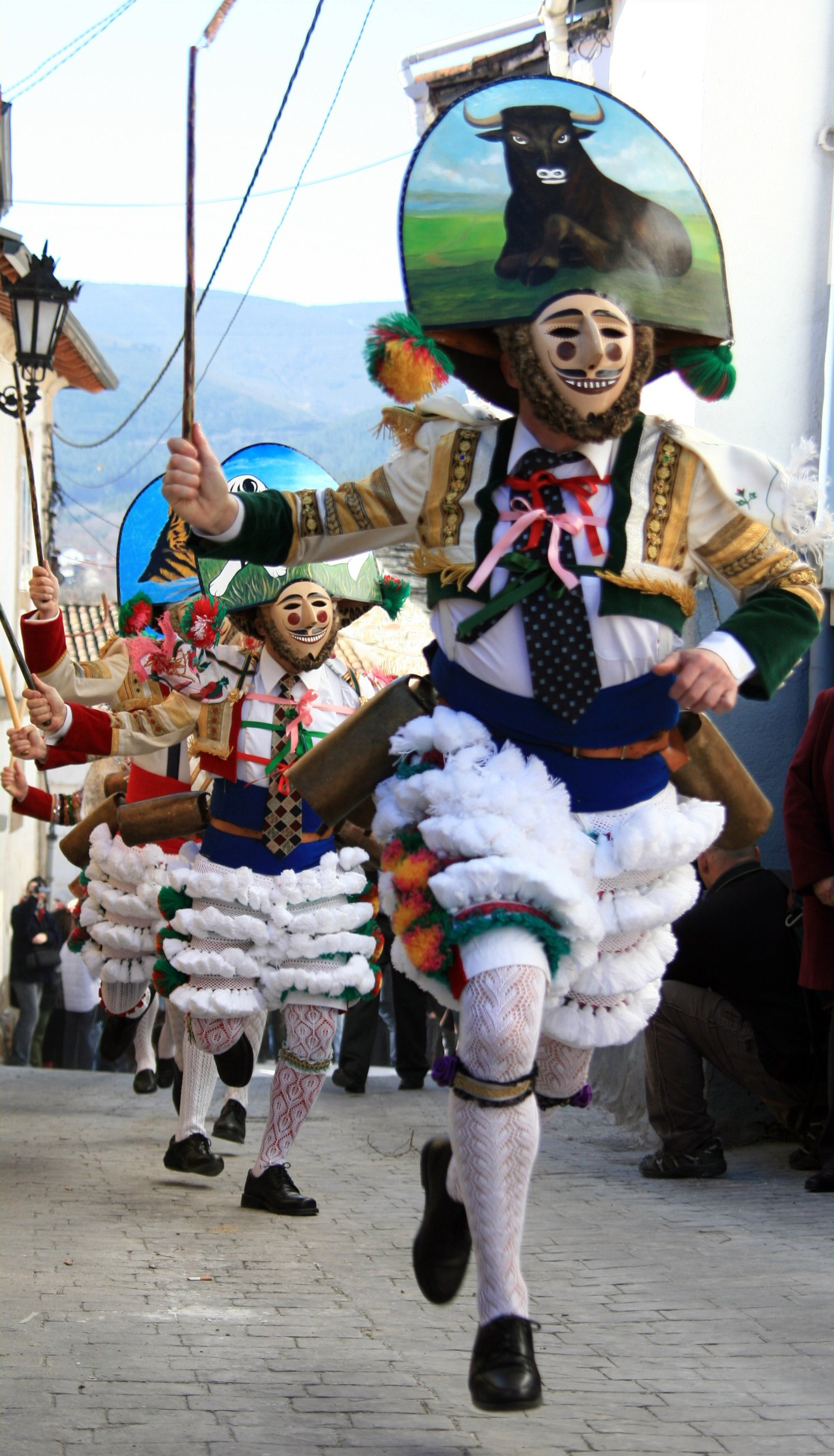 * ''Entroido'', or Carnival, is a traditional celebration in Galicia, historically disliked and even forbidden by the Catholic Church. Famous celebrations are held in Laza, Spain, Laza, Verín, and Xinzo de Limia.
* Corpus Christi (feast), Festa do Corpus Christi in Ponteareas, has been observed since 1857 on the weekend following Corpus Christi (feast), Corpus Christi (a movable feast) and is known for its floral carpets. It was declared a Festival of Tourist Interest in 1968 and a Festival of National Tourist Interest in 1980.
* Pontevedra Feira Franca, Feira Franca, the first weekend of September, in
* ''Entroido'', or Carnival, is a traditional celebration in Galicia, historically disliked and even forbidden by the Catholic Church. Famous celebrations are held in Laza, Spain, Laza, Verín, and Xinzo de Limia.
* Corpus Christi (feast), Festa do Corpus Christi in Ponteareas, has been observed since 1857 on the weekend following Corpus Christi (feast), Corpus Christi (a movable feast) and is known for its floral carpets. It was declared a Festival of Tourist Interest in 1968 and a Festival of National Tourist Interest in 1980.
* Pontevedra Feira Franca, Feira Franca, the first weekend of September, in
 A golden chalice enclosed in a field of azure (heraldry), azure has been the symbol of Galicia since the 13th century. Originated as a Canting arms due to the phonetic similarity between the words "chalice" and ''Galyce'' ("Galicia" in old Norman language), the first documented mention of this emblem is on the ''Segar's Roll'', an English medieval roll of arms where are represented all the Christian kingdoms of 13th-century Europe. In the following centuries, the Galician emblem was variating; diverse shapes and several chalices (initially three and later one or five), wouldn't be until the 16th century that its number was fixed finally as one single chalice. Centuries after, a field of crosses was slowly added to the azure background, and latterly also a silver host. Since then basically, the emblem of the kingdom would be kept until nowadays.
The ancient flag of the Kingdom of Galicia was based mainly on its coat of arms until the 19th century. However, when in 1833 the Government of Spain decided to abolish the kingdom and divided it into four provinces, the Galician emblem, as well as the flag, lost its legal status and international validity. It wouldn't be until the late 19th century that some Galician intellectuals (nationalist politicians and writers) began to use a new flag as a symbol of renewed national unity for Galicia. That flag, which was composed of a diagonal stripe over a white background, was designated the "official flag of Galicia" in 1984, after the fall of Franco's dictatorship. In addition, the Royal Academy of Galicia asked the Galician government to incorporate the ancient coat of arms of the kingdom onto the modern flag, being present in it since then.
In addition to its coat of arms and flag, Galicia also has its own anthem. While it is true that the Kingdom of Galicia had during centuries a kind of unofficial anthem known as the "Solemn March of the kingdom", the Galician current anthem was not created until 1907, although its composition had begun already in 1880. Titled "Os Pinos" ("The Pines"), the Galician anthem lyrics were written by Eduardo Pondal, one of the greatest modern Galician poets, and its music was composed by Pascual Veiga. Performed for the first time in 1907 in Havana (Cuba) by Galician emigrants, the anthem was banned from 1927 by diverse Spanish Governments until 1977 when it was officially established by the Galician authorities.
A golden chalice enclosed in a field of azure (heraldry), azure has been the symbol of Galicia since the 13th century. Originated as a Canting arms due to the phonetic similarity between the words "chalice" and ''Galyce'' ("Galicia" in old Norman language), the first documented mention of this emblem is on the ''Segar's Roll'', an English medieval roll of arms where are represented all the Christian kingdoms of 13th-century Europe. In the following centuries, the Galician emblem was variating; diverse shapes and several chalices (initially three and later one or five), wouldn't be until the 16th century that its number was fixed finally as one single chalice. Centuries after, a field of crosses was slowly added to the azure background, and latterly also a silver host. Since then basically, the emblem of the kingdom would be kept until nowadays.
The ancient flag of the Kingdom of Galicia was based mainly on its coat of arms until the 19th century. However, when in 1833 the Government of Spain decided to abolish the kingdom and divided it into four provinces, the Galician emblem, as well as the flag, lost its legal status and international validity. It wouldn't be until the late 19th century that some Galician intellectuals (nationalist politicians and writers) began to use a new flag as a symbol of renewed national unity for Galicia. That flag, which was composed of a diagonal stripe over a white background, was designated the "official flag of Galicia" in 1984, after the fall of Franco's dictatorship. In addition, the Royal Academy of Galicia asked the Galician government to incorporate the ancient coat of arms of the kingdom onto the modern flag, being present in it since then.
In addition to its coat of arms and flag, Galicia also has its own anthem. While it is true that the Kingdom of Galicia had during centuries a kind of unofficial anthem known as the "Solemn March of the kingdom", the Galician current anthem was not created until 1907, although its composition had begun already in 1880. Titled "Os Pinos" ("The Pines"), the Galician anthem lyrics were written by Eduardo Pondal, one of the greatest modern Galician poets, and its music was composed by Pascual Veiga. Performed for the first time in 1907 in Havana (Cuba) by Galician emigrants, the anthem was banned from 1927 by diverse Spanish Governments until 1977 when it was officially established by the Galician authorities.
Dolmen axeitos.JPG, ''Anta'' ( dolmen) at Axeitos, Santa Uxía de Ribeira, Ribeira. Hundreds of megaliths are still preserved in Galicia
Cabo Fisterra desde o Monte Pindo.jpg, ''Fisterra'' or Cape Finisterre, meaning 'Land's End', one of the westernmost points in continental Europe
Breogan e Torre de Hércules.jpg, Torre de Hércules, Tower of Hercules, a Roman lighthouse and a World Heritage monument,
''Spanish Galicia''
London: John Lane The Bodley Head Ltd. * Meakin, Annette M. B. (1909)
''Galicia: The Switzerland of Spain''
London: Methuen & Co.
autonomous community
eu, autonomia erkidegoa
ca, comunitat autònoma
gl, comunidade autónoma
oc, comunautat autonòma
an, comunidat autonoma
ast, comunidá autónoma
, alt_name =
, map =
, category = Autonomous administra ...
of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the northwest Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
, it includes the provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Lugo, Ourense, and Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
.
Galicia is located in Atlantic Europe. It is bordered by Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
to the south, the Spanish autonomous communities of Castile and León and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
to the east, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the west, and the Cantabrian Sea
The Cantabrian Sea; french: Mer Cantabrique, gl, Mar Cantábrico, ast, Mar Cantábricu, eu, Kantauri. is the term used mostly in Spain to describe the coastal sea of the Atlantic Ocean that borders the northern coast of Spain and the southwe ...
to the north. It had a population of 2,701,743 in 2018 and a total area of . Galicia has over of coastline, including its offshore islands and islets, among them Cíes Islands, Ons, Sálvora
Sálvora Island ( gl, Illa de Sálvora ; es, Isla de Sálvora ) is a small island located on the Ría de Arousa, coast of Galicia, Spain. It belongs to the municipality of Santa Uxía de Ribeira and is integrated in the Atlantic Islands of Galici ...
, Cortegada Island
Cortegada is an almost tidal island (it is possible to go walking when the lowest tides happen, but a small amount of water flow does not disappear) in a coastal inlet near Pontevedra in Galicia, Spain. It is part of the Atlantic Islands of Galici ...
, which together form the Atlantic Islands of Galicia National Park, and the largest and most populated, A Illa de Arousa
A Illa de Arousa ( es, La isla de Arosa) is the only island municipality in Galicia, Spain in the province of Pontevedra. It is located in the heart of the Ria de Arousa. According to 2021 INE the island's population was 4,951 inhabitants. The po ...
.
The area now called Galicia was first inhabited by humans during the Middle Paleolithic period, and takes its name from the Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; grc, Καλλαϊκοί) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, a ...
, the Celtic people
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
living north of the Douro
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part o ...
River during the last millennium BC. Galicia was incorporated into the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
at the end of the Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what tod ...
in 19 BC, and was made a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
in the 3rd century AD. In 410, the Germanic Suebi established a kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
with its capital in Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
; this kingdom was incorporated into that of the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
in 585. In 711, the Islamic Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
invaded the Iberian Peninsula conquering the Visigoth kingdom of Hispania by 718, but soon Galicia was incorporated into the Christian kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of ...
by 740. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the kingdom of Galicia
The Kingdom of Galicia ( gl, Reino de Galicia, or ''Galiza''; es, Reino de Galicia; pt, Reino da Galiza; la, Galliciense Regnum) was a political entity located in southwestern Europe, which at its territorial zenith occupied the entire north ...
was occasionally ruled by its own kings, but most of the time it was leagued to the kingdom of Leon
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
and later to that of Castile, while maintaining its own legal and customary practices and culture. From the 13th century on, the kings of Castile, as kings of Galicia, appointed an '' Adiantado-mór'', whose attributions passed to the ''Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
and Captain General
Captain general (and its literal equivalent in several languages) is a high military rank of general officer grade, and a gubernatorial title.
History
The term "Captain General" started to appear in the 14th century, with the meaning of Comma ...
of the Kingdom of Galiza'' from the last years of the 15th century. The Governor also presided the ''Real Audiencia
A ''Real Audiencia'' (), or simply an ''Audiencia'' ( ca, Reial Audiència, Audiència Reial, or Audiència), was an appellate court in Spain and its empire. The name of the institution literally translates as Royal Audience. The additional des ...
do Reino de Galicia'', a royal tribunal and government body. From the 16th century, the representation and voice of the kingdom was held by an assembly of deputies and representatives of the cities of the kingdom, the ''Cortes'' or '' Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia.'' This institution was forcibly discontinued in 1833 when the kingdom was divided into four administrative provinces with no legal mutual links. During the 19th and 20th centuries, demand grew for self-government and for the recognition of the culture of Galicia. This resulted in the Statute of Autonomy of 1936, soon frustrated by Franco's ''coup d'état'' and subsequent long dictatorship. After democracy was restored the legislature passed the Statute of Autonomy of 1981, approved in referendum and currently in force, providing Galicia with self-government.
The interior of Galicia is characterized by a hilly landscape; mountain ranges rise to in the east and south. The coastal areas are mostly an alternate series of rias and beaches. The climate of Galicia is usually temperate and rainy, with markedly drier summers; it is usually classified as Oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
. Its topographic and climatic conditions have made animal husbandry and farming the primary source of Galicia's wealth for most of its history, allowing for a relatively high density of population. Except shipbuilding and food processing, Galicia was based on a farming and fishing economy until after the mid-20th century, when it began to industrialize. In 2018, the nominal gross domestic product was €62.900 billion, with a nominal GDP per capita of €23,300. Galicia is characterised, unlike other Spanish regions, by the absence of a metropolis dominating the territory. Indeed, the urban network is made up of 7 main cities (the four provincial capitals A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, Ourense and Lugo, the political capital Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
and the industrial cities Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
and Ferrol and other small towns. The population is largely concentrated in two main areas: from Ferrol to A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
on the northern coast, and in the Rías Baixas
The Rías Baixas (Galician language, Galician for "Lower Rias") are a series of four estuarine inlets located on the southwestern coast of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Spain. They are the Ría de Muros e Noia, the Ría de Arousa, the Ria de Ponteved ...
region in the southwest, including the cities of Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, and the interior city of Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
. There are smaller populations around the interior cities of Lugo and Ourense. The political capital is Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
, in the province of A Coruña
The province of A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical en, link=no, Corunna) is the northwesternmost province of Spain, and one of the four provinces which constitute the autonomous community of Galicia. This province is surrounded by the At ...
. Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
, in the province of Pontevedra
Pontevedra is a province of Spain along the country's Atlantic coast in southwestern Europe. The province forms the southwestern part of the autonomous community of Galicia. It is bordered by the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, and Ourense, ...
, is the largest municipality in Galicia and also the most populated city. Two languages are official and widely used today in Galicia: the native Galician, a Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language f ...
closely related to Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
with which it shares the Galician-Portuguese
Galician-Portuguese ( gl, galego-portugués or ', pt, galego-português or ), also known as Old Portuguese or as Medieval Galician when referring to the history of each modern language, was a West Iberian Romance language spoken in the Middle ...
medieval literature; and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, usually called ''Castilian''. While most Galicians are bilingual, a 2013 survey reported that 51% of the Galician population spoke Galician most often on a day-to-day basis, while 48% most often used Spanish.
Toponymy
 The name ''Galicia'' derives from the Latin toponym Callaecia, later ''
The name ''Galicia'' derives from the Latin toponym Callaecia, later ''Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
'', related to the name of an ancient Celtic tribe that resided north of the Douro
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part o ...
river, the Gallaeci or Callaeci in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, or (''Kallaïkoí'') in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
. These '' Callaeci'' were the first tribe in the area to help the Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. ...
against the invading Romans. The Romans applied their name to all the other tribes in the northwest who spoke the same language and lived the same life.
The toponymy of the name has been studied since the 7th century by authors such as Isidore of Seville, who wrote that "Galicians are called so, because of their fair skin, as the Gauls", relating the name to the Greek word for milk. (See the etymology of the word ''galaxy''.) In the 21st century, some scholars (J.J. Moralejo, Carlos Búa) have derived the name of the ancient Callaeci either from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
*kl(H)-no- 'hill', through a local relational suffix -aik-, also attested in Celtiberian, so meaning 'the hill (people)'; or either from Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celti ...
*kallī- 'forest', so meaning 'the forest (people)'. In any case, ''Galicia'', being ''per se'' a derivation of the ethnic name ''Kallaikói'', means 'the land of the Galicians'.
Another recent proposal comes from linguist Francesco Benozzo after identifying the root ''gall-'' / ''kall-'' in a number of Celtic words with the meaning "stone" or "rock", as follows: ''gall'' (old Irish), ''gal'' (Middle Welsh), ''gailleichan'' (Scottish Gaelic), ''kailhoù'' (Breton), ''galagh'' (Manx) and ''gall'' (Gaulish). Hence, Benozzo explains the ethnonym ''Callaeci'' as being "the stone people" or "the people of the stone" ("those who work with stones"), about the builders of the ancient megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
s and stone formations so common in Galicia.
The name evolved during the Middle Ages from ''Gallaecia,'' sometimes written ''Galletia,'' to ''Gallicia''. In the 13th century, with the written emergence of the Galician language, ''Galiza'' became the most usual written form of the name of the country, being replaced during the 15th and 16th centuries by the current form, ''Galicia'', which is also the spelling of the name in Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
. The historical denomination ''Galiza'' became popular again during the end of the 19th and the first three-quarters of the 20th century and is still used with some frequency today. The Xunta de Galicia
The Xunta de Galicia (; "Regional Government of Galicia") is the collective decision-making body of the government of the autonomous community of Galicia, composed of the President, the Vice-President(s) and the specialized ministers (''Consell ...
, the local devolved government
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
, uses ''Galicia''. The Royal Galician Academy
The Royal Galician Academy ( gl, Real Academia Galega, RAG) is an institution dedicated to the study of Galician culture and especially the Galician language; it promulgates norms of grammar, spelling, and vocabulary and works to promote the l ...
, the institution responsible for regulating the Galician language, whilst recognizing ''Galiza'' as a legitimate current denomination, has stated that the only official name of the country is ''Galicia''.
Due to Galicia's history and culture with mythology, the land has been called "''Terra Meiga''" (land of the witches/witch(ing) land).
History
Prehistory and antiquity
 The oldest attestation of human presence in Galicia has been found in the Eirós Cave, in the municipality of
The oldest attestation of human presence in Galicia has been found in the Eirós Cave, in the municipality of Triacastela
Triacastela is a municipality in the province of Lugo, Galicia, Spain. It gets its name from the three castles that once stood here, none of which exist today. Norman (Viking) invaders in 968 A.D. pillaged here, eventually to be defeated at Cebrei ...
, which has preserved animal remains and Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
stone objects from the Middle Paleolithic. The earliest culture to have left significant architectural traces is the Megalithic culture, which expanded along the western European coasts during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
and Calcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
eras. Thousands of Megalithic tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
are distributed throughout the country, mostly along the coastal areas. Within each tumulus is a stone burial chamber known locally as ''anta'' ( dolmen), frequently preceded by a corridor. Galicia was later influenced by the Bell Beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from a ...
. Its rich mineral deposits of tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
led to the development of Bronze Age metallurgy, and the commerce of bronze and gold items all along the Atlantic coast of Western Europe. A shared elite culture evolved in this region during the Atlantic Bronze Age.
 Dating from the end of the Megalithic era, and up to the Bronze Age, numerous stone carvings (petroglyphs) are found in open air. They usually represent cup and ring marks, labyrinths, deer, Bronze Age weapons, and riding and hunting scenes. Large numbers of these stone carvings can be found in the Rías Baixas regions, at places such as Tourón and Campo Lameiro.
The Castro culture ('Culture of the Castles') developed during the Iron Age, and flourished during the second half of the first millennium BC. It is usually considered a local evolution of the Atlantic Bronze Age, with later developments and influences overlapping into the Roman era. Geographically, it corresponds to the people the Romans called
Dating from the end of the Megalithic era, and up to the Bronze Age, numerous stone carvings (petroglyphs) are found in open air. They usually represent cup and ring marks, labyrinths, deer, Bronze Age weapons, and riding and hunting scenes. Large numbers of these stone carvings can be found in the Rías Baixas regions, at places such as Tourón and Campo Lameiro.
The Castro culture ('Culture of the Castles') developed during the Iron Age, and flourished during the second half of the first millennium BC. It is usually considered a local evolution of the Atlantic Bronze Age, with later developments and influences overlapping into the Roman era. Geographically, it corresponds to the people the Romans called Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; grc, Καλλαϊκοί) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, a ...
, which were composed of a large series of nations or tribes, among them the ''Artabri'', ''Bracari'', ''Limici'', ''Celtici'', ''Albiones'' and ''Lemavi''. They were capable fighters: Strabo described them as the most difficult foes the Romans encountered in conquering Lusitania, while Appian mentions their warlike spirit, noting that the women bore their weapons side by side with their men, frequently preferring death to captivity. According to Pomponius Mela all the inhabitants of the coastal areas were Celtic people
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
by the time of Augustus (29 BC – 19 BC). The Romans were interested in Galicia mainly for its mineral resources, most notably gold. Under Roman rule, most Galician hillforts began to be – sometimes forcibly – abandoned, and Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; grc, Καλλαϊκοί) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, a ...
served frequently in the Roman army as auxiliary troops. Romans brought new technologies, new travel routes, new forms of organizing property, and a new language; latin language, Latin. The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
established its control over Galicia through camps (''castra'') as ''Aquis Querquennis'', Ciadella camp or Lugo, Lucus Augusti ( Lugo), roads (''viae'') and monuments as the lighthouse known as ''Tower of Hercules'', in A Coruña, Corunna, but the remoteness and lesser interest of the country since the 2nd century of our era, when the gold mines stopped being productive, led to a lesser degree of ''Romanization''. In the 3rd century, it was made a province, under the name Gallaecia, which included also northern Portugal, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, and a large section of what today is known as Castile and León.
Early Middle Ages
 In the early 5th century, the deep crisis suffered by the
In the early 5th century, the deep crisis suffered by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
allowed different tribes of Central Europe ( Suebi, Vandals and Alans, Alani) to cross the Rhine and penetrate the rule on 31 December 406. Its progress towards the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
forced the Roman authorities to establish a treaty (''foedus'') by which the Suebi would settle peacefully and govern Galicia as imperial allies. So, from 409 Galicia was taken by the Suebi, forming the first medieval kingdom to be created in Europe, in 411, even before the fall of the Roman Empire, being also the first Germanic kingdom to mint coinage in Roman lands. During this period a Britons (historical), Briton colony and bishopric (see Mailoc) was established in Northern Galicia (Britonia), probably as foederati and allies of the Suebi. In 585, the Visigothic King Leovigild invaded the Suebic kingdom of Galicia and defeated it, bringing it under Visigoth control.
Later the Arab Empire, Muslims invaded Spain (711), but the Arabs and Moors never managed to have any real control over Galicia, which was later incorporated into the expanding Christian Kingdom of Asturias, usually known as Gallaecia or Galicia (''Yillīqiya'' and ''Galīsiya'') by Muslim chroniclers, as well as by many European contemporaries.Alfonso II of Asturias was addressed as: ''"DCCXCVIII. Venit etiam et legatus Hadefonsi regis Galleciae et Asturiae, nomine Froia, papilionem mirae pulchritudinis praesentans. (...) Hadefonsus rex Galleciae et Asturiae praedata Olisipona ultima Hispaniae civitate insignia victoriae suae loricas, mulos captivosque Mauros domno regi per legatos suos Froiam et Basiliscum hiemis tempore misit".'' (ANNALES REGNI FRANCORUM); ''"Hadefuns rex Gallaeciae Carolo prius munera pretiosa itemque manubias suas pro munere misit".'' (CODEX AUGIENSIS); ''"Galleciarum princeps"'' (VITA LUDOVICI) Cf. López Carreira, Anselmo (2005): ''O Reino medieval de Galicia''. A Nosa Terra, Vigo. pp. 211–248. This era consolidated Galicia as a Christian society which spoke a Romance languages, Romance language. During the next century Galician noblemen took northern Portugal, conquering Coimbra in 871, thus freeing what was considered the southernmost city of ancient Galicia.
High and Low Middle Ages
 In the 9th century, the rise of the cult of the James, son of Zebedee, Apostle James in
In the 9th century, the rise of the cult of the James, son of Zebedee, Apostle James in Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
gave Galicia particular symbolic importance among Christians, an importance it would hold throughout the ''Reconquista''. As the Middle Ages went on, Santiago became a major pilgrim destination and the Way of Saint James (Camiño de Santiago) a major pilgrim road, a route for the propagation of Romanesque art and the words and music of the troubadors. During the 10th and 11th centuries, a period during which Galician nobility become related to the royal family, Galicia was at times headed by its own List of Galician monarchs, native kings, while Vikings (locally known as ''Leodemanes'' or ''Lordomanes'') occasionally raided the coasts. The Towers of Catoira (Pontevedra) were built as a system of fortifications to prevent and stop the Viking raids on Santiago de Compostela.
In 1063, Ferdinand I of Castile divided his realm among his sons, and the Kingdom of Galicia was granted to Garcia II of Galicia. In 1072, it was forcibly annexed by Garcia's brother Alfonso VI of León; from that time Galicia was united with the Kingdom of León under the same monarchs. In the 13th century Alfonso X of Castile standardized the Castilian language (i.e. Spanish) and made it the language of court and government. Nevertheless, in his Kingdom of Galicia the Galician language was the only language spoken, and the most used in government and legal uses, as well as in Galician-Portuguese lyric, literature.
During the 14th and 15th centuries, the progressive distancing of the kings from Galician affairs left the kingdom in the hands of the local knights, counts, and bishops, who frequently fought each other to increase their fiefs, or simply to plunder the lands of others. At the same time, the deputies of the Kingdom in the ''Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia, Cortes'' stopped being called. The Kingdom of Galicia, slipping away from the control of the King, responded with a century of fiscal insubordination.
 On the other hand, the lack of an effective royal justice system in the Kingdom led to the social conflict known as the ''Irmandiño, Guerras Irmandiñas'' ('Wars of the brotherhoods'), when leagues of peasants and burghers, with the support of several knights, noblemen, and under legal protection offered by the remote king, toppled many of the castles of the Kingdom and briefly drove the noblemen into Portugal and Castile. Soon after, in the late 15th century, in the dynastic conflict between Isabella I of Castile and Joanna La Beltraneja, part of the Galician aristocracy supported Joanna. After Isabella's victory, she initiated an administrative and political reform which the chronicler Zurita y Castro, Jeronimo, Jeronimo Zurita defined as "doma del Reino de Galicia": 'It was then when the taming of Galicia began, because not just the local lords and knights, but all the people of that nation were the ones against the others very bold and warlike'. These reforms, while establishing a local government and tribunal (the ''Real Audiencia del Reino de Galicia''), and bringing the nobleman under submission, also brought most Galician monasteries and institutions under Castilian control, in what has been criticized as a process of centralisation. At the same time the kings began to call the Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia, ''Xunta'' or ''Cortes'' of the Kingdom of Galicia, an assembly of deputies or representatives of the cities of the Kingdom, to ask for monetary and military contributions. This assembly soon developed into the voice and legal representation of the Kingdom, and the depositary of its will and laws.
On the other hand, the lack of an effective royal justice system in the Kingdom led to the social conflict known as the ''Irmandiño, Guerras Irmandiñas'' ('Wars of the brotherhoods'), when leagues of peasants and burghers, with the support of several knights, noblemen, and under legal protection offered by the remote king, toppled many of the castles of the Kingdom and briefly drove the noblemen into Portugal and Castile. Soon after, in the late 15th century, in the dynastic conflict between Isabella I of Castile and Joanna La Beltraneja, part of the Galician aristocracy supported Joanna. After Isabella's victory, she initiated an administrative and political reform which the chronicler Zurita y Castro, Jeronimo, Jeronimo Zurita defined as "doma del Reino de Galicia": 'It was then when the taming of Galicia began, because not just the local lords and knights, but all the people of that nation were the ones against the others very bold and warlike'. These reforms, while establishing a local government and tribunal (the ''Real Audiencia del Reino de Galicia''), and bringing the nobleman under submission, also brought most Galician monasteries and institutions under Castilian control, in what has been criticized as a process of centralisation. At the same time the kings began to call the Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia, ''Xunta'' or ''Cortes'' of the Kingdom of Galicia, an assembly of deputies or representatives of the cities of the Kingdom, to ask for monetary and military contributions. This assembly soon developed into the voice and legal representation of the Kingdom, and the depositary of its will and laws.
Early Modern
 The establishment of the Santa Hermandad in 1480, and the
The establishment of the Santa Hermandad in 1480, and the Real Audiencia
A ''Real Audiencia'' (), or simply an ''Audiencia'' ( ca, Reial Audiència, Audiència Reial, or Audiència), was an appellate court in Spain and its empire. The name of the institution literally translates as Royal Audience. The additional des ...
del Reino de Galicia in 1500—a tribunal and executive body directed by the Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
-Captain General
Captain general (and its literal equivalent in several languages) is a high military rank of general officer grade, and a gubernatorial title.
History
The term "Captain General" started to appear in the 14th century, with the meaning of Comma ...
as a direct representative of the King—implied initially the submission of the Kingdom to the Crown, after a century of unrest and fiscal insubordination. As a result, from 1480 to 1520 the Kingdom of Galicia contributed more than 10% of the total earnings of the Crown of Castille, including the Americas, well over its economic relevance. Like the rest of Spain, the 16th century was marked by population growth up to 1580, when the simultaneous wars with the Netherlands, France, and England hampered Galicia's Atlantic commerce, which consisted mostly in the exportation of sardines, wood, and some cattle and wine.
In the late years of the 15th century the written form of the Galician language began a slow decline as it was increasingly replaced by Spanish, which would culminate in the ''Séculos Escuros'' "the Dark Centuries" of the language, roughly from the 16th century through to the mid-18th century, when written Galician almost completely disappeared except for private or occasional uses but the spoken language remained the common language of the people in the villages and even the cities.
From that moment Galicia, which participated to a minor extent in the American expansion of the Spanish Empire, found itself at the center of the Atlantic wars fought by Spain against the French and the Protestant powers of England and the Netherlands, whose privateers attacked the coastal areas, but major assaults were not common as the coastline was difficult and the harbors easily defended. The most famous assaults were upon the city of Vigo by Francis Drake, Sir Francis Drake in 1585 and 1589, and the siege of A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
in 1589 by the ''English Armada''. Galicia also suffered occasional slave raids by Barbary pirates, but not as frequently as the Mediterranean coastal areas. The most famous Barbary attack was the bloody sack of the town of Cangas do Morrazo, Cangas in 1617. At the time, the king's petitions for money and troops became more frequent, due to the human and economic exhaustion of Castile; the Junta of the Kingdom of Galicia (the local ''Cortes'' or representative assembly) was initially receptive to these petitions, raising large sums, accepting the conscription of the men of the kingdom, and even commissioning a new naval squadron which was sustained with the incomes of the Kingdom.
 After the rupture of the wars with Portuguese Restoration War, Portugal and Reapers' War, Catalonia, the ''Junta'' changed its attitude, this time due to the exhaustion of Galicia, now involved not just in naval or oversea operations, but also in an exhausting war with the Portuguese, war which produced thousands of casualties and refugees and was heavily disturbing to the local economy and commerce. So, in the second half of the 17th century the ''Junta'' frequently denied or considerably reduced the initial petitions of the monarch, and though the tension didn't rise to the levels experienced in Portugal or Catalonia, there were frequent urban mutinies and some voices even asked for the secession of the Kingdom of Galicia.
After the rupture of the wars with Portuguese Restoration War, Portugal and Reapers' War, Catalonia, the ''Junta'' changed its attitude, this time due to the exhaustion of Galicia, now involved not just in naval or oversea operations, but also in an exhausting war with the Portuguese, war which produced thousands of casualties and refugees and was heavily disturbing to the local economy and commerce. So, in the second half of the 17th century the ''Junta'' frequently denied or considerably reduced the initial petitions of the monarch, and though the tension didn't rise to the levels experienced in Portugal or Catalonia, there were frequent urban mutinies and some voices even asked for the secession of the Kingdom of Galicia.
Late Modern and Contemporary
 During the Peninsular War the successful uprising of the local people against the new French authorities, together with the support of the British Army, limited the occupation to six months in 1808–1809. During the pre-war period the Supreme Council of the Kingdom of Galicia (''Junta Suprema del Reino de Galicia''), auto-proclaimed interim sovereign in 1808, was the sole government of the country and mobilized near 40,000 men against the invaders.
The 1833 territorial division of Spain put a formal end to the Kingdom of Galicia, unifying Spain into a single centralized monarchy. Instead of seven provinces and a regional administration, Galicia was reorganized into the current four provinces. Although it was recognized as a "historical region", that status was strictly honorific. In reaction, Galician nationalism, nationalist and federalism, federalist movements arose.
During the Peninsular War the successful uprising of the local people against the new French authorities, together with the support of the British Army, limited the occupation to six months in 1808–1809. During the pre-war period the Supreme Council of the Kingdom of Galicia (''Junta Suprema del Reino de Galicia''), auto-proclaimed interim sovereign in 1808, was the sole government of the country and mobilized near 40,000 men against the invaders.
The 1833 territorial division of Spain put a formal end to the Kingdom of Galicia, unifying Spain into a single centralized monarchy. Instead of seven provinces and a regional administration, Galicia was reorganized into the current four provinces. Although it was recognized as a "historical region", that status was strictly honorific. In reaction, Galician nationalism, nationalist and federalism, federalist movements arose.
 The liberalism, liberal General Miguel Solís Cuetos led a Solís Uprising, separatist coup attempt in 1846 against the authoritarianism, authoritarian regime of Ramón María Narváez. Solís and his forces were defeated at the Battle of Cacheiras, 23 April 1846, and the survivors, including Solís himself, were shot. They have taken their place in Galician memory as the Martyrs of Carral or simply the Martyrs of Liberty.
Defeated on the military front, Galicians turned to culture. The ''Rexurdimento'' focused on the recovery of the Galician language as a vehicle of social and cultural expression. Among the writers associated with this movement are Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal.
In the early 20th century came another turn toward nationalist politics with ''Galician Solidarity, Solidaridad Gallega'' (1907–1912) modeled on ''Catalan Solidarity (1906), Solidaritat Catalana'' in Catalonia. Solidaridad Gallega failed, but in 1916 ''Irmandades da Fala'' (Brotherhood of the Language) developed first as a cultural association but soon as a full-blown nationalist movement. Vicente Risco and Ramón Otero Pedrayo were outstanding cultural figures of this movement, and the magazine ''Nós (Galicia), Nós'' ('Us'), founded in 1920, its most notable cultural institution, Lois Peña Novo the outstanding political figure.
The liberalism, liberal General Miguel Solís Cuetos led a Solís Uprising, separatist coup attempt in 1846 against the authoritarianism, authoritarian regime of Ramón María Narváez. Solís and his forces were defeated at the Battle of Cacheiras, 23 April 1846, and the survivors, including Solís himself, were shot. They have taken their place in Galician memory as the Martyrs of Carral or simply the Martyrs of Liberty.
Defeated on the military front, Galicians turned to culture. The ''Rexurdimento'' focused on the recovery of the Galician language as a vehicle of social and cultural expression. Among the writers associated with this movement are Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal.
In the early 20th century came another turn toward nationalist politics with ''Galician Solidarity, Solidaridad Gallega'' (1907–1912) modeled on ''Catalan Solidarity (1906), Solidaritat Catalana'' in Catalonia. Solidaridad Gallega failed, but in 1916 ''Irmandades da Fala'' (Brotherhood of the Language) developed first as a cultural association but soon as a full-blown nationalist movement. Vicente Risco and Ramón Otero Pedrayo were outstanding cultural figures of this movement, and the magazine ''Nós (Galicia), Nós'' ('Us'), founded in 1920, its most notable cultural institution, Lois Peña Novo the outstanding political figure.
 The Second Spanish Republic was declared in 1931. During the republic, the Partido Galeguista (1931), Partido Galeguista (PG) was the most important of a shifting collection of Galician nationalist parties. Following a referendum on a Galician Statute of Autonomy (1936), Galician Statute of Autonomy, Galicia was granted the status of an autonomous region.
Galicia was spared the worst of the fighting in that war: it was one of the areas where the initial coup attempt at the outset of the war was successful, and it remained in Nationalist hands (Franco's army) throughout the war. While there were no pitched battles, there was repression and death: all political parties were abolished, as were all labor unions and Galician nationalist organizations as the ''Seminario de Estudos Galegos''. Galicia's statute of autonomy was annulled (as were those of Catalonia and the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque provinces once those were conquered). According to Carlos Fernández Santander, at least 4,200 people were killed either extrajudicially or after summary trials, among them republicans, communists, Galician nationalists, socialists, and anarchists. Victims included the civil governors of all four Galician provinces; Juana Capdevielle, the wife of the governor of A Coruña; mayors such as Ánxel Casal of Santiago de Compostela, of the Partido Galeguista; prominent socialists such as Jaime Quintanilla in Ferrol and Emilio Martínez Garrido in
The Second Spanish Republic was declared in 1931. During the republic, the Partido Galeguista (1931), Partido Galeguista (PG) was the most important of a shifting collection of Galician nationalist parties. Following a referendum on a Galician Statute of Autonomy (1936), Galician Statute of Autonomy, Galicia was granted the status of an autonomous region.
Galicia was spared the worst of the fighting in that war: it was one of the areas where the initial coup attempt at the outset of the war was successful, and it remained in Nationalist hands (Franco's army) throughout the war. While there were no pitched battles, there was repression and death: all political parties were abolished, as were all labor unions and Galician nationalist organizations as the ''Seminario de Estudos Galegos''. Galicia's statute of autonomy was annulled (as were those of Catalonia and the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque provinces once those were conquered). According to Carlos Fernández Santander, at least 4,200 people were killed either extrajudicially or after summary trials, among them republicans, communists, Galician nationalists, socialists, and anarchists. Victims included the civil governors of all four Galician provinces; Juana Capdevielle, the wife of the governor of A Coruña; mayors such as Ánxel Casal of Santiago de Compostela, of the Partido Galeguista; prominent socialists such as Jaime Quintanilla in Ferrol and Emilio Martínez Garrido in Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
; Popular Front (Spain), Popular Front deputies Antonio Bilbatúa, José Miñones, Díaz Villamil, Ignacio Seoane, and former deputy Heraclio Botana); soldiers who had not joined the rebellion, such as Generals Rogelio Caridad Pita and Enrique Salcedo Molinuevo and Admiral Antonio Azarola; and the founders of the PG, Alexandre Bóveda and Víctor Casas, as well as other professionals akin to republicans and nationalists, as the journalist Manuel Lustres Rivas or physician Luis Poza Pastrana. Many others were forced to escape into exile, or were victims of other reprisals and removed from their jobs and positions.
General Francisco Franco – himself a Galician from Ferrol – ruled as dictator from the civil war until he died in 1975. Franco's centralizing regime suppressed any official use of the Galician language, including the use of Galician names for newborns, although its everyday oral use was not forbidden. Among the attempts at resistance were small leftist guerrilla groups such as those led by José Castro Veiga ("O Piloto") and Benigno Andrade ("Foucellas"), both of whom were ultimately captured and executed. In the 1960s, ministers such as Manuel Fraga Iribarne introduced some reforms allowing technocrats affiliated with Opus Dei to modernize administration in a way that facilitated capitalism, capitalist economic development. However, for decades Galicia was largely confined to the role of a supplier of raw materials and energy to the rest of Spain, causing environmental havoc and leading to a wave of migration to Venezuela and to various parts of Europe. Unión Fenosa, Fenosa, the monopolistic supplier of electricity, built hydroelectric dams, flooding many Galician river valleys.
The Galician economy finally began to modernize with a French Citroën factory in Vigo, the modernization of the canning industry and the fishing fleet, and eventually a modernization of small peasant farming practices, especially in the production of cows' milk. In the province of Ourense, businessman and politician Eulogio Gómez Franqueira gave impetus to the raising of livestock and poultry by establishing the Cooperativa Orensana S.A. (Coren).
During the last decade of Franco's rule, there was a renewal of nationalist feeling in Galicia. The early 1970s were a time of unrest among university students, workers, and farmers. In 1972, general strikes in Vigo and Ferrol cost the lives of Amador Rey and Daniel Niebla. Later, the bishop of Mondoñedo- Ferrol, Miguel Anxo Araúxo Iglesias, wrote a pastoral letter that was not well received by the Franco regime, about a demonstration in Navantia, Bazán (Ferrol) where two workers died.
As part of the Spanish transition to democracy, transition to democracy upon the death of Franco in 1975, Galicia regained its status as an autonomous region within Spain with the Statute of Autonomy of 1981, which begins, "Galicia, historical nationality, is constituted as an Autonomous Community to access to its self-government, in agreement with the Spanish Constitution and with the present Statute (...)". Varying degrees of Nationalisms and regionalisms of Spain, nationalist or independentist sentiment are evident at the political level. The ''Bloque Nacionalista Galego'' or BNG, is a conglomerate of left-wing parties and individuals that claims Galician political status as a nation.
Xunta de Galicia
The Xunta de Galicia (; "Regional Government of Galicia") is the collective decision-making body of the government of the autonomous community of Galicia, composed of the President, the Vice-President(s) and the specialized ministers (''Consell ...
. Fraga was associated with the ''People's Party (Spain), Partido Popular'' ('People's Party', Spain's main national conservative party) since its founding. In 2002, when the oil tanker Prestige (oil tanker), Prestige sank and covered the Galician coast in oil, Fraga was accused by the grassroots movement ''Plataforma Nunca Mais, Nunca Mais'' ("Never again") of having been unwilling to react. In the 2005 Galician elections, the 'People's Party' lost its absolute majority, though remaining (barely) the largest party in the parliament, with 43% of the total votes. As a result, power passed to a coalition of the ''Socialists' Party of Galicia, Partido dos Socialistas de Galicia'' (PSdeG) ('Galician Socialists' Party'), a federal sister-party of Spain's main social-democratic party, the ''Partido Socialista Obrero Español'' (PSOE, 'Spanish Socialist Workers Party') and the nationalist ''Bloque Nacionalista Galego'' (BNG). As the senior partner in the new coalition, the PSdeG nominated its leader, Emilio Pérez Touriño, to serve as Galicia's new president, with Anxo Quintana, the leader of BNG, as its vice president.
In 2009, the PSdG-BNG coalition lost the elections, and the government went back to the People's Party (conservative), even though the PSdG-BNG coalition obtained the most votes.
Geography
 Galicia has a surface area of .Galicia 08
Galicia has a surface area of .Galicia 08Xunta de Galicia, Consellaría de Cultura e Deporte. Its northernmost point, at 43°47′N, is Estaca de Bares Point, Estaca de Bares (also the northernmost point of Spain); its southernmost, at 41°49′N, is on the Portuguese border in the Baixa Limia-Serra do Xurés Natural Park. The easternmost longitude is at 6°42′W on the border between the province of Ourense and the Castile and León, Castilian-Leonese province of Zamora) its westernmost at 9°18′W reached in two places: the A Nave Cape in Fisterra (also known as Finisterre), and Cape Touriñán, both in the province of A Coruña.
Topography
 Topographically, a remarkable feature of Galicia is the presence of many firth-like inlets along the coast, Estuary, estuaries that were drowned with rising sea levels after the Quaternary glaciation, ice age. These are called ''Ria, rías'' and are divided into the smaller ''Rías Altas'' ("High Rías"), and the larger ''
Topographically, a remarkable feature of Galicia is the presence of many firth-like inlets along the coast, Estuary, estuaries that were drowned with rising sea levels after the Quaternary glaciation, ice age. These are called ''Ria, rías'' and are divided into the smaller ''Rías Altas'' ("High Rías"), and the larger ''Rías Baixas
The Rías Baixas (Galician language, Galician for "Lower Rias") are a series of four estuarine inlets located on the southwestern coast of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Spain. They are the Ría de Muros e Noia, the Ría de Arousa, the Ria de Ponteved ...
'' ("Low Rías"). The ''Rías Altas'' include Ribadeo, Foz, Viveiro, O Barqueiro, Ortigueira, Cedeira, Ferrol, Betanzos, A Coruña, Corme e Laxe and Camariñas. The Rías Baixas, found south of Fisterra, include Corcubión, Muros e Noia, Ría de Arousa, Arousa, Pontevedra and Vigo. The Rías Altas can sometimes refer only to those east of Estaca de Bares Point, Estaca de Bares, with the others being called ''Rías Medias'' ("Intermediate Rías").
Erosion by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
has contributed to the great number of cape (geography), capes. Besides the aforementioned Estaca de Bares in the far north, separating the Atlantic Ocean from the Cantabrian Sea, other notable capes are Cape Ortegal, Cape Prior, Punta Santo Adrao, Cape Vilán, Cape Touriñán (westernmost point in Galicia), Cape Finisterre or Fisterra, considered by the Ancient Rome, Romans, along with Finistère in Brittany and Land's End in Cornwall, to be the end of the known world.
 All along the Galician coast are various archipelagos near the mouths of the ''rías''. These archipelagos provide protected deepwater harbors and also provide habitat for seagoing birds. A 2007 inventory estimates that the Galician coast has 316 archipelagos, islets, and freestanding rocks. Among the most important of these are the archipelagos of Cíes Islands, Cíes, Ons, and
All along the Galician coast are various archipelagos near the mouths of the ''rías''. These archipelagos provide protected deepwater harbors and also provide habitat for seagoing birds. A 2007 inventory estimates that the Galician coast has 316 archipelagos, islets, and freestanding rocks. Among the most important of these are the archipelagos of Cíes Islands, Cíes, Ons, and Sálvora
Sálvora Island ( gl, Illa de Sálvora ; es, Isla de Sálvora ) is a small island located on the Ría de Arousa, coast of Galicia, Spain. It belongs to the municipality of Santa Uxía de Ribeira and is integrated in the Atlantic Islands of Galici ...
. Together with Cortegada Island
Cortegada is an almost tidal island (it is possible to go walking when the lowest tides happen, but a small amount of water flow does not disappear) in a coastal inlet near Pontevedra in Galicia, Spain. It is part of the Atlantic Islands of Galici ...
, these make up the Atlantic Islands of Galicia National Park. Other significant islands are Islas Malveiras, Islas Sisargas, and, the largest and holding the largest population, A Illa de Arousa, Arousa Island.
The coast of this 'green corner' of the Iberian Peninsula, some in length, attracts great numbers of tourists, although real estate development in the 2000–2010 decade has degraded it partially.
 Galicia is quite mountainous, a fact which has contributed to isolate the rural areas, hampering communications, most notably in the inland. The main mountain range is the Macizo Galaico (Serra do Eixe, Serra da Lastra, Serra do Courel), also known as ''Macizo Galaico-Leonés'', located in the eastern parts, bordering with Castile and León. Noteworthy mountain ranges are O Xistral (northern province of Lugo, Lugo), the Serra dos Ancares (on the border with Province of León, León and
Galicia is quite mountainous, a fact which has contributed to isolate the rural areas, hampering communications, most notably in the inland. The main mountain range is the Macizo Galaico (Serra do Eixe, Serra da Lastra, Serra do Courel), also known as ''Macizo Galaico-Leonés'', located in the eastern parts, bordering with Castile and León. Noteworthy mountain ranges are O Xistral (northern province of Lugo, Lugo), the Serra dos Ancares (on the border with Province of León, León and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
), O Courel (on the border with León), O Eixe (the border between Province of Ourense, Ourense and Province of Zamora, Zamora), Serra de Queixa (in the center of Ourense province), O Faro (the border between Lugo and Pontevedra), Cova da Serpe (border of Lugo and A Coruña), Montemaior (A Coruña), Montes do Testeiro, Serra do Suído, and Faro de Avión (between Pontevedra and Ourense); and, to the south, A Peneda, O Xurés and O Larouco, all on the border of Ourense and Portugal.
The highest point in Galicia is Trevinca or Pena Trevinca (), located in the Serra do Eixe, at the border between Ourense and León and Zamora provinces. Other tall peaks are Pena Survia () in the Serra do Eixe, O Mustallar () in Os Ancares, and Cabeza de Manzaneda () in Serra de Queixa, where there is a ski resort.
Hydrography
 Galicia is poetically known as the "country of the Rivers of Galicia, thousand rivers" ("o país dos mil ríos"). The largest and most important of these rivers is the Minho River, Miño, poetically known as ''O Pai Miño'' (Father Miño), which is long and discharges per second, with its affluent the Sil (river), Sil, which has created a spectacular canyon. Most of the rivers in the inland are tributaries of this river system, which drains some . Other rivers run directly into the
Galicia is poetically known as the "country of the Rivers of Galicia, thousand rivers" ("o país dos mil ríos"). The largest and most important of these rivers is the Minho River, Miño, poetically known as ''O Pai Miño'' (Father Miño), which is long and discharges per second, with its affluent the Sil (river), Sil, which has created a spectacular canyon. Most of the rivers in the inland are tributaries of this river system, which drains some . Other rivers run directly into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
or the Cantabrian Sea
The Cantabrian Sea; french: Mer Cantabrique, gl, Mar Cantábrico, ast, Mar Cantábricu, eu, Kantauri. is the term used mostly in Spain to describe the coastal sea of the Atlantic Ocean that borders the northern coast of Spain and the southwe ...
, most of them having short courses. Only the Navia (river), Navia, Ulla (river), Ulla, Tambre, and Limia have courses longer than .
Galicia's many hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams take advantage of the steep, deep, narrow rivers and their canyons. Due to their steep course, few of Galicia's rivers are navigable, other than the lower portion of the Miño and the portions of various rivers that have been dammed into reservoirs. Some rivers are navigable by small boats in their lower reaches: this is taken great advantage of in several semi-aquatic festivals and pilgrimages.
Environment
 Galicia has preserved some of its dense forests. It is relatively unpolluted, and its landscapes composed of green hills, cliffs, and ''rias'' are generally different from what is commonly understood as Spanish landscape. Nevertheless, Galicia has some important environmental problems.
Deforestation and forest fires are a problem in many areas, as is the continual spread of the eucalyptus tree, a species imported from Australia, actively promoted by the paper industry since the mid-20th century. Galicia is one of the more forested areas of Spain, but the majority of Galicia's plantations, usually growing eucalyptus or pine, lack any formal management. Massive eucalyptus plantation, especially of ''Eucalyptus globulus'', began in the Francisco Franco era, largely on behalf of the paper company Empresa Nacional de Celulosas de España (ENCE) in
Galicia has preserved some of its dense forests. It is relatively unpolluted, and its landscapes composed of green hills, cliffs, and ''rias'' are generally different from what is commonly understood as Spanish landscape. Nevertheless, Galicia has some important environmental problems.
Deforestation and forest fires are a problem in many areas, as is the continual spread of the eucalyptus tree, a species imported from Australia, actively promoted by the paper industry since the mid-20th century. Galicia is one of the more forested areas of Spain, but the majority of Galicia's plantations, usually growing eucalyptus or pine, lack any formal management. Massive eucalyptus plantation, especially of ''Eucalyptus globulus'', began in the Francisco Franco era, largely on behalf of the paper company Empresa Nacional de Celulosas de España (ENCE) in Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, which wanted it for its pulp. Galician photographer Delmi Álvarez began documenting the fires in Galicia in 2006 in a project called ''Queiman Galiza (Burn Galicia).''. Wood products figure significantly in Galicia's economy. Apart from tree plantations, Galicia is also notable for the extensive surface occupied by meadows used for animal husbandry, especially cattle, an important activity. Hydroelectric development in most rivers has been a serious concern for local conservationists during the last decades.
Fauna, most notably the Eurasian wolf, European wolf, has suffered because of the actions of livestock owners and farmers, and because of the loss of habitats, whilst the native deer species have declined because of hunting and development.
Oil spills are a major issue. The Prestige oil spill in 2002 spilled more oil than the Exxon Valdez in Alaska.Gaia VincPrestige oil spill far worse than thought
''New Scientist'', August 27, 2003
Biodiversity
 The animals most often thought of as being "typical" of Galicia are the livestock raised there. The Galician horse is native to the region, as is the Galician Blond cow and the domestic fowl known as the ''galiña de Mos (Spain), Mos''. The last is an endangered species, although it is showing signs of a comeback since 2001.
Galicia is home to one of the largest populations of Iberian wolf, wolves in western Europe. Galicia's woodlands and mountains are also home to rabbits, hares, wild boars, and roe deer, all of which are popular with hunters. Several important bird migration routes pass through Galicia, and some of the community's relatively few environmentally protected areas are Special Protection Areas (such as on the Ría de Ribadeo) for these birds. From a domestic point of view, Galicia has been credited by the author Manuel Rivas as the "land of one million cows". Galician Blond and Holstein cattle coexist on meadows and farms.
The animals most often thought of as being "typical" of Galicia are the livestock raised there. The Galician horse is native to the region, as is the Galician Blond cow and the domestic fowl known as the ''galiña de Mos (Spain), Mos''. The last is an endangered species, although it is showing signs of a comeback since 2001.
Galicia is home to one of the largest populations of Iberian wolf, wolves in western Europe. Galicia's woodlands and mountains are also home to rabbits, hares, wild boars, and roe deer, all of which are popular with hunters. Several important bird migration routes pass through Galicia, and some of the community's relatively few environmentally protected areas are Special Protection Areas (such as on the Ría de Ribadeo) for these birds. From a domestic point of view, Galicia has been credited by the author Manuel Rivas as the "land of one million cows". Galician Blond and Holstein cattle coexist on meadows and farms.
Climate
 Being located on the Atlantic coastline, Galicia has a very mild climate for the latitude and the marine influence affects most of the province to various degrees. In comparison to similar latitudes on the other side of the Atlantic, winters are exceptionally mild, with consistent rainfall. At sea level snow is exceptional, with temperatures just occasionally dropping below freezing; on the other hand, snow regularly falls in the eastern mountains from November to May. Overall, the climate of Galicia is comparable to the Pacific Northwest; the warmest coastal station of Pontevedra has a yearly mean temperature of . Ourense located somewhat inland is only slightly warmer with . Lugo, to the north, is colder, with , similar to the of Portland, Oregon.
In coastal areas summers are tempered, with daily maximums averaging around in Vigo. Temperatures are further cooler in A Coruña, with a subdued normal. Temperatures are much higher in inland areas such as Ourense, where days above are regular.
Being located on the Atlantic coastline, Galicia has a very mild climate for the latitude and the marine influence affects most of the province to various degrees. In comparison to similar latitudes on the other side of the Atlantic, winters are exceptionally mild, with consistent rainfall. At sea level snow is exceptional, with temperatures just occasionally dropping below freezing; on the other hand, snow regularly falls in the eastern mountains from November to May. Overall, the climate of Galicia is comparable to the Pacific Northwest; the warmest coastal station of Pontevedra has a yearly mean temperature of . Ourense located somewhat inland is only slightly warmer with . Lugo, to the north, is colder, with , similar to the of Portland, Oregon.
In coastal areas summers are tempered, with daily maximums averaging around in Vigo. Temperatures are further cooler in A Coruña, with a subdued normal. Temperatures are much higher in inland areas such as Ourense, where days above are regular.
 The lands of Galicia are ascribed to two different areas in the Köppen climate classification: a south area (roughly, the province of Ourense and Province of Pontevedra, Pontevedra) with appreciable summer drought, classified as a Mediterranean climate, warm-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csb''), with mild temperatures and rainfall usual throughout the year; and the western and northern coastal regions, the provinces of province of Lugo, Lugo and province of A Coruña, A Coruña, which are characterized by their Oceanic climate (''Cfb''), with a more uniform precipitation distribution along the year, and milder summers. However, precipitation in southern coastal areas are often classified as oceanic since the averages remain significantly higher than a typical Mediterranean climate.
As an example,
The lands of Galicia are ascribed to two different areas in the Köppen climate classification: a south area (roughly, the province of Ourense and Province of Pontevedra, Pontevedra) with appreciable summer drought, classified as a Mediterranean climate, warm-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csb''), with mild temperatures and rainfall usual throughout the year; and the western and northern coastal regions, the provinces of province of Lugo, Lugo and province of A Coruña, A Coruña, which are characterized by their Oceanic climate (''Cfb''), with a more uniform precipitation distribution along the year, and milder summers. However, precipitation in southern coastal areas are often classified as oceanic since the averages remain significantly higher than a typical Mediterranean climate.
As an example, Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
, the capital city, has an average of 129 rainy days (> 1 mm) and per year (with just 17 rainy days in the three summer months) and 2,101 sunlight hours per year, with just 6 days with frosts per year. But the colder city of Lugo, to the east, has an average of 1,759 sunlight hours per year, 117 days with precipitations (> 1 mm) totalling , and 40 days with frosts per year. The more mountainous parts of the provinces of Ourense and Lugo receive significant snowfall during the winter months. The sunniest city is Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
with 2,223 sunny hours per year.
Climate data for some locations in Galicia (average 1981–2010):
Government and politics
Local government
Galicia has partial self-governance, in the form of adevolved government
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
, established on 16 March 1978 and reinforced by the Galician Statute of Autonomy, ratified on 28 April 1981. There are three separation of powers, branches of government: the executive branch, the Xunta de Galicia
The Xunta de Galicia (; "Regional Government of Galicia") is the collective decision-making body of the government of the autonomous community of Galicia, composed of the President, the Vice-President(s) and the specialized ministers (''Consell ...
, consisting of the President and the other independently elected councillors; the legislative branch consisting of the Parliament of Galicia, Galician Parliament; and the judicial branch consisting of the High Court of Galicia and lower courts.
Executive
 The Xunta de Galicia is a collective entity with executive and administrative power. It consists of the President of the Xunta of Galicia, President, a vice president, and twelve councillors. Administrative power is largely delegated to dependent bodies. The Xunta also coordinates the activities of the provincial councils ( gl, deputacións) located in
The Xunta de Galicia is a collective entity with executive and administrative power. It consists of the President of the Xunta of Galicia, President, a vice president, and twelve councillors. Administrative power is largely delegated to dependent bodies. The Xunta also coordinates the activities of the provincial councils ( gl, deputacións) located in A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, Ourense and Lugo.
The President of the Xunta directs and coordinates the actions of the Xunta. He or she is simultaneously the representative of the autonomous community and of the Spanish state in Galicia. He or she is a member of the parliament and is elected by its deputies and then formally named by the monarch of Spain.
Legislative
 The Parliament of Galicia, Galician Parliament consists of 75 deputies elected by universal suffrage, universal adult suffrage under a system of proportional representation. The franchise includes also Galicians who reside abroad. Elections occur every four years.
The last elections, held 12 July 2020, resulted in the following distribution of seats:
* People's Party of Galicia, Partido Popular de Galicia (PPdeG): 41 deputies (47.98% of popular vote)
* Galician Nationalist Bloc, Bloque Nacionalista Galego (BNG): 19 deputies (23.80% of popular vote)
* Socialists' Party of Galicia, Partido Socialista de Galicia (PSdeG-PSOE): 15 deputies (19.38% of popular vote)
The Parliament of Galicia, Galician Parliament consists of 75 deputies elected by universal suffrage, universal adult suffrage under a system of proportional representation. The franchise includes also Galicians who reside abroad. Elections occur every four years.
The last elections, held 12 July 2020, resulted in the following distribution of seats:
* People's Party of Galicia, Partido Popular de Galicia (PPdeG): 41 deputies (47.98% of popular vote)
* Galician Nationalist Bloc, Bloque Nacionalista Galego (BNG): 19 deputies (23.80% of popular vote)
* Socialists' Party of Galicia, Partido Socialista de Galicia (PSdeG-PSOE): 15 deputies (19.38% of popular vote)
Judicial
Municipal governments
 There are 314 municipalities ( gl, concellos) in Galicia, each of which is run by a mayor–council government known as a .
There is a further subdivision of local government known as an ; each has its own council () and mayor (). There are nine of these in Galicia: Arcos da Condesa, Bembrive, Camposancos, Chenlo, Morgadáns, Pazos de Reis, Queimadelos, Vilasobroso, Mondariz, Vilasobroso and Berán.
Galicia is also traditionally subdivided in some 3,700 civil Parish (administrative division), parishes, each one comprising one or more ''vilas'' (towns), ''aldeas'' (villages), ''lugares'' (hamlets) or ''barrios'' (neighbourhoods).
There are 314 municipalities ( gl, concellos) in Galicia, each of which is run by a mayor–council government known as a .
There is a further subdivision of local government known as an ; each has its own council () and mayor (). There are nine of these in Galicia: Arcos da Condesa, Bembrive, Camposancos, Chenlo, Morgadáns, Pazos de Reis, Queimadelos, Vilasobroso, Mondariz, Vilasobroso and Berán.
Galicia is also traditionally subdivided in some 3,700 civil Parish (administrative division), parishes, each one comprising one or more ''vilas'' (towns), ''aldeas'' (villages), ''lugares'' (hamlets) or ''barrios'' (neighbourhoods).
National government
Galicia's interests are represented at the national level by 25 elected deputies in the Congress of Deputies (Spain), Congress of Deputies and 19 senators in the Spanish Senate, Senate – of these, 16 are elected and 3 are appointed by the Galician parliament.Administrative divisions
Before the 1833 territorial division of Spain, Galicia was divided into seven administrativeprovinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
:
*A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
*Santiago de Compostela, Santiago
*Betanzos
*Province of Mondoñedo, Mondoñedo
* Lugo
* Ourense
*Tui, Galicia, Tui
From 1833, the seven original provinces of the 15th century were consolidated into four:
*A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, capital: A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
*Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, capital: Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
* Ourense; capital: Ourense
* Lugo; capital: Lugo
Economy
 Textiles, fishing, livestock, forestry, and car manufacturing are the most dynamic sectors of the Galician economy.
The companies based in the province of Coruña generate 70% of the entrepreneurial output of Galicia. Arteixo, an industrial municipality in the A Coruña metropolitan area, is the headquarters of Inditex, the world's largest fashion retailer. Of their eight brands, Zara (retailer), Zara is the best-known; indeed, it is the best-known Spanish brand of any sort on an international basis. For 2007, Inditex had 9,435 million euros in sales for a net profit of 1,250 million euros. The company president, Amancio Ortega, is the richest person in Spain and indeed Europe with a net worth of 45 billion euros.
A major economic sector of Galicia is its fishing Industry; the main ports are port of A Coruña, A Coruña, Port of Marín and Ria de Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra, Port of Vigo, Vigo and Ferrol. Related to this fact, the European Fisheries Control Agency, which coordinates fishing controls in European Union waters, is based in Vigo.
Galicia is a land of economic contrast. While the western coast, with its major population centers and its fishing and manufacturing industries, is prosperous and increasing in population, the rural hinterland—the provinces of Ourense and Lugo—is economically dependent on traditional agriculture, based on small landholdings called ''minifundios''. However, the rise of tourism, sustainable forestry, and organic and traditional agriculture are bringing other possibilities to the Galician economy without compromising the preservation of the natural resources and the local culture.
Textiles, fishing, livestock, forestry, and car manufacturing are the most dynamic sectors of the Galician economy.
The companies based in the province of Coruña generate 70% of the entrepreneurial output of Galicia. Arteixo, an industrial municipality in the A Coruña metropolitan area, is the headquarters of Inditex, the world's largest fashion retailer. Of their eight brands, Zara (retailer), Zara is the best-known; indeed, it is the best-known Spanish brand of any sort on an international basis. For 2007, Inditex had 9,435 million euros in sales for a net profit of 1,250 million euros. The company president, Amancio Ortega, is the richest person in Spain and indeed Europe with a net worth of 45 billion euros.
A major economic sector of Galicia is its fishing Industry; the main ports are port of A Coruña, A Coruña, Port of Marín and Ria de Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra, Port of Vigo, Vigo and Ferrol. Related to this fact, the European Fisheries Control Agency, which coordinates fishing controls in European Union waters, is based in Vigo.
Galicia is a land of economic contrast. While the western coast, with its major population centers and its fishing and manufacturing industries, is prosperous and increasing in population, the rural hinterland—the provinces of Ourense and Lugo—is economically dependent on traditional agriculture, based on small landholdings called ''minifundios''. However, the rise of tourism, sustainable forestry, and organic and traditional agriculture are bringing other possibilities to the Galician economy without compromising the preservation of the natural resources and the local culture.
, FaroDeVigo.es, 12 September 2007. Retrieved 9 November 2008. Other companies with a large number of workers and a significant asset turnover, turnover are San José, based in
Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, belonging to the construction sector, and Gadisa and Vego, based in A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
and Froiz, based in Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, linked to the retail sector.
Galicia is home to the Savings bank (Spain), savings bank, and to Spain's two oldest commercial banks Banco Etcheverría (the oldest) and Banco Pastor, owned since 2011 by Banco Popular Español.
Galicia was late to catch the tourism boom that has swept Spain in recent decades, but the coastal regions (especially the Rías Baixas
The Rías Baixas (Galician language, Galician for "Lower Rias") are a series of four estuarine inlets located on the southwestern coast of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Spain. They are the Ría de Muros e Noia, the Ría de Arousa, the Ria de Ponteved ...
and Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
) are now significant tourist destinations and are especially popular with visitors from other regions in Spain, where the majority of tourists come from. In 2007, 5.7 million tourists visited Galicia, an 8% growth over the previous year, and part of a continual pattern of growth in this sector. 85% of tourists who visit Galicia visit Santiago de Compostela. Tourism constitutes 12% of Galician GDP and employs about 12% of the regional workforce.
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the autonomous community was 62.6 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 5.2% of Spanish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 24,900 euros or 82% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 95% of the EU average.
The unemployment rate stood at 15.7% in 2017 and was lower than the national average.
Transportation
 Galicia's main airport is Santiago de Compostela Airport. Having been used by 2,083,873 passengers in 2014, it connects the Galician capital with cities in Spain as well as several major European cities. There are two other domestic airports in Galicia: A Coruña Airport – Alvedro and Vigo-Peinador Airport.
The most important Galician fishing port is the Port of Vigo; It is one of the European's leading fishing ports, with an annual catch worth 1,500 million euros. In 2007 the port took in of fish and seafood, and about of other cargoes. Other important ports are
Galicia's main airport is Santiago de Compostela Airport. Having been used by 2,083,873 passengers in 2014, it connects the Galician capital with cities in Spain as well as several major European cities. There are two other domestic airports in Galicia: A Coruña Airport – Alvedro and Vigo-Peinador Airport.
The most important Galician fishing port is the Port of Vigo; It is one of the European's leading fishing ports, with an annual catch worth 1,500 million euros. In 2007 the port took in of fish and seafood, and about of other cargoes. Other important ports are A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Port of Marín and Ria de Pontevedra, Marín-Pontevedra, Ferrol and the smaller port of Vilagarcía de Arousa, as well as important recreational ports in Pontevedra marina, Pontevedra capital city and Burela. Beyond these, Galicia has 120 other organized ports.
 includes ''Highways in Spain, autopistas'' and ''autovías'' connecting the major cities, as well as national and secondary roads to the rest of the municipalities. The Autovía A-6 connects
includes ''Highways in Spain, autopistas'' and ''autovías'' connecting the major cities, as well as national and secondary roads to the rest of the municipalities. The Autovía A-6 connects A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
and Lugo to Madrid, entering Galicia at Pedrafita do Cebreiro. The Autovía A-52 connects O Porriño, Ourense and Benavente, Zamora, Benavente, and enters Galicia at A Gudiña. Two more autovías are under construction. Autovía A-8 enters Galicia on the Cantabrian coast, and ends in Baamonde (Lugo province). Autovía A-76 enters Galicia in Valdeorras; it is an upgrade of the existing N-120 to Ourense.
Within Galicia are the Autopista AP-9 from Ferrol to Vigo and the Autopista AP-53 (also known as AG-53, because it was initially built by the Xunta de Galicia) from Santiago de Compostela, Santiago to Ourense. Additional roads under construction include Autovía A-54 from Santiago de Compostela to Lugo, the Autovía A-57 that will pass through Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
and Autovía A-56 from Lugo to Ourense. The Xunta de Galicia has built roads connecting comarcal capitals, such as the before mentioned AG-53, Autovía AG-55 connecting A Coruña to Carballo or AG-41 connecting Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
to Sanxenxo.
The first railway line in Galicia was inaugurated on 15 September 1873. It ran from O Carril, Vilagarcía da Arousa, O Carril, Vilagarcía da Arousa to Cornes, Conxo, Santiago de Compostela. A second line was inaugurated in 1875, connecting A Coruña and Lugo. In 1883, Galicia was first connected by rail to the rest of Spain, by way of O Barco de Valdeorras. Galicia today has roughly of rail lines. Several lines operated by Adif and Renfe Operadora connect all the important Galician cities. A line operated by FEVE connects Ferrol to Ribadeo and Oviedo. An electrified line is the Ponferrada-Monforte de Lemos- Ourense-Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
line. Several high-speed rail lines are under construction. Among these are the Olmedo-Zamora-Galicia high-speed rail line that opened partly in 2011, and the AVE Atlantic Axis route, which will connect all of the major Galician Atlantic coast cities A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
and Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
to Portugal. Another projected AVE line will connect Ourense to Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
and Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
.
Demographics
Population
A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
-Ferrol, A Coruña, Ferrol metropolitan area has become increasingly dominant in terms of population. The population of the city of A Coruña in 1900 was 43,971. The population of the rest of the province, including the City and Naval Station of nearby Ferrol and Santiago de Compostela, was 653,556. A Coruña's growth occurred after the Spanish Civil War at the same speed as other major Galician cities, but since the revival of democracy after the death of Francisco Franco, A Coruña has grown at a faster rate than all the other Galician cities.
During the mid-20th century, the population rapidly increased in A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Vigo, and to a lesser degree, other major Galician cities, like Ourense, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
or Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
as the rural population declined after the Spanish Civil War: many villages and hamlets of the four provinces of Galicia disappeared or nearly disappeared during the same period. Economic development and mechanization of agriculture resulted in the fields being abandoned, and most of the population moved to find jobs in the main cities. The number of people working in the Tertiary sector of industry, tertiary and Quaternary sector of industry, quaternary sectors of the economy increased significantly.
Since 1999, the absolute number of births in Galicia has been increasing. In 2006, 21,392 births were registered in Galicia, 300 more than in 2005, according to the Instituto Galego de Estatística. Since 1981, the Galician life expectancy has increased by five years, thanks to a higher quality of life.
* Birth rate (2006): 7.9 per 1,000 (all of Spain: 11.0 per 1,000)
* Death rate (2006): 10.8 per 1,000 (all of Spain: 8.4 per 1,000)
* Life expectancy at birth (2005): 80.4 years (all of Spain: 80.2 years)
** Male: 76.8 years (all of Spain: 77.0 years)
** Female: 84.0 years (all of Spain: 83.5 years)
Roman Catholicism is, by far, the largest religion in Galicia. In 2012, the proportion of Galicians that identify themselves as Roman Catholic was 82.2%.
Urbanization
The principal cities are the four capitalsA Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, Ourense and Lugo, Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
– the political capital and archiepiscopal seat – and the industrial cities Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
and Ferrol.
A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
Praza Maior de Lugo, II.JPG, Lugo
Praza do Ferro (Ourense).jpg, Ourense
Pontevedra-Remodelaciones (14316250282).jpg, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
Grande place devant la cathédrale.jpg, Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
Vigo dende o monte do castro.jpg, Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
View of Ferrol Port.jpg, Ferrol
Migration
Like many rural areas of Western Europe, Galicia's history has been defined by mass emigration. Significant internal migration took place from Galicia in the late 19th and early 20th centuries to the industrialized Spanish cities of Barcelona, Bilbao, Zaragoza and Madrid. Other Galicians emigrated to Latin America – Argentina, Uruguay, Venezuela, Mexico, Brazil and Cuba in particular. The two cities with the greatest number of people of Galician descent outside Galicia are Buenos Aires, Argentina, and nearby Montevideo, Uruguay. Immigration from Galicia was so significant in these areas that Argentines and Uruguayans now commonly refer to all Spaniards as ''gallegos'' (Galicians). During the Spain under Francisco Franco, Franco years, there was a new wave of emigration out of Galicia to other European countries, most notably to France, Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. Many of these immigrant or expatriate communities have their groups or clubs, which they formed in the first decades of settling in a new place. The Galician diaspora is so widespread that websites such as Fillos de Galicia have been created in the 21st century to organize and form a network of ethnic Galicians throughout the world. After this, a third wave was a Spanish internal emigration to heavier industrialised areas of Spain, like the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country or Catalonia. The proportion of foreign-born people in Galicia is only 2.9 percent compared to a national figure of 10 percent; among the autonomous communities, only Extremadura has a lower percentage of immigrants. Of the foreign nationals resident in Galicia, 17.93 percent are the ethnically related Portuguese people, Portuguese, 10.93 percent are Colombian people, Colombian and 8.74 percent Brazilian people, Brazilian.Language
 Galicia has two official languages: Galician (Galician: ''galego'') and Spanish (also known in Spain as ''Castellano'', i.e. ''"Castilian"''), both of them Romance languages. Galician originated regionally; the latter was associated with County of Castile, Castile. Galician is recognized in the Statute of Autonomy of Galicia as the ''lingua propia'' ("own language") of Galicia.
Galician is closely related to
Galicia has two official languages: Galician (Galician: ''galego'') and Spanish (also known in Spain as ''Castellano'', i.e. ''"Castilian"''), both of them Romance languages. Galician originated regionally; the latter was associated with County of Castile, Castile. Galician is recognized in the Statute of Autonomy of Galicia as the ''lingua propia'' ("own language") of Galicia.
Galician is closely related to Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
. Both share a common medieval phase known as Galician-Portuguese
Galician-Portuguese ( gl, galego-portugués or ', pt, galego-português or ), also known as Old Portuguese or as Medieval Galician when referring to the history of each modern language, was a West Iberian Romance language spoken in the Middle ...
. The independence of Portugal since the late Middle Ages has favored the divergence of the Galician and Portuguese languages as they developed.Galician), Ethnologue. Retrieved 19 February 2010. Though considered to be independent languages in Galicia, the shared history between Galician and Portuguese has been widely acknowledged; in 2014, the Galician parliament approved Law 1/2014 on the promotion of Portuguese and links with the Lusophony. The official Galician language has been standardized by the Real Academia Galega based on literary tradition. Although there are local dialects, Galician media conform to this standard form, which is also used in primary, secondary, and university education. There are more than three million Galician speakers in the world. Galician ranks in the lower orders of the 150 most widely spoken languages on earth. For more than four centuries of Castilian domination, Spanish was the only official language in Galicia. Galician faded from day-to-day use in urban areas. Since the re-establishment of democracy in Spain—in particular since the passage and implementation of the ''Lei de Normalización Lingüística'' ("Law of Linguistic Normalization", Ley 3/1983, 15 June 1983)—the first generation of students in mass education has attended schools conducted in Galician. (Spanish is also taught.) Since the late 20th century and the establishment of Galicia's autonomy, the Galician language is resurgent. In the cities, it is generally used as a second language for most. According to a 2001 census, 99.16 percent of the population of Galicia understood the language, 91.04 percent spoke it, 68.65 percent could read it and 57.64 percent could write it.Plano Xeral de Normalización da lingua galega
, Xunta de Galicia. (In Galician.) p. 38. The first two numbers (understanding and speaking) were roughly the same as responses a decade earlier. But there were great gains in the percentage of the population who could read and write Galician: a decade earlier, only 49.3 percent of the population could read Galician, and 34.85 percent could write it. During the Francisco Franco, Franco era, the teaching of Galician was prohibited. Today older people may speak the language but have no written competence because of those years. Among the regional languages of Spain, Galician has the highest percentage of speakers in its population. The earliest known document in Galician-Portuguese dates from 1228. The ''Foro do bo burgo do Castro Caldelas'' was granted by Alfonso IX of León to the town of Burgo, in Castro Caldelas, after the model of the constitutions of the town of Allariz. A distinct Galician literature emerged during the Middle Ages: In the 13th century important contributions were made to the Romance canon in Galician-Portuguese, the most notable those by the troubadour Martín Codax, the priest Airas Nunes, King Dinis of Portugal, Denis of Portugal, and King Alfonso X of Castile, ''Alfonso O Sabio'' ("Alfonso the Wise"), the same monarch who began the process of standardization of the Spanish language. During this period, Galician-Portuguese was considered the language of love poetry in the Iberian Romance languages, Romance linguistic culture. The names and memories of Codax and other popular cultural figures are well preserved in modern Galicia.
Religion
 Christianity is the most widely practised religion in Galicia. It was introduced in Late Antiquity and was practiced alongside the native Celtic religion for a few centuries which, incidentally, was re-established as an officially recognised religion in 2015. Still, today about 77.7% of Galicians identify as Catholic. Most Christians adhere to Roman Catholicism, though only 32.1% of the population described themselves as active members. The Catholic Church in Galicia has had its primatial seat in
Christianity is the most widely practised religion in Galicia. It was introduced in Late Antiquity and was practiced alongside the native Celtic religion for a few centuries which, incidentally, was re-established as an officially recognised religion in 2015. Still, today about 77.7% of Galicians identify as Catholic. Most Christians adhere to Roman Catholicism, though only 32.1% of the population described themselves as active members. The Catholic Church in Galicia has had its primatial seat in Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
since the 12th century.
Since the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the Galician Catholic Church has been organized into five ecclesiastical dioceses (Diocese of Lugo, Lugo, Diocese of Ourense, Ourense, Archdiocese of Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Diocese of Mondoñedo-Ferrol, Mondoñedo-Ferrol and Diocese of Tui-Vigo, Tui-Vigo). While these may have coincided with contemporary 15th-century civil provinces, they no longer have the same boundaries as the modern civil provincial divisions. The church is led by one archbishop and four bishops. The five dioceses of Galicia are divided into 163 districts and 3,792 parishes. A few are governed by administrators, the remainder by parish priests.
The patron saint of Galicia is Saint James the Greater. According to Roman Catholic Church, Catholic tradition, his body was discovered in 814 near Compostela. After that date, the relics of Saint James attracted an extraordinary number of pilgrims. Since the 9th century these relics have been kept in the heart of the church – the modern-day cathedral – dedicated to him. There are many other Galician and associated saints; some of the best-known are: Ansurius, Saint Ansurius, Rudesind, Saint Rudesind, Marina of Aguas Santas, Saint Mariña of Augas Santas, Senorina, Saint Senorina, Trahamunda and Froilan.
Education
Galicia's education system is administered by the regional government's Ministry of Education and University Administration. 76% of Galician teenagers achieve a high school diploma, high school degree – ranked fifth out of the 17 autonomous communities. There are three public universities in Galicia: University of A Coruña with campuses inA Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
and Ferrol, University of Santiago de Compostela with campuses in Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
and Lugo and the University of Vigo with campuses in Pontevedra Campus, Pontevedra, Ourense and Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
.
Health care
Galicia's Publicly funded health care, public healthcare system is the (SERGAS). It is administered by the regional government's Ministry of Health.Culture
Architecture
 Hundreds of ancient standing stone monuments like dolmens, menhirs, and megalithic Tumulus, tumuli were erected during the prehistoric period in Galicia. Amongst the best-known are the dolmens of Dombate, Corveira, Axeitos of Pedra da Arca, and menhirs like the Lapa de Gargñáns. From the Iron Age, Galicia has a rich heritage based mainly on a great number of hill forts, few of them excavated like Baroña, Sta. Tegra, San Cibrao de Lás and Formigueiros among others. With the introduction of Ancient Roman architecture, there was a development of basilicas, castra, city walls, cities, villas, Roman temples, Roman roads, and the Roman bridge of Ponte Vella. It was the Romans who founded some of the first cities in Galicia like Lugo and Ourense. Perhaps the best-known examples are the Roman Walls of Lugo and the Tower of Hercules in
Hundreds of ancient standing stone monuments like dolmens, menhirs, and megalithic Tumulus, tumuli were erected during the prehistoric period in Galicia. Amongst the best-known are the dolmens of Dombate, Corveira, Axeitos of Pedra da Arca, and menhirs like the Lapa de Gargñáns. From the Iron Age, Galicia has a rich heritage based mainly on a great number of hill forts, few of them excavated like Baroña, Sta. Tegra, San Cibrao de Lás and Formigueiros among others. With the introduction of Ancient Roman architecture, there was a development of basilicas, castra, city walls, cities, villas, Roman temples, Roman roads, and the Roman bridge of Ponte Vella. It was the Romans who founded some of the first cities in Galicia like Lugo and Ourense. Perhaps the best-known examples are the Roman Walls of Lugo and the Tower of Hercules in A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
.
Cuisine
 Galician cuisine often uses fish and shellfish. The ''empanada'' is a meat or fish pie, with a bread-like base, top, and crust with the meat or fish filling usually being in a tomato sauce including onions and garlic. ''Caldo galego'' is a hearty soup whose main ingredients are potatoes and a local vegetable named Rapini, grelo (broccoli rabe). The latter is also employed in ''lacón con grelos'', a typical carnival dish, consisting of pork shoulder boiled with ''grelos'', potatoes, and chorizo. ''Centolla'' is the equivalent of king crab. It is prepared by being boiled alive, having its main body opened like a shell, and then having its innards mixed vigorously. Another popular dish is octopus, boiled (traditionally in a copper pot) and served on a wooden plate, cut into small pieces, and laced with olive oil, sea salt, and ''pimentón'' (Spanish paprika). This dish is called ''pulpo a la gallega'' or in Galician ''polbo á feira'', which roughly translates as 'fair-style octopus', most commonly translated as 'Galician-style octopus'. There are several regional varieties of cheese. The best-known one is the so-called ''tetilla cheese, tetilla'', named after its breast-like shape. Other highly regarded varieties include the San Simón cheese from Vilalba and the creamy cheese produced in the Arzúa-Ulloa area. A classical is ''filloas'', crêpe-like pancakes made with flour, broth or milk, and eggs. When cooked at a pig slaughter festival, they may also contain the animal's blood. A famous almond cake called ''Tarta de Santiago'' (St. James' cake) is a Galician sweet specialty mainly produced in Santiago de Compostela and all around Galicia.
Galician cuisine often uses fish and shellfish. The ''empanada'' is a meat or fish pie, with a bread-like base, top, and crust with the meat or fish filling usually being in a tomato sauce including onions and garlic. ''Caldo galego'' is a hearty soup whose main ingredients are potatoes and a local vegetable named Rapini, grelo (broccoli rabe). The latter is also employed in ''lacón con grelos'', a typical carnival dish, consisting of pork shoulder boiled with ''grelos'', potatoes, and chorizo. ''Centolla'' is the equivalent of king crab. It is prepared by being boiled alive, having its main body opened like a shell, and then having its innards mixed vigorously. Another popular dish is octopus, boiled (traditionally in a copper pot) and served on a wooden plate, cut into small pieces, and laced with olive oil, sea salt, and ''pimentón'' (Spanish paprika). This dish is called ''pulpo a la gallega'' or in Galician ''polbo á feira'', which roughly translates as 'fair-style octopus', most commonly translated as 'Galician-style octopus'. There are several regional varieties of cheese. The best-known one is the so-called ''tetilla cheese, tetilla'', named after its breast-like shape. Other highly regarded varieties include the San Simón cheese from Vilalba and the creamy cheese produced in the Arzúa-Ulloa area. A classical is ''filloas'', crêpe-like pancakes made with flour, broth or milk, and eggs. When cooked at a pig slaughter festival, they may also contain the animal's blood. A famous almond cake called ''Tarta de Santiago'' (St. James' cake) is a Galician sweet specialty mainly produced in Santiago de Compostela and all around Galicia.
 Galicia has 30 products with ''Denominación de origen, Denominación de orixe'' (D.O.), some of them with ''Denominación de Orixe Protexida'' (D.O.P.). D.O. and D.O.P. are part of a system of regulation of quality and geographical origin among Spain's finest producers. Galicia produces a number of high-quality Galician wines, including Albariño, Ribeiro (DO), Ribeiro, Ribeira Sacra, Monterrei and Valdeorras. The grape varieties used are local and rarely found outside Galicia and Northern Portugal. Just as notably from Galicia comes the spirit ''Augardente''—the name means burning water—often referred to as Orujo in Spain and internationally or as Orujo, caña in Galicia. This spirit is made from the distillation of the pomace of grapes.
Galicia has 30 products with ''Denominación de origen, Denominación de orixe'' (D.O.), some of them with ''Denominación de Orixe Protexida'' (D.O.P.). D.O. and D.O.P. are part of a system of regulation of quality and geographical origin among Spain's finest producers. Galicia produces a number of high-quality Galician wines, including Albariño, Ribeiro (DO), Ribeiro, Ribeira Sacra, Monterrei and Valdeorras. The grape varieties used are local and rarely found outside Galicia and Northern Portugal. Just as notably from Galicia comes the spirit ''Augardente''—the name means burning water—often referred to as Orujo in Spain and internationally or as Orujo, caña in Galicia. This spirit is made from the distillation of the pomace of grapes.
Music
Folk and traditionally based music
 The traditional music of Galicia and
The traditional music of Galicia and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
features highly distinctive folk styles that have some similarities with the neighboring area of Cantabria. The music is characterized by the use of bagpipes.
*Luar na Lubre: a band inspired by traditional Galician music. They have collaborated with Mike Oldfield and other musicians.
*Carlos Núñez Muñoz, Carlos Núñez: he has also collaborated with a great number of artists, being notable for his long-term friendship with The Chieftains.
*Susana Seivane: virtuoso piper. She descends from a family of pipe makers and stated she preferred pipes instead of dolls during her childhood.
*Milladoiro
*Cristina Pato: bagpiper and member of Yo-Yo Ma's Silk Road Ensemble.
*Tanxugueiras
*Berrogüetto
*Sangre de Muerdago: forest folk band led by Pablo C. Ursusson, member of the legendary Galician neo Crust punk, crust band Ekkaia.
Pop and rock
*Andrés Suárez: singer-songwriter from Ferrol, known for his poetic, insightful and often romantic lyrics. *Los Suaves: hard rock/heavy metal music, heavy metal band active since the early 1980s, from Ourense *Deluxe (music group), Deluxe: pop/rock band fromA Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
led by Xoel López
*Siniestro Total: punk rock
*Os Resentidos: led by Antón Reixa in the 1980s
*Heredeiros da Crus: rock band singing in Galician language
*Iván Ferreiro
*Xoel Lopez
*Bala (band), Bala
*Triángulo de Amor Bizarro
*Arrythmia
*Broa
*Chicharrón
Hip-hop
*Dios Ke Te Crew: a powerful band of hip-hop with socially compromised lyrics. *Ezetaerre *Malandrómeda *Rebeliom do InframundoLiterature, poetry and philosophy
As with many other Romance languages,Galician-Portuguese
Galician-Portuguese ( gl, galego-portugués or ', pt, galego-português or ), also known as Old Portuguese or as Medieval Galician when referring to the history of each modern language, was a West Iberian Romance language spoken in the Middle ...
emerged as a literary language in the Middle Ages, during the 12th and 13th centuries, when a Galician-Portuguese lyric, rich lyric tradition developed, followed by a minor prose tradition, whilst being the predominant language used for legal and private texts till the 15th century. However, in the face of the hegemony of Spanish, during the so-called ''Séculos Escuros'' ("Dark Centuries") from 1530 to the late 18th century, it fell from major literary or legal written use.
 As a literary language it was revived again during the 18th and, most notably, the 19th-century (''Rexurdimento'' ''Resurgence'') with such writers as Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal. In the 20th century, before the Spanish Civil War the ''Irmandades da Fala'' ("Brotherhood of the Language") and ''Nós (Galicia), Grupo Nós'' included such writers as Vicente Risco, Ramón Cabanillas and Castelao. Public use of Galician was largely suppressed during the Franco dictatorship but has been resurgent since the restoration of democracy. Though written primarily in Castilian, several works by the Nobel laureate Camilo José Cela, notably ''Mazurka for Two Dead Men'', are set in the author's native Galicia and make frequent allusions to Galician folklore, customs, and language. Other notable Galician authors who wrote mostly in Spanish, but always around Galician subjects, are Valle-Inclán, Wenceslao Fernández Flórez, Emilia Pardo Bazán and Gonzalo Torrente Ballester. Contemporary writers in Galician include Xosé Luís Méndez Ferrín, Manuel Rivas, Chus Pato, and Suso de Toro.
As a literary language it was revived again during the 18th and, most notably, the 19th-century (''Rexurdimento'' ''Resurgence'') with such writers as Rosalía de Castro, Manuel Murguía, Manuel Leiras Pulpeiro, and Eduardo Pondal. In the 20th century, before the Spanish Civil War the ''Irmandades da Fala'' ("Brotherhood of the Language") and ''Nós (Galicia), Grupo Nós'' included such writers as Vicente Risco, Ramón Cabanillas and Castelao. Public use of Galician was largely suppressed during the Franco dictatorship but has been resurgent since the restoration of democracy. Though written primarily in Castilian, several works by the Nobel laureate Camilo José Cela, notably ''Mazurka for Two Dead Men'', are set in the author's native Galicia and make frequent allusions to Galician folklore, customs, and language. Other notable Galician authors who wrote mostly in Spanish, but always around Galician subjects, are Valle-Inclán, Wenceslao Fernández Flórez, Emilia Pardo Bazán and Gonzalo Torrente Ballester. Contemporary writers in Galician include Xosé Luís Méndez Ferrín, Manuel Rivas, Chus Pato, and Suso de Toro.
Public holidays
* (St. Joseph's Day) on 19 March (strictly religious) * (May Day) on 1 May * (Galician Literature Day) on 17 May * (Galicia's National Day) also known as St. James the Great, St. James the Apostle Day on 25 July * on 15 August (strictly religious)Festivals
 * ''Entroido'', or Carnival, is a traditional celebration in Galicia, historically disliked and even forbidden by the Catholic Church. Famous celebrations are held in Laza, Spain, Laza, Verín, and Xinzo de Limia.
* Corpus Christi (feast), Festa do Corpus Christi in Ponteareas, has been observed since 1857 on the weekend following Corpus Christi (feast), Corpus Christi (a movable feast) and is known for its floral carpets. It was declared a Festival of Tourist Interest in 1968 and a Festival of National Tourist Interest in 1980.
* Pontevedra Feira Franca, Feira Franca, the first weekend of September, in
* ''Entroido'', or Carnival, is a traditional celebration in Galicia, historically disliked and even forbidden by the Catholic Church. Famous celebrations are held in Laza, Spain, Laza, Verín, and Xinzo de Limia.
* Corpus Christi (feast), Festa do Corpus Christi in Ponteareas, has been observed since 1857 on the weekend following Corpus Christi (feast), Corpus Christi (a movable feast) and is known for its floral carpets. It was declared a Festival of Tourist Interest in 1968 and a Festival of National Tourist Interest in 1980.
* Pontevedra Feira Franca, Feira Franca, the first weekend of September, in Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
recreates an open market that first occurred in 1467. The fair commemorates the height of Pontevedra's prosperity in the 15th and 16th centuries, through historical recreation, theater, animation, and demonstration of artistic activities. Held annually since 2000.
* Arde Lucus, in June, celebrates the Celtic and Roman history of the city of Lugo, with recreations of Celtic weddings, Roman circus, etc.
* Bonfires of Saint John, ''Noite de San Xoán'' or ''Noite da Queima'' is widely spread in all Galician territory, celebrated as a welcome to the summer solstice since the Celtic period, and Christianized in Midsummer, Saint John's day eve. Bonfires are believed to make ''meigas'' (malicious or fallen witches), flee. They are particularly relevant in the city of A Coruña, Corunna, where it became Fiestas of National Tourist Interest of Spain, Fiesta of National Tourist Interest of Spain. The whole city participates in making great bonfires in each district, whereas the centre of the party is located on the beaches of Riazor and Orzan, in the very city heart, where hundreds of bonfires of different sizes are lighted. Also, grilled sardines are very typical.
* Rapa das Bestas ("shearing of the beasts") in Sabucedo, the first weekend in July, is the most famous of several ''rapas'' in Galicia and was declared a Festival of National Tourist Interest in 1963. Wild colts are driven down from the mountains and brought to a closed area known as a ''curro'', where their manes are cut and the animals are marked and assisted after a long winter in the hills. In Sabucedo, unlike in other ''rapas'', the ''aloitadores'' ("fighters") each take on their task with no assistance.
* Festival de Ortigueira (Ortigueira's Festival of Celtic World) lasts four days in July, in Ortigueira. First celebrated in 1978–1987 and revived in 1995, the festival is based on Celtic culture, folk music, and the encounter of different peoples throughout Spain and the world. Attended by over 100,000 people, it is considered a Festival of National Tourist Interest.
* Festa da Dorna, 24 July, in Santa Uxía de Ribeira, Ribeira. Founded in 1948, declared a Galician Festival of Tourist Interest in 2005. Founded as a joke by a group of friends, it includes the Gran Prix de Carrilanas, a regatta of hand-made boats; the Icarus Prize for Unmotorized Flight; and a musical competition, the Canción de Tasca.
* Festas do Apóstolo Santiago (Festas of the Apostle James): the events in honor of the patron saint of Galicia last for half a month. The religious celebrations take place on 24 July. Celebrants set off fireworks, including a pyrotechnic castle in the form of the façade of the cathedral.
* Romería Vikinga de Catoira ("Viking Festival of Catoira"), the first Sunday in August, is a secular festival that has occurred since 1960 and was declared a Festival of International Tourist Interest in 2002. It commemorates the historic defense of Galicia and the treasures of Santiago de Compostela from Normans, Norman and Saracen pirate attacks.
* Festas da Peregrina in Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
, 2nd week of August, celebrating the Pilgrim Virgin of Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
. There is a bullfighting festival at the same time. Pontevedra is the only city where there is a Plaza de Toros de Pontevedra, permanent bullring.
* Festa de San Froilán, 4–12 October, celebrating the patron saint of the city of Lugo. A Festival of National Tourist Interest, the festival was attended by 1,035,000 people in 2008. It is most famous for the booths serving ''polbo á feira'', an octopus dish.
* Festa do marisco (Seafood Festival), October, in O Grove. Established in 1963; declared a Festival of National Tourist Interest in the 1980s.
In 2015 only five ''Bullfighting, corridas'' took place within Galicia.
In addition, recent studies have stated that 92% of Galicians are firmly against bullfighting, the highest rate in Spain. Despite this, popular associations, such as ''Galicia Mellor Sen Touradas'' ("Galicia Better without Bullfights"), have blamed politicians for having no compromise to abolish it and have been very critical of local councils', especially those governed by the PP and PSOE, payment of subsidies for corridas. The province government of Pontevedra stopped the end of these subsidies and declared the province "free of bullfights". The province government of A Coruña approved a document supporting the abolition of these events.
Media
Television
Televisión de Galicia (TVG) is the autonomous community's public channel, which has broadcast since 24 July 1985 and is part of the Compañía de Radio-Televisión de Galicia (CRTVG). TVG broadcasts throughout Galicia and has two international channels, Galicia Televisión Europa and Galicia Televisión América, available throughout the European Union and the Americas through Hispasat. CRTVG also broadcasts a digital terrestrial television (DTT) channel known as G2 (TV channel), tvG2 and is considering adding further DTT channels, with a 24-hour news channel projected for 2010.Radio
Radio Galega (RG) is the autonomous community's public radio station and is part of CRTVG. Radio Galega began broadcasting on 24 February 1985, with regular programming starting on 29 March 1985. There are two regular broadcast channels: Radio Galega and Radio Galega Música. In addition, there is a DTT and internet channel, Son Galicia Radio, dedicated specifically to Galician music. Galicia has several free and community radio stations. Cuac FM is the headquarters of the Community Media Network (which brings together media non-profit oriented and serves their community). CUAC FM (A Coruña), Radio Filispim (Ferrol), Radio Roncudo (corme), Kalimera Radio (Santiago de Compostela), Radio Piratona (Vigo) and Radio Clavi (Lugo) are part of the Galician Network of Free and Association of Community Radio Broadcasters(ReGaRLiC)Press
The most widely distributed newspaper in Galicia is ''La Voz de Galicia'', with 12 local editions and a national edition. Other major newspapers are ''El Correo Gallego'' (Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
), ''Faro de Vigo'' (Vigo
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
), ''Diario de Pontevedra'' (Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
), ''El Progreso (newspaper), El Progreso'' (Lugo), ''La Región'' (province of Ourense, Ourense), and ''Galicia Hoxe'' – The first daily newspaper to publish exclusively in Galician. Other newspapers are ''El Diario de Ferrol, Diario de Ferrol'', the sports paper ''DxT Campeón'', ''El Ideal Gallego'' from A Coruña, the ''Heraldo de Vivero'', ''Atlántico Diario'' from Vigo and the ''Xornal de Galicia''.
Sport
Galicia has a long sporting tradition dating back to the early 20th century when the majority of sports clubs in Spain were founded. The most popular and well-supported teams in the region are Deportivo La Coruña and Celta Vigo. When the two sides play, it is referred to as the Galician derby. Deportivo was champion of La Liga in the 1999–2000 season. Pontevedra CF fromPontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
and Racing de Ferrol, Racing Ferrol from Ferrol are two other notable clubs from Galicia as well as CD Lugo and SD Compostela. The Galician Football Federation periodically fields a Galicia national football team, national team against international opposition. This fact causes some political controversy because matches involving other national football teams different from the Spanish official national team threaten its status as the only national football team of the State. The policy of centralization in sport is very strong as it is systematically used as a patriotic device with which to build a symbol of the supposed unity of Spain which is a plurinational state.
Football aside, the most popular team sports in Galicia are futsal, Team handball, handball and basketball. In basketball, Obradoiro CAB is the most successful team of note, and currently, the only Galician team that plays in the Liga ACB; other teams are CB Breogan, Club Ourense Baloncesto and OAR Ferrol. In the sport of handball, CB Cangas, Club Balonmán Cangas plays in the top-flight (Liga ASOBAL). The sport is particularly popular in the province of Pontevedra with the three other Galician teams in the top two divisions: SD Teucro (Pontevedra), Octavio Pilotes Posada (Vigo) and SD Chapela (Redondela).
In roller hockey HC Liceo La Coruña, HC Liceo is the most successful Galician team, in any sport, with numerous European and World titles. In futsal teams, Lobelle Santiago and Azkar Lugo.
Galicia is also known for its tradition of participation in water sports both at sea and in rivers; these include rowing (sport), rowing, yachting, canoeing and surfing. Its athletes have regularly won medals in the Olympics; currently, the most notable examples are David Cal, Carlos Pérez Rial, and Fernando Echavarri.
Galician triathlon contenders Francisco Javier Gómez Noya and Iván Raña have been world champions. In 2006 the cyclist Oscar Pereiro won the Tour de France after the disqualification of American Floyd Landis, gaining the top position on the penultimate day of the race. Galicians are also prominent athletes in the sport of mountaineering—Chus Lago is the third woman to reach the summit of Everest without supplemental oxygen.
Emerging sports
Since 2011, several Gaelic football teams have been set up in Galicia. The first was A Coruña Fillos de Breogán, Fillos de Breogán (A Coruña), followed Artabros (Oleiros), Irmandinhos (A Estrada), SDG Corvos (Pontevedra), and Suebia (Santiago de Compostela) with talk of creating a Galician league. Galicia also fielded a Gaelic football side (recognised as national by the Gaelic Athletic Association, GAA) that beat Brittany in July 2012 and was reported in the Spanish nationwide press. Rugby union, Rugby is growing in popularity, although the success of local teams is hampered by the absence of experienced ex-pat players from English-speaking countries typically seen at teams based on the Mediterranean coast or in the big cities. Galicia has a long-established Rugby Federation that organises its own women's, children's, and men's leagues. Galicia has also fielded a national side for friendly matches against other regions of Spain and Portugal. A team of ex-pat Galicians in Salvador, Brazil have also formed Galicia Rugby, a sister team of the local football club.Symbols
 A golden chalice enclosed in a field of azure (heraldry), azure has been the symbol of Galicia since the 13th century. Originated as a Canting arms due to the phonetic similarity between the words "chalice" and ''Galyce'' ("Galicia" in old Norman language), the first documented mention of this emblem is on the ''Segar's Roll'', an English medieval roll of arms where are represented all the Christian kingdoms of 13th-century Europe. In the following centuries, the Galician emblem was variating; diverse shapes and several chalices (initially three and later one or five), wouldn't be until the 16th century that its number was fixed finally as one single chalice. Centuries after, a field of crosses was slowly added to the azure background, and latterly also a silver host. Since then basically, the emblem of the kingdom would be kept until nowadays.
The ancient flag of the Kingdom of Galicia was based mainly on its coat of arms until the 19th century. However, when in 1833 the Government of Spain decided to abolish the kingdom and divided it into four provinces, the Galician emblem, as well as the flag, lost its legal status and international validity. It wouldn't be until the late 19th century that some Galician intellectuals (nationalist politicians and writers) began to use a new flag as a symbol of renewed national unity for Galicia. That flag, which was composed of a diagonal stripe over a white background, was designated the "official flag of Galicia" in 1984, after the fall of Franco's dictatorship. In addition, the Royal Academy of Galicia asked the Galician government to incorporate the ancient coat of arms of the kingdom onto the modern flag, being present in it since then.
In addition to its coat of arms and flag, Galicia also has its own anthem. While it is true that the Kingdom of Galicia had during centuries a kind of unofficial anthem known as the "Solemn March of the kingdom", the Galician current anthem was not created until 1907, although its composition had begun already in 1880. Titled "Os Pinos" ("The Pines"), the Galician anthem lyrics were written by Eduardo Pondal, one of the greatest modern Galician poets, and its music was composed by Pascual Veiga. Performed for the first time in 1907 in Havana (Cuba) by Galician emigrants, the anthem was banned from 1927 by diverse Spanish Governments until 1977 when it was officially established by the Galician authorities.
A golden chalice enclosed in a field of azure (heraldry), azure has been the symbol of Galicia since the 13th century. Originated as a Canting arms due to the phonetic similarity between the words "chalice" and ''Galyce'' ("Galicia" in old Norman language), the first documented mention of this emblem is on the ''Segar's Roll'', an English medieval roll of arms where are represented all the Christian kingdoms of 13th-century Europe. In the following centuries, the Galician emblem was variating; diverse shapes and several chalices (initially three and later one or five), wouldn't be until the 16th century that its number was fixed finally as one single chalice. Centuries after, a field of crosses was slowly added to the azure background, and latterly also a silver host. Since then basically, the emblem of the kingdom would be kept until nowadays.
The ancient flag of the Kingdom of Galicia was based mainly on its coat of arms until the 19th century. However, when in 1833 the Government of Spain decided to abolish the kingdom and divided it into four provinces, the Galician emblem, as well as the flag, lost its legal status and international validity. It wouldn't be until the late 19th century that some Galician intellectuals (nationalist politicians and writers) began to use a new flag as a symbol of renewed national unity for Galicia. That flag, which was composed of a diagonal stripe over a white background, was designated the "official flag of Galicia" in 1984, after the fall of Franco's dictatorship. In addition, the Royal Academy of Galicia asked the Galician government to incorporate the ancient coat of arms of the kingdom onto the modern flag, being present in it since then.
In addition to its coat of arms and flag, Galicia also has its own anthem. While it is true that the Kingdom of Galicia had during centuries a kind of unofficial anthem known as the "Solemn March of the kingdom", the Galician current anthem was not created until 1907, although its composition had begun already in 1880. Titled "Os Pinos" ("The Pines"), the Galician anthem lyrics were written by Eduardo Pondal, one of the greatest modern Galician poets, and its music was composed by Pascual Veiga. Performed for the first time in 1907 in Havana (Cuba) by Galician emigrants, the anthem was banned from 1927 by diverse Spanish Governments until 1977 when it was officially established by the Galician authorities.
Galicians
Honour
Galicia Peak in Vinson Massif, Antarctica is named after the autonomous community of Galicia.Image gallery
A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and s ...
Muros_de_San_Cibrao_de_Las.jpg, Gates of the Iron Age oppidum of San Cibrao de Las, one of the largest ''Castro culture, castros'' of Galicia
Gaiteiros em romaria galega.jpg, ''Gaiteiros'', or bagpipe players. ''Gaita'' ('bagpipe') is the most representative Galician musical instrument
Queimada_Galicia_4.jpg, ''Queimada (drink), Queimada'', a traditional drink obtained after partially burning local ''aguardiente, augardente'' (grappa)
2015 Hórreo de Lira. Carnota. Galiza 2.jpg, A ''hórreo'' or ''cabaceiro'' or ''canastro'', a traditional and ubiquitous granary
Iglesia de San Jorge, La Coruña, España, 2015-09-25, DD 42.jpg, A ''cruceiro'', or wayside cross, and San Xurxo church in A Coruña
Ciervo cuernos.jpg, Millenarian rock carvings, ''Laxe dos carballos'' at Campo Lameiro, in this detail depicts a deer hit by several spears
Pontevedra 13 Praza da leña.jpg, Plaza de la Leña, Leña square, Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
Castelo (Monforte de Lemos).jpg, Castle and Monastery of San Vicente do Pino, Monforte de Lemos
Muralla.Lugo.Galicia.jpg, Roman Walls of Lugo, a World Heritage monument
Dorna a vela.jpg, A traditional ''dorna'', a fisherman boat common in the Ria de Arousa
Faro Silleiro.jpg, The rocky coast of Cabo Silleiro, Baiona, Pontevedra, Baiona
See also
*List of castros in Galicia *Timeline of Galician historyNotes
References
Bibliography
* Bell, Aubrey F. B. (1922)''Spanish Galicia''
London: John Lane The Bodley Head Ltd. * Meakin, Annette M. B. (1909)
''Galicia: The Switzerland of Spain''
London: Methuen & Co.
External links
* * {{authority control Galicia (Spain), Autonomous communities of Spain Green Spain NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Regions of Europe with multiple official languages