FinFET on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
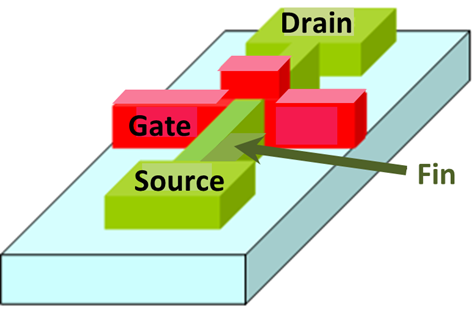 A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a
"The Silicon Age: Trends in Semiconductor Devices Industry
, 2022
multigate device
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be control ...
, a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs cont ...
) built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, forming a double or even multi gate structure. These devices have been given the generic name "FinFETs" because the source/drain region forms fins on the silicon surface. The FinFET devices have significantly faster switching times and higher current density than planar CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technology.
FinFET is a type of non-planar transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, or "3D" transistor. It is the basis for modern nanoelectronic
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical pr ...
semiconductor device fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are p ...
. Microchips utilizing FinFET gates first became commercialized in the first half of the 2010s, and became the dominant gate design at 14 nm, 10 nm
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths.
__TOC__
Overview
Detailed list
To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^ ...
and 7 nm
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors defines the 7 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 10 nm node. It is based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, ...
process nodes.
It is common for a single FinFET transistor to contain several fins, arranged side by side and all covered by the same gate, that act electrically as one, to increase drive strength and performance.
History
After the MOSFET was first demonstrated by Mohamed Atalla andDawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng ( ko, 강대원; May 4, 1931 – May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effe ...
of Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial Research and development, research and scientific developm ...
in 1960, the concept of a double-gate
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be contro ...
thin-film transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, becaus ...
(TFT) was proposed by H.R. Farrah ( Bendix Corporation) and R.F. Steinberg in 1967. A double-gate MOSFET was later proposed by Toshihiro Sekigawa of the Electrotechnical Laboratory (ETL) in a 1980 patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
describing the planar XMOS transistor. Sekigawa fabricated the XMOS transistor with Yutaka Hayashi at the ETL in 1984. They demonstrated that short-channel effects can be significantly reduced by sandwiching a fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (SOI) device between two gate electrode
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control ...
s connected together.
The first FinFET transistor type was called a "Depleted Lean-channel Transistor" or "DELTA" transistor, which was first fabricated in Japan by Hitachi Central Research Laboratory's Digh Hisamoto, Toru Kaga, Yoshifumi Kawamoto and Eiji Takeda in 1989. The gate of the transistor can cover and electrically contact the semiconductor channel fin on both the top and the sides or only on the sides. The former is called a ''tri-gate transistor'' and the latter a ''double-gate transistor''. A double-gate transistor optionally can have each side connected to two different terminal or contacts. This variant is called ''split transistor''. This enables more refined control of the operation of the transistor.
Indonesian engineer Effendi Leobandung, while working at the University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota, formally the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, (UMN Twin Cities, the U of M, or Minnesota) is a public land-grant research university in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. ...
, published a paper with Stephen Y. Chou at the 54th Device Research Conference in 1996 outlining the benefit of cutting a wide CMOS transistor into many channels with narrow width to improve device scaling and increase device current by increasing the effective device width. This structure is what a modern FinFET looks like. Although some device width is sacrificed by cutting it into narrow widths, the conduction of the side wall of narrow fins more than make up for the loss, for tall fins. The device had a 35 nm channel width and 70 nm channel length.
The potential of Digh Hisamoto's research on DELTA transistors drew the attention of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which in 1997 awarded a contract to a research group at UC Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant uni ...
to develop a deep sub-micron transistor based on DELTA technology. The group was led by Hisamoto along with TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC; also called Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's most valuable semiconductor company, the world' ...
's Chenming Hu
Chenming Calvin Hu (; born 1947) is a Chinese-American electronic engineer who specializes in microelectronics. He is TSMC Distinguished Professor Emeritus in the electronic engineering and computer science department of the University of Califo ...
. The team made the following breakthroughs between 1998 and 2004.
*1998 N-channel FinFET ( 17 nm) Digh Hisamoto, Chenming Hu, Tsu-Jae King Liu
Tsu-Jae King Liu is an American academic and engineer who serves as the Dean and Roy W. Carlson Professor of Engineering at the UC Berkeley College of Engineering.
Liu is an electrical engineer with extensive expertise and achievements in both ...
, Jeffrey Bokor, Wen-Chin Lee, Jakub Kedzierski, Erik Anderson, Hideki Takeuchi, Kazuya Asano
*1999 P-channel FinFET ( sub-50 nm) Digh Hisamoto, Chenming Hu, Xuejue Huang, Wen-Chin Lee, Charles Kuo, Leland Chang, Jakub Kedzierski, Erik Anderson, Hideki Takeuchi
*2001 15 nm FinFET Chenming Hu, Yang-Kyu Choi, Nick Lindert, P. Xuan, S. Tang, D. Ha, Erik Anderson, Tsu-Jae King Liu, Jeffrey Bokor
*2002 10 nm FinFET Shibly Ahmed, Scott Bell, Cyrus Tabery, Jeffrey Bokor, David Kyser, Chenming Hu, Tsu-Jae King Liu, Bin Yu, Leland Chang
*2004 High-κ/metal gate
A metal gate, in the context of a lateral metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) stack, is the gate electrode separated by an oxide from the transistor's channel – the gate material is made from a metal. In most MOS transistors since about the mid ...
FinFET D. Ha, Hideki Takeuchi, Yang-Kyu Choi, Tsu-Jae King Liu, W. Bai, D.-L. Kwong, A. Agarwal, M. Ameen
They coined the term "FinFET" (fin field-effect transistor) in a December 2000 paper, used to describe a non-planar, double-gate transistor built on an SOI substrate.
In 2006, a team of Korean researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the National Nano Fab Center developed a 3 nm transistor, the world's smallest nanoelectronic
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical pr ...
device, based on gate-all-around (GAA) FinFET technology. In 2011, Rice University
William Marsh Rice University (Rice University) is a private research university in Houston, Texas. It is on a 300-acre campus near the Houston Museum District and adjacent to the Texas Medical Center. Rice is ranked among the top universities ...
researchers Masoud Rostami and Kartik Mohanram demonstrated that FinFETs can have two electrically independent gates, which gives circuit designers more flexibility to design with efficient, low-power gates.
In 2020, Chenming Hu received the IEEE Medal of Honor award for his development of the FinFET, which the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) credited with taking transistors to the third dimension and extending Moore's law.
Commercialization
The industry's first 25 nanometer transistor operating on just 0.7volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defin ...
s was demonstrated in December 2002 by TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC; also called Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's most valuable semiconductor company, the world' ...
. The "Omega FinFET" design, named after the similarity between the Greek letter "Omega
Omega (; capital: Ω, lowercase: ω; Ancient Greek ὦ, later ὦ μέγα, Modern Greek ωμέγα) is the twenty-fourth and final letter in the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system/ isopsephy ( gematria), it has a value of 800. The ...
" and the shape in which the gate wraps around the source/drain structure, has a gate delay of just 0.39 picosecond (ps) for the N-type transistor and 0.88 ps for the P-type.
In 2004, Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
demonstrated a "Bulk FinFET" design, which made it possible to mass-produce FinFET devices. They demonstrated dynamic random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the ...
( DRAM) manufactured with a 90nm Bulk FinFET process.
In 2011, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
demonstrated tri-gate transistor
The 22 nm node is the process step following 32 nm process, 32 nm in CMOS MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. The typical half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features in an array) for a memory cell using the process is arou ...
s, where the gate surrounds the channel on three sides, allowing for increased energy efficiency and lower gate delay—and thus greater performance—over planar transistors.
Commercially produced chips at 22 nm
The 22 nm node is the process step following 32 nm in CMOS MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. The typical half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features in an array) for a memory cell using the process is around 22 nm. ...
and below have generally utilised FinFET gate designs (but planar processes do exist down to 18 nm, with 12 nm in development). Intel's tri-gate variant were announced at 22 nm in 2011 for its Ivy Bridge microarchitecture. These devices shipped from 2012 onwards. From 2014 onwards, at 14 nm (or 16 nm) major foundries (TSMC, Samsung, GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. (GF or GloFo) is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company incorporated in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD, ...
) utilised FinFET designs.
In 2013, SK Hynix
SK hynix Inc. is a South Korean supplier of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips and flash memory chips. Hynix is the world's second-largest memory chipmaker (after Samsung Electronics) and the world's third-largest semiconductor company. ...
began commercial mass-production of a 16nm process, TSMC began production of a 16nm FinFET process, and Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, a ...
began production of a 10nm process. TSMC began production of a 7 nm
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors defines the 7 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 10 nm node. It is based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, ...
process in 2017, and Samsung began production of a 5 nm
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems defines the 5 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 7 nm node. In 2020, Samsung and TSMC entered volume production of 5 nm chips, ...
process in 2018. In 2019, Samsung announced plans for the commercial production of a 3nm GAAFET
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be contro ...
process by 2021.
Commercial production of nanoelectronic
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical pr ...
FinFET semiconductor memory began in the 2010s. In 2013, SK Hynix began mass-production of 16nm NAND flash memory, and Samsung Electronics began production of 10nm multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash memory. In 2017, TSMC began production of SRAM memory using a 7 nm process.
See also
*Transistor count
The transistor count is the number of transistors in an electronic device (typically on a single substrate or "chip"). It is the most common measure of integrated circuit complexity (although the majority of transistors in modern microprocessors ...
References
{{Electronic components Transistor types Field-effect transistors MOSFETs Semiconductor devices Indonesian inventions Japanese inventions Taiwanese inventionsExternal links
"The Silicon Age: Trends in Semiconductor Devices Industry
, 2022