Roumanians in New York 1891.JPG on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated
U.S. Library of Congress
"however it is one interpretation of census data results. The subject of Moldovan vs Romanian ethnicity touches upon the sensitive topic of
Moldova's national identity
page 108 sqq. Romanians also form an ethnic minority in several nearby countries of Central and
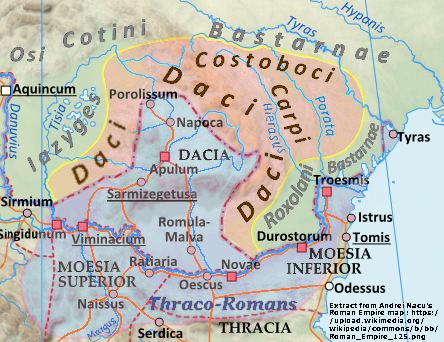 Inhabited by the ancient Dacians, part of today's territory of Romania was conquered by the
Inhabited by the ancient Dacians, part of today's territory of Romania was conquered by the  The colonisation with Roman or Romanized elements, the use of the
The colonisation with Roman or Romanized elements, the use of the

 During the
During the  Additionally, in medieval times there were other lands known by the name 'Vlach' (such as Great Vlachia, situated between
Additionally, in medieval times there were other lands known by the name 'Vlach' (such as Great Vlachia, situated between

 In the context of the
In the context of the
 The origins of the
The origins of the
 The name ''Romanian'' is derived from
The name ''Romanian'' is derived from

 Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia, Argentina, and New Zealand among many other countries. Italy and Spain have been popular emigration destinations, due to a relatively low language barrier, and both are each now home to about a million Romanians. With respect to geopolitical identity, many individuals of Romanian ethnicity in Moldova prefer to identify themselves as
Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia, Argentina, and New Zealand among many other countries. Italy and Spain have been popular emigration destinations, due to a relatively low language barrier, and both are each now home to about a million Romanians. With respect to geopolitical identity, many individuals of Romanian ethnicity in Moldova prefer to identify themselves as
File:A Vlaicu II 01.jpg, Aurel Vlaicu, early pioneer of aviation
File:Traian Vuia.jpg, Traian Vuia, pioneer of aviation
File:Petrache Poenaru - Foto01.jpg, Petrache Poenaru, inventor of the fountain pen
File:Nicolae Paulescu.jpg, Nicolae Paulescu, pioneer of insulin development
File:Victor Babes.jpg, Victor Babeș, physician and bacteriologist, pioneer of microbiology
File:EmilRacovitza1935.jpg, Emil Racoviță, co-founder of Biospeleology, biospeology
In the arts and culture, prominent figures were George Enescu (music composer, violinist, professor of Sir Yehudi Menuhin), Constantin Brâncuși (sculptor), Eugène Ionesco (playwright), Mircea Eliade (historian of religion and novelist), Emil Cioran (essayist, Prix de l'Institut Français for stylism) and Angela Gheorghiu (soprano). More recently, filmmakers such as Cristi Puiu and Cristian Mungiu have attracted international acclaim, as has fashion designer Ioana Ciolacu.
File:Eugene Ionesco 01.jpg, Eugen Ionescu, famous playwright
File:Mircea Eliade young.jpg, Mircea Eliade, writer and historian of religions
File:Cioran in Romania.jpg, Emil Cioran, essayist and philosopher
File:Georges Enesco 1930.jpg, George Enescu, renowned music composer
File:Celibidache At Curtis Single.jpg, Sergiu Celibidache, honored conductor and music teacher
File:Constantin Brancusi c.1905.jpg, Constantin Brâncuși, reputed sculptor
In sports, Romanians have excelled in a variety of fields, such as football (Gheorghe Hagi), gymnastics (Nadia Comăneci, Lavinia Miloșovici etc.), tennis (Ilie Năstase, Ion Țiriac, Simona Halep), rowing (Ivan Patzaichin) and handball (four times men's World Men's Handball Championship, World Cup winners).
Count Dracula is a worldwide icon of Romania. This character was created by the Irish fiction writer Bram Stoker, based on some stories spread in the late
File:Biserica „Sf. Nicolae” sat Densuș, comuna Densuș, jud. Hunedoara.jpg, Romano-Gothic Densuș Church, Hunedoara, Transylvania
File:Biserica Strei (Grigore Roibu).jpg, Romano-Gothic Dormition of the Theotokos Church, Strei, Strei Church, Hunedoara, Transylvania
File:Biserica Sfantu Nicolae.JPG, St. Nicholas Church, Brașov, Transylvania
File:Biserica Sf.Ioan Botezatorul.jpg, Nativity of St. John the Baptist Church, Piatra Neamț, Nativity of St. John the Baptist Church, Piatra Neamț, Moldavia
File:Catedrala Mitropolitana02.JPG, Metropolitan Cathedral, Iași, Moldavia
File:Manastirea putna1.jpg, Putna Monastery, Bukovina
Romanian Catholics are present in
File:Bucharest Day 3 - Cathedral Plaza (9338457546).jpg, Roman Catholic Saint Joseph Cathedral, Bucharest, Wallachia
File:Alba Iulia - Catedrala Sf.Mihail Aprilie 2013.JPG, Roman Catholic St. Michael's Cathedral, Alba Iulia, Transylvania
File:Blaj Catedrala greco catolica (3).jpg, Greek Catholic Holy Trinity Cathedral, Blaj, Transylvania
File:Centrul Vechi Baia Mare.jpg, Greek Catholic Assumption of Mary Cathedral, Baia Mare, Transylvania
File:Biserica Sf. Ioan Nepomuk din Suceava44.jpg, Roman Catholic St. John of Nepomuk Church, Suceava, Bukovina
File:Timisoara - Catholic Dome in Union Square.jpg, Roman Catholic St. George's Cathedral, Timișoara, St. George's Cathedral in Timișoara, Banat
There are no official dates for the adoption of religions by the Romanians. Based on linguistic and archaeological findings, historians suggest that the Romanians' ancestors acquired polytheistic religions in the Roman era, later adopting Christianity, certainly by the 4th century CE when decreed by Emperor Constantine as the official religion of the Roman Empire. Like in all other Romance languages, the basic Romanian words related to Christianity are inherited from Latin, such as ''God'' (''Dumnezeu'' < ), ''church'' ( < ), ''cross'' ( < , -), ''angel'' ( < ), ''saint'' (regional: < ), ''Christmas'' ( < , -), ''Christians, Christian'' ( < ), ''Easter'' ( < ), ''sin'' ( < ), ''to baptise'' ( < ), ''priest'' ( < ), ''to pray'' ( < ), ''faith'' ( < ), and so on.
After the East–West Schism, Great Schism, there existed a Catholic Bishopric of Cumania (later, separate bishoprics in both
 According to an Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a among Romanians is entirely from the Eastern European variety Z282 and may be a result of Baltic, Thracian or Slavic descent. R1a-Z280 outnumbers R1a-M458 among Romanians, the opposite phenomena is typical for Poles, Czechs and Bulgarians. 12% of the Romanians belong to R1b, the Alpino-Italic branch R1b-U152 is at 2% per 330 samples, a lower frequency recorded than other Balkan peoples. The branches R1b-U106, R1b-DF27 and R1b-L21 make up 1% respectively. The eastern branches R1b-M269* and L23* (Z2103) make up 7% and outnumber the Atlantic branches, they prevail in parts of east, central Europe and as a result of Greek colonisation – in parts of Sicily as well. 8% of the Romanians belong to E1b1b1a1 (E-M78) per 265 samples. Other studies analyzing the haplogroup frequency among Romanians came to similar results.
Showing the importance of geography, a 2017 paper concentrated on the mtDNA, and showed how Romania has been "a major crossroads between Asia and Europe" and thus "experienced continuous migration and invasion episodes"; while stating that "previous studies" show Romanians "exhibit genetic similarity with other Europeans" and "another study pointed to possible segregation within the Middle East populations". The paper also mentions how "signals of Asian maternal lineages were observed in all Romanian historical provinces, indicating gene flow along the migration routes through East Asia and Europe, during different time periods, namely, the Upper Paleolithic period and/or, with a likely greater preponderance, the Middle Ages", at low frequency (2.24%). It concludes that "our current findings based on the mtDNA analysis of populations in historical provinces of Romania suggest similarity between populations in
According to an Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a among Romanians is entirely from the Eastern European variety Z282 and may be a result of Baltic, Thracian or Slavic descent. R1a-Z280 outnumbers R1a-M458 among Romanians, the opposite phenomena is typical for Poles, Czechs and Bulgarians. 12% of the Romanians belong to R1b, the Alpino-Italic branch R1b-U152 is at 2% per 330 samples, a lower frequency recorded than other Balkan peoples. The branches R1b-U106, R1b-DF27 and R1b-L21 make up 1% respectively. The eastern branches R1b-M269* and L23* (Z2103) make up 7% and outnumber the Atlantic branches, they prevail in parts of east, central Europe and as a result of Greek colonisation – in parts of Sicily as well. 8% of the Romanians belong to E1b1b1a1 (E-M78) per 265 samples. Other studies analyzing the haplogroup frequency among Romanians came to similar results.
Showing the importance of geography, a 2017 paper concentrated on the mtDNA, and showed how Romania has been "a major crossroads between Asia and Europe" and thus "experienced continuous migration and invasion episodes"; while stating that "previous studies" show Romanians "exhibit genetic similarity with other Europeans" and "another study pointed to possible segregation within the Middle East populations". The paper also mentions how "signals of Asian maternal lineages were observed in all Romanian historical provinces, indicating gene flow along the migration routes through East Asia and Europe, during different time periods, namely, the Upper Paleolithic period and/or, with a likely greater preponderance, the Middle Ages", at low frequency (2.24%). It concludes that "our current findings based on the mtDNA analysis of populations in historical provinces of Romania suggest similarity between populations in
File:Ion Theodorescu-Sion - Tarani din Abrud.jpg, Painting of Transylvanian Romanian peasants from Abrud by Ion Theodorescu-Sion
File:Barabás Román család.jpg, Romanian family going to a fair, early 19th century
File:Costumes of Peasants from Romania, Hungary, Slovakia and Germany.jpg, Traditional Romanian peasant costumes at the left, followed from left to right by Hungarian, Slavic and German ones
File:Über Land und Meer - Romanians in Transylvania, 1872.jpg, Romanians from
A Concise History of RomaniansThe Romanian nation in the beginning of the 20th century
{{Authority control Romanian people, Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Moldova Ethnic groups in Ukraine Indigenous peoples of Ukraine Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Vojvodina Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Hungary Eastern Romance people Romance peoples Ethnic groups divided by international borders
exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
''Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture
The culture of Romania is an umbrella term used to encapsulate the ideas, customs and social behaviours of the people of Romania that developed due to the country's distinct geopolitical history and evolution. It is theorized and speculated that ...
and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spellings: Rumanian or Roumanian; autonym: ''limba română'' , or ''românește'', ) is the official and main language of Romania and the Republic of Moldova. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in ...
, they live primarily in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
. The 2011 Romanian census
The 2011 Romanian census was a census held in Romania between 20 and 31 October 2011. It was performed by some 120,000 census takers in around 101,000 statistic sectors throughout the country established by the National Institute of Statistics (IN ...
found that just under 89% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians.
In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
, the majority of Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians ( ro, moldoveni , Moldovan Cyrillic: молдовень), are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and the largest ethnic group of the Republic of Moldova (75.1% of the population as of 2014) and a sign ...
were counted as ethnic Romanians.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congress
"however it is one interpretation of census data results. The subject of Moldovan vs Romanian ethnicity touches upon the sensitive topic of
Moldova's national identity
page 108 sqq. Romanians also form an ethnic minority in several nearby countries of Central and
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
.
Estimates of the number of Romanian people worldwide vary from 24 to 30 million, in part depending on whether the definition of the term "Romanian" includes natives of both Romania and Moldova, their respective diasporas, and native speakers of both Romanian and other Balkan Romance languages
Daco-Romance languages, also known as Balkan-Romance languages form the sub-branch of the Romance language family.
Languages
Daco-Romance comprises Romanian (or Daco-Romanian), Aromanian (or Macedo-Romanian), Megleno-Romanian and Istro-Ro ...
. Other speakers of the latter languages are the Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
, the Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites ( ruq, Miglinits), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs ( ruq, Vlaș), are a small Eastern Romance people, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis re ...
, and the Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
, which may be considered Romanian subgroups or separated yet related ethnicities.
History
Antiquity
 Inhabited by the ancient Dacians, part of today's territory of Romania was conquered by the
Inhabited by the ancient Dacians, part of today's territory of Romania was conquered by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in 106, when Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
's army defeated the army of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
's ruler Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
(''see Dacian Wars''). The Roman administration withdrew two centuries later, under the pressure of the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
and Carpi.
Two theories account for the origin of the Romanian people. One, known as the Daco-Roman continuity theory, posits that they are descendants of Romans and Romanized indigenous peoples living in the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
Province of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
, while the other posits that the Romanians are descendants of Romans and Romanized indigenous populations of the former Roman provinces of Illyricum, Moesia, Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek D ...
, and Macedonia, and the ancestors of Romanians later migrated from these Roman provinces south of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
into the area which they inhabit today.
According to the first theory, the Romanians are descended from indigenous populations that inhabited what is now Romania and its immediate environs: Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
(more specifically the Dacians and Getae) and Roman legionaries and colonists. In the course of the two wars with the Roman legions, in 101 through 102 AD and 105 through 106 AD respectively, the emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
succeeded in defeating the Dacians and the greatest part of Dacia became a Roman province.
 The colonisation with Roman or Romanized elements, the use of the
The colonisation with Roman or Romanized elements, the use of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
language and the assimilation of Roman civilisation as well as the intense development of urban centres led to the Romanization of part of the autochthonous population in Dacia. This process was probably concluded by the 10th century when the assimilation of the Slavs by the Daco-Romanians was completed.
According to the south-of-the-Danube origin theory, the Romanians' ancestors, a combination of Romans and Romanized peoples of Illyria, Moesia and Thrace, moved northward across the Danube river into modern-day Romania. Small population groups speaking several versions of Romanian ( Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian and Istro-Romanian) still exist south of the Danube in Greece, Albania, Macedonia, Bulgaria and Serbia, but it is not known whether they themselves migrated from more northern parts of the Balkans, including Dacia. The south-of-the Danube theory usually favours northern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and/or Moesia (modern day Serbia and Northern Bulgaria) as the more specific places of Romanian ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
.
Small genetic differences were reportedly found among Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
an (Greece, Albania) populations and especially those of the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
– Carpathian (Romania, Moldova, Ukraine) region. Despite this low level of differentiation between them, tree reconstruction and principal component analyses allowed a distinction between Balkan–Carpathian (Romanians, Moldovans, Ukrainians, Macedonians, and Gagauzes) and Balkan Mediterranean (Greeks, Albanians, Turks) population groups. The genetic affinities among Dniester–Carpathian and southeastern European populations do not reflect their linguistic relationships. According to the report, the results indicate that the ethnic and genetic differentiations occurred in these regions to a considerable extent independently of each other.
Middle Ages to Early Modern Age
During theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Romanians were mostly known as Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
, a blanket term ultimately of Germanic origin, from the word Walha
''Walhaz'' is a reconstructed Proto-Germanic word meaning 'foreigner', or more specifically 'Roman', 'Romance-speaker' or '(romanized) Celt', and survives in English as ' Welsh'. The term was used by the ancient Germanic peoples to describe inh ...
, used by ancient Germanic peoples to refer to Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
-speaking and Celtic neighbours. Besides the separation of some groups (Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
, Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites ( ruq, Miglinits), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs ( ruq, Vlaș), are a small Eastern Romance people, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis re ...
, and Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
) during the Age of Migration, many Vlachs could be found all over the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, across Carpathian Mountains as far north as Poland and as far west as the regions of Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
(part of the modern Czech Republic), some went as far east as Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
of western Ukraine, and the present-day Croatia where the Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци or , ; it, Morlacchi; ro, Morlaci) has been an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach p ...
gradually disappeared, while the Catholic and Orthodox Vlachs took Croat and Serb national identity.
Because of the migrations that followed – such as those of Slavs, Bulgars, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, and Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
– the Romanians were organised in agricultural communes ( obști), developing large centralised states only in the 14th century, when the Danubian Principalities of in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
emerged to fight the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.

 During the
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
the Bulgarian Empire controlled vast areas to the north of the river Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
(with interruptions) from its establishment in 681 to its fragmentation in 1371–1422. These lands were called by contemporary Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
historians Bulgaria across the Danube, or Transdanubian Bulgaria. Original information for the centuries-old Bulgarian rule there is scarce as the archives of the Bulgarian rulers were destroyed and little is mentioned for this area in Byzantine or Hungarian manuscripts. During the First Bulgarian Empire, the Dridu culture developed in the beginning of the 8th century and flourished until the 11th century. It represents an early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
archaeological culture which emerged in the region of the Lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
. In Bulgaria it is usually referred to as Pliska-Preslav culture.
During the late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
, prominent medieval Romanian monarchs such as Bogdan of Moldavia, Stephen the Great, Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder ( ro, Mircea cel Bătrân, ; c. 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited t ...
, Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( ro, Mihai Viteazul or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593 – 1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Transylvania (1599 – 1600). ...
, or Vlad the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ro, Vlad Țepeș ) or Vlad Dracula (; ro, Vlad Drăculea ; 1428/311476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most im ...
took part actively in the history of Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
by waging tumultuous wars and leading noteworthy crusades against the then continuously expanding Ottoman Empire, at times allied with either the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
or the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
in these causes.
Eventually the entire Balkan peninsula was annexed by the Ottoman Empire. However, Moldavia and Wallachia (extending to Dobruja and Bulgaria) were not entirely subdued by the Ottomans as both principalities became autonomous (which was not the case of other Ottoman territorial possessions in Europe). Transylvania, a third region inhabited by an important majority of Romanian speakers, was a vassal state of the Ottomans until 1687, when the principality became part of the Habsburg possessions. The three principalities were united for several months in 1600 under the authority of Wallachian Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. T ...
Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( ro, Mihai Viteazul or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593 – 1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Transylvania (1599 – 1600). ...
.
 Additionally, in medieval times there were other lands known by the name 'Vlach' (such as Great Vlachia, situated between
Additionally, in medieval times there were other lands known by the name 'Vlach' (such as Great Vlachia, situated between Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, The ...
and the western Pindus
The Pindus (also Pindos or Pindhos; el, Πίνδος, Píndos; sq, Pindet; rup, Pindu) is a mountain range located in Northern Greece and Southern Albania. It is roughly 160 km (100 miles) long, with a maximum elevation of 2,637 metres ...
mountains, originally within the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, but after the 13th century autonomous or semi-independent; White Wallachia
White Wallachia (Greek: Ασπροβλαχία, romanized: ''Asprovlachía)'', sometimes referred to simply as Vlachia, Wallachia or Asen's Wallachia by Western sources, was a rarely used Byzantine term for the region between the Danube and the Bal ...
, a Byzantine denomination for the region between the Danube River and the Balkans; Moravian Wallachia
Moravian Wallachia ( cs, Moravské Valašsko, or simply ''Valašsko''; ro, Valahia Moravă) is a mountainous ethnoregion located in the easternmost part of Moravia in the Czech Republic, near the Slovak border, roughly centered on the cities Vs ...
, a region in south-eastern Czech Republic).
Up until 1541, Transylvania was part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, later (due to the conquest of Hungary by the Ottoman Empire) was a self-governed Principality governed by the Hungarian nobility. In 1699 it became a part of the Habsburg lands
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
. By the end of the 18th century, the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
was awarded by the Ottomans with the region of Bukovina and, in 1812, the Russians occupied the eastern half of Moldavia, known as Bessarabia.
Late Modern Age to Contemporary Era


 In the context of the
In the context of the 1848
1848 is historically famous for the wave of revolutions, a series of widespread struggles for more liberal governments, which broke out from Brazil to Hungary; although most failed in their immediate aims, they significantly altered the polit ...
Romanticist
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
and liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
revolutions across Europe, the events that took place in the Grand Principality of Transylvania
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and co ...
were the first of their kind to unfold in the Romanian-speaking territories. On the one hand, the Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania ( ...
and the Transylvanian Romanians (with consistent support on behalf of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
) successfully managed to oppose the goals of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 or fully Hungarian Civic Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas. Although t ...
, with the two noteworthy historical figures leading the common Romanian-Saxon side at the time being Avram Iancu and Stephan Ludwig Roth.
On the other hand, the Wallachian revolutions of 1821
Events
January–March
* January 21 – Peter I Island in the Antarctic is first sighted, by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen.
* January 28 – Alexander Island, the largest in Antarctica, is first discovered by Fabian Gottlieb von B ...
and 1848
1848 is historically famous for the wave of revolutions, a series of widespread struggles for more liberal governments, which broke out from Brazil to Hungary; although most failed in their immediate aims, they significantly altered the polit ...
as well as the Moldavian Revolution of 1848
The Moldavian Revolution of 1848 is the name used for the unsuccessful Romanian liberal and Romantic nationalist movement inspired by the Revolutions of 1848 in the principality of Moldavia. Initially seeking accommodation within the political f ...
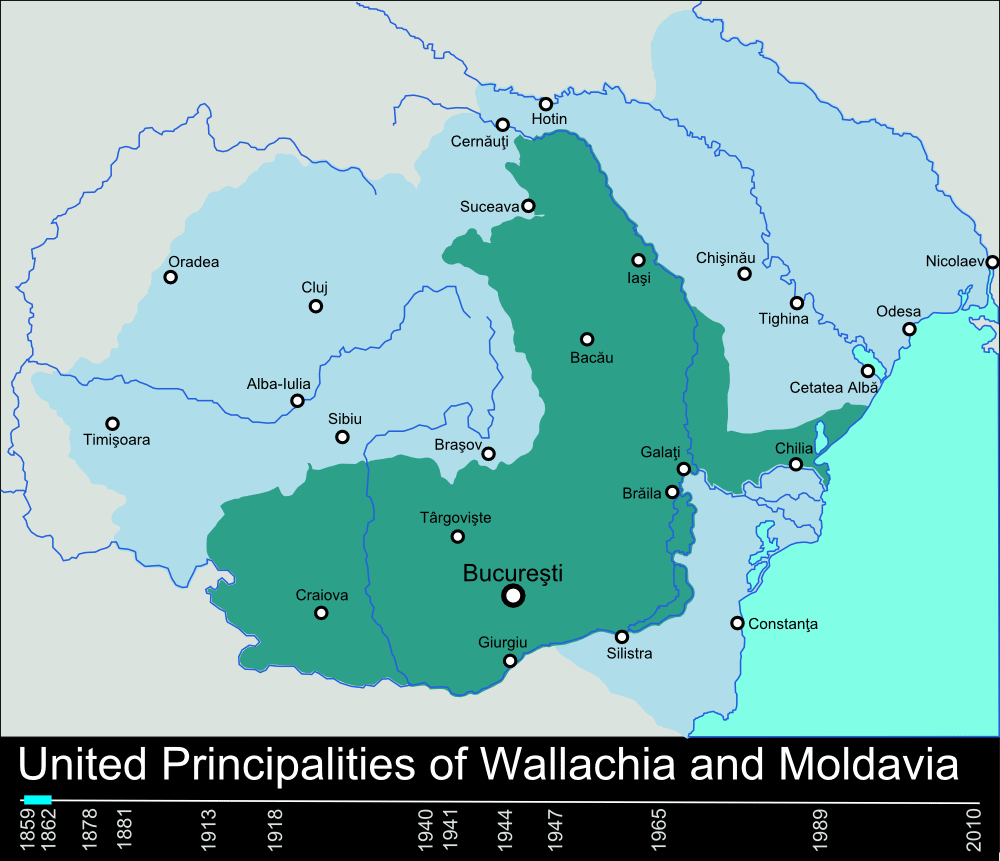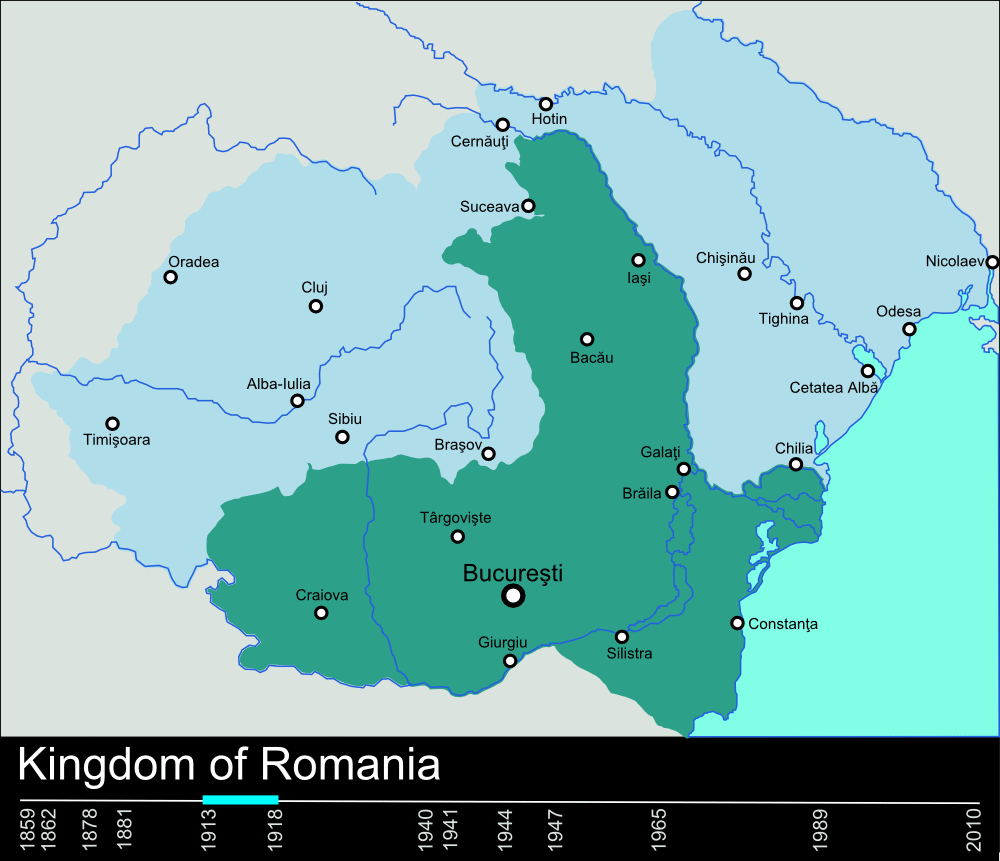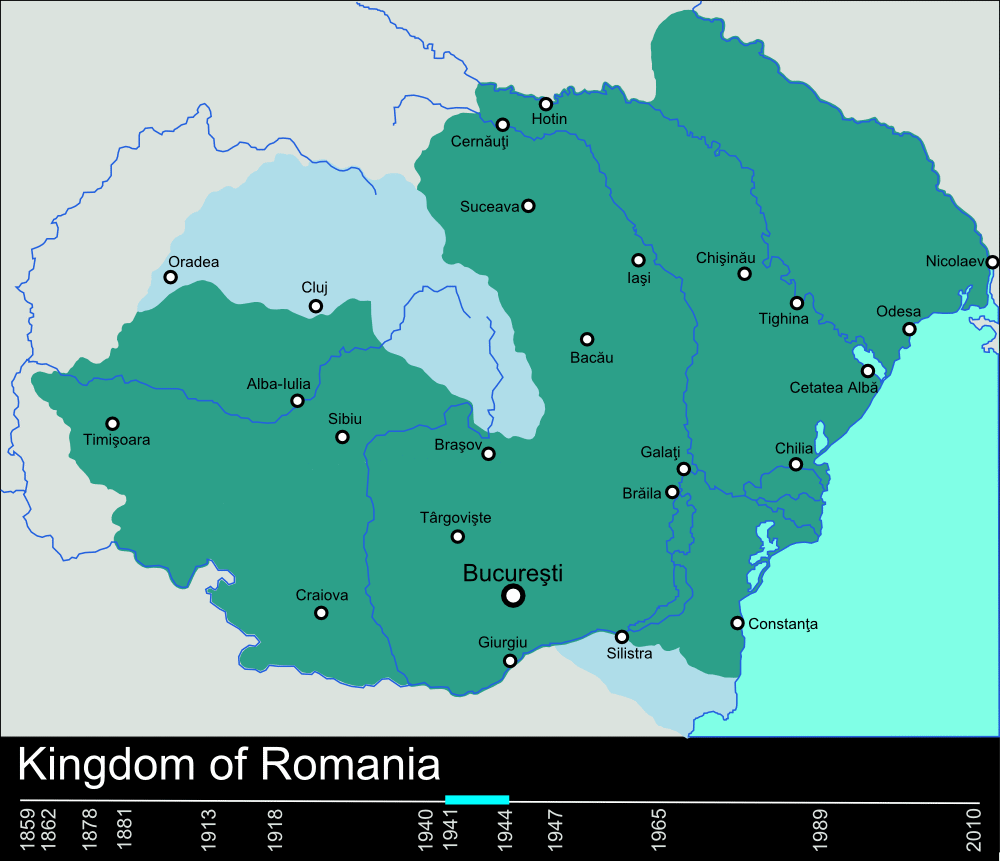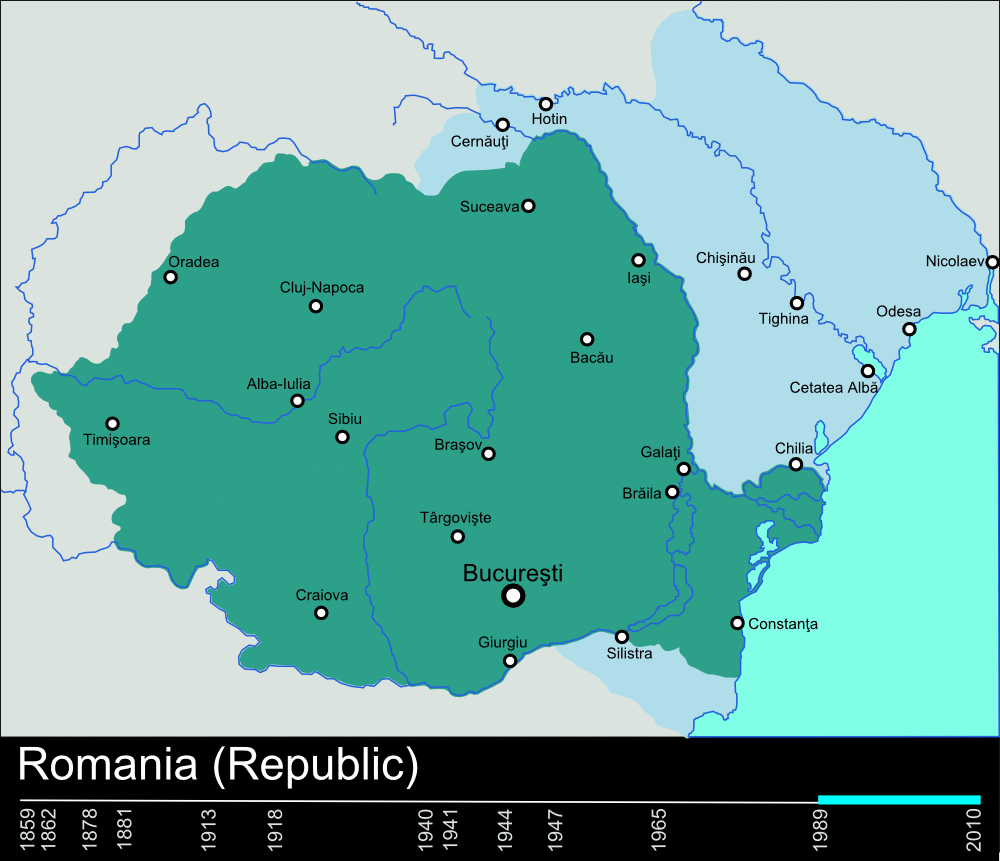
, which aimed for independence from Ottoman and Russian foreign rulership, represented important impacts in the process of spreading the liberal ideology in the eastern and southern Romanian lands, in spite of the fact that all three eventually failed. Nonetheless, in 1859, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
elected the same ruler, namely Alexander John Cuza
Alexandru Ioan Cuza (, or Alexandru Ioan I, also anglicised as Alexander John Cuza; 20 March 1820 – 15 May 1873) was the first ''domnitor'' (Ruler) of the Romanian Principalities through his double election as prince of Moldavia on 5 Janua ...
(who reigned as ''Domnitor
''Domnitor'' (Romanian pl. ''Domnitori'') was the official title of the ruler of Romania between 1862 and 1881. It was usually translated as "prince" in other languages and less often as "grand duke". Derived from the Romanian word "''domn''" ...
'') and were thus unified ''de facto'', resulting in the United Romanian Principalities for the period between 1859 and 1881.
During the 1870s, the United Romanian Principalities (then led by Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
( en, Nothing without God)
, national_anthem =
, common_languages = German
, religion = Roman Catholic
, currency =
, title_leader = Prince
, leader1 ...
Domnitor Carol I) fought a War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List o ...
against the Ottomans, with Romania's independence being formally recognised in 1878 at the Treaty of Berlin. Although the newly founded Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
initially allied with Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, Romania refused to enter World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
on the side of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
, because it was obliged to wage war only if Austria-Hungary was attacked. In 1916, Romania joined the war on the side of the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
.
As a result, at the end of the war, Transylvania, Bessarabia, and Bukovina were awarded to Romania, through a series of international peace treaties, resulting in an enlarged and far more powerful kingdom under King Ferdinand I. As of 1920, the Romanian people was believed to number over 15 million solely in the region of the Romanian kingdom, a figure larger than the populations of Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands combined.
During the interwar period, two additional monarchs came to the Romanian throne, namely Carol II
Carol II (4 April 1953) was King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until his forced abdication on 6 September 1940. The eldest son of Ferdinand I, he became crown prince upon the death of his grand-uncle, King Carol I in 1914. He was the first of th ...
and Michael I Michael I may refer to:
* Pope Michael I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark in 743–767
* Michael I Rhangabes, Byzantine Emperor (died in 844)
* Michael I Cerularius, Patriarch Michael I of Constantin ...
. This short-lived period was marked, at times, by political instabilities and efforts of maintaining a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
in favour of other, totalitarian regimes such as an absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism (European history), Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute pow ...
or a military dictatorship.
During World War II, the Kingdom of Romania lost territory both to the east and west, as Northern Transylvania became part of Hungary through the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
, while Bessarabia and northern Bukovina were taken by the Soviets and included in the Moldavian SSR
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic ( ro, Republica Sovietică Socialistă Moldovenească, Moldovan Cyrillic: ) was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 194 ...
, respectively Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
. The eastern territory losses were facilitated by the Molotov-Ribbentrop Nazi-Soviet non-aggression pact.
After the end of the war, the Romanian Kingdom managed to regain territories lost westward but was nonetheless not given Bessarabia and northern Bukovina, the aforementioned regions being forcefully incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. Subsequently, the Soviet Union imposed a Communist government and King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
Michael
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian an ...
was forced to abdicate and leave for exile. Nicolae Ceaușescu became the head of the Romanian Communist Party in 1965 and his severe rule of the 1980s was ended by the Romanian Revolution of 1989.
The 1989 revolution brought to power the dissident communist Ion Iliescu (backed by the National Salvation Front (Romania), FSN). He remained in power as head of state until 1996, when he was defeated by Romanian Democratic Convention, CDR-supported Emil Constantinescu at the 1996 Romanian general election, 1996 general elections, the first in post-Communist Romania that saw a peaceful transition of power. Following Constantinescu's only term as president from 1996 to 2000, Iliescu was re-elected in late 2000 for another term of four years. In 2004, Traian Băsescu, the National Liberal Party (Romania), PNL-Democratic Party (Romania), PD candidate, was elected president. Five years later, Băsescu was narrowly re-elected for a second term at the 2009 Romanian presidential election, 2009 presidential elections.
In 2014, the National Liberal Party (Romania), PNL-Democratic Liberal Party (Romania), PDL candidate Klaus Iohannis won a surprise victory over former Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister and Social Democratic Party (Romania), PSD-supported contender Victor Ponta in the second round of the 2014 Romanian presidential election, 2014 presidential elections. Thus, Iohannis became the first Romanian president stemming from an Ethnic minorities in Romania, ethnic minority of the country (as he belongs to the Germans of Romania, Romanian-German community, being a Transylvanian Saxons, Transylvanian Saxon). In 2019, the PNL-supported Iohannis was re-elected for a second term as president after a second round landslide victory at the 2019 Romanian presidential election.
In the meantime, Romania's major foreign policy achievements were the alignment with Western Europe and the United States of America, United States by joining the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) back in 2004 and the European Union three years later, in 2007.
Historiography
Modern Romanian historiography blends European historical traditions of imperialism with Christianity, mostly emphasizing the Europeaness of Romanians in the mythology of theirethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
(and de-emphasizing the collective histories of the Ottoman past). This is similar to the role of Hellenism in Greek historiography, although it begins about one century earlier than Hellenism. Since the 17th century, the Latin origins of the Romanian people have been central in Romanian historiography, to an extent described as "a constant, and even obsessive, preoccupation". The roots of this Latin historical tradition lie with Trajan's Dacian Wars, which either annihilated or fully assilimiated the indigenous Dacians that lived in modern Romania.
Language
 The origins of the
The origins of the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spellings: Rumanian or Roumanian; autonym: ''limba română'' , or ''românește'', ) is the official and main language of Romania and the Republic of Moldova. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in ...
, a Romance language, can be traced back to the Roman colonisation of the region. The basic vocabulary is of Latin origin, although there are some substratum words that are sometimes assumed to be of Dacian language, Dacian origin.
During the Middle Ages, Romanian was isolated from the other Romance languages, and borrowed words from the nearby Slavic languages (see Slavic influence on Romanian). Later on, it borrowed a number of words from German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, and Turkish language, Turkish. During the modern era, most neologisms Re-latinization of Romanian, were borrowed from French language, French and Italian language, Italian, though the language has increasingly begun to adopt English borrowings.
The Moldovan language, in its official form, is practically identical to Romanian, although there are some differences in colloquial speech. In the de facto independent (but internationally unrecognised) region of Transnistria, the official script used to write Moldovan is Cyrillic.
Since 2013, the Romanian Language Day is celebrated on 31 August in Romania. A similar holiday also exists in Moldova on the same day since 1990. It is known as "Limba noastră (public holiday), Limba noastră".
As of 2017, an Ethnologue estimation puts the (worldwide) number of Romanian speakers at approximately 24.15 million. The 24.15 million, however, represent only speakers of Romanian language, Romanian, not all of whom are necessarily ethnic Romanians. Also, this number does not include ethnic-Romanians who no longer speak the Romanian language.
Surnames
Many Romanian surnames have the suffix ''-escu'' or (less commonly) ''-așcu'' or ''-ăscu'' which corresponds to the Latin suffix ''-iscus'' and means "belonging to the people". For example, ''Petrescu'' used to be ''Petre's kin''. Similar suffixes such as ''-asco'', ''-asgo'', ''-esque'', ''-ez'', etc. are present in other Latin-derived languages. Many Romanians in France changed this ending of their surnames to ''-esco'', because the way it is pronounced in French better approximates the Romanian pronunciation of ''-escu''. Another widespread suffix of Romanian surnames is ''-eanu'' (or ''-an'', ''-anu''), which indicates the geographical origin. Some examples are: Moldoveanu/Moldovan/Moldovanu, from the region ofMoldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
or from Moldova River, river Moldova, Munteanu 'from mountains', Jianu 'from Jiu river region', Prut''eanu'', meaning 'from the Prut river', Mureș''anu'', meaning 'from the Mureș River, Mureș river', and Petr''eanu'' (meaning 'the son of Petre').
Other suffixes are ''-aru'' (or ''-oru'', ''-ar'', ''-or''), which indicates an occupation (like ''Feraru'' (meaning 'smith' or ''Morar'' meaning 'miller'), and ''-ei'', usually preceded by ''A-'' in front of a female name, which is a Latin inherited female genitive, like in ''Amariei'' (meaning ''of Maria''), ''Aelenei'' (meaning ''of Elena''). These matrilineal-rooted surnames are common in the historical region of Moldavia.
*The most common surnames are ''Pop''/''Popa'' ('the priest')—almost 200,000 Romanians have this surname
*—''Popescu'' ('son of the priest') —almost 150,000 have this name
*— and ''Ionescu'' ('John's (Ion's) son').
Names for Romanians
In English, Romanians are usually called Romanians and very rarely Rumanians or Roumanians, except in some historical texts, where they are called Roumans orVlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
.
Etymology of the name ''Romanian'' ()
 The name ''Romanian'' is derived from
The name ''Romanian'' is derived from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
wikt:romanus, ''romanus'', meaning "Roman people, Roman". Under regular phonetical changes that are typical to the Romanian language, the name over the centuries transformed into . An older form of was still in use in some regions. Socio-linguistic evolutions in the late 18th century led to a gradual preponderance of the spelling form, which was then generalised during the National awakening of Romania of early 19th century. Until the 19th century, the term Romanian denoted the speakers of the Daco-Romanian dialect of the Romanian language, thus being a much more distinct concept than that of Romania, the country of the Romanians. Prior to 1859, the Romanians were part of different state entities, with the Moldavians and the Wallachians being split off and having shaped separate political identities, possessing states of their own, while the rest of the Romanians were part of other states. However, eventually they retained their Romanian cultural and ethnic identity up to today. Some authors argue that the Romanians, with the exception of the Rhaeto-Romance languages, Rhaeto-Romance-speaking peoples, are the only ones that have designated themselves as "Romans" since the fall of the Roman Empire.Vladimír Baar, Daniel Jakubek, (2017) Divided National Identity in Moldova, Journal of Nationalism, Memory & Language Politics, Volume 11: Issue 1, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/jnmlp-2017-0004.
Several historical sources show the use of the term "Romanian" among the medieval or early modern Romanian population. One of the earliest examples comes from the ''Nibelungenlied'', a German epic poem from before 1200 in which a "Duke Ramunc from the land of Vlachs (Wallachia)" is mentioned. "Vlach" was an exonym used almost exclusively for the Romanians during the Middle Ages. It has been argued by some Romanian researchers that "Ramunc" was not the name of the duke, but a name that highlighted his ethnicity. Other old documents, especially Byzantine or Hungarian ones, make a correlation between the old Romanians as Romans or their descendants. Several other documents, notably from Italian travelers into Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania, speak of the self-identification, language and culture of the Romanians, showing that they designated themselves as "Romans" or related to them in up to 30 works. One example is Tranquillo Andronico's 1534 writing that states that the Vlachs "now call themselves Romans". Another one is Francesco della Valle's 1532 manuscripts that state that the Romanians from Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania preserved the name "Roman" and cites the sentence "''Sti Rominest?''" (''?'', "do you speak Romanian?"). Authors that travelled to modern Romania who wrote about it in 1574, 1575 and 1666 also noted the use of the term "Romanian". From the Middle Ages, Romanians bore two names, the exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
(one given to them by foreigners) ''Wallachians'' or ''Vlachs'', under its various forms (''vlah'', ''valah'', ''valach'', ''voloh'', ''blac'', ''olăh'', ''vlas'', ''ilac'', ''ulah'', etc.), and the endonym (the name they used for themselves) ''Romanians'' (/).
Other researchers have expressed a different point of view and have doubted or denied the continuity of the ethonym "Romanian" from "Roman", at least on an ethnic sense. For example, Onoriu Colăcel considers that the terms "Romania" and "Romanian" would only have appeared during the 19th century. According to Vladimír Baar and Daniel Jakubek, typically pro-Russian authors in Moldova tend to argue that "Romanian" as an ethnonym is only a mere recent product from Romanian nationalist historical myths despite the attestation of this name in old documents. Examples of this would include Petr Shornikov, Mikhail Guboglo and Valentin Dergachev. According to Tomasz Kamusella, at the time of the rise of Romanian nationalism during the early 19th century, the political leaders of Wallachia and Moldavia were aware that the name ''România'' was identical to ''Romania'', a name that had been used for the former Byzantine Empire by its inhabitants. Kamusella continues by stating that they preferred this ethnonym in order to stress their presumed link with Ancient Rome and that it became more popular as a nationalistic form of referring to all Romanian-language speakers as a distinct and separate nation during the 1820s. Raymond Detrez asserts that , derived from the Latin , acquired at a certain point the same meaning of the Greek ; that of Orthodox Christian. Wolfgang Dahmen claims that the meaning of ''romanus'' (Roman) as "Christian", as opposed to "pagan", which used to mean "non-Roman", may have contributed to the preservation of this word as an ethonym of the Romanian people, under the meaning of "Christian".
Daco-Romanian
To distinguish Romanians from the other Romanic peoples of the Balkans (Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, and Istro-Romanians), the term Daco-Romanian is sometimes used to refer to those who speak the standardRomanian language
Romanian (obsolete spellings: Rumanian or Roumanian; autonym: ''limba română'' , or ''românește'', ) is the official and main language of Romania and the Republic of Moldova. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in ...
and live in the former territory of ancient Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
(today comprising mostly Romania and Moldova), although some Daco-Romanian speakers can be found in Vlachs of Serbia, the eastern part of Central Serbia (which was part of ancient Moesia).
Etymology of the term Vlach
The name of "Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
" is an exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
that was used by Slavs to refer to all Romanized natives of the Balkans. It holds its origin from ancient Germanic—being a cognate to "Welsh" and "Walloon"—and perhaps even further back in time, from the Latin, Roman name Volcae, which was originally a Celtic tribe. From the Slavs, it was passed on to other peoples, such as the Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
(''Oláh'') and Greeks (''Vlachoi'') (see the Etymology section of Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
). Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, the Southern region of Romania, takes its name from the same source.
Nowadays, the term Vlach is more often used to refer to the Romanized populations of the Balkans who speak Romanian language, Daco-Romanian, Aromanian, Istro-Romanian, and Megleno-Romanian.
Anthroponyms
These are family names that have been derived from either ''Vlach'' or ''Romanian''. Most of these names have been given when a Romanian settled in a non-Romanian region. Examples: Oláh (37,147 Hungarians have this name), Vlach, Vlahuta, Vlasa, Vlasi, Vlašic, Vlasceanu, Vlachopoulos, Voloh, Volyh, Vlack, Flack, and Vlax.Romanians outside Romania
 Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia, Argentina, and New Zealand among many other countries. Italy and Spain have been popular emigration destinations, due to a relatively low language barrier, and both are each now home to about a million Romanians. With respect to geopolitical identity, many individuals of Romanian ethnicity in Moldova prefer to identify themselves as
Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia, Argentina, and New Zealand among many other countries. Italy and Spain have been popular emigration destinations, due to a relatively low language barrier, and both are each now home to about a million Romanians. With respect to geopolitical identity, many individuals of Romanian ethnicity in Moldova prefer to identify themselves as Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians ( ro, moldoveni , Moldovan Cyrillic: молдовень), are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and the largest ethnic group of the Republic of Moldova (75.1% of the population as of 2014) and a sign ...
.
The contemporary total population of ethnic Romanians cannot be stated with any degree of certainty. A disparity can be observed between official sources (such as census counts) where they exist, and estimates which come from non-official sources and interested groups. Several inhibiting factors (not unique to this particular case) contribute towards this uncertainty, which may include:
*A degree of overlap may exist or be shared between Romanian and other ethnic identities in certain situations, and census or survey respondents may elect to identify with one particular ancestry but not another, or instead identify with multiple ancestries;In an ever more globalized world the incredibly diverse and widespread phenomenon of migration has played a significant role in the ways in which notions such as "home," "membership" or "national belonging" have constantly been disputed and negotiated in both sending and receiving societies. – ''Rogers Brubaker, Citizenship and Nationhood '' (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1994).
*Counts and estimates may inconsistently distinguish between Romanian nationality and Romanian ethnicity (i.e. not all Romanian nationals identify with Romanian ethnicity, and vice versa);
*The measurements and methodologies employed by governments to enumerate and describe the ethnicity and ancestry of their citizens vary from country to country. Thus the census definition of "Romanian" might variously mean Romanian-born, of Romanian parentage, or also include other ethnic identities as Romanian which otherwise are identified separately in other contexts;
For example, the decennial US Census of 2000 calculated (based on a statistical sampling of household data) that there were 367,310 respondents indicating Romanian ancestry (roughly 0.1% of the total population).
The actual total recorded number of foreign-born Romanians was only 136,000. However, some non-specialist organisations have produced estimates which are considerably higher: a 2002 study by the Romanian-American Network Inc. mentions an estimated figure of 1,200,000 for the number of Romanian-Americans. Which makes the United States home to the largest Romanian community outside Romania.
This estimate notes however that "...other immigrants of Romanian national minority groups have been included such as: Armenians of Romania, Armenians, Germans of Romania, Germans, Romani people in Romania, Gypsies, Hungarians in Romania, Hungarians, History of the Jews in Romania, Jews, and Ukrainians of Romania, Ukrainians". It also includes an unspecified allowance for second- and third-generation Romanians, and an indeterminate number living in Canada. An error range for the estimate is not provided. For the United States 2000 Census figures, almost 20% of the total population did not classify or report an ancestry, and the census is also subject to undercounting, an incomplete (67%) response rate, and sampling error in general.
Culture
Contributions to contemporary culture
Romanians have played and contributed a major role in the advancement of the arts, culture, sciences, technology and engineering. In the history of aviation, Traian Vuia and Aurel Vlaicu built and tested some of the earliest aircraft designs, while Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Victor Babeș discovered more than 50 germs and a cure for a disease named after him, babesiosis; biologist Nicolae Paulescu was among the first scientists to identify insulin. Another biologist, Emil Palade, received the Nobel Prize for his contributions to cell biology. George Constantinescu created the theory of sonics, while mathematician Ștefan Odobleja has been claimed as "the ideological father behind cybernetics" – his work ''The Consonantist Psychology'' (Paris, 1938) was supposedly the main source of inspiration for N. Wiener's ''Cybernetics'' (Paris, 1948). Lazăr Edeleanu was the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine and also invented the modern method of Oil refinery, refining crude oil.Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
by the frustrated German tradesmen of Kronstadt (Brașov) and on some Vampire folklore by region#Romania, vampire folk tales about the historic Romanian figure of Prince Vlad III Dracula, Vlad Țepeș.
Religion
Almost 90% of all Romanians consider themselves religious. The vast majority are Eastern Orthodox Christians, belonging to the Romanian Orthodox Church (a branch of Eastern Orthodoxy, or Eastern Orthodox Church, together with the Greek Orthodox, Orthodox Church of Georgia and Russian Orthodox Churches, among others). Romanians form the List of contemporary ethnic groups, third largest ethno-linguistic group among Eastern Orthodox in the world. According to the 2011 census, 93.6% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identified themselves as Romanian Orthodox (in comparison to 81% of Romania's total population, including other ethnic groups). However, the actual rate of church attendance is significantly lower and many Romanians are only nominally believers. For example, according to a 2006 Eurobarometer poll, only 23% of Romanians attend church once a week or more. A 2006 poll conducted by the Open Society Foundations found that only 33% of Romanians attended church once a ''month'' or more.Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, Banat, Bukovina, Bucharest, and parts of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
, belonging to both the Roman Catholicism in Romania, Roman Catholic Church (297,246 members) and the Romanian Church United with Rome, Greek-Catholic, Romanian Greek-Catholic Catholic Church (124,563 members). According to the 2011 census, 2.5% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identified themselves as Catholic (in comparison to 5% of Romania's total population, including other ethnic groups). Around 1.6% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identify themselves as Pentecostal, with the population numbering 276,678 members. Smaller percentages are Protestant, Jews, Muslims, agnostic, atheist, or practice a traditional religion.
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
). However, this seems to be the exception, rather than the rule, as in both Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
the state religion was Eastern Orthodox. Until the 17th century, the official language of the liturgy was Old Church Slavonic. Then, it gradually changed to Romanian.
According to a survey that took place in 2011, despite 94% of respondents answered positively for believing in God, 42% support the vision of Christian dogma that there is a God incarnated into a human being. While 34% of respondents said that there is only one true religion, 38% believe that there is one true religion and that other religions contain some basic truths, according to 18% there is one true religion and all major world religions contain some fundamental truths. 88% of Romanians believe in the existence of a soul, 87% believe in sin and the existence of heaven, 60% believe in an "evil eye", 25% believe in horoscopes and 23% in Extraterrestrial life, aliens. According to a 2004 survey, 80% consider themselves not superstitious and the same amount believe in angels, about 40% believe they have had dreams that became deja vu and 19% believe in ghosts.
Symbols
In addition to the colours of the History of Romania, Romanian flag, each historical province of Romania has its own characteristic symbol: * Banat: Trajan's Bridge * Dobruja: Dolphin *Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
(including Bukovina and Bessarabia): Aurochs/Wisent
* Oltenia: Lion
* Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
(including Crișana and Maramureș): Black eagle or Turul
* Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
: Eagle
The coat of arms of Romania combines these together.
Customs
Relationship to other ethnic groups
The closest ethnic groups to the Romanians are the other Romanic peoples of Southeastern Europe: theAromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
(Macedonia (region), Macedo-Romanians), the Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites ( ruq, Miglinits), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs ( ruq, Vlaș), are a small Eastern Romance people, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis re ...
, and the Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
. The Istro-Romanians are the closest ethnic group to the Romanians, and it is believed they left Maramureș, Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
about a thousand years ago and settled in Istria, Croatia. Numbering about 500 people still living in the original villages of Istria while the majority left for other countries after World War II (mainly to Italy, United States, Canada, Spain, Germany, France, Sweden, Switzerland, Romania, and Australia), they speak the Istro-Romanian language, the closest living relative of Romanian. On the other hand, the Aromanians and the Megleno-Romanians are Romance peoples who live south of the Danube, mainly in Greece, Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria although some of them migrated to Romania in the 20th century. It is believed that they diverged from the Romanians in the 7th to 9th century, and currently speak the Aromanian language and Megleno-Romanian language, both of which are Balkan Romance languages, like Romanian, and are sometimes considered by traditional Romanian linguists to be dialects of Romanian.
Genetics
According to a triple analysis – Autosome, autosomal, mitochondrial and Y-DNA, paternal — of available data from large-scale studies, the whole genome Single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP data situates Romanians are most closely related to Bulgarians, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians and, to some extent, Greeks, followed by other European populations, which form a coherent cluster among worldwide populations. "Most South Slavs are separated from the rest of the Balto-Slavic populations and form a sparse group of populations with internal differentiation into ''western'' (Slovenians, Croatians and Bosnians) and ''eastern'' (Macedonians and Bulgarians) regions of the Balkan Peninsula with Serbians placed in-between... Furthermore, Slovenians lie close to the non-Slavic-speaking Hungarians, whereas ''eastern'' South Slavs group is located together with non-Slavic-speaking but geographically neighboring Romanians and, to some extent, with Greeks." The prevailing Y-chromosome inWallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
(Ploiești, Dolj County, Dolj), Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
(Piatra Neamț, Buhuși), Dobruja (Constanța), and northern Republic of Moldova is recorded to be Haplogroup I (Y-DNA), Haplogroup I. On the basis of 361 samples, Haplogroup I occurs at 32% in Romanians. The frequency of I2a1 (I-P37) in the Balkans today is owed to indigenous European hunter-gatherers tribes, and was present before the Early Slavs, Slavic expansion.
 According to an Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a among Romanians is entirely from the Eastern European variety Z282 and may be a result of Baltic, Thracian or Slavic descent. R1a-Z280 outnumbers R1a-M458 among Romanians, the opposite phenomena is typical for Poles, Czechs and Bulgarians. 12% of the Romanians belong to R1b, the Alpino-Italic branch R1b-U152 is at 2% per 330 samples, a lower frequency recorded than other Balkan peoples. The branches R1b-U106, R1b-DF27 and R1b-L21 make up 1% respectively. The eastern branches R1b-M269* and L23* (Z2103) make up 7% and outnumber the Atlantic branches, they prevail in parts of east, central Europe and as a result of Greek colonisation – in parts of Sicily as well. 8% of the Romanians belong to E1b1b1a1 (E-M78) per 265 samples. Other studies analyzing the haplogroup frequency among Romanians came to similar results.
Showing the importance of geography, a 2017 paper concentrated on the mtDNA, and showed how Romania has been "a major crossroads between Asia and Europe" and thus "experienced continuous migration and invasion episodes"; while stating that "previous studies" show Romanians "exhibit genetic similarity with other Europeans" and "another study pointed to possible segregation within the Middle East populations". The paper also mentions how "signals of Asian maternal lineages were observed in all Romanian historical provinces, indicating gene flow along the migration routes through East Asia and Europe, during different time periods, namely, the Upper Paleolithic period and/or, with a likely greater preponderance, the Middle Ages", at low frequency (2.24%). It concludes that "our current findings based on the mtDNA analysis of populations in historical provinces of Romania suggest similarity between populations in
According to an Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a among Romanians is entirely from the Eastern European variety Z282 and may be a result of Baltic, Thracian or Slavic descent. R1a-Z280 outnumbers R1a-M458 among Romanians, the opposite phenomena is typical for Poles, Czechs and Bulgarians. 12% of the Romanians belong to R1b, the Alpino-Italic branch R1b-U152 is at 2% per 330 samples, a lower frequency recorded than other Balkan peoples. The branches R1b-U106, R1b-DF27 and R1b-L21 make up 1% respectively. The eastern branches R1b-M269* and L23* (Z2103) make up 7% and outnumber the Atlantic branches, they prevail in parts of east, central Europe and as a result of Greek colonisation – in parts of Sicily as well. 8% of the Romanians belong to E1b1b1a1 (E-M78) per 265 samples. Other studies analyzing the haplogroup frequency among Romanians came to similar results.
Showing the importance of geography, a 2017 paper concentrated on the mtDNA, and showed how Romania has been "a major crossroads between Asia and Europe" and thus "experienced continuous migration and invasion episodes"; while stating that "previous studies" show Romanians "exhibit genetic similarity with other Europeans" and "another study pointed to possible segregation within the Middle East populations". The paper also mentions how "signals of Asian maternal lineages were observed in all Romanian historical provinces, indicating gene flow along the migration routes through East Asia and Europe, during different time periods, namely, the Upper Paleolithic period and/or, with a likely greater preponderance, the Middle Ages", at low frequency (2.24%). It concludes that "our current findings based on the mtDNA analysis of populations in historical provinces of Romania suggest similarity between populations in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
," on one hand, and between Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
, and Dobruja and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
on the other, "supported both by the observed clines in haplogroup frequencies for several European and Asian maternal lineages and Multidimensional scaling, MDS analyses."
According to an autosomal DNA analysis of various eastern Europeans and adjacent populations, the Romanians are most closely related to Bulgarians and Macedonians. Most West Slavs, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, and Austrians were found to share as many identical by-descent segments with South Slavs as with Romanians, Torbeshi and Gagauzes. While Romanians display close relationship to surrounding European populations, they display some substructure in respect to geographic patterns. Romanians display a slightly higher affinity for Anatolian and Middle Eastern populations, compared to other Eastern Europeans.
Gallery
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, late 19th century
File:Bucovina.jpg, Romanian peasant costume from Bukovina, early 20th century
File:Bukovynski rumuny.jpg, Romanians from Bukovina, early 20th century postcard
File:Bouquet - Wallachians.jpg, Romanians from Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, early 19th century
File:Rumuni (vlasi) Ždrelo.JPG, Romanians from central Serbia, late 19th century
File:Wallachian infantery marching, 1837.jpg, Romanian infantrymen from Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, early 19th century
File:Roumanians in New York 1891.JPG, Romanian immigrants in New York City, late 19th century
File:Ipolit Strambu - Ciobanas.jpg, Painting of a young Wallachian shepherd in the early 20th century by Ipolit Strâmbu
File:Harvest time in Romania, 1920.jpg, Romanian peasants during the harvest season (1920)
File:Roumanophones 1856.jpeg, Mid-19th century French map depicting Romanians in Central and Eastern Europe
File:RomaniansInBalkans.png, Modern distribution of the Eastern Romance-speaking ethnic groups (including, most notably, the Romanians)
File:Austria-Hungary (ethnic).jpg, Romanians in Central Europe (coloured in blue), 1880
File:Austro-Ungaria si Romania (harta etnica).jpg, Ethnic map of Austria-Hungary and Romania, 1892
File:Romanians before WW1.jpg, British map depicting territories inhabited by Eastern Romance peoples before the outbreak of World War I
File:Sprachatlas Weigand 67.JPG, Romanian speakers in Central and Eastern Europe, early 20th century
File:GreaterRomaniaHistoricRegions.png, Map of the Kingdom of Romania at its greatest extent (1920–1940)
File:SE Europe Romanians.png, Geographic distribution of ethnic Romanians in the early 21st century
File:Map-balkans-vlachs.png, Notable regions with inhabited by Eastern Romance speakers at the beginning of the 21st century
File:Daco-Romanians (subgroups).PNG, Map highlighting the three main sub-groups of Daco-Romanians
File:Romania harta etnica 2011.PNG, Geographic distribution of Romanians in Romania (coloured in purple) at commune level (2011 census)
File:Harta etnica 2011 JUD.png, Geographic distribution of Romanian in Romania (coloured in purple) at county level (2011 census)
See also
* List of Romanians, List of notable Romanians * Romance languages * Slavic influence on Romanian * Legacy of the Roman Empire * Romanian diaspora * Romanians in Germany * Romanian British * Romanian French * Romanian Australians * Romanian Americans * Romanian Canadians * Romanians of Serbia * Romanian language in Serbia * Romanians in Ukraine, Romanians of Ukraine * Romanians in Hungary, Romanians of Hungary * Romanians in Bulgaria, Romanians of Bulgaria * History of Romania * Origin of the Romanians * Thraco-Roman * Daco-Roman * Brodnici *Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци or , ; it, Morlacchi; ro, Morlaci) has been an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach p ...
* Moravian Wallachia
Moravian Wallachia ( cs, Moravské Valašsko, or simply ''Valašsko''; ro, Valahia Moravă) is a mountainous ethnoregion located in the easternmost part of Moravia in the Czech Republic, near the Slovak border, roughly centered on the cities Vs ...
* Culture of Romania
* Art of Romania
* Geography of Romania
* Folklore of Romania
* Music of Romania
* Sport in Romania
* Name of Romania
* Romanian cuisine
* Romanian literature
* Minorities of Romania
Notes and references
External links
A Concise History of Romanians
{{Authority control Romanian people, Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Moldova Ethnic groups in Ukraine Indigenous peoples of Ukraine Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Vojvodina Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Hungary Eastern Romance people Romance peoples Ethnic groups divided by international borders