Rhodes Filerimos3 tango7174.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of
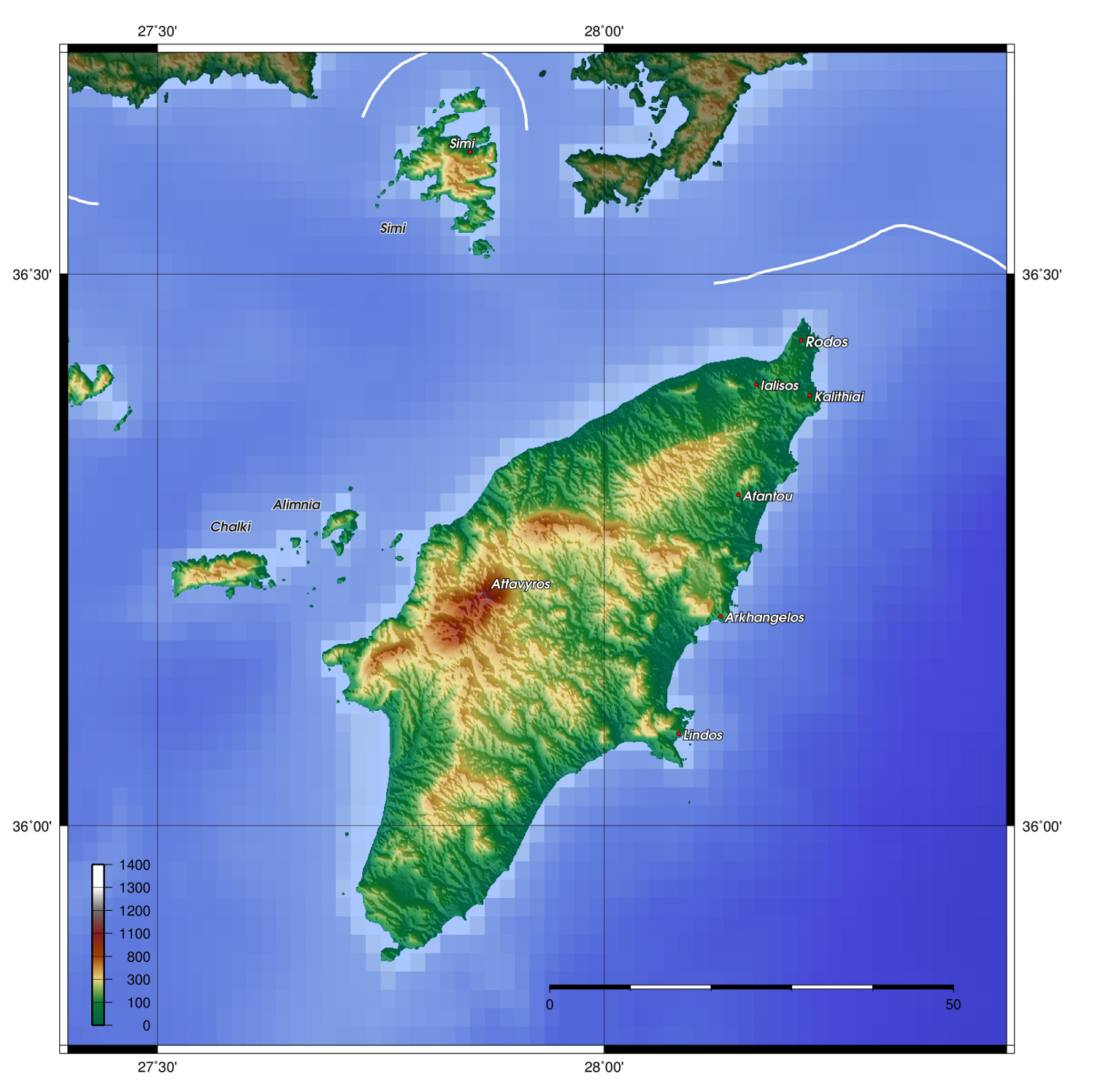

 The island of Rhodes is shaped like a
The island of Rhodes is shaped like a
"> making it the warmest area in Greece. Moreover, according to the
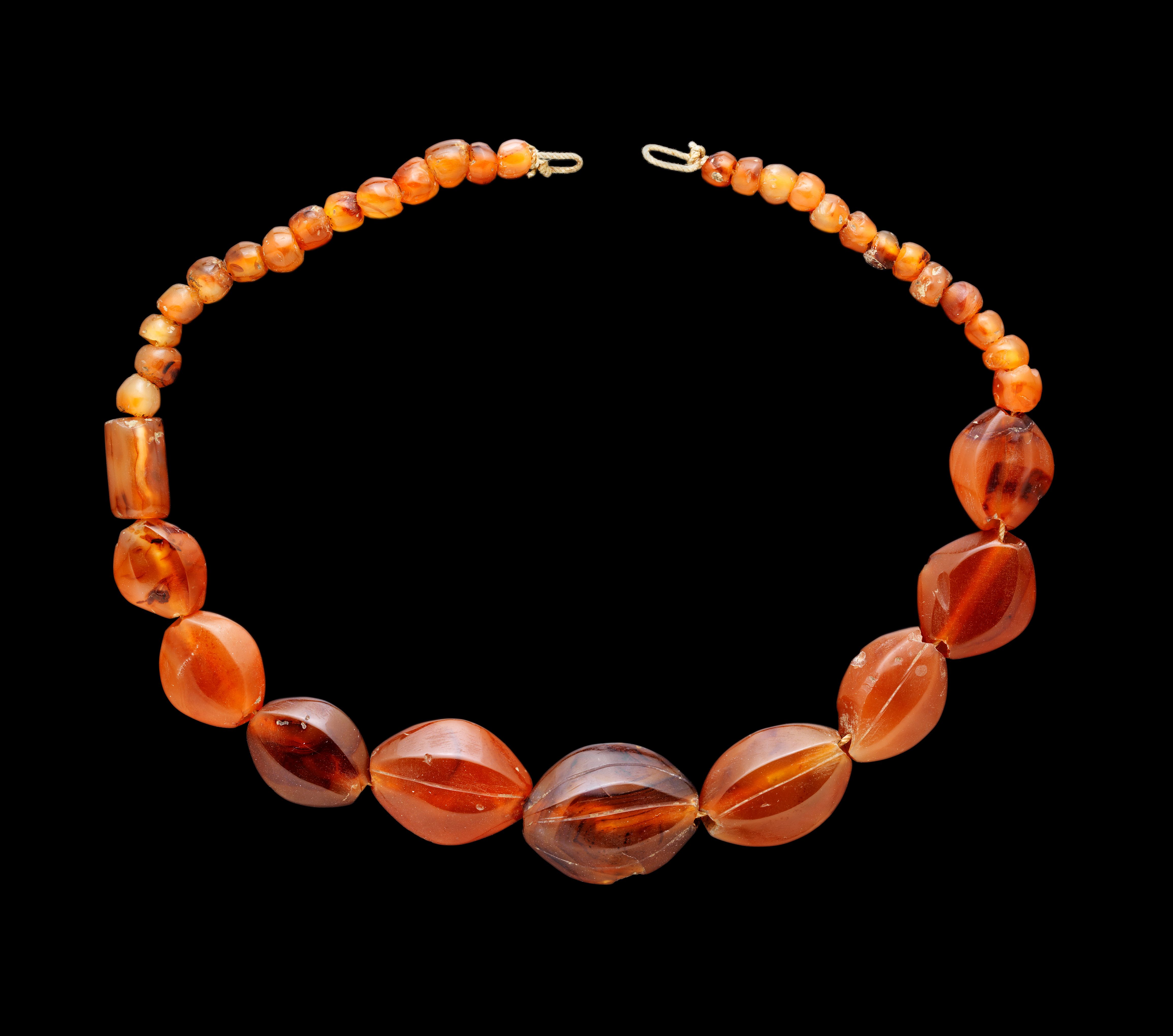 In the 15th century BCE,
In the 15th century BCE,
 In the 8th century BC, the island's settlements started to form, with the coming of the
In the 8th century BC, the island's settlements started to form, with the coming of the
 The
The
 Following the death of Alexander, his generals (
Following the death of Alexander, his generals (
 Despite being exhausted by the Second Punic War against Hannibal (218–201 BC) the Romans agreed to intervene, still angry over the Macedonian alliance with Carthage that had led to the
Despite being exhausted by the Second Punic War against Hannibal (218–201 BC) the Romans agreed to intervene, still angry over the Macedonian alliance with Carthage that had led to the
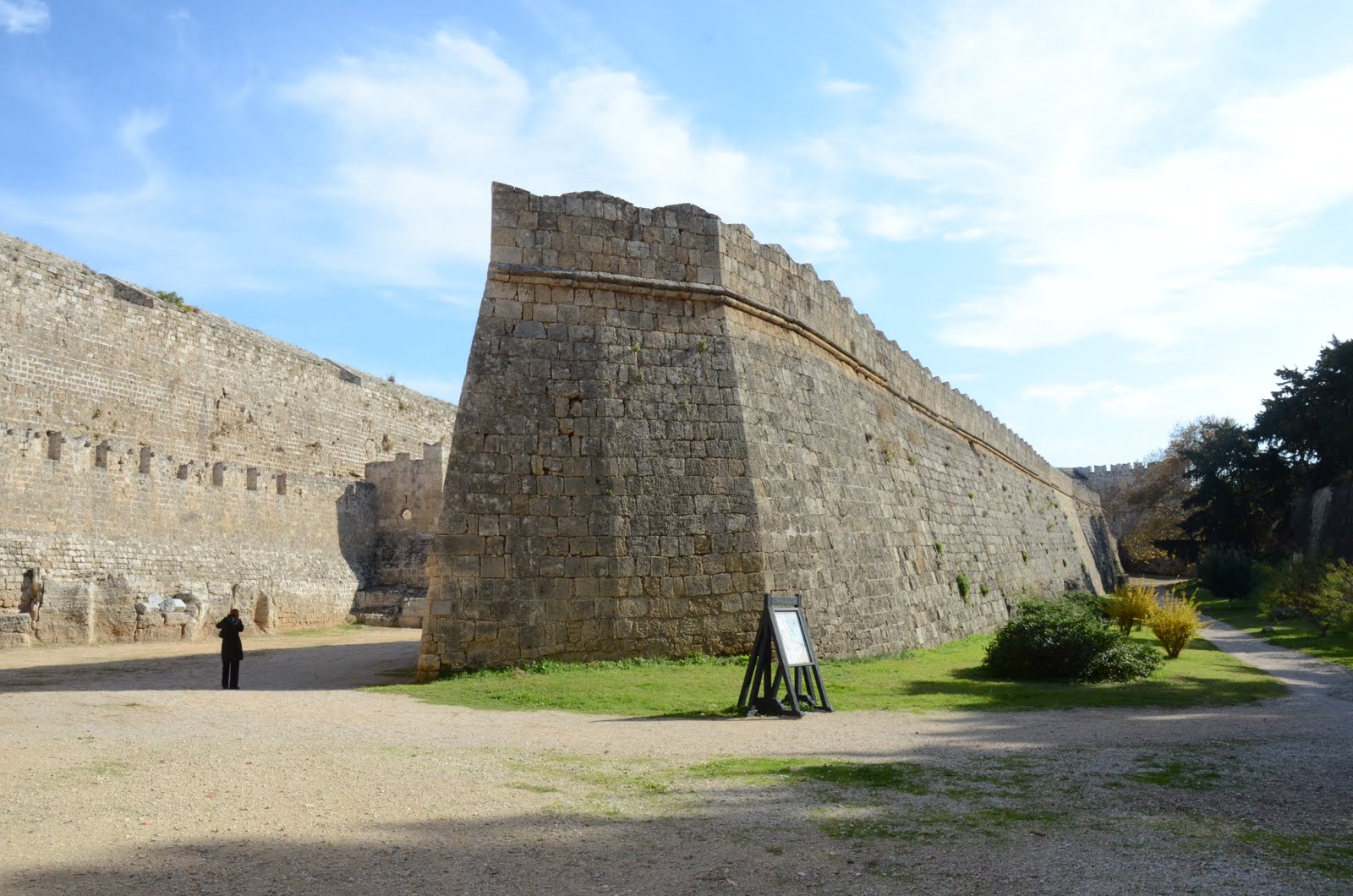 As Byzantine central power weakened under the
As Byzantine central power weakened under the

 In 1306–1310, the Byzantine era of the island's history came to an end when the island was occupied by the
In 1306–1310, the Byzantine era of the island's history came to an end when the island was occupied by the

 In the 19th century the island was populated by ethnic groups from the surrounding nations, including Jews, whose presence goes back 2,300 years. Under Ottoman rule, they generally did fairly well, but discrimination and bigotry occasionally arose. In February 1840, the Jews of Rhodes were falsely accused by the Greek Orthodox community of ritually murdering a Christian boy. This became known as the Rhodes blood libel.
Austria opened a post-office at ''RHODUS'' (Venetian name) before 1864, as witnessed by stamps with
In the 19th century the island was populated by ethnic groups from the surrounding nations, including Jews, whose presence goes back 2,300 years. Under Ottoman rule, they generally did fairly well, but discrimination and bigotry occasionally arose. In February 1840, the Jews of Rhodes were falsely accused by the Greek Orthodox community of ritually murdering a Christian boy. This became known as the Rhodes blood libel.
Austria opened a post-office at ''RHODUS'' (Venetian name) before 1864, as witnessed by stamps with
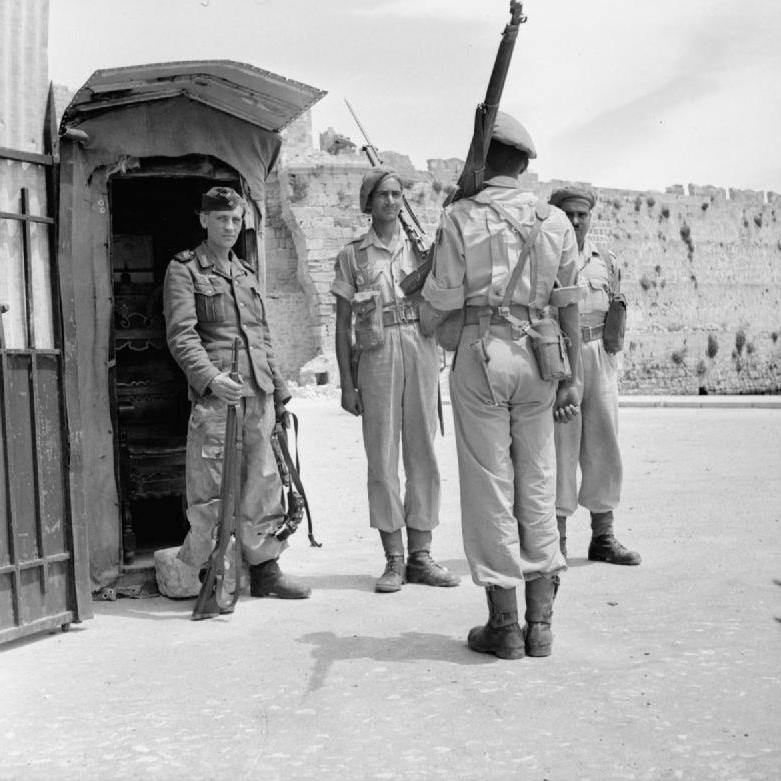 On 8 May 1945, the Germans under Otto Wagener surrendered Rhodes as well as the Dodecanese as a whole to the British, who soon after then occupied the islands as a military protectorate.
At the Paris Peace Treaties, Rhodes, together with the other islands of the Dodecanese, was united with
On 8 May 1945, the Germans under Otto Wagener surrendered Rhodes as well as the Dodecanese as a whole to the British, who soon after then occupied the islands as a military protectorate.
At the Paris Peace Treaties, Rhodes, together with the other islands of the Dodecanese, was united with
 Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean
The South Aegean ( el, Περιφέρεια Νοτίου Αιγαίου, translit=Periféria Notíou Eyéou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It consists of the Cyclades and Dodecanese island groups in the central and ...
administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. The city of Rhodes had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022 the island has population of 124,851 people. It is located northeast of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
, southeast of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522.
Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2 ...
. The Medieval Old Town of the City of Rhodes has been declared a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
. Today, it is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Europe.
Name
The island has been known as (Ródos) in Greek throughout its history. It was also called Lindos ( grc, Λίνδος). In addition, the island has been called inItalian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, in Turkish, and or in Ladino.
Other ancient names were Ρόδη (Rodē), Τελχινίς (Telchinis) and Ηλιάς (Helias).
''The Travels of Sir John Mandeville
Sir John Mandeville is the supposed author of ''The Travels of Sir John Mandeville'', a travel memoir which first circulated between 1357 and 1371. The earliest-surviving text is in French.
By aid of translations into many other languages, the ...
'' incorrectly reports that Rhodes was formerly called "Collosus", through a conflation of the Colossus of Rhodes and Paul
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
* Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chri ...
's ''Epistle to the Colossians
The Epistle to the Colossians is the twelfth book of the New Testament. It was written, according to the text, by Paul the Apostle and Timothy, and addressed to the church in Colossae, a small Phrygian city near Laodicea and approximately f ...
'', which refers to Colossae
Colossae (; grc-gre, Κολοσσαί) was an ancient city of Phrygia in Asia Minor, and one of the most celebrated cities of southern Anatolia (modern Turkey). The Epistle to the Colossians, an early Christian text which identifies its autho ...
.
The island's name might be derived from ''erod'', Phoenician for snake, since the island was home to many snakes in antiquity.
Geography


 The island of Rhodes is shaped like a
The island of Rhodes is shaped like a spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
head, long and wide, with a total area of approximately and a coastline of approximately . Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
is the main bedrock. The city of Rhodes is located at the northern tip of the island, as well as the site of the ancient and modern commercial harbours. The main airport is the Diagoras International Airport
Rhodes International Airport "Diagoras" (Greek: Διεθνής Αερολιμένας Ρόδου "Διαγόρας"), or Diagoras International Airport , is located on the West side of the island of Rhodes in Greece. The facility is located ju ...
(IATA code: RHO), located to the southwest of the city in Paradisi. The road network radiates from the city along the east and west coasts.
Outside the city of Rhodes, the island is dotted with small villages of whitewashed homes and spa resorts, among them Faliraki
Faliraki ( el, Φαληράκι) is the primary seaside resort village on the Greek island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek island ...
, Lindos, Kremasti
Kremasti ( el, Κρεμαστή) is a town on the Greek island of Rhodes (', ''Ródhos''). Located on the west coast of the island, Kremasti is 12 kilometers from the capital of Rhodes, on the road to the airport. It has a population of 5,363 ...
, Haraki
Charaki ( el, Χαράκι) is a small fishing village on the east coast of the island of Rhodes, Greece. In addition to its fishing trade, Charaki is also a small holiday resort, with the usual tavernas, restaurants and bars. Charaki has a ...
, Pefkos
Pefkos or Pefki, Greek: Πεύκος (Πεύκοι), is a well known beach resort located on eastern coast of Rhodes, just southwest of Lindos, and from the capital city Rhodes. The island of Rhodes is the largest of the Dodecanese islands, on ...
, Archangelos, Afantou
Afantou ( el, Αφάντου) is a village and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the ...
, Koskinou, Embona
Embonas ( gr, Έμπωνας), sometimes transliterated Emponas, is a Greek mountain village, seat of the municipal unit of Attavyros, on the island of Rhodes, South Aegean region. In 2011 its population was 1,242; 1,061 in the village proper and ...
(Attavyros), Paradisi, and Trianta (Ialysos).
Rhodes is situated east-southeast from the Greek mainland, and from the southern shore of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. Mount Attavyros
Attavyros ( el, Αττάβυρος) or Atavyros (Ατάβυρος) is the highest mountain on the island of Rhodes in the Dodecanese in Greece. It rises to a height of 1,215 m. It lies to the south of the village of Embonas.
In Greek mythology ...
, at , is the island's highest point of elevation.
Flora
The interior of the island is mountainous, sparsely inhabited and covered with forests ofpine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
(''Pinus brutia
''Pinus brutia'', commonly known as the Turkish pine, is a species of pine native to the eastern Mediterranean region. The bulk of its range is in Turkey.
Turkish pine is also known by several other common names: Calabrian pine (from a naturali ...
'') and cypress (''Cupressus sempervirens''). While the shores are rocky, the island has arable strips of land where citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
fruit, wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
grapes, vegetables, olives
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'M ...
and other crops are grown. Many flowering plants for which the island is named are abundant.
Fauna
The Rhodian population offallow deer
''Dama'' is a genus of deer in the subfamily Cervinae, commonly referred to as fallow deer.
Name
The name fallow is derived from the deer's pale brown colour. The Latin word ''dāma'' or ''damma'', used for roe deer, gazelles, and antelopes ...
was found to be genetically distinct in 2005, and to be of urgent conservation concern. In Petaloudes
Petaloudes ( el, Πεταλούδες) is a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. Its population was 1 ...
Valley (Greek for "Valley of the Butterflies"), large numbers of tiger moths gather during the summer months.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes include the 226 BC earthquake that destroyed the Colossus of Rhodes; one on 3 May 1481 which destroyed much of the city of Rhodes; and one on 26 June 1926. On 15 July 2008, Rhodes was struck by a 6.3 magnitude earthquake causing minor damage to a few old buildings and one death.Climate
Rhodes has a hot-summerMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(''Csa'' in the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
) with mild winters and hot summers. The South East of the island experiences a significantly warmer climate with Lindos registering for the period 2010-2019 a mean annual temperature of ,National Observatory of Athens
The National Observatory of Athens (NOA; el, Εθνικό Αστεροσκοπείο Αθηνών) is a research institute in Athens, Greece. Founded in 1842, it is the oldest research foundation in Greece, as it was the first scientific rese ...Hellenic National Meteorological Service
The Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) ( el, Εθνική Μετεωρολογική Υπηρεσία (ΕΜΥ)) is a government agency responsible for making weather forecasts and observations for Greece. HNMS was founded in 1931 under ...
, South East Rhodes records the highest mean annual sunshine in Greece with over 3,100 hours.
History
Prehistory
The island was inhabited in theNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period although little remains of this culture.
Minoan Era
In the 16th century BC, the Minoans came to Rhodes. Later Greek mythology recalled a Rhodian race called theTelchines
In Greek mythology, the Telchines ( grc, Τελχῖνες, ''Telkhines'') were the original inhabitants of the island of Rhodes and were known in Crete and Cyprus.
Family
Their parents were either Pontus and Gaia or Tartarus and Nemesis or else ...
and associated the island of Rhodes with Danaus; it was sometimes nicknamed ''Telchinis''.
Mycenaean Era
 In the 15th century BCE,
In the 15th century BCE, Mycenaean Greeks
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
invaded. After the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near ...
, the first renewed outside contacts were with Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
.
In the '' Digesta seu Pandectae'' (533), the second volume of the codification of laws ordered by Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
(527–565) of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, a legal opinion written by the Roman jurist Paulus at the beginning of the Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensio ...
in 235 AD was included about the ''Lex Rhodia
Lex or LEX may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lex'', a daily featured column in the ''Financial Times''
Games
* Lex, the mascot of the word-forming puzzle video game ''Bookworm''
* Lex, the protagonist of the word-forming puzzle video ga ...
'' ("Rhodian law") that articulates the general average principle of marine insurance established on the island of Rhodes in approximately 1000 to 800 BC as a member of the Doric Hexapolis, plausibly by the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns during the proposed Dorian invasion and emergence of the purported Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
during the Greek Dark Ages (c. 1100–c. 750) that led to the proliferation of the Doric Greek dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
. The law of general average constitutes the fundamental principle that underlies all insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge ...
.
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
mentions that Rhodes participated in the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ...
under the leadership of Tlepolemus
In Greek mythology, Tlepolemus (; Ancient Greek: Τληπόλεμος ''Tlēpólemos'') was the leader of the Rhodian forces in the Trojan War.Homer, ''Iliad'2.653–70
Family
Tlepolemus was a son of Heracles and Astyoche, daughter of Phylas, ...
.
Archaic Era
 In the 8th century BC, the island's settlements started to form, with the coming of the
In the 8th century BC, the island's settlements started to form, with the coming of the Dorians
The Dorians (; el, Δωριεῖς, ''Dōrieîs'', singular , ''Dōrieús'') were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans, and Ionian ...
, who built the three important cities of Lindos, Ialyssos
Ialysos ( el, Ιαλυσός, before 1976: Τριάντα ''Trianta'') is a town and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of wh ...
and Kameiros
Camirus or Kamiros ( grc, Κάμιρος; ) or Cameirus or Kameiros (Κάμειρος) was a city of ancient Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Its site is on the northwest coast of the island, west of the modern village of Kalavarda.
History ...
, which together with Kos
Kos or Cos (; el, Κως ) is a Greek island, part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 36,986 (2021 census), ...
, Cnidus
Knidos or Cnidus (; grc-gre, Κνίδος, , , Knídos) was a Greek city in ancient Caria and part of the Dorian Hexapolis, in south-western Asia Minor, modern-day Turkey. It was situated on the Datça peninsula, which forms the southern side o ...
and Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was located i ...
(on the mainland) made up the so-called Dorian Hexapolis
The Doric or Dorian Hexapolis ( grc-gre, Δωρικὴ Ἑξάπολις or Δωριέων Ἑξάπολις) was a federation of six cities of Dorian foundation in southwest Asia Minor and adjacent islands, largely coextensive with the region ...
(Greek for six cities).
In Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar ...
's ode, the island was said to be born of the union of Helios the sun god and the nymph Rhodos
In Greek mythology, Rhodos/Rhodus () or Rhode (), was the goddess and personification of the island of Rhodes and a wife of the sun god Helios.
Parentage
Various parents were given for Rhodos. Pindar makes her a daughter of Aphrodite with no ...
, and the cities were named for their three sons. The ''rhoda'' is a pink hibiscus
''Hibiscus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. The genus is quite large, comprising several hundred species that are native to warm temperate, subtropical and tropical regions throughout the world. Member species ...
, native to the island. Diodorus Siculus added that Actis, one of the sons of Helios and Rhode, travelled to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. He built the city of Heliopolis and taught the Egyptians astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
.
In the second half of the 8th century BC, the sanctuary of Athena received votive gifts that are markers for cultural contacts: small ivories from the Near East and bronze objects from Syria. At Kameiros
Camirus or Kamiros ( grc, Κάμιρος; ) or Cameirus or Kameiros (Κάμειρος) was a city of ancient Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Its site is on the northwest coast of the island, west of the modern village of Kalavarda.
History ...
on the northwest coast, a former Bronze Age site, where the temple was founded in the 8th century BC, there is another notable contemporaneous sequence of carved ivory figurines. The cemeteries of Kameiros and Ialyssos yielded several exquisite exemplars of the Orientalizing Rhodian jewelry, dated in the 7th and early 6th centuries BC.
Classical Era
 The
The Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
invaded and overran the island, but they were in turn defeated by forces from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in 478 BC. The Rhodian cities joined the Athenian League
The Athenian League was an English amateur football league for clubs in and around London. The league was originally to be called the Corinthian League,Athenian Football League minutes 1912-1921 (National Football Museum, Preston). but this nam ...
. When the Peloponnesian War broke out in 431 BC, Rhodes remained largely neutral, although it remained a member of the League. The war lasted until 404 BC, but by this time Rhodes had withdrawn entirely from the conflict and decided to go her own way.
In 408 BC, the cities united to form one territory. They built the city of Rhodes, a new capital on the northern end of the island. Its regular plan was, according to Strabo, superintended by the Athenian architect Hippodamus
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; 498 – 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to b ...
.
In 357 BC, the island was conquered by the king Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by ...
of Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined ...
; then it fell again to the Persians in 340 BC. Their rule was also short.
Hellenistic and Roman periods
Rhodes then became a part of the growing empire ofAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 332 BC, after he defeated the Persians.
 Following the death of Alexander, his generals (
Following the death of Alexander, his generals (Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
) vied for control of the kingdom. Three — Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, Seleucus, and Antigonus — succeeded in dividing the kingdom among themselves. Rhodes formed strong commercial and cultural ties with the Ptolemies in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, and together formed the Rhodo-Egyptian alliance that controlled trade throughout the Aegean in the 3rd century BC.
The city developed into a maritime, commercial and cultural center; its coins circulated nearly everywhere in the Mediterranean. Its famous schools of philosophy, science, literature and rhetoric shared masters with Alexandria: the Athenian rhetorician Aeschines
Aeschines (; Greek: , ''Aischínēs''; 389314 BC) was a Greek statesman and one of the ten Attic orators.
Biography
Although it is known he was born in Athens, the records regarding his parentage and early life are conflicting; but it seems ...
, who formed a school at Rhodes; Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and t ...
, who wrote about Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He ...
and Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason an ...
in the ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason ...
''; the observations and works of the astronomers Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; el, Ἵππαρχος, ''Hipparkhos''; BC) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equi ...
and Geminus
Geminus of Rhodes ( el, Γεμῖνος ὁ Ῥόδιος), was a Greek astronomer and mathematician, who flourished in the 1st century BC. An astronomy work of his, the ''Introduction to the Phenomena'', still survives; it was intended as an int ...
; and the rhetorician Dionysius Thrax
Dionysius Thrax ( grc-gre, Διονύσιος ὁ Θρᾷξ ''Dionýsios ho Thrâix'', 170–90 BC) was a Greek grammarian and a pupil of Aristarchus of Samothrace. He was long considered to be the author of the earliest grammatical text on the G ...
. Its school of sculptors developed, under Pergamese influence, a rich, dramatic style that can be characterized as "Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
Baroque". Agesander of Rhodes
Agesander (also ''Agesandros'', ''Hagesander'', ''Hagesandros'', or ''Hagesanderus''; grc, Ἀγήσανδρος or grc, Ἁγήσανδρος) was one, or more likely, several Greek sculptors from the island of Rhodes, working in the first cent ...
, with two other Rhodian sculptors, carved the famous ''Laocoön group
Laocoön (; grc, , Laokóōn, , gen.: ), is a figure in Greek and Roman mythology and the Epic Cycle. Laocoon was a Trojan priest. He and his two young sons were attacked by giant serpents, sent by the gods. The story of Laocoön has been the s ...
'', now in the Vatican Museums
The Vatican Museums ( it, Musei Vaticani; la, Musea Vaticana) are the public museums of the Vatican City. They display works from the immense collection amassed by the Catholic Church and the papacy throughout the centuries, including several of ...
, and the large sculptures rediscovered at Sperlonga in the villa of Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
, probably in the early Imperial period.
In 305 BC, Antigonus directed his son, Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
, to besiege Rhodes in an attempt to break its alliance with Egypt. Demetrius created huge siege engines
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while other ...
, including a battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried b ...
and a siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
called Helepolis
Helepolis ( el, ἑλέπολις, meaning: "Taker of Cities") is the Greek name for a movable siege tower.
The most famous was that invented by Polyidus of Thessaly, and improved by Demetrius I of Macedon and Epimachus of Athens, for the S ...
that weighed . Despite this engagement, in 304 BC after only one year, he relented and signed a peace agreement, leaving behind a huge store of military equipment. The Rhodians sold the equipment and used the money to erect a statue of their sun god, Helios, the statue since called the Colossus of Rhodes. The Rhodians celebrated in honour of Helios a grand festival, the Halieia
The Halieia ( grc, Ἁλίεια, ) or Halia was one of the principal festivals celebrated on the island of Rhodes in honour of their patron god Helios, the Sun.Smith, s. vHalia/ref> It was held every year in summer, with gymnic and musical conte ...
.
Throughout the 3rd century BC, Rhodes attempted to secure her independence and her commerce, most especially her virtual control over the grain trade in the eastern Mediterranean. Both of these goals were dependent upon no one of the three great Hellenistic states achieving dominance, and consequently the Rhodians pursued a policy of maintaining a balance of power among the Antigonids, Seleucids and Ptolemies, even if that meant going to war with her traditional ally, Egypt. To this end they employed as leverage their economy and their excellent navy, which was manned by proverbially the finest sailors in the Mediterranean world: "If we have ten Rhodians, we have ten ships."
The Rhodians also established their dominance on the shores of Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined ...
across from their island, which became known as the "Rhodian Peraia
The Rhodian Peraea or Peraia ( grc, ἡ τῶν Ῥοδίων περαία, 3=''peraia'' of the Rhodians) was the name for the southern coast of the region of Caria in western Asia Minor during the 5th–1st centuries BC, when the area was control ...
". It extended roughly from the modern city of Muğla
Muğla () is a city in southwestern Turkey. The city is the center of the District of Menteşe and Muğla Province, which stretches along Turkey's Aegean coast. Muğla's center is situated inland at an altitude of 660 m and lies at a dista ...
(ancient ''Mobolla'') in the north and Kaunos
Kaunos (Carian: ''Kbid'';. Translator Chris Markham.
Lycian: ''Khbide''; Ancient Greek: ; la, Caunus) was a city of ancient Caria and in Anatolia, a few kilometres west of the modern town of Dalyan, Muğla Province, Turkey.
The Calbys ...
bordering Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
in the south, near the present-day Dalyan, Turkey.
Rhodes successfully carried on this policy through the course of the third century BC, an impressive achievement for what was essentially a democratic state. By the end of that period, however, the balance of power was crumbling, as declining Ptolemaic power made Egypt an attractive target for Seleucid ambitions. In 203/2 BC the young and dynamic kings of Antigonid Macedon and Seleucid Asia, Philip V and Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
, agreed to accept—at least temporarily—their respective military ambitions: Philip's campaign in the Aegean and western Anatolia and Antiochus' plan for Egypt. Heading a coalition of small states, the Rhodians checked Philip's navy, but not his superior army. Without a third power to which to turn, the Rhodians (along with ambassadors from Pergamum, Egypt, and Athens) appealed in 201 BC to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
.

 Despite being exhausted by the Second Punic War against Hannibal (218–201 BC) the Romans agreed to intervene, still angry over the Macedonian alliance with Carthage that had led to the
Despite being exhausted by the Second Punic War against Hannibal (218–201 BC) the Romans agreed to intervene, still angry over the Macedonian alliance with Carthage that had led to the First Macedonian War
The First Macedonian War (214–205 BC) was fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) against Carthage. The ...
from 214–205 BC. The Senate saw the appeal from Rhodes and her allies as the opportunity to pressure Philip. The result was the Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Min ...
(200–196 BC), which Rome won and greatly reduced Macedon's power, prestige, and territory. Rhodian independence was preserved. Rhodian influence in the Aegean was cemented through the organization of the Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name ...
into the Second Nesiotic League under Rhodian leadership.
The Romans withdrew from Greece after the end of the conflict, but the resulting power vacuum quickly drew in Antiochus III and subsequently the Romans. The Roman–Seleucid War
The Seleucid War (192–188 BC), also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the A ...
lasted from 192–188 BC with Rome, Rhodes, Pergamon, and other Roman-allied Greek states defeated the Seleucids and their allies, the last Mediterranean power that might even vaguely threaten Roman dominance. Having provided Rome with valuable naval help in her first foray into Asia, the Rhodians were rewarded with territory and enhanced status by the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae ...
(188 BC). The Romans once again evacuated the east – the Senate preferred clients to provinces – but it was clear that Rome now ruled the Mediterranean and Rhodian autonomy was ultimately dependent upon good relations with them.
Those good graces soon evaporated in the wake of the Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman ...
(171–168 BC). In 169 BC, during the war against Perseus, Rhodes sent Agepolis as ambassador to the consul Quintus Marcius Philippus, and then to Rome in the following year, hoping to turn the Senate against the war.
Rhodes remained scrupulously neutral during the war, but in the view of hostile elements in the Senate she had been a bit too friendly with the defeated King Perseus. Some actually proposed declaring war on the island republic, but this was averted. In 164 BC, Rhodes became a "permanent ally" of Rome, which was essentially a reduction to client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
of nominal but meaningless independence. It was said that the Romans ultimately turned against the Rhodians because the islanders were the only people they had encountered who were more arrogant than themselves.
After surrendering its independence, Rhodes became a cultural and educational center for Roman noble families. It was especially noted for its teachers of rhetoric, such as Hermagoras and the unknown author of ''Rhetorica ad Herennium
The ''Rhetorica ad Herennium'' (''Rhetoric for Herennius''), formerly attributed to Cicero or Cornificius, but in fact of unknown authorship, sometimes ascribed to an unnamed doctor, is the oldest surviving Latin book on rhetoric, dating from the ...
''. At first, the state was an important ally of Rome and enjoyed numerous privileges, but these were later lost in various machinations of Roman politics. Cassius eventually invaded the island and sacked the city. In the early Imperial period Rhodes became a favorite place for political exiles.
In the 1st century AD, the Emperor Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
spent a brief term of exile on Rhodes. By tradition, Paul the Apostle evangelized and helped establish an early Christian church on the island during the first century.
In ancient times there was a Roman saying: " Hic Rhodus, hic salta!"—"Here is Rhodes, jump here!" (as translated from Ancient Greek "Αὐτοῦ γὰρ καὶ Ῥόδος καὶ πήδημα"), an admonition to prove one's idle boasts by deed, rather than boastful talk. It comes from an Aesop's fable called " The Boastful Athlete" and was cited by Hegel, Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
, and Kierkegaard.
Byzantine period
In 395 with the division of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
, the long Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
period began for Rhodes. In Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, the island was the capital of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of the Islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
, headed by a ''praeses
''Praeses'' (Latin ''praesides'') is a Latin word meaning "placed before" or "at the head". In antiquity, notably under the Roman Dominate, it was used to refer to Roman governors; it continues to see some use for various modern positions.
...
'' (''hegemon
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over other city-states. ...
'' in Greek), and encompassing most of the Aegean islands, with twenty cities. Correspondingly, the island was also the metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big ci ...
of the ecclesiastical province of Cyclades, with eleven suffragan sees.
Beginning from ca. 600 AD, its influence in maritime issues was manifested in the collection of maritime laws known as " Rhodian Sea Law" (''Nomos Rhodion Nautikos''), accepted throughout the Mediterranean and in use throughout Byzantine times (and influencing the development of admiralty law up to the present). In 622/3, during the climactic Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, Rhodes was captured by the Sasanian navy
The Sasanian navy was the naval force of the Sasanian Empire active since its establishment. It operated in the Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, the Red Sea, and briefly in the Mediterranean Sea.
Sources
Not much is known about the Sasanian navy ...
.
Rhodes was occupied by the Islamic Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
forces of Caliph Muawiyah I in 654, who carried off the remains of the Colossus of Rhodes. The island was again captured by the Arabs in 673 as part of their first attack on Constantinople. When their fleet was destroyed by Greek fire before Constantinople and by storms on its return trip, however, the Umayyads evacuated their troops in 679/80 as part of the Byzantine–Umayyad peace treaty. In 715 the Byzantine fleet dispatched against the Arabs launched a rebellion at Rhodes, which led to the installation of Theodosios III
Theodosius III ( el, Θεοδόσιος, Theodósios) was Byzantine emperor from May 715 to 25 March 717. Before rising to power and seizing the throne of the Byzantine Empire, he was a tax collector in Adramyttium. In 715, the Byzantine n ...
on the Byzantine throne.
From the early 8th to the 12th centuries, Rhodes belonged to the Cibyrrhaeot Theme
The Cibyrrhaeot Theme, more properly the Theme of the Cibyrrhaeots ( gr, θέμα Κιβυρραιωτῶν, thema Kibyrrhaiōtōn), was a Byzantine theme encompassing the southern coast of Asia Minor from the early 8th to the late 12th centuries ...
of the Byzantine Empire, and was a centre for shipbuilding and commerce. In 1090, it was occupied by the forces of the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, after the long period of chaos resulting from the Battle of Manzikert. Rhodes was recaptured by the Emperor Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
during the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic r ...
.
Angeloi
The House of Angelos (; gr, Ἄγγελος), feminine form Angelina (), plural Angeloi (), was a Byzantine Greek noble lineage which rose to prominence through the marriage of its founder, Constantine Angelos, with Theodora Komnene, the young ...
emperors (1185–1204), in the first half of the 13th century, Rhodes became the centre of an independent domain under Leo Gabalas
Leo Gabalas ( el, ) was a Byzantine Greek magnate and independent ruler of a domain, centered on the island of Rhodes and including nearby Aegean islands, which was established in the aftermath of the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire by the ...
and his brother John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, until it was occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
by the Genoese in 1248–1250. The Genoese were evicted by the Empire of Nicaea, after which the island became a regular province of the Nicaean state (and after 1261 of the restored Byzantine Empire). In 1305, the island was given as a fief to Andrea Morisco, a Genoese adventurer who had entered Byzantine service.
Crusader and Ottoman rule

 In 1306–1310, the Byzantine era of the island's history came to an end when the island was occupied by the
In 1306–1310, the Byzantine era of the island's history came to an end when the island was occupied by the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
. Under the rule of the newly named "Knights of Rhodes", the city was rebuilt into a model of the European medieval ideal. Many of the city's famous monuments, including the Palace of the Grand Master, were built during this period.
The strong walls which the knights had built withstood the attacks of the Sultan of Egypt in 1444, and a siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
by the Ottomans under Mehmed II in 1480. Eventually, however, Rhodes fell
A fell (from Old Norse ''fell'', ''fjall'', "mountain"Falk and Torp (2006:161).) is a high and barren landscape feature, such as a mountain or moor-covered hill. The term is most often employed in Fennoscandia, Iceland, the Isle of Man, pa ...
to the large army of Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
in December 1522. The Sultan deployed 400 ships delivering 100,000 men to the island (200,000 in other sources). Against this force the Knights, under Grand Master Philippe Villiers de L'Isle-Adam
Fra' Philippe de Villiers de L'Isle-Adam (1464 – 21 August 1534) was a prominent member of the Knights Hospitaller at Rhodes and later Malta. Having risen to the position of Prior of the ''Langue of Auvergne'', he was elected 44th Grand ...
, had about 7,000 men-at-arms and their fortifications. The siege lasted six months, at the end of which the surviving defeated Hospitallers were allowed to withdraw to the Kingdom of Sicily. Despite the defeat, both Christians and Muslims seem to have regarded the conduct of Villiers de L'Isle-Adam as extremely valiant, and the Grand Master was proclaimed a Defender of the Faith by Pope Adrian VI (see Knights of Cyprus and Rhodes). The knights would later move their base of operations to Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
.
Rhodes was thereafter a possession of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(see Sanjak of Rhodes
The Sanjak of Rodos or Rhodes (Ottoman Turkish: ''Sancak-i/Liva-i Rodos''; el, λιβάς/σαντζάκι Ρόδου) was a second-level Ottoman province (''sanjak'' or '' liva'') encompassing the Dodecanese or Southern Sporades islands, with R ...
) for nearly four centuries.
Modern history

 In the 19th century the island was populated by ethnic groups from the surrounding nations, including Jews, whose presence goes back 2,300 years. Under Ottoman rule, they generally did fairly well, but discrimination and bigotry occasionally arose. In February 1840, the Jews of Rhodes were falsely accused by the Greek Orthodox community of ritually murdering a Christian boy. This became known as the Rhodes blood libel.
Austria opened a post-office at ''RHODUS'' (Venetian name) before 1864, as witnessed by stamps with
In the 19th century the island was populated by ethnic groups from the surrounding nations, including Jews, whose presence goes back 2,300 years. Under Ottoman rule, they generally did fairly well, but discrimination and bigotry occasionally arose. In February 1840, the Jews of Rhodes were falsely accused by the Greek Orthodox community of ritually murdering a Christian boy. This became known as the Rhodes blood libel.
Austria opened a post-office at ''RHODUS'' (Venetian name) before 1864, as witnessed by stamps with Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his ...
's head.
Italian occupation
In 1912, Italy seized Rhodes from the Ottomans during theItalo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War ( tr, Trablusgarp Savaşı, "Tripolitanian War", it, Guerra di Libia, "War of Libya") was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911, to 18 October 1912. As a result o ...
. The island's population was spared the "exchange of the minorities" between Greece and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. Rhodes and the rest of the Dodecanese Islands were assigned to Italy in the Treaty of Ouchy. Turkey ceded them officially to Italy with the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne. It then became the core of their possession of the ''Isole Italiane dell'Egeo
The Italian Islands of the Aegean ( it, Isole italiane dell'Egeo; el, Ἰταλικαὶ Νῆσοι Αἰγαίου Πελάγους) were an archipelago of fourteen islands (the Dodecanese, except Kastellorizo) in the southeastern Aegean Sea, ...
''. The island was greatly improved (mainly the capital, called "Rodi" in Italian) under the more than thirty years of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
's rule.
Thousands of Italian colonists settled in the island, mainly in the capital "Rodi", while some of them founded farm villages (like "Peveragno Rodio" (1929), "Campochiaro" (1935), "San Marco" (1936) and "Savona" (1938): in the Dodecanese islands was officially proposed the creation in 1940 of the " Provincia italiana di Rodi". In the late 1930s, Mussolini embarked on a program of Italianization, attempting to make the island of Rhodes a transportation hub that would facilitate the spread of Italian culture in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
. The Fascist program coincided with improvements to infrastructure.
Following the Italian Armistice of 8 September 1943, the British attempted to get the Italian garrison on Rhodes to change sides. This was anticipated by the German Army, which succeeded in occupying the island with the Battle of Rhodes. In great measure, the German occupation caused the British failure in the subsequent Dodecanese Campaign.
After September 1943, the Jews, who had been protected by the Italian government, were persecuted by the Nazi Germans and sent to concentration camps. However, the Turkish Consul Selahattin Ülkümen succeeded, at considerable risk to himself and his family, in saving 42 Jewish families, about 200 persons in total, who had Turkish citizenship or were members of Turkish citizens' families.
 On 8 May 1945, the Germans under Otto Wagener surrendered Rhodes as well as the Dodecanese as a whole to the British, who soon after then occupied the islands as a military protectorate.
At the Paris Peace Treaties, Rhodes, together with the other islands of the Dodecanese, was united with
On 8 May 1945, the Germans under Otto Wagener surrendered Rhodes as well as the Dodecanese as a whole to the British, who soon after then occupied the islands as a military protectorate.
At the Paris Peace Treaties, Rhodes, together with the other islands of the Dodecanese, was united with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
in February 1947. 6,000 Italian colonists were forced to abandon the island and returned to Italy.
Contemporary period
In 1949, Rhodes was the venue for negotiations betweenIsrael
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, and Syria, concluding with the 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,
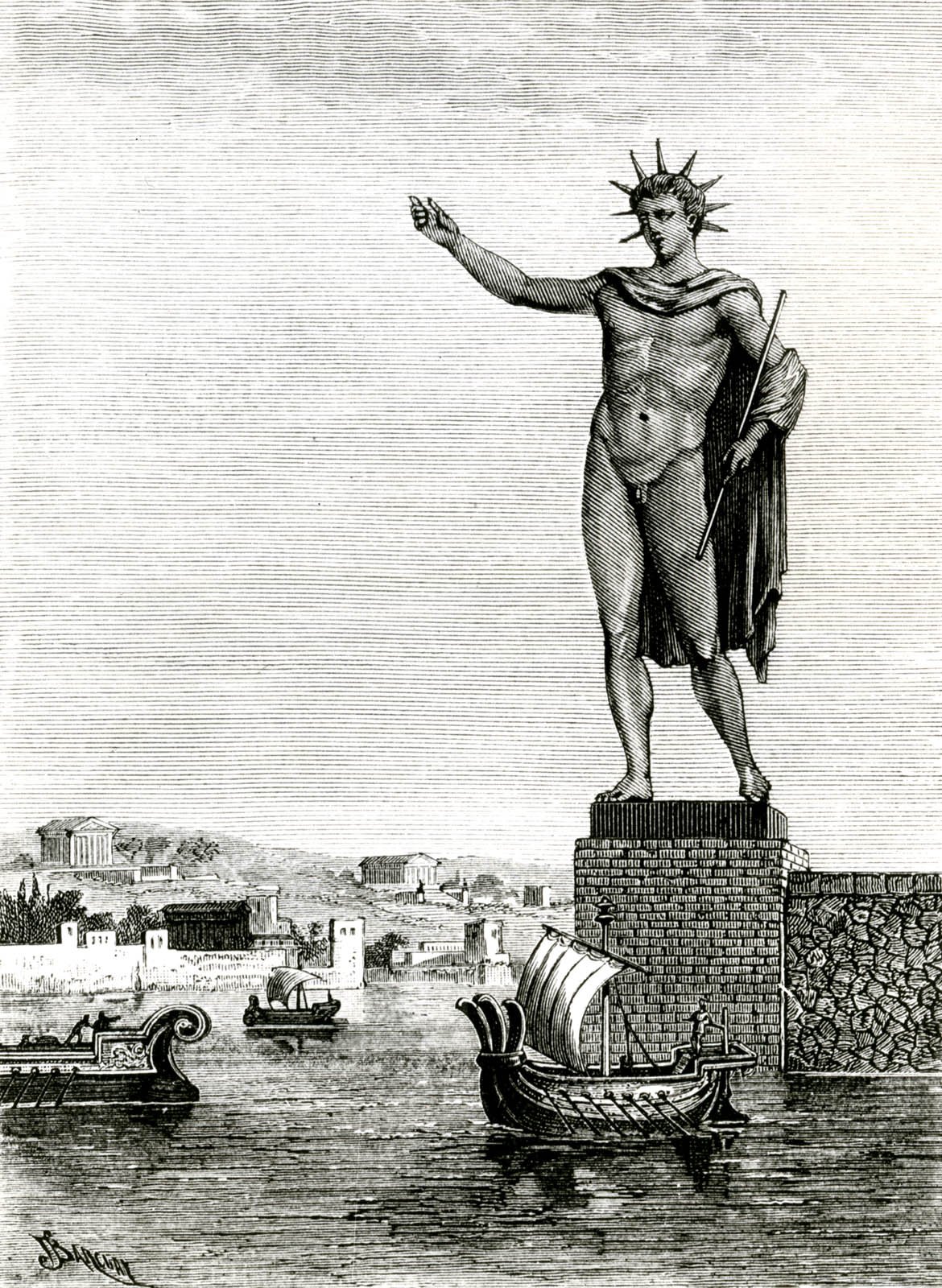
 The Colossus of Rhodes was considered to be one of the
The Colossus of Rhodes was considered to be one of the



 The present municipality Rhodes was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 10 former municipalities, that became municipal units (constituent communities in parentheses):
*
The present municipality Rhodes was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 10 former municipalities, that became municipal units (constituent communities in parentheses):
*
 The economy is tourist-oriented, and the most developed sector is service. Tourism has elevated Rhodes economically, compared to the rest of Greece.
Small industries process imported raw materials for local retail, though other industry includes agricultural goods production, stockbreeding, fishery and winery.
The economy is tourist-oriented, and the most developed sector is service. Tourism has elevated Rhodes economically, compared to the rest of Greece.
Small industries process imported raw materials for local retail, though other industry includes agricultural goods production, stockbreeding, fishery and winery.
 Rhodes has two airports, but only one is public. Diagoras Airport, southwest of Rhodes City, is the fourth biggest by passenger volume in Greece, and the main entrance/exit point to the island for both locals and tourists. The island is well connected with other major Greek cities and islands as well as with major European capitals and cities via charter flights. Until 1977, Rhodes Maritsa Airport, built in 1938, was a public airport; it is now used by the
Rhodes has two airports, but only one is public. Diagoras Airport, southwest of Rhodes City, is the fourth biggest by passenger volume in Greece, and the main entrance/exit point to the island for both locals and tourists. The island is well connected with other major Greek cities and islands as well as with major European capitals and cities via charter flights. Until 1977, Rhodes Maritsa Airport, built in 1938, was a public airport; it is now used by the

 Rhodes has five ports, three of them in Rhodes City, one in the west coast near Kamiros and one in east coast near
Rhodes has five ports, three of them in Rhodes City, one in the west coast near Kamiros and one in east coast near
 *Football: AS Rodos and Diagoras F.C. are the island's biggest teams and rivals. The latter competed in the 2018–19 season at the national level third tier (
*Football: AS Rodos and Diagoras F.C. are the island's biggest teams and rivals. The latter competed in the 2018–19 season at the national level third tier (International Island Games Association website
. Retrieved 27 June 2018. Since 2019 is suspended from competition.

 Rhodian tradition in cuisine is rich. Koriantolino and Souma (colorless alcoholic beverage produced from grape distillation) are the main alcoholic drinks of Rhodes. Local foods include:
*Escharitis, type of bread
* Pitaroudia
*Milla and Tsiriggia, meat fat
* Pougia pie
*Lakani, goat meat with chickpeas
*Lópia (beans) with goat
*Matsi, hand made pasta used to make Koulouría, a traditional recipe
*Synoro, traditional cheese
* Tahinopita
*Zvigoi, type of
Rhodian tradition in cuisine is rich. Koriantolino and Souma (colorless alcoholic beverage produced from grape distillation) are the main alcoholic drinks of Rhodes. Local foods include:
*Escharitis, type of bread
* Pitaroudia
*Milla and Tsiriggia, meat fat
* Pougia pie
*Lakani, goat meat with chickpeas
*Lópia (beans) with goat
*Matsi, hand made pasta used to make Koulouría, a traditional recipe
*Synoro, traditional cheese
* Tahinopita
*Zvigoi, type of
 * Agesander (1st century BC), sculptor
* Apollonius Molon (fl. 70s BC), Greek
* Agesander (1st century BC), sculptor
* Apollonius Molon (fl. 70s BC), Greek


Official website
{{Authority control Rhodes, Dodecanese Dorian colonies Greek city-states Hellenic Navy bases Islands of the South Aegean Landforms of Rhodes (regional unit) Mediterranean islands Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Municipalities of the South Aegean Phoenician colonies in Greece Populated places in Rhodes
 The Colossus of Rhodes was considered to be one of the
The Colossus of Rhodes was considered to be one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2 ...
. This giant bronze statue was documented as once standing at the harbour. It was completed in 280 BC and destroyed in an earthquake in 224 BC. No trace of the statue remains today.
Historical sites on the island of Rhodes include the Acropolis of Lindos, the Acropolis of Rhodes The Acropolis of Rhodes ( ell, Ακρόπολη της Ρόδου) is the acropolis, or upper town, of ancient Rhodes dating from the 5th century BC and located 3 kilometers SW from the centre of the modern city. Situated on Monte Smith overlooking ...
with the Temple of Pythian Apollo and an ancient theatre and stadium, ancient Ialysos
Ialysos ( el, Ιαλυσός, before 1976: Τριάντα ''Trianta'') is a town and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which ...
, ancient Kamiros, the Governor's Palace, Rhodes Old Town (walled medieval city), the Palace of the Grand Masters, Kahal Shalom Synagogue
The Kahal Shalom Synagogue ( he, בית הכנסת קהל קדוש שלום, or ''Beit HaKnesset Kahal Kadosh Shalom'' meaning ''Synagogue of the Holy Congregation of Peace'', el, Συναγωγή ''Καχάλ Σαλόμ'', italic=unset) is a Sep ...
in the Jewish Quarter, the Archaeological Museum, the ruins of the castle of Monolithos, the castle of Kritinia, St. Catherine Hospice
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an ...
and Rhodes Footbridge
__NOTOC__
The Rhodes Footbridge is an ancient Greek arch bridge in the city of Rhodes, Greece. Dating to the 4th century BC or early Hellenistic period, the modest structure represents the oldest known Greek bridge with a voussoir arch.
Constr ...
.
Religion

Christianity
The predominant religion isGreek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
; the island is the seat of the Metropolis of Rhodes.
There is a Latin Catholic
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
minority on the island of 2,000, many of whom are descendants of Italians who remained after the end of the Italian occupation, pastorally served by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rhodes
The Archdiocese of Rhodes ( la, Archidioecesis Rhodiensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Greece. The archdiocese is directly exempt to the Holy See and not part of an ecclesiastical province. ...
.
Islam
Rhodes has a Turkish Muslim minority, which includesGreek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity) dates to the period of Ottoman rule in the southern Balkans. They consist primarily of th ...
whose ancestors from Crete and the Dodecanese converted to Islam in the Ottoman period. Although a remnant from Ottoman Turkish times they were not required in the population exchange of 1923–24 to resettle in Turkey like the Turkish, Greek, and other Muslim communities living mainly in Macedonia and other parts of Northern Greece
Northern Greece ( el, Βόρεια Ελλάδα, Voreia Ellada) is used to refer to the northern parts of Greece, and can have various definitions.
Administrative regions of Greece
Administrative term
The term "Northern Greece" is widely used ...
because unlike these areas the Dodecanese Islands were under Italian administration at the time. They are organized around the Turkish Association of Rhodes ( tr, Rodos Türk Derneği), which gives the figure 3,500 for the population they bring together and represent for the island. The number of the Turks in Rhodes could be as many as 4,000.
Judaism
The Jewish community of Rhodes goes back 2,300 years. ''Kahal Shalom Synagogue
The Kahal Shalom Synagogue ( he, בית הכנסת קהל קדוש שלום, or ''Beit HaKnesset Kahal Kadosh Shalom'' meaning ''Synagogue of the Holy Congregation of Peace'', el, Συναγωγή ''Καχάλ Σαλόμ'', italic=unset) is a Sep ...
'', established in 1557, during the Ottoman era, is the oldest synagogue in Greece and still stands in the Jewish quarter ('' La Juderia'') of the old town of Rhodes. At its peak in the 1920s, the Jewish community was one-third of the town's total population. In the 1940s, there were about 2000 Jews of various ethnic backgrounds. The Nazis deported and killed most of the community during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
. ''Kahal Shalom'' has been renovated with the help of foreign donors but few Jews live year-round in Rhodes today, so services are not held on a regular basis.
The Jewish Museum of Rhodes The Jewish Museum of Rhodes ( el, Εβραϊκό Μουσείο της Ρόδου) is a museum located in the Old Town of the island of Rhodes, eastern Greece. It was established by Aron Hasson of the Rhodes Jewish Historical Foundation in 1997 to ...
was established in 1997 to preserve the Jewish history and culture of the Jews of Rhodes. It is adjacent to the Kahal Shalom Synagogue
The Kahal Shalom Synagogue ( he, בית הכנסת קהל קדוש שלום, or ''Beit HaKnesset Kahal Kadosh Shalom'' meaning ''Synagogue of the Holy Congregation of Peace'', el, Συναγωγή ''Καχάλ Σαλόμ'', italic=unset) is a Sep ...
.
Government

Afantou
Afantou ( el, Αφάντου) is a village and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the ...
(Afantou, Archipoli)
* Archangelos (Archangelos, Malonas, Masari)
*Attavyros
Attavyros ( el, Αττάβυρος) or Atavyros (Ατάβυρος) is the highest mountain on the island of Rhodes in the Dodecanese in Greece. It rises to a height of 1,215 m. It lies to the south of the village of Embonas.
In Greek mythology ...
(Embonas, Kritinia, Monolithos, Siana, Agios Isidoros)
*Ialysos
Ialysos ( el, Ιαλυσός, before 1976: Τριάντα ''Trianta'') is a town and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which ...
*Kallithea
Kallithea (Greek: Καλλιθέα, meaning "beautiful view") is a district of Athens and a municipality in south Athens regional unit. It is the eighth largest municipality in Greece (96,118 inhabitants, 2021 census) and the fourth biggest i ...
(Kalythies, Koskinou, Psinthos)
*Kameiros
Camirus or Kamiros ( grc, Κάμιρος; ) or Cameirus or Kameiros (Κάμειρος) was a city of ancient Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Its site is on the northwest coast of the island, west of the modern village of Kalavarda.
History ...
(Soroni, Apollona, Dimylia, Kalavarda
Kalavarda is a small town in the island of Rhodes, Greece with a population of about 502. It's about 28 kilometers from the island's capital, Rhodes, and about 52 Kilometers from the city Lindos
Lindos (; grc-gre, Λίνδος) is an archaeolo ...
, Platania, Salakos, Fanes)
* Lindos ( Lindos, Kalathos, Laerma, Lardos, Pylona)
*Petaloudes
Petaloudes ( el, Πεταλούδες) is a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. Its population was 1 ...
(Kremasti, Pastida, Maritsa, Paradeisi, Theologos, Damatria)
*Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
*South Rhodes
South Rhodes ( el, Νότια Ρόδος - ''Nótia Ródos'') is a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδο� ...
(Gennadi, Apolakkia, Arnitha, Asklipieio, Vati, Istrios, Kattavia, Lachania, Mesanagros, Profilia)
The municipality has an area of 1400.681 km2. It covers the island of Rhodes and a few uninhabited offshore islets. Rhodes city was the capital of the former Dodecanese Prefecture. Rhodes is the most populated island of the South Aegean
The South Aegean ( el, Περιφέρεια Νοτίου Αιγαίου, translit=Periféria Notíou Eyéou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It consists of the Cyclades and Dodecanese island groups in the central and ...
Region.
Towns and villages
Rhodes has 43 towns and villages:Economy
 The economy is tourist-oriented, and the most developed sector is service. Tourism has elevated Rhodes economically, compared to the rest of Greece.
Small industries process imported raw materials for local retail, though other industry includes agricultural goods production, stockbreeding, fishery and winery.
The economy is tourist-oriented, and the most developed sector is service. Tourism has elevated Rhodes economically, compared to the rest of Greece.
Small industries process imported raw materials for local retail, though other industry includes agricultural goods production, stockbreeding, fishery and winery.
Transportation
Air
Hellenic Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 8 November
, equipment =
, equipment_label ...
and occasionally for car races.
There are also two inoperative airfields. Kalathos Airfield, north of Lindos, and Kattavia Airstrip, to the south of the island, were built by the Italians during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. Neither remain operational.
Two pilot schools offer aviation services (small plane rental and island hopping).
Sea

 Rhodes has five ports, three of them in Rhodes City, one in the west coast near Kamiros and one in east coast near
Rhodes has five ports, three of them in Rhodes City, one in the west coast near Kamiros and one in east coast near Lardos
Lardos ( gr, Λάρδος) is a Greek village on the Lardos stream, also called Fonias, located at the eastern part of the island of Rhodes, South Aegean region. In 2011 its population was 1,380.
Overview
The village is about 54 km south of the t ...
.
*Central Port: located in the city of Rhodes serves exclusively international traffic consisting of scheduled services to/from Turkey, cruise ships and yachts. Since Summer 2012, the port is also a homeport for Costa Cruises during the summer period.
*Kolona Port: opposite and north of the central port, serves intra-Dodecanese traffic and all sizes yachts.
*Akandia Port: the new port of the island, south and next to the central port, being built since the 1960s, for domestic, cargo and general purpose traffic. Since 2017 summer a passenger terminal is finally in use hosting a cafe and waiting lounges.
*Mandraki Port: the oldest port of the island, in the center of Rhodes city. Many cruise boats begin their daily trips to Symi island or to the southern east coast until Lindos.
*Kamiros Skala Dock: south west of the city near Ancient Kamiros ruins serves mainly the island of Halki
*Lardos Dock: formerly servicing local industries, now under development as an alternative port for times when the central port is inaccessible due to weather conditions. It is situated in a rocky shore near the village of Lardos in south east Rhodes.
Road network
The road network of the island is mostly paved and consists of 3 national roads plus one planned, 40 provincial and numerous local. These are the four major island arteries: * Rhodes-Kamiros Province Avenue: Province road 2 tillKalavarda
Kalavarda is a small town in the island of Rhodes, Greece with a population of about 502. It's about 28 kilometers from the island's capital, Rhodes, and about 52 Kilometers from the city Lindos
Lindos (; grc-gre, Λίνδος) is an archaeolo ...
village and 21 from there till Kamiros with two lane that runs through the west coast north to south and connects Rhodes City with Diagoras Airport and Kamiros.
*Rhodes-Lindos National Avenue ( Greek National Road 95): Four and two lane, runs mainly inland north to south and connects Rhodes City with Lindos. Part from Rhodes Town until Kolympia is now 4 lanes, the rest until Lindos is 2 lanes.
*Rhodes-Kallithea-Faliraki Province Avenue 4: Two lanes, runs through the east coast north to south and connects Rhodes City with Kallithea monument and Faliraki Resort.
*Tsairi-Airport National Avenue ( Greek National Road 100): Four and two lane, runs inland east to west and connects the east coast with the west and the airport.
*Lindos-Katavia Province Road 1: Two lane, begins just before Lindos and though villages and resorts leads to Katavia village, the southernmost of the island, from where a further deviation leads to Prasonissi.
*Rhodes Town Ring Road (Phase 1): Beginning from the new marina and ending to Rhodes-Kallithea province avenue is a four lane expressway.
Future roads:
*Further widening of Rhodes-Lindos National Avenue ( Greek National Road 95) from Kolympia to Lindos. This is to be four lane with a jersey barrier
A Jersey barrier, Jersey wall, or Jersey bump is a modular concrete or plastic barrier employed to separate lanes of traffic. It is designed to minimize vehicle damage in cases of incidental contact while still preventing vehicle crossovers resu ...
in the middle. A tender is expected to take place by end of 2019 so as constructions can begin.
*Ring Road phases 2, 3, and 4 pending; phase 2 will extend the expressway to Greek National Road 95 and then to Rhodes General Hospital where it supposedly will connect to also planned new Rhodes City-Airport expressway. In June 2018 Rhodes municipality stated that plans for the final 700 meters of the ring road leading to Akandia Port are pending approval. Phases 3 and 4 which plan to run the ring road from hospital hill down to Ixia and then through Kritika back to the town will most probably never occur.
*Plans also exist for a new four lane express road connecting Rhodes Town with Diagoras Airport. The road, recognised as National back in 2014, will follow existing Provincial Road 3 routing with a total length of 8.6 km and including 3 main junctions and is intended to relieve congestion on the coastal west avenue. The so-called Leoforos Mesogeion is vastly anticipated and is a top priority for local authorities.
Bus
Bus services are handled by two operators: *RODA: Municipal bus company that serves Rhodes city as well suburban areas (Koskinou, Faliraki, Ialysos, Kremasti, Airport, Pastida, Maritsa, Paradeisi) and the west coast of the island *KTEL: Limited liability private transport company that serve villages and resorts in the east coast of the islandCars and motorbikes
Families in Rhodes often own more than one car, along with a motorbike. Traffic jams are common particularly in the summer months as vehicles more than double while parking spots downtown and around the old town are limited and can't cope with demand. Moreover, the island is served by 450 taxis and some 200 public and private buses adding to the traffic burden.Sports
Gamma Ethniki
The Gamma Ethniki ( el, Γ΄ Εθνική Ερασιτεχνική Κατηγορία, C National Amateur Division) is the third highest football league in Greece.
History
The Gamma Ethniki began in 1965 as an amateur championship, while in 198 ...
) along with GAS Ialysos and both achieved promotion to ( Greek Football League). AS Rodos competed in 1st tier of the local league and ranking 1st achieved promotion and is returning after one year to (Gamma Ethniki
The Gamma Ethniki ( el, Γ΄ Εθνική Ερασιτεχνική Κατηγορία, C National Amateur Division) is the third highest football league in Greece.
History
The Gamma Ethniki began in 1965 as an amateur championship, while in 198 ...
) which from 2019–20 season becomes tier 4. Local football leagues (organized at the prefecture-level) contain three divisions with more than 50 teams. Many stadiums are grass-covered.
*Basketball: Colossus BC sponsors professional basketball and after more than a decade of presence in the top-level Greek Basket League
The Greek Basket League (GBL), often also referred to as the Greek A1 Basketball League, or Greek Basketball Championship (originally called Panhellenic Basketball Championship), and also known as the Stoiximan Basket League for sponsorship reaso ...
was relegated to Greek A2 Basket League. The local league includes a single division with two groups, one for Rhodes and the other for the other islands, with 7 and 5 teams respectively. Three indoor courts exist in Rhodes City, and one each in Ialysos, Kremasti, and Faliraki. Archangelos town will also get an indoor court according to Rhodes municipality planned works and regional government's approved funds.
*Volleyball: Rodion Athlisis managed to escape local obscurity and until 2018–19 season competed at the national level second-tier failing to achieve promotion to the first level in playoffs for three consecutive seasons. This unlucky streak caused team sponsors to withdraw from the men's team and focus solely on developing youth academies.
*Water polo: mostly amateur-based. There is not any single public indoor pool on the island.
*Rugby: introduced in 2007. Teams compete at the national level.
*Tennis: Rhodes Tennis Club (Ροδιακός Όμιλος Αντισφαίρισης) promotes officially tennis since 1949. Club operates on two separate locations, one downtown next to the casino and one next to Kallipateira National Athletic Centre.
*Sailing: Island has competed at the international level
*Cycling: For a long period of time Rhodes had the only velodrome in Greece. For the moment, the island is the seat of the Dodecanissos Local Cycling Committee. Most notable cycling clubs are Rodilios CC, Diagoras GC, Elafos CC Elafos may refer to several places in Greece:
* Elafos, Ioannina, a village in the Dodoni
* Elafos, Larissa, a village in the Agia
* Elafos, Pieria, a village in the Katerini
Katerini ( el, Κατερίνη, ''Kateríni'', ) is a city and munic ...
, Iviskos CC, all based in the city of Rhodes, plus Antaios SC of Kremasti
Kremasti ( el, Κρεμαστή) is a town on the Greek island of Rhodes (', ''Ródhos''). Located on the west coast of the island, Kremasti is 12 kilometers from the capital of Rhodes, on the road to the airport. It has a population of 5,363 ...
and Athlos SC of Paradeisi. In Rhodes, the International Tour of Rhodes, part of UCI Europe Tour
The UCI Continental Circuits are a series of road bicycle racing competitions which were introduced in 2005 by the Union Cycliste Internationale (UCI) to expand cycling around the world. The five circuits (representing the continents of Africa, the ...
Cycling Calendar, is annually organized.
*Rhodes competed in the bi-annual Island Games
The Island Games (currently known as the NatWest International Island Games for sponsorship reasons) are biennial international multi-sports events organised by the International Island Games Association (IIGA). Competitor teams each represent d ...
, which it hosted in 2007.. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
Cuisine


 Rhodian tradition in cuisine is rich. Koriantolino and Souma (colorless alcoholic beverage produced from grape distillation) are the main alcoholic drinks of Rhodes. Local foods include:
*Escharitis, type of bread
* Pitaroudia
*Milla and Tsiriggia, meat fat
* Pougia pie
*Lakani, goat meat with chickpeas
*Lópia (beans) with goat
*Matsi, hand made pasta used to make Koulouría, a traditional recipe
*Synoro, traditional cheese
* Tahinopita
*Zvigoi, type of
Rhodian tradition in cuisine is rich. Koriantolino and Souma (colorless alcoholic beverage produced from grape distillation) are the main alcoholic drinks of Rhodes. Local foods include:
*Escharitis, type of bread
* Pitaroudia
*Milla and Tsiriggia, meat fat
* Pougia pie
*Lakani, goat meat with chickpeas
*Lópia (beans) with goat
*Matsi, hand made pasta used to make Koulouría, a traditional recipe
*Synoro, traditional cheese
* Tahinopita
*Zvigoi, type of loukoumades
Lokma, also known by their Greek name, loukoumades, are pastries made of leavened and deep fried dough balls, soaked in syrup or honey, sometimes coated with cinnamon or other ingredients. The dish was described as early as the 13th century by a ...
* Melekouni
*Fanouropita
Fanouropita is a sweet pie recipe from Greek cuisine and is traditionally a Lenten cake, also called "The lost and found cake." It is traditionally served in St. Fanourios Memorial Day on August 27, given to Greek Orthodox believers as a bless ...
*Takakia (Mantinades)
*Katimeria (tiganites, pancakes)
* Amygdalota, white almond cookies
*Moschopougia
Notable people
 * Agesander (1st century BC), sculptor
* Apollonius Molon (fl. 70s BC), Greek
* Agesander (1st century BC), sculptor
* Apollonius Molon (fl. 70s BC), Greek rhetorician
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
had a celebrated school on the island; his students included Marcus Tullius Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
* Apollonius (3rd century BC), epic poet
*Chares of Lindos
Chares of Lindos (; grc-gre, Χάρης ὁ Λίνδιος, ''gen.:'' Χάρητος; before 305 BC-c. 280 BC) was a Greek sculptor born on the island of Rhodes. He was a pupil of Lysippos. Chares constructed the Colossus of Rhodes in 282 ...
(3rd century BC), sculptor
* Cleobulus of Lindos (6th century BC), philosopher and one of the Seven Sages of Ancient Greece
* Diagoras (5th century BC), boxer, multiple Olympic winner
*Dinocrates
Dinocrates of Rhodes (also Deinocrates, Dimocrates, Cheirocrates and Stasicrates; grc-gre, Δεινοκράτης ὁ Ῥόδιος, fl. last quarter of the 4th century BC) was a Greek architect and technical adviser for Alexander the Great. He i ...
(4th century BC), architect and technical adviser for Alexander the Great
* Hecato (c. 100 BC), Stoic philosopher
*Hieronymus
Hieronymus, in English pronounced or , is the Latin form of the Ancient Greek name (Hierṓnymos), meaning "with a sacred name". It corresponds to the English given name Jerome.
Variants
* Albanian: Jeronimi
* Arabic: جيروم (Jerome)
* Basq ...
, (c.290-c.230 BC), Peripatetic philosopher
*Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; el, Ἵππαρχος, ''Hipparkhos''; BC) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equi ...
, (2nd century BC), astronomer, mathematician, geographer, founder of trigonometry
*Joannicius II of Constantinople
Joannicius II of Lindos ( el, ) (? – 1659 or 1660) was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople four times from 1646 to 1656.
Life
Joannicius was a native of Lindos on the island of Rhodes. He was appointed Metropolitan of Ganos and Chora in 1 ...
, Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople ( Istanbul), New Rome and '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of ...
*Leonidas
Leonidas I (; grc-gre, Λεωνίδας; died 19 September 480 BC) was a List of kings of Sparta#Heraclids, king of the Greek city-state of Sparta, and the 17th of the List of kings of Sparta#Agiad dynasty, Agiad line, a dynasty which claimed d ...
(2nd century BC), athlete
*Memnon
In Greek mythology, Memnon (; Ancient Greek: Μέμνων means 'resolute') was a king of Aethiopia and son of Tithonus and Eos. As a warrior he was considered to be almost Achilles' equal in skill. During the Trojan War, he brought an army t ...
(380–333 BC), commander of mercenary army
*Mentor
Mentorship is the influence, guidance, or direction given by a mentor. A mentor is someone who teaches or gives help and advice to a less experienced and often younger person. In an organizational setting, a mentor influences the personal and p ...
(385–340 BC), mercenary soldier
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
, brother of Memnon
*Panaetius
Panaetius (; grc-gre, Παναίτιος, Panaítios; – ) of Rhodes was an ancient Greek Stoic philosopher. He was a pupil of Diogenes of Babylon and Antipater of Tarsus in Athens, before moving to Rome where he did much to introduce Stoic do ...
(c. 185 – c. 110/109 BC), Stoic philosopher
*Timocreon
Timocreon of Ialysus in Rhodes ( grc-gre, Τιμοκρέων, ''gen''.: Τιμοκρέοντος) was a Greek lyric poet who flourished about 480 BC, at the time of the Persian Wars. His poetry survives only in a very few fragments, and some claim ...
(5th century BC), poet
*Braith Anasta
Braith Anastasakis (born 14 January 1982), better known as Braith Anasta, is an Australian former professional rugby league footballer who played as a and in the 2000s and 2010s. An Australian and Greek international, Anasta played in the NR ...
, rugby league player and NRL premiership winner (ancestral ties to the island through his father, Petros ("Peter") Anastasakis)
*Lawrence Durrell
Lawrence George Durrell (; 27 February 1912 – 7 November 1990) was an expatriate British novelist, poet, dramatist, and travel writer. He was the eldest brother of naturalist and writer Gerald Durrell.
Born in India to British colonial p ...
, writer and poet, author of The Alexandria Quartet
''The Alexandria Quartet'' is a tetralogy of novels by British writer Lawrence Durrell, published between 1957 and 1960. A critical and commercial success, the first three books present three perspectives on a single set of events and characters ...
, resided on Rhodes 1945–1947. In 1953 his travel book about Rhodes – Reflections on a Marine Venus – was published.
*Stergos Felegakis, professional football player
*Reşit Galip, Turkish politician, one of the first ministers of education of the Republic of Turkey
*Nick Galis, basketball player, FIBA Hall of Fame and Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame member (his father was born in a small village called Agios Isidoros, Rhodes, Agios Isidoros)
*Ferruccio Lamborghini (1916–1993), Italian automobile designer, was stationed on the island as an air-force mechanic in WW2
*George Marshall (gunner), George Marshall (1781-1855) author and Master Gunner, United States Navy
*Murat Reis the Elder, Murat Reiz Plaku Albanian Navy Commander
*:el:Παναγιώτης Ρόδιος, Panagiotis Rodios, revolutionary and Hellenic Army officer
*Niki Xanthou, long jumper
*:el:Ιωάννης Ζίγδης, Ioannis Zigdis (1913–1997), politician and economist
Tourism
Rhodes is one of the most attractive tourist destinations in Greece. AfterCrete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
, the island is the most visited destination in Greece, with arrivals standing at 1,785,305 in 2013. In 2014 they stood at 1,931,005, while in 2015 the arrival number reduced slightly and stood at 1,901,000. The average length of stay is estimated at 8 days. Guests from Great Britain, Israel, France, Italy, Sweden and Norway are the ones that constitute the biggest portion in terms of the arrivals by country. In Rhodes, the supply of available rooms is high, since more than 550 hotels are operating in the island, the majority of which are two star hotels.
In popular culture
*"Wikt:hic Rhodus, hic salta, Hic Rhodus, hic salta!", a phrase from antiquity *Movies shot on the island include ''The Guns of Navarone (film), The Guns of Navarone'' (1961), ''Kiss the Girls (1965 film), Kiss the Girls'' by Giannis Dalianidis (1965), and ''Escape to Athena'' (1979). Rhodes was also the setting of Agatha Christie's "Triangle at Rhodes."Panoramas


See also
*95th National Guard Higher Command (Greece) *Ancient regions of Anatolia *Brygindara *Medieval RoseCitations
General and cited sources
*John Boardman (art historian), Boardman, John ed., ''The Oxford History of Classical Art'', 1993, OUP, * * * *External links
Official website
{{Authority control Rhodes, Dodecanese Dorian colonies Greek city-states Hellenic Navy bases Islands of the South Aegean Landforms of Rhodes (regional unit) Mediterranean islands Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Municipalities of the South Aegean Phoenician colonies in Greece Populated places in Rhodes