Fort Duquesne on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a
 Fort Duquesne, built at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers which forms the Ohio River, was considered strategically important for controlling the Ohio Country,"The Diaries of George Washington, Vol. 1", Donald Jackson, ed., Dorothy Twohig, assoc. ed
Fort Duquesne, built at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers which forms the Ohio River, was considered strategically important for controlling the Ohio Country,"The Diaries of George Washington, Vol. 1", Donald Jackson, ed., Dorothy Twohig, assoc. ed
Library of Congress American Memory site
/ref> both for settlement and for trade. The English merchant In the early 1750s, the French began construction of a line of forts, starting with
In the early 1750s, the French began construction of a line of forts, starting with

 Following
Following
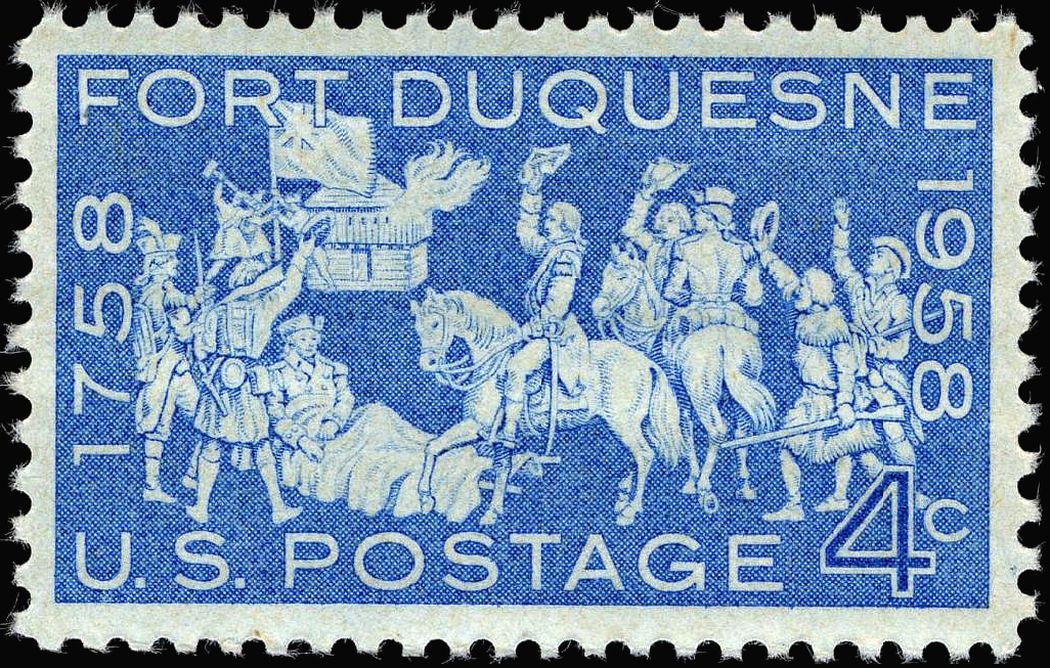 On November 25, 1958, the 200th anniversary of the capture of Fort Duquesne, the
On November 25, 1958, the 200th anniversary of the capture of Fort Duquesne, the
E'book
*
E'book
fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed as Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
. Fort Duquesne was destroyed by the French, prior to British conquest during the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
, known as the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
on the North American front. The British replaced it, building Fort Pitt between 1759 and 1761. The site of both forts is now occupied by Point State Park
Point State Park (locally known as The Point) is a Pennsylvania state park on in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
Built on land acqu ...
, where the outlines of the two forts have been laid in brick.
Background
 Fort Duquesne, built at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers which forms the Ohio River, was considered strategically important for controlling the Ohio Country,"The Diaries of George Washington, Vol. 1", Donald Jackson, ed., Dorothy Twohig, assoc. ed
Fort Duquesne, built at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers which forms the Ohio River, was considered strategically important for controlling the Ohio Country,"The Diaries of George Washington, Vol. 1", Donald Jackson, ed., Dorothy Twohig, assoc. edLibrary of Congress American Memory site
/ref> both for settlement and for trade. The English merchant
William Trent
William Trent (February 13, 1715–1787) was an American fur trader and merchant based in colonial Pennsylvania. He was commissioned as a captain of the Virginia Regiment in the early stages of the French and Indian War, when he served on the we ...
had established a highly successful trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
at the forks as early as the 1740s, to do business with a number of nearby Native American villages. Both the French and the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
were keen to gain advantage in the area.
As the area was within the drainage basin of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
, the French had claimed it as theirs. They controlled New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
(Quebec), the Illinois Country along the Mississippi, and La Louisiane
Louisiana (french: La Louisiane; ''La Louisiane Française'') or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, ...
(the ports of and Mobile, Alabama, and environs).
 In the early 1750s, the French began construction of a line of forts, starting with
In the early 1750s, the French began construction of a line of forts, starting with Fort Presque Isle
Fort Presque Isle (also Fort de la Presqu'île) was a fort built by French soldiers in summer 1753 along Presque Isle Bay at present-day Erie, Pennsylvania, to protect the northern terminus of the Venango Path. It was the first of the French p ...
on Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also h ...
in present-day Erie, Pennsylvania
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 ...
, followed by Fort Le Boeuf
Fort Le Bœuf (often referred to as Fort de la Rivière au Bœuf) was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek (in the drainage area of the River Ohio), in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort ...
, about 15 miles south in present-day Waterford, Pennsylvania
Waterford is a borough in Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,475 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Erie Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Waterford is an independent municipality located entirely within (and surroun ...
, and Fort Machault
Fort Machault (, ) was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. (Present-day Franklin developed here later.) The fort helped the French control these waterway ...
, on the Allegheny River in Venango County in present-day Franklin, Pennsylvania
Franklin is a city and the county seat of Venango County, Pennsylvania. The population was 6,097 in the 2020 census. Franklin is part of the Oil City, PA Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Franklin is known for its three-day autumn festival in Oc ...
.
Robert Dinwiddie
Robert Dinwiddie (1692 – 27 July 1770) was a British colonial administrator who served as lieutenant governor of colonial Virginia from 1751 to 1758, first under Governor Willem Anne van Keppel, 2nd Earl of Albemarle, and then, from July 1756 ...
, Lieutenant Governor of the Virginia Colony
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
, thought these forts threatened extensive claims to the land area by Virginians (including himself) of the Ohio Company. In late autumn 1753, Dinwiddie dispatched a young Virginia militia officer named George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
to the area to deliver a letter to the French commander at Fort Le Boeuf, asking them to leave. Washington was also to assess French strength and intentions. After reaching Fort Le Boeuf in December, Washington was politely rebuffed by the French.
Fort's construction and replacement


Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
's return to Virginia in January 1754, Dinwiddie sent Virginians to build Fort Prince George
Fort Prince George was an uncompleted fort on what is now the site of Pittsburgh, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela Rivers in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. The site was originally a trading post established by Ohio Company t ...
at the Forks of the Ohio
Point State Park (locally known as The Point) is a Pennsylvania state park on in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
Built on land acqui ...
. Work began on the fort on February 17. By April 18, a much larger French force of five hundred under the command of Claude-Pierre Pécaudy de Contrecœur arrived at the forks, forcing the small British garrison to surrender. The French knocked down the tiny British fort and built Fort Duquesne, named in honor of Marquis Duquesne, the governor-general of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
. The fort was built on the same model as the French Fort Frontenac
Fort Frontenac was a French trading post and military fort built in July 1673 at the mouth of the Cataraqui River where the St. Lawrence River leaves Lake Ontario (at what is now the western end of the La Salle Causeway), in a location traditio ...
on Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border ...
.''France in America'', Fitzhenry & Whiteside Limited, p. 181
Meanwhile, Washington, newly promoted to Colonel of the newly created Virginia Regiment
The Virginia Regiment was formed in 1754 by Virginia's Royal Governor Robert Dinwiddie, as a provincial corps. The regiment served in the French and Indian War, with members participating in actions at Jumonville Glen and Fort Necessity in 1754, ...
, set out on 2 April 1754 with a small force to build a road to, and then defend, Fort Prince George. Washington was at Wills Creek in north central Maryland when he received news of the fort's surrender. On May 25, Washington assumed command of the expedition upon the death of Colonel Joshua Fry. Two days later, Washington encountered a Canadian scouting party near a place now known as Jumonville Glen (several miles east of present-day Uniontown). Washington attacked the French Canadians, killing 10 in the early morning hours, and took 21 prisoners, of whom many were ritually killed by the Native American allies of the British.
The Battle of Jumonville Glen is widely considered the formal start of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, the North American front of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
.
Washington ordered construction of Fort Necessity
Fort Necessity National Battlefield is a National Battlefield in Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States, which preserves the site of the Battle of Fort Necessity. The battle, which took place on July 3, 1754, was an early battle of the ...
at a large clearing known as the Great Meadows. On 3 July 1754, the counterattacking French and Canadians forced Washington to surrender Fort Necessity. After disarming them, they released Washington and his men to return home.
Although Fort Duquesne's location at the forks looked strong on a map—controlling the confluence of three rivers—the reality was rather different. The site was low, swampy, and prone to flooding. In addition, the position was dominated by highlands across the Monongahela River, which would allow an enemy to bombard the fort with ease. Pécaudy de Contrecœur was preparing to abandon the fort in the face of Braddock's advance in 1755. He was able to retain it due to the advancing British force being annihilated (see below). When the Forbes expedition
The Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the now historic trail, the Forbes ...
approached in 1758, the French had initial success in the Battle of Fort Duquesne
The Battle of Fort Duquesne was British assault on the eponymous French fort (later the site of Pittsburgh) that was repulsed with heavy losses on 14 September 1758, during the French and Indian War.
The attack on Fort Duquesne was part of a la ...
against the English vanguard, but were forced to abandon the fort in the face of the much superior size of Forbes' main force.
The French held the fort successfully early in the war, turning back the expedition led by General Edward Braddock
Major-General Edward Braddock (January 1695 – 13 July 1755) was a British officer and commander-in-chief for the Thirteen Colonies during the start of the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the North American front of what is known in Europe ...
during the 1755 Battle of the Monongahela
The Battle of the Monongahela (also known as the Battle of Braddock's Field and the Battle of the Wilderness) took place on 9 July 1755, at the beginning of the French and Indian War, at Braddock's Field in what is now Braddock, Pennsylvania, e ...
. George Washington served as one of General Braddock's aides. A smaller attack by James Grant in September 1758 was repulsed with heavy losses. Two months later, on November 25, the Forbes Expedition
The Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the now historic trail, the Forbes ...
under the Scotsman General John Forbes took possession Fort Duquesne after the French destroyed and abandoned the site.
Present-day site
Fort Duquesne was built at the point of land of the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, where they form the Ohio River. Since the late 20th century, this area of downtown Pittsburgh has been preserved asPoint State Park
Point State Park (locally known as The Point) is a Pennsylvania state park on in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
Built on land acqu ...
, or simply, "the Point." The park includes a brick outline of the fort's walls, as well as outlines to mark the later Fort Pitt.
In May 2007, Thomas Kutys, an archaeologist with A.D. Marble & Company, a Cultural Resource Management firm based in Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, discovered a stone and brick drain on the Fort Duquesne site. It is thought to have drained one of the fort's many buildings. Due to its depth in the ground, this drain may be all of the fort that has survived. The entire northern half of the former fort site was disrupted and destroyed by the heavy industrial development of the area in the 19th century.
Commemoration
U.S. Post Office
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the executive branch of the Federal government of the Uni ...
issued a 4-cent Fort Duquesne bicentennial commemorative stamp
A commemorative stamp is a postage stamp, often issued on a significant date such as an anniversary, to honor or commemorate a place, event, person, or object. The ''subject'' of the commemorative stamp is usually spelled out in print, unlike defi ...
. It was first released for sale at the post office in Pittsburgh. The design was reproduced from a composite drawing, using various figures taken from an etching by T.B. Smith and a painting portraying the British occupation of the site as the Fort Duquesne blockhouse burns in the background.
Colonel Washington is depicted on horseback in the center, while General Forbes, who was debilitated by intestinal disease, is shown lying on a stretcher. The stamp also depicts Colonel Henry Bouquet
Henry Bouquet (born Henri Louis Bouquet; 1719 – 2 September 1765) was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American ...
, who was second in command to the ailing Forbes, and other figures who represent the Virginia militia and provincial army.
In media
'' Old Fort Duquesne, or, Captain Jack, the Scout'', is an historical novel by Charles McKnight, a retelling of the events of Fort Duquesne during theFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
.
Fort Duquesne appears in episode seven of the first season of the TV series Timeless.
Fort Duquesne also appears in the video game ''Assassin's Creed III
''Assassin's Creed III'' is a 2012 action-adventure video game developed by Ubisoft Montreal and published by Ubisoft for PlayStation 3, Xbox 360, Wii U, and Microsoft Windows. It is the fifth major installment in the ''Assassin's Creed'' serie ...
'', although it looks nothing like its real-life counterpart, and is referred to as Fort Duquesne long after the British rebuilt it. It is one of the main forts in the game that Connor has to conquer and reclaim for the Continental Army.
See also
*Great Britain in the Seven Years' War
Great Britain was one of the major participants in the Seven Years' War, which in fact lasted nine years, between 1754 and 1763. British involvement in the conflict began in 1754 in what became known as the French and Indian War. However th ...
* France in the Seven Years' War
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
* List of French forts in North America
This is a list of forts in New France built by the French government or French chartered companies in what later became Canada, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and the United States. They range from large European-type citadels like at Quebec City to ...
* Battle of Fort Duquesne
The Battle of Fort Duquesne was British assault on the eponymous French fort (later the site of Pittsburgh) that was repulsed with heavy losses on 14 September 1758, during the French and Indian War.
The attack on Fort Duquesne was part of a la ...
Further reading
E'book
*
E'book
References
Bibliography
*Anderson, Fred. ''Crucible of War: The Seven Years' War and the Fate of Empire in British North America, 1754–1766''. New York: Knopf, 2000. . *Hunter, William A. ''Forts on the Pennsylvania Frontier, 1753–1758''. Originally published 1960; Wennawoods reprint, 1999. * Stotz, Charles Morse. ''Outposts Of The War For Empire: The French and English In Western Pennsylvania: Their Armies, Their Forts, Their People 1749–1764''. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press, 2005. . * {{authority control 1754 establishments in the French colonial empire Duquesne Duquesne French-American culture in Pennsylvania Duquesne Duquesne Government buildings completed in 1754 History of Pittsburgh Infrastructure completed in 1754