Fort Pitt (Pennsylvania) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Fort Pitt was a
Fort Pitt was a
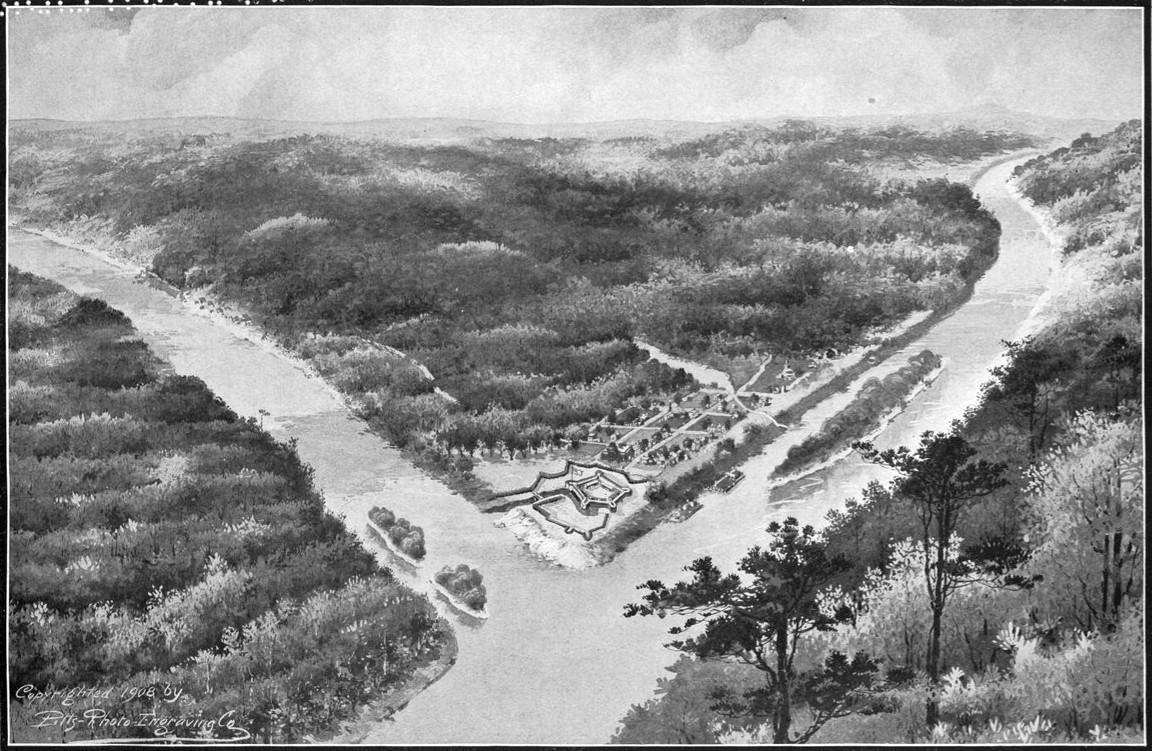 In April 1754, the French began building
In April 1754, the French began building
 After the colonial war and in the face of continued broken treaties, broken promises and encroachment by the Europeans, in 1763 the western Lenape and Shawnee took part in a Native uprising known as
After the colonial war and in the face of continued broken treaties, broken promises and encroachment by the Europeans, in 1763 the western Lenape and Shawnee took part in a Native uprising known as
 Notice was given to area residents of an auction of all salvageable remains of the fort on August 3, 1797 after the U.S. Army decommissioned the site.
In the 20th century, the city of Pittsburgh commissioned archeological excavation of the foundations of Fort Pitt. Afterward, some of the fort was reconstructed to give visitors at Point State Park a sense of the size of the fort. In this rebuilt section, the
Notice was given to area residents of an auction of all salvageable remains of the fort on August 3, 1797 after the U.S. Army decommissioned the site.
In the 20th century, the city of Pittsburgh commissioned archeological excavation of the foundations of Fort Pitt. Afterward, some of the fort was reconstructed to give visitors at Point State Park a sense of the size of the fort. In this rebuilt section, the
Fort Pitt Museum and Bushy Run Battlefield360° panorama of the Blockhouse exterior360° panorama of the Blockhouse interior
{{Authority control Pitt Pitt Pitt Pontiac's War Pitt History of Pittsburgh Pitt Government buildings completed in 1761 Infrastructure completed in 1761 1761 establishments in Pennsylvania
 Fort Pitt was a
Fort Pitt was a fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
built by British forces between 1759 and 1761 during the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, where the Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of ...
is formed in western Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
(modern day Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
). It was near (but not directly on) the site of Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
, a French colonial fort built in 1754 as tensions increased between Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
in both Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
. The French destroyed Fort Duquesne in 1758 when they retreated under British attack.
British colonial protection of this area ultimately led to the development of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
and Allegheny County, Pennsylvania
Allegheny County () is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in Southwestern Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,250,578, making it the state's second-most populous county, following Philadelphia Co ...
by British-American colonists and immigrants.
Location and construction
 In April 1754, the French began building
In April 1754, the French began building Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
on the site of the small British Fort Prince George
Fort Prince George was an uncompleted fort on what is now the site of Pittsburgh, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela Rivers in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. The site was originally a trading post established by Ohio Company t ...
at the beginning of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
(AKA Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
). The Braddock expedition, a 1755 British attempt to take Fort Duquesne, met with defeat at the Battle of the Monongahela at present-day Braddock, Pennsylvania. The French garrison later defeated an attacking British regiment in September 1758 at the Battle of Fort Duquesne. French Colonel de Lignery ordered Fort Duquesne destroyed and abandoned at the approach of General John Forbes' expedition in late November.
A number of factors contributed to this strategic withdrawal. In August of 1758 the French Fort Frontenac
Fort Frontenac was a French trading post and military fort built in July 1673 at the mouth of the Cataraqui River where the St. Lawrence River leaves Lake Ontario (at what is now the western end of the La Salle Causeway), in a location traditiona ...
, at the head of Lake Ontario, was captured by British Gen. Bradstreet, severing the supply lines to French fortifications across the frontier. Fort Duquesne was the southernmost of these. Short on materiel, French commander François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery
François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery (24 August 1703 – 29 July 1759) was a colonial military leader in the French province of Canada. Active in the defense of New France during the Seven Years' War (also known as the French and Indian War ...
was forced to dismiss elements under his command down the Ohio River to their bases in Illinois and Louisiana, and send others overland north to Ft. Presque Isle. Those Native who may have remained at Fort Duquesne were likely eager to return to their winter longhouses before the weather changed. Consequently, the fort was further undermanned, possibly left with as few as 200 regulars.
The late October Treaty of Easton with several Native tribes involved in the war largely dissolved the alliance that had enabled French military dominance in the region. Chiefs of 13 American Indian nations agreed to negotiate peace with the colonial governments of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
and to abandon any alliances with the French. The nations were primarily the Six Nations of the Iroquois League
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
, bands of the Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
(Delaware), and the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
. They agreed to the treaty based on the colonial governments' promising to respect their rights to hunting and territory in the Ohio Country, to prohibit establishing new settlements west of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
, and to withdraw British and colonial military troops after the war.
The French commander, anticipating an attack along Braddock’s road, had spent some effort fortifying positions there. (Forbes had several times advanced men along that route as a feint.) From prisoners captured during Maj. James Grant James Grant may refer to:
Politics and law
* Sir James Grant, 1st Baronet (died 1695), Scottish lawyer
*Sir James Grant, 6th Baronet (1679–1747), Scottish Whig politician
*Sir James Grant, 8th Baronet (1738–1811), Scottish member of parliament
...
’s catastrophic attack on Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
, de Lignery was reportedly surprised to learn of a fortified encampment of British troops only 50 miles away at Ligonier, Pennsylvania
Ligonier is a borough in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,513 at the 2020 census. Ligonier was settled in the 1760s. The borough is well known for nearby Idlewild Park, one of the oldest amusement parks in t ...
, with substantial reserves behind. He was also certainly cognizant of the British lightning raid on the Native village of Kittanning (40 miles north on the Allegheny River) two years earlier. Thus, a British attack from the north was a distinct possibility. Forbes had indeed contemplated an attack further north on Fort Machault
Fort Machault (, ) was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. (Present-day Franklin developed here later.) The fort helped the French control these waterway ...
(later, Ft. Venango; modern-day Franklin, PA.)
Finding himself in an under-manned, flood-prone fort in a weak defensive position, vulnerable to attack from three directions, and running low on provisions, de Lignery retreated north. He destroyed the stores and many of the structures as 1500 advance British troops under the command of Forbes drew within 10 miles. The French never returned to the region.
The British built a new fort and named it Fort Pitt, after William Pitt the Elder
William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham, (15 November 170811 May 1778) was a British statesman of the Whig group who served as Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1766 to 1768. Historians call him Chatham or William Pitt the Elder to distinguish ...
. The fort was built from 1759 to 1761 during the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
(Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
), next to the site of former Fort Duquesne. It was built in the popular pentagram shape, with bastions at the star points, by Captain Harry Gordon, a British Engineer in the 60th Royal American Regiment.
Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–17 ...
, an effort to drive settlers out of the Native American territory. The American Indians' siege of Fort Pitt began on June 22, 1763, but they found it too well-fortified to be taken by force. In negotiations during the siege, Captain Simeon Ecuyer, the commander of Fort Pitt, gave two Delaware emissaries blankets that had been exposed to smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
. The potential of this act to cause an epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
among the American Indians was clearly understood. Commander William Trent wrote that he hoped "it will have the desired effect." Colonel Henry Bouquet
Henry Bouquet (born Henri Louis Bouquet; 1719 – 2 September 1765) was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American ...
, leading a relief force, would discuss similar tactics with Commander-in-Chief Jeffery Amherst. The effectiveness of these attempts to spread the disease are unknown, although it is known that the method used is inefficient compared to respiratory transmission, and it is difficult to differentiate from naturally occurring epidemics resulting from previous contacts with colonists.
During and after Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–17 ...
, epidemics of smallpox among Native Americans devastated the tribes of Ohio Valley
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illin ...
and the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
areas. On August 1, 1763, most of the American Indians broke off the siege to intercept the approaching force under Colonel Bouquet. In the Battle of Bushy Run
The Battle of Bushy Run was fought on August 5–6, 1763, in western Pennsylvania, between a British column under the command of Colonel Henry Bouquet and a combined force of Delaware, Shawnee, Mingo, and Huron warriors. This action occurred du ...
, Bouquet fought off the American Indian attack and relieved Fort Pitt on August 10.
In 1772, after Pontiac's War, the British commander at Fort Pitt sold the building to two colonists, William Thompson and Alexander Ross. At that time, the Pittsburgh area was claimed by the colonies of both Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, which struggled for power over the region. After Virginians took control of Fort Pitt, they called it Fort Dunmore, in honour of Virginia's Governor Lord Dunmore
Earl of Dunmore is a title in the Peerage of Scotland.
History
The title was created in 1686 for Lord Charles Murray, second son of John Murray, 1st Marquess of Atholl. He was made Lord Murray of Blair, Moulin and Tillimet (or Tullimet) and V ...
. The fort served as a staging ground in Dunmore's War of 1774.
American Revolutionary War
During theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, Fort Pitt served as a headquarters for the western theatre of the war. In 1778, Sampson Mathews, George Clymer
George Clymer (March 16, 1739January 23, 1813) was an American politician, abolitionist and Founding Father of the United States, one of only six founders who signed both the Declaration of Independence and U.S. Constitution. He was among the e ...
, and Samuel Washington
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bib ...
were sent as representatives for the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
to the western frontier to report on security of the American border. Congress had learned of British governor Henry Hamilton's efforts to pit local Indian tribes against the lightly guarded American western border, and feared attack. From Fort Pitt, the committee reported back to Congress the seriousness of the threat, leading Congress to send 3,000 militiamen to the western frontier,Pieper, Thomas, and Gidney, James (1980). Fort Laurens, 1778-1779: The Revolutionary War in Ohio. Kent State University Press, p 13. https://books.google.com/books?id=9aoJVOjymwIC&dq=%22sampson+matthews%22&source=gbs_navlinks_s Retrieved March 2, 2013. including George Rogers Clark
George Rogers Clark (November 19, 1752 – February 13, 1818) was an American Surveying, surveyor, soldier, and militia officer from Virginia who became the highest-ranking American patriot military officer on the northwestern frontier duri ...
. Clark finally captured Hamilton in winter 1779—a success that encouraged the alliance with France.English, William Hayden (1896). Conquest of the Country Northwest of the River Ohio, 1778–1783, and Life of Gen. George Rogers Clark, vol 2. Bowen-Merrill, Indianapolis.
In present-day Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and t ...
, the British garrisoned Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
.
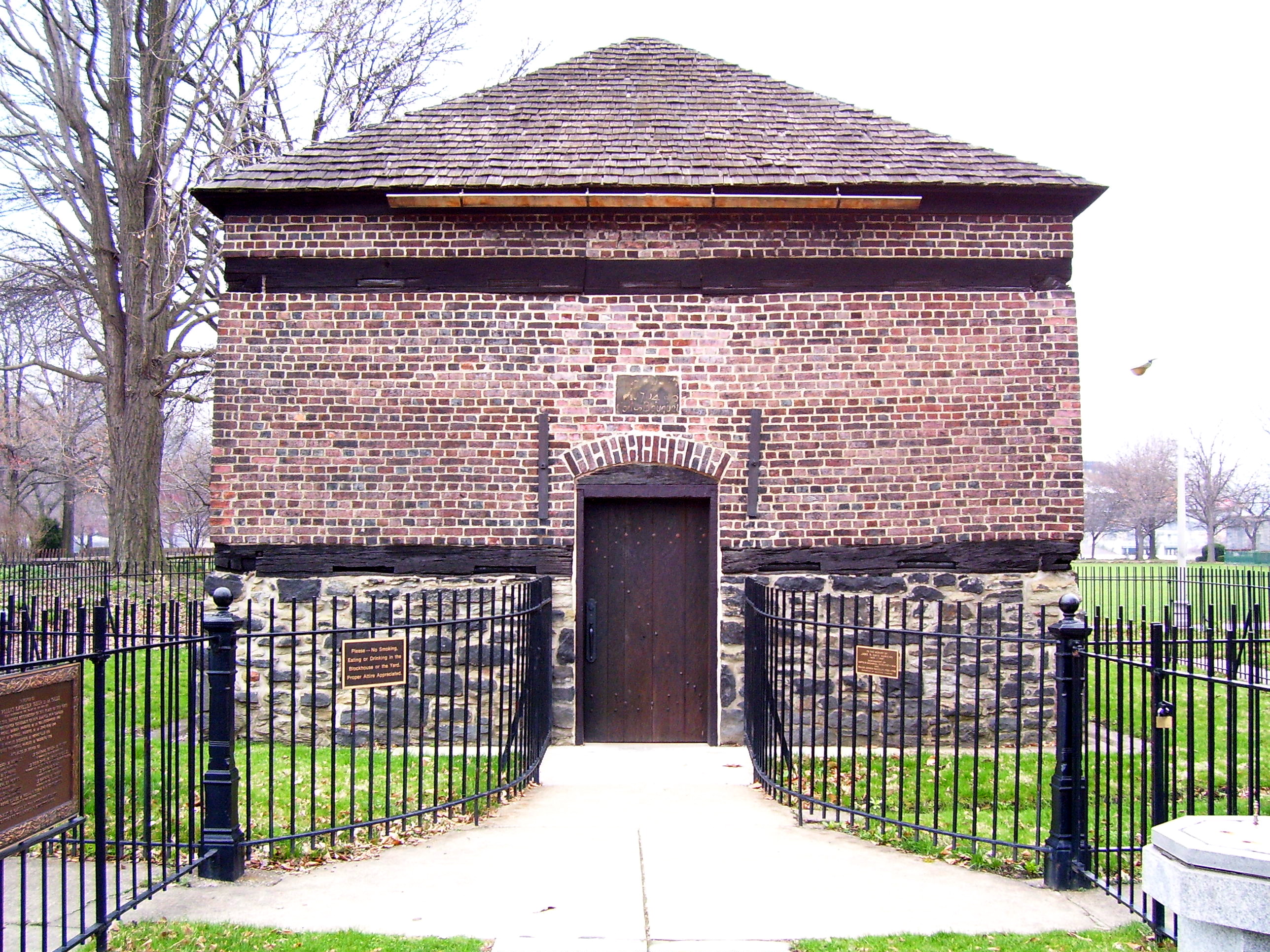
A redoubt, a small brick outbuilding called the Blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
, survives in Point State Park
Point State Park (locally known as The Point) is a Pennsylvania state park on in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
Built on land acqu ...
as the sole remnant of Fort Pitt. Erected in 1764, it is believed to be the oldest building still standing in Pittsburgh. Used for many years as a private residence, the blockhouse was purchased and preserved for many years by the local chapter of the Daughters of the American Revolution
The Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) is a lineage-based membership service organization for women who are directly descended from a person involved in the United States' efforts towards independence.
A non-profit group, they promote ...
.
Later history
 Notice was given to area residents of an auction of all salvageable remains of the fort on August 3, 1797 after the U.S. Army decommissioned the site.
In the 20th century, the city of Pittsburgh commissioned archeological excavation of the foundations of Fort Pitt. Afterward, some of the fort was reconstructed to give visitors at Point State Park a sense of the size of the fort. In this rebuilt section, the
Notice was given to area residents of an auction of all salvageable remains of the fort on August 3, 1797 after the U.S. Army decommissioned the site.
In the 20th century, the city of Pittsburgh commissioned archeological excavation of the foundations of Fort Pitt. Afterward, some of the fort was reconstructed to give visitors at Point State Park a sense of the size of the fort. In this rebuilt section, the Fort Pitt Museum
Fort Pitt Museum is an indoor/outdoor museum that is administered by the Senator John Heinz History Center in downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania in the United States. It is at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny Rivers ...
is housed in the Monongahela Bastion, and excavated portions of the fort were filled in.
Fort Pitt Foundry
The Fort Pitt Foundry was a nineteenth-century iron foundry in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was originally established at Fifth Avenue and Smithfield Street in 1804 by Joseph McClurg, grandfather of Joseph W. McClurg, and his son Alex McClurg, ...
was an important armament
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
s manufacturing center for the Federal government during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
, under the charge of William Metcalf.
Popular culture
*The ''Allegheny Uprising
''Allegheny Uprising'' (released in the UK as ''The First Rebel'') is a 1939 American Adventure Western film directed by William A. Seiter and starring Claire Trevor and John Wayne. Based on the 1937 novel ''The First Rebel'' by Neil H. Swanson, ...
'' (1939) starred John Wayne
Marion Robert Morrison (May 26, 1907 – June 11, 1979), known professionally as John Wayne and nicknamed The Duke or Duke Wayne, was an American actor who became a popular icon through his starring roles in films made during Hollywood's Go ...
and Claire Trevor
Claire Trevor ( Wemlinger; March 8, 1910April 8, 2000) was an American actress. She appeared in 65 feature films from 1933 to 1982, winning the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actress for her role in ''Key Largo'' (1948), and received nomina ...
.
*In Cecil B. DeMille's ''Unconquered
Unconquered or The Unconquered may refer to:
Films
* ''Unconquered'' (1917 film), a drama film by Frank Reicher
* ''Unconquered'' (1947 film), an adventure film by Cecil B. DeMille
* ''The Unconquered'' (documentary) or ''Helen Keller in Her Sto ...
'' (1947), starring Gary Cooper
Gary Cooper (born Frank James Cooper; May 7, 1901May 13, 1961) was an American actor known for his strong, quiet screen persona and understated acting style. He won the Academy Award for Best Actor twice and had a further three nominations, a ...
and Paulette Goddard
Paulette Goddard (born Marion Levy; June 3, 1910 – April 23, 1990) was an American actress notable for her film career in the Golden Age of Hollywood.
Born in Manhattan and raised in Kansas City, Missouri, Goddard initially began her career ...
, Howard Da Silva
Howard Da Silva (born Howard Silverblatt, May 4, 1909 – February 16, 1986) was an American actor, director and musical performer on stage, film, television and radio. He was cast in dozens of productions on the New York stage, appeared in mo ...
played a gunrunner and Boris Karloff
William Henry Pratt (23 November 1887 – 2 February 1969), better known by his stage name Boris Karloff (), was an English actor. His portrayal of Frankenstein's monster in the horror film ''Frankenstein'' (1931) (his 82nd film) established ...
a Seneca chief who lead an American Indian uprising in 1763. Cooper and Goddard save Fort Pitt.
*The video game ''Assassin's Creed III
''Assassin's Creed III'' is a 2012 action-adventure video game developed by Ubisoft Montreal and published by Ubisoft for PlayStation 3, Xbox 360, Wii U, and Microsoft Windows. It is the fifth major installment in the ''Assassin's Creed'' serie ...
'' (2012) features Fort Pitt, but it is referred to as "Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
", although some of the action takes place after the Braddock and Forbes expeditions, when Pitt had been built to replace Duquesne.
*Conrad Richter
Conrad Michael Richter (October 13, 1890 – October 30, 1968) was an American novelist whose lyrical work is concerned largely with life on the American frontier in various periods. His novel '' The Town'' (1950), the last story of his trilogy '' ...
's youth novel, '' The Light in the Forest'' (1953), is partially set at Fort Pitt.
* Aerials of the fort can be seen during the opening credits of the film “Groundhog Day” as the live truck leaves the downtown area on its way to Punxsutawney.
See also
*Great Britain in the Seven Years' War
Great Britain was one of the major participants in the Seven Years' War, which in fact lasted nine years, between 1754 and 1763. British involvement in the conflict began in 1754 in what became known as the French and Indian War. However th ...
* Fort Dunmore, a later fort on the same site
* Fort Fayette, a later fort by Gen. Anthony Wayne on the same site
References
Further reading
*O'Meara, Walter. ''Guns at the Forks''. Pittsburgh, PA: University of Pittsburgh Press, 1965. . * Stotz, Charles Morse. ''Outposts Of The War For Empire: The French And English In Western Pennsylvania: Their Armies, Their Forts, Their People 1749-1764.'' Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press, 2005. . *Durant, Samuel W., plate IV, ''History of Allegheny Co., Pennsylvania : with illustrations descriptive of its scenery, palatial residences, public buildings, fine blocks, and important manufactories'', Philadelphia: L. H. Everts, 1876. *External links
Fort Pitt Museum and Bushy Run Battlefield
{{Authority control Pitt Pitt Pitt Pontiac's War Pitt History of Pittsburgh Pitt Government buildings completed in 1761 Infrastructure completed in 1761 1761 establishments in Pennsylvania