Submarine recharging (JMSDF).jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A submarine (or sub) is a
HMS/m ''Tireless''
at
HMS/m ''A.1''
at
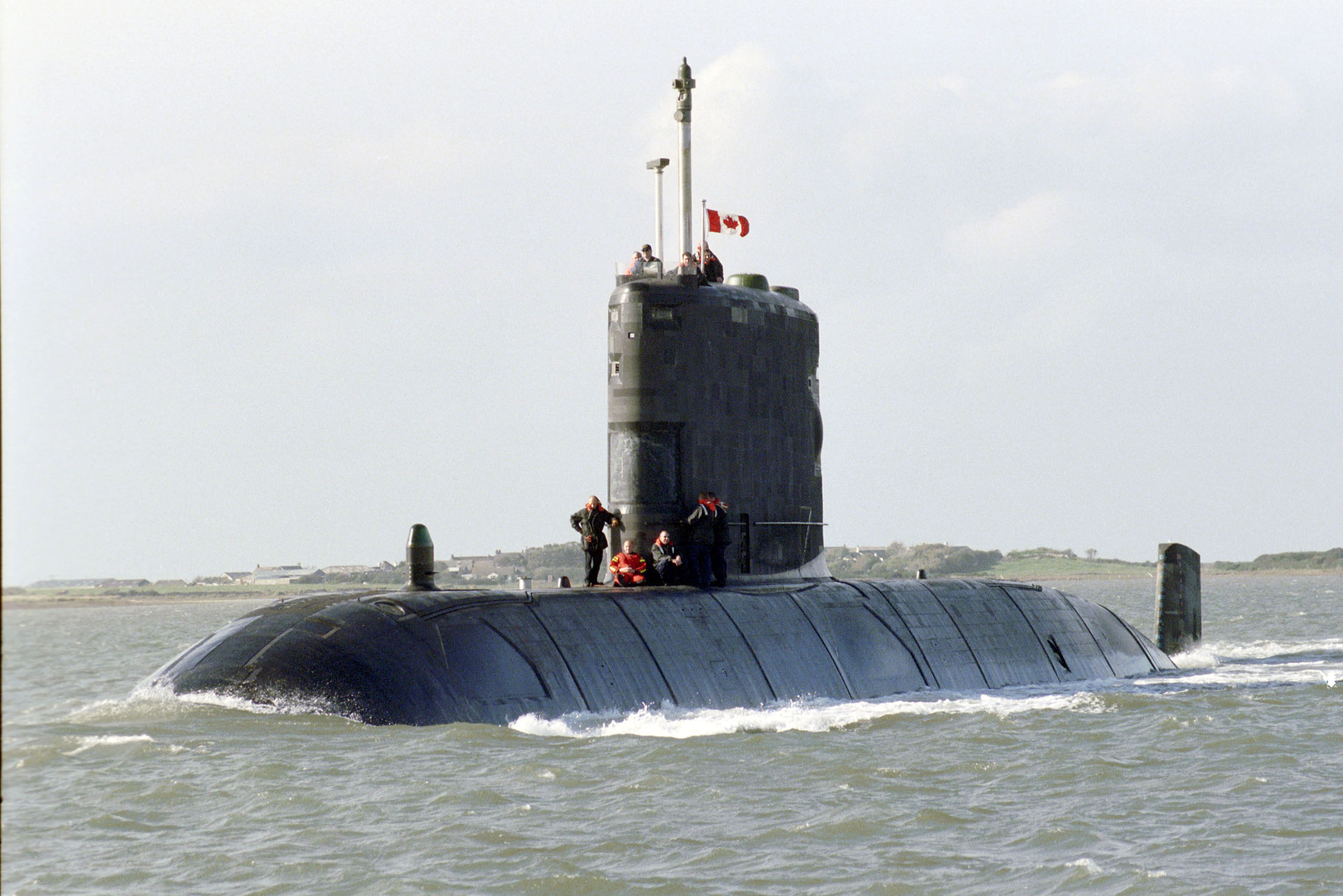
and in at a speech in Washington, Adm. Sir Philip Jones announced "that the name ''Dreadnought'' will return as lead boat and class name" for Dreadnought-class submarine, Britain’s latest ballistic missile submarinesbr>
/ref>

 In 1800, France built , a human-powered submarine designed by American
In 1800, France built , a human-powered submarine designed by American
 The first submarine not relying on human power for propulsion was the French (''Diver''), launched in 1863, which used compressed air at .
The first submarine not relying on human power for propulsion was the French (''Diver''), launched in 1863, which used compressed air at .  A reliable means of propulsion for the submerged vessel was only made possible in the 1880s with the advent of the necessary electric battery technology. The first electrically powered boats were built by Isaac Peral y Caballero in
A reliable means of propulsion for the submerged vessel was only made possible in the 1880s with the advent of the necessary electric battery technology. The first electrically powered boats were built by Isaac Peral y Caballero in 
 Commissioned in June 1900, the French steam and electric employed the now typical double-hull design, with a pressure hull inside the outer shell. These 200-ton ships had a range of over underwater. The French submarine ''Aigrette'' in 1904 further improved the concept by using a diesel rather than a gasoline engine for surface power. Large numbers of these submarines were built, with seventy-six completed before 1914.
The Royal Navy commissioned five s from
Commissioned in June 1900, the French steam and electric employed the now typical double-hull design, with a pressure hull inside the outer shell. These 200-ton ships had a range of over underwater. The French submarine ''Aigrette'' in 1904 further improved the concept by using a diesel rather than a gasoline engine for surface power. Large numbers of these submarines were built, with seventy-six completed before 1914.
The Royal Navy commissioned five s from
 Military submarines first made a significant impact in
Military submarines first made a significant impact in
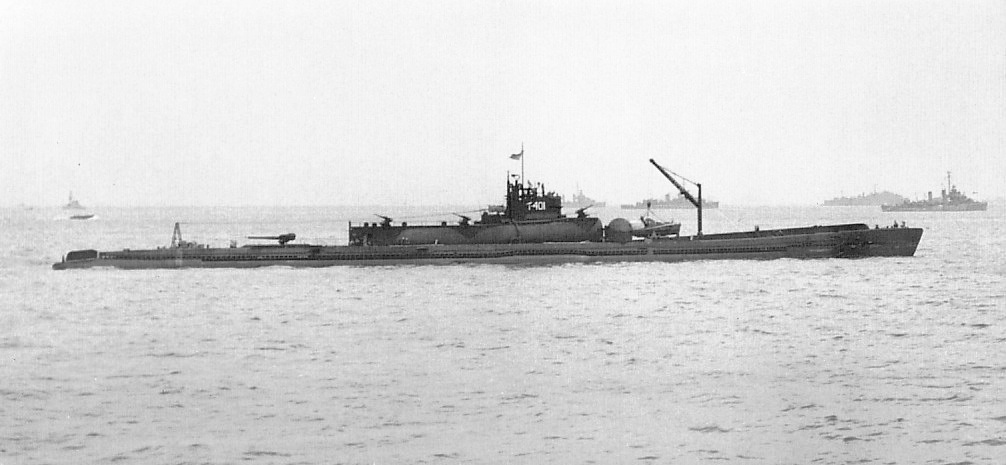
 During
During
 The first launch of a cruise missile ( SSM-N-8 Regulus) from a submarine occurred in July 1953, from the deck of , a World War II fleet boat modified to carry the missile with a
The first launch of a cruise missile ( SSM-N-8 Regulus) from a submarine occurred in July 1953, from the deck of , a World War II fleet boat modified to carry the missile with a

 Before and during
Before and during
File:PX-8 Mésoscaphe - Swiss Submarine (15722856966).jpg, Model of the Mésoscaphe ''Auguste Piccard''
File:AtlantisSubInterior3497.JPG, Interior of the tourist submarine ''Atlantis'' whilst submerged
File:AtlantisVIISubmarineClip3494.jpg, Tourist submarine ''Atlantis''
 * 1903 –
* 1903 –

 All surface ships, as well as surfaced submarines, are in a positively
All surface ships, as well as surfaced submarines, are in a positively
 The hydrostatic effect of variable ballast tanks is not the only way to control the submarine underwater. Hydrodynamic maneuvering is done by several control surfaces, collectively known as diving planes or hydroplanes, which can be moved to create hydrodynamic forces when a submarine moves longitudinally at sufficient speed. In the classic cruciform stern configuration, the horizontal stern planes serve the same purpose as the trim tanks, controlling the trim. Most submarines additionally have forward horizontal planes, normally placed on the bow until the 1960s but often on the sail on later designs, where they are closer to the center of gravity and can control depth with less effect on the trim.
The hydrostatic effect of variable ballast tanks is not the only way to control the submarine underwater. Hydrodynamic maneuvering is done by several control surfaces, collectively known as diving planes or hydroplanes, which can be moved to create hydrodynamic forces when a submarine moves longitudinally at sufficient speed. In the classic cruciform stern configuration, the horizontal stern planes serve the same purpose as the trim tanks, controlling the trim. Most submarines additionally have forward horizontal planes, normally placed on the bow until the 1960s but often on the sail on later designs, where they are closer to the center of gravity and can control depth with less effect on the trim.
 An obvious way to configure the control surfaces at the stern of a submarine is to use vertical planes to control yaw and horizontal planes to control pitch, which gives them the shape of a cross when seen from astern of the vessel. In this configuration, which long remained the dominant one, the horizontal planes are used to control the trim and depth and the vertical planes to control sideways maneuvers, like the rudder of a surface ship.
Alternatively, the rear control surfaces can be combined into what has become known as an x-stern or an x-rudder. Although less intuitive, such a configuration has turned out to have several advantages over the traditional cruciform arrangement. First, it improves maneuverability, horizontally as well as vertically. Second, the control surfaces are less likely to get damaged when landing on, or departing from, the seabed as well as when mooring and unmooring alongside. Finally, it is safer in that one of the two diagonal lines can counteract the other with respect to vertical as well as horizontal motion if one of them accidentally gets stuck.
An obvious way to configure the control surfaces at the stern of a submarine is to use vertical planes to control yaw and horizontal planes to control pitch, which gives them the shape of a cross when seen from astern of the vessel. In this configuration, which long remained the dominant one, the horizontal planes are used to control the trim and depth and the vertical planes to control sideways maneuvers, like the rudder of a surface ship.
Alternatively, the rear control surfaces can be combined into what has become known as an x-stern or an x-rudder. Although less intuitive, such a configuration has turned out to have several advantages over the traditional cruciform arrangement. First, it improves maneuverability, horizontally as well as vertically. Second, the control surfaces are less likely to get damaged when landing on, or departing from, the seabed as well as when mooring and unmooring alongside. Finally, it is safer in that one of the two diagonal lines can counteract the other with respect to vertical as well as horizontal motion if one of them accidentally gets stuck.
 The x-stern was first tried in practice in the early 1960s on the USS ''Albacore'', an experimental submarine of the US Navy. While the arrangement was found to be advantageous, it was nevertheless not used on US production submarines that followed due to the fact that it requires the use of a computer to manipulate the control surfaces to the desired effect. Instead, the first to use an x-stern in standard operations was the Swedish Navy with its ''Sjöormen'' class, the lead submarine of which was launched in 1967, before the ''Albacore'' had even finished her test runs. Since it turned out to work very well in practice, all subsequent classes of Swedish submarines ( ''Näcken'', ''Västergötland'', ''Gotland'', and ''Blekinge'' class) have or will come with an x-rudder.
The x-stern was first tried in practice in the early 1960s on the USS ''Albacore'', an experimental submarine of the US Navy. While the arrangement was found to be advantageous, it was nevertheless not used on US production submarines that followed due to the fact that it requires the use of a computer to manipulate the control surfaces to the desired effect. Instead, the first to use an x-stern in standard operations was the Swedish Navy with its ''Sjöormen'' class, the lead submarine of which was launched in 1967, before the ''Albacore'' had even finished her test runs. Since it turned out to work very well in practice, all subsequent classes of Swedish submarines ( ''Näcken'', ''Västergötland'', ''Gotland'', and ''Blekinge'' class) have or will come with an x-rudder.
 The Kockums shipyard responsible for the design of the x-stern on Swedish submarines eventually exported it to Australia with the ''Collins'' class as well as to Japan with the ''Sōryū'' class. With the introduction of the type 212, the German and Italian Navies came to feature it as well. The US Navy with its ''Columbia'' class, the British Navy with its ''Dreadnought'' class, and the French Navy with its ''Barracuda'' class are all about to join the x-stern family. Hence, as judged by the situation in the early 2020s, the x-stern is about to become the dominant technology.
When a submarine performs an emergency surfacing, all depth and trim control methods are used simultaneously, together with propelling the boat upwards. Such surfacing is very quick, so the sub may even partially jump out of the water, potentially damaging submarine systems.
The Kockums shipyard responsible for the design of the x-stern on Swedish submarines eventually exported it to Australia with the ''Collins'' class as well as to Japan with the ''Sōryū'' class. With the introduction of the type 212, the German and Italian Navies came to feature it as well. The US Navy with its ''Columbia'' class, the British Navy with its ''Dreadnought'' class, and the French Navy with its ''Barracuda'' class are all about to join the x-stern family. Hence, as judged by the situation in the early 2020s, the x-stern is about to become the dominant technology.
When a submarine performs an emergency surfacing, all depth and trim control methods are used simultaneously, together with propelling the boat upwards. Such surfacing is very quick, so the sub may even partially jump out of the water, potentially damaging submarine systems.
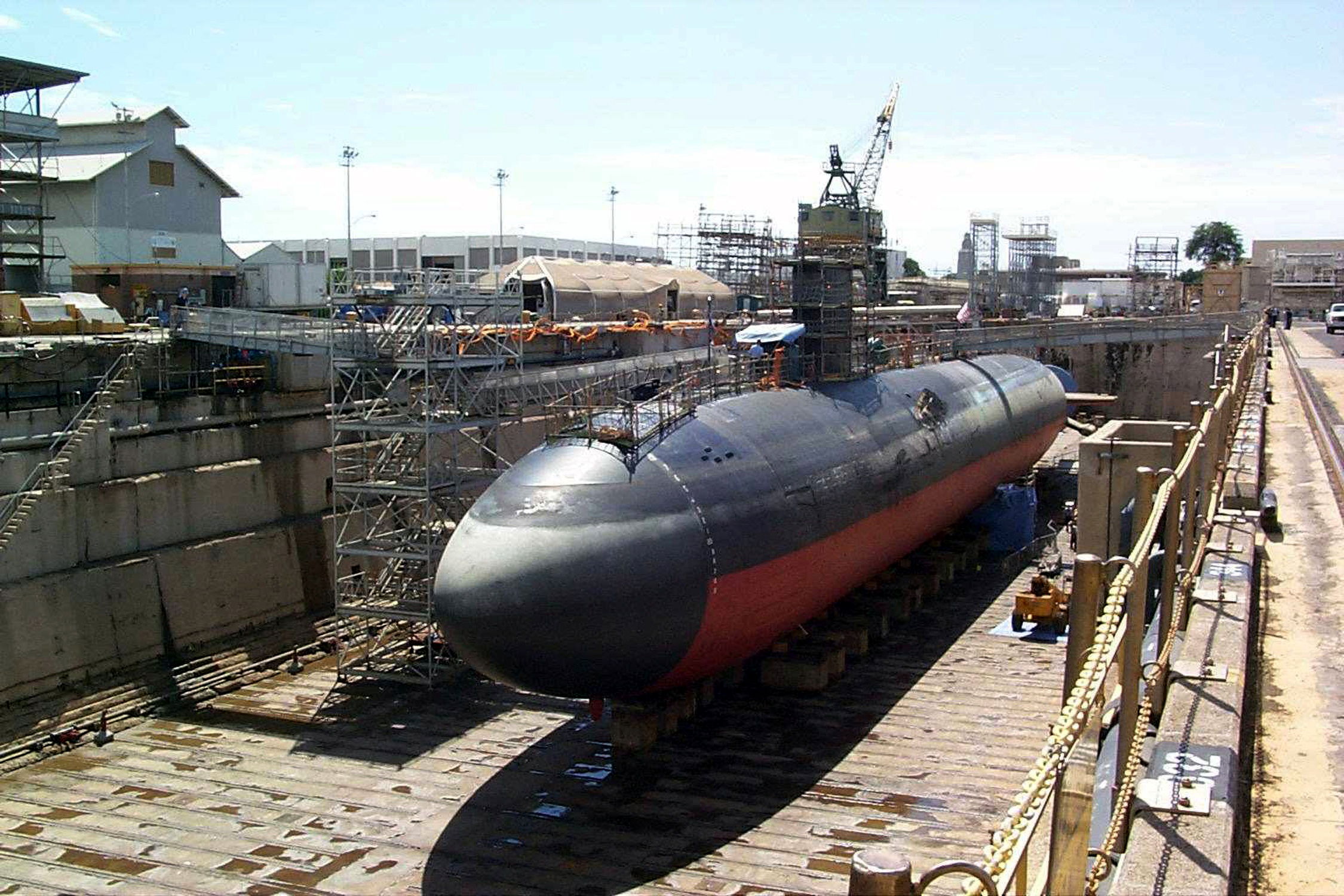 Modern submarines are cigar-shaped. This design, also used in very early submarines, is sometimes called a "
Modern submarines are cigar-shaped. This design, also used in very early submarines, is sometimes called a "
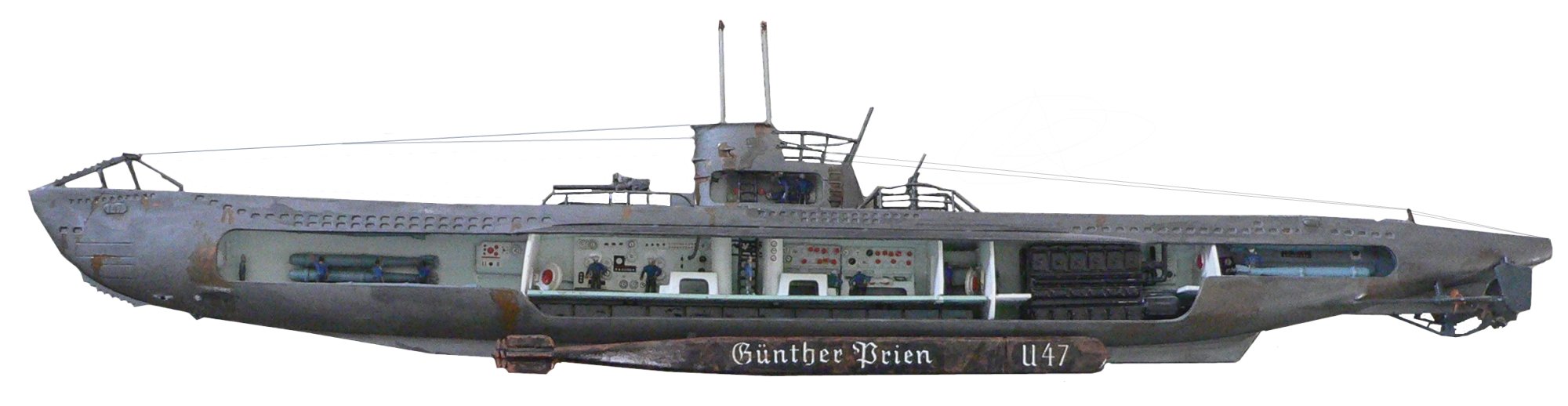
 Modern submarines and submersibles usually have, as did the earliest models, a single hull. Large submarines generally have an additional hull or hull sections outside. This external hull, which actually forms the shape of submarine, is called the outer hull ('' casing'' in the Royal Navy) or light hull, as it does not have to withstand a pressure difference. Inside the outer hull there is a strong hull, or
Modern submarines and submersibles usually have, as did the earliest models, a single hull. Large submarines generally have an additional hull or hull sections outside. This external hull, which actually forms the shape of submarine, is called the outer hull ('' casing'' in the Royal Navy) or light hull, as it does not have to withstand a pressure difference. Inside the outer hull there is a strong hull, or  After World War II, approaches split. The Soviet Union changed its designs, basing them on German developments. All post-World War II heavy Soviet and Russian submarines are built with a double hull structure. American and most other Western submarines switched to a primarily single-hull approach. They still have light hull sections in the bow and stern, which house main ballast tanks and provide a hydrodynamically optimized shape, but the main cylindrical hull section has only a single plating layer. Double hulls are being considered for future submarines in the United States to improve payload capacity, stealth and range.
After World War II, approaches split. The Soviet Union changed its designs, basing them on German developments. All post-World War II heavy Soviet and Russian submarines are built with a double hull structure. American and most other Western submarines switched to a primarily single-hull approach. They still have light hull sections in the bow and stern, which house main ballast tanks and provide a hydrodynamically optimized shape, but the main cylindrical hull section has only a single plating layer. Double hulls are being considered for future submarines in the United States to improve payload capacity, stealth and range.
 The pressure hull is generally constructed of thick high-strength steel with a complex structure and high strength reserve, and is separated by watertight bulkheads into several compartments. There are also examples of more than two hulls in a submarine, like the , which has two main pressure hulls and three smaller ones for control room, torpedoes and steering gear, with the missile launch system between the main hulls, all surrounded and supported by the outer light hydrodynamic hull. When submerged the pressure hull provides most of the buoyancy for the whole vessel.
The dive depth cannot be increased easily. Simply making the hull thicker increases the structural weight and requires reduction of onboard equipment weight, and increasing the diameter requires a proportional increase in thickness for the same material and architecture, ultimately resulting in a pressure hull that does not have sufficient buoyancy to support its own weight, as in a bathyscaphe. This is acceptable for civilian research submersibles, but not military submarines, which need to carry a large equipment, crew, and weapons load to fulfill their function. Construction materials with greater
The pressure hull is generally constructed of thick high-strength steel with a complex structure and high strength reserve, and is separated by watertight bulkheads into several compartments. There are also examples of more than two hulls in a submarine, like the , which has two main pressure hulls and three smaller ones for control room, torpedoes and steering gear, with the missile launch system between the main hulls, all surrounded and supported by the outer light hydrodynamic hull. When submerged the pressure hull provides most of the buoyancy for the whole vessel.
The dive depth cannot be increased easily. Simply making the hull thicker increases the structural weight and requires reduction of onboard equipment weight, and increasing the diameter requires a proportional increase in thickness for the same material and architecture, ultimately resulting in a pressure hull that does not have sufficient buoyancy to support its own weight, as in a bathyscaphe. This is acceptable for civilian research submersibles, but not military submarines, which need to carry a large equipment, crew, and weapons load to fulfill their function. Construction materials with greater
 The first submarines were propelled by humans. The first mechanically driven submarine was the 1863 French , which used compressed air for propulsion. Anaerobic propulsion was first employed by the Spanish '' Ictineo II'' in 1864, which used a solution of
The first submarines were propelled by humans. The first mechanically driven submarine was the 1863 French , which used compressed air for propulsion. Anaerobic propulsion was first employed by the Spanish '' Ictineo II'' in 1864, which used a solution of
 While most early submarines used a direct mechanical connection between the combustion engine and the propeller, an alternative solution was considered as well as implemented at a very early stage. That solution consists in first converting the work of the combustion engine into electric energy via a dedicated generator. This energy is then used to drive the propeller via the electric motor and, to the extent required, for charging the batteries. In this configuration, the electric motor is thus responsible for driving the propeller at all times, regardless of whether air is available so that the combustion engine can also be used or not.
Among the pioneers of this alternative solution was the very first submarine of the Swedish Navy, HMS ''Hajen'' (later renamed ''Ub no 1''), launched in 1904. While its design was generally inspired by the first submarine commissioned by the US Navy, USS ''Holland'', it deviated from the latter in at least three significant ways: by adding a periscope, by replacing the gasoline engine by a semidiesel engine (a
While most early submarines used a direct mechanical connection between the combustion engine and the propeller, an alternative solution was considered as well as implemented at a very early stage. That solution consists in first converting the work of the combustion engine into electric energy via a dedicated generator. This energy is then used to drive the propeller via the electric motor and, to the extent required, for charging the batteries. In this configuration, the electric motor is thus responsible for driving the propeller at all times, regardless of whether air is available so that the combustion engine can also be used or not.
Among the pioneers of this alternative solution was the very first submarine of the Swedish Navy, HMS ''Hajen'' (later renamed ''Ub no 1''), launched in 1904. While its design was generally inspired by the first submarine commissioned by the US Navy, USS ''Holland'', it deviated from the latter in at least three significant ways: by adding a periscope, by replacing the gasoline engine by a semidiesel engine (a  In the following years, the Swedish Navy added another seven submarines in three different classes ( ''2nd'' class, ''Laxen'' class, and ''Braxen'' class) using the same propulsion technology but fitted with true diesel engines rather than semidiesels from the outset. Since by that time, the technology was usually based on the diesel engine rather than some other type of combustion engine, it eventually came to be known as
In the following years, the Swedish Navy added another seven submarines in three different classes ( ''2nd'' class, ''Laxen'' class, and ''Braxen'' class) using the same propulsion technology but fitted with true diesel engines rather than semidiesels from the outset. Since by that time, the technology was usually based on the diesel engine rather than some other type of combustion engine, it eventually came to be known as  Another early adopter of diesel–electric transmission was the
Another early adopter of diesel–electric transmission was the
 The problem of the diesels causing a vacuum in the submarine when the head valve is submerged still exists in later model diesel submarines but is mitigated by high-vacuum cut-off sensors that shut down the engines when the vacuum in the ship reaches a pre-set point. Modern snorkel induction masts have a fail-safe design using compressed air, controlled by a simple electrical circuit, to hold the "head valve" open against the pull of a powerful spring. Seawater washing over the mast shorts out exposed electrodes on top, breaking the control, and shutting the "head valve" while it is submerged. US submarines did not adopt the use of snorkels until after WWII.
The problem of the diesels causing a vacuum in the submarine when the head valve is submerged still exists in later model diesel submarines but is mitigated by high-vacuum cut-off sensors that shut down the engines when the vacuum in the ship reaches a pre-set point. Modern snorkel induction masts have a fail-safe design using compressed air, controlled by a simple electrical circuit, to hold the "head valve" open against the pull of a powerful spring. Seawater washing over the mast shorts out exposed electrodes on top, breaking the control, and shutting the "head valve" while it is submerged. US submarines did not adopt the use of snorkels until after WWII.

 During World War II,
During World War II,
 Steam power was resurrected in the 1950s with a nuclear-powered steam turbine driving a generator. By eliminating the need for atmospheric oxygen, the time that a submarine could remain submerged was limited only by its food stores, as breathing air was recycled and fresh water distilled from seawater. More importantly, a nuclear submarine has unlimited range at top speed. This allows it to travel from its operating base to the combat zone in a much shorter time and makes it a far more difficult target for most anti-submarine weapons. Nuclear-powered submarines have a relatively small battery and diesel engine/generator powerplant for emergency use if the reactors must be shut down.
Nuclear power is now used in all large submarines, but due to the high cost and large size of nuclear reactors, smaller submarines still use diesel–electric propulsion. The ratio of larger to smaller submarines depends on strategic needs. The US Navy,
Steam power was resurrected in the 1950s with a nuclear-powered steam turbine driving a generator. By eliminating the need for atmospheric oxygen, the time that a submarine could remain submerged was limited only by its food stores, as breathing air was recycled and fresh water distilled from seawater. More importantly, a nuclear submarine has unlimited range at top speed. This allows it to travel from its operating base to the combat zone in a much shorter time and makes it a far more difficult target for most anti-submarine weapons. Nuclear-powered submarines have a relatively small battery and diesel engine/generator powerplant for emergency use if the reactors must be shut down.
Nuclear power is now used in all large submarines, but due to the high cost and large size of nuclear reactors, smaller submarines still use diesel–electric propulsion. The ratio of larger to smaller submarines depends on strategic needs. The US Navy,
p. 14 The reactor accident in 1968 resulted in 9 fatalities and 83 other injuries. The accident in 1985 resulted in 10 fatalities and 49 other radiation injuries.

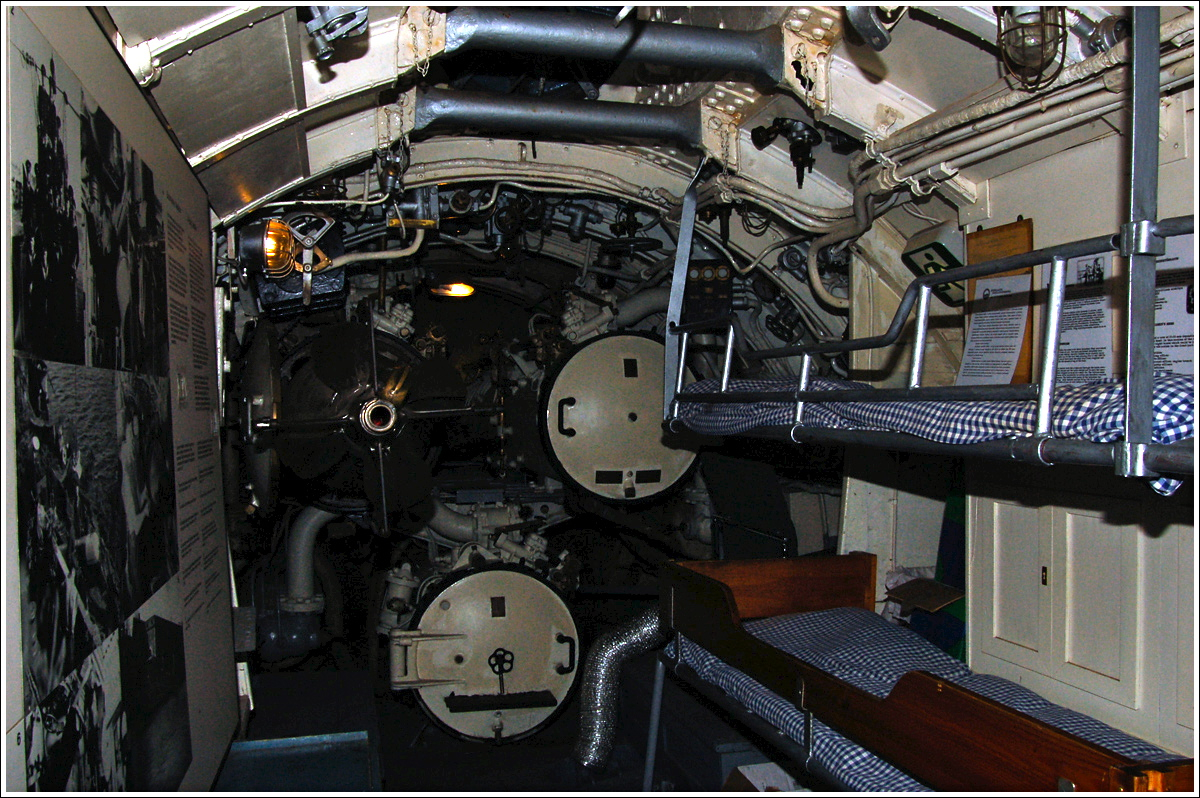 The success of the submarine is inextricably linked to the development of the
The success of the submarine is inextricably linked to the development of the
 Early submarines had few navigation aids, but modern subs have a variety of navigation systems. Modern military submarines use an inertial guidance system for navigation while submerged, but drift error unavoidably builds over time. To counter this, the crew occasionally uses the
Early submarines had few navigation aids, but modern subs have a variety of navigation systems. Modern military submarines use an inertial guidance system for navigation while submerged, but drift error unavoidably builds over time. To counter this, the crew occasionally uses the
 A typical nuclear submarine has a crew of over 80; conventional boats typically have fewer than 40. The conditions on a submarine can be difficult because crew members must work in isolation for long periods of time, without family contact, and in cramped conditions. Submarines normally maintain
A typical nuclear submarine has a crew of over 80; conventional boats typically have fewer than 40. The conditions on a submarine can be difficult because crew members must work in isolation for long periods of time, without family contact, and in cramped conditions. Submarines normally maintain

 In an emergency, submarines can transmit a signal to other ships. The crew can use escape sets such as the
In an emergency, submarines can transmit a signal to other ships. The crew can use escape sets such as the
''The Fleet Type Submarine Online''
US Navy submarine training manuals, 1944–1946 * American Society of Safety Engineers. Journal of Professional Safety. ''Submarine Accidents: A 60-Year Statistical Assessment''. C. Tingle. September 2009. pp. 31–39
Ordering full article
o
{{Authority control Electric vehicles Pressure vessels Ship types English inventions Dutch inventions 17th-century introductions
watercraft
Any vehicle used in or on water as well as underwater, including boats, ships, hovercraft and submarines, is a watercraft, also known as a water vessel or waterborne vessel. A watercraft usually has a propulsive capability (whether by sail, ...
capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''.
Definition
This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the a ...
s and robots "\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, ...
and the wet sub
A wet sub is a type of underwater vehicle, either a submarine or a submersible, that does not provide a dry environment for its occupants. It is also described as an underwater vehicle where occupants are exposed to ambient environment during oper ...
. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size.
Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918), and are now used in many navies
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includ ...
, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
s (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, blockade running, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmisher ...
, conventional land attack (for example, using a cruise missile), and covert insertion of special forces. Civilian uses include marine science
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dyna ...
, salvage, exploration, and facility inspection and maintenance. Submarines can also be modified for specialized functions such as search-and-rescue missions and undersea cable Submarine cable is any electrical cable that is laid on the seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the ...
repair. They are also used in tourism and undersea archaeology
Underwater archaeology is archaeology practiced underwater. As with all other branches of archaeology, it evolved from its roots in pre-history and in the classical era to include sites from the historical and industrial eras. Its acceptance ha ...
. Modern deep-diving submarines derive from the bathyscaphe, which evolved from the diving bell
A diving bell is a rigid chamber used to transport divers from the surface to depth and back in open water, usually for the purpose of performing underwater work. The most common types are the open-bottomed wet bell and the closed bell, which c ...
.
Most large submarines consist of a cylindrical body with hemispherical (or conical) ends and a vertical structure, usually located amidships, that houses communications and sensing devices as well as periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
s. In modern submarines, this structure is the " sail" in American usage and "fin" in European usage. A " conning tower" was a feature of earlier designs: a separate pressure hull above the main body of the boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on inl ...
that allowed the use of shorter periscopes. There is a propeller (or pump jet) at the rear, and various hydrodynamic control fins. Smaller, deep-diving, and specialty submarines may deviate significantly from this traditional design. Submarines dive and resurface by means of diving planes and changing the amount of water and air in ballast tanks to affect their buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the ...
.
Submarines encompass a wide range of types and capabilities. They include small autonomous examples using A-Navigation and one- or two-person subs that operate for a few hours, to vessels that can remain submerged for six months—such as the Russian , the biggest submarines ever built. Submarines can work at greater depths than are survivable or practical for human divers
Diver or divers may refer to:
*Diving (sport), the sport of performing acrobatics while jumping or falling into water
*Practitioner of underwater diving, including:
**scuba diving,
**freediving,
**surface-supplied diving,
**saturation diving, a ...
.
History
Etymology
The word ''submarine'' simply means 'underwater' or 'under-sea' (as insubmarine canyon
A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope, sometimes extending well onto the continental shelf, having nearly vertical walls, and occasionally having canyon wall heights of up to 5 km, from c ...
, submarine pipeline
A submarine pipeline (also known as marine, subsea or offshore pipeline) is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench.Dean, p. 338-340Gerwick, p. 583-585 In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it cross ...
) though as a noun it generally refers to a vessel that can travel underwater. The term is a contraction of ''submarine boat''. and occurs as such in several languages, e.g. French (), and Spanish (), although others retain the original term, such as Dutch (), German (), Swedish (), and Russian (: ), all of which mean 'submarine boat'. By naval tradition, submarines are still usually referred to as ''boats'' rather than as ''ships'', regardless of their size. Although referred to informally as ''boats'', U.S. submarines employ the designation USS (United States Ship
United States Ship (abbreviated as USS or U.S.S.) is a ship prefix used to identify a commissioned ship of the United States Navy and applies to a ship only while it is in commission. Before commissioning, the vessel may be referred to as a " pr ...
) at the beginning of their names, such as . In the Royal Navy, the designation HMS can refer to "His Majesty's Ship" or "His Majesty's Submarine", though the latter is sometimes rendered "HMS/m" For example, seHMS/m ''Tireless''
at
IWM IWM may refer to:
* Imperial War Museum, British national museum organisation
* Information Warfare Monitor
* iShares Russell 2000, NYSE Arca symbol
* Integrated Woz Machine, Apple computer floppy drives
* Intelligent workload management of comp ...
HMS/m ''A.1''
at
Historic England
Historic England (officially the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England) is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is tasked w ...
and submarines are generally referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships''.The Submarine service page on the official website of the Royal Navy refers to "These powerful boatand in at a speech in Washington, Adm. Sir Philip Jones announced "that the name ''Dreadnought'' will return as lead boat and class name" for Dreadnought-class submarine, Britain’s latest ballistic missile submarinesbr>
/ref>
Early human-powered submersibles

16th and 17th centuries
According to a report in ''Opusculum Jean Taisnier, Taisnieri'' published in 1562: In 1578, the English mathematician William Bourne recorded in his book ''Inventions or Devises'' one of the first plans for an underwater navigation vehicle. A few years later the Scottish mathematician and theologianJohn Napier
John Napier of Merchiston (; 1 February 1550 – 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8th Laird of Merchiston. His Latinized name was Ioan ...
wrote in his ''Secret Inventions'' (1596) that "These inventions besides devises of sayling under water with divers, other devises and strategems for harming of the enemyes by the Grace of God and worke of expert Craftsmen I hope to perform." It's unclear whether he ever carried out his idea.
Jerónimo de Ayanz y Beaumont (1553-1613) created detailed designs for two types of air-renovated submersible vehicles. They were equipped with oars, autonomous floating snorkels worked by inner pumps, portholes and gloves used for the crew to manipulate underwater objects. Ayanaz planned to use them for warfare, using them to approach enemy ships undetected and set up timed gunpowder charges on their hulls.
The first submersible of whose construction there exists reliable information was designed and built in 1620 by Cornelis Drebbel, a Dutchman in the service of James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
. It was propelled by means of oars.
18th century
By the mid-18th century, over a dozen patents for submarines/submersible boats had been granted in England. In 1747, Nathaniel Symons patented and built the first known working example of the use of a ballast tank for submersion. His design used leather bags that could fill with water to submerge the craft. A mechanism was used to twist the water out of the bags and cause the boat to resurface. In 1749, theGentlemen's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1922. It was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (from the French ''magazine'' ...
reported that a similar design had initially been proposed by Giovanni Borelli
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli (; 28 January 1608 – 31 December 1679) was a Renaissance Italian physiologist, physicist, and mathematician. He contributed to the modern principle of scientific investigation by continuing Galileo's practice of testi ...
in 1680. Further design improvement stagnated for over a century, until application of new technologies for propulsion and stability.
The first military submersible was (1775), a hand-powered acorn-shaped device designed by the American David Bushnell
David Bushnell (August 30, 1740 – 1824 or 1826), of Westbrook, Connecticut, was an American inventor, a patriot, one of the first American combat engineers, a teacher, and a medical doctor.
Bushnell invented the first submarine to be used in ...
to accommodate a single person. It was the first verified submarine capable of independent underwater operation and movement, and the first to use screws for propulsion.
19th century
 In 1800, France built , a human-powered submarine designed by American
In 1800, France built , a human-powered submarine designed by American Robert Fulton
Robert Fulton (November 14, 1765 – February 24, 1815) was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the (also known as ''Clermont''). In 1807, that steamboa ...
. They gave up on the experiment in 1804, as did the British, when they reconsidered Fulton's submarine design.
In 1850, Wilhelm Bauer
Wilhelm Bauer (23 December 1822 – 20 June 1875) was a German inventor and engineer who built several hand-powered submarines.
Biography
Wilhelm Bauer was born in Dillingen in the Kingdom of Bavaria. His father was a sergeant of a Bavarian ...
's Brandtaucher
''Brandtaucher'' ( German for ''Fire-diver'') was a submersible designed by the Bavarian inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer and built by Schweffel & Howaldt in Kiel for Schleswig-Holstein's Flotilla (part of the ''Reichsflotte'') in 1850. ...
was built in Germany. It remains the oldest known surviving Submarine in the world.
In 1864, late in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
, the Confederate navy
The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the American ...
's became the first military submarine to sink an enemy vessel, the Union sloop-of-war , using a gun-powder-filled keg on a spar as a torpedo charge. The ''Hunley'' also sank, as the explosion's shock waves killed its crew instantly, preventing them from pumping the bilge or propelling the submarine.
In 1866, was the first submarine to successfully dive, cruise underwater, and resurface under the crew's control. The design by German American Julius H. Kroehl (in German, ''Kröhl'') incorporated elements that are still used in modern submarines.
In 1866, was built at the Chilean government's request by Karl Flach, a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
engineer and immigrant. It was the fifth submarine built in the world and, along with a second submarine, was intended to defend the port of Valparaiso against attack by the Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, ...
during the Chincha Islands War
The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War ( es, Guerra hispano-sudamericana), was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The ...
.
Mechanically powered submarines
Submarines could not be put into widespread or routine service use by navies until suitable engines were developed. The era from 1863 to 1904 marked a pivotal time in submarine development, and several important technologies appeared. A number of nations built and used submarines.Diesel electric
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
propulsion became the dominant power system and equipment such as the periscope became standardized. Countries conducted many experiments on effective tactics and weapons for submarines, which led to their large impact in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
1863–1904
 The first submarine not relying on human power for propulsion was the French (''Diver''), launched in 1863, which used compressed air at .
The first submarine not relying on human power for propulsion was the French (''Diver''), launched in 1863, which used compressed air at . Narcís Monturiol
Narcís Monturiol i Estarriol (; Narciso Monturiol Estarriol, in Spanish, 28 September 1819 – 6 September 1885) was a Spanish inventor, artist and engineer born in Figueres, Catalonia, Spain. He was the inventor of the first air-independent an ...
designed the first air-independent and combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
-powered submarine, , which was launched in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, Spain in 1864.
The submarine became a potentially viable weapon with the development of the Whitehead torpedo
The Whitehead torpedo was the first self-propelled or "locomotive" torpedo ever developed. It was perfected in 1866 by Robert Whitehead from a rough design conceived by Giovanni Luppis of the Austro-Hungarian Navy in Fiume. It was driven by a t ...
, designed in 1866 by British engineer Robert Whitehead
Robert Whitehead (3 January 1823 – 14 November 1905) was an English engineer who was most famous for developing the first effective self-propelled naval torpedo.
Early life
He was born in Bolton, England, the son of James Whitehead, ...
, the first practical self-propelled or "locomotive" torpedo. The spar torpedo
A spar torpedo is a weapon consisting of a bomb placed at the end of a long pole, or spar, and attached to a boat. The weapon is used by running the end of the spar into the enemy ship. Spar torpedoes were often equipped with a barbed spear at ...
that had been developed earlier by the Confederate States Navy
The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the Navy, naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the Amer ...
was considered to be impracticable, as it was believed to have sunk both its intended target, and probably ''H. L. Hunley'', the submarine that deployed it.
The Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
inventor John Philip Holland
John Philip Holland ( ga, Seán Pilib Ó hUallacháin/Ó Maolchalann) (24 February 184112 August 1914) was an Irish engineer who developed the first submarine to be formally commissioned by the US Navy, and the first Royal Navy submarine, ''Ho ...
built a model submarine in 1876 and in 1878 demonstrated the Holland I prototype. This was followed by a number of unsuccessful designs. In 1896, he designed the Holland Type VI submarine, which used internal combustion engine power on the surface and electric battery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
power underwater. Launched on 17 May 1897 at Navy Lt. Lewis Nixon's Crescent Shipyard
Crescent Shipyard, located on Newark Bay in Elizabeth, New Jersey, built a number of ships for the United States Navy and allied nations as well during their production run, which lasted about ten years while under the Crescent name and banner. ...
in Elizabeth, New Jersey, ''Holland VI'' was purchased by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
on 11 April 1900, becoming the Navy's first commissioned submarine, christened .
Discussions between the English clergyman and inventor George Garrett and the Swedish industrialist Thorsten Nordenfelt
Thorsten Nordenfelt (1 March 1842 – 8 February 1920), was a Swedish inventor and industrialist.
Career
Nordenfelt was born in Örby outside Kinna, Sweden, the son of a colonel. The surname was and is often spelled Nordenfeldt, though Thorsten ...
led to the first practical steam-powered submarines, armed with torpedoes and ready for military use. The first was ''Nordenfelt I'', a 56-tonne, vessel similar to Garrett's ill-fated (1879), with a range of , armed with a single torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
, in 1885.
 A reliable means of propulsion for the submerged vessel was only made possible in the 1880s with the advent of the necessary electric battery technology. The first electrically powered boats were built by Isaac Peral y Caballero in
A reliable means of propulsion for the submerged vessel was only made possible in the 1880s with the advent of the necessary electric battery technology. The first electrically powered boats were built by Isaac Peral y Caballero in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
(who built ), Dupuy de Lôme (who built ) and Gustave Zédé
Gustave Zédé was a French naval engineer and pioneering designer of submarines.
Early life
He was born in Paris in February 1825. After studying at the École Polytechnique in November 1843 he qualified in 1845 as a Marine engineer and went t ...
(who built ''Sirène'') in France, and James Franklin Waddington (who built ''Porpoise'') in England. Peral's design featured torpedoes and other systems that later became standard in submarines.

 Commissioned in June 1900, the French steam and electric employed the now typical double-hull design, with a pressure hull inside the outer shell. These 200-ton ships had a range of over underwater. The French submarine ''Aigrette'' in 1904 further improved the concept by using a diesel rather than a gasoline engine for surface power. Large numbers of these submarines were built, with seventy-six completed before 1914.
The Royal Navy commissioned five s from
Commissioned in June 1900, the French steam and electric employed the now typical double-hull design, with a pressure hull inside the outer shell. These 200-ton ships had a range of over underwater. The French submarine ''Aigrette'' in 1904 further improved the concept by using a diesel rather than a gasoline engine for surface power. Large numbers of these submarines were built, with seventy-six completed before 1914.
The Royal Navy commissioned five s from Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public i ...
, Barrow-in-Furness
Barrow-in-Furness is a port town in Cumbria, England. Historic counties of England, Historically in Lancashire, it was incorporated as a municipal borough in 1867 and merged with Dalton-in-Furness Urban District in 1974 to form the Borough of B ...
, under licence from the Holland Torpedo Boat Company from 1901 to 1903. Construction of the boats took longer than anticipated, with the first only ready for a diving trial at sea on 6 April 1902. Although the design had been purchased entirely from the US company, the actual design used was an untested improvement to the original Holland design using a new petrol engine.
These types of submarines were first used during the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–05. Due to the blockade at Port Arthur, the Russians sent their submarines to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, c ...
, where by 1 January 1905 there were seven boats, enough to create the world's first "operational submarine fleet". The new submarine fleet began patrols on 14 February, usually lasting for about 24 hours each. The first confrontation with Japanese warships occurred on 29 April 1905 when the Russian submarine ''Som'' was fired upon by Japanese torpedo boats, but then withdrew.
World War I
 Military submarines first made a significant impact in
Military submarines first made a significant impact in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Forces such as the U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s of Germany saw action in the First Battle of the Atlantic
The Atlantic U-boat campaign of World War I (sometimes called the "First Battle of the Atlantic", in reference to the World War II campaign of that name) was the prolonged naval conflict between German submarines and the Allied navies in Atla ...
, and were responsible for sinking , which was sunk as a result of unrestricted submarine warfare
Unrestricted submarine warfare is a type of naval warfare in which submarines sink merchant ships such as freighters and tankers without warning, as opposed to attacks per prize rules (also known as "cruiser rules") that call for warships to s ...
and is often cited among the reasons for the entry of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
into the war.
At the outbreak of the war, Germany had only twenty submarines immediately available for combat, although these included vessels of the diesel-engined '' U-19'' class, which had a sufficient range of and speed of to allow them to operate effectively around the entire British coast., By contrast, the Royal Navy had a total of 74 submarines, though of mixed effectiveness. In August 1914, a flotilla of ten U-boats sailed from their base in Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
to attack Royal Navy warships in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
in the first submarine war patrol in history.
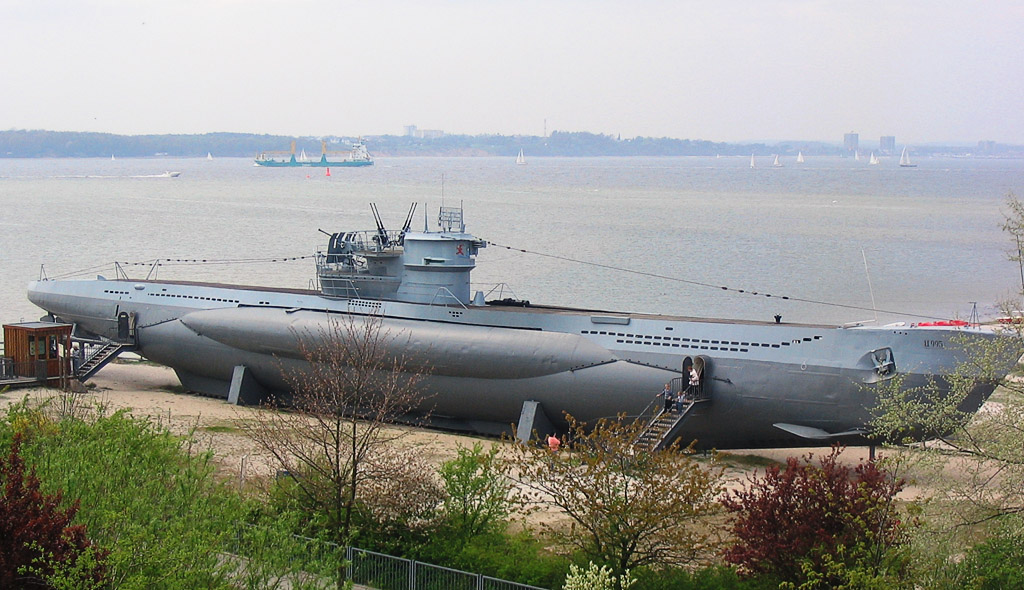
The U-boats' ability to function as practical war machines relied on new tactics, their numbers, and submarine technologies such as combination diesel–electric power system developed in the preceding years. More submersibles than true submarines, U-boats operated primarily on the surface using regular engines, submerging occasionally to attack under battery power. They were roughly triangular in cross-section, with a distinct keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
to control rolling while surfaced, and a distinct bow. During World War I more than 5,000 Allied ships were sunk by U-boats.
The British responded to the German developments in submarine technology with the creation of the K-class submarines. However, these submarines were notoriously dangerous to operate due to their various design flaws and poor maneuverability.
World War II

 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Germany used submarines to devastating effect in the Battle of the Atlantic, where it attempted to cut Britain's supply routes by sinking more merchant ship
A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are ...
s than Britain could replace. These merchant ships were vital to supply Britain's population with food, industry with raw material, and armed forces with fuel and armaments. Although the U-boats had been updated in the interwar years, the major innovation was improved communications, encrypted using the Enigma cipher machine. This allowed for mass-attack naval tactics
Naval tactics and doctrine is the collective name for methods of engaging and defeating an enemy ship or fleet in battle at sea during naval warfare, the naval equivalent of military tactics on land.
Naval tactics are distinct from naval strat ...
(''Rudeltaktik'', commonly known as " wolfpack"), but was also ultimately the U-boats' downfall. By the end of the war, almost 3,000 Allied ships (175 warships, 2,825 merchantmen) had been sunk by U-boats. Although successful early in the war, Germany's U-boat fleet suffered heavy casualties, losing 793 U-boats and about 28,000 submariners out of 41,000, a casualty rate of about 70%.
The Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrend ...
operated the most varied fleet of submarines of any navy, including ''Kaiten
were crewed torpedoes and suicide craft, used by the Imperial Japanese Navy in the final stages of World War II.
History
In recognition of the unfavorable progress of the war, towards the end of 1943 the Japanese high command considered s ...
'' crewed torpedoes, midget submarines ( and es), medium-range submarines, purpose-built supply submarines and long-range fleet submarine
A fleet submarine is a submarine with the speed, range, and endurance to operate as part of a navy's battle fleet. Examples of fleet submarines are the British First World War era K class and the American World War II era ''Gato'' class.
The t ...
s. They also had submarines with the highest submerged speeds during World War II (s) and submarines that could carry multiple aircraft (s). They were also equipped with one of the most advanced torpedoes of the conflict, the oxygen-propelled Type 95. Nevertheless, despite their technical prowess, Japan chose to use its submarines for fleet warfare, and consequently were relatively unsuccessful, as warships were fast, maneuverable and well-defended compared to merchant ships.
The submarine force was the most effective anti-ship weapon in the American arsenal. Submarines, though only about 2 percent of the U.S. Navy, destroyed over 30 percent of the Japanese Navy, including 8 aircraft carriers, 1 battleship and 11 cruisers. US submarines also destroyed over 60 percent of the Japanese merchant fleet, crippling Japan's ability to supply its military forces and industrial war effort. Allied submarines in the Pacific War
Allied submarines were used extensively during the Pacific War and were a key contributor to the defeat of the Empire of Japan.
During the war, submarines of the United States Navy were responsible for 56% of Japan's merchant marine losses; ...
destroyed more Japanese shipping than all other weapons combined. This feat was considerably aided by the Imperial Japanese Navy's failure to provide adequate escort forces for the nation's merchant fleet.
During World War II, 314 submarines served in the US Navy, of which nearly 260 were deployed to the Pacific.O'Kane, p. 333 When the Japanese attacked Hawaii in December 1941, 111 boats were in commission; 203 submarines from the , , and es were commissioned during the war. During the war, 52 US submarines were lost to all causes, with 48 directly due to hostilities. US submarines sank 1,560 enemy vessels, a total tonnage of 5.3 million tons (55% of the total sunk).Blair, p. 878
The Royal Navy Submarine Service
The Royal Navy Submarine Service is one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. It is sometimes known as the Silent Service, as submarines are generally required to operate undetected.
The service operates six fleet submarines ( SSNs) ...
was used primarily in the classic Axis blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
. Its major operating areas were around Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
(against the Axis supply routes to North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
), and in the Far East. In that war, British submarines sank 2 million tons of enemy shipping and 57 major warships, the latter including 35 submarines. Among these is the only documented instance of a submarine sinking another submarine while both were submerged. This occurred when engaged
An engagement or betrothal is the period of time between the declaration of acceptance of a marriage proposal and the marriage itself (which is typically but not always commenced with a wedding). During this period, a couple is said to be ''fi ...
; the ''Venturer'' crew manually computed a successful firing solution against a three-dimensionally maneuvering target using techniques which became the basis of modern torpedo computer targeting systems. Seventy-four British submarines were lost, the majority, forty-two, in the Mediterranean.
Cold-War military models
 The first launch of a cruise missile ( SSM-N-8 Regulus) from a submarine occurred in July 1953, from the deck of , a World War II fleet boat modified to carry the missile with a
The first launch of a cruise missile ( SSM-N-8 Regulus) from a submarine occurred in July 1953, from the deck of , a World War II fleet boat modified to carry the missile with a nuclear warhead
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
. ''Tunny'' and its sister boat, , were the United States' first nuclear deterrent patrol submarines. In the 1950s, nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
partially replaced diesel–electric propulsion. Equipment was also developed to extract oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
from sea water. These two innovations gave submarines the ability to remain submerged for weeks or months. Most of the naval submarines built since that time in the US, the Soviet Union/Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, Britain, and France have been powered by nuclear reactors.
In 1959–1960, the first ballistic missile submarines were put into service by both the United States () and the Soviet Union () as part of the Cold War nuclear deterrent
Nuclear strategy involves the development of doctrines and strategies for the production and use of nuclear weapons.
As a sub-branch of military strategy, nuclear strategy attempts to match nuclear weapons as means to political ends. In addit ...
strategy.
During the Cold War, the US and the Soviet Union maintained large submarine fleets that engaged in cat-and-mouse games. The Soviet Union lost at least four submarines during this period: was lost in 1968 (a part of which the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
retrieved from the ocean floor with the Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in th ...
-designed ship ''Glomar Explorer''), in 1970, in 1986, and in 1989 (which held a depth record among military submarines—). Many other Soviet subs, such as (the first Soviet nuclear submarine, and the first Soviet sub to reach the North Pole) were badly damaged by fire or radiation leaks. The US lost two nuclear submarines during this time: due to equipment failure during a test dive while at its operational limit, and due to unknown causes.
During India's intervention in the Bangladesh Liberation War, the Pakistan Navy's sank the Indian frigate . This was the first sinking by a submarine since World War II. During the same war, , a ''Tench''-class submarine on loan to Pakistan from the US, was sunk by the Indian Navy
The Indian Navy is the maritime branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. As a blue-water navy, it operates si ...
. It was the first submarine combat loss since World War II. In 1982 during the Falklands War, the Argentine cruiser was sunk by the British submarine , the first sinking by a nuclear-powered submarine in war. Some weeks later, on 16 June, during the Lebanon War, an unnamed Israeli submarine torpedoed and sank the Lebanese coaster ''Transit'', which was carrying 56 Palestinian refugees to Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
, in the belief that the vessel was evacuating anti-Israeli militias. The ship was hit by two torpedoes, managed to run aground but eventually sank. There were 25 dead, including her captain. The Israeli Navy
The Israeli Navy ( he, חיל הים הישראלי, ''Ḥeil HaYam HaYisraeli'' (English: The Israeli Sea Corps); ar, البحرية الإسرائيلية) is the naval warfare service arm of the Israel Defense Forces, operating primarily in ...
disclosed the incident in November 2018.
21st century
Usage
Military

 Before and during
Before and during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the primary role of the submarine was anti-surface ship warfare. Submarines would attack either on the surface using deck guns, or submerged using torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
es. They were particularly effective in sinking Allied transatlantic shipping in both World Wars, and in disrupting Japanese supply routes and naval operations in the Pacific in World War II.
Mine-laying submarines were developed in the early part of the 20th century. The facility was used in both World Wars. Submarines were also used for inserting and removing covert agents and military forces in special operations
Special operations (S.O.) are military activities conducted, according to NATO, by "specially designated, organized, selected, trained, and equipped forces using unconventional techniques and modes of employment". Special operations may include ...
, for intelligence gathering, and to rescue aircrew during air attacks on islands, where the airmen would be told of safe places to crash-land so the submarines could rescue them. Submarines could carry cargo through hostile waters or act as supply vessels for other submarines.
Submarines could usually locate and attack other submarines only on the surface, although managed to sink with a four torpedo spread while both were submerged. The British developed a specialized anti-submarine submarine in WWI, the R class. After WWII, with the development of the homing torpedo, better sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
systems, and nuclear propulsion
Nuclear propulsion includes a wide variety of propulsion methods that use some form of nuclear reaction as their primary power source. The idea of using nuclear material for propulsion dates back to the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 it was ...
, submarines also became able to hunt each other effectively.
The development of submarine-launched ballistic missile and submarine-launched cruise missiles gave submarines a substantial and long-ranged ability to attack both land and sea targets with a variety of weapons ranging from cluster bombs to nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s.
The primary defense of a submarine lies in its ability to remain concealed in the depths of the ocean. Early submarines could be detected by the sound they made. Water is an excellent conductor of sound (much better than air), and submarines can detect and track comparatively noisy surface ships from long distances. Modern submarines are built with an emphasis on stealth. Advanced propeller designs, extensive sound-reducing insulation, and special machinery help a submarine remain as quiet as ambient ocean noise, making them difficult to detect. It takes specialized technology to find and attack modern submarines.
Active sonar uses the reflection of sound emitted from the search equipment to detect submarines. It has been used since WWII by surface ships, submarines and aircraft (via dropped buoys and helicopter "dipping" arrays), but it reveals the emitter's position, and is susceptible to counter-measures.
A concealed military submarine is a real threat, and because of its stealth, can force an enemy navy to waste resources searching large areas of ocean and protecting ships against attack. This advantage was vividly demonstrated in the 1982 Falklands War when the British nuclear-powered
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
submarine sank the Argentine cruiser . After the sinking the Argentine Navy recognized that they had no effective defense against submarine attack, and the Argentine surface fleet withdrew to port for the remainder of the war, though an Argentine submarine remained at sea.
Civilian
Although the majority of the world's submarines are military, there are some civilian submarines, which are used for tourism, exploration, oil and gas platform inspections, and pipeline surveys. Some are also used in illegal activities. The Submarine Voyage ride opened atDisneyland
Disneyland is a theme park in Anaheim, California. Opened in 1955, it was the first theme park opened by The Walt Disney Company and the only one designed and constructed under the direct supervision of Walt Disney. Disney initially envision ...
in 1959, but although it ran under water it was not a true submarine, as it ran on tracks and was open to the atmosphere. The first tourist submarine was , which went into service in 1964 at Expo64. By 1997 there were 45 tourist submarines operating around the world. Submarines with a crush depth
Depth ratings are primary design parameters and measures of a submarine's ability to operate underwater. The depths to which submarines can dive are limited by the strengths of their hulls.
Ratings
The hull of a submarine must be able to with ...
in the range of are operated in several areas worldwide, typically with bottom depths around , with a carrying capacity of 50 to 100 passengers.
In a typical operation a surface vessel carries passengers to an offshore operating area and loads them into the submarine. The submarine then visits underwater points of interest such as natural or artificial reef structures. To surface safely without danger of collision the location of the submarine is marked with an air release and movement to the surface is coordinated by an observer in a support craft.
A recent development is the deployment of so-called narco-submarine
A narco-submarine (also called a drug sub or narco sub) is a type of custom ocean-going self-propelled typically semi-submersible (sometimes fully-submersible) vessel built for smugglers.
Newer submarines are 'nearly-fully' submersible to be ...
s by South American drug smugglers to evade law enforcement detection. Although they occasionally deploy true submarines, most are self-propelled semi-submersible
Semi-submersible may refer to a self-propelled vessel, such as:
* Heavy-lift ship, which partially submerge to allow their cargo (another ship) to float into place for transport
*Narco-submarine, some of which remained partially on the surface
* ...
s, where a portion of the craft remains above water at all times. In September 2011, Colombian authorities seized a 16-meter-long submersible that could hold a crew of 5, costing about $2 million. The vessel belonged to FARC
The Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia – People's Army ( es, link=no, Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de ColombiaEjército del Pueblo, FARC–EP or FARC) is a Marxist–Leninist guerrilla group involved in the continuing Colombian confl ...
rebels and had the capacity to carry at least 7 tonnes of drugs.
Polar operations
 * 1903 –
* 1903 – Simon Lake
Simon Lake (September 4, 1866 – June 23, 1945) was a Quaker American mechanical engineer and naval architect who obtained over two hundred patents for advances in naval design and competed with John Philip Holland to build the first submarines f ...
submarine ''Protector'' surfaced through ice off Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is an American seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, and northeast of New Yor ...
.McLaren, Alfred S., CAPT USN "Under the Ice in Submarines" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' July 1981, pp. 105–9
* 1930 – operated under ice near Spitsbergen.
* 1937 – Soviet submarine ''Krasnogvardeyets'' operated under ice in the Denmark Strait
The Denmark Strait () or Greenland Strait ( , 'Greenland Sound') is an oceanic strait between Greenland to its northwest and Iceland to its southeast. The Norwegian island of Jan Mayen lies northeast of the strait.
Geography
The strait connect ...
.
* 1941–45 – German U-boats operated under ice from the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
to the Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, t ...
.
* 1946 – used upward-beamed fathometer in Operation Nanook
Operation Nanook (OP NANOOK; french: Opération Nanook) is an annual sovereignty operation and manoeuvre warfare exercise conducted by the Canadian Armed Forces in the Arctic. Sovereignty patrols in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and northern C ...
in the Davis Strait
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The strait was named for the English explorer John ...
.
* 1946–47 – used under-ice sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
in Operation High Jump in the Antarctic.
* 1947 – used upward-beamed echo sounder under pack ice in the Chukchi Sea.
* 1948 – developed techniques for making vertical ascents and descents through polynya
A polynya () is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as a geographical term for an area of unfrozen seawater within otherwise contiguous pack ice or fast ice. It is a loanword from the Russian полынья (), which r ...
s in the Chukchi Sea.
* 1952 – used an expanded upward-beamed sounder array in the Beaufort Sea.
* 1957 – reached 87 degrees north near Spitsbergen.
* 3 August 1958 – ''Nautilus'' used an inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (dir ...
to reach the North Pole.
* 17 March 1959 – surfaced through the ice at the north pole.
* 1960 – transited under ice over the shallow ( deep) Bering-Chukchi shelf.
* 1960 – transited the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
under ice.
* 1962 – Soviet reached the north pole.
* 1970 – carried out an extensive undersea mapping survey of the Siberian continental shelf.
* 1971 – reached the North Pole.
* conducted three Polar Exercises: 1976 (with US actor Charlton Heston aboard); 1984 joint operations with ; and 1990 joint exercises with .
* 6 May 1986 – , and meet and surface together at the Geographic North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Mag ...
. First three-submarine surfacing at the Pole.
* 19 May 1987 – joined and at the North Pole.
* March 2007 – participated in the Joint US Navy/Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
Ice Exercise 2007 (ICEX-2007) in the Arctic Ocean with the .
* March 2009 – took part in Ice Exercise 2009 to test submarine operability and war-fighting capability in Arctic conditions.
Technology
Buoyancy and trim
 All surface ships, as well as surfaced submarines, are in a positively
All surface ships, as well as surfaced submarines, are in a positively buoyant
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pr ...
condition, weighing less than the volume of water they would displace if fully submerged. To submerge hydrostatically, a ship must have negative buoyancy, either by increasing its own weight or decreasing its displacement of water. To control their displacement and weight, submarines have ballast tanks, which can hold varying amounts of water and air.
For general submersion or surfacing, submarines use the main ballast tanks (MBTs), which are ambient pressure tanks, filled with water to submerge, or with air to surface. While submerged, MBTs generally remain flooded, which simplifies their design, and on many submarines these tanks are a section of the space between the light hull and the pressure hull. For more precise control of depth, submarines use smaller depth control tanks (DCTs)—also called hard tanks (due to their ability to withstand higher pressure), or trim tanks. These are variable buoyancy pressure vessel
A variable buoyancy pressure vessel system is a type of rigid buoyancy control device for diving systems that retains a constant volume and varies its density by changing the weight (mass) of the contents, either by moving the ambient fluid into a ...
s, a type of buoyancy control device. The amount of water in depth control tanks can be adjusted to hydrostatically change depth or to maintain a constant depth as outside conditions (mainly water density) change. Depth control tanks may be located either near the submarine's center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
, to minimise the effect on trim, or separated along the length of the hull so they can also be used to adjust static trim by transfer of water between them.
When submerged, the water pressure on a submarine's hull can reach for steel submarines and up to for titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
submarines like , while interior pressure remains relatively unchanged. This difference results in hull compression, which decreases displacement. Water density also marginally increases with depth, as the salinity and pressure are higher. This change in density incompletely compensates for hull compression, so buoyancy decreases as depth increases. A submerged submarine is in an unstable equilibrium, having a tendency to either sink or float to the surface. Keeping a constant depth requires continual operation of either the depth control tanks or control surfaces.
Submarines in a neutral buoyancy condition are not intrinsically trim-stable. To maintain desired longitudinal trim, submarines use forward and aft trim tanks. Pumps move water between the tanks, changing weight distribution and pitching the sub up or down. A similar system may be used to maintain transverse trim.
Control surfaces
 The hydrostatic effect of variable ballast tanks is not the only way to control the submarine underwater. Hydrodynamic maneuvering is done by several control surfaces, collectively known as diving planes or hydroplanes, which can be moved to create hydrodynamic forces when a submarine moves longitudinally at sufficient speed. In the classic cruciform stern configuration, the horizontal stern planes serve the same purpose as the trim tanks, controlling the trim. Most submarines additionally have forward horizontal planes, normally placed on the bow until the 1960s but often on the sail on later designs, where they are closer to the center of gravity and can control depth with less effect on the trim.
The hydrostatic effect of variable ballast tanks is not the only way to control the submarine underwater. Hydrodynamic maneuvering is done by several control surfaces, collectively known as diving planes or hydroplanes, which can be moved to create hydrodynamic forces when a submarine moves longitudinally at sufficient speed. In the classic cruciform stern configuration, the horizontal stern planes serve the same purpose as the trim tanks, controlling the trim. Most submarines additionally have forward horizontal planes, normally placed on the bow until the 1960s but often on the sail on later designs, where they are closer to the center of gravity and can control depth with less effect on the trim.
 An obvious way to configure the control surfaces at the stern of a submarine is to use vertical planes to control yaw and horizontal planes to control pitch, which gives them the shape of a cross when seen from astern of the vessel. In this configuration, which long remained the dominant one, the horizontal planes are used to control the trim and depth and the vertical planes to control sideways maneuvers, like the rudder of a surface ship.
Alternatively, the rear control surfaces can be combined into what has become known as an x-stern or an x-rudder. Although less intuitive, such a configuration has turned out to have several advantages over the traditional cruciform arrangement. First, it improves maneuverability, horizontally as well as vertically. Second, the control surfaces are less likely to get damaged when landing on, or departing from, the seabed as well as when mooring and unmooring alongside. Finally, it is safer in that one of the two diagonal lines can counteract the other with respect to vertical as well as horizontal motion if one of them accidentally gets stuck.
An obvious way to configure the control surfaces at the stern of a submarine is to use vertical planes to control yaw and horizontal planes to control pitch, which gives them the shape of a cross when seen from astern of the vessel. In this configuration, which long remained the dominant one, the horizontal planes are used to control the trim and depth and the vertical planes to control sideways maneuvers, like the rudder of a surface ship.
Alternatively, the rear control surfaces can be combined into what has become known as an x-stern or an x-rudder. Although less intuitive, such a configuration has turned out to have several advantages over the traditional cruciform arrangement. First, it improves maneuverability, horizontally as well as vertically. Second, the control surfaces are less likely to get damaged when landing on, or departing from, the seabed as well as when mooring and unmooring alongside. Finally, it is safer in that one of the two diagonal lines can counteract the other with respect to vertical as well as horizontal motion if one of them accidentally gets stuck.
 The x-stern was first tried in practice in the early 1960s on the USS ''Albacore'', an experimental submarine of the US Navy. While the arrangement was found to be advantageous, it was nevertheless not used on US production submarines that followed due to the fact that it requires the use of a computer to manipulate the control surfaces to the desired effect. Instead, the first to use an x-stern in standard operations was the Swedish Navy with its ''Sjöormen'' class, the lead submarine of which was launched in 1967, before the ''Albacore'' had even finished her test runs. Since it turned out to work very well in practice, all subsequent classes of Swedish submarines ( ''Näcken'', ''Västergötland'', ''Gotland'', and ''Blekinge'' class) have or will come with an x-rudder.
The x-stern was first tried in practice in the early 1960s on the USS ''Albacore'', an experimental submarine of the US Navy. While the arrangement was found to be advantageous, it was nevertheless not used on US production submarines that followed due to the fact that it requires the use of a computer to manipulate the control surfaces to the desired effect. Instead, the first to use an x-stern in standard operations was the Swedish Navy with its ''Sjöormen'' class, the lead submarine of which was launched in 1967, before the ''Albacore'' had even finished her test runs. Since it turned out to work very well in practice, all subsequent classes of Swedish submarines ( ''Näcken'', ''Västergötland'', ''Gotland'', and ''Blekinge'' class) have or will come with an x-rudder.
 The Kockums shipyard responsible for the design of the x-stern on Swedish submarines eventually exported it to Australia with the ''Collins'' class as well as to Japan with the ''Sōryū'' class. With the introduction of the type 212, the German and Italian Navies came to feature it as well. The US Navy with its ''Columbia'' class, the British Navy with its ''Dreadnought'' class, and the French Navy with its ''Barracuda'' class are all about to join the x-stern family. Hence, as judged by the situation in the early 2020s, the x-stern is about to become the dominant technology.
When a submarine performs an emergency surfacing, all depth and trim control methods are used simultaneously, together with propelling the boat upwards. Such surfacing is very quick, so the sub may even partially jump out of the water, potentially damaging submarine systems.
The Kockums shipyard responsible for the design of the x-stern on Swedish submarines eventually exported it to Australia with the ''Collins'' class as well as to Japan with the ''Sōryū'' class. With the introduction of the type 212, the German and Italian Navies came to feature it as well. The US Navy with its ''Columbia'' class, the British Navy with its ''Dreadnought'' class, and the French Navy with its ''Barracuda'' class are all about to join the x-stern family. Hence, as judged by the situation in the early 2020s, the x-stern is about to become the dominant technology.
When a submarine performs an emergency surfacing, all depth and trim control methods are used simultaneously, together with propelling the boat upwards. Such surfacing is very quick, so the sub may even partially jump out of the water, potentially damaging submarine systems.
Hull
Overview
 Modern submarines are cigar-shaped. This design, also used in very early submarines, is sometimes called a "
Modern submarines are cigar-shaped. This design, also used in very early submarines, is sometimes called a "teardrop hull
A teardrop hull is a submarine hull design which emphasizes submerged performance over surfaced performance. It was somewhat commonly used in the early stages of submarine development, but was gradually abandoned in the early 20th century in fav ...
". It reduces hydrodynamic drag when the sub is submerged, but decreases the sea-keeping capabilities and increases drag while surfaced. Since the limitations of the propulsion systems of early submarines forced them to operate surfaced most of the time, their hull designs were a compromise. Because of the slow submerged speeds of those subs, usually, well below 10 kt (18 km/h), the increased drag for underwater travel was acceptable. Late in World War II, when technology allowed faster and longer submerged operation and increased aircraft surveillance forced submarines to stay submerged, hull designs became teardrop shaped again to reduce drag and noise. was a unique research submarine that pioneered the American version of the teardrop hull form (sometimes referred to as an "Albacore hull") of modern submarines. On modern military submarines the outer hull is covered with a layer of sound-absorbing rubber, or anechoic plating, to reduce detection.
The occupied pressure hulls of deep-diving submarines such as are spherical instead of cylindrical. This allows a more even distribution of stress and efficient use of materials to withstand external pressure as it gives the most internal volume for structural weight and is the most efficient shape to avoid buckling instability in compression. A frame is usually affixed to the outside of the pressure hull, providing attachment for ballast and trim systems, scientific instrumentation, battery packs, syntactic flotation foam, and lighting.
A raised tower on top of a standard submarine accommodates the periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
and electronics masts, which can include radio, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, electronic warfare
Electronic warfare (EW) is any action involving the use of the electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum) or directed energy to control the spectrum, attack an enemy, or impede enemy assaults. The purpose of electronic warfare is to deny the opponen ...
, and other systems. It might also include a snorkel mast. In many early classes of submarines (see history), the control room, or "conn", was located inside this tower, which was known as the " conning tower". Since then, the conn has been located within the hull of the submarine, and the tower is now called the "sail" or "fin". The conn is distinct from the "bridge", a small open platform in the top of the sail, used for observation during surface operation.
"Bathtubs" are related to conning towers but are used on smaller submarines. The bathtub is a metal cylinder surrounding the hatch that prevents waves from breaking directly into the cabin. It is needed because surfaced submarines have limited freeboard
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard
is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relativ ...
, that is, they lie low in the water. Bathtubs help prevent swamping the vessel.
Single and double hulls
 Modern submarines and submersibles usually have, as did the earliest models, a single hull. Large submarines generally have an additional hull or hull sections outside. This external hull, which actually forms the shape of submarine, is called the outer hull ('' casing'' in the Royal Navy) or light hull, as it does not have to withstand a pressure difference. Inside the outer hull there is a strong hull, or
Modern submarines and submersibles usually have, as did the earliest models, a single hull. Large submarines generally have an additional hull or hull sections outside. This external hull, which actually forms the shape of submarine, is called the outer hull ('' casing'' in the Royal Navy) or light hull, as it does not have to withstand a pressure difference. Inside the outer hull there is a strong hull, or pressure hull
A submarine hull has two major components, the ''light hull'' and the ''pressure hull''. The light hull (''casing'' in British usage) of a submarine is the outer non-watertight hull which provides a hydrodynamically efficient shape. The pressure ...
, which withstands sea pressure and has normal atmospheric pressure inside.
As early as World War I, it was realized that the optimal shape for withstanding pressure conflicted with the optimal shape for seakeeping and minimal drag at the surface, and construction difficulties further complicated the problem. This was solved either by a compromise shape, or by using two layered hulls: the internal strength hull for withstanding pressure, and an external fairing for hydrodynamic shape. Until the end of World War II, most submarines had an additional partial casing on the top, bow and stern, built of thinner metal, which was flooded when submerged. Germany went further with the Type XXI, a general predecessor of modern submarines, in which the pressure hull was fully enclosed inside the light hull, but optimized for submerged navigation, unlike earlier designs that were optimized for surface operation.
 After World War II, approaches split. The Soviet Union changed its designs, basing them on German developments. All post-World War II heavy Soviet and Russian submarines are built with a double hull structure. American and most other Western submarines switched to a primarily single-hull approach. They still have light hull sections in the bow and stern, which house main ballast tanks and provide a hydrodynamically optimized shape, but the main cylindrical hull section has only a single plating layer. Double hulls are being considered for future submarines in the United States to improve payload capacity, stealth and range.
After World War II, approaches split. The Soviet Union changed its designs, basing them on German developments. All post-World War II heavy Soviet and Russian submarines are built with a double hull structure. American and most other Western submarines switched to a primarily single-hull approach. They still have light hull sections in the bow and stern, which house main ballast tanks and provide a hydrodynamically optimized shape, but the main cylindrical hull section has only a single plating layer. Double hulls are being considered for future submarines in the United States to improve payload capacity, stealth and range.
Pressure hull
 The pressure hull is generally constructed of thick high-strength steel with a complex structure and high strength reserve, and is separated by watertight bulkheads into several compartments. There are also examples of more than two hulls in a submarine, like the , which has two main pressure hulls and three smaller ones for control room, torpedoes and steering gear, with the missile launch system between the main hulls, all surrounded and supported by the outer light hydrodynamic hull. When submerged the pressure hull provides most of the buoyancy for the whole vessel.
The dive depth cannot be increased easily. Simply making the hull thicker increases the structural weight and requires reduction of onboard equipment weight, and increasing the diameter requires a proportional increase in thickness for the same material and architecture, ultimately resulting in a pressure hull that does not have sufficient buoyancy to support its own weight, as in a bathyscaphe. This is acceptable for civilian research submersibles, but not military submarines, which need to carry a large equipment, crew, and weapons load to fulfill their function. Construction materials with greater
The pressure hull is generally constructed of thick high-strength steel with a complex structure and high strength reserve, and is separated by watertight bulkheads into several compartments. There are also examples of more than two hulls in a submarine, like the , which has two main pressure hulls and three smaller ones for control room, torpedoes and steering gear, with the missile launch system between the main hulls, all surrounded and supported by the outer light hydrodynamic hull. When submerged the pressure hull provides most of the buoyancy for the whole vessel.
The dive depth cannot be increased easily. Simply making the hull thicker increases the structural weight and requires reduction of onboard equipment weight, and increasing the diameter requires a proportional increase in thickness for the same material and architecture, ultimately resulting in a pressure hull that does not have sufficient buoyancy to support its own weight, as in a bathyscaphe. This is acceptable for civilian research submersibles, but not military submarines, which need to carry a large equipment, crew, and weapons load to fulfill their function. Construction materials with greater specific strength
The specific strength is a material's (or muscle's) strength (force per unit area at failure) divided by its density. It is also known as the strength-to-weight ratio or strength/weight ratio or strength-to-mass ratio. In fiber or textile applic ...
and specific modulus
Specific modulus is a materials property consisting of the elastic modulus per mass density of a material. It is also known as the stiffness to weight ratio or specific stiffness. High specific modulus materials find wide application in aerospace a ...
are needed.
WWI submarines had hulls of carbon steel, with a maximum depth. During WWII, high-strength alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
ed steel was introduced, allowing depths. High-strength alloy steel remains the primary material for submarines today, with depths, which cannot be exceeded on a military submarine without design compromises. To exceed that limit, a few submarines were built with titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
hulls. Titanium alloys can be stronger than steel, lighter, and most importantly, have higher immersed specific strength
The specific strength is a material's (or muscle's) strength (force per unit area at failure) divided by its density. It is also known as the strength-to-weight ratio or strength/weight ratio or strength-to-mass ratio. In fiber or textile applic ...
and specific modulus
Specific modulus is a materials property consisting of the elastic modulus per mass density of a material. It is also known as the stiffness to weight ratio or specific stiffness. High specific modulus materials find wide application in aerospace a ...
. Titanium is also not ferromagnetic, important for stealth. Titanium submarines were built by the Soviet Union, which developed specialized high-strength alloys. It has produced several types of titanium submarines. Titanium alloys allow a major increase in depth, but other systems must be redesigned to cope, so test depth was limited to for the , the deepest-diving combat submarine. An may have successfully operated at , though continuous operation at such depths would produce excessive stress on many submarine systems. Titanium does not flex as readily as steel, and may become brittle after many dive cycles. Despite its benefits, the high cost of titanium construction led to the abandonment of titanium submarine construction as the Cold War ended. Deep-diving civilian submarines have used thick acrylic
Acrylic may refer to:
Chemicals and materials
* Acrylic acid, the simplest acrylic compound
* Acrylate polymer, a group of polymers (plastics) noted for transparency and elasticity
* Acrylic resin, a group of related thermoplastic or thermosett ...
pressure hulls. Although the specific strength and specific modulus of acrylic are not very high, the density is only 1.18g/cm3, so it is only very slightly denser than water, and the buoyancy penalty of increased thickness is correspondingly low.
The deepest deep-submergence vehicle
A deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) is a deep-diving crewed submersible that is self-propelled. Several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs. DSVs are commonly divided into two types: research DSVs, which are used for ex ...
(DSV) to date is ''Trieste''. On 5 October 1959, ''Trieste'' departed San Diego for Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
aboard the freighter ''Santa Maria'' to participate in '' Project Nekton'', a series of very deep dives in the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maximum known ...
. On 23 January 1960, ''Trieste'' reached the ocean floor in the Challenger Deep (the deepest southern part of the Mariana Trench), carrying Jacques Piccard
Jacques Piccard (28 July 19221 November 2008) was a Swiss oceanographer and engineer, known for having developed underwater submarines for studying ocean currents. In the Challenger Deep, he and Lt. Don Walsh of the United States Navy were the f ...
(son of Auguste) and Lieutenant Don Walsh
Don Walsh (born November 2, 1931) is an American oceanographer, explorer and marine policy specialist. He and Jacques Piccard were aboard the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' when it made a record maximum descent into the Challenger Deep on January 2 ...
, USN. This was the first time a vessel, crewed or uncrewed, had reached the deepest point in the Earth's oceans. The onboard systems indicated a depth of , although this was later revised to and more accurate measurements made in 1995 have found the Challenger Deep slightly shallower, at .
Building a pressure hull is difficult, as it must withstand pressures at its required diving depth. When the hull is perfectly round in cross-section, the pressure is evenly distributed, and causes only hull compression. If the shape is not perfect, the hull deflects more in some places and buckling
In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape ( deformation) of a structural component under load, such as the bowing of a column under compression or the wrinkling of a plate under shear. If a structure is subjected to a ...
instabity is the usual failure mode
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human er ...
. Inevitable minor deviations are resisted by stiffener rings, but even a one-inch (25 mm) deviation from roundness results in over 30 percent decrease of maximal hydrostatic load and consequently dive depth. The hull must therefore be constructed with high precision. All hull parts must be welded without defects, and all joints are checked multiple times with different methods, contributing to the high cost of modern submarines. (For example, each attack submarine costs US$2.6 billion
Billion is a word for a large number, and it has two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000, i.e. one thousand million, or (ten to the ninth power), as defined on the short scale. This is its only current meaning in English.
* 1,000,000,000,000, i. ...
, over US$200,000 per ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
of displacement.)
Propulsion
 The first submarines were propelled by humans. The first mechanically driven submarine was the 1863 French , which used compressed air for propulsion. Anaerobic propulsion was first employed by the Spanish '' Ictineo II'' in 1864, which used a solution of
The first submarines were propelled by humans. The first mechanically driven submarine was the 1863 French , which used compressed air for propulsion. Anaerobic propulsion was first employed by the Spanish '' Ictineo II'' in 1864, which used a solution of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, manganese dioxide, and potassium chlorate to generate sufficient heat to power a steam engine, while also providing oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
for the crew. A similar system was not employed again until 1940 when the German Navy tested a hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%� ...
-based system, the Walter turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating ...
, on the experimental V-80 submarine and later on the naval and type XVII submarines; the system was further developed for the British , completed in 1958.
Until the advent of nuclear marine propulsion
Nuclear marine propulsion is propulsion of a ship or submarine with heat provided by a nuclear reactor. The power plant heats water to produce steam for a turbine used to turn the ship's propeller through a gearbox or through an electric generato ...
, most 20th-century submarines used electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate for ...
s and batteries for running underwater and combustion engines on the surface, and for battery recharging. Early submarines used gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organi ...
(petrol) engines but this quickly gave way to kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
(paraffin) and then diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
engines because of reduced flammability and, with diesel, improved fuel-efficiency and thus also greater range. A combination of diesel and electric propulsion became the norm.
Initially, the combustion engine and the electric motor were in most cases connected to the same shaft so that both could directly drive the propeller. The combustion engine was placed at the front end of the stern section with the electric motor behind it followed by the propeller shaft. The engine was connected to the motor by a clutch and the motor in turn connected to the propeller shaft by another clutch.
With only the rear clutch engaged, the electric motor could drive the propeller, as required for fully submerged operation. With both clutches engaged, the combustion engine could drive the propeller, as was possible when operating on the surface or, at a later stage, when snorkeling. The electric motor would in this case serve as a generator to charge the batteries or, if no charging was needed, be allowed to rotate freely. With only the front clutch engaged, the combustion engine could drive the electric motor as a generator for charging the batteries without simultaneously forcing the propeller to move.
The motor could have multiple armatures on the shaft, which could be electrically coupled in series for slow speed and in parallel for high speed (these connections were called "group down" and "group up", respectively).
Diesel–electric transmission
 While most early submarines used a direct mechanical connection between the combustion engine and the propeller, an alternative solution was considered as well as implemented at a very early stage. That solution consists in first converting the work of the combustion engine into electric energy via a dedicated generator. This energy is then used to drive the propeller via the electric motor and, to the extent required, for charging the batteries. In this configuration, the electric motor is thus responsible for driving the propeller at all times, regardless of whether air is available so that the combustion engine can also be used or not.
Among the pioneers of this alternative solution was the very first submarine of the Swedish Navy, HMS ''Hajen'' (later renamed ''Ub no 1''), launched in 1904. While its design was generally inspired by the first submarine commissioned by the US Navy, USS ''Holland'', it deviated from the latter in at least three significant ways: by adding a periscope, by replacing the gasoline engine by a semidiesel engine (a
While most early submarines used a direct mechanical connection between the combustion engine and the propeller, an alternative solution was considered as well as implemented at a very early stage. That solution consists in first converting the work of the combustion engine into electric energy via a dedicated generator. This energy is then used to drive the propeller via the electric motor and, to the extent required, for charging the batteries. In this configuration, the electric motor is thus responsible for driving the propeller at all times, regardless of whether air is available so that the combustion engine can also be used or not.
Among the pioneers of this alternative solution was the very first submarine of the Swedish Navy, HMS ''Hajen'' (later renamed ''Ub no 1''), launched in 1904. While its design was generally inspired by the first submarine commissioned by the US Navy, USS ''Holland'', it deviated from the latter in at least three significant ways: by adding a periscope, by replacing the gasoline engine by a semidiesel engine (a hot-bulb engine
The hot-bulb engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignites by coming in contact with a red-hot metal surface inside a bulb, followed by the introduction of air (oxygen) compressed into the hot-bulb chamber by the rising p ...
primarily meant to be fueled by kerosene, later replaced by a true diesel engine) and by severing the mechanical link between the combustion engine and the propeller by instead letting the former drive a dedicated generator. By so doing, it took three significant steps toward what was eventually to become the dominant technology for conventional (i.e., non-nuclear) submarines.
 In the following years, the Swedish Navy added another seven submarines in three different classes ( ''2nd'' class, ''Laxen'' class, and ''Braxen'' class) using the same propulsion technology but fitted with true diesel engines rather than semidiesels from the outset. Since by that time, the technology was usually based on the diesel engine rather than some other type of combustion engine, it eventually came to be known as
In the following years, the Swedish Navy added another seven submarines in three different classes ( ''2nd'' class, ''Laxen'' class, and ''Braxen'' class) using the same propulsion technology but fitted with true diesel engines rather than semidiesels from the outset. Since by that time, the technology was usually based on the diesel engine rather than some other type of combustion engine, it eventually came to be known as diesel–electric transmission
A diesel–electric transmission, or diesel–electric powertrain is a transmission system for vehicles powered by diesel engines in road, rail, and marine transport. Diesel–electric transmission is based on petrol–electric transmission, a ...
.
Like many other early submarines, those initially designed in Sweden were quite small (less than 200 tonnes) and thus confined to littoral operation. When the Swedish Navy wanted to add larger vessels, capable of operating further from the shore, their designs were purchased from companies abroad that already had the required experience: first Italian ( Fiat- Laurenti) and later German (A.G. Weser
Aktien-Gesellschaft „Weser" (abbreviated A.G. „Weser”) was one of the major Germany, German shipbuilding companies, located at the Weser River in Bremen. Founded in 1872 it was finally closed in 1983. All together, A.G. „Weser" built abo ...
and IvS). As a side-effect, the diesel–electric transmission was temporarily abandoned.
However, diesel–electric transmission was immediately reintroduced when Sweden began designing its own submarines again in the mid 1930s. From that point onwards, it has been consistently used for all new classes of Swedish submarines, albeit supplemented by air-independent propulsion (AIP) as provided by Stirling engine
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas (the ''working fluid'') between different temperatures, resulting in a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical work.
More specif ...
s beginning with HMS ''Näcken'' in 1988.
 Another early adopter of diesel–electric transmission was the
Another early adopter of diesel–electric transmission was the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, whose Bureau of Engineering proposed its use in 1928. It was subsequently tried in the S-class submarines , , and before being put into production with the ''Porpoise'' class of the 1930s. From that point onwards, it continued to be used on most US conventional submarines.
Apart from the British U-class and some submarines of the Imperial Japanese Navy that used separate diesel generators for low speed running, few navies other than those of Sweden and the US made much use of diesel–electric transmission before 1945. After World War II, by contrast, it gradually became the dominant mode of propulsion for conventional submarines. However, its adoption was not always swift. Notably, the Soviet Navy did not introduce diesel–electric transmission on its conventional submarines until 1980 with its ''Paltus'' class.
If diesel–electric transmission had only brought advantages and no disadvantages in comparison with a system that mechanically connects the diesel engine to the propeller, it would undoubtedly have become dominant much earlier. The disadvantages include the following:
* It entails a loss of fuel-efficiency as well as power by converting the output of the diesel engine into electricity. While both generators and electric motors are known to be very efficient, their efficiency nevertheless falls short of 100 percent.
* It requires an additional component in the form of a dedicated generator. Since the electric motor is always used to drive the propeller it can no longer step in to take on generator service as well.
* It does not allow the diesel engine and the electrical motor to join forces by simultaneously driving the propeller mechanically for maximum speed when the submarine is surfaced or snorkeling. This may, however, be of little practical importance inasmuch as the option it prevents is one that would leave the submarine at a risk of having to dive with its batteries at least partly depleted.
The reason why diesel–electric transmission has become the dominant alternative in spite of these disadvantages is of course that it also comes with many advantages and that, on balance, these have eventually been found to be more important. The advantages include the following:
* It reduces external noise by severing the direct and rigid mechanical link between the relatively noisy diesel engine(s) on the one hand and the propeller shaft(s) and hull on the other. With stealth being of paramount importance to submarines, this is a very significant advantage.
* It increases the readiness to dive, which is of course of vital importance for a submarine. The only thing required from a propulsion point of view is to shut down the diesel(s).
* It makes the speed of the diesel engine(s) temporarily independent of the speed of the submarine. This in turn often makes it possible to run the diesel(s) at close to optimal speed from a fuel-efficiency as well as durability point of view. It also makes it possible to reduce the time spent surfaced or snorkeling by running the diesel(s) at maximum speed without affecting the speed of the submarine itself.
* It eliminates the clutches otherwise required to connect the diesel engine, the electric motor, and the propeller shaft. This in turn saves space, increases reliability and reduces maintenance costs.
* It increases flexibility with regard to how the driveline components are configured, positioned, and maintained. For example, the diesel no longer has to be aligned with the electric motor and propeller shaft, two diesels can be used to power a single propeller (or vice versa), and one diesel can be turned off for maintenance as long as a second is available to provide the required amount of electricity.
* It facilitates the integration of additional primary sources of energy, beside the diesel engine(s), such as various kinds of air-independent power (AIP) systems. With one or more electric motors always driving the propeller(s), such systems can easily be introduced as yet another source of electric energy in addition to the diesel engine(s) and the batteries.
Snorkel
During World War II the Germans experimented with the idea of the ''schnorchel'' (snorkel) from captured Dutch submarines but did not see the need for them until rather late in the war. The ''schnorchel'' is a retractable pipe that supplies air to the diesel engines while submerged atperiscope depth
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
, allowing the boat to cruise and recharge its batteries while maintaining a degree of stealth.
Especially as first implemented however, it turned out to be far from a perfect solution. There were problems with the device's valve sticking shut or closing as it dunked in rough weather. Since the system used the entire pressure hull as a buffer, the diesels would instantaneously suck huge volumes of air from the boat's compartments, and the crew often suffered painful ear injuries. Speed was limited to , lest the device snap from stress. The ''schnorchel'' also created noise that made the boat easier to detect with sonar, yet more difficult for the on-board sonar to detect signals from other vessels. Finally, allied radar eventually became sufficiently advanced that the ''schnorchel'' mast could be detected beyond visual range.
While the snorkel renders a submarine far less detectable, it is thus not perfect. In clear weather, diesel exhausts can be seen on the surface to a distance of about three miles, while "periscope feather" (the wave created by the snorkel or periscope moving through the water) is visible from far off in calm sea conditions. Modern radar is also capable of detecting a snorkel in calm sea conditions.
 The problem of the diesels causing a vacuum in the submarine when the head valve is submerged still exists in later model diesel submarines but is mitigated by high-vacuum cut-off sensors that shut down the engines when the vacuum in the ship reaches a pre-set point. Modern snorkel induction masts have a fail-safe design using compressed air, controlled by a simple electrical circuit, to hold the "head valve" open against the pull of a powerful spring. Seawater washing over the mast shorts out exposed electrodes on top, breaking the control, and shutting the "head valve" while it is submerged. US submarines did not adopt the use of snorkels until after WWII.
The problem of the diesels causing a vacuum in the submarine when the head valve is submerged still exists in later model diesel submarines but is mitigated by high-vacuum cut-off sensors that shut down the engines when the vacuum in the ship reaches a pre-set point. Modern snorkel induction masts have a fail-safe design using compressed air, controlled by a simple electrical circuit, to hold the "head valve" open against the pull of a powerful spring. Seawater washing over the mast shorts out exposed electrodes on top, breaking the control, and shutting the "head valve" while it is submerged. US submarines did not adopt the use of snorkels until after WWII.
Air-independent propulsion

 During World War II,
During World War II, German Type XXI submarine
Type XXI submarines were a class of German diesel–electric ''Elektroboot'' (German: "electric boat") submarines designed during the Second World War. One hundred and eighteen were completed, with four being combat-ready. During the war only t ...
s (also known as "''Elektroboote''") were the first submarines designed to operate submerged for extended periods. Initially they were to carry hydrogen peroxide for long-term, fast air-independent propulsion, but were ultimately built with very large batteries instead. At the end of the War, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Soviets experimented with hydrogen peroxide/kerosene (paraffin) engines that could run surfaced and submerged. The results were not encouraging. Though the Soviet Union deployed a class of submarines with this engine type (codenamed by NATO), they were considered unsuccessful.
The United States also used hydrogen peroxide in an experimental midget submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, ...
, X-1. It was originally powered by a hydrogen peroxide/diesel engine and battery system until an explosion of her hydrogen peroxide supply on 20 May 1957. X-1 was later converted to use diesel–electric drive.
Today several navies use air-independent propulsion. Notably Sweden uses Stirling technology on the and s. The Stirling engine is heated by burning diesel fuel with liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an app ...
from cryogenic tanks. A newer development in air-independent propulsion is hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
fuel cells, first used on the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Type 212 submarine
The German Type 212 class (German: U-Boot-Klasse 212 A), also Italian ''Todaro'' class, is a diesel-electric submarine developed by Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft AG (HDW) for the German and Italian navies. It features diesel propulsion and a ...
, with nine 34 kW or two 120 kW cells. Fuel cells are also used in the new Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
s although with the fuel stored as ethanol and then converted into hydrogen before use.
One new technology that is being introduced starting with the Japanese Navy's eleventh ''Sōryū''-class submarine (JS ''Ōryū'') is a more modern battery, the lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also s ...
. These batteries have about double the electric storage of traditional batteries, and by changing out the lead-acid batteries in their normal storage areas plus filling up the large hull space normally devoted to AIP engine and fuel tanks with many tons of lithium-ion batteries, modern submarines can actually return to a "pure" diesel–electric configuration yet have the added underwater range and power normally associated with AIP equipped submarines.
Nuclear power
 Steam power was resurrected in the 1950s with a nuclear-powered steam turbine driving a generator. By eliminating the need for atmospheric oxygen, the time that a submarine could remain submerged was limited only by its food stores, as breathing air was recycled and fresh water distilled from seawater. More importantly, a nuclear submarine has unlimited range at top speed. This allows it to travel from its operating base to the combat zone in a much shorter time and makes it a far more difficult target for most anti-submarine weapons. Nuclear-powered submarines have a relatively small battery and diesel engine/generator powerplant for emergency use if the reactors must be shut down.
Nuclear power is now used in all large submarines, but due to the high cost and large size of nuclear reactors, smaller submarines still use diesel–electric propulsion. The ratio of larger to smaller submarines depends on strategic needs. The US Navy,
Steam power was resurrected in the 1950s with a nuclear-powered steam turbine driving a generator. By eliminating the need for atmospheric oxygen, the time that a submarine could remain submerged was limited only by its food stores, as breathing air was recycled and fresh water distilled from seawater. More importantly, a nuclear submarine has unlimited range at top speed. This allows it to travel from its operating base to the combat zone in a much shorter time and makes it a far more difficult target for most anti-submarine weapons. Nuclear-powered submarines have a relatively small battery and diesel engine/generator powerplant for emergency use if the reactors must be shut down.
Nuclear power is now used in all large submarines, but due to the high cost and large size of nuclear reactors, smaller submarines still use diesel–electric propulsion. The ratio of larger to smaller submarines depends on strategic needs. The US Navy, French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
, and the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
operate only nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed. Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion, ...
s, which is explained by the need for distant operations. Other major operators rely on a mix of nuclear submarines for strategic purposes and diesel–electric submarines for defense. Most fleets have no nuclear submarines, due to the limited availability of nuclear power and submarine technology.
Diesel–electric submarines have a stealth advantage over their nuclear counterparts. Nuclear submarines generate noise from coolant pumps and turbo-machinery needed to operate the reactor, even at low power levels. Some nuclear submarines such as the American can operate with their reactor coolant pumps secured, making them quieter than electric subs. A conventional submarine operating on batteries is almost completely silent, the only noise coming from the shaft bearings, propeller, and flow noise around the hull, all of which stops when the sub hovers in mid-water to listen, leaving only the noise from crew activity. Commercial submarines usually rely only on batteries, since they operate in conjunction with a mother ship.
Several serious nuclear and radiation accidents have involved nuclear submarine mishaps. The reactor accident in 1961 resulted in 8 deaths and more than 30 other people were over-exposed to radiation.Strengthening the Safety of Radiation Sourcesp. 14 The reactor accident in 1968 resulted in 9 fatalities and 83 other injuries. The accident in 1985 resulted in 10 fatalities and 49 other radiation injuries.
Alternative
Oil-fired steam turbines powered the British K-class submarines, built duringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and later, to give them the surface speed to keep up with the battle fleet. The K-class subs were not very successful, however.
Toward the end of the 20th century, some submarines—such as the British ''Vanguard'' class—began to be fitted with pump-jet
A pump-jet, hydrojet, or water jet is a marine system that produces a jet of water for propulsion. The mechanical arrangement may be a ducted propeller ( axial-flow pump), a centrifugal pump, or a mixed flow pump which is a combination of bot ...
propulsors instead of propellers. Though these are heavier, more expensive, and less efficient than a propeller, they are significantly quieter, providing an important tactical advantage.
Armament
 The success of the submarine is inextricably linked to the development of the
The success of the submarine is inextricably linked to the development of the torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
, invented by Robert Whitehead
Robert Whitehead (3 January 1823 – 14 November 1905) was an English engineer who was most famous for developing the first effective self-propelled naval torpedo.
Early life
He was born in Bolton, England, the son of James Whitehead, ...
in 1866. His invention is essentially the same now as it was 140 years ago. Only with self-propelled torpedoes could the submarine make the leap from novelty to a weapon of war. Until the perfection of the guided torpedo, multiple "straight-running" torpedoes were required to attack a target. With at most 20 to 25 torpedoes stored on board, the number of attacks was limited. To increase combat endurance most World War I submarines functioned as submersible gunboats, using their deck gun
A deck gun is a type of naval artillery mounted on the deck of a submarine. Most submarine deck guns were open, with or without a shield; however, a few larger submarines placed these guns in a turret.
The main deck gun was a dual-purpose ...
s against unarmed targets, and diving to escape and engage enemy warships. The importance of guns encouraged the development of the unsuccessful Submarine Cruiser such as the French and the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
's and M-class submarines. With the arrival of anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are t ...
(ASW) aircraft, guns became more for defense than attack. A more practical method of increasing combat endurance was the external torpedo tube, loaded only in port.
The ability of submarines to approach enemy harbours covertly led to their use as minelayer
A minelayer is any warship, submarine or military aircraft deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing control ...
s. Minelaying submarines of World War I and World War II were specially built for that purpose. Modern submarine-laid mines, such as the British Mark 5 Stonefish and Mark 6 Sea Urchin, can be deployed from a submarine's torpedo tubes.
After World War II, both the US and the USSR experimented with submarine-launched cruise missiles such as the SSM-N-8 Regulus and P-5 Pyatyorka
The P-5 ''"Pyatyorka"'' (russian: П-5 «Пятёрка»; "Pyatyorka", "fiver" in English), also known by the NATO codename SS-N-3C Shaddock, is a Cold War era turbojet-powered cruise missile of the Soviet Union, designed by the Chelomey desig ...
. Such missiles required the submarine to surface to fire its missiles. They were the forerunners of modern submarine-launched cruise missiles, which can be fired from the torpedo tubes of submerged submarines, for example, the US BGM-109 Tomahawk and Russian RPK-2 Viyuga
The RPK-2 Vyuga (, ''blizzard''; NATO reporting name: SS-N-15 Starfish), also designated as 81R, is a Soviet submarine-launched, nuclear-armed anti-submarine missile system, launched exclusively through torpedo tubes. The system was designed in ...
and versions of surface-to-surface anti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. A goo ...
s such as the Exocet
The Exocet () is a French-built anti-ship missile whose various versions can be launched from surface vessels, submarines, helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
Etymology
The missile's name was given by M. Guillot, then the technical director ...
and Harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal ...
, encapsulated for submarine launch. Ballistic missiles can also be fired from a submarine's torpedo tubes, for example, missiles such as the anti-submarine SUBROC
The UUM-44 SUBROC (SUBmarine ROCket) was a type of submarine-launched rocket deployed by the United States Navy as an anti-submarine weapon. It carried a 250 kiloton thermonuclear warhead configured as a nuclear depth bomb.
Development
SUBROC ...
. With internal volume as limited as ever and the desire to carry heavier warloads, the idea of the external launch tube was revived, usually for encapsulated missiles, with such tubes being placed between the internal pressure and outer streamlined hulls.
The strategic mission of the SSM-N-8 and the P-5 was taken up by submarine-launched ballistic missile beginning with the US Navy's Polaris missile, and subsequently the Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a ...
and Trident
A trident is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm.
The trident is the weapon of Poseidon, or Neptune, the God of the Sea in classical mythology. The trident may occasionally be held by other mari ...
missiles.
Germany is working on the torpedo tube-launched short-range IDAS missile, which can be used against ASW helicopters, as well as surface ships and coastal targets.
Sensors
A submarine can have a variety of sensors, depending on its missions. Modern military submarines rely almost entirely on a suite of passive and activesonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
s to locate targets. Active sonar relies on an audible "ping" to generate echoes to reveal objects around the submarine. Active systems are rarely used, as doing so reveals the sub's presence. Passive sonar is a set of sensitive hydrophones set into the hull or trailed in a towed array, normally trailing several hundred feet behind the sub. The towed array is the mainstay of NATO submarine detection systems, as it reduces the flow noise heard by operators. Hull mounted sonar is employed in addition to the towed array, as the towed array can't work in shallow depth and during maneuvering. In addition, sonar has a blind spot "through" the submarine, so a system on both the front and back works to eliminate that problem. As the towed array trails behind and below the submarine, it also allows the submarine to have a system both above and below the thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
at the proper depth; sound passing through the thermocline is distorted resulting in a lower detection range.
Submarines also carry radar equipment to detect surface ships and aircraft. Submarine captains are more likely to use radar detection gear than active radar to detect targets, as radar can be detected far beyond its own return range, revealing the submarine. Periscopes are rarely used, except for position fixes and to verify a contact's identity.
Civilian submarines, such as the or the Russian ''Mir'' submersibles, rely on small active sonar sets and viewing ports to navigate. The human eye cannot detect sunlight below about underwater, so high intensity lights are used to illuminate the viewing area.
Navigation
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
to obtain an accurate position. The periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
—a retractable tube with a prism
Prism usually refers to:
* Prism (optics), a transparent optical component with flat surfaces that refract light
* Prism (geometry), a kind of polyhedron
Prism may also refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Prism (geology), a type of sedimentary ...
system that provides a view of the surface—is only used occasionally in modern submarines, since the visibility range is short. The and s use photonics masts rather than hull-penetrating optical periscopes. These masts must still be deployed above the surface, and use electronic sensors for visible light, infrared, laser range-finding, and electromagnetic surveillance. One benefit to hoisting the mast above the surface is that while the mast is above the water the entire sub is still below the water and is much harder to detect visually or by radar.
Communication
Military submarines use several systems to communicate with distant command centers or other ships. One isVLF
Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave a ...
(very low frequency) radio, which can reach a submarine either on the surface or submerged to a fairly shallow depth, usually less than . ELF
An elf () is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic mythology and folklore. Elves appear especially in North Germanic mythology. They are subsequently mentioned in Snorri Sturluson's Icelandic Prose Edda. He distinguishes "ligh ...
(extremely low frequency) can reach a submarine at greater depths, but has a very low bandwidth and is generally used to call a submerged sub to a shallower depth where VLF signals can reach. A submarine also has the option of floating a long, buoyant wire antenna to a shallower depth, allowing VLF transmissions by a deeply submerged boat.
By extending a radio mast, a submarine can also use a "burst transmission
In telecommunication, a burst transmission or data burst is the broadcast of a relatively high-bandwidth transmission over a short period.
Burst transmission can be intentional, broadcasting a compressed message at a very high data signaling rate ...
" technique. A burst transmission takes only a fraction of a second, minimizing a submarine's risk of detection.
To communicate with other submarines, a system known as Gertrude is used. Gertrude is basically a sonar telephone. Voice communication from one submarine is transmitted by low power speakers into the water, where it is detected by passive sonars on the receiving submarine. The range of this system is probably very short, and using it radiates sound into the water, which can be heard by the enemy.
Civilian submarines can use similar, albeit less powerful systems to communicate with support ships or other submersibles in the area.
Life support systems
Withnuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
or air-independent propulsion, submarines can remain submerged for months at a time. Conventional diesel submarines must periodically resurface or run on snorkel to recharge their batteries. Most modern military submarines generate breathing oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
by electrolysis of fresh water (using a device called an " Electrolytic Oxygen Generator"). Emergency oxygen can be produced by burning sodium chlorate
Sodium chlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na ClO3. It is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 300 °C to release oxygen and leaves sodium chloride. Sever ...
candles. Atmosphere control equipment includes a Carbon dioxide scrubber
A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or ...
, which uses a spray of monoethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid ...
(MEA) absorbent to remove the gas from the air, after which the MEA is heated in a boiler to release the CO2 which is then pumped overboard. Emergency scrubbing can also be done with lithium hydroxide, which is consumable. A machine that uses a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
to convert carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
into carbon dioxide (removed by the scrubber) and bonds hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
produced from the ship's storage battery with oxygen in the atmosphere to produce water, is also used. An atmosphere monitoring system samples the air from different areas of the ship for nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen, hydrogen, R-12 and R-114 refrigerants, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
, and other gases. Poisonous gases are removed, and oxygen is replenished by use of an oxygen bank located in a main ballast tank. Some heavier submarines have two oxygen bleed stations (forward and aft). The oxygen in the air is sometimes kept a few percent less than atmospheric concentration to reduce fire risk.
Fresh water is produced by either an evaporator or a reverse osmosis unit. The primary use for fresh water is to provide feedwater for the reactor and steam propulsion plants. It is also available for showers, sinks, cooking and cleaning once propulsion plant needs have been met. Seawater is used to flush toilets, and the resulting "blackwater" is stored in a sanitary tank until it is blown overboard using pressurized air or pumped overboard by using a special sanitary pump. The blackwater-discharge system requires skill to operate, and isolation valves must be closed before discharge. The German Type VIIC boat was lost with casualties because of human error
Human error refers to something having been done that was " not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits".Senders, J.W. and Moray, N.P. (1991) Human ...
while using this system. Water from showers and sinks is stored separately in "grey water
Greywater (or grey water, sullage, also spelled gray water in the United States) refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except for the wastewater fro ...
" tanks and discharged overboard using drain pumps.
Trash on modern large submarines is usually disposed of using a tube called a Trash Disposal Unit (TDU), where it is compacted into a galvanized steel can. At the bottom of the TDU is a large ball valve. An ice plug is set on top of the ball valve to protect it, the cans atop the ice plug. The top breech door is shut, and the TDU is flooded and equalized with sea pressure, the ball valve is opened and the cans fall out assisted by scrap iron weights in the cans. The TDU is also flushed with seawater to ensure it is completely empty and the ball valve is clear before closing the valve.
Crew
 A typical nuclear submarine has a crew of over 80; conventional boats typically have fewer than 40. The conditions on a submarine can be difficult because crew members must work in isolation for long periods of time, without family contact, and in cramped conditions. Submarines normally maintain
A typical nuclear submarine has a crew of over 80; conventional boats typically have fewer than 40. The conditions on a submarine can be difficult because crew members must work in isolation for long periods of time, without family contact, and in cramped conditions. Submarines normally maintain radio silence
In telecommunications, radio silence or Emissions Control (EMCON) is a status in which all fixed or mobile radio stations in an area are asked to stop transmitting for safety or security reasons.
The term "radio station" may include anything ca ...
to avoid detection. Operating a submarine is dangerous, even in peacetime, and many submarines have been lost in accidents.
Women
Most navies prohibited women from serving on submarines, even after they had been permitted to serve on surface warships. TheRoyal Norwegian Navy
The Royal Norwegian Navy ( no, Sjøforsvaret, , Sea defence) is the branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces responsible for naval operations of Norway. , the Royal Norwegian Navy consists of approximately 3,700 personnel (9,450 in mobilized state, ...
became the first navy to allow women on its submarine crews in 1985. The Royal Danish Navy
The Royal Danish Navy ( da, Søværnet) is the sea-based branch of the Danish Defence force. The RDN is mainly responsible for maritime defence and maintaining the sovereignty of Danish territorial waters (incl. Faroe Islands and Greenland). O ...
allowed female submariners in 1988. Others followed suit including the Swedish Navy (1989), the Royal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of ...
(1998), the Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, ...
(1999), the German Navy
The German Navy (, ) is the navy of Germany and part of the unified ''Bundeswehr'' (Federal Defense), the German Armed Forces. The German Navy was originally known as the ''Bundesmarine'' (Federal Navy) from 1956 to 1995, when ''Deutsche Mari ...
(2001) and the Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack submar ...
(2002). In 1995, Solveig Krey of the Royal Norwegian Navy became the first female officer to assume command on a military submarine, HNoMS ''Kobben''.
On 8 December 2011, British Defence Secretary
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Philip Hammond
Philip Hammond, Baron Hammond of Runnymede (born 4 December 1955) is a British politician and life peer who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2016 to 2019, Foreign Secretary from 2014 to 2016, and Defence Secretary from 2011 to 2014. ...
announced that the UK's ban on women in submarines was to be lifted from 2013. Previously there were fears that women were more at risk from a build-up of carbon dioxide in the submarine. But a study showed no medical reason to exclude women, though pregnant women would still be excluded. Similar dangers to the pregnant woman and her fetus barred women from submarine service in Sweden in 1983, when all other positions were made available for them in the Swedish Navy. Today, pregnant women are still not allowed to serve on submarines in Sweden. However, the policymakers thought that it was discriminatory with a general ban and demanded that women should be tried on their individual merits and have their suitability evaluated and compared to other candidates. Further, they noted that a woman complying with such high demands is unlikely to become pregnant. In May 2014, three women became the RN's first female submariners.
Women have served on US Navy surface ships since 1993, and , began serving on submarines for the first time. Until presently, the Navy allowed only three exceptions to women being on board military submarines: female civilian technicians for a few days at most, women midshipmen on an overnight during summer training for Navy ROTC and Naval Academy
A naval academy provides education for prospective naval officers.
See also
* Military academy
A military academy or service academy is an educational institution which prepares candidates for service in the officer corps. It normally pro ...
, and family members for one-day dependent cruises. In 2009, senior officials, including then-Secretary of the Navy Ray Mabus
Raymond Edwin Mabus Jr. (; born October 11, 1948) is an American politician and lawyer. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 75th United States Secretary of the Navy from 2009 to 2017. Mabus previously served as the State Auditor ...
, Joint Chief of Staff Admiral Michael Mullen
Michael Glenn Mullen (born October 4, 1946) is a retired United States Navy admiral, who served as the 17th chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff from October 1, 2007, to September 30, 2011.
Mullen previously served as the Navy's 28th chief of ...
, and Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Gary Roughead
Gary Roughead ( "rough head"; born July 15, 1951) is a former United States Navy officer who served as the 29th Chief of Naval Operations from September 29, 2007 to September 22, 2011. He previously served as Commander, United States Fleet Forces ...
, began the process of finding a way to implement women on submarines. The US Navy rescinded its "no women on subs" policy in 2010.
Both the US and British navies operate nuclear-powered submarines that deploy for periods of six months or longer. Other navies that permit women to serve on submarines operate conventionally powered submarines, which deploy for much shorter periods—usually only for a few months. Prior to the change by the US, no nation using nuclear submarines permitted women to serve on board.
In 2011, the first class of female submarine officers graduated from Naval Submarine School's Submarine Officer Basic Course (SOBC) at the Naval Submarine Base New London
Naval Submarine Base New London is the primary United States Navy East Coast submarine base, also known as the "Home of the Submarine Force." It is located in Groton, Connecticut directly across the Thames River from its namesake city of New L ...
. Additionally, more senior ranking and experienced female supply officers from the surface warfare specialty attended SOBC as well, proceeding to fleet Ballistic Missile (SSBN) and Guided Missile (SSGN) submarines along with the new female submarine line officers beginning in late 2011. By late 2011, several women were assigned to the ''Ohio''-class ballistic missile submarine . On 15 October 2013, the US Navy announced that two of the smaller ''Virginia''-class attack submarines, and , would have female crew-members by January 2015.
In 2020, Japan's national naval submarine academy accepted its first female candidate.
Abandoning the vessel

 In an emergency, submarines can transmit a signal to other ships. The crew can use escape sets such as the
In an emergency, submarines can transmit a signal to other ships. The crew can use escape sets such as the Submarine Escape Immersion Equipment
Submarine Escape Immersion Equipment (SEIE), also known as Submarine Escape ''and'' Immersion Equipment, is a whole-body suit and one-man life raft that was first produced in 1952. It was designed by British company RFD Beaufort Limited and allow ...
to abandon the submarine via an escape trunk, which is a small airlock
An airlock, air-lock or air lock, often abbreviated to just lock, is a compartment with doors which can be sealed against pressure which permits the passage of people and objects between environments of differing pressure or atmospheric compo ...
compartment that provides a route for crew to escape from a downed submarine at ambient pressure in small groups, while minimising the amount of water admitted to the submarine. The crew can avoid lung injury from over-expansion of air in the lungs due to the pressure change known as pulmonary barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in tensi ...
by maintaining an open airway and exhaling during the ascent. Following escape from a pressurized submarine, in which the air pressure is higher than atmospheric due to water ingress or other reasons, the crew is at risk of developing decompression sickness
Decompression sickness (abbreviated DCS; also called divers' disease, the bends, aerobullosis, and caisson disease) is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during decompressio ...
on return to surface pressure.
An alternative escape means is via a deep-submergence rescue vehicle
A deep-submergence rescue vehicle (DSRV) is a type of deep-submergence vehicle used for rescue of downed submarines and clandestine missions. While DSRV is the term most often used by the United States Navy, other nations have different design ...
that can dock onto the disabled submarine, establish a seal around the escape hatch, and transfer personnel at the same pressure as the interior of the submarine. If the submarine has been pressurised the survivors can lock into a decompression chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of ...
on the submarine rescue ship and transfer under pressure for safe surface decompression.
See also
*Autonomous underwater vehicle
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) is a robot that travels underwater without requiring input from an operator. AUVs constitute part of a larger group of undersea systems known as unmanned underwater vehicles, a classification that includ ...
* Coastal submarine
A coastal submarine or littoral submarine is a small, maneuverable submarine with shallow draft well suited to navigation of coastal channels and harbors. Although size is not precisely defined, coastal submarines are larger than midget submarine ...
* Columbia-class submarine
The ''Columbia''-class submarine (formerly known as the ''Ohio'' Replacement Submarine and SSBN-X Future Follow-on Submarine) is an upcoming class of nuclear submarines designed to replace the ballistic missile submarines in the United States N ...
* Depth charge
* Fictional submarines
* Flying submarine
* List of ships sunk by submarines by death toll
* List of submarine actions
* List of submarine classes
* List of submarine museums
* List of submarines of World War II
* List of specifications of submarines of World War II
Submarines of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—incl ...
* List of sunken nuclear submarines
Nine nuclear submarines have sunk, either by accident or scuttling. The Soviet Navy has lost five (one of which sank twice), the Russian Navy two, and the United States Navy (USN) two.
Three were lost with all hands - the two from the United Sta ...
* Merchant submarine
A merchant submarine is a type of submarine intended for trade, and being without armaments, it is not considered a warship like most other types of submarines. The intended use would be blockade running, or to dive under Arctic ice.
Strictly ...
* Nuclear navy
A nuclear navy, or nuclear-powered navy, refers to the portion of a navy consisting of naval ships powered by nuclear marine propulsion. The concept was revolutionary for naval warfare when first proposed. Prior to nuclear power, submarines were ...
* Semi-submersible naval vessel
A semi-submersible naval vessel is a hybrid warship, that combines the properties of a surface ship and submarine by using water ballast to partially immerse and minimize its above-waterline profile, thereby improving its stealth characteristics wh ...
* Submarine films
The submarine film is a subgenre of war film in which the majority of the plot revolves around a submarine below the ocean's surface. Films of this subgenre typically focus on a small but determined crew of submariners battling against enemy sub ...
* Submarine power cable
* Submarine simulator, a computer game genre
* Supercavitation
Supercavitation is the use of a cavitation bubble to reduce skin friction drag on a submerged object and enable high speeds. Applications include torpedoes and propellers, but in theory, the technique could be extended to an entire underwater v ...
* Unmanned underwater vehicle
Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUV), sometimes known as underwater drones, are submersible vehicles that can operate underwater without a human occupant. These vehicles may be divided into two categories: remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROU ...
By country
*List of submarine operators
The following countries operate or have operated submarines for naval or other military purposes.
Countries with currently operational submarines
* Algeria
* Australia
* Azerbaijan
* Bangladesh
* Brazil
* Canada
* Chile
* Colombia
* Ecuador
...
* Australia – Collins-class submarine
* Bangladesh- Submarines of the Bangladesh Navy
* Britain – List of submarines of the Royal Navy, List of submarine classes of the Royal Navy
* China – Submarines of the People's Liberation Army Navy
The People's Liberation Army Navy Submarine Force (PLANSF) is the submarine service of the People's Liberation Army Navy. It consists of all types of submarines in operational service organized into three fleets: the North Sea Fleet, the East Se ...
* France – Submarines in the French Navy, List of submarines of the French Navy, List of French submarine classes and types
* Germany – List of U-boats of Germany
Germany has commissioned over 1,500 U-boats (german: Unterseeboot) into its various navies from 1906 to the present day. The submarines have usually been designated with a ''U'' followed by a number, although World War I coastal submarines and coa ...
* India – Submarines of the Indian Navy
This is a list of known submarines of the Indian Navy, grouped by class, and pennant numbers within the class.
In service
Under construction
Planned
Decommissioned
See also
; Indian navy related lists
* Aircraft of the Ind ...
* Israel – Dolphin-class submarine
The ''Dolphin'' class (Hebrew: הצוללות מסדרת דולפין) is a diesel-electric submarine developed in Israel and constructed by Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft AG (HDW) in Kiel, Germany, for the Israeli Navy. The first boats of the c ...
* Japan – Imperial Japanese Navy submarines
Imperial Japanese Navy submarines originated with the purchase of five Holland type submarines from the United States in 1904. Japanese submarine forces progressively built up strength and expertise, becoming by the beginning of World War II one ...
,
* The Netherlands – List of submarines of the Netherlands
This is a list of submarines of the Netherlands navy.
Submarines built before 1940
Until the ''O 19'' class there was distinction made between ''O'' submarines used for European home waters and ''K'' submarines used for colonial service.
Submar ...
* Pakistan –
* Romania – Romanian submarines of World War II During the Second World War, the Royal Romanian Navy operated a total of 9 submarines: three fleet submarines and six midget submarines. These vessels fought on the Axis side during the war. Only two of them survived the war and continued to serve i ...
* Russia – List of Soviet and Russian submarine classes
Submarines of the Soviet Navy were developed by numbered "projects", which were sometimes but not always given names. During the
Cold War, NATO nations referred to these classes by NATO reporting names, based on intelligence data, which did not ...
, Future Russian submarines
* Soviet Union –
* Spain – List of submarines of the Spanish Navy
The list of submarines in the Spanish Navy, commissioned or otherwise operated by the Spanish Navy.
Peral "submarine torpedo boat"
* Peral Submarine, ''Peral'' 1888 – 1890. Preserved as museum ship at Cartagena.
Isaac Peral class submarine ...
* Singapore –
* Turkey – List of submarines of the Turkish Navy
This is a list of Turkish Navy submarines that have served from 10 July 1920Cevat Ülkekul"Kurtuluş Savaşı'nda Türk Denizcileri ve Cumhuriyet Bahriyesinin Kuruluşu", Piri Reis Symposium, Office of Navigation of Hydrography and Oceanography. ...
* United States – Submarines in the US Navy, List of submarines of the US Navy, List of US submarine classes, Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory
The Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory (NSMRL) is located on the New London Submarine Base in Groton, Connecticut. The laboratory's mission is to protect the health of American sailors, focused on submarines and scuba diving. It is a su ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
General history * ''Histoire des sous-marins: des origines à nos jours'' by Jean-Marie Mathey and Alexandre Sheldon-Duplaix. (Boulogne-Billancourt: ETAI, 2002). * Culture * Redford, Duncan. ''The Submarine: A Cultural History From the Great War to Nuclear Combat'' (I.B. Tauris, 2010) 322 pages; focus on British naval and civilian understandings of submarine warfare, including novels and film. Submarines before 1914 * 1900/Russo-Japanese War 1904–1905 * * * * * World War II * * * * * * Cold War * ''Hide and seek: the untold story of Cold War espionage at sea'', by Peter Huchthausen and Alexandre Sheldon-Duplaix. (Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2008, ) *External links
* – ''Submarine boat'' *''The Fleet Type Submarine Online''
US Navy submarine training manuals, 1944–1946 * American Society of Safety Engineers. Journal of Professional Safety. ''Submarine Accidents: A 60-Year Statistical Assessment''. C. Tingle. September 2009. pp. 31–39
Ordering full article
o
{{Authority control Electric vehicles Pressure vessels Ship types English inventions Dutch inventions 17th-century introductions