(man)
it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Sicilian
, demographics1_info1 = 98%
, demographics1_title2 =
, demographics1_info2 =
, demographics1_title3 =
, demographics1_info3 =
, timezone1 =
CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast En ...
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST =
CEST CEST or cest may refer to:
* Central European Summer Time (UTC+2), daylight saving time observed in the central European time zone
* Cognitive-Experiential Self-Theory
* Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer, a subset of Magnetization transfer in ...
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code_type =
ISO 3166 code
, area_code = IT-82
, blank_name_sec1 =
GDP (nominal)
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, blank_info_sec1 = €89.2 billion (2018)
, blank1_name_sec1 =
GDP per capita
, blank1_info_sec1 = €17,800 (2018)
, blank2_name_sec1 =
HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
(2019)
, blank2_info_sec1 = 0.845
·
21st of 21
, blank_name_sec2 =
NUTS Region
, blank_info_sec2 = ITG
, website
, footnotes =
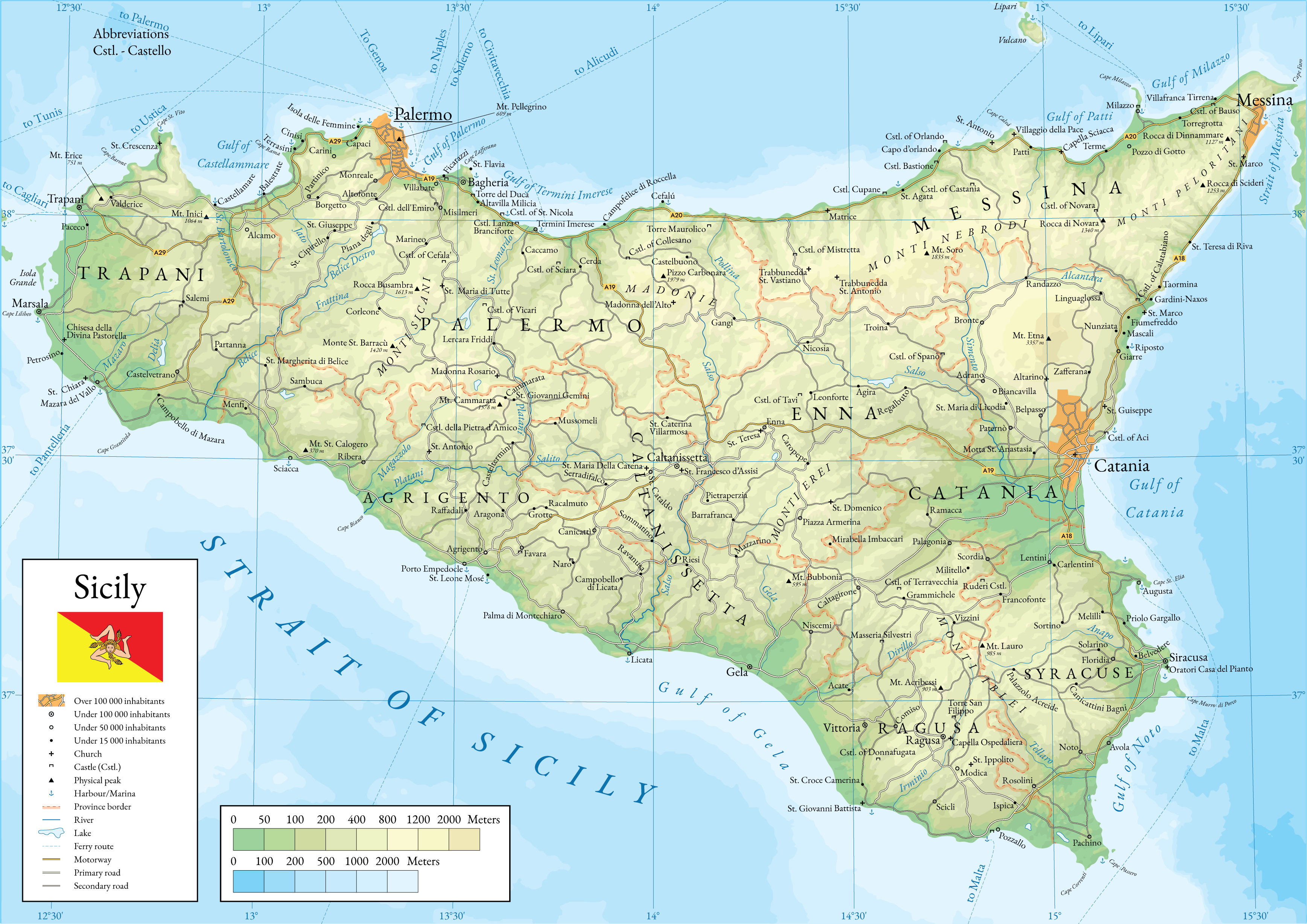
Sicily ( it, Sicilia , ) is the
list of islands in the Mediterranean, largest island in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
and one of the 20
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. The
Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
divides it from the region of
Calabria in Southern Italy. It is one of the five
Italian autonomous regions and is officially referred to as ''Regione Siciliana''. The region has 5 million inhabitants. Its
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
is
Palermo.
Sicily is in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the
Italian Peninsula in
continental Europe, from which it is separated by the narrow
Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
. Its most prominent landmark is
Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
.
The earliest
archaeological evidence of human activity on the island dates from as early as 12,000 BC. By around 750 BC, Sicily had three
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n and a dozen
Greek colonies
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that i ...
and it was later the site of the
Sicilian Wars
The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC.
Carthage's econo ...
and the
Punic Wars. After the end of the Roman province of
Sicilia
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
with the fall of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in the 5th century AD, Sicily was ruled during the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
by the
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
, the
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
, the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, and the
Emirate of Sicily. The
Norman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern ...
led to the creation of the
County of Sicily
The County of Sicily, also known as County of Sicily and Calabria, was a Norman state comprising the islands of Sicily and Malta and part of Calabria from 1071 until 1130. The county began to form during the Christian reconquest of Sicily (106 ...
in 1071, that was succeeded by
Kingdom of Sicily, a state that existed from 1130 until 1816. Later, it was unified under the
House of Bourbon with the
Kingdom of Naples as the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island became part of
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in 1860 following the
Expedition of the Thousand
The Expedition of the Thousand ( it, Spedizione dei Mille) was an event of the Italian Risorgimento that took place in 1860. A corps of volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi sailed from Quarto, near Genoa (now Quarto dei Mille) and landed in Mars ...
, a revolt led by
Giuseppe Garibaldi during the
Italian unification, and a plebiscite. Sicily was given special status as an
autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
on 15 May 1946, 18 days before the
Italian institutional referendum of 1946.
Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the
arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
,
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
,
literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
,
cuisine, and
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
.
Geography

Sicily has a roughly triangular shape, earning it the name ''Trinacria''.
To the north-east, it is separated from
Calabria and the rest of the Italian mainland by the
Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
, about wide in the north, and about wide in the southern part. The northern and southern coasts are each about long measured as a straight line, while the eastern coast measures around ; total coast length is
estimated
Estimation (or estimating) is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is der ...
at . The total area of the island is , while the
Autonomous Region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
of Sicily (which includes smaller surrounding islands) has an area of .
The terrain of inland Sicily is mostly hilly and is intensively cultivated wherever possible. Along the northern coast, the mountain ranges of
Madonie
The Madonie (; Sicilian: ''Madunìi'') are one of the principal mountain ranges on the island of Sicily, located in the Northern part of the island.
Its name comes from the feud of Madonìa which belonged to the noble family of La Farina from P ...
, ,
Nebrodi
The Nebrodi ( scn, Munti Nèbbrudi; it, Monti Nebrodi, ; la, Nebrōdēs montēs) is a mountain range that runs along the north east of Sicily. Together with the Madonie and the Peloritani, they form the Sicilian Apennines.
The mountains run ...
, , and
Peloritani
The Peloritani ( Sicilian: , it, Monti Peloritani) are a mountain range of north-eastern Sicily, in southern Italy, extending for some from Capo Peloro to the Nebrodi Mountains. On the north and east they are bordered by the Tyrrhenian ...
, , are an extension of the mainland
Apennines. The cone of
Mount Etna dominates the eastern coast. In the southeast lie the lower
Hyblaean Mountains
The Hyblaean Mountains ( scn, Munt'Ibblei; it, Monti Iblei; la, Hyblaei montes) is a mountain range in south-eastern Sicily, Italy. It straddles the provinces of Ragusa, Syracuse and Catania. The highest peak of the range is Monte Lauro, at 98 ...
, .
The mines of the
Enna
Enna ( or ; grc, Ἔννα; la, Henna, less frequently ), known from the Middle Ages until 1926 as Castrogiovanni ( scn, Castrugiuvanni ), is a city and located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering ...
and
Caltanissetta
Caltanissetta (; scn, Nissa or ) is a ''comune'' in the central interior of Sicily, Italy, and the capital of the Province of Caltanissetta. Its inhabitants are called ''Nisseni''.
In 2017, the city had a population of 62,797. It is the 14th ...
districts were part of a leading
sulphur-producing area throughout the 19th century, but have declined since the 1950s.
Sicily and its surrounding small islands have some highly active volcanoes. This is due to the fact Sicily is geographically on the northern edge of the
African continental plate. Mount Etna is the largest active volcano in Europe and casts black ash over the island with its recurrent eruptions. It currently stands high, though this varies with summit eruptions; the mountain is lower now than it was in 1981. It is the highest mountain in Italy south of the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
. Etna covers an area of with a basal circumference of . This makes it by far the largest of the three
active volcanoes in Italy, being about two and a half times the height of the next largest,
Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
. In
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities ...
, the deadly monster
Typhon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
was trapped under the mountain by
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
, the god of the sky. Mount Etna is widely regarded as a cultural symbol and icon of Sicily.
File:Mt Etna and Catania1.jpg, Mount Etna rising over suburbs of Catania
The
Aeolian Islands in the
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian pe ...
, to the northeast of mainland Sicily form a volcanic complex.
The three volcanoes of
Vulcano
Vulcano ( scn, Vurcanu) or Vulcan is a small volcanic island belonging to Italy in the Tyrrhenian Sea, about north of Sicily and located at the southernmost end of the seven Aeolian Islands. The island is known for its volcanic activity and ...
,
Stromboli and
Lipari
Lipari (; scn, Lìpari) is the largest of the Aeolian Islands in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the northern coast of Sicily, southern Italy; it is also the name of the island's main town and ''comune'', which is administratively part of the Metropo ...
are also currently active, although the latter is usually dormant. Off the southern coast of Sicily, the underwater volcano of
Ferdinandea
Ferdinandea Island (also Graham Island, Graham Bank or Graham Shoal; french: Ile Julia) is a certain volcanic island/seamount in the Mediterranean Sea near the island of Sicily that has, on more than one occasion, risen above the Mediterranean v ...
, which is part of the larger
Empedocles volcano, last erupted in 1831. It is located between the coast of
Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
and the island of
Pantelleria
Pantelleria (; Sicilian: ''Pantiddirìa'', Maltese: ''Pantellerija'' or ''Qawsra''), the ancient Cossyra or Cossura, is an Italian island and comune in the Strait of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea, southwest of Sicily and east of the Tunisi ...
(which itself is a dormant volcano).
From a geographical perspective, also forming a part of Sicily is the Maltese Archipelago, the islands home to the
republic of Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
.
The
autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
also includes several neighbouring islands: the
Aegadian Islands, the Aeolian Islands, Pantelleria and
Lampedusa
Lampedusa ( , , ; scn, Lampidusa ; grc, Λοπαδοῦσσα and Λοπαδοῦσα and Λοπαδυῦσσα, Lopadoûssa; mt, Lampeduża) is the largest island of the Italian Pelagie Islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
The ''comune'' of L ...
.
Rivers

Several rivers
drain the island, most of which flow through the central area and enter the sea at the south of the island. The
Salso
The Salso ( Sicilian: ''Salsu''), also known as the Imera Meridionale (Greek: ; Latin Himera), is a river of Sicily. It rises in the Madonie Mountains (Latin: Nebrodes Mons; Sicilian: Munti Madunìi) and, traversing the provinces of Enna and Ca ...
flows through parts of Enna and Caltanissetta before entering the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
at the port of
Licata
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''comune'' located on the south coast of Sicily, at the mouth of the Salso River (the ancient ''Himera''), about midway between Ag ...
. To the east, the
Alcantara flows through the province of
Messina and enters the sea at
Giardini Naxos
Giardini NaxosSometimes spelled as Giardini-Naxos. However, the official form as used in the statuto comunale'' is not hyphenated. ( scn, Giaddini; English language, English translation: Naxos Gardens) is a ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of M ...
, and the
Simeto
The Simeto (; scn, Simetu; la, Symaethus; el, Σύμαιθος) is a long river in Sicily, southern Italy. At , it is the second longest river on the island after the Salso (also known as Southern Imera), but the most important in terms of wat ...
, which flows into the
Ionian Sea south of
Catania. Other important rivers on the island are the
Belice
The Belice, , is a river of western Sicily. It is about long. From its main source near Piana degli Albanesi it runs south and west for as the Belice Destro ("right Belice") until it is joined near Poggioreale by its secondary branch, the Be ...
and
Platani in the southwest.
Climate

Sicily has a typical
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
with mild and wet winters and hot, dry summers with very changeable intermediate seasons. On the coasts, especially in the south-west, the climate is affected by the African currents and summers can be scorching.
Snow falls above 900–1000 metres, but it can fall in the hills. The interior mountains, especially
Nebrodi
The Nebrodi ( scn, Munti Nèbbrudi; it, Monti Nebrodi, ; la, Nebrōdēs montēs) is a mountain range that runs along the north east of Sicily. Together with the Madonie and the Peloritani, they form the Sicilian Apennines.
The mountains run ...
,
Madonie
The Madonie (; Sicilian: ''Madunìi'') are one of the principal mountain ranges on the island of Sicily, located in the Northern part of the island.
Its name comes from the feud of Madonìa which belonged to the noble family of La Farina from P ...
, and
Etna, enjoy a full mountain climate, with heavy snowfalls during winter. The summit of Mount Etna is usually snow-capped from October to May.
On the other hand, especially in the summer, it is not unusual that there is the
sirocco
Sirocco ( ), scirocco, or, rarely, siroc (see below) is a Mediterranean wind that comes from the Sahara and can reach hurricane speeds in North Africa and Southern Europe, especially during the summer season.
Names
''Sirocco'' derives from ...
, the wind from the Sahara. Rainfall is scarce, and water proves deficient in some provinces where a water crisis can happen occasionally.
According to the Regional Agency for Waste and Water, on 10 August 1999, the weather station of
Catenanuova
Catenanuova ( Sicilian: ''Catinanova'') is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Enna, in the region of Sicily in southern Italy.
Geography
Catenanuova is located in the Dittaino valley, East from its provincial capital Enna and west fr ...
(EN) recorded a maximum temperature of . The official European record – measured by minimum/maximum thermometers – is held by Athens, Greece, which reported a maximum of in 1977. Total precipitation is highly variable, generally increasing with elevation. In general, the southern and southeast coast receives the least rainfall (less than ), and the northern and northeastern highlands the most (over ).
Flora and fauna


Sicily is an often-quoted example of man-made
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
, which has occurred since Roman times when the island was turned into an agricultural region.
[ This gradually dried the climate, leading to a decline in rainfall and the drying of rivers. The central and southwest provinces are practically devoid of any forest. In Northern Sicily, there are three important forests; near Mount Etna, in the Nebrodi Mountains and in the ]Bosco della Ficuzza
Bosco may refer to:
People Given name Bosco
* Bosco (drag queen) (born 1993), Drag Queen
* Bosco Lin Chi-nan (born 1943), Taiwanese bishop
* Bosco Frontán (born 1984), Uruguayan soccer player
* Bosco Hogan (born 1949), Irish actor
* Bosco Lo ...
Natural Reserve near Palermo. The Nebrodi Mountains Regional Park, established on 4 August 1993 and covering , is the largest protected natural area of Sicily; and contains the largest forest in Sicily, the Caronia
Caronia ( Sicilian: ''Carunìa'', Greek: ( Ptol.) or ( Diod. et al.), Latin: ''Calacte'' or ''Cale Acte'') is a town and '' comune'' on the north coast of Sicily, in the province of Messina, about half way between Tyndaris (modern Tindari) ...
. The Hundred Horse Chestnut (), in Sant'Alfio
Saint Alphys (in Italian: Sant'Alfio) or ( scn, Sant'Arfiu) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania in the Italian region Sicily, about east of Palermo and about north of Catania.
Saint Alphys borders the following mu ...
, on the eastern slopes of Mount Etna, is the largest and oldest known chestnut tree in the world at 2,000 – 4,000 years old.
Sicily has a wide variety of fauna. Species include the European wildcat
The European wildcat (''Felis silvestris'') is a small wildcat species native to continental Europe, Scotland, Turkey and the Caucasus. It inhabits forests from the Iberian Peninsula, Italy, Central and Eastern Europe to the Caucasus. Its fur i ...
, red fox, least weasel, pine marten
The European pine marten (''Martes martes''), also known as the pine marten, is a mustelid native to and widespread in most of Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus and parts of Iran, Iraq and Syria. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. ...
, roe deer
The roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''), also known as the roe, western roe deer, or European roe, is a species of deer. The male of the species is sometimes referred to as a roebuck. The roe is a small deer, reddish and grey-brown, and well-adapt ...
, fallow deer
''Dama'' is a genus of deer in the subfamily Cervinae, commonly referred to as fallow deer.
Name
The name fallow is derived from the deer's pale brown colour. The Latin word ''dāma'' or ''damma'', used for roe deer, gazelles, and antelopes ...
,wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, crested porcupine
The crested porcupine (''Hystrix cristata''), also known as the African crested porcupine, is a species of rodent in the family Hystricidae native to Italy, North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
Characteristics
The adult crested porcupine h ...
, European hedgehog
The European hedgehog (''Erinaceus europaeus''), also known as the West European hedgehog or common hedgehog, is a hedgehog species native to Europe from Iberia and Italy northwards into Scandinavia and westwards into the British Isles.Harris, S ...
, common toad
The common toad, European toad, or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the toad (''Bufo bufo'', from Latin ''bufo'' "toad"), is a frog found throughout most of Europe (with the exception of Ireland, Iceland, and some Mediterranean islands), in ...
, ''Vipera aspis
''Vipera aspis'' is a viper species found in southwestern Europe.
Its common names include asp, asp viper,Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. 2003. ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Krieger Publishing Company, Malab ...
'', golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds of ...
, peregrine falcon, Eurasian hoopoe
The Eurasian hoopoe (''Upupa epops'') is the most widespread species of the genus '' Upupa''. It is a distinctive cinnamon coloured bird with black and white wings, a tall erectile crest, a broad white band across a black tail, and a long narrow ...
and black-winged stilt
The black-winged stilt (''Himantopus himantopus'') is a widely distributed very long-legged wader in the avocet and stilt family ( Recurvirostridae). The scientific name ''H. himantopus'' is sometimes applied to a single, almost cosmopolitan sp ...
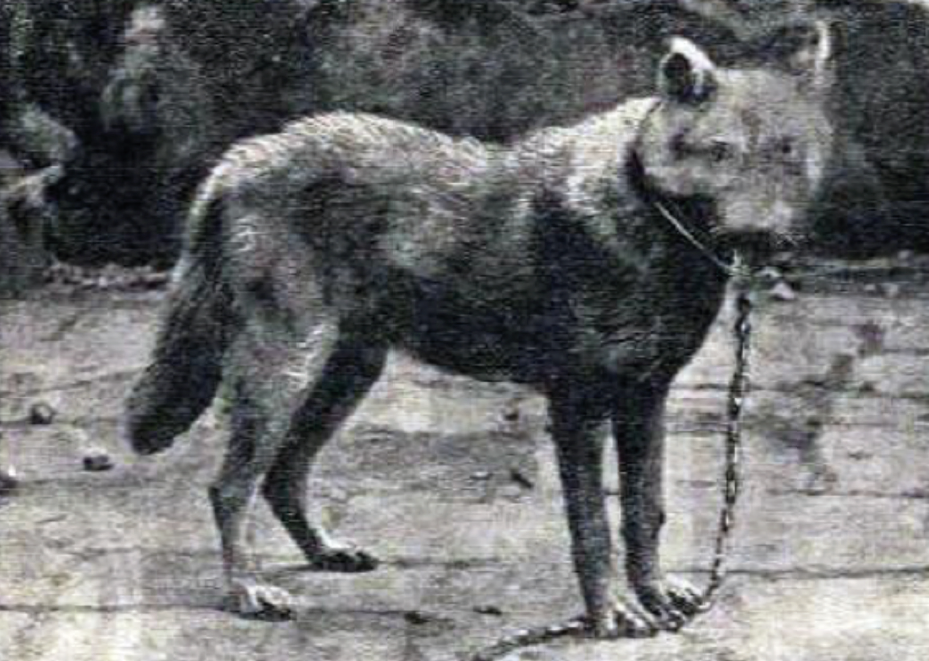
. The Sicilian wolf
The Sicilian wolf (''Canis lupus cristaldii'') ( scn, lupu sicilianu) is an extinct subspecies of the gray wolf that was endemic to Sicily. It was paler than the mainland Italian wolf and comparable in size to the extant Arabian wolf and extinc ...
(''Canis lupus cristaldii'') was an endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
wolf subspecies that was driven to extinction in the 20th century.
The Zingaro Natural Reserve is one of the best examples of unspoiled coastal wilderness in Sicily.
Surrounding waters including the Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
are home to varieties of birds and marine life, including larger species such as greater flamingo
The greater flamingo (''Phoenicopterus roseus'') is the most widespread and largest species of the flamingo family. It is found in Africa, the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East, and in southern Europe.
Taxonomy
The greater flamingo was desc ...
and fin whale
The fin whale (''Balaenoptera physalus''), also known as finback whale or common rorqual and formerly known as herring whale or razorback whale, is a cetacean belonging to the parvorder of baleen whales. It is the second-longest species of ce ...
.
History
The name ''Sicilia
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
'' was given to the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
in 241 BC. It is derived from the name of the Sikeloi, who inhabited the eastern part of the island.
The ancient name of the island is ''Trinacria'' (Greek Τρινακρία "having three headlands") for its triangular shape, likely a re-interpretation of earlier (Homeric
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
) ''Thrinacia
In Greek mythology, the Cattle of Helios (, ''Ēelíoio bóes''), also called the Oxen of the Sun, are cattle pastured on the island of Thrinacia (sometimes identified with Sicily).
Mythology
Helios, who in Greek mythology is the god of the Sun ...
''.
The Greek name was rendered as ''Trīnācrĭa'' in classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later period ...
(Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
, Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
).
Prehistory
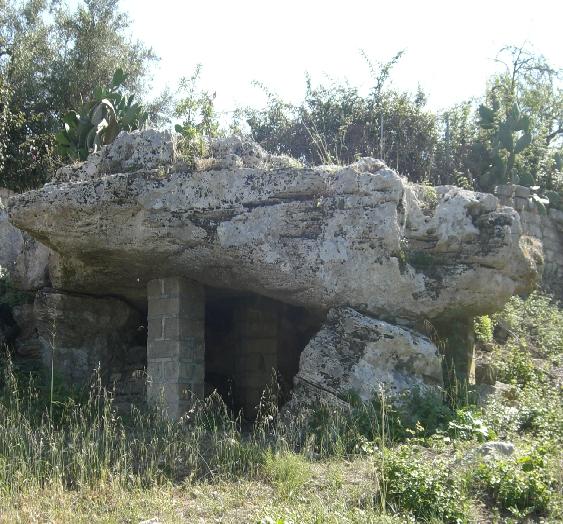

 The original classical-era inhabitants of Sicily comprised three defined groups of the ancient peoples of Italy. The most prominent and by far the earliest of these, the
The original classical-era inhabitants of Sicily comprised three defined groups of the ancient peoples of Italy. The most prominent and by far the earliest of these, the Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ...
, who (Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
writes) arrived from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
(perhaps Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
). Some modern scholars, however, suggest classifying the Sicani as possibly an Illyrian tribe. Important historical evidence has been discovered in the form of cave drawings by the Sicani, dated from the end of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
epoch around 8000 BC.Sicilian hippopotamus
''Hippopotamus pentlandi'' is an extinct hippopotamus from Sicily. It arrived during the Pleistocene. It is the largest of the insular dwarf hippos known from the Pleistocene of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to ...
and the Sicilian dwarf elephant. The Elymians
The Elymians ( grc-gre, Ἔλυμοι, ''Élymoi''; Latin: ''Elymi'') were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, the Elymians ...
, thought to have come from the area of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
, became the next tribe to join the Sicanians on Sicily.
 Recent discoveries of dolmens on the island (dating to the second half of the third millennium BC) seem to offer new insights into the culture of primitive Sicily.
Recent discoveries of dolmens on the island (dating to the second half of the third millennium BC) seem to offer new insights into the culture of primitive Sicily.Liguria
it, Ligure
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
; they arrived from mainland Italy in 1200 BC and forced the Sicanians to move back across Sicily and to settle in the middle of the island.Milazzo
Milazzo ( Sicilian: ''Milazzu''; la, Mylae; ) is a town (''comune'') in the Metropolitan City of Messina, Sicily, southern Italy; it is the largest commune in the Metropolitan City after Messina and Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto. The town has a p ...
) and the Morgetes of Morgantina
Morgantina (Μοργάντιον / Μοργαντίνη in ancient greek) is an archaeological site in east central Sicily, southern Italy. It is sixty kilometres from the coast of the Ionian Sea, in the province of Enna. The closest modern ...
.
Antiquity
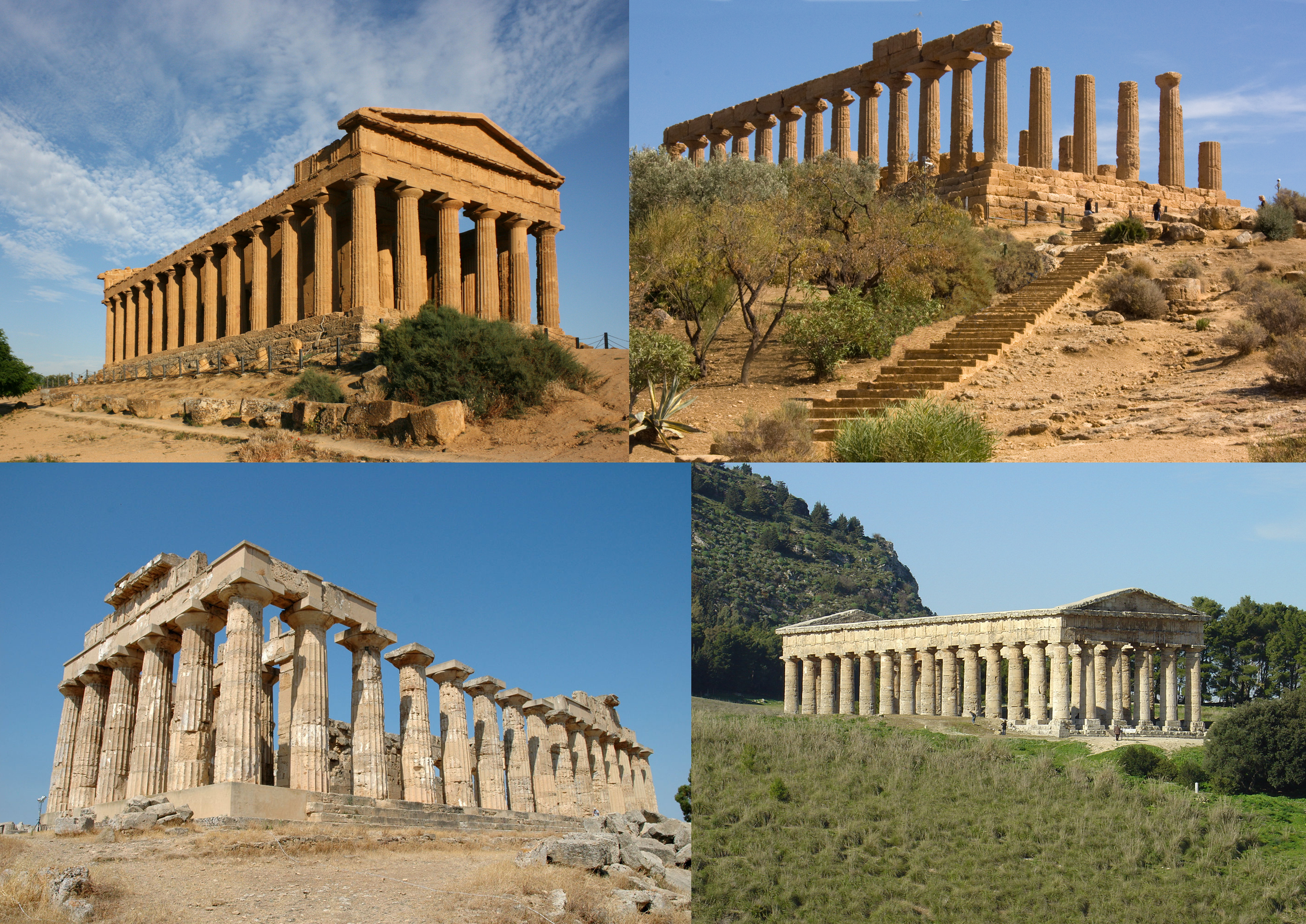
 The
The Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n settlements in the western part of the island predate the arrival of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonists.Akragas
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of ...
, Selinunte
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Selīnoûs ; la, Selīnūs , ; scn, Silinunti ) was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modion ...
, Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
, Himera
Himera (Greek: ), was a large and important ancient Greek city, situated on the north coast of Sicily at the mouth of the river of the same name (the modern Imera Settentrionale), between Panormus (modern Palermo) and Cephaloedium (modern Cef ...
and Zancle
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in t ...
. The native Sicani and Sicel peoples became absorbed into the Hellenic culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Minoan and later in Mycenaean Greece, continuing most notably into Classical Greece, while influencing the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire. Other cultu ...
with relative ease, and the area became part of '' Magna Graecia'' - along with the coasts of the south of the Italian peninsula, which the Greeks had also colonised. Sicily had very fertile soils, and the successful introduction of olives and grape vine
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, ...
s fostered a great deal of profitable trading.Greek culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Minoan and later in Mycenaean Greece, continuing most notably into Classical Greece, while influencing the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire. Other cul ...
significantly included Greek religion, and the settlers built many temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
s throughout Sicily, including several in the ''Valley of the Temples'' at Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
.
Politics on the island became intertwined with those of Greece; Syracuse became desired by the Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
s who set out on the Sicilian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devas ...
(415–413 BC) during the Peloponnesian War. Syracuse gained Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
and Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government refor ...
as allies and, as a result, defeated the Athenian expedition. The victors destroyed the Athenian army and their ships, selling most of the survivors into slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Greek Syracuse controlled eastern Sicily while
Greek Syracuse controlled eastern Sicily while Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
controlled the West. The two cultures began to clash, leading to the Greek-Punic wars
The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC.
Carthage's econo ...
(between 580 and 265 BC). The Greek states had begun to make peace with the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
in 262 BC, and the Romans sought to annex
Annex or Annexe refers to a building joined to or associated with a main building, providing additional space or accommodations.
It may also refer to:
Places
* The Annex, a neighbourhood in downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada
* The Annex (New H ...
Sicily as their republic's first province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
. Rome attacked Carthage's holdings in Sicily in the First Punic War (264 to 241 BC) and won, making Sicily the first Roman province outside of the Italian Peninsula by 242 BC.Roman consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
M. Valerian told the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
in 210 BC that "no Carthaginian remains in Sicily".
As the Roman Republic's granary
A granary is a storehouse or room in a barn for threshed grain or animal feed. Ancient or primitive granaries are most often made of pottery. Granaries are often built above the ground to keep the stored food away from mice and other animals ...
, Sicily ranked as an important province, divided into two quaestorships: Syracuse to the east and Lilybaeum to the west.Latin language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of t ...
to the island, which underwent a slow process of latinisation but Sicily was remained largely Greek in a cultural sense and the Greek language did not become extinct on the island, facilitating its re-hellenisation under the Byzantines.Verres
Gaius Verres (c. 120–43 BC) was a Roman magistrate, notorious for his misgovernment of Sicily. His extortion of local farmers and plundering of temples led to his prosecution by Cicero, whose accusations were so devastating that his defence adv ...
became governor of Sicily (73 to 71 BC). In 70 BC noted figure Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
condemned the misgovernment of Verres in his oration ''In Verrem
"In Verrem" ("Against Verres") is a series of speeches made by Cicero in 70 BC, during the corruption and extortion trial of Gaius Verres, the former governor of Sicily. The speeches, which were concurrent with Cicero's election to the aedileshi ...
''.
Various groups used the island as a power base at different times: slave insurgents occupied it during the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
(135−132 BC) and Second (104−100 BC) Servile Wars
The Servile Wars were a series of three slave revolts ("servile" is derived from "''servus''", Latin for "slave") in the late Roman Republic.
Wars
* First Servile War (135−132 BC) — in Sicily, led by Eunus, a former slave claiming to be a ...
, and Sextus Pompey
Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius ( 67 – 35 BC), also known in English as Sextus Pompey, was a Roman military leader who, throughout his life, upheld the cause of his father, Pompey the Great, against Julius Caesar and his supporters during the las ...
had his headquarters there during the Sicilian revolt of 44 to 36 BC. Christianity first appeared in Sicily during the years following AD 200; between this time and AD 313, when Emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
finally lifted the prohibition on Christianity, a significant number of Sicilians
Sicilians or the Sicilian people are a Romance speaking people who are indigenous to the island of Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the largest and most populous of the autonomous regions of Italy.
Origin and i ...
had become martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
s, including Agatha, Christina, Lucy
Lucy is an English feminine given name derived from the Latin masculine given name Lucius with the meaning ''as of light'' (''born at dawn or daylight'', maybe also ''shiny'', or ''of light complexion''). Alternative spellings are Luci, Luce, Lu ...
, and Euplius.
Germanic rule (469–535)
The Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
began falling apart after the invasion of Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
, Alans, and Sueves across the Rhine on the last day of 406. Eventually the Vandals, after roaming about western and southern Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
(present-day Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
) for 20 years, moved to North Africa in 429 and occupied Carthage in 439. The Franks moved south from present-day Belgium. The Visigoths moved west and eventually settled in Aquitaine in 418; the Burgundians settled in present-day Savoy in 443. The Vandals found themselves in a position to threaten Sicily – only 100 miles away from their North African bases.Gaiseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric ( la, Gaisericus, Geisericus; reconstructed Vandalic: ) was King of the Vandals and Alans (428–477), ruling a kingdom he established, and was one of the key players in the diff ...
, laid siege to Palermo in 440 as the opening act in an attempt to wrest the island from Roman rule. The Vandals made another attempt to take the island one year after the 455 sack of Rome, at Agrigento, but were defeated decisively by Ricimir in a naval victory off Corsica in 456. The island remained under Roman rule until 469. The Vandals lost possession of the island 8 years later in 477 to the East Germanic tribe
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
of the Ostrogoths, who then controlled Italy and Dalmatia.Ostrogothic
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
conquest of Sicily (and of Italy as a whole) under Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
began in 488. The Byzantine Emperor Zeno
Zeno ( grc, Ζήνων) may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 BC), ...
had appointed Theodoric as a military commander in Italy. The Goths were Germanic, but Theodoric fostered Roman culture and government and allowed freedom of religion. In 461 from the age of seven or eight until 17 or 18 Theodoric had become a Byzantine hostage; he resided in the great palace of Constantinople, was favored by Emperor Leo I
The LEO I (Lyons Electronic Office I) was the first computer used for commercial business applications.
The prototype LEO I was modelled closely on the Cambridge EDSAC. Its construction was overseen by Oliver Standingford, Raymond Thompson and ...
() and learned to read and write and do arithmetic.
Byzantine period (535–965)
 After taking areas occupied by the Vandals in North Africa, Justinian decided to retake Italy as an ambitious attempt to recover the lost provinces in the West. The re-conquests marked an end to over 150 years of accommodationist policies with tribal invaders. His first target was Sicily (known as the
After taking areas occupied by the Vandals in North Africa, Justinian decided to retake Italy as an ambitious attempt to recover the lost provinces in the West. The re-conquests marked an end to over 150 years of accommodationist policies with tribal invaders. His first target was Sicily (known as the Gothic War (535–554)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the last ...
began between the Ostrogoths and the Eastern Roman Empire, also known as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
). His general Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terr ...
was assigned the task. Sicily was used as a base for the Byzantines to conquer the rest of Italy, with Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, Rome, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
. It took five years before the Ostrogoth capital Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the ca ...
fell in 540.Totila
Totila, original name Baduila (died 1 July 552), was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the t ...
counterattacked, moving down the Italian peninsula, plundering and conquering Sicily in 550. Totila was defeated and killed in the Battle of Taginae
At the Battle of Taginae (also known as the Battle of Busta Gallorum) in June/July 552, the forces of the Byzantine Empire under Narses broke the power of the Ostrogoths in Italy, and paved the way for the temporary Byzantine reconquest of the It ...
by Byzantine general Narses
, image=Narses.jpg
, image_size=250
, caption=Man traditionally identified as Narses, from the mosaic depicting Justinian and his entourage in the Basilica of San Vitale, Ravenna
, birth_date=478 or 480
, death_date=566 or 573 (aged 86/95)
, allegi ...
in 552 but Italy was in ruins.Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
to Syracuse in 660. The following year he launched an assault from Sicily against the Lombard Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy of Benevento (after 774, Principality of Benevento) was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conq ...
, which occupied most of southern Italy.Constantine IV
Constantine IV ( la, Constantinus; grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantînos; 650–685), called the Younger ( la, iunior; grc-gre, ὁ νέος, ho néos) and sometimes incorrectly the Bearded ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, Πωγων ...
succeeded him. A brief usurpation in Sicily by Mezezius
Mizizios or Mezezius ( el, Μιζίζιος; hy, Մժէժ, ''Mžēž'' or ''Mzhezh'') was an Armenian noble who served as a general of Byzantium, later usurping the Byzantine throne in Sicily from 668 to 669.
Origin and early career
According ...
was quickly suppressed by this emperor. Contemporary accounts report that the Greek language was widely spoken on the island during this period. In 740 Emperor Leo III the Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian ( gr, Λέων ὁ Ἴσαυρος, Leōn ho Isauros; la, Leo Isaurus; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was Byzantine Emperor from 717 until his death in 741 and founder of the Isaurian dynasty. He put an e ...
transferred Sicily from the jurisdiction of the church of Rome to that of Constantinople, placing the island within the eastern branch of the Church.
In 826 Euphemius, the Byzantine commander in Sicily, having apparently killed his wife, forced a nun to marry him. Emperor Michael II caught wind of the matter and ordered general Constantine to end the marriage and cut off Euphemius' head. Euphemius rose up, killed Constantine, and then occupied Syracuse; he, in turn, was defeated and driven out to North Africa.Aghlabid
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a ...
Emir of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, in return for a position as a general and a place of safety. A Muslim army was then sent to the island consisting of Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s, Berbers, Cretans
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
, and Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
.Muslim conquest of Sicily
The Muslim conquest of Sicily began in June 827 and lasted until 902, when the last major Byzantine stronghold on the island, Taormina, fell. Isolated fortresses remained in Byzantine hands until 965, but the island was henceforth under Musli ...
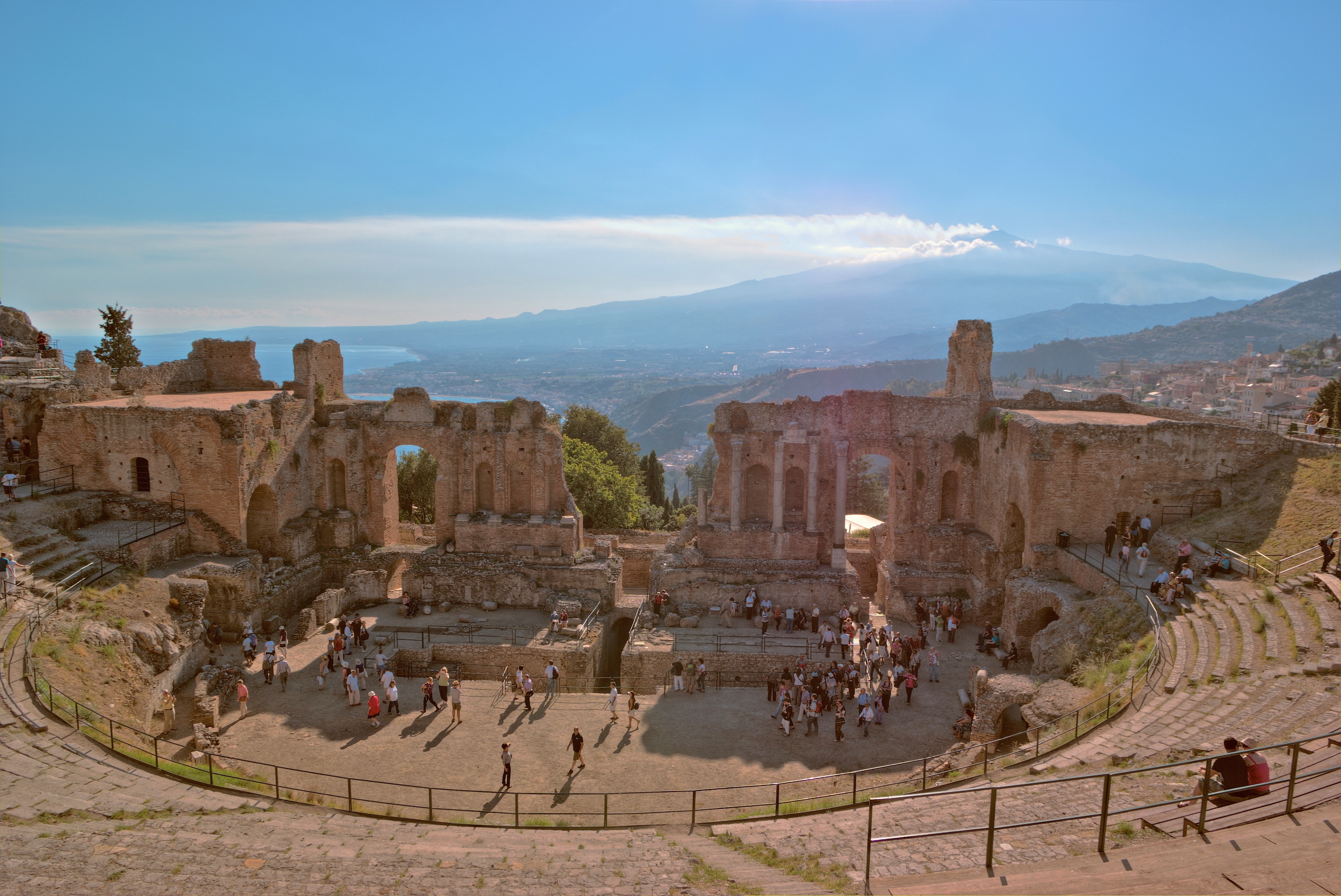
was a see-saw affair and met with fierce resistance. It took over a century for Byzantine Sicily to be conquered; the largest city, Syracuse, held out until 878 and the Greek city of Taormina
Taormina ( , , also , ; scn, Taurmina) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on ...
fell in 962. It was not until 965 that all of Sicily was conquered by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
.George Maniakes
George Maniakes (, transliterated as Georgios Maniaces, Maniakis, or Maniaches, , ; died 1043) was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire of Byzantine Greek origin
during the 11 ...
, but it was their Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
mercenaries who would eventually complete the island's reconquest at the end of the century.
Arab Period (827–1091)
 The Arabs initiated land reforms, which increased productivity and encouraged the growth of
The Arabs initiated land reforms, which increased productivity and encouraged the growth of smallholding
A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technology ...
s, undermining the dominance of the latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious" and ''fundus'', "farm, estate") is a very extensive parcel of privately owned land. The latifundia of Roman history were great landed estates specializing in agriculture destined for export: grain, o ...
. The Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
further improved irrigation systems. The language spoken in Sicily under Arab rule was Siculo-Arabic
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, الْلهجَة الْعَرَبِيَة الْصَقلِيَة), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century ...
and Arabic influence is still present in some Sicilian words today. Although long extinct in Sicily, the language has developed into what is now the Maltese language
Maltese ( mt, Malti, links=no, also ''L-Ilsien Malti'' or '), is a Semitic language derived from late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance superstrata spoken by the Maltese people. It is the national language of Malta and the only offic ...
on the islands of Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
today.
 A description of Palermo was given by
A description of Palermo was given by Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
, an Arab merchant who visited Sicily in 950. A walled suburb, called the Al-Kasr (the palace), is the centre of Palermo to this day, with the great Friday mosque on the site of the later Roman cathedral. The suburb of al-Khalisa (modern Kalsa
Kalsa or Mandamento Tribunali is a historical quarter of the Italian city of Palermo in Sicily. It is sometimes referred to as la Kalsa or the Kalsa.
Names
The common name of the quarter, ''Kalsa'', derives from the district's historic Arabic ...
) contained the Sultan's palace, baths, a mosque, government offices, and a private prison. Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
reckoned 7,000 individual butchers trading in 150 shops. During Muslim rule agricultural products such as oranges, lemons, pistachio and sugarcane were brought to Sicily.Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a c ...
; later it was the centre of the Emirate of Sicily, which was under the nominal suzerainty of the Fatimid Caliphate. During the reign of this dynasty revolts by Byzantine Sicilians continuously occurred especially in the east where Greek-speaking Christians predominated. Parts of the island were re-occupied before revolts were being quashed. Under the Arab rule the island was divided in three administrative regions, or "vals", roughly corresponding to the three "points" of Sicily: Val di Mazara
Mazara del Vallo (; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Trapani, southwestern Sicily, Italy. It lies mainly on the left bank at the mouth of the Mazaro river.
It is an agricultural and fishing centre and its port gives shelter to the ...
in the west; Val Demone
Val Demone or Val di Demona (English: 'Valley of Demona') is a historical and geographical region encompassing the north-eastern third of Sicily. Historically, it was one of the three valli of Sicily.
Val Demone was the last part of the island to ...
in the northeast; and Val di Noto
Val di Noto (English: ''Province of Noto'') is a historical and geographical area encompassing the south-eastern third of Sicily; it is dominated by the limestone Hyblaean plateau. Historically, it was one of the three valli of Sicily.
History
...
in the southeast. As dhimmis, that is as members of a protected class of approved monotheists the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christians were allowed freedom of religion, but had to pay a tax, the jizya (in lieu of the obligatory alms tax, the zakat, paid by Muslims), and were restricted from active participation in public affairs. By the 11th century, the Emirate of Sicily began to fragment as intra-dynastic quarreling fractured the Muslim regime.
Norman Sicily (1038–1198)

 In 1038, seventy years after losing their last cities in Sicily, the Byzantines under the Greek general
In 1038, seventy years after losing their last cities in Sicily, the Byzantines under the Greek general George Maniakes
George Maniakes (, transliterated as Georgios Maniaces, Maniakis, or Maniaches, , ; died 1043) was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire of Byzantine Greek origin
during the 11 ...
invaded the island together with their Varangian guard, Varangian and Normans, Norman mercenaries. Maniakes was killed in a Byzantine civil war in 1043 before completing a reconquest and the Byzantines withdrew. Later the Normans invaded in 1061 and after taking Apulia and Calabria, Roger I of Sicily, Roger I occupied Messina with an army of 700 knights.["Italy during the Crusades – Sicily under the Normans"](_blank)
– History of the Crusades – Boise State University – Retrieved 15 July 2011. In 1068, Roger I was victorious at Misilmeri. Most crucial was the siege of Palermo, whose fall in 1071 eventually resulted in all Sicily coming under Norman control.
Kingdom of Sicily
 While Roger I died in 1101, his wife Adelaide del Vasto, Adelaide ruled until 1112 when their son Roger II of Sicily came of age.
While Roger I died in 1101, his wife Adelaide del Vasto, Adelaide ruled until 1112 when their son Roger II of Sicily came of age.["Norman Sicily of the 12th Century"](_blank)
– Inter-American Institute for Advanced Studies in Cultural History – Retrieved 15 July 2011.
However this situation changed as the Normans imported immigrants from Normandy, England, Lombardy, Piedmont, Provence and Campania to secure the island. Linguistically, the island shifted from being one-third Greek- and two-thirds Arabic-speaking at the time of the Norman conquest to becoming fully Linguistic Latinisation, Latinised. After a century, the Norman Hauteville family, Hauteville dynasty died out; the last direct descendant and heir of Roger II, Constance of Sicily, Constance, married Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Henry VI.
After a century, the Norman Hauteville family, Hauteville dynasty died out; the last direct descendant and heir of Roger II, Constance of Sicily, Constance, married Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Henry VI. Strong opposition to French officialdom due to mistreatment and taxation saw the local peoples of Sicily rise up, leading in 1282 to an insurrection known as the War of the Sicilian Vespers, which eventually saw almost the entire French population on the island killed.
Strong opposition to French officialdom due to mistreatment and taxation saw the local peoples of Sicily rise up, leading in 1282 to an insurrection known as the War of the Sicilian Vespers, which eventually saw almost the entire French population on the island killed. The onset of the Spanish Inquisition in 1492 led to Ferdinand II of Aragon, Ferdinand II decreeing the expulsion of all Jews from Sicily.
The onset of the Spanish Inquisition in 1492 led to Ferdinand II of Aragon, Ferdinand II decreeing the expulsion of all Jews from Sicily.
Italian unification
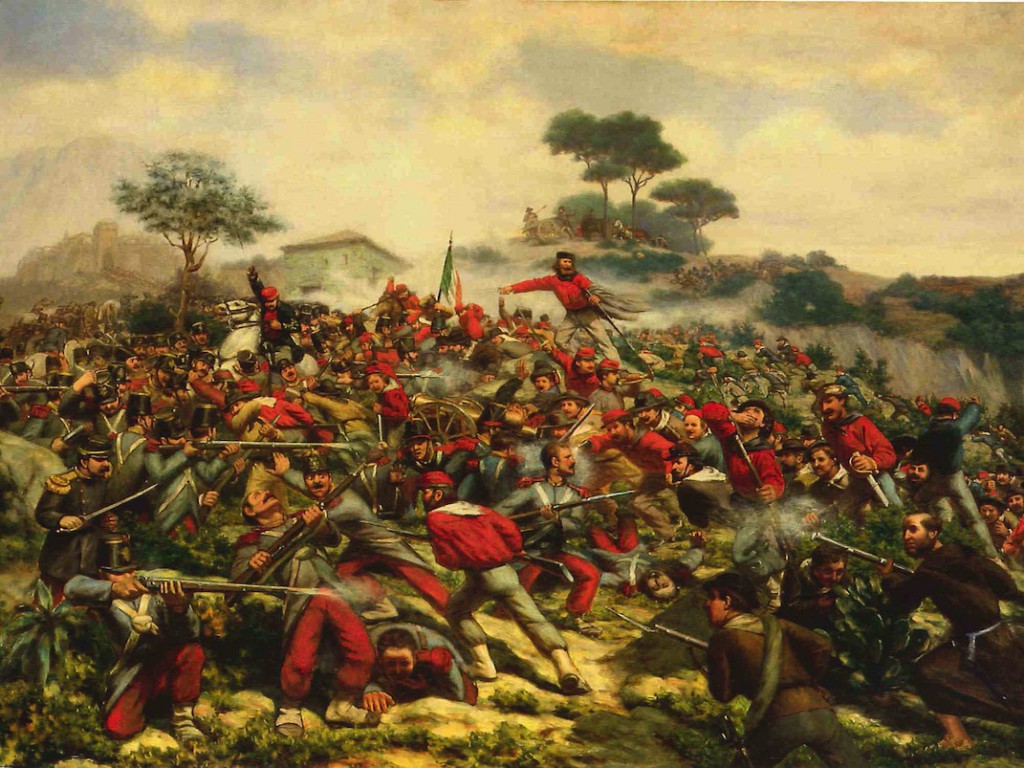 The
The Expedition of the Thousand
The Expedition of the Thousand ( it, Spedizione dei Mille) was an event of the Italian Risorgimento that took place in 1860. A corps of volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi sailed from Quarto, near Genoa (now Quarto dei Mille) and landed in Mars ...
led by Giuseppe Garibaldi captured Sicily in 1860, as part of the .
20th and 21st centuries
In the 1920s, the Italian fascism, Fascist regime began a stronger military action against the Mafia, which was led by prefect Cesare Mori, who was known as the "Iron Prefect" because of his iron-fisted campaigns. This was the first time in which an operation against the Sicilian mafia ended with considerable success.autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
. Both the partial Italian land reform and special funding from the Italian government's ''Cassa per il Mezzogiorno'' (Fund for the South) from 1950 to 1984 helped the Sicilian economy. During this period, the economic and social condition of the island was generally improved thanks to important investments on infrastructures such as motorways and airports, and thanks to the creation of important industrial and commercial areas. In the 1980s, the Mafia was deeply weakened by a second important campaign led by magistrates Giovanni Falcone and Paolo Borsellino. Between 1990 and 2005, the unemployment rate fell from about 23% to 11%.
The Cosa Nostra has traditionally been the most powerful group in Sicily, especially around Palermo. A police investigation in summer 2019 also confirmed strong links between the Palermo area Sicilian Mafia and American organized crime, particularly the Gambino crime family. According to ''La Repubblica'', "Off they go, through the streets of Passo di Rigano, Boccadifalco, Torretta and at the same time, Brooklyn, Staten Island, New Jersey. Because from Sicily to the US, the old mafia has returned".
Demographics
 About five million people live in Sicily, making it the List of regions of Italy#List of regions, fourth most populated region in Italy. In the first century after the Italian unification, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of the emigration of millions of people to Northern Italy, other European countries, North America, South America and Australia. Like the South of Italy and Sardinia, immigration to the island is very low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy instead, due to better employment and industrial opportunities. According to Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT figures from 2017, show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total 5,029,615 population; Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora, Sri Lankans, Albanians, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the official language is Italian and the primary religion is Roman Catholicism.
About five million people live in Sicily, making it the List of regions of Italy#List of regions, fourth most populated region in Italy. In the first century after the Italian unification, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of the emigration of millions of people to Northern Italy, other European countries, North America, South America and Australia. Like the South of Italy and Sardinia, immigration to the island is very low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy instead, due to better employment and industrial opportunities. According to Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT figures from 2017, show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total 5,029,615 population; Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora, Sri Lankans, Albanians, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the official language is Italian and the primary religion is Roman Catholicism.
Emigration
 Sicilian emigration started shortly after the Italian unification and has not stopped ever since.
After the Italian unification, Sicily, along with the entire Italian peninsula, has also been strongly marked by Forced displacement, coerced emigration. Most of the assets of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies's former national bank, ''Banco di Napoli, Banco delle Due Sicilie'', were transferred to Piedmont. During the first decades of Risorgimento, a rising number of southern Italian manufactories were driven into ruin due to high taxation imposed by the central government. Furthermore, an embargo imposed on goods coming from southern Italian manufacturers, that effectively barred them from exporting to the north and abroad, were also key factors that led to further impoverishment of the entire region.
The aforementioned factors, along with a failed land reform, resulted in a never-before-seen wave of Sicilians emigrating, first to the United States between the 1880s and the 1920s, later to Northern Italy, and from the 1960s onwards also to Belgium, France, Germany, Switzerland, as well as Australia and South America.
Today, Sicily is the Italian region with the highest number of expatriates: as of 2017, 750,000 Sicilians, 14.4% of the island's population, lived abroad. For lack of employment, every year many Sicilians, especially young graduates, still leave the island to seek jobs abroad. Today, an estimated 10 million people of Sicilian origins live around the world.
Sicilian emigration started shortly after the Italian unification and has not stopped ever since.
After the Italian unification, Sicily, along with the entire Italian peninsula, has also been strongly marked by Forced displacement, coerced emigration. Most of the assets of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies's former national bank, ''Banco di Napoli, Banco delle Due Sicilie'', were transferred to Piedmont. During the first decades of Risorgimento, a rising number of southern Italian manufactories were driven into ruin due to high taxation imposed by the central government. Furthermore, an embargo imposed on goods coming from southern Italian manufacturers, that effectively barred them from exporting to the north and abroad, were also key factors that led to further impoverishment of the entire region.
The aforementioned factors, along with a failed land reform, resulted in a never-before-seen wave of Sicilians emigrating, first to the United States between the 1880s and the 1920s, later to Northern Italy, and from the 1960s onwards also to Belgium, France, Germany, Switzerland, as well as Australia and South America.
Today, Sicily is the Italian region with the highest number of expatriates: as of 2017, 750,000 Sicilians, 14.4% of the island's population, lived abroad. For lack of employment, every year many Sicilians, especially young graduates, still leave the island to seek jobs abroad. Today, an estimated 10 million people of Sicilian origins live around the world.
Largest cities
These are the ten largest cities of Sicily:
Religion
 As in most Italian regions, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religious denomination in Sicily, and the church still plays an important role in the lives of most people. There is also a notable small minority of Eastern-rite Byzantine Catholics which has a mixed congregation of ethnic Albanians; it is operated by the Italo-Albanian Catholic Church. Most people still attend church weekly or at least for religious festivals, and many people get married in churches. There was a wide presence of Jews in Sicily for at least 1,400 years and possibly for more than 2,000 years. Some scholars believe that the Sicilian Jewry are partial ancestors of the Ashkenazi Jews. However, much of the Jewish community faded away when they were Expulsion of the Jews from Sicily, expelled from the island in 1492. Islam was present during the Emirate of Sicily, although Muslims were also expelled. Today, mostly due to immigration to the island, there are also several religious minorities, such as Jehovah's Witnesses, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism. There are also a some evangelicalism, Evangelical Christians who live on the island.
As in most Italian regions, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religious denomination in Sicily, and the church still plays an important role in the lives of most people. There is also a notable small minority of Eastern-rite Byzantine Catholics which has a mixed congregation of ethnic Albanians; it is operated by the Italo-Albanian Catholic Church. Most people still attend church weekly or at least for religious festivals, and many people get married in churches. There was a wide presence of Jews in Sicily for at least 1,400 years and possibly for more than 2,000 years. Some scholars believe that the Sicilian Jewry are partial ancestors of the Ashkenazi Jews. However, much of the Jewish community faded away when they were Expulsion of the Jews from Sicily, expelled from the island in 1492. Islam was present during the Emirate of Sicily, although Muslims were also expelled. Today, mostly due to immigration to the island, there are also several religious minorities, such as Jehovah's Witnesses, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism. There are also a some evangelicalism, Evangelical Christians who live on the island.
Politics
The politics of Sicily takes place in a framework of a presidential system, presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Government is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Regional Government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Sicilian Regional Assembly. The capital of Sicily is Palermo.
Traditionally, Sicily votes for centre-right parties during elections. From 1943-51, there was also a separatism, separatist political party called Sicilian Independence Movement (''Movimento Indipendentista Siciliano'', MIS). Their most successful result was at the Italian general election, 1946, 1946 general election, when MIS obtained 0.7% of national votes (8.8% of votes in Sicily), and four seats. However, the movement lost all their seats following the Italian general election, 1948, 1948 general election and the 1951 regional election. Even though it has never been formally disbanded, today the movement is no longer part of the politics of Sicily. After World War II, Sicily became a stronghold of the Christian Democracy (Italy), Christian Democracy, in opposition to the Italian Communist Party. The Italian Communist Party, Communists and their successors (the Democratic Party of the Left, the Democrats of the Left and the present-day Democratic Party (Italy), Democratic Party) had never won any seats in the region until Sicilian regional election, 2012, 2012. Sicily is now governed by a centre-right coalition. Nello Musumeci is the current President and has served since 2017.
Sicily’s internal politics are heavily corrupt, since they are very influenced by the Sicilian Mafia.
Administrative divisions
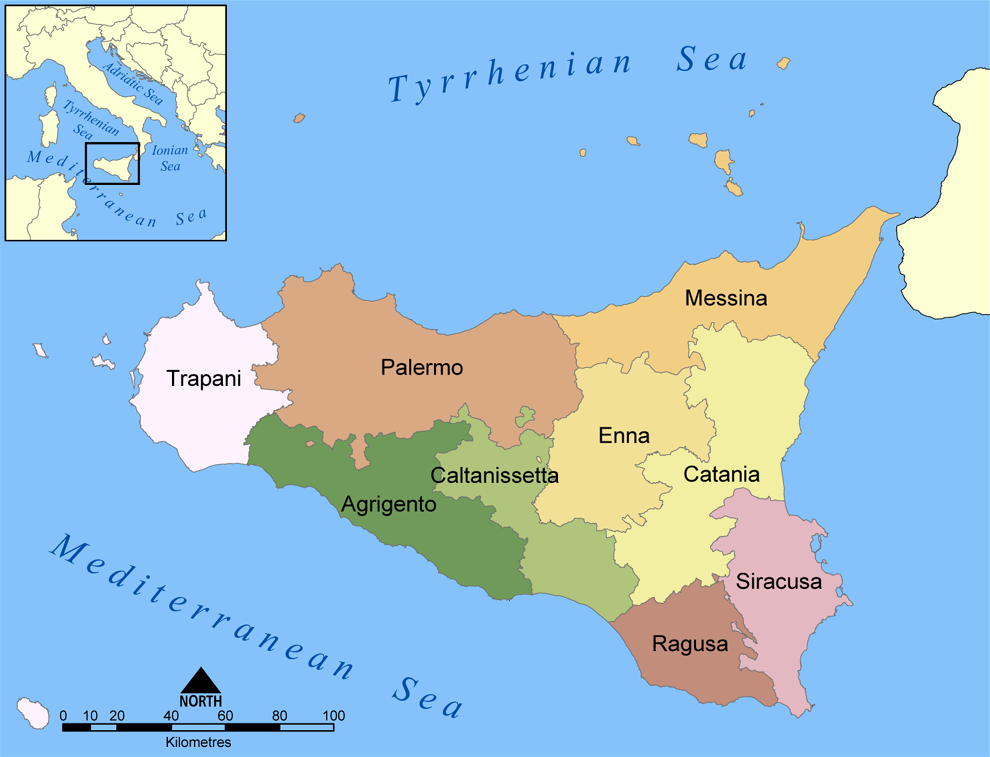 Administratively, Sicily is divided into nine provinces, each with a capital city of the same name as the province. Small surrounding islands are also part of various Sicilian provinces: the Aeolian Islands (Messina), isle of Ustica (Palermo), Aegadian Islands (Trapani), isle of
Administratively, Sicily is divided into nine provinces, each with a capital city of the same name as the province. Small surrounding islands are also part of various Sicilian provinces: the Aeolian Islands (Messina), isle of Ustica (Palermo), Aegadian Islands (Trapani), isle of Pantelleria
Pantelleria (; Sicilian: ''Pantiddirìa'', Maltese: ''Pantellerija'' or ''Qawsra''), the ancient Cossyra or Cossura, is an Italian island and comune in the Strait of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea, southwest of Sicily and east of the Tunisi ...
(Trapani) and Pelagian Islands (Agrigento).
Economy
 Thanks to regular growth in recent years, Sicily is the eighth largest regional economy of Italy in terms of total GDP (see List of Italian regions by GDP (PPP), List of Italian regions by GDP). A series of reforms and investments in agriculture, such as the introduction of modern irrigation systems, has made this important industry competitive. In the 1970s, some factories were opened, resulting in growth in the industrial sector. In recent years the service industry has become more important due to the opening of several shopping malls and some modest growth in financial and telecommunication activities. Tourism is an important source of income for the island, which attracts visitors due to its rich natural and historical heritage. Today Sicily is investing a large amount of money into the development of its hospitality industry, to attract even more tourism. However, Sicily continues to have a GDP per capita below the Italian average, and higher unemployment than the rest of Italy. This difference is mostly caused by the negative influence of the Mafia, which is still active in some areas, although it is much weaker than in the past.
Thanks to regular growth in recent years, Sicily is the eighth largest regional economy of Italy in terms of total GDP (see List of Italian regions by GDP (PPP), List of Italian regions by GDP). A series of reforms and investments in agriculture, such as the introduction of modern irrigation systems, has made this important industry competitive. In the 1970s, some factories were opened, resulting in growth in the industrial sector. In recent years the service industry has become more important due to the opening of several shopping malls and some modest growth in financial and telecommunication activities. Tourism is an important source of income for the island, which attracts visitors due to its rich natural and historical heritage. Today Sicily is investing a large amount of money into the development of its hospitality industry, to attract even more tourism. However, Sicily continues to have a GDP per capita below the Italian average, and higher unemployment than the rest of Italy. This difference is mostly caused by the negative influence of the Mafia, which is still active in some areas, although it is much weaker than in the past.
Agriculture
 Sicily has long been noted for its fertile soil, which is the result of past volcanic eruptions. The local agriculture is also helped by the pleasant climate of the island. The main agricultural products are wheat, Diamante citron, citrons, oranges ''(Blood orange, Arancia Rossa di Sicilia IGP)'', lemons, tomatoes ''(Pomodoro di Pachino, Pomodoro di Pachino IGP)'', olives, olive oil, artichokes, Opuntia ficus-indica, prickly pear ''(Fico d'India dell' Etna DOP)'', almonds, grapes, pistachios ''(Pistacchio di Bronte, Sicily, Bronte DOP)'' and wine. Cattle and sheep are raised. The production of cheese is particularly important thanks to the Ragusano cheese, Ragusano DOP and the Pecorino Siciliano, Pecorino Siciliano DOP. Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa is noted for its honey (''Miele Ibleo'') and chocolate (''Cioccolato di Modica IGP'') products.
Sicily has long been noted for its fertile soil, which is the result of past volcanic eruptions. The local agriculture is also helped by the pleasant climate of the island. The main agricultural products are wheat, Diamante citron, citrons, oranges ''(Blood orange, Arancia Rossa di Sicilia IGP)'', lemons, tomatoes ''(Pomodoro di Pachino, Pomodoro di Pachino IGP)'', olives, olive oil, artichokes, Opuntia ficus-indica, prickly pear ''(Fico d'India dell' Etna DOP)'', almonds, grapes, pistachios ''(Pistacchio di Bronte, Sicily, Bronte DOP)'' and wine. Cattle and sheep are raised. The production of cheese is particularly important thanks to the Ragusano cheese, Ragusano DOP and the Pecorino Siciliano, Pecorino Siciliano DOP. Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa is noted for its honey (''Miele Ibleo'') and chocolate (''Cioccolato di Modica IGP'') products.[economia-sicilia](_blank)
insicilia.org. Retrieved on 19 December 2012.
Sicily is the third largest wine producer in Italy, after Veneto and Emilia Romagna (and Italy is the world's largest wine producer). The region is known mainly for fortified Marsala wines. In recent decades the wine industry has improved, new winemakers are experimenting with less-well-known native varieties, and Sicilian wines have become better known.Pantelleria
Pantelleria (; Sicilian: ''Pantiddirìa'', Maltese: ''Pantellerija'' or ''Qawsra''), the ancient Cossyra or Cossura, is an Italian island and comune in the Strait of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea, southwest of Sicily and east of the Tunisi ...
wines; Malvasia#Italian varieties, Malvasia di Lipari, used for the Malvasia#Italian varieties, Malvasia di Lipari DOC wine; and Catarratto, mostly used to make a white wine, Alcamo wine, Alcamo DOC. Furthermore, in Sicily, high-quality wines are also produced using non-native varieties like Syrah, Chardonnay and Merlot.
Sicily is also known for its liqueurs, such as Amaro Averna, produced in Caltanissetta
Caltanissetta (; scn, Nissa or ) is a ''comune'' in the central interior of Sicily, Italy, and the capital of the Province of Caltanissetta. Its inhabitants are called ''Nisseni''.
In 2017, the city had a population of 62,797. It is the 14th ...
, and the local limoncello.
Fishing is another fundamental resource for Sicily. It has important tuna, sardine, swordfish and European anchovy fisheries. Mazara del Vallo is the largest fishing centre in Sicily and one of the most important in Italy.[Economia Regione Siciliana]
Esploriamo.com. Retrieved on 18 December 2012.
Industry and manufacturing

 Improvements in Sicily's road system have helped to promote industrial development. The region has three important industrial districts:
* '' Catania Industrial District'', where there are several food industries and one of the best European electronics industry centres called ''Etna Valley'' (in honour of the best known Silicon Valley) which contains offices and factories of international companies such as STMicroelectronics and Numonyx;
Improvements in Sicily's road system have helped to promote industrial development. The region has three important industrial districts:
* '' Catania Industrial District'', where there are several food industries and one of the best European electronics industry centres called ''Etna Valley'' (in honour of the best known Silicon Valley) which contains offices and factories of international companies such as STMicroelectronics and Numonyx;Enna
Enna ( or ; grc, Ἔννα; la, Henna, less frequently ), known from the Middle Ages until 1926 as Castrogiovanni ( scn, Castrugiuvanni ), is a city and located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering ...
Industrial District'' in which there are food industries.
In Palermo there are important shipyards (such as Fincantieri), Mechanical engineering, mechanical factories of famous Italian companies as Ansaldo Breda, publishing and textile industries. chemical industry, Chemical industries are also in the Province of Messina (Milazzo
Milazzo ( Sicilian: ''Milazzu''; la, Mylae; ) is a town (''comune'') in the Metropolitan City of Messina, Sicily, southern Italy; it is the largest commune in the Metropolitan City after Messina and Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto. The town has a p ...
) and in the Province of Caltanissetta (Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
).
Statistics
GDP growth
A table showing Sicily's different GDP (nominal and per capita) growth between 2000 and 2008:
Economic sectors
After the table which shows Sicily's GDP growth,
Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate stood at 21.5% in 2018 and was one of the highest in Italy and Europe.
Transport
Roads

 Highways have been built and expanded in the last four decades. The most prominent Sicilian roads are the motorways (known as ) in the north of the island. Much of the motorway network is elevated on pillars due to the island's mountainous terrain. Other main roads in Sicily are the ''Strade Statali'', such as the SS.113 that connects Trapani to Messina (via Palermo), the SS.114 Messina- Syracuse (via Catania) and the SS.115 Syracuse-Trapani (via Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa,
Highways have been built and expanded in the last four decades. The most prominent Sicilian roads are the motorways (known as ) in the north of the island. Much of the motorway network is elevated on pillars due to the island's mountainous terrain. Other main roads in Sicily are the ''Strade Statali'', such as the SS.113 that connects Trapani to Messina (via Palermo), the SS.114 Messina- Syracuse (via Catania) and the SS.115 Syracuse-Trapani (via Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
and Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
).
Railways
 The first railway in Sicily was opened in 1863 (Palermo-Bagheria) and today all of the Sicilian provinces are served by a network of railway services, linking to most major cities and towns; this service is operated by Trenitalia. Of the of railway tracks in use, over 60% has been Railway electrification system, electrified whilst the remaining are serviced by Dieselisation, diesel engines. 88% of the lines (1.209 km) are single-track and only are double-track serving the two main routes, Messina-Palermo (Tyrrhenian Sea, Tyrrhenian) and Messina-Catania-Syracuse (Ionian Sea, Ionian), which are the main lines of this region. Of the narrow-gauge railways the Ferrovia Circumetnea is the only one that still operates, going round Mount Etna. From the major cities of Sicily, there are services to
The first railway in Sicily was opened in 1863 (Palermo-Bagheria) and today all of the Sicilian provinces are served by a network of railway services, linking to most major cities and towns; this service is operated by Trenitalia. Of the of railway tracks in use, over 60% has been Railway electrification system, electrified whilst the remaining are serviced by Dieselisation, diesel engines. 88% of the lines (1.209 km) are single-track and only are double-track serving the two main routes, Messina-Palermo (Tyrrhenian Sea, Tyrrhenian) and Messina-Catania-Syracuse (Ionian Sea, Ionian), which are the main lines of this region. Of the narrow-gauge railways the Ferrovia Circumetnea is the only one that still operates, going round Mount Etna. From the major cities of Sicily, there are services to Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, Rome and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
; this is achieved by the trains being loaded onto ferries which cross the Strait.
In Catania there is an Rapid transit, underground railway service (metropolitana di Catania); in Palermo the national railway operator Trenitalia operates a commuter rail (Palermo metropolitan railway service), the Sicilian Capital is also served by 4 AMAT (Comunal Public Transport Operator) tramlines; Messina is served by a Trams in Messina, tramline.
Airports
Mainland Sicily has several airports that serve numerous Italian and European destinations and some extra-European.
* Catania-Fontanarossa Airport, located on the east coast, is the busiest on the island (and one of the busiest in all of Italy).
* Palermo International Airport, which is also a substantially large airport with many national and international flights.
* Trapani-Birgi Airport, a military-civil joint-use airport (third for traffic on the island). Recently the airport has seen an increase in traffic thanks to a low-cost carrier.
* Comiso Airport, Comiso-Ragusa Airport, has recently been refurbished and re-converted from military use to a civil airport. It was opened to commercial traffic and general aviation on 30 May 2013.
* Palermo-Boccadifalco Airport is the old airport of Palermo and is currently used for general aviation and as a base for the Guardia di Finanza and police helicopters.
* Naval Air Station Sigonella, NAS Sigonella Airport, it is an Italian Air Force and US Navy installation.
* Lampedusa Airport.
* Pantelleria Airport.
Ports
 By sea, Sicily is served by several ferry routes and cargo ports, and in all major cities, cruise ships dock on a regular basis.
* Mainland Italy: Ports connecting to the mainland are Messina (route to Villa San Giovanni and Salerno), the busiest passenger port in Italy, Palermo (routes to Genoa, Civitavecchia and
By sea, Sicily is served by several ferry routes and cargo ports, and in all major cities, cruise ships dock on a regular basis.
* Mainland Italy: Ports connecting to the mainland are Messina (route to Villa San Giovanni and Salerno), the busiest passenger port in Italy, Palermo (routes to Genoa, Civitavecchia and Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
) and Catania (route to Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
).
* Sicily's small surrounding islands: The port of Milazzo
Milazzo ( Sicilian: ''Milazzu''; la, Mylae; ) is a town (''comune'') in the Metropolitan City of Messina, Sicily, southern Italy; it is the largest commune in the Metropolitan City after Messina and Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto. The town has a p ...
serves the Aeolian Islands, the ports of Trapani and Marsala the Aegadian Islands and the port of Porto Empedocle the Pelagie Islands. From Palermo there is a service to the island of Ustica and to Sardinia.
* International connections: From Palermo and Trapani there are weekly services to Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and there is also a daily service between Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
and Port of Pozzallo, Pozzallo.
* Commercial and cargo ports: The port of Augusta, Sicily, Augusta is the fifth-largest cargo port in Italy and handles tonnes of goods. Other major cargo ports are Palermo, Catania, Trapani, Port of Pozzallo, Pozzallo and Termini Imerese.
* Touristic ports: Several ports along the Sicilian coast are in the service of private boats that need to moor on the island. The main ports for this traffic are in Marina di Ragusa, Riposto, Portorosa, Syracuse, Cefalù and Sciacca. In Sicily, Palermo is also a major centre for boat rental, with or without crew, in the Mediterranean.
* Fishing ports: Like all islands, Sicily also has many fishing ports. The most important is in Mazara del Vallo followed by Castellamare del Golfo, Licata
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''comune'' located on the south coast of Sicily, at the mouth of the Salso River (the ancient ''Himera''), about midway between Ag ...
, Scoglitti and Portopalo di Capo Passero.
Planned bridge
Plans for a bridge linking Sicily to the mainland have been discussed since 1865. Throughout the last decade, plans were developed for a road and rail link to the mainland via what would be the world's longest suspension bridge, the Strait of Messina Bridge. Planning for the project has experienced several false starts over the past few years. On 6 March 2009, Silvio Berlusconi's government declared that the construction works for the Messina Bridge would begin on 23 December 2009, and announced a pledge of €1.3 billion as a contribution to the bridge's total cost, estimated at €6.1 billion.
The plan has been criticized by environmental associations and some local Sicilians and Calabrians, concerned with its environmental impact, economical sustainability and even possible infiltrations by organized crime.
Tourism
 Sicily's sunny, dry climate, scenery, cuisine, history, and architecture attract many tourists from mainland Italy and abroad. The tourist season peaks in the summer months, although people visit the island all year round. Mount Etna, the beaches, the archaeological sites, and major cities such as Palermo, Catania, Syracuse and Ragusa, Sicily, Ragusa are the favourite tourist destinations, but the old town of
Sicily's sunny, dry climate, scenery, cuisine, history, and architecture attract many tourists from mainland Italy and abroad. The tourist season peaks in the summer months, although people visit the island all year round. Mount Etna, the beaches, the archaeological sites, and major cities such as Palermo, Catania, Syracuse and Ragusa, Sicily, Ragusa are the favourite tourist destinations, but the old town of Taormina
Taormina ( , , also , ; scn, Taurmina) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on ...
and the neighbouring seaside resort of Giardini Naxos
Giardini NaxosSometimes spelled as Giardini-Naxos. However, the official form as used in the statuto comunale'' is not hyphenated. ( scn, Giaddini; English language, English translation: Naxos Gardens) is a ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of M ...
draw visitors from all over the world, as do the Aeolian Islands, Erice, Castellammare del Golfo, Cefalù, Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
, the Pelagie Islands and Capo d'Orlando. The last features some of the best-preserved temples of the ancient Greek period. Many Mediterranean cruise ships stop in Sicily, and many wine tourists also visit the island.
Some scenes of several Hollywood and Cinecittà films were shot in Sicily. This increased the attraction of Sicily as a tourist destination.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
 There are seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites on Sicily. By the order of inscription:
* Valle dei Templi (1997) is one of the most outstanding examples of Magna Graecia, Greater Greece art and architecture, and is one of the main attractions of Sicily as well as a national monument of Italy. The site is located in
There are seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites on Sicily. By the order of inscription:
* Valle dei Templi (1997) is one of the most outstanding examples of Magna Graecia, Greater Greece art and architecture, and is one of the main attractions of Sicily as well as a national monument of Italy. The site is located in Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
.
* Villa Romana del Casale (1997) is a Roman villa built in the first quarter of the 4th century and located about outside the town of Piazza Armerina. It contains the richest, largest and most complex collection of Roman mosaics in the world.[R. J. A. Wilson: ''Piazza Armerina''. In: Akiyama, Terakazu (Ed.): ''The dictionary of Art. Vol. 24: Pandolfini to Pitti.'' Oxford 1998, .]
* Aeolian Islands (2000) are a Volcano, volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian pe ...
, named after the demigod of the winds Aeolus. The Aeolian Islands are a tourist destination in the summer, and attract up to 200,000 visitors annually.
* Val di Noto, Late Baroque Towns of the Val di Noto (2002) "represent the culmination and final flowering of Baroque art in Europe". It includes several towns: Caltagirone, Militello in Val di Catania, Catania, Modica, Noto, Palazzolo Acreide, Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa and Scicli.
* Necropolis of Pantalica (2005) is a large Necropolis in Sicily with over 5,000 tombs dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC. Syracuse is notable for its rich Greek history, culture, amphitheatres and architecture. They are situated in south-eastern Sicily.
* Mount Etna (2013) is one of the most active volcanoes in the world and is in an almost constant state of activity and generated myths, legends and naturalistic observation from Greek, Celts and Roman classic and medieval times.
* Arab-Norman Palermo and the cathedral churches of Cefalù and Monreale; includes a series of nine civil and religious structures dating from the era of the Norman kingdom of Sicily (1130–1194)

Tentative Sites
 * Taormina, Taormina and Isola Bella;
* Motya and Marsala, Libeo Island: The Phoenician-Punic Civilisation in Italy;
* Scala dei Turchi;
*
* Taormina, Taormina and Isola Bella;
* Motya and Marsala, Libeo Island: The Phoenician-Punic Civilisation in Italy;
* Scala dei Turchi;
* Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
.
Archeological sites
Because many different cultures settled, dominated or invaded the island, Sicily has a huge variety of archaeological sites. Also, some of the most notable and best preserved temples and other structures of the Greek world are located in Sicily. Here is a short list of the major archaeological sites:
* Sicels/Sicans/Elymians/Greeks: Segesta, Eryx (Sicily), Eryx, Ispica, Cava Ispica, Thapsos, Pantalica;
* Greeks: Syracuse, Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
, Segesta, Selinunte
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Selīnoûs ; la, Selīnūs , ; scn, Silinunti ) was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modion ...
, Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
, Kamarina, Sicily, Kamarina, Himera
Himera (Greek: ), was a large and important ancient Greek city, situated on the north coast of Sicily at the mouth of the river of the same name (the modern Imera Settentrionale), between Panormus (modern Palermo) and Cephaloedium (modern Cef ...
, Megara Hyblaea, Naxos (Sicily), Naxos, Heraclea Minoa;
* Phoenicians: Motya, Soluntum, Marsala, Palermo;
* Romans: Piazza Armerina, Centuripe, Taormina
Taormina ( , , also , ; scn, Taurmina) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on ...
, Palermo;
* Arabs: Palermo, Mazara del Vallo.
The excavation and restoration of one of Sicily's best known archaeological sites, the Valle dei Templi, Valley of the Temples in Agrigento, was at the direction of the archaeologist Domenico Lo Faso Pietrasanta, Domenico Antonio Lo Faso Pietrasanta, Fifth Duke of Serradifalco, known in archaeological circles simply as ''"Serradifalco"''. He also oversaw the restoration of ancient sites at Segesta, Selinunte
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Selīnoûs ; la, Selīnūs , ; scn, Silinunti ) was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modion ...
, Syracuse, Sicily, Siracusa and Taormina
Taormina ( , , also , ; scn, Taurmina) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on ...
.
Castles
In Sicily there are hundreds of castles, the most relevant are:
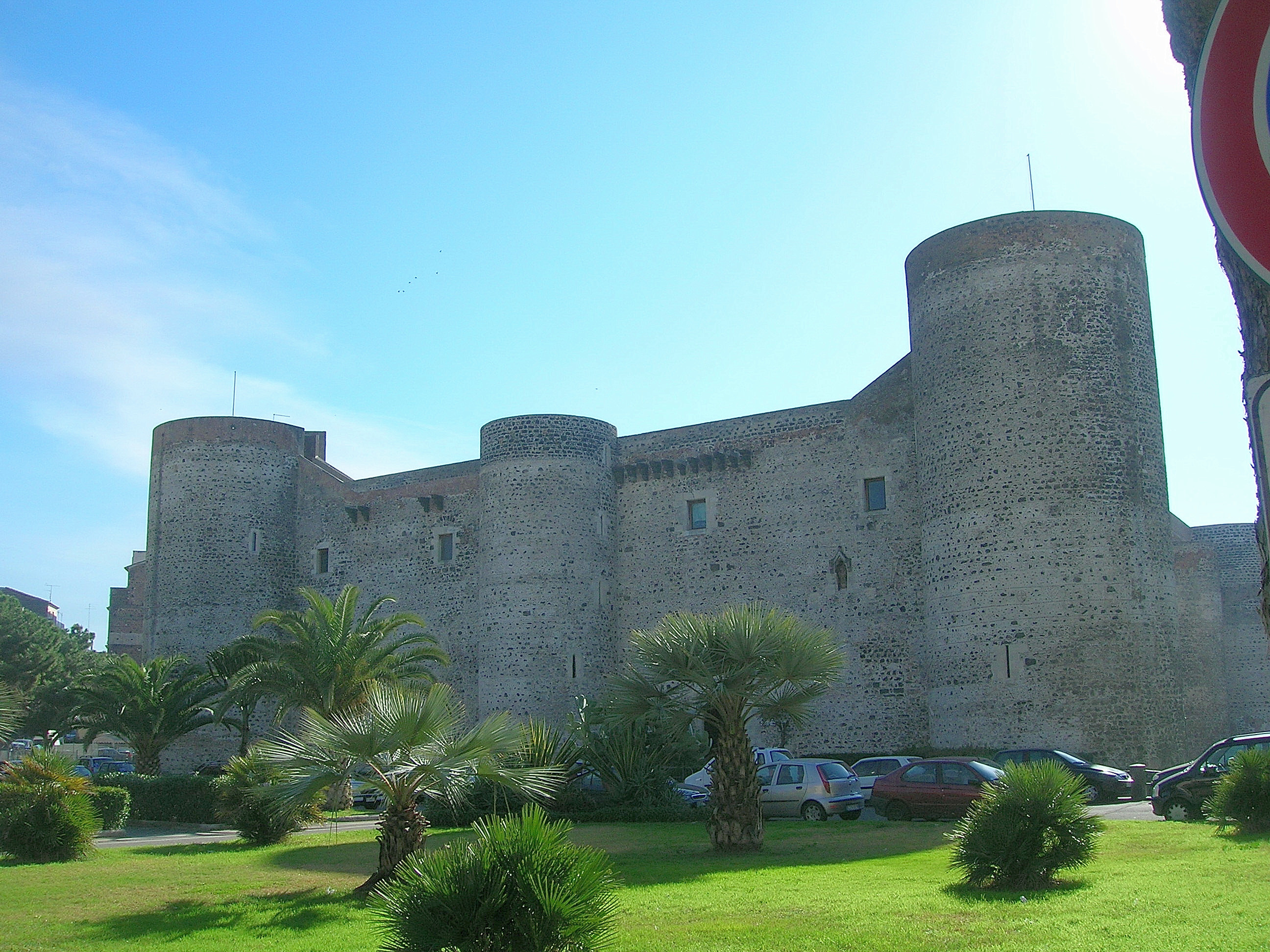




Coastal towers
The Coastal towers in Sicily (''Torri costiere della Sicilia'') are 218 old watchtowers along the coast. In Sicily, the first coastal towers date back to 1313 and 1345 of the Aragonese monarchy. From 1360 the threat came from the south, from North Africa to Maghreb, mainly to Barbary pirates and corsairs of Barbary Coast. In 1516, the Turks settled in Algiers, and from 1520, the corsair Hayreddin Barbarossa under the command of Ottoman Empire, operated from that harbour.
Most existing towers were built on architectural designs of the Florentine architect Camillo Camilliani from [1583] to 1584 and involved the coastal periple of Sicily. The typology changed completely in '800, because of the new higher fire volumes of cannon vessels, the towers were built on the type of Martello towers that the British built in the UK and elsewhere in the British Empire.
The decline of Mediterranean piracy caused by the Second Barbary War led to a smaller number of coastal towers built during the 19th Century.
File:Torre-Capo-Rama-bjs.jpg, Torre-Capo-Rama (Terrasini)
File:Altavilla Milicia BW 2012-10-08 18-04-22 b.JPG, Torre di (Altavilla Milicia)
File:Torre dello Spalmatore - Ustica.jpg, Torre Spalmatore (Ustica)
File:D7A 1568 bis Torre Pozzillo.jpg, Torre Pozzillo (Cinisi)
File:Ligny Tower - Trapani.jpg, Ligny Tower - (Trapani)
File:Trapani.jpg, Torre Nubia (Paceco)
File:Torre di Manfria (Gela).jpg, Torre Manfria (Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
)
File:Torre Cabrera, Marina di Ragusa.jpg, Torre Cabrera (Marina di Ragusa) (Marina di Ragusa)
File:Pozzallo-TorreCabrera.JPG, Torre Cabrera (Pozzallo) (Pozzallo)
File:Vignazzi Tower.JPG, Vignazza Tower (Giardini Naxos
Giardini NaxosSometimes spelled as Giardini-Naxos. However, the official form as used in the statuto comunale'' is not hyphenated. ( scn, Giaddini; English language, English translation: Naxos Gardens) is a ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of M ...
)
Culture
Sicily has long been associated with the arts; many poets, writers, philosophy, philosophers, intellectuals, architects and painters have roots on the island. The history of prestige in this field can be traced back to Greek philosopher Archimedes, a Syracuse native who has gone on to become renowned as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Gorgias and Empedocles are two other highly noted early Sicilian-Greek philosophers, while the Syracusan-Greek Epicharmus of Kos, Epicharmus is held to be the inventor of comedy.
Art and architecture
 Baglio are traditional living structures in Western Sicily.
Baglio are traditional living structures in Western Sicily.
Ceramics
Terracotta ceramics (art), ceramics from the island are well known, the art of ceramics on Sicily goes back to the original ancient peoples named the Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ...
ans, it was then perfected during the period of Greek colonisation and is still prominent and distinct to this day. Nowadays, Caltagirone is one of the most important centres in Sicily for the artistic production of ceramics and terra-cotta sculptures. Famous painters include Renaissance artist Antonello da Messina, Pietro Novelli, Bruno Caruso, Renato Guttuso and Greek born Giorgio de Chirico who is commonly dubbed the "father of Surrealist art" and founder of the metaphysical art movement. The most noted architects are Filippo Juvarra (one of the most important figures of the Italian Baroque) and Ernesto Basile.
Sicilian Baroque
 The Sicilian Baroque has a unique architectural identity. Noto, Caltagirone, Catania, Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, Modica, Scicli and particularly Acireale contain some of Italy's best examples of Baroque architecture, carved in the local red sandstone. Noto provides one of the best examples of the Baroque architecture brought to Sicily.
The Baroque style in Sicily was largely confined to buildings erected by the church, and palazzo, palazzi built as private residences for the Sicilian aristocracy. The earliest examples of this style in Sicily lacked individuality and were typically heavy-handed pastiches of buildings seen by Sicilian visitors to Rome, Florence, and
The Sicilian Baroque has a unique architectural identity. Noto, Caltagirone, Catania, Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, Modica, Scicli and particularly Acireale contain some of Italy's best examples of Baroque architecture, carved in the local red sandstone. Noto provides one of the best examples of the Baroque architecture brought to Sicily.
The Baroque style in Sicily was largely confined to buildings erected by the church, and palazzo, palazzi built as private residences for the Sicilian aristocracy. The earliest examples of this style in Sicily lacked individuality and were typically heavy-handed pastiches of buildings seen by Sicilian visitors to Rome, Florence, and Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
. However, even at this early stage, provincial architects had begun to incorporate certain vernacular features of Sicily's older architecture. By the middle of the 18th century, when Sicily's Baroque architecture was noticeably different from that of the mainland, it typically included at least two or three of the following features, coupled with a unique freedom of design that is more difficult to characterize in words.
Music and film
 Palermo hosts the Teatro Massimo which is the largest opera house in Italy and the third largest in all of Europe.
In Catania there is another important opera house, the Teatro Massimo Bellini with 1,200 seats, which is considered one of the best European opera houses for its acoustics.
Sicily's composers vary from Vincenzo Bellini, Sigismondo d'India, Giovanni Pacini and Alessandro Scarlatti, to contemporary composers such as Salvatore Sciarrino and Silvio Amato.
Palermo hosts the Teatro Massimo which is the largest opera house in Italy and the third largest in all of Europe.
In Catania there is another important opera house, the Teatro Massimo Bellini with 1,200 seats, which is considered one of the best European opera houses for its acoustics.
Sicily's composers vary from Vincenzo Bellini, Sigismondo d'India, Giovanni Pacini and Alessandro Scarlatti, to contemporary composers such as Salvatore Sciarrino and Silvio Amato.

 Many award-winning and acclaimed films of Italian cinema have been filmed in Sicily, amongst the most noted of which are: Luchino Visconti, Visconti's ''"La Terra Trema"'' and ''"Il Gattopardo"'', Pietro Germi's ''"Divorce, Italian Style, Divorzio all'Italiana''" and ''"Seduced and Abandoned (1964 film), Sedotta e Abbandonata''", Giuseppe Tornatore, Tornatore's ''"Cinema Paradiso''".
Many award-winning and acclaimed films of Italian cinema have been filmed in Sicily, amongst the most noted of which are: Luchino Visconti, Visconti's ''"La Terra Trema"'' and ''"Il Gattopardo"'', Pietro Germi's ''"Divorce, Italian Style, Divorzio all'Italiana''" and ''"Seduced and Abandoned (1964 film), Sedotta e Abbandonata''", Giuseppe Tornatore, Tornatore's ''"Cinema Paradiso''".
Literature
 The golden age of Sicilian poetry began in the early 13th century with the Sicilian School of Giacomo da Lentini, which was highly influential on Italian literature. Some of the most noted figures among writers and poets are Luigi Pirandello (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1934), Salvatore Quasimodo (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1959), Giovanni Verga (the father of the ''Italian Verismo (literature), Verismo''), Domenico Tempio, Giovanni Meli, Luigi Capuana, Mario Rapisardi, Federico de Roberto, Leonardo Sciascia, Vitaliano Brancati, Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, Elio Vittorini, Vincenzo Consolo and Andrea Camilleri (noted for his novels and short stories with the fictional character Salvo Montalbano, Inspector Salvo Montalbano as protagonist). On the political side notable philosophers include Gaetano Mosca and Giovanni Gentile who wrote ''The Doctrine of Fascism''.
The golden age of Sicilian poetry began in the early 13th century with the Sicilian School of Giacomo da Lentini, which was highly influential on Italian literature. Some of the most noted figures among writers and poets are Luigi Pirandello (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1934), Salvatore Quasimodo (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1959), Giovanni Verga (the father of the ''Italian Verismo (literature), Verismo''), Domenico Tempio, Giovanni Meli, Luigi Capuana, Mario Rapisardi, Federico de Roberto, Leonardo Sciascia, Vitaliano Brancati, Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, Elio Vittorini, Vincenzo Consolo and Andrea Camilleri (noted for his novels and short stories with the fictional character Salvo Montalbano, Inspector Salvo Montalbano as protagonist). On the political side notable philosophers include Gaetano Mosca and Giovanni Gentile who wrote ''The Doctrine of Fascism''.
Language
Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian and Sicilian language, Sicilian, a distinct and historical Romance languages, Romance language. Some of the Sicilian language, Sicilian words are loan words from Greek language, Greek, Catalan language, Catalan, French, Arabic language, Arabic, Spanish and other languages. Dialects related to Sicilian are also spoken in Calabria and Apulia, Salento; it had a significant influence on the Maltese language
Maltese ( mt, Malti, links=no, also ''L-Ilsien Malti'' or '), is a Semitic language derived from late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance superstrata spoken by the Maltese people. It is the national language of Malta and the only offic ...
. However, the use of Sicilian language, Sicilian is limited to informal contexts (mostly in family) and in a majority of cases it is replaced by the so-called ''regional Italian of Sicily'', an Regional Italian, Italian dialect that is a kind of mix between Italian and Sicilian.
Sicilian was an early influence in the development of the first Italian standard, although its use remained confined to an intellectual elite. This was a literary language in Sicily created under the auspices of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II and his court of notaries, or ''Magna Curia'', which, headed by Giacomo da Lentini, also gave birth to the Sicilian School, widely inspired by troubadour literature. Its linguistic and poetic heritage was later assimilated into the Florentine by Dante Alighieri, the father of modern Italian who, in his , claims that "In effect, this vernacular seems to deserve higher praise than the others since all the poetry written by Italians can be called Sicilian". It is in this language that appeared the first sonnet, whose invention is attributed to Giacomo da Lentini himself.
Science
Catania has one of the four laboratories of the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (National Institute for Nuclear Physics) in which there is a cyclotron that uses protons both for nuclear physics experiments and for particle therapy to treat cancer (proton therapy). Noto has one of the largest radio telescopes in Italy that performs geodetic and astronomical observations. There are observatories in Palermo and Catania, managed by the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (National Institute for Astrophysics). In the ''Observatory of Palermo'' the astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi discovered the first and the largest asteroid to be identified Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres (today considered a dwarf planet) on 1 January 1801; Catania has two observatories, one of which is situated on Mount Etna at .
Syracuse is also an experimental centre for solar technologies through the creation of the project Archimede solar power plant that is the first concentrated solar power, concentrated solar power plant to use molten salt for heat transfer and storage which is integrated with a combined-cycle gas facility. All the plant is owned and operated by Enel. The touristic town of Erice is also an important science place thanks to the Ettore Majorana Foundation and Centre for Scientific Culture which
embraces 123 schools from all over the world, covering all branches of science, offering courses, seminars, workshops, and annual meetings. It was founded by the physicist Antonino Zichichi in honour of another scientist of the island, Ettore Majorana known for the Majorana equation and Majorana fermions. Sicily's famous scientists include also Stanislao Cannizzaro (chemist), Giovanni Battista Hodierna and Niccolò Cacciatore (astronomers).

Education
Sicily has four universities:
* The University of Catania dates back to 1434 and it is the oldest university in Sicily. Nowadays it hosts 12 faculties and over 62,000 students and it offers undergraduate and postgraduate programs. Catania hosts also the ''Scuola superiore di Catania, Scuola Superiore'', an academic institution linked to the University of Catania, aiming for excellence in education.
* The University of Palermo is the island's second-oldest university. It was officially founded in 1806, although historical records indicate that medicine and law have been taught there since the late 15th century. The Orto botanico di Palermo (Palermo botanical gardens) is home to the university's Department of Botany and is also open to visitors.
* The University of Messina, founded in 1548 by Ignatius of Loyola. It is organized in 11 Faculties.
* The Kore University of Enna founded in 1995, is the latest Sicilian university and the first university founded in Sicily after the Italian Unification.
Cuisine
 The island has a long history of producing a variety of noted cuisines and wines, to the extent that Sicily is sometimes nicknamed ''God's Kitchen'' because of this. Every part of Sicily has its speciality (e.g. Cassata is typical of Palermo although available everywhere in Sicily, as is Granita). The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general public. The savoury dishes of Sicily are viewed to be healthy diet, healthy, using fresh vegetables and fruits, such as tomatoes, artichokes, olives (including olive oil), citrus, apricots, aubergines, onions, beans, raisins commonly coupled with seafood, freshly caught from the surrounding coastlines, including tuna, sea bream, European seabass, sea bass, cuttlefish, swordfish, sardines, and others.
The island has a long history of producing a variety of noted cuisines and wines, to the extent that Sicily is sometimes nicknamed ''God's Kitchen'' because of this. Every part of Sicily has its speciality (e.g. Cassata is typical of Palermo although available everywhere in Sicily, as is Granita). The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general public. The savoury dishes of Sicily are viewed to be healthy diet, healthy, using fresh vegetables and fruits, such as tomatoes, artichokes, olives (including olive oil), citrus, apricots, aubergines, onions, beans, raisins commonly coupled with seafood, freshly caught from the surrounding coastlines, including tuna, sea bream, European seabass, sea bass, cuttlefish, swordfish, sardines, and others. The most well-known part of Sicilian cuisine is the rich sweet dishes including ice creams and pastry, pastries. Cannoli (singular: ''cannolo''), a tube-shaped shell of fried pastry dough filled with a sweet filling usually containing ricotta, is strongly associated with Sicily worldwide.
The most well-known part of Sicilian cuisine is the rich sweet dishes including ice creams and pastry, pastries. Cannoli (singular: ''cannolo''), a tube-shaped shell of fried pastry dough filled with a sweet filling usually containing ricotta, is strongly associated with Sicily worldwide.Enna
Enna ( or ; grc, Ἔννα; la, Henna, less frequently ), known from the Middle Ages until 1926 as Castrogiovanni ( scn, Castrugiuvanni ), is a city and located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering ...
), braccilatte (a Sicilian version of doughnuts), buccellato, ciarduna, pignolo (macaroon), pignoli, Biscotti Regina, giurgiulena, frutta martorana, cassata, pignolata, granita, cuccidati (a variety of fig cookie; also known as buccellati) and cuccìa are some notable sweet dishes.
Sports
 The most popular sport in Sicily is association football, football, which came to the fore in the late 19th century under the influence of the English. Some of the oldest football clubs in Italy are from Sicily: the three most successful are U.S. Città di Palermo, Palermo, Calcio Catania, Catania, and A.C.R. Messina, Messina, which have played 29, 17 and 5 seasons in the Serie A respectively. No club from Sicily has ever won Serie A, but football is still deeply embedded in local culture and all over Sicily most towns have a representative team.
The most popular sport in Sicily is association football, football, which came to the fore in the late 19th century under the influence of the English. Some of the oldest football clubs in Italy are from Sicily: the three most successful are U.S. Città di Palermo, Palermo, Calcio Catania, Catania, and A.C.R. Messina, Messina, which have played 29, 17 and 5 seasons in the Serie A respectively. No club from Sicily has ever won Serie A, but football is still deeply embedded in local culture and all over Sicily most towns have a representative team.
Popular culture


 Each town and city has its own patron saint, and the feast days are marked by colourful processions through the streets with marching bands and displays of fireworks.
Sicilian religious festivals also include the ''presepe vivente'' (living nativity scene), which takes place at Christmas time. Deftly combining religion and folklore, it is a constructed mock 19th-century Sicilian village, complete with a nativity scene, and has people of all ages dressed in the costumes of the period, some impersonating the Holy Family, and others working as artisans of their particular assigned trade. It is normally concluded on Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany, often highlighted by the arrival of the magi on horseback.
Oral tradition plays a large role in Sicilian folklore. Many stories passed down from generation to generation involve a character named "Giufà". Anecdotes from this character's life preserve Sicilian culture as well as convey moral messages.
Sicilians also enjoy outdoor festivals, held in the local square or ''piazza'' where live music and dancing are performed on stage, and food fairs or ''sagre'' are set up in booths lining the square. These offer various local specialties, as well as typical Sicilian food. Normally these events are concluded with fireworks. A noted ''sagra'' is the ''Sagra del Carciofo'' or ''Artichoke Festival'', which is held annually in Ramacca in April. The most important traditional event in Sicily is the carnival. Famous carnivals are in Acireale, Misterbianco, Regalbuto, Paternò, Sciacca, Termini Imerese.
Each town and city has its own patron saint, and the feast days are marked by colourful processions through the streets with marching bands and displays of fireworks.
Sicilian religious festivals also include the ''presepe vivente'' (living nativity scene), which takes place at Christmas time. Deftly combining religion and folklore, it is a constructed mock 19th-century Sicilian village, complete with a nativity scene, and has people of all ages dressed in the costumes of the period, some impersonating the Holy Family, and others working as artisans of their particular assigned trade. It is normally concluded on Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany, often highlighted by the arrival of the magi on horseback.
Oral tradition plays a large role in Sicilian folklore. Many stories passed down from generation to generation involve a character named "Giufà". Anecdotes from this character's life preserve Sicilian culture as well as convey moral messages.
Sicilians also enjoy outdoor festivals, held in the local square or ''piazza'' where live music and dancing are performed on stage, and food fairs or ''sagre'' are set up in booths lining the square. These offer various local specialties, as well as typical Sicilian food. Normally these events are concluded with fireworks. A noted ''sagra'' is the ''Sagra del Carciofo'' or ''Artichoke Festival'', which is held annually in Ramacca in April. The most important traditional event in Sicily is the carnival. Famous carnivals are in Acireale, Misterbianco, Regalbuto, Paternò, Sciacca, Termini Imerese.
 The Opera dei Pupi (Opera of the Puppets; Sicilian language, Sicilian: Òpira dî pupi) is a marionette theatrical representation of Frankish romantic poems such as the Song of Roland or ''Orlando furioso'' that is one of the characteristic cultural traditions of Sicily. The sides of donkey carts are decorated with intricate, painted scenes; these same tales are enacted in traditional puppet theatres featuring hand-made marionettes of wood. The opera of the puppets and the Sicilian tradition of ''cantastorî'' (singers of tales) are rooted in the Provençal troubadour tradition in Sicily during the reign of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, in the first half of the 13th century. A great place to see this marionette art is the puppet theatres of Palermo. The Sicilian marionette theatre Opera dei Pupi was proclaimed in 2001 and inscribed in 2008 in the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists.
Today, there are only a few troupes that maintain the tradition. They often perform for tourists. However, there are no longer the great historical families of marionettists, such as the Greco of Palermo; the Gaspare Canino, Canino of Partinico and Alcamo; Crimi, Trombetta and Napoli of Catania, Pennisi and Macri of Acireale, Profeta of
The Opera dei Pupi (Opera of the Puppets; Sicilian language, Sicilian: Òpira dî pupi) is a marionette theatrical representation of Frankish romantic poems such as the Song of Roland or ''Orlando furioso'' that is one of the characteristic cultural traditions of Sicily. The sides of donkey carts are decorated with intricate, painted scenes; these same tales are enacted in traditional puppet theatres featuring hand-made marionettes of wood. The opera of the puppets and the Sicilian tradition of ''cantastorî'' (singers of tales) are rooted in the Provençal troubadour tradition in Sicily during the reign of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, in the first half of the 13th century. A great place to see this marionette art is the puppet theatres of Palermo. The Sicilian marionette theatre Opera dei Pupi was proclaimed in 2001 and inscribed in 2008 in the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists.
Today, there are only a few troupes that maintain the tradition. They often perform for tourists. However, there are no longer the great historical families of marionettists, such as the Greco of Palermo; the Gaspare Canino, Canino of Partinico and Alcamo; Crimi, Trombetta and Napoli of Catania, Pennisi and Macri of Acireale, Profeta of Licata
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''comune'' located on the south coast of Sicily, at the mouth of the Salso River (the ancient ''Himera''), about midway between Ag ...
, Gargano and Grasso of Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
. One can, however, admire the richest collection of marionettes at the Museo Internazionale delle Marionette Antonio Pasqualino and at the Museo Etnografico Siciliano Giuseppe Pitrè in Palermo. Other elaborate marionettes are on display at the Museo Civico Vagliasindi in Randazzo.
Traditional items
 The Sicilian cart is an ornate, colourful style of a horse- or donkey-drawn cart native to Sicily. Sicilian woodcarver George Petralia states that horses were mostly used in the city and flat plains, while donkeys or mules were more often used in rough terrain for hauling heavy loads. The cart has two wheels and is primarily handmade out of wood with iron components.
The Sicilian coppola (cap), coppola is a traditional kind of flat cap typically worn by men in Sicily. First used by English nobles during the late 18th century, the ''tascu'' began being used in Sicily in the early 20th century as a flat cap, driving cap, usually worn by car drivers. The ''coppola'' is usually made in tweed (cloth), tweed. Today it is widely regarded as a definitive symbol of Sicilian heritage.
The Sicilian cart is an ornate, colourful style of a horse- or donkey-drawn cart native to Sicily. Sicilian woodcarver George Petralia states that horses were mostly used in the city and flat plains, while donkeys or mules were more often used in rough terrain for hauling heavy loads. The cart has two wheels and is primarily handmade out of wood with iron components.
The Sicilian coppola (cap), coppola is a traditional kind of flat cap typically worn by men in Sicily. First used by English nobles during the late 18th century, the ''tascu'' began being used in Sicily in the early 20th century as a flat cap, driving cap, usually worn by car drivers. The ''coppola'' is usually made in tweed (cloth), tweed. Today it is widely regarded as a definitive symbol of Sicilian heritage.
Flag and emblem
The Flag of Sicily, regarded as a regional icon, was first adopted in 1282, after the Sicilian Vespers of Palermo. It is characterised by the presence of the triskelion, triskeles in the middle, depicting the head of Medusa and three wheat ears representing the extreme fertility of the land of Sicily.[Radicini, Ninni. "The Trinacria: History and Mythology , The Symbol of the Hellenic Nature of Sicily , Article by Ninni Radicini." The Trinacria: History and Mythology , The Symbol of the Hellenic Nature of Sicily , Article by Ninni Radicini. N.p., n.d. Web. 9 November 2014.] In early mythology, when Medusa was slain and beheaded by Perseus, the Medusa head was placed in the centre of Athena's shield.[Trabia, Carlo. "The Trinacria - Best of Sicily Magazine." The Trinacria - Best of Sicily Magazine. N.p., n.d. Web. 9 November 2014.] Palermo and Corleone were the first two cities to found a confederation against the Capetian House of Anjou, Angevin rule. The triskeles symbol came to be on the Sicilian flag in 1943 during World War II when Andrea Finocchiaro Aprile led an independence movement, in collaboration with the allies. Their plan was to help Sicily become independent and form a free republic. The colours, likewise introduced in the 1940s, respectively represent the cities of Palermo and Corleone. The separatist behind the movement used a yellow and red flag with the Trinacria in the centre of it. When World War II ended, Sicily was recognized as an autonomous region in the Italian Republic.
The flag became the official public flag of the ''Regione Siciliana'' in January 2000, after the passing of an apposite regional law which advocates its use on public buildings, schools and city halls along with the national Flag of Italy, Italian flag and the flag of EU, European one.
Familiar as an ancient symbol of the region, the Triskelion is also featured on Greek coins of Syracuse, such as coins of Agathocles (317–289 BC).The symbol dates back to when Sicily was part of Magna Graecia, the colonial extension of Greece beyond the Aegean Sea, Aegean.[Matthews, Jeff (2005]
Symbols of Naples
The triskelion was revived, as a neoclassicism, neoclassic – and non-House of Bourbon, Bourbon – emblem for the new Napoleonic Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, by Joachim Murat in 1808. In the case of Sicily, the triskelion symbol is said to represent the three Cape (geography), capes (headlands or promontory, promontories of the island of Sicily, namely: Punta del Faro, Pelorus (Peloro, Tip of Faro, Messina: North-East); Capo Passero, Pachynus (Passero, Syracuse: South); and Marsala, Lilybæum (Lilibeo, Cape Boeo, Marsala: West), which form three points of a triangle.
See also
* List of islands of Italy
* List of people from Sicily
References
Further reading
* Alio, Jacqueline (2018) ''Sicilian Studies: A Guide and Syllabus for Educators'' (Trinacria Editions, New York, ).
* Bonacini, Elisa (2007) ''Il territorio calatino nella Sicilia imperiale e tardoromana'' (British Archeological Reports, International Series: 1694) Archaeopress, Oxford, England, , in Italian with abstract in English
* Chaney, Edward. (2000), "British and American Travellers in Sicily from the eighth to the twentieth century", The Evolution of the Grand Tour, Routledge.
* Leighton, Robert (1999) ''Sicily before History'' (Duckworth, London; Cornell University Press, Ithaca).
* Mendola, Louis; Alio, Jacqueline (2013) ''The Peoples of Sicily: A Multicultural Legacy'' (Trinacria Editions, New York, ).
* Spadi, Fabio. (2001
"The Bridge on the Strait of Messina: 'Lowering' the Right of Innocent Passage?"
''International and Comparative Law Quarterly'' 50: 411 ff.
* "From Rome to Sicily: Plane or Train?
Expert Travel Advice, The New York Times, 7 February 2008
The New York Times.
*Attilio L. Vinci, ''Magica Sicilia'', Campo, Alcamo (Trapani), 2018.
*
*
*
* ''To Noto: or London to Sicily in a Ford'' (London, 1989) by Duncan Fallowell
External links
*
Sicilian Region — Official website
The Wonders of Sicily – The Cities, Architecture, Culture, History, People
Piccolo, Salvatore (2018). ''Bronze Age Sicily''. World History Encyclopedia.
*
Piccolo, Salvatore (2018). ''The Dolmens of Sicily''. World History Encyclopedia.
{{Coord, 37, 30, N, 14, 00, E, scale:2500000_source:GNS, display=title
Sicily,
Former countries in Europe
Islands of Italy
Mediterranean
Mediterranean islands
NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
Regions of Italy
Wine regions of Italy
Autonomous regions of Italy
 Sicily ( it, Sicilia , ) is the list of islands in the Mediterranean, largest island in the
Sicily ( it, Sicilia , ) is the list of islands in the Mediterranean, largest island in the  Sicily has a roughly triangular shape, earning it the name ''Trinacria''.
To the north-east, it is separated from Calabria and the rest of the Italian mainland by the
Sicily has a roughly triangular shape, earning it the name ''Trinacria''.
To the north-east, it is separated from Calabria and the rest of the Italian mainland by the  Several rivers drain the island, most of which flow through the central area and enter the sea at the south of the island. The
Several rivers drain the island, most of which flow through the central area and enter the sea at the south of the island. The  Sicily has a typical
Sicily has a typical 
 Sicily is an often-quoted example of man-made
Sicily is an often-quoted example of man-made  Recent discoveries of dolmens on the island (dating to the second half of the third millennium BC) seem to offer new insights into the culture of primitive Sicily. It is well known that the Mediterranean region went through quite intricate prehistory, so much so that it is difficult to piece together the muddle of different peoples who have followed each other. The impact of two influences is clear, however: the European one coming from the Northwest, and the Mediterranean influence of a clear eastern heritage.
No evidence survives of any warring between the tribes, but the Sicanians moved eastwards when the Elymians settled in the northwest corner of the island. The Sicels are thought to have originated in
Recent discoveries of dolmens on the island (dating to the second half of the third millennium BC) seem to offer new insights into the culture of primitive Sicily. It is well known that the Mediterranean region went through quite intricate prehistory, so much so that it is difficult to piece together the muddle of different peoples who have followed each other. The impact of two influences is clear, however: the European one coming from the Northwest, and the Mediterranean influence of a clear eastern heritage.
No evidence survives of any warring between the tribes, but the Sicanians moved eastwards when the Elymians settled in the northwest corner of the island. The Sicels are thought to have originated in 
 The
The  Greek Syracuse controlled eastern Sicily while
Greek Syracuse controlled eastern Sicily while  After taking areas occupied by the Vandals in North Africa, Justinian decided to retake Italy as an ambitious attempt to recover the lost provinces in the West. The re-conquests marked an end to over 150 years of accommodationist policies with tribal invaders. His first target was Sicily (known as the
After taking areas occupied by the Vandals in North Africa, Justinian decided to retake Italy as an ambitious attempt to recover the lost provinces in the West. The re-conquests marked an end to over 150 years of accommodationist policies with tribal invaders. His first target was Sicily (known as the  The Arabs initiated land reforms, which increased productivity and encouraged the growth of
The Arabs initiated land reforms, which increased productivity and encouraged the growth of  A description of Palermo was given by
A description of Palermo was given by  In 1038, seventy years after losing their last cities in Sicily, the Byzantines under the Greek general
In 1038, seventy years after losing their last cities in Sicily, the Byzantines under the Greek general  While Roger I died in 1101, his wife Adelaide del Vasto, Adelaide ruled until 1112 when their son Roger II of Sicily came of age. Having succeeded his brother Simon of Sicily, Simon as Count of Sicily, Roger II was ultimately able to raise the status of the island to a kingdom in 1130, along with his other holdings, which included the Maltese Islands and the Duchies of Duchy of Apulia, Apulia and Duchy of Calabria, Calabria.
Roger II appointed the powerful Greek George of Antioch to be his "emir of emirs" and continued the syncretism of his father. During this period, the Kingdom of Sicily was prosperous and politically powerful, becoming one of the wealthiest states in all of Europe—even wealthier than the Kingdom of England.
The court of Roger II became the most luminous centre of culture in the Mediterranean, both from Europe and the Middle East, like the multi-ethnic Caliphate of Córdoba, then only just eclipsed. This attracted scholars, scientists, poets, artists, and artisans of all kinds. Laws were issued in the language of the community to whom they were addressed in Norman Sicily, at the time when the culture was still heavily Arab and Greek. Governance was by rule of law which promoted justice. Muslims, Jews, Byzantine Greeks, Lombards, and Normans worked together fairly amicably. During this time many extraordinary buildings were constructed."Norman Sicily of the 12th Century"
While Roger I died in 1101, his wife Adelaide del Vasto, Adelaide ruled until 1112 when their son Roger II of Sicily came of age. Having succeeded his brother Simon of Sicily, Simon as Count of Sicily, Roger II was ultimately able to raise the status of the island to a kingdom in 1130, along with his other holdings, which included the Maltese Islands and the Duchies of Duchy of Apulia, Apulia and Duchy of Calabria, Calabria.
Roger II appointed the powerful Greek George of Antioch to be his "emir of emirs" and continued the syncretism of his father. During this period, the Kingdom of Sicily was prosperous and politically powerful, becoming one of the wealthiest states in all of Europe—even wealthier than the Kingdom of England.
The court of Roger II became the most luminous centre of culture in the Mediterranean, both from Europe and the Middle East, like the multi-ethnic Caliphate of Córdoba, then only just eclipsed. This attracted scholars, scientists, poets, artists, and artisans of all kinds. Laws were issued in the language of the community to whom they were addressed in Norman Sicily, at the time when the culture was still heavily Arab and Greek. Governance was by rule of law which promoted justice. Muslims, Jews, Byzantine Greeks, Lombards, and Normans worked together fairly amicably. During this time many extraordinary buildings were constructed."Norman Sicily of the 12th Century" Strong opposition to French officialdom due to mistreatment and taxation saw the local peoples of Sicily rise up, leading in 1282 to an insurrection known as the War of the Sicilian Vespers, which eventually saw almost the entire French population on the island killed. During the war, the Sicilians turned to Peter III of Aragon, son-in-law of the last Hohenstaufen king, for support after being rejected by the Pope. Peter gained control of Sicily from the French, who, however, retained control of the Kingdom of Naples. A crusade was launched in August 1283 against Peter III and the Kingdom of Aragon by Pope Martin IV (a pope from Île-de-France), but it failed. The wars continued until the peace of Caltabellotta in 1302, which saw Peter's son Frederick III of Sicily, Frederick III recognized as the king of the Isle of Sicily, while Charles II of Naples, Charles II was recognized as the king of Naples by Pope Boniface VIII. Sicily was ruled as an independent kingdom by relatives of the kings of Aragon until 1409 and then as part of the Crown of Aragon. In October 1347, in Messina, Sicily, the Black Death first arrived in Europe.
Between the 15th-18th centuries, waves of Greeks from the Peloponnese (such as the Maniots) and Arvanites migrated to Sicily in large numbers to escape persecution after the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans, Ottoman conquest of the Peloponnese. They brought with them Eastern Orthodoxy as well as the Greek language, Greek and Arvanitika languages to the island, once again adding onto the extensive Byzantine/Greek Culture, Greek influence.
Strong opposition to French officialdom due to mistreatment and taxation saw the local peoples of Sicily rise up, leading in 1282 to an insurrection known as the War of the Sicilian Vespers, which eventually saw almost the entire French population on the island killed. During the war, the Sicilians turned to Peter III of Aragon, son-in-law of the last Hohenstaufen king, for support after being rejected by the Pope. Peter gained control of Sicily from the French, who, however, retained control of the Kingdom of Naples. A crusade was launched in August 1283 against Peter III and the Kingdom of Aragon by Pope Martin IV (a pope from Île-de-France), but it failed. The wars continued until the peace of Caltabellotta in 1302, which saw Peter's son Frederick III of Sicily, Frederick III recognized as the king of the Isle of Sicily, while Charles II of Naples, Charles II was recognized as the king of Naples by Pope Boniface VIII. Sicily was ruled as an independent kingdom by relatives of the kings of Aragon until 1409 and then as part of the Crown of Aragon. In October 1347, in Messina, Sicily, the Black Death first arrived in Europe.
Between the 15th-18th centuries, waves of Greeks from the Peloponnese (such as the Maniots) and Arvanites migrated to Sicily in large numbers to escape persecution after the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans, Ottoman conquest of the Peloponnese. They brought with them Eastern Orthodoxy as well as the Greek language, Greek and Arvanitika languages to the island, once again adding onto the extensive Byzantine/Greek Culture, Greek influence.
 The
The  About five million people live in Sicily, making it the List of regions of Italy#List of regions, fourth most populated region in Italy. In the first century after the Italian unification, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of the emigration of millions of people to Northern Italy, other European countries, North America, South America and Australia. Like the South of Italy and Sardinia, immigration to the island is very low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy instead, due to better employment and industrial opportunities. According to Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT figures from 2017, show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total 5,029,615 population; Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora, Sri Lankans, Albanians, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the official language is Italian and the primary religion is Roman Catholicism.
About five million people live in Sicily, making it the List of regions of Italy#List of regions, fourth most populated region in Italy. In the first century after the Italian unification, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of the emigration of millions of people to Northern Italy, other European countries, North America, South America and Australia. Like the South of Italy and Sardinia, immigration to the island is very low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy instead, due to better employment and industrial opportunities. According to Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT figures from 2017, show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total 5,029,615 population; Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora, Sri Lankans, Albanians, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the official language is Italian and the primary religion is Roman Catholicism.
 Sicilian emigration started shortly after the Italian unification and has not stopped ever since.
After the Italian unification, Sicily, along with the entire Italian peninsula, has also been strongly marked by Forced displacement, coerced emigration. Most of the assets of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies's former national bank, ''Banco di Napoli, Banco delle Due Sicilie'', were transferred to Piedmont. During the first decades of Risorgimento, a rising number of southern Italian manufactories were driven into ruin due to high taxation imposed by the central government. Furthermore, an embargo imposed on goods coming from southern Italian manufacturers, that effectively barred them from exporting to the north and abroad, were also key factors that led to further impoverishment of the entire region.
The aforementioned factors, along with a failed land reform, resulted in a never-before-seen wave of Sicilians emigrating, first to the United States between the 1880s and the 1920s, later to Northern Italy, and from the 1960s onwards also to Belgium, France, Germany, Switzerland, as well as Australia and South America.
Today, Sicily is the Italian region with the highest number of expatriates: as of 2017, 750,000 Sicilians, 14.4% of the island's population, lived abroad. For lack of employment, every year many Sicilians, especially young graduates, still leave the island to seek jobs abroad. Today, an estimated 10 million people of Sicilian origins live around the world.
Sicilian emigration started shortly after the Italian unification and has not stopped ever since.
After the Italian unification, Sicily, along with the entire Italian peninsula, has also been strongly marked by Forced displacement, coerced emigration. Most of the assets of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies's former national bank, ''Banco di Napoli, Banco delle Due Sicilie'', were transferred to Piedmont. During the first decades of Risorgimento, a rising number of southern Italian manufactories were driven into ruin due to high taxation imposed by the central government. Furthermore, an embargo imposed on goods coming from southern Italian manufacturers, that effectively barred them from exporting to the north and abroad, were also key factors that led to further impoverishment of the entire region.
The aforementioned factors, along with a failed land reform, resulted in a never-before-seen wave of Sicilians emigrating, first to the United States between the 1880s and the 1920s, later to Northern Italy, and from the 1960s onwards also to Belgium, France, Germany, Switzerland, as well as Australia and South America.
Today, Sicily is the Italian region with the highest number of expatriates: as of 2017, 750,000 Sicilians, 14.4% of the island's population, lived abroad. For lack of employment, every year many Sicilians, especially young graduates, still leave the island to seek jobs abroad. Today, an estimated 10 million people of Sicilian origins live around the world.
 As in most Italian regions, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religious denomination in Sicily, and the church still plays an important role in the lives of most people. There is also a notable small minority of Eastern-rite Byzantine Catholics which has a mixed congregation of ethnic Albanians; it is operated by the Italo-Albanian Catholic Church. Most people still attend church weekly or at least for religious festivals, and many people get married in churches. There was a wide presence of Jews in Sicily for at least 1,400 years and possibly for more than 2,000 years. Some scholars believe that the Sicilian Jewry are partial ancestors of the Ashkenazi Jews. However, much of the Jewish community faded away when they were Expulsion of the Jews from Sicily, expelled from the island in 1492. Islam was present during the Emirate of Sicily, although Muslims were also expelled. Today, mostly due to immigration to the island, there are also several religious minorities, such as Jehovah's Witnesses, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism. There are also a some evangelicalism, Evangelical Christians who live on the island.
As in most Italian regions, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religious denomination in Sicily, and the church still plays an important role in the lives of most people. There is also a notable small minority of Eastern-rite Byzantine Catholics which has a mixed congregation of ethnic Albanians; it is operated by the Italo-Albanian Catholic Church. Most people still attend church weekly or at least for religious festivals, and many people get married in churches. There was a wide presence of Jews in Sicily for at least 1,400 years and possibly for more than 2,000 years. Some scholars believe that the Sicilian Jewry are partial ancestors of the Ashkenazi Jews. However, much of the Jewish community faded away when they were Expulsion of the Jews from Sicily, expelled from the island in 1492. Islam was present during the Emirate of Sicily, although Muslims were also expelled. Today, mostly due to immigration to the island, there are also several religious minorities, such as Jehovah's Witnesses, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism. There are also a some evangelicalism, Evangelical Christians who live on the island.
 Administratively, Sicily is divided into nine provinces, each with a capital city of the same name as the province. Small surrounding islands are also part of various Sicilian provinces: the Aeolian Islands (Messina), isle of Ustica (Palermo), Aegadian Islands (Trapani), isle of
Administratively, Sicily is divided into nine provinces, each with a capital city of the same name as the province. Small surrounding islands are also part of various Sicilian provinces: the Aeolian Islands (Messina), isle of Ustica (Palermo), Aegadian Islands (Trapani), isle of  Thanks to regular growth in recent years, Sicily is the eighth largest regional economy of Italy in terms of total GDP (see List of Italian regions by GDP (PPP), List of Italian regions by GDP). A series of reforms and investments in agriculture, such as the introduction of modern irrigation systems, has made this important industry competitive. In the 1970s, some factories were opened, resulting in growth in the industrial sector. In recent years the service industry has become more important due to the opening of several shopping malls and some modest growth in financial and telecommunication activities. Tourism is an important source of income for the island, which attracts visitors due to its rich natural and historical heritage. Today Sicily is investing a large amount of money into the development of its hospitality industry, to attract even more tourism. However, Sicily continues to have a GDP per capita below the Italian average, and higher unemployment than the rest of Italy. This difference is mostly caused by the negative influence of the Mafia, which is still active in some areas, although it is much weaker than in the past.
Thanks to regular growth in recent years, Sicily is the eighth largest regional economy of Italy in terms of total GDP (see List of Italian regions by GDP (PPP), List of Italian regions by GDP). A series of reforms and investments in agriculture, such as the introduction of modern irrigation systems, has made this important industry competitive. In the 1970s, some factories were opened, resulting in growth in the industrial sector. In recent years the service industry has become more important due to the opening of several shopping malls and some modest growth in financial and telecommunication activities. Tourism is an important source of income for the island, which attracts visitors due to its rich natural and historical heritage. Today Sicily is investing a large amount of money into the development of its hospitality industry, to attract even more tourism. However, Sicily continues to have a GDP per capita below the Italian average, and higher unemployment than the rest of Italy. This difference is mostly caused by the negative influence of the Mafia, which is still active in some areas, although it is much weaker than in the past.
 Sicily has long been noted for its fertile soil, which is the result of past volcanic eruptions. The local agriculture is also helped by the pleasant climate of the island. The main agricultural products are wheat, Diamante citron, citrons, oranges ''(Blood orange, Arancia Rossa di Sicilia IGP)'', lemons, tomatoes ''(Pomodoro di Pachino, Pomodoro di Pachino IGP)'', olives, olive oil, artichokes, Opuntia ficus-indica, prickly pear ''(Fico d'India dell' Etna DOP)'', almonds, grapes, pistachios ''(Pistacchio di Bronte, Sicily, Bronte DOP)'' and wine. Cattle and sheep are raised. The production of cheese is particularly important thanks to the Ragusano cheese, Ragusano DOP and the Pecorino Siciliano, Pecorino Siciliano DOP. Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa is noted for its honey (''Miele Ibleo'') and chocolate (''Cioccolato di Modica IGP'') products.economia-sicilia
Sicily has long been noted for its fertile soil, which is the result of past volcanic eruptions. The local agriculture is also helped by the pleasant climate of the island. The main agricultural products are wheat, Diamante citron, citrons, oranges ''(Blood orange, Arancia Rossa di Sicilia IGP)'', lemons, tomatoes ''(Pomodoro di Pachino, Pomodoro di Pachino IGP)'', olives, olive oil, artichokes, Opuntia ficus-indica, prickly pear ''(Fico d'India dell' Etna DOP)'', almonds, grapes, pistachios ''(Pistacchio di Bronte, Sicily, Bronte DOP)'' and wine. Cattle and sheep are raised. The production of cheese is particularly important thanks to the Ragusano cheese, Ragusano DOP and the Pecorino Siciliano, Pecorino Siciliano DOP. Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa is noted for its honey (''Miele Ibleo'') and chocolate (''Cioccolato di Modica IGP'') products.economia-sicilia
 Improvements in Sicily's road system have helped to promote industrial development. The region has three important industrial districts:
* '' Catania Industrial District'', where there are several food industries and one of the best European electronics industry centres called ''Etna Valley'' (in honour of the best known Silicon Valley) which contains offices and factories of international companies such as STMicroelectronics and Numonyx;
* '' Syracuse Petrochemical District'' with chemical industry, chemical industries, oil refineries and important power stations (as the innovative Archimede combined cycle power plant);
* the latest ''
Improvements in Sicily's road system have helped to promote industrial development. The region has three important industrial districts:
* '' Catania Industrial District'', where there are several food industries and one of the best European electronics industry centres called ''Etna Valley'' (in honour of the best known Silicon Valley) which contains offices and factories of international companies such as STMicroelectronics and Numonyx;
* '' Syracuse Petrochemical District'' with chemical industry, chemical industries, oil refineries and important power stations (as the innovative Archimede combined cycle power plant);
* the latest ''
 Highways have been built and expanded in the last four decades. The most prominent Sicilian roads are the motorways (known as ) in the north of the island. Much of the motorway network is elevated on pillars due to the island's mountainous terrain. Other main roads in Sicily are the ''Strade Statali'', such as the SS.113 that connects Trapani to Messina (via Palermo), the SS.114 Messina- Syracuse (via Catania) and the SS.115 Syracuse-Trapani (via Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa,
Highways have been built and expanded in the last four decades. The most prominent Sicilian roads are the motorways (known as ) in the north of the island. Much of the motorway network is elevated on pillars due to the island's mountainous terrain. Other main roads in Sicily are the ''Strade Statali'', such as the SS.113 that connects Trapani to Messina (via Palermo), the SS.114 Messina- Syracuse (via Catania) and the SS.115 Syracuse-Trapani (via Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, 

 The first railway in Sicily was opened in 1863 (Palermo-Bagheria) and today all of the Sicilian provinces are served by a network of railway services, linking to most major cities and towns; this service is operated by Trenitalia. Of the of railway tracks in use, over 60% has been Railway electrification system, electrified whilst the remaining are serviced by Dieselisation, diesel engines. 88% of the lines (1.209 km) are single-track and only are double-track serving the two main routes, Messina-Palermo (Tyrrhenian Sea, Tyrrhenian) and Messina-Catania-Syracuse (Ionian Sea, Ionian), which are the main lines of this region. Of the narrow-gauge railways the Ferrovia Circumetnea is the only one that still operates, going round Mount Etna. From the major cities of Sicily, there are services to
The first railway in Sicily was opened in 1863 (Palermo-Bagheria) and today all of the Sicilian provinces are served by a network of railway services, linking to most major cities and towns; this service is operated by Trenitalia. Of the of railway tracks in use, over 60% has been Railway electrification system, electrified whilst the remaining are serviced by Dieselisation, diesel engines. 88% of the lines (1.209 km) are single-track and only are double-track serving the two main routes, Messina-Palermo (Tyrrhenian Sea, Tyrrhenian) and Messina-Catania-Syracuse (Ionian Sea, Ionian), which are the main lines of this region. Of the narrow-gauge railways the Ferrovia Circumetnea is the only one that still operates, going round Mount Etna. From the major cities of Sicily, there are services to  There are seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites on Sicily. By the order of inscription:
* Valle dei Templi (1997) is one of the most outstanding examples of Magna Graecia, Greater Greece art and architecture, and is one of the main attractions of Sicily as well as a national monument of Italy. The site is located in
There are seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites on Sicily. By the order of inscription:
* Valle dei Templi (1997) is one of the most outstanding examples of Magna Graecia, Greater Greece art and architecture, and is one of the main attractions of Sicily as well as a national monument of Italy. The site is located in  * Taormina, Taormina and Isola Bella;
* Motya and Marsala, Libeo Island: The Phoenician-Punic Civilisation in Italy;
* Scala dei Turchi;
*
* Taormina, Taormina and Isola Bella;
* Motya and Marsala, Libeo Island: The Phoenician-Punic Civilisation in Italy;
* Scala dei Turchi;
* 
 Baglio are traditional living structures in Western Sicily.
Baglio are traditional living structures in Western Sicily.
 The Sicilian Baroque has a unique architectural identity. Noto, Caltagirone, Catania, Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, Modica, Scicli and particularly Acireale contain some of Italy's best examples of Baroque architecture, carved in the local red sandstone. Noto provides one of the best examples of the Baroque architecture brought to Sicily.
The Baroque style in Sicily was largely confined to buildings erected by the church, and palazzo, palazzi built as private residences for the Sicilian aristocracy. The earliest examples of this style in Sicily lacked individuality and were typically heavy-handed pastiches of buildings seen by Sicilian visitors to Rome, Florence, and
The Sicilian Baroque has a unique architectural identity. Noto, Caltagirone, Catania, Ragusa, Italy, Ragusa, Modica, Scicli and particularly Acireale contain some of Italy's best examples of Baroque architecture, carved in the local red sandstone. Noto provides one of the best examples of the Baroque architecture brought to Sicily.
The Baroque style in Sicily was largely confined to buildings erected by the church, and palazzo, palazzi built as private residences for the Sicilian aristocracy. The earliest examples of this style in Sicily lacked individuality and were typically heavy-handed pastiches of buildings seen by Sicilian visitors to Rome, Florence, and  Palermo hosts the Teatro Massimo which is the largest opera house in Italy and the third largest in all of Europe.
In Catania there is another important opera house, the Teatro Massimo Bellini with 1,200 seats, which is considered one of the best European opera houses for its acoustics.
Sicily's composers vary from Vincenzo Bellini, Sigismondo d'India, Giovanni Pacini and Alessandro Scarlatti, to contemporary composers such as Salvatore Sciarrino and Silvio Amato.
Palermo hosts the Teatro Massimo which is the largest opera house in Italy and the third largest in all of Europe.
In Catania there is another important opera house, the Teatro Massimo Bellini with 1,200 seats, which is considered one of the best European opera houses for its acoustics.
Sicily's composers vary from Vincenzo Bellini, Sigismondo d'India, Giovanni Pacini and Alessandro Scarlatti, to contemporary composers such as Salvatore Sciarrino and Silvio Amato.

 Many award-winning and acclaimed films of Italian cinema have been filmed in Sicily, amongst the most noted of which are: Luchino Visconti, Visconti's ''"La Terra Trema"'' and ''"Il Gattopardo"'', Pietro Germi's ''"Divorce, Italian Style, Divorzio all'Italiana''" and ''"Seduced and Abandoned (1964 film), Sedotta e Abbandonata''", Giuseppe Tornatore, Tornatore's ''"Cinema Paradiso''".
Many award-winning and acclaimed films of Italian cinema have been filmed in Sicily, amongst the most noted of which are: Luchino Visconti, Visconti's ''"La Terra Trema"'' and ''"Il Gattopardo"'', Pietro Germi's ''"Divorce, Italian Style, Divorzio all'Italiana''" and ''"Seduced and Abandoned (1964 film), Sedotta e Abbandonata''", Giuseppe Tornatore, Tornatore's ''"Cinema Paradiso''".
 The golden age of Sicilian poetry began in the early 13th century with the Sicilian School of Giacomo da Lentini, which was highly influential on Italian literature. Some of the most noted figures among writers and poets are Luigi Pirandello (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1934), Salvatore Quasimodo (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1959), Giovanni Verga (the father of the ''Italian Verismo (literature), Verismo''), Domenico Tempio, Giovanni Meli, Luigi Capuana, Mario Rapisardi, Federico de Roberto, Leonardo Sciascia, Vitaliano Brancati, Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, Elio Vittorini, Vincenzo Consolo and Andrea Camilleri (noted for his novels and short stories with the fictional character Salvo Montalbano, Inspector Salvo Montalbano as protagonist). On the political side notable philosophers include Gaetano Mosca and Giovanni Gentile who wrote ''The Doctrine of Fascism''.
The golden age of Sicilian poetry began in the early 13th century with the Sicilian School of Giacomo da Lentini, which was highly influential on Italian literature. Some of the most noted figures among writers and poets are Luigi Pirandello (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1934), Salvatore Quasimodo (Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel laureate, 1959), Giovanni Verga (the father of the ''Italian Verismo (literature), Verismo''), Domenico Tempio, Giovanni Meli, Luigi Capuana, Mario Rapisardi, Federico de Roberto, Leonardo Sciascia, Vitaliano Brancati, Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, Elio Vittorini, Vincenzo Consolo and Andrea Camilleri (noted for his novels and short stories with the fictional character Salvo Montalbano, Inspector Salvo Montalbano as protagonist). On the political side notable philosophers include Gaetano Mosca and Giovanni Gentile who wrote ''The Doctrine of Fascism''.

 The island has a long history of producing a variety of noted cuisines and wines, to the extent that Sicily is sometimes nicknamed ''God's Kitchen'' because of this. Every part of Sicily has its speciality (e.g. Cassata is typical of Palermo although available everywhere in Sicily, as is Granita). The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general public. The savoury dishes of Sicily are viewed to be healthy diet, healthy, using fresh vegetables and fruits, such as tomatoes, artichokes, olives (including olive oil), citrus, apricots, aubergines, onions, beans, raisins commonly coupled with seafood, freshly caught from the surrounding coastlines, including tuna, sea bream, European seabass, sea bass, cuttlefish, swordfish, sardines, and others.
The island has a long history of producing a variety of noted cuisines and wines, to the extent that Sicily is sometimes nicknamed ''God's Kitchen'' because of this. Every part of Sicily has its speciality (e.g. Cassata is typical of Palermo although available everywhere in Sicily, as is Granita). The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general public. The savoury dishes of Sicily are viewed to be healthy diet, healthy, using fresh vegetables and fruits, such as tomatoes, artichokes, olives (including olive oil), citrus, apricots, aubergines, onions, beans, raisins commonly coupled with seafood, freshly caught from the surrounding coastlines, including tuna, sea bream, European seabass, sea bass, cuttlefish, swordfish, sardines, and others.
 The most well-known part of Sicilian cuisine is the rich sweet dishes including ice creams and pastry, pastries. Cannoli (singular: ''cannolo''), a tube-shaped shell of fried pastry dough filled with a sweet filling usually containing ricotta, is strongly associated with Sicily worldwide. Biancomangiare, biscotti ennesi (cookies native to
The most well-known part of Sicilian cuisine is the rich sweet dishes including ice creams and pastry, pastries. Cannoli (singular: ''cannolo''), a tube-shaped shell of fried pastry dough filled with a sweet filling usually containing ricotta, is strongly associated with Sicily worldwide. Biancomangiare, biscotti ennesi (cookies native to 
 The Sicilian cart is an ornate, colourful style of a horse- or donkey-drawn cart native to Sicily. Sicilian woodcarver George Petralia states that horses were mostly used in the city and flat plains, while donkeys or mules were more often used in rough terrain for hauling heavy loads. The cart has two wheels and is primarily handmade out of wood with iron components.
The Sicilian coppola (cap), coppola is a traditional kind of flat cap typically worn by men in Sicily. First used by English nobles during the late 18th century, the ''tascu'' began being used in Sicily in the early 20th century as a flat cap, driving cap, usually worn by car drivers. The ''coppola'' is usually made in tweed (cloth), tweed. Today it is widely regarded as a definitive symbol of Sicilian heritage.
The Sicilian cart is an ornate, colourful style of a horse- or donkey-drawn cart native to Sicily. Sicilian woodcarver George Petralia states that horses were mostly used in the city and flat plains, while donkeys or mules were more often used in rough terrain for hauling heavy loads. The cart has two wheels and is primarily handmade out of wood with iron components.
The Sicilian coppola (cap), coppola is a traditional kind of flat cap typically worn by men in Sicily. First used by English nobles during the late 18th century, the ''tascu'' began being used in Sicily in the early 20th century as a flat cap, driving cap, usually worn by car drivers. The ''coppola'' is usually made in tweed (cloth), tweed. Today it is widely regarded as a definitive symbol of Sicilian heritage.