Tsiolkovsky rocket equation.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) was a Russian and Soviet
Tsiolkovsky spent most of his life in a
. Informatics.org (19 September 1935). Retrieved 4 May 2012. Additionally, inspired by the fiction of Jules Verne, Tsiolkovsky theorized many aspects of space travel and Despite the youth's growing knowledge of physics, his father was concerned that he would not be able to provide for himself financially as an adult and brought him back home at the age of 19 after learning that he was overworking himself and going hungry. Afterwards, Tsiolkovsky passed the teacher's exam and went to work at a school in
Despite the youth's growing knowledge of physics, his father was concerned that he would not be able to provide for himself financially as an adult and brought him back home at the age of 19 after learning that he was overworking himself and going hungry. Afterwards, Tsiolkovsky passed the teacher's exam and went to work at a school in
 In 1926–1929, roughly at the same time when
In 1926–1929, roughly at the same time when  Tsiolkovsky championed the idea of the diversity of life in the universe and was the first theorist and advocate of human spaceflight.
Tsiolkovsky never built a rocket; he apparently did not expect many of his theories to ever be implemented.
Hearing problems did not prevent the scientist from having a good understanding of music, as outlined in his work "The Origin of Music and Its Essence."
Tsiolkovsky championed the idea of the diversity of life in the universe and was the first theorist and advocate of human spaceflight.
Tsiolkovsky never built a rocket; he apparently did not expect many of his theories to ever be implemented.
Hearing problems did not prevent the scientist from having a good understanding of music, as outlined in his work "The Origin of Music and Its Essence."
 Tsiolkovsky wrote a book called ''The Will of the Universe: The Unknown Intelligence'' in 1928 in which he propounded a philosophy of panpsychism. He believed humans would eventually colonize the Milky Way galaxy. His thought preceded the
Tsiolkovsky wrote a book called ''The Will of the Universe: The Unknown Intelligence'' in 1928 in which he propounded a philosophy of panpsychism. He believed humans would eventually colonize the Milky Way galaxy. His thought preceded the
 * In 1964, The Monument to the Conquerors of Space was erected to celebrate the achievements of the Soviet people in space exploration. Located in Moscow, the monument is 107 meters (350 feet) tall and covered with titanium cladding. The main part of the monument is a giant obelisk topped by a rocket and resembling in shape the exhaust plume of the rocket. A statue of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the precursor of astronautics, is located in front of the obelisk.
* The State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics in Kaluga now bears his name. His residence during the final months of his life (also in Kaluga) was converted into a memorial museum a year after his death.
* The town Uglegorsk in
* In 1964, The Monument to the Conquerors of Space was erected to celebrate the achievements of the Soviet people in space exploration. Located in Moscow, the monument is 107 meters (350 feet) tall and covered with titanium cladding. The main part of the monument is a giant obelisk topped by a rocket and resembling in shape the exhaust plume of the rocket. A statue of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the precursor of astronautics, is located in front of the obelisk.
* The State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics in Kaluga now bears his name. His residence during the final months of his life (also in Kaluga) was converted into a memorial museum a year after his death.
* The town Uglegorsk in
 *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Review
* Georgiy Stepanovich Vetrov (1994). ''S. P. Korolyov and Space: First steps''. M. Nauka. .
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky. The collection of philosophical works. Biography, books, audiobooks, articles, photographs, video. Russian and English.
Tsiolkovsky's house
The house museum of Tsiolkovsky
Historic images * ttp://www.russianspaceweb.com/tsiolkovsky.html Tsiolkovskyfrom Russianspaceweb.com
Spaceflight or Extinction: Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Excerpts from "The Aims of Astronautics", ''The Call of the Cosmos''
by Vladimir V. Lytkin, Tsiolkovskiy Museum, Kaluga.
Tsiolkovski: The Cosmic Scientist and His Cosmic Philosophy
by Daniel H. Shubin.
The Path to the Stars: Collection of Science Fiction Works
The Call of the Cosmos
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tsiolkovsky, Konstantin 1857 births 1935 deaths Cosmists Early rocketry Early spaceflight scientists People from Spassky District, Ryazan Oblast People from Spassky Uyezd (Ryazan Governorate) Philosophers of ethics and morality Philosophers of technology Philosophical cosmologists Recipients of the Order of Saint Stanislaus (Russian), 3rd class Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 3rd class Rocket science pioneers Rocket scientists Russian aerospace engineers Russian atheists Russian inventors Russian people of Polish descent Russian people of Tatar descent Russian science fiction writers Soviet aerospace engineers Scientists with disabilities
rocket scientist
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
who pioneered astronautic theory. Along with the Frenchman Robert Esnault-Pelterie Robert Albert Charles Esnault-Pelterie (8 November 1881 – 6 December 1957) was a French aircraft designer and spaceflight theorist. He is referred to as being one of the founders of modern rocketry and astronautics, along with the Russian Kons ...
, the Germans Hermann Oberth and Fritz von Opel
Fritz Adam Hermann von Opel (4 May 1899 – 8 April 1971) was a German rocket technology pioneer and automotive executive, nicknamed "Rocket-Fritz". He is remembered mostly for his spectacular demonstrations of rocket propulsion that earned him an ...
, and the American Robert H. Goddard
Robert Hutchings Goddard (October 5, 1882 – August 10, 1945) was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket. Goddard successfully laun ...
, he is one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics
Astronautics (or cosmonautics) is the theory and practice of travel beyond Earth's atmosphere into outer space. Spaceflight is one of its main applications and space science its overarching field.
The term ''astronautics'' (originally ''astron ...
. His works later inspired leading Soviet rocket-engineers Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (russian: Сергей Павлович Королёв, Sergey Pavlovich Korolyov, sʲɪrˈɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪtɕ kərɐˈlʲɵf, Ru-Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.ogg; ukr, Сергій Павлович Корольов, ...
and Valentin Glushko
Valentin Petrovich Glushko (russian: Валенти́н Петро́вич Глушко́; uk, Валентин Петрович Глушко, Valentyn Petrovych Hlushko; born 2 September 1908 – 10 January 1989) was a Soviet engineer and the ...
, who contributed to the success of the Soviet space program
The Soviet space program (russian: Космическая программа СССР, Kosmicheskaya programma SSSR) was the national space program of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), active from 1955 until the dissoluti ...
.
log house
A log house, or log building, is a structure built with horizontal logs interlocked at the corners by notching. Logs may be round, squared or hewn to other shapes, either handcrafted or milled. The term " log cabin" generally refers to a sm ...
on the outskirts of Kaluga, about southwest of Moscow. A recluse by nature, his unusual habits made him seem bizarre to his fellow townsfolk.
Early life
Tsiolkovsky was born in Izhevskoye (now inSpassky District
Spassky District is the name of several administrative and municipal districts in Russia. The name is generally derived from or related to the root "''spas''" ("savior")—usually alluding to the concept of the Christian faith.
* Spassky District ...
, Ryazan Oblast
Ryazan Oblast ( rus, Рязанская область, r=Ryazanskaya oblast, p=rʲɪˈzanskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Ryazan, which is the oblast's largest city.
Geo ...
), in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, to a middle-class family. His father, Makary Edward Erazm Ciołkowski, was a Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
forester of Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
faith who relocated to Russia; his Russian Orthodox
Russian Orthodoxy (russian: Русское православие) is the body of several churches within the larger communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, whose liturgy is or was traditionally conducted in Church Slavonic language. Most ...
mother was of mixed Volga Tatar
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after ...
and Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
origin. His father was successively a forester, teacher, and minor government official. At the age of 10, Konstantin caught scarlet fever and lost his hearing. When he was 13, his mother died. He was not admitted to elementary schools because of his hearing problem, so he was self-taught. As a reclusive home-schooled child, he passed much of his time by reading books and became interested in mathematics and physics. As a teenager, he began to contemplate the possibility of space travel.
Tsiolkovsky spent three years attending a Moscow library, where Russian cosmism
Russian cosmism, also cosmism, is a philosophical and cultural movement that emerged in Russia at the turn of the 19th century, and again, at the beginning of the 20th century. At the beginning of the 20th century, there was a burst of scientifi ...
proponent Nikolai Fyodorov worked. He later came to believe that colonizing space would lead to the perfection of the human species, with immortality and a carefree existence.The life of Konstantin Eduardovitch Tsiolkovsky 1857–1935. Informatics.org (19 September 1935). Retrieved 4 May 2012. Additionally, inspired by the fiction of Jules Verne, Tsiolkovsky theorized many aspects of space travel and
rocket propulsion
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
. He is considered the father of spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in o ...
and the first person to conceive the space elevator
A space elevator, also referred to as a space bridge, star ladder, and orbital lift, is a proposed type of planet-to-space transportation system, often depicted in science fiction. The main component would be a cable (also called a space tethe ...
, becoming inspired in 1895 by the newly constructed Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; french: links=yes, tour Eiffel ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower.
Locally nicknamed "' ...
in Paris.
 Despite the youth's growing knowledge of physics, his father was concerned that he would not be able to provide for himself financially as an adult and brought him back home at the age of 19 after learning that he was overworking himself and going hungry. Afterwards, Tsiolkovsky passed the teacher's exam and went to work at a school in
Despite the youth's growing knowledge of physics, his father was concerned that he would not be able to provide for himself financially as an adult and brought him back home at the age of 19 after learning that he was overworking himself and going hungry. Afterwards, Tsiolkovsky passed the teacher's exam and went to work at a school in Borovsk
Borovsk (russian: Бо́ровск) is a town and the administrative center of Borovsky District of Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the Protva River just south from the oblast's border with Moscow Oblast. Population: 12,000 (1969).
History
...
near Moscow. He also met and married his wife Varvara Sokolova during this time. Despite being stuck in Kaluga, a small town far from major learning centers, Tsiolkovsky managed to make scientific discoveries on his own.
The first two decades of the 20th century were marred by personal tragedy. Tsiolkovsky's son Ignaty committed suicide in 1902, and in 1908 many of his accumulated papers were lost in a flood. In 1911, his daughter Lyubov was arrested for engaging in revolutionary activities.
Scientific achievements
Tsiolkovsky stated that he developed the theory of rocketry only as a supplement to philosophical research on the subject. He wrote more than 400 works including approximately 90 published pieces on space travel and related subjects. Among his works are designs for rockets with steering thrusters, multistage boosters, space stations,airlock
An airlock, air-lock or air lock, often abbreviated to just lock, is a compartment with doors which can be sealed against pressure which permits the passage of people and objects between environments of differing pressure or atmospheric compo ...
s for exiting a spaceship into the vacuum of space, and closed-cycle biological systems to provide food and oxygen for space colonies.
Tsiolkovsky's first scientific study dates back to 1880–1881. He wrote a paper called "Theory of Gases," in which he outlined the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, but after submitting it to the Russian Physico-Chemical Society (RPCS), he was informed that his discoveries had already been made 25 years earlier. Undaunted, he pressed ahead with his second work, "The Mechanics of the Animal Organism". It received favorable feedback, and Tsiolkovsky was made a member of the Society. Tsiolkovsky's main works after 1884 dealt with four major areas: the scientific rationale for the all-metal balloon (airship), streamlined airplanes and trains, hovercraft, and rockets for interplanetary travel.
In 1892, he was transferred to a new teaching post in Kaluga where he continued to experiment. During this period, Tsiolkovsky began working on a problem that would occupy much of his time during the coming years: an attempt to build an all-metal dirigible that could be expanded or shrunk in size.
Tsiolkovsky developed the first aerodynamics laboratory in Russia in his apartment. In 1897, he built the first Russian wind tunnel with an open test section and developed a method of experimentation using it. In 1900, with a grant from the Academy of Sciences, he made a survey using models of the simplest shapes and determined the drag coefficients of the sphere, flat plates, cylinders, cones, and other bodies. Tsiolkovsky's work in the field of aerodynamics was a source of ideas for Russian scientist Nikolay Zhukovsky Nikolay Zhukovsky may refer to:
*Nikolay Zhukovsky (revolutionary) (1833–1895), Russian revolutionary
*Nikolay Zhukovsky (scientist)
Nikolay Yegorovich Zhukovsky ( rus, Никола́й Его́рович Жуко́вский, p=ʐʊˈkofskʲ ...
, the father of modern aerodynamics and hydrodynamics. Tsiolkovsky described the airflow around bodies of different geometric shapes, but because the RPCS did not provide any financial support for this project, he was forced to pay for it largely out of his own pocket.
Tsiolkovsky studied the mechanics of lighter-than-air powered flying machines. He first proposed the idea of an all-metal dirigible and built a model of it. The first printed work on the airship was "A Controllable Metallic Balloon" (1892), in which he gave the scientific and technical rationale for the design of an airship with a metal sheath. Tsiolkovsky was not supported on the airship project, and the author was refused a grant to build the model. An appeal to the General Aviation Staff of the Russian army also had no success. In 1892, he turned to the new and unexplored field of heavier-than-air aircraft. Tsiolkovsky's idea was to build an airplane with a metal frame. In the article "An Airplane or a Birdlike (Aircraft) Flying Machine" (1894) are descriptions and drawings of a monoplane, which in its appearance and aerodynamics anticipated the design of aircraft that would be constructed 15 to 18 years later. In an Aviation Airplane, the wings have a thick profile with a rounded front edge and the fuselage is faired. But work on the airplane, as well as on the airship, did not receive recognition from the official representatives of Russian science, and Tsiolkovsky's further research had neither monetary nor moral support. In 1914, he displayed his models of all-metal dirigibles at the Aeronautics Congress in St. Petersburg but met with a lukewarm response.
Disappointed at this, Tsiolkovsky gave up on space and aeronautical problems with the onset of World War I and instead turned his attention to the problem of alleviating poverty. This occupied his time during the war years until the Russian Revolution in 1917.
Starting in 1896, Tsiolkovsky systematically studied the theory of motion of rocket apparatus. Thoughts on the use of the rocket principle in the cosmos were expressed by him as early as 1883, and a rigorous theory of rocket propulsion was developed in 1896. Tsiolkovsky derived the formula, which he called the "formula of aviation", now known as Tsiolkovsky rocket equation
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) ...
, establishing the relationship between:
* change in the rocket's speed ()
* exhaust velocity
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is ...
of the engine ()
* initial () and final () mass of the rocket
:
After writing out this equation, Tsiolkovsky recorded the date: 10 May 1897. In the same year, the formula for the motion of a body of variable mass was published in the thesis of the Russian mathematician I. V. Meshchersky ("Dynamics of a Point of Variable Mass," I. V. Meshchersky, St. Petersburg, 1897).
His most important work, published in May 1903, was ''Exploration of Outer Space by Means of Rocket Devices'' (russian: link=no, Исследование мировых пространств реактивными приборами). Tsiolkovsky calculated, using the Tsiolkovsky equation, that the horizontal speed required for a minimal orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
around the Earth is 8,000 m/s (5 miles per second) and that this could be achieved by means of a multistage rocket
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of another stage; a ''parallel'' stage i ...
fueled by liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an app ...
and liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully l ...
. In the article "Exploration of Outer Space by Means of Rocket Devices", it was suggested for the first time that a rocket could perform space flight. In this article and its sequels (1911 and 1914), he developed some ideas of missiles and considered the use of liquid rocket engines.
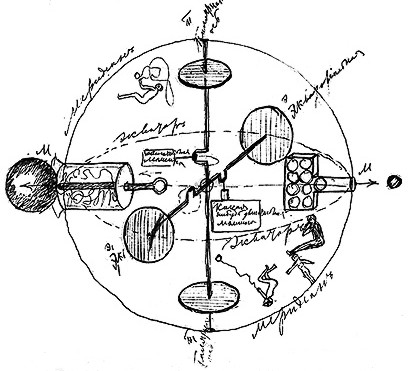
The outward appearance of Tsiolkovsky's spacecraft design, published in 1903, was a basis for modern spaceship design. The design had a hull divided into three main sections. The pilot and copilot were in the first section, the second and third sections held the liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen needed to fuel the spacecraft.
However, the result of the first publication was not what Tsiolkovsky expected. No foreign scientists appreciated his research, which today is a major scientific discipline. In 1911, he published the second part of the work "Exploration of Outer Space by Means of Rocket Devices". Here Tsiolkovsky evaluated the work needed to overcome the force of gravity, determined the speed needed to propel the device into the solar system ("escape velocity"), and examined calculation of flight time. The publication of this article made a splash in the scientific world, Tsiolkovsky found many friends among his fellow scientists.
 In 1926–1929, roughly at the same time when
In 1926–1929, roughly at the same time when Fritz von Opel
Fritz Adam Hermann von Opel (4 May 1899 – 8 April 1971) was a German rocket technology pioneer and automotive executive, nicknamed "Rocket-Fritz". He is remembered mostly for his spectacular demonstrations of rocket propulsion that earned him an ...
's rocket-powered Opel RAK
Opel-RAK were a series of rocket vehicles produced by German automobile manufacturer Fritz von Opel, of the Opel car company, in association with others, including Max Valier, Julius Hatry, and Friedrich Wilhelm Sander. Opel RAK is generally con ...
land vehicles and aircraft were demonstrated to the public, Tsiolkovsky solved the practical problem regarding the role played by rocket fuel in getting to escape velocity and leaving the Earth. He showed that the final speed of the rocket depends on the rate of gas flowing from it and on how the weight of the fuel relates to the weight of the empty rocket.
Tsiolkovsky conceived a number of ideas that have been later used in rockets. They include: gas rudders (graphite) for controlling a rocket's flight and changing the trajectory of its center of mass, the use of components of the fuel to cool the outer shell of the spacecraft (during re-entry to Earth) and the walls of the combustion chamber and nozzle, a pump system for feeding the fuel components, the optimal descent trajectory of the spacecraft while returning from space, etc. In the field of rocket propellants, Tsiolkovsky studied a large number of different oxidizers and combustible fuels and recommended specific pairings: liquid oxygen and hydrogen, and oxygen with hydrocarbons. Tsiolkovsky did much fruitful work on the creation of the theory of jet aircraft, and invented his chart Gas Turbine Engine. In 1927, he published the theory and design of a train on an air cushion. He first proposed a "bottom of the retractable body" chassis. However, space flight and the airship were the main problems to which he devoted his life. Tsiolkovsky had been developing the idea of the hovercraft since 1921, publishing a fundamental paper on it in 1927, entitled "Air Resistance and the Express Train" (russian: link=no, Сопротивление воздуха и скорый по́езд). In 1929, Tsiolkovsky proposed the construction of multistage rockets in his book ''Space Rocket Trains'' (russian: link=no, Космические ракетные поезда).
 Tsiolkovsky championed the idea of the diversity of life in the universe and was the first theorist and advocate of human spaceflight.
Tsiolkovsky never built a rocket; he apparently did not expect many of his theories to ever be implemented.
Hearing problems did not prevent the scientist from having a good understanding of music, as outlined in his work "The Origin of Music and Its Essence."
Tsiolkovsky championed the idea of the diversity of life in the universe and was the first theorist and advocate of human spaceflight.
Tsiolkovsky never built a rocket; he apparently did not expect many of his theories to ever be implemented.
Hearing problems did not prevent the scientist from having a good understanding of music, as outlined in his work "The Origin of Music and Its Essence."
Later life
Tsiolkovsky supported theBolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
, and eager to promote science and technology, the new Soviet government elected him a member of the Socialist Academy The Socialist Academy of Social Sciences (SAON) was an educational establishment created in Russia in October 1918 with “the aim of studying and teaching social studies from the point of view of scientific socialism.” The original name of the ac ...
in 1918. He worked as a high school mathematics teacher until retiring in 1920 at the age of 63. In 1921, he received a lifetime pension.
In his late lifetime Tsiolkovsky was honored for his pioneering work. However, from the mid 1920s onwards the importance of his other work was acknowledged, and he was honoured for it and the Soviet state provided financial backing for his research. He was initially popularized in Soviet Russia in 1931–1932 mainly by two writers: Yakov Perelman
Yakov Isidorovich Perelman (russian: Яков Исидорович Перельман; – 16 March 1942) was a Russian and Soviet science writer and author of many popular science books, including ''Physics Can Be Fun'' and ''Mathematics Can B ...
and Nikolai Rynin. Tsiolkovsky died in Kaluga on 19 September 1935 after undergoing an operation for stomach cancer. He bequeathed his life's work to the Soviet state.
Legacy
Tsiolkovsky influenced later rocket scientists throughout Europe, likeWernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( , ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German and American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and Allgemeine SS, as well as the leading figure in the develop ...
. Soviet search teams at Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, en, " Peene iverMouth") is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is part of the ''Amt'' (collective municipality) of Usedom-Nord. The commu ...
found a German translation of a book by Tsiolkovsky of which "almost every page...was embellished by von Braun's comments and notes." Leading Soviet rocket-engine designer Valentin Glushko
Valentin Petrovich Glushko (russian: Валенти́н Петро́вич Глушко́; uk, Валентин Петрович Глушко, Valentyn Petrovych Hlushko; born 2 September 1908 – 10 January 1989) was a Soviet engineer and the ...
and rocket designer Sergey Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (russian: Сергей Павлович Королёв, Sergey Pavlovich Korolyov, sʲɪrˈɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪtɕ kərɐˈlʲɵf, Ru-Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.ogg; ukr, Сергій Павлович Корольов, ...
studied Tsiolkovsky's works as youths, and both sought to turn Tsiolkovsky's theories into reality. In particular, Korolev saw traveling to Mars as the more important priority, until in 1964 he decided to compete with the American Project Apollo for the Moon.
In 1989, Tsiolkovsky was inducted into the International Air & Space Hall of Fame
The International Air & Space Hall of Fame is an honor roll of people, groups, organizations, or things that have contributed significantly to the advancement of aerospace flight and technology, sponsored by the San Diego Air & Space Museum. Si ...
at the San Diego Air & Space Museum
San Diego Air & Space Museum (SDASM, formerly the San Diego Aerospace Museum) is an aviation and space exploration museum in San Diego, California, United States. The museum is located in Balboa Park and is housed in the former Ford Building, ...
.
Philosophical work
 Tsiolkovsky wrote a book called ''The Will of the Universe: The Unknown Intelligence'' in 1928 in which he propounded a philosophy of panpsychism. He believed humans would eventually colonize the Milky Way galaxy. His thought preceded the
Tsiolkovsky wrote a book called ''The Will of the Universe: The Unknown Intelligence'' in 1928 in which he propounded a philosophy of panpsychism. He believed humans would eventually colonize the Milky Way galaxy. His thought preceded the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 during 1957, and continuin ...
by several decades, and some of what he foresaw in his imagination has come into being since his death. Tsiolkovsky also did not believe in traditional religious cosmology, but instead (and to the chagrin of the Soviet authorities) he believed in a cosmic being that governed humans as "marionettes, mechanical puppets, machines, movie characters", thereby adhering to a mechanical view of the universe, which he believed would be controlled in the millennia to come through the power of human science and industry. In a short article in 1933, he explicitly formulated what was later to be known as the Fermi paradox
The Fermi paradox is the discrepancy between the lack of conclusive evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life and the apparently high a priori likelihood of its existence, and by extension of obtaining such evidence. As a 2015 article put it, ...
.
He wrote a few works on ethics, espousing negative utilitarianism
Negative utilitarianism is a form of negative consequentialism that can be described as the view that people should minimize the total amount of aggregate suffering, or that they should minimize suffering and then, secondarily, maximize the tota ...
.
Tributes
 * In 1964, The Monument to the Conquerors of Space was erected to celebrate the achievements of the Soviet people in space exploration. Located in Moscow, the monument is 107 meters (350 feet) tall and covered with titanium cladding. The main part of the monument is a giant obelisk topped by a rocket and resembling in shape the exhaust plume of the rocket. A statue of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the precursor of astronautics, is located in front of the obelisk.
* The State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics in Kaluga now bears his name. His residence during the final months of his life (also in Kaluga) was converted into a memorial museum a year after his death.
* The town Uglegorsk in
* In 1964, The Monument to the Conquerors of Space was erected to celebrate the achievements of the Soviet people in space exploration. Located in Moscow, the monument is 107 meters (350 feet) tall and covered with titanium cladding. The main part of the monument is a giant obelisk topped by a rocket and resembling in shape the exhaust plume of the rocket. A statue of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the precursor of astronautics, is located in front of the obelisk.
* The State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics in Kaluga now bears his name. His residence during the final months of his life (also in Kaluga) was converted into a memorial museum a year after his death.
* The town Uglegorsk in Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrat ...
was renamed '' Tsiolkovsky'' by President of Russia
The president of the Russian Federation ( rus, Президент Российской Федерации, Prezident Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the head of state of the Russian Federation. The president leads the executive branch of the federal ...
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
in 2015.
* The crater Tsiolkovskiy (the most prominent crater on the far side of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
) was named after him, while asteroid 1590 Tsiolkovskaja was named after his wife. (The Soviet Union obtained naming rights by operating Luna 3
Luna 3, or E-2A No.1 ( rus, Луна 3}) was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1959 as part of the Luna programme. It was the first mission to photograph the far side of the Moon and the third Soviet space probe to be sent to the neighborhood of th ...
, the first space device to successfully transmit images of the side of the Moon not seen from Earth.)
* The Tsiolkovsky Memorial Apartment. A museum created in Borovsk
Borovsk (russian: Бо́ровск) is a town and the administrative center of Borovsky District of Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the Protva River just south from the oblast's border with Moscow Oblast. Population: 12,000 (1969).
History
...
where he lived and had started his career as a teacher..
* There is a statue of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky directly outside the Sir Thomas Brisbane Planetarium
The Sir Thomas Brisbane Planetarium is located on the grounds of the Brisbane Botanic Gardens in the suburb of Mount Coot-tha, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. The Planetarium was officially opened on 24 May 1978.
The Planetarium is named af ...
in Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Queensland, and the third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of approximately 2.6 million. Brisbane lies at the centre of the South ...
, Queensland, Australia.
* There is a Google Doodle
A Google Doodle is a special, temporary alteration of the logo on Google's homepages intended to commemorate holidays, events, achievements, and notable historical figures. The first Google Doodle honored the 1998 edition of the long-running an ...
honoring the famous pioneer.
* There is a Tsiolkovsky exhibit on display at the Museum of Jurassic Technology
The Museum of Jurassic Technology at 9341 Venice Boulevard in the Palms district of Los Angeles, California, was founded by David Hildebrand Wilson and Diana Drake Wilson in 1988.Tony Perrottet" The Museum of Jurassic Technology: A throwback to t ...
in Los Angeles, California.
*There is a 1 ruble 1987 coin commemorating the 130th anniversary of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky's birth.
In popular culture
* Tsiolkovsky was consulted for the script to the 1936 Soviet science-fiction film, '' Kosmicheskiy reys''. * In Altman's 1979 post-apocalyptic film ''Quintet'', the motto of the charity house run by the character St. Christopher is taken from Tsiolkovsky: "The Earth is the cradle of the mind, but one cannot live in the cradle forever." * In 1972 science fiction movie Solaris directed by Andrey Tarkovski, a portrait of Tsiolkovsky appears, soon after the beginning of the movie, decorating the wall of the meeting room of the committee discussing the future of `solaristics'. * SF writerAlexander Belyaev
Alexander Romanovich Belyaev (russian: Алекса́ндр Рома́нович Беля́ев, ; – 6 January 1942) was a Soviet Russian writer of science fiction. His works from the 1920s and 1930s made him a highly regarded figure in Russia ...
has written a book in which a city and a space station are named after him.
* A lunar station is named Tsiolkovsky in Stanisław Lem
Stanisław Herman Lem (; 12 September 1921 – 27 March 2006) was a Polish writer of science fiction and essays on various subjects, including philosophy, futurology, and literary criticism. Many of his science fiction stories are of satirical ...
's novel ''Tales of Pirx the Pilot
''Tales of Pirx the Pilot'' is a science fiction stories collection by Polish author Stanisław Lem, about a spaceship pilot named Pirx.
The first collection of stories about Pirx was published in 1965 in the Soviet Union in Russian under the ...
'', story "The Conditional Reflex".
* The Soviet ship in Harry Turtledove
Harry Norman Turtledove (born June 14, 1949) is an American author who is best known for his work in the genres of alternate history, historical fiction, fantasy, science fiction, and mystery fiction. He is a student of history and completed hi ...
's 1990 Mars exploration novel ''A World of Difference'' is named ''Tsiolkovsky''.
* In Princeton physicist and space colony advocate Gerard K. O'Neill's 1981 book of futurism, '' 2081: A Hopeful View of the Human Future'', the protagonist rides a spaceship named the ''Konstantin Tsiolokovsky'' from his home in a space colony at twice the orbital radius of Pluto to the Earth of 2081.
* A space station is named Tsiolkovsky 1 in William Gibson
William Ford Gibson (born March 17, 1948) is an American-Canadian speculative fiction writer and essayist widely credited with pioneering the science fiction subgenre known as ''cyberpunk''. Beginning his writing career in the late 1970s, hi ...
's 1981 short story "Hinterlands
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
".
* The character Aeolia Schenberg in the anime series ''Mobile Suit Gundam 00
is a Japanese anime television series, the eleventh installment in Sunrise (company), Sunrise studio's long-running ''Gundam'' franchise comprising two seasons. The series is set on a futuristic Earth and is centered on the exploits of the f ...
'' is based on Tsiolkovsky.
* The '' Zvezda'' module of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
has photos of Tsiolkovsky and Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who became the first human to journey into outer space. T ...
posted on the wall above the aft hatchway.
* The Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
-based space elevator
A space elevator, also referred to as a space bridge, star ladder, and orbital lift, is a proposed type of planet-to-space transportation system, often depicted in science fiction. The main component would be a cable (also called a space tethe ...
s in the Horus Heresy novel ''Mechanicum'' by Graham McNeill
Graham McNeill is a British novelist and video game writer. He is best known for his Warhammer Fantasy and Warhammer 40,000 novels, and his previous role as games designer for Games Workshop. He is currently working as a Senior Writer and Junio ...
, set in the ''Warhammer 40k
''Warhammer 40,000'' is a miniature wargame produced by Games Workshop. It is the most popular miniature wargame in the world, and is particularly popular in the United Kingdom. The first edition of the rulebook was published in September 1987, ...
'' universe, are called "Tsiolkovsky Towers". Location of "Tsiolkovsky towers" noted in a story-related map, with several mentions in the book's body matter, including pp. 218, 368, 370, and others.
* The science ship, SS Tsiolkovsky (NCC-53911) in the 1987 '' Star Trek: The Next Generation'' episode " The Naked Now" is named after him.
* Episode eight of '' Denpa Onna to Seishun Otoko'' is called "Tsiolkovsky's Prayer".
* In the comic book series '' Assassin's Creed: The Fall'', the leader of the Assassin Order reads from ''The Will of the Universe''.
* In a 2015 episode of '' Murdoch Mysteries'', set in about 1905, James Pendrick works with Tsiolkovsky's daughter to build a suborbital rocket based on his ideas and be the first man in space; a second rocket built to the same design is adapted as a ballistic missile for purposes of extortion.
* In the 2015 video game ''SOMA
Soma may refer to:
Businesses and brands
* SOMA (architects), a New York–based firm of architects
* Soma (company), a company that designs eco-friendly water filtration systems
* SOMA Fabrications, a builder of bicycle frames and other bicycle ...
'', which deals with topics of transhumanism, a character, Neil Tsiolkovsky, is likely named after him.
Works
 *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
See also
*Cosmonauts Alley
Cosmonauts Alley (russian: аллея Космонавтов) is a wide avenue in northern Moscow leading to the Russian Memorial Museum of Cosmonautics and the Monument to the Conquerors of Space. The pedestrian-only avenue connects the museum a ...
, a Russian monument park where Tsiolkovsky is honored
* History of the internal combustion engine
Various scientists and engineers contributed to the development of internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794 Robert Street patented an i ...
* Robert Esnault-Pelterie Robert Albert Charles Esnault-Pelterie (8 November 1881 – 6 December 1957) was a French aircraft designer and spaceflight theorist. He is referred to as being one of the founders of modern rocketry and astronautics, along with the Russian Kons ...
, a Frenchman who independently arrived at Tsiolkovsky's rocket equation
* Russian cosmism
Russian cosmism, also cosmism, is a philosophical and cultural movement that emerged in Russia at the turn of the 19th century, and again, at the beginning of the 20th century. At the beginning of the 20th century, there was a burst of scientifi ...
* Russian philosophy
* Soviet space program
The Soviet space program (russian: Космическая программа СССР, Kosmicheskaya programma SSSR) was the national space program of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), active from 1955 until the dissoluti ...
* Timeline of hydrogen technologies
This is a timeline of the history of hydrogen technology.
Timeline
16th century
* c. 1520 – First recorded observation of hydrogen by Paracelsus through dissolution of metals (iron, zinc, and tin) in sulfuric acid.
17th century
* 1625 – F ...
Citations
Cited sources
*Further reading
*Review
* Georgiy Stepanovich Vetrov (1994). ''S. P. Korolyov and Space: First steps''. M. Nauka. .
External links
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky. The collection of philosophical works. Biography, books, audiobooks, articles, photographs, video. Russian and English.
Tsiolkovsky's house
The house museum of Tsiolkovsky
Historic images * ttp://www.russianspaceweb.com/tsiolkovsky.html Tsiolkovskyfrom Russianspaceweb.com
Spaceflight or Extinction: Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Excerpts from "The Aims of Astronautics", ''The Call of the Cosmos''
by Vladimir V. Lytkin, Tsiolkovskiy Museum, Kaluga.
Tsiolkovski: The Cosmic Scientist and His Cosmic Philosophy
by Daniel H. Shubin.
The Path to the Stars: Collection of Science Fiction Works
The Call of the Cosmos
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tsiolkovsky, Konstantin 1857 births 1935 deaths Cosmists Early rocketry Early spaceflight scientists People from Spassky District, Ryazan Oblast People from Spassky Uyezd (Ryazan Governorate) Philosophers of ethics and morality Philosophers of technology Philosophical cosmologists Recipients of the Order of Saint Stanislaus (Russian), 3rd class Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 3rd class Rocket science pioneers Rocket scientists Russian aerospace engineers Russian atheists Russian inventors Russian people of Polish descent Russian people of Tatar descent Russian science fiction writers Soviet aerospace engineers Scientists with disabilities