Fishing weir on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A fishing weir, fish weir, fishgarth or kiddle is an obstruction placed in tidal waters, or wholly or partially across a river, to direct the passage of, or trap fish. A weir may be used to trap marine fish in the
 In Great Britain the traditional form was one or more rock weirs constructed in
In Great Britain the traditional form was one or more rock weirs constructed in
BBC Wales North West website retrieved 7 August 2007. The medieval fish weir at Traeth Lligwy, Moelfre, Anglesey (pictured) was scheduled as an Ancient Monument in 2002.
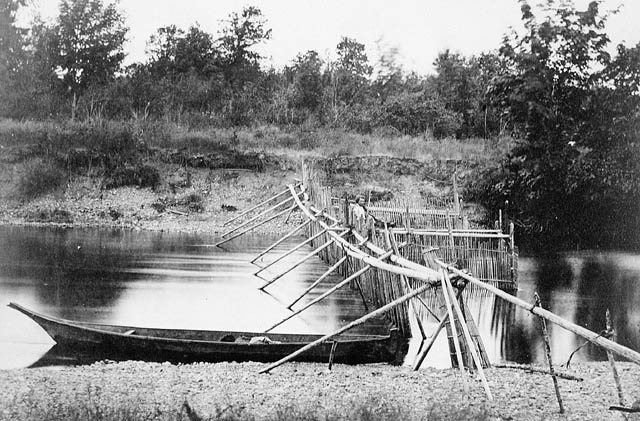

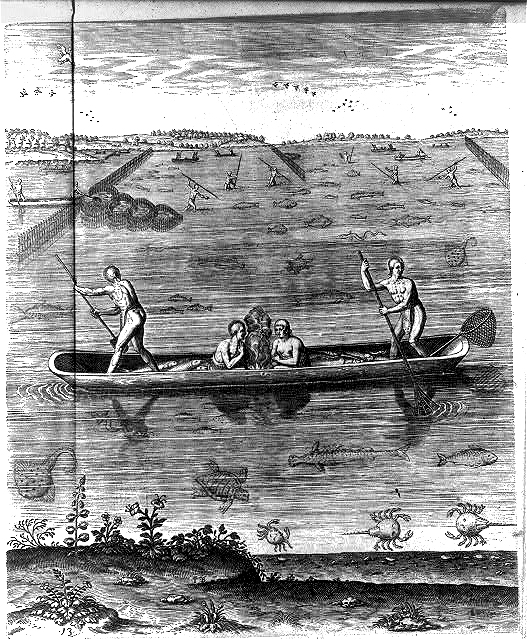 In Virginia, the Native Americans built V-shaped stone weirs in the
In Virginia, the Native Americans built V-shaped stone weirs in the
intertidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species ...
as the tide recedes, fish such as salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
as they attempt to swim upstream to breed in a river, or eels as they migrate downstream. Alternatively, fish weirs can be used to channel fish to a particular location, such as to a fish ladder. Weirs were traditionally built from wood or stones. The use of fishing weirs as fish traps probably dates back prior to the emergence of modern humans, and have since been used by many societies around the world.
History
The English word 'weir' comes from the Anglo-Saxon ''wer,'' one meaning of which is a device to trap fish. A line of stones dating to the Acheulean in Kenya may have been a stone tidal weir in a prehistoric lake, which if true would make this technology older thanmodern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
. In Ireland, fish traps in association with weirs have been found that date from 8,000 years ago. Stone tidal weirs were used around the world and by 1707, 160 such structures, some of which reached 360 metres in length, were in use along the coast of the Shimabara Peninsula of Japan.
In medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, large fishing weir structures were constructed from wood posts and wattle fences. V-shaped structures in rivers could be as long as and worked by directing fish towards fish traps or nets. Such weirs were frequently the cause of disputes between various classes of river users and tenants of neighbouring land. Basket weir fish traps are shown in medieval illustrations and surviving examples have been found. Basket weirs are about long and comprise two wicker cones, one inside the other—easy for fish to get into but difficult to escape.
In September 2014 researchers from University of Victoria investigated what may turn out to be a 14,000-year-old fish weir in of water off the coast of Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; hai, X̱aaydag̱a Gwaay.yaay / , literally "Islands of the Haida people") is an archipelago located between off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Heca ...
, British Columbia.
Great Britain
 In Great Britain the traditional form was one or more rock weirs constructed in
In Great Britain the traditional form was one or more rock weirs constructed in tidal race
Tidal race or tidal rapid is a natural occurrence whereby a fast-moving tide passes through a constriction, resulting in the formation of waves, eddies and hazardous currents. The constriction can be a passage where the sides narrow, for example ...
s or on a sandy beach, with a small gap that could be blocked by wattle fences when the tide turned to flow out again.
Wales
Surviving examples, but no longer in use, can be seen in theMenai Strait
The Menai Strait ( cy, Afon Menai, the "river Menai") is a narrow stretch of shallow tidal water about long, which separates the island of Anglesey from the mainland of Wales. It varies in width from from Fort Belan to Abermenai Point to from ...
, with the best preserved examples to be found at Ynys Gored Goch (Red Weir Island) dating back to around 1842. Also surviving are 'goredi' (originally twelve in number) on the beach at Aberarth, Ceredigion. Another ancient example was at Rhos Fynach
Rhos-on-Sea ( cy, Llandrillo-yn-Rhos) is a seaside resort and community in Conwy County Borough, Wales. The population was 7,593 at the 2011 census. It adjoins Colwyn Bay and is named after the Welsh kingdom of Rhos established there in late ...
in North Wales, which survived in use until World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.Reid, Ian (2001): "Rhos-on-Sea Heritage Trail".BBC Wales North West website retrieved 7 August 2007. The medieval fish weir at Traeth Lligwy, Moelfre, Anglesey (pictured) was scheduled as an Ancient Monument in 2002.
England
Fish weirs were an obstacle to shipping and a threat to fish stocks, for which reasons over the course of history several attempts were made to control their proliferation. TheMagna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
of 1215 includes a clause embodying the barons' demands for the removal of the king's weirs and others:
A statute was passed during the reign of King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
(1327–1377) and was reaffirmed by King Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in Englan ...
in 1472 A further regulation was enacted under King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
, apparently at the instigation of Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell (; 1485 – 28 July 1540), briefly Earl of Essex, was an English lawyer and statesman who served as chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false char ...
, when in 1535 commissioners were appointed in each county to oversee the "putting-down" of weirs. The words of the commission were as follows:
All weirs noisome to the passage of ships or boats to the hurt of passages or ways and causeys ''(i.e. causeways)'' shall be pulled down and those that be occasion of drowning of any lands or pastures by stopping of waters and also those that are the destruction of the increase of fish, by the discretion of the commissioners, so that if any of the before-mentioned depend or may grow by reason of the same weir then there is no redemption but to pull them down, although the same weirs have stood since 500 years before theThe king did not exempt himself from the regulation and by the destruction of royal weirs lost 500 marks in annual income. TheConquest Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms. Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, ....
Lisle Papers The Lisle Papers are the correspondence received in Calais between 1533 and 1540 by Arthur Plantagenet, 1st Viscount Lisle (c.1480-1542), Lord Deputy of Calais, an illegitimate son of King Edward IV and an uncle of King Henry VIII, and by his wife, ...
provide a detailed contemporary narrative of the struggle of the owners of the weir at Umberleigh in Devon to be exempted from this 1535 regulation. The Salmon Fisheries Act 1861 (relevant provisions re-enacted since) bans their use except wherever their almost continuous use can be traced to before the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
(1215).
North America

 In Virginia, the Native Americans built V-shaped stone weirs in the
In Virginia, the Native Americans built V-shaped stone weirs in the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
and James River
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to Chesap ...
. These were described in 1705 in ''The History and Present State of Virginia, In Four Parts'' by Robert Beverley Jr:
This practice was taken up by the early settlers but the Maryland General Assembly ordered the weirs to be destroyed on the Potomac in 1768. Between 1768 and 1828 considerable efforts were made to destroy fish weirs that were an obstruction to navigation and from the mid-1800s, those that were assumed to be detrimental to sports fishing.
In the Back Bay
Back Bay is an officially recognized neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, built on reclaimed land in the Charles River basin. Construction began in 1859, as the demand for luxury housing exceeded the availability in the city at the time, and t ...
area of Boston, Massachusetts, wooden stake remains of the Boylston Street Fishweir have been documented during excavations for subway tunnels and building foundations. The Boylston Street Fishweir was actually a series of fish weirs built and maintained near the tidal shoreline between 3,700 and 5,200 years ago.
Natives in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
use weirs that stretch across the entire river to retain shad
The Alosinae, or the shads,Alosinae
Shubenacadie, Nine Mile, and Stewiacke rivers, and use nets to scoop the trapped fish. Various weir patterns were used on tidal waters to retain a variety of different species, which are still used today. V-shaped weirs with circular formations to hold the fish during high tides are used on the
Nature, 408(6809):190–193 These earthworks cover over , and appear to have supported a large and dense population around 3000 BCE.Erickson, Clark (2000b): "AN ARTIFICIAL LANDSCAPE-SCALE FISHERY IN THE BOLIVIAN AMAZON"
University of Pennsylvania website retrieved 12 Oct. 2007 Stone fish weirs were in use 6,000 years ago in
File:Ålegård.gif, 19th-century fishing weir used to trap eels on the Danish coast
File:Indian fish weir Smith River Henry County Virginia.JPG, The Martinsville Fish Dam Virginia, an historic Native American Indian fishing weir built with rocks
File:Fish trap Menai Strait.jpg, Remains of an ancient stone fishing weir in the tidal
Prehistoric Fishweirs in Eastern North America
– master's thesis on fish weirs {{DEFAULTSORT:Fishing Weir Fishing equipment Weirs Native American tools
Shubenacadie, Nine Mile, and Stewiacke rivers, and use nets to scoop the trapped fish. Various weir patterns were used on tidal waters to retain a variety of different species, which are still used today. V-shaped weirs with circular formations to hold the fish during high tides are used on the
Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is t ...
to fish herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Ocean ...
, which follow the flow of water. Similar V-shaped weirs are also used in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
to corral salmon to the end of the "V" during the changing of the tides.
The Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.
In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree o ...
of the Hudson Bay Lowlands
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many ...
used weirs consisting of a fence of poles and a trap across fast flowing rivers. The fish were channelled by the poles up a ramp and into a box-like structure made of poles lashed together. The top of the ramp remained below the surface of the water but slightly above the top of the box so that the flow of the water and the overhang of the ramp stopped the fish from escaping from the box. The fish were then scooped out of the box with a dip net.
South America
A large series of fish weirs, canals and artificial islands was built by an unknown pre-Columbian culture in the Baures region ofBolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, part of the Llanos de Moxos.Erickson, Clark (2000): "An artificial landscape-scale fishery in the Bolivian Amazon".Nature, 408(6809):190–193 These earthworks cover over , and appear to have supported a large and dense population around 3000 BCE.Erickson, Clark (2000b): "AN ARTIFICIAL LANDSCAPE-SCALE FISHERY IN THE BOLIVIAN AMAZON"
University of Pennsylvania website retrieved 12 Oct. 2007 Stone fish weirs were in use 6,000 years ago in
Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island ( es, Isla de Chiloé, , ) also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern ...
off the coast of Chile.
Asia and Oceania
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
had the world's largest tidal weirs that trap fish at low tide and were in use until the 1950s. Yap in the western pacific has the longest continual use of fish weirs made of stones since before European contact.
Gallery
Menai Strait
The Menai Strait ( cy, Afon Menai, the "river Menai") is a narrow stretch of shallow tidal water about long, which separates the island of Anglesey from the mainland of Wales. It varies in width from from Fort Belan to Abermenai Point to from ...
in Wales
File:Double-Heart of Stacked Stones 20150721.jpg, Double Heart fishing weir in Penghu
The Penghu (, Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, located approximately west from the main island of Taiwan, covering an area ...
, Taiwan
File:澎湖石滬 1.jpg, Fishing weir, Penghu
The Penghu (, Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, located approximately west from the main island of Taiwan, covering an area ...
County
File:Yana.jpg, Fishing weir on the rapidly flowing Mogami River
The is a river in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan.
Description and history
It is 224 km long and has a watershed of 7,040 km2. It is regarded as one of the three most rapid rivers of Japan (along with the Fuji River and the Kuma River).
...
in Japan
File:Fishing at the falls Dem Rep Congo.jpg, Fishing weirs using baskets at a river waterfall, Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
File:Ancient Fishing Weir - geograph.org.uk - 637068.jpg, Ancient V-shaped fishing weir at Countisbury Cove, Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lor ...
File:Weervisserij Oosterschelde.jpg, Modern anchovy weir in the Oosterschelde
The Eastern Scheldt ( nl, Oosterschelde) is a former estuary in the province of Zeeland, Netherlands, between Schouwen-Duiveland and Tholen on the north and Noord-Beveland and Zuid-Beveland on the south. It also features the largest nati ...
near Bergen op Zoom in the Netherlands (aerial view)
See also
* Fish screen * Mnjikaning Fish Weirs *Tailrace fishing
Tailrace fishing is angling immediately below natural or man-made dams or restrictions to the flow of water on rivers, canals, streams or any other flowing current. Fishing in a tailrace requires a distinct set of skills in that lures or bait mu ...
* Weir
A weir or low head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the river level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
* Desert kite
References
External links
Prehistoric Fishweirs in Eastern North America
– master's thesis on fish weirs {{DEFAULTSORT:Fishing Weir Fishing equipment Weirs Native American tools