Footwashing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''
Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''
 Christian denominations that observe foot washing do so on the basis of the authoritative example and command of
Christian denominations that observe foot washing do so on the basis of the authoritative example and command of
 In 1955
In 1955
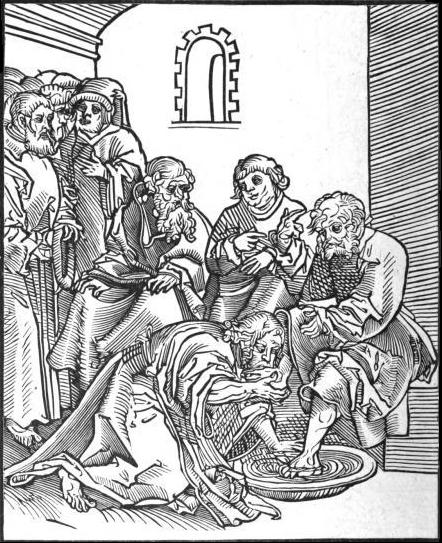 Foot washing rites are practiced by many
Foot washing rites are practiced by many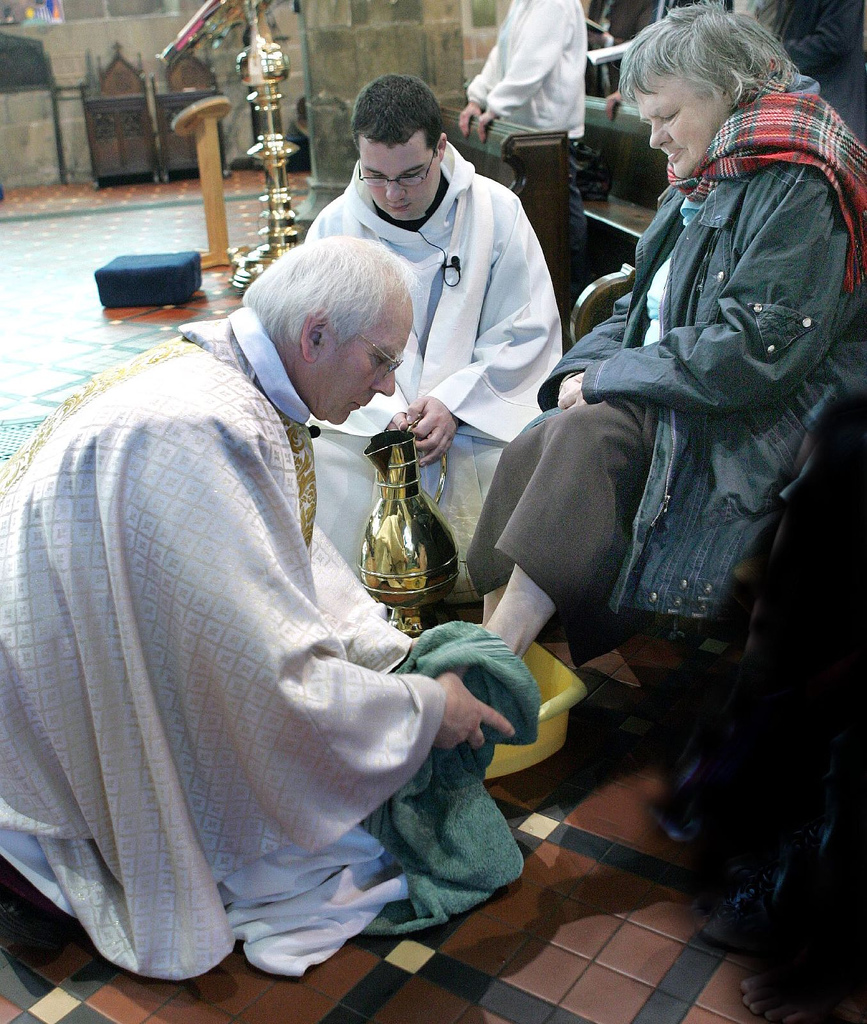  Though history shows that foot washing has at times been practiced in connection with baptism, and at times as a separate occasion, by far its most common practice has been in connection with the
Though history shows that foot washing has at times been practiced in connection with baptism, and at times as a separate occasion, by far its most common practice has been in connection with the
 After
After
 Foot washing rites are also observed in the
Foot washing rites are also observed in the
 Many
Many
Anabaptists and Footwashing
nbsp;– a series of articles on history and current practice among
Footwashing as an act of building community
nbsp;– a Brethren viewpoint
nbsp;– a
Footwashing as a Means of Grace
(a
Washing of the Feet : Hidden Significance of the Gnostic story in the Fourth Gospel
The Footwashing Ritual and the Sacrament of Holy Orders: A New Look at John 13
nbsp;– a
Washing of Feet on Maundy Thursday
Armenian Apostolic Church
article from ''The Washington Post'', 2 April 2006 * {{Gospel of John Barefoot Gestures of respect Gospel of John Hygiene Last Supper Latter Day Saint ordinances, rituals, and symbolism Latter Day Saint temple practices Ritual purity in Christianity Sacraments Water and religion
 Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''
Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''mandatum
Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''mandatum'' meaning "command"), or Washing of the Saints' Feet, Washing of the Feet, or Pedelavium or Pedilavium, is a religious rite observed by various Christian denominations. The Latin word ...
'' meaning "command"), or Washing of the Saints' Feet, Washing of the Feet, or Pedelavium or Pedilavium, is a religious rite Rite may refer to:
* Ritual, an established ceremonious act
* Rite of passage, a ceremonious act associated with social transition
Religion
* Rite (Christianity), a sacred ritual or liturgical tradition in various Christian denominations
* Cath ...
observed by various Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
denominations. The Latin word ''mandatum'' is the first word sung at the ceremony of the washing of the feet, "''Mandatum novum do vobis ut diligatis invicem sicut dilexi vos''", from the text of John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
13:34 in the Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible.
The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels u ...
("I give you a new commandment, That ye love one another as I have loved you", ). This is also seen as referring to the commandment of Christ that believers should emulate his loving humility in the washing of the feet (). The term ''mandatum'' (''mandé'', maundy), therefore, was applied to the rite of foot-washing on the Thursday preceding Easter Sunday, called Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
.
John 13:2–17 recounts Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
' performance of this action. In verses 13:14–17, He instructs His disciples
A disciple is a follower and student of a mentor, teacher, or other figure. It can refer to:
Religion
* Disciple (Christianity), a student of Jesus Christ
* Twelve Apostles of Jesus, sometimes called the Twelve Disciples
* Seventy disciples in t ...
:
Footwashing was practiced by the early Church, prior to receiving the Eucharist, and was recorded by the early Christian apologist Tertullian
Tertullian (; la, Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus; 155 AD – 220 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of L ...
, who discussed it involving a basin of "water for the saints' feet", along with a "linen towel".
Many denominations (including Anglicans
Anglicanism is a Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia ...
, Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, Methodists, Presbyterians
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
, Mennonites
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
, and Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
) therefore observe the liturgical washing of the feet on Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
of Holy Week
Holy Week ( la, Hebdomada Sancta or , ; grc, Ἁγία καὶ Μεγάλη Ἑβδομάς, translit=Hagia kai Megale Hebdomas, lit=Holy and Great Week) is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. In Eastern Churches, w ...
. Moreover, for some denominations, foot-washing was an example, a pattern. Many groups throughout Church history and many modern denominations have practiced foot washing as a church ordinance including Adventists
Adventism is a branch of Protestant Christianity that believes in the imminent Second Coming (or the "Second Advent") of Jesus Christ. It originated in the 1830s in the United States during the Second Great Awakening when Baptist preacher Wil ...
, Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
, Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul com ...
, Free Will Baptists, and Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement
.
Background
The root of this practice is to be found in the hospitality customs of ancient civilizations, especially wheresandals
Sandals are an open type of footwear, consisting of a sole held to the wearer's foot by straps going over the instep and around the ankle. Sandals can also have a heel. While the distinction between sandals and other types of footwear can som ...
were the chief footwear. A host would provide water for guests to wash their feet, provide a servant to wash the feet of the guests or even serve the guests by washing their feet. This is mentioned in several places in the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
(e.g. Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
; ; ; ; I Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Jos ...
; et al.), as well as other religious and historical documents. A typical Eastern host might bow, greet, and kiss his guest, then offer water to allow the guest to wash his feet or have servants do it. Though the wearing of sandals might necessitate washing the feet, the water was also offered as a courtesy even when shoes were worn.
I Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Jos ...
is the first biblical passage where an honored person offers to wash feet as a sign of humility. In John 12, Mary of Bethany
Mary of Bethany is a biblical figure mentioned only by name in the Gospel of John in the Christian New Testament. Together with her siblings Lazarus and Martha, she is described by John as living in the village of Bethany, a small village in Jud ...
anointed Jesus' feet presumably in gratitude for raising her brother Lazarus from the dead, and in preparation for his death and burial. The Bible records washing of the saint's feet being practised by the primitive church
The history of Christianity concerns the Christian religion, Christian countries, and the Christians with their various denominations, from the 1st century to the present. Christianity originated with the ministry of Jesus, a Jewish teac ...
in I Timothy perhaps in reference to piety, submission and/or humility. There are several names for this practice: ''maundy'', ''foot washing'', ''washing the saints' feet'', ''pedilavium'', and ''mandatum''.
The foot washing, described in the thirteenth chapter of the Gospel of John, is concerned with the Latin title of ''Servus servorum dei
Servant of the servants of God ( la, servus servorum Dei) is one of the titles of the pope and is used at the beginning of papal bulls.
History
Pope Gregory I (pope from 590 to 604) was the first pope to use this title extensively to refer t ...
'' ("Servant of the Servant of God"), which was historically reserved to the Bishops and to the Pope, also called the Bishop of Rome
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
. Jesus Christ, the Son of God, commissioned the Twelve to be Servant of the Servant of God, and this calling to the Imitation of Christ has been firstly extended to all the bishops of the Church as the direct successors of the Apostles. The Apostles received the Holy Spirit from Jesus in the gospel of John chapter 20.22 and in fullness upon the day of the Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christian holiday which takes place on the 50th day (the seventh Sunday) after Easter Sunday. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles and other followers ...
in chapter 2 of the Book of Acts, for the evangelization
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are ...
and salvation of all the human race. This belief is common to Catholics, to some denominations of the Western Christianity, and is consistent and in keeping with Eastern Christian beliefs.
A main point of contention between Eastern Orthodox Christians and Western Christians is the '' Filioque'' doctrine, and the subsequent understanding concerning the progression and movement of the Holy Spirit. The Filioque doctrine is rejected by many Eastern Orthodox, whereas it is advanced by most Western Christians. Western Christians maintain that the Holy Spirit proceeds simultaneous from God the Father and God the Son, whereas many Eastern Christians maintain that God the Holy Spirit proceeds uniquely from God the Father
God the Father is a title given to God in Christianity. In mainstream trinity, trinitarian Christianity, God the Father is regarded as the first person of the Trinity, followed by the second person, God the Son Jesus Christ, and the third pers ...
: Eastern Christians subsequently believe that the Apostles received the Holy Spirit with his seven gifts from God the Father, and all the bishops onward, like their successors. However, this variance in belief does not impact the words of Christ and the command to his apostles to be the Servant of the Servant of God.
It is also recalled in the Latin text of the ''Magnificat'', for which God "regarded the lowliness" of Mary, Mother of Jesus, and, by effect of that, "magnified" her ("He hath put down the mighty from their seat: and hath exalted the humble and meek."). God also did the same to all the other creatures, both before and after the Incarnation, for:
* Jesus Christ God: as affirmed in ;
* all the angels: the Satan's mighty pride to be like God made him the fallen angel
In the Abrahamic religions, fallen angels are angels who were expelled from heaven. The literal term "fallen angel" never appears in any Abrahamic religious texts, but is used to describe angels cast out of heaven"Mehdi Azaiez, Gabriel Said ...
before the starting of the creation, and also it was punished with the promised mission of a woman (Mary), a Servant of God, which would have bruise his head (). On the opposite side, the lowliness of St Michael the Archangel made him the head of the hierarchy of angels
In the angelology of different religions, a hierarchy of angels is a ranking system of angels. Higher ranks have more power or authority over lower ranks, and with different ranks having differences in appearance, such as varying numbers of win ...
;
* all the human creatures: according to the promise of Jesus in .
Biblical reference
 Christian denominations that observe foot washing do so on the basis of the authoritative example and command of
Christian denominations that observe foot washing do so on the basis of the authoritative example and command of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
as found in ( NKJV):
Jesus demonstrates the custom of the time when he comments on the lack of hospitality in one Pharisee
The Pharisees (; he, פְּרוּשִׁים, Pərūšīm) were a Jews, Jewish social movement and a school of thought in the Levant during the time of Second Temple Judaism. After the Siege of Jerusalem (AD 70), destruction of the Second Temp ...
's home by not providing water to wash his feet in Luke 7:44:
History
The rite of foot washing finds its roots in scripture, where Jesus tells his followers "to wash one another's feet" (cf. ). After the death of the apostles or the end of theApostolic Age
Christianity in the 1st century covers the formative history of Christianity from the start of the ministry of Jesus (–29 AD) to the death of the last of the Twelve Apostles () and is thus also known as the Apostolic Age. Early Christianity ...
, the practice was continued.
Footwashing was practiced in the early centuries of post-apostolic Christianity, with Tertullian
Tertullian (; la, Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus; 155 AD – 220 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of L ...
(145–220) mentioning the practice as being a part of Christian worship
In Christianity, worship is the act of attributing reverent honour and homage to God. In the New Testament, various words are used to refer to the term worship. One is ("to worship") which means to bow down to God or kings.
Throughout most ...
in his ''De Corona''. Footwashing was done with a basin "of water for the saints' feet" and a "linen towel", prior to the reception of the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institu ...
. Additionally, in the 1st century, Christian women went to locations in which marginalized people resided (such as prisons) and washed their feet. The early Church Father Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria ( grc , Κλήμης ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς; – ), was a Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen ...
linked the new sandals given by to Prodigal Son
The Parable of the Prodigal Son (also known as the parable of the Two Brothers, Lost Son, Loving Father, or of the Forgiving Father) is one of the parables of Jesus Christ in the Bible, appearing in Luke 15:11–32. Jesus shares the parable wit ...
with feetwashing, describing "non-perishable shoes that are only fit to be worn by those who have had their feet washed by Jesus, the Teacher and Lord." The early Church thus saw footwashing to be connected to repentance
Repentance is reviewing one's actions and feeling contrition or regret for past wrongs, which is accompanied by commitment to and actual actions that show and prove a change for the better.
In modern times, it is generally seen as involving a co ...
, involving a spiritual cleansing by Jesus.
Around 256 AD, Cyprian
Cyprian (; la, Thaschus Caecilius Cyprianus; 210 – 14 September 258 AD''The Liturgy of the Hours according to the Roman Rite: Vol. IV.'' New York: Catholic Book Publishing Company, 1975. p. 1406.) was a bishop of Carthage and an early Christ ...
, the bishop of Carthage
The Archdiocese of Carthage, also known as the Church of Carthage, was a Latin Catholic diocese established in Carthage, Roman Empire, in the 2nd century. Agrippin was the first named bishop, around 230 AD. The temporal importance of the city of ...
, wrote about footwashing teaching "the hands how to act in service".
It was practiced by the Church at Milan (c. 380) and is mentioned by the '' Council of Elvira'' (300). The Church Fathers Origen
Origen of Alexandria, ''Ōrigénēs''; Origen's Greek name ''Ōrigénēs'' () probably means "child of Horus" (from , "Horus", and , "born"). ( 185 – 253), also known as Origen Adamantius, was an early Christian scholar, ascetic, and the ...
, as well as John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of ...
and Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
(c. 400) encouraged the practice as an imitation of Christ.
Observance of foot washing at the time of baptism was maintained in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, northern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
.
According to the ''Mennonite Encyclopedia'' " St. Benedict's ''Rule'' (529) for the Benedictine Order
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
prescribed hospitality feetwashing in addition to a communal feetwashing for humility"; a statement confirmed by the Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
. It apparently was established in the Roman church, though not in connection with baptism, by the 8th century.
The Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
counted footwashing among the sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
s, though it was not practiced that often.
The Synod of Toledo (694) "declared that footwashing should be observed on Maundy Thursday" and Roman Catholic churches thus came to observe footwashing on that day.
The Albigenses
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follo ...
and the Waldenses' practiced footwashing as a rite Rite may refer to:
* Ritual, an established ceremonious act
* Rite of passage, a ceremonious act associated with social transition
Religion
* Rite (Christianity), a sacred ritual or liturgical tradition in various Christian denominations
* Cath ...
.
There is some evidence that it was observed by the early Hussites
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Huss ...
; and the practice was a meaningful part of the 16th century radical reformation
The Radical Reformation represented a response to corruption both in the Catholic Church and in the expanding Magisterial Protestant movement led by Martin Luther and many others. Beginning in Germany and Switzerland in the 16th century, the Ra ...
, which resulted in Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
denominations regularly practicing footwashing as an ordinance.
Denominations practicing ritual feet washing
The ritual washing of feet is currently practiced in many religious denominations including those listed below.Roman Catholic
InCatholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, the ritual washing of feet is now associated with the Mass of the Lord's Supper, which celebrates in a special way the Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
of Jesus, before which he washed the feet of his twelve apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and minist ...
.
Evidence for the practice on this day goes back at least to the latter half of the 12th century, when "the pope washed the feet of twelve sub-deacons after his Mass and of thirteen poor men after his dinner." From 1570 to 1955, the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
printed, after the text of the Holy Thursday Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
, a rite of washing of feet unconnected with the Mass. For many years Pius IX
Pope Pius IX ( it, Pio IX, ''Pio Nono''; born Giovanni Maria Mastai Ferretti; 13 May 1792 – 7 February 1878) was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878, the longest verified papal reign. He was notable for convoking the First Vatican ...
performed the foot washing in the sala over the portico of Saint Peter's, Rome.
 In 1955
In 1955 Pope Pius XII
Pope Pius XII ( it, Pio XII), born Eugenio Maria Giuseppe Giovanni Pacelli (; 2 March 18769 October 1958), was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 2 March 1939 until his death in October 1958. Before his e ...
revised the ritual and inserted it into the Mass. Since then, the rite is celebrated after the homily
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ex ...
that follows the reading of the gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
account of how Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
washed the feet of his twelve apostles (). Some persons who have been selected – usually twelve, but the Roman Missal does not specify the number – are led to chairs prepared in a suitable place. The priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in partic ...
goes to each and, with the help of the ministers, pours water over each one's feet and dries them. There are some advocates of restricting this ritual to clergy or at least men.
In a notable break from the 1955 norms, Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013 ...
washed the feet of two women and Muslims at a juvenile detention center in Rome 2013. In 2016 it was announced that the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
had been revised to permit women to have their feet washed on Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
; previously it permitted only males to do so. In 2016 Catholic priests around the world washed both women's and men's feet on Holy Thursday "their gesture of humility represented to many the progress of inclusion in the Catholic church."
At one time, most of the European monarchs also performed the Washing of Feet in their royal courts on Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
, a practice continued by the Austro-Hungarian Emperor and the King of Spain
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
up to the beginning of the 20th century (see Royal Maundy
Royal Maundy is a religious service in the Church of England held on Maundy Thursday, the day before Good Friday. At the service, the British monarch or a royal official ceremonially distributes small silver coins known as "Maundy money" (legal ...
). In 1181 Roger de Moulins
Roger de Moulins was eighth Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller from 1177 to his death in 1187. He succeeded Jobert of Syria.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). " St John of Jerusalem, Knights of the Order of the Hospital of". ''Encyclopædia Britann ...
, Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
issued a statute declaring, "In Lent every Saturday, they are accustomed to celebrate maundy for thirteen poor persons, and to wash their feet, and to give to each a shirt and new breeches and new shoes, and to three chaplains, or to three clerics out of the thirteen, three deniers and to each of the others, two deniers".
Lutheran, Anglican and Methodist
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
and Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
churches, whereby foot washing is most often experienced in connection with Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
services and, sometimes, at ordination services where the Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
may wash the feet of those who are to be ordained. In certain Methodist connexions, such as the Missionary Methodist Church and the New Congregational Methodist Church, footwashing is practiced at the time that the Lord's Supper is celebrated.
 Though history shows that foot washing has at times been practiced in connection with baptism, and at times as a separate occasion, by far its most common practice has been in connection with the
Though history shows that foot washing has at times been practiced in connection with baptism, and at times as a separate occasion, by far its most common practice has been in connection with the Lord's supper
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institut ...
service. There has been some revival of the practice as other liturgical churches have also rediscovered the practice.
Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic
TheEastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
and Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of ...
practice the ritual of the Washing of Feet on Holy and Great Thursday (Maundy Thursday) according to their ancient rites. The service may be performed either by a bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
, washing the feet of twelve priests; or by an Hegumen
Hegumen, hegumenos, or igumen ( el, ἡγούμενος, trans. ), is the title for the head of a monastery in the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, similar to the title of abbot. The head of a convent of nuns is called a hegumenia ...
(Abbot) washing the feet of twelve members of the brotherhood of his monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
. The ceremony takes place at the end of the Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy ( grc-gre, Θεία Λειτουργία, Theia Leitourgia) or Holy Liturgy is the Eucharistic service of the Byzantine Rite, developed from the Antiochene Rite of Christian liturgy which is that of the Ecumenical Patriarchate ...
.
 After
After Holy Communion
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
, and before the dismissal, the brethren all go in procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
to the place where the Washing of Feet is to take place (it may be in the center of the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-typ ...
, in the narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narth ...
, or a location outside). After a psalm and some troparia (hymns) an ektenia
An ektenia (from el, ἐκτενής , translit=ektenés; literally, "diligence"), often called by the better known English word litany, consists of a series of petitions occurring in the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic liturgies. The pr ...
(litany) is recited, and the bishop or abbot reads a prayer. Then the deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Chur ...
reads the account in the Gospel of John, while the clergy perform the roles of Christ and his apostles as each action is chanted by the deacon. The deacon stops when the dialogue between Jesus and Peter begins. The senior-ranking clergyman among those whose feet are being washed speaks the words of Peter, and the bishop or abbot speaks the words of Jesus. Then the bishop or abbot himself concludes the reading of the Gospel, after which he says another prayer and sprinkles all of those present with the water that was used for the foot washing. The procession then returns to the church and the final dismissal is given as normal.
Oriental Orthodox
 Foot washing rites are also observed in the
Foot washing rites are also observed in the Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent ...
churches on Maundy Thursday.
In the Coptic Orthodox Church
The Coptic Orthodox Church ( cop, Ϯⲉⲕ̀ⲕⲗⲏⲥⲓⲁ ⲛ̀ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ⲛ̀ⲟⲣⲑⲟⲇⲟⲝⲟⲥ, translit=Ti.eklyseya en.remenkimi en.orthodoxos, lit=the Egyptian Orthodox Church; ar, الكنيسة القبطي� ...
the service is performed by the parish priest. He blesses the water for the foot washing with the cross, just as he would for blessing holy water
Holy water is water that has been blessed by a member of the clergy or a religious figure, or derived from a well or spring considered holy. The use for cleansing prior to a baptism and spiritual cleansing is common in several religions, from ...
and he washes the feet of the entire congregation.
In the Syrian Orthodox Church, this service is performed by a bishop or priest. There will be some 12 selected men, both priests and the lay people, and the bishop or priest will wash and kiss the feet of those 12 men. It is not merely a dramatization of the past event. Further it is a prayer where the whole congregation prays to wash and cleanse them of their sins.
Moravian
TheMoravian Church
The Moravian Church ( cs, Moravská církev), or the Moravian Brethren, formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination, denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohem ...
has historically practiced footwashing (pedelavium). This reflected the emphasis Moravians place on practicing customs of the early Church
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
, such as the Lovefeast
An agape feast or lovefeast (also spelled love feast or love-feast, sometimes capitalized) is a communal meal shared among Christians. The name comes from ''agape'', a Greek term for 'love' in its broadest sense.
The lovefeast custom originat ...
. In 1818, the practice was made no longer compulsory, though it continues in the present-day. Traditionally, Moravian Christians practiced footwashing before partaking in the Lord's Supper
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institut ...
, although in most Moravian congregations, these rites are observed chiefly on Maundy Thursday
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during Holy Week that commemorates the Washing of th ...
.
Anabaptist
Groups descending from the 1708Schwarzenau Brethren
The Schwarzenau Brethren, the German Baptist Brethren, Dunkers, Dunkards, Tunkers, or sometimes simply called the German Baptists, are an Anabaptist group that dissented from Roman Catholic, Lutheran and Reformed European state churches during t ...
, such as the Grace Brethren, Church of the Brethren
The Church of the Brethren is an Anabaptist Christian denomination in the Schwarzenau Brethren (german: link=no, Schwarzenauer Neutäufer "Schwarzenau New Baptists") tradition that was organized in 1708 by Alexander Mack in Schwarzenau, Germ ...
, Brethren Church, Brethren in Christ, Old German Baptist Brethren, and the Dunkard Brethren Dunkard may refer to:
*
* Dunkard Township, Greene County, Pennsylvania – administrative territorial subdivision in the United States
* Dunkard Creek – stream in Greene County, Pennsylvania and Monongalia County, West Virginia
{{disambi ...
regularly practice foot washing (generally called "feetwashing") as one of three ordinances that compose their Lovefeast
An agape feast or lovefeast (also spelled love feast or love-feast, sometimes capitalized) is a communal meal shared among Christians. The name comes from ''agape'', a Greek term for 'love' in its broadest sense.
The lovefeast custom originat ...
, the others being the Eucharist and a fellowship meal. Historically related groups such as the Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churc ...
and most Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
s also wash feet, tracing the practice to the 1632 Dordrecht Confession of Faith. For members, this practice promotes humility towards and care for others, resulting in a higher egalitarianism among members.
Baptist
Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul com ...
observe the literal washing of feet as a third ordinance. The communion and foot washing service is practiced regularly by members of the Separate Baptists in Christ, General Association of Baptists
Though the annual meeting of this group is denominated The General Association of The Baptists, they are most widely known as the Kindred Associations of Baptists. Other names associated with these churches are the Baptist Church of Christ, ''Th ...
, Free Will Baptists, Primitive Baptists
Primitive Baptists – also known as Hard Shell Baptists, Foot Washing Baptists or Old School Baptists – are conservative Baptists adhering to a degree of Calvinist beliefs who coalesced out of the controversy among Baptists in the early 19th c ...
, Union Baptists, Old Regular Baptist
The Old Regular Baptist denomination is one of the oldest in Appalachia with roots in both the Regular and Separate Baptists of the American Colonies and the Particular Baptist of Great Britain. This group has seen a marked decline in its member ...
, Christian Baptist Church of God. Feet washing is also practiced as a third ordinance by many Southern Baptist
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptists, Baptist denomination, and the Protestantism in the United States, largest Protestantism, Protestant and Christia ...
s, General Baptist
General Baptists are Baptists who hold the ''general'' or unlimited atonement view, the belief that Jesus Christ died for the entire world and not just for the chosen elect. General Baptists are theologically Arminian, which distinguishes them from ...
s, and Independent Baptist
Independent Baptist churches (some also called Independent Fundamental Baptist or IFB) are Christian congregations, generally holding to conservative (primarily fundamentalist) Baptist beliefs. Although some Independent Baptist churches refuse a ...
s.
Pentecostal
VariousPentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestantism, Protestant Charismatic Christianity, Charismatic Christian movementJoseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, h ...
introduced the original temple rites of the Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist movement founded by Jo ...
in Kirtland, Ohio
Kirtland is a city in Lake County, Ohio, United States. The population was 6,937 at the 2020 census. Kirtland is known for being the early headquarters of the Latter Day Saint movement from 1831 to 1837 and is the site of the movement's first ...
, which primarily involved foot washing, followed by speaking in tongues
Speaking in tongues, also known as glossolalia, is a practice in which people utter words or speech-like sounds, often thought by believers to be languages unknown to the speaker. One definition used by linguists is the fluid vocalizing of sp ...
and visions. This foot washing took place exclusively among men, and was based upon the Old
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
* Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, M ...
and New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
. After Joseph Smith was initiated into the first three degrees of Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, this was adapted into the whole body Endowment ritual more similar to contemporary Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into se ...
practice, which is nearly identical to Masonic temple
A Masonic Temple or Masonic Hall is, within Freemasonry, the room or edifice where a Masonic Lodge meets. Masonic Temple may also refer to an abstract spiritual goal and the conceptual ritualistic space of a meeting.
Development and history
I ...
rites, and does not specifically involve the feet.
In 1843, Smith included a foot washing element in the faith's second anointing ceremony in which elite married couples are anointed as heavenly monarchs and priests.
The observance of ''washing the saints' feet'' is quite varied, but a typical service follows the partaking of unleavened bread and wine. Deacons (in many cases) place pans of water in front of pews that have been arranged for the service. The men and women participate in separate groups, men washing men's feet and women washing women's feet. Each member of the congregation takes a turn washing the feet of another member. Each foot is placed one at a time into the basin of water, is washed by cupping the hand and pouring water over the foot, and is dried with a long towel girded around the waist of the member performing the washing. Most of these services appear to be quite moving to the participants.
Restorationist
TheTrue Jesus Church
The True Jesus Church (TJC) is a non-denominational Christian Church that originated in Beijing, China, during the Pentecostal movement in the early twentieth century. The True Jesus Church is currently one of the largest Christian groups in Chin ...
includes footwashing as a scriptural sacrament based on . Like the other two sacraments, namely Baptism and the Lord's Supper, members of the church believe that footwashing imparts salvific grace to the recipient—in this case, to have a part with Christ ().
Most Church of God denominations also include footwashing in their Passover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
ceremony based on John 13:1–11.
Seventh-day Adventist
MostSeventh-day Adventist
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
congregations schedule an opportunity for foot washing preceding each quarterly (four times a year) Communion service. As with their "open" Communion, all believers in attendance, not just members or pastors, are invited to share in the washing of feet with another: men with men, women with women, and frequently, spouse with spouse. This service is alternatively called the Ordinance of Foot-Washing or the Ordinance of Humility. Its primary purpose is to renew the cleansing that only comes from Christ, but secondarily to seek and celebrate reconciliation with another member before Communion/the Lord's Supper.
Progressive Judaism
A number of Jewish rabbis who disagree with the initiation custom of ''brit milah
The ''brit milah'' ( he, בְּרִית מִילָה ''bərīṯ mīlā'', ; Ashkenazi pronunciation: , " covenant of circumcision"; Yiddish pronunciation: ''bris'' ) is the ceremony of circumcision in Judaism. According to the Book of Genes ...
'', or circumcision of a male baby, instead have offered '' brit shalom'', or a multi-part naming ceremony which eschews circumcision. One portion of the ritual, '' Brit rechitzah'', involves the washing of the baby's feet.
See also
* ''Christ Washing the Disciples' Feet'' (Tintoretto) * Washing of feet and farewell (The Last Supper in Christian Art) *Water and religion
Water is considered a purifier in most religions.
Holy water
Some faiths use water especially prepared for religious purposes (holy water in most Christian denominations, ''mambuha'' in Mandaeism, ''amrita'' in Sikhism and Hinduism). Many reli ...
* Ablution in Christianity
Notes
References
* * Historical and Informational ** ''Appalachian Mountain Religion: a History'', by Deborah Vansau McCauley () ** ''Catholic Encyclopedia'', Charles G. Herbermann, Edward A. Pace, Condé B. Pallen, Thomas J. Shahan, and John J. Wynne, editors ** ''Eerdman's Handbook to the History of Christianity'', Tim Dowley, et al., editors ** ''Encyclopedia of Religion in the South'', Samuel S. Hill, editor ** '' Foxfire 7'', Paul F. Gillespie, editor ** ''Manners and Customs of Bible Lands'', by Fred H. Wight ** ''Mennonite Encyclopedia
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radica ...
(Vol. 2)'', Cornelius J. Dyck, Dennis D. Martin, et al., editors
* Historical and Theological (con)
** ''Footwashing by the Master and by the Saints'', by Elam J. Daniels
** ''Manual of Church Order (ch. 6)'', by J. L. Dagg
* Historical and Theological (pro)
** ''The Washing of the Saints' Feet'', by J. Matthew Pinson (Randall House, 2006, )
** ''A Free Will Baptist Handbook: Heritage, Beliefs, and Ministries'', by J. Matthew Pinson
** ''Baptist Doctrine: the Doctrine of Foot Washing'', by R. L. Vaughn
** ''Footwashing in John 13 and the Johannine Community'', by John Christopher Thomas
** ''Washing the Saints' Feet shown to be an Ordinance of Christ'', by Joseph Sorsby
See also
*
*
External links
Anabaptists and Footwashing
nbsp;– a series of articles on history and current practice among
Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
s, Grace Brethren and Church of the Brethren
The Church of the Brethren is an Anabaptist Christian denomination in the Schwarzenau Brethren (german: link=no, Schwarzenauer Neutäufer "Schwarzenau New Baptists") tradition that was organized in 1708 by Alexander Mack in Schwarzenau, Germ ...
.
*
Footwashing as an act of building community
nbsp;– a Brethren viewpoint
nbsp;– a
liturgical
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
viewpoint
Footwashing as a Means of Grace
(a
United Methodist
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelica ...
approach) by Gregory S. Neal
Washing of the Feet : Hidden Significance of the Gnostic story in the Fourth Gospel
The Footwashing Ritual and the Sacrament of Holy Orders: A New Look at John 13
nbsp;– a
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
viewpoint of the import of footwashing as relates to the sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
of Holy Orders.
Washing of Feet on Maundy Thursday
Armenian Apostolic Church
article from ''The Washington Post'', 2 April 2006 * {{Gospel of John Barefoot Gestures of respect Gospel of John Hygiene Last Supper Latter Day Saint ordinances, rituals, and symbolism Latter Day Saint temple practices Ritual purity in Christianity Sacraments Water and religion