Obliquity berger 0 to 1000000.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's
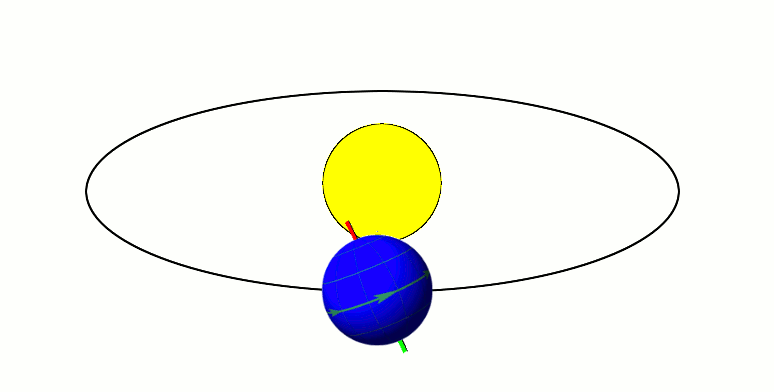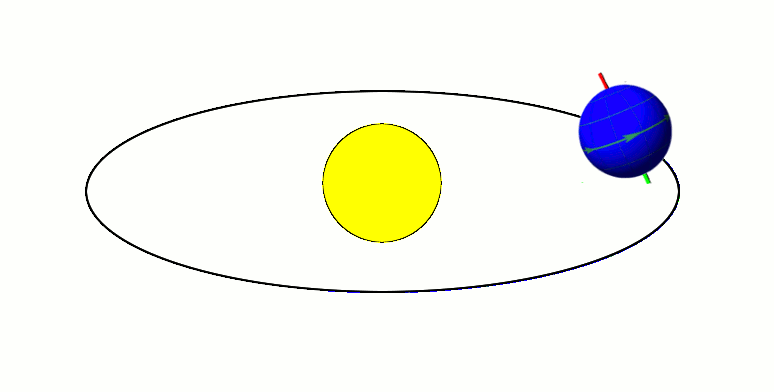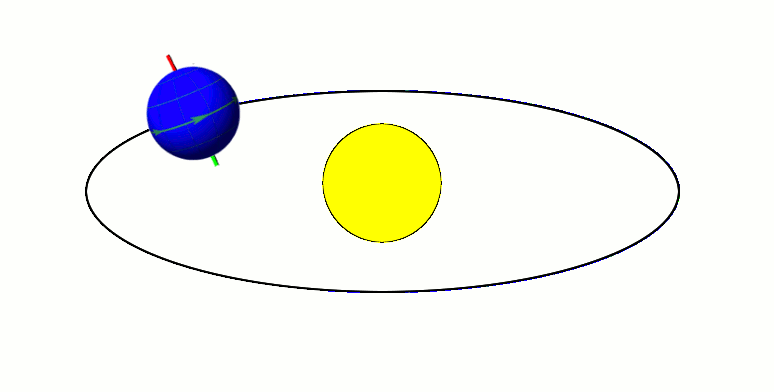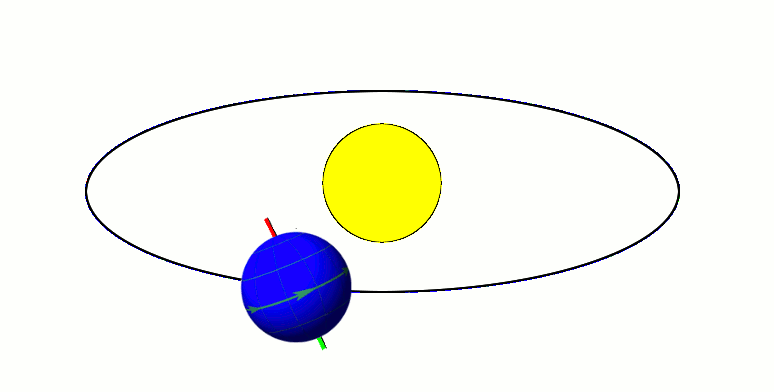 Earth's axis remains tilted in the same direction with reference to the background stars throughout a year (regardless of where it is in its orbit). This means that one pole (and the associated hemisphere of Earth) will be directed away from the Sun at one side of the orbit, and half an orbit later (half a year later) this pole will be directed towards the Sun. This is the cause of Earth's seasons.
Earth's axis remains tilted in the same direction with reference to the background stars throughout a year (regardless of where it is in its orbit). This means that one pole (and the associated hemisphere of Earth) will be directed away from the Sun at one side of the orbit, and half an orbit later (half a year later) this pole will be directed towards the Sun. This is the cause of Earth's seasons. 
 The exact angular value of the obliquity is found by observation of the motions of Earth and
The exact angular value of the obliquity is found by observation of the motions of Earth and
National Space Science Data Center
*
Obliquity of the Ecliptic Calculator
{{Climate oscillations Precession Planetary science
rotational axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rota ...
and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
ial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination.
At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane.
The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane
Plane(s) most often refers to:
* Aero- or airplane, a powered, fixed-wing aircraft
* Plane (geometry), a flat, 2-dimensional surface
Plane or planes may also refer to:
Biology
* Plane (tree) or ''Platanus'', wetland native plant
* Planes (gen ...
through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines.
Earth's obliquity oscillates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees on a 41,000-year cycle. Based on a continuously updated formula (here Laskar, 1986, though since 2006 the IMCCE and the IAU recommend the P03 model), Earth's mean obliquity (without taking into account the nutation in obliquity) is currently about and decreasing; according to P03 astronomical model, its value (without taking into account the nutation in obliquity) was 23°26′11.570″ (23.4365472133°) on January 1, 2021, 0 TT.
Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed more toward the Sun on one side of the orbit, and more away from the Sun on the other side—the cause of the seasons on Earth.
Standards
There are two standard methods of specifying a planet's tilt. One way is based on the planet's ''north pole'', defined in relation to the direction of Earth's north pole, and the other way is based on the planet's ''positive pole'', defined by theright-hand rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors.
Most of th ...
:
* The International Astronomical Union (IAU) defines the ''north pole'' of a planet as that which lies on Earth's north side of the invariable plane of the Solar System; under this system, Venus is tilted 3° and rotates retrograde, opposite that of most of the other planets.
* The IAU also uses the right-hand rule to define a ''positive pole'' for the purpose of determining orientation. Using this convention, Venus is tilted 177° ("upside down") and rotates prograde.
Earth
Earth's orbital plane is known as the ecliptic plane, and Earth's tilt is known to astronomers as the ''obliquity of the ecliptic'', being the angle between the ecliptic and the celestial equator on thecelestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
. It is denoted by the Greek letter '' ε''.
Earth currently has an axial tilt of about 23.44°. This value remains about the same relative to a stationary orbital plane throughout the cycles of axial precession. But the ecliptic (i.e., Earth's orbit) moves due to planetary perturbations
Perturbation or perturb may refer to:
* Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly
* Perturbation (geology), changes in the nature of alluvial deposits over time
* Perturbatio ...
, and the obliquity of the ecliptic is not a fixed quantity. At present, it is decreasing at a rate of about 46.8″ per century
A century is a period of 100 years. Centuries are numbered ordinally in English and many other languages. The word ''century'' comes from the Latin ''centum'', meaning ''one hundred''. ''Century'' is sometimes abbreviated as c.
A centennial or ...
''(see details in Short term
Short may refer to:
Places
* Short (crater), a lunar impact crater on the near side of the Moon
* Short, Mississippi, an unincorporated community
* Short, Oklahoma, a census-designated place
People
* Short (surname)
* List of people known as ...
below)''.
History
Earth's obliquity may have been reasonably accurately measured as early as 1100 BC in India and China. The ancient Greeks had good measurements of the obliquity since about 350 BC, whenPytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéas ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explor ...
of Marseilles measured the shadow of a gnomon
A gnomon (; ) is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields.
History
A painted stick dating from 2300 BC that was excavated at the astronomical site of Taosi is the ol ...
at the summer solstice. About 830 AD, the Caliph Al-Mamun of Baghdad directed his astronomers to measure the obliquity, and the result was used in the Arab world for many years. In 1437, Ulugh Beg determined the Earth's axial tilt as 23°30′17″ (23.5047°).
It was widely believed, during the Middle Ages, that both precession and Earth's obliquity oscillated around a mean value, with a period of 672 years, an idea known as ''trepidation
Trepidation (from Lat. ''trepidus'', "trepidatious"), in now-obsolete medieval theories of astronomy, refers to hypothetical oscillation in the precession of the equinoxes. The theory was popular from the 9th to the 16th centuries.
The origin o ...
'' of the equinoxes. Perhaps the first to realize this was incorrect (during historic time) was Ibn al-Shatir in the fourteenth century and the first to realize that the obliquity is decreasing at a relatively constant rate was Fracastoro
Girolamo Fracastoro ( la, Hieronymus Fracastorius; c. 1476/86 August 1553) was an Italian physician, poet, and scholar in mathematics, geography and astronomy. Fracastoro subscribed to the philosophy of atomism, and rejected appeals to hidden c ...
in 1538. The first accurate, modern, western observations of the obliquity were probably those of Tycho Brahe from Denmark, about 1584, although observations by several others, including al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
, al-Tusi, Purbach, Regiomontanus, and Walther
Walther is a masculine given name and a surname. It is a German form of Walter, which is derived from the Old High German ''Walthari'', containing the elements ''wald'' -"power", "brightness" or "forest" and ''hari'' -"warrior".
The name was fir ...
, could have provided similar information.
Seasons
 Earth's axis remains tilted in the same direction with reference to the background stars throughout a year (regardless of where it is in its orbit). This means that one pole (and the associated hemisphere of Earth) will be directed away from the Sun at one side of the orbit, and half an orbit later (half a year later) this pole will be directed towards the Sun. This is the cause of Earth's seasons.
Earth's axis remains tilted in the same direction with reference to the background stars throughout a year (regardless of where it is in its orbit). This means that one pole (and the associated hemisphere of Earth) will be directed away from the Sun at one side of the orbit, and half an orbit later (half a year later) this pole will be directed towards the Sun. This is the cause of Earth's seasons. Summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
occurs in the Northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
when the north pole is directed toward the Sun. Variations in Earth's axial tilt can influence the seasons and is likely a factor in long-term climatic change
''Climatic Change'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media covering cross-disciplinary work on all aspects of climate change and variability. It was established in 1978 and the editors-in-chief ...
''(also see Milankovitch cycles)''.
Oscillation
Short term
planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young ...
over many years. Astronomers produce new fundamental ephemerides as the accuracy of observation
Observation is the active acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The ...
improves and as the understanding of the dynamics increases, and from these ephemerides various astronomical values, including the obliquity, are derived.
Annual almanacs are published listing the derived values and methods of use. Until 1983, the Astronomical Almanac's angular value of the mean obliquity for any date was calculated based on the work of Newcomb, who analyzed positions of the planets until about 1895:
:
where is the obliquity and is tropical centuries from B1900.0
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to pertu ...
to the date in question.
From 1984, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's DE series of computer-generated ephemerides took over as the fundamental ephemeris A fundamental ephemeris of the Solar System is a model of the objects of the system in space, with all of their positions and motions accurately represented. It is intended to be a high-precision primary reference for prediction and observation of t ...
of the Astronomical Almanac. Obliquity based on DE200, which analyzed observations from 1911 to 1979, was calculated:
:
where hereafter is Julian centuries from J2000.0
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to pertu ...
.
JPL's fundamental ephemerides have been continually updated. For instance, according to IAU resolution in 2006 in favor of the P03 astronomical model, the ''Astronomical Almanac'' for 2010 specifies:''Astronomical Almanac 2010'', p. B52
:
These expressions for the obliquity are intended for high precision over a relatively short time span, perhaps several centuries. J. Laskar computed an expression to order good to 0.02″ over 1000 years and several arcseconds over 10,000 years.
:
where here is multiples of 10,000 Julian years from J2000.0
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to pertu ...
.See table 8 and eq. 35 in and erratum to article
Units in article are arcseconds, which may be more convenient.
These expressions are for the so-called ''mean'' obliquity, that is, the obliquity free from short-term variations. Periodic motions of the Moon and of Earth in its orbit cause much smaller (9.2 arcseconds) short-period (about 18.6 years) oscillations of the rotation axis of Earth, known as nutation, which add a periodic component to Earth's obliquity. The ''true'' or instantaneous obliquity includes this nutation.
Long term
Usingnumerical methods
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods th ...
to simulate Solar System behavior, long-term changes in Earth's orbit, and hence its obliquity, have been investigated over a period of several million years. For the past 5 million years, Earth's obliquity has varied between and , with a mean period of 41,040 years. This cycle is a combination of precession and the largest term in the motion of the ecliptic. For the next 1 million years, the cycle will carry the obliquity between and .
The Moon has a stabilizing effect on Earth's obliquity. Frequency map analysis conducted in 1993 suggested that, in the absence of the Moon, the obliquity could change rapidly due to orbital resonances and chaotic behavior of the Solar System, reaching as high as 90° in as little as a few million years ''(also see Orbit of the Moon)''.
However, more recent numerical simulations made in 2011 indicated that even in the absence of the Moon, Earth's obliquity might not be quite so unstable; varying only by about 20–25°. To resolve this contradiction, diffusion rate of obliquity has been calculated, and it was found that it takes more than billions of years for Earth's obliquity to reach near 90°. The Moon's stabilizing effect will continue for less than 2 billion years. As the Moon continues to recede from Earth due to tidal acceleration, resonances may occur which will cause large oscillations of the obliquity.
Solar System bodies
All four of the innermost, rocky planets of the Solar System may have had large variations of their obliquity in the past. Since obliquity is the angle between the axis of rotation and the direction perpendicular to the orbital plane, it changes as the orbital plane changes due to the influence of other planets. But the axis of rotation can also move ( axial precession), due to torque exerted by the Sun on a planet's equatorial bulge. Like Earth, all of the rocky planets show axial precession. If the precession rate were very fast the obliquity would actually remain fairly constant even as the orbital plane changes. The rate varies due to tidal dissipation and core-mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
interaction, among other things. When a planet's precession rate approaches certain values, orbital resonances may cause large changes in obliquity. The amplitude of the contribution having one of the resonant rates is divided by the difference between the resonant rate and the precession rate, so it becomes large when the two are similar.
Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
and Venus have most likely been stabilized by the tidal dissipation of the Sun. Earth was stabilized by the Moon, as mentioned above, but before its formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
, Earth, too, could have passed through times of instability. Mars's obliquity is quite variable over millions of years and may be in a chaotic state; it varies as much as 0° to 60° over some millions of years, depending on perturbations
Perturbation or perturb may refer to:
* Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly
* Perturbation (geology), changes in the nature of alluvial deposits over time
* Perturbatio ...
of the planets. Some authors dispute that Mars's obliquity is chaotic, and show that tidal dissipation and viscous core-mantle coupling are adequate for it to have reached a fully damped state, similar to Mercury and Venus.
The occasional shifts in the axial tilt of Mars have been suggested as an explanation for the appearance and disappearance of rivers and lakes over the course of the existence of Mars. A shift could cause a burst of methane into the atmosphere, causing warming, but then the methane would be destroyed and the climate would become arid again.
The obliquities of the outer planets are considered relatively stable.
Extrasolar planets
The stellar obliquity , i.e. the axial tilt of a star with respect to the orbital plane of one of its planets, has been determined for only a few systems. But for 49 stars as of 2012, the sky-projected spin-orbit misalignment has been observed, which serves as a lower limit to . Most of these measurements rely on the Rossiter–McLaughlin effect. So far, it has not been possible to constrain the obliquity of an extrasolar planet. But the rotational flattening of the planet and the entourage of moons and/or rings, which are traceable with high-precision photometry, e.g. by the space-basedKepler space telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orb ...
, could provide access to in the near future.
Astrophysicists have applied tidal theories to predict the obliquity of extrasolar planets
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
. It has been shown that the obliquities of exoplanets in the habitable zone around low-mass stars tend to be eroded in less than 109 years,
which means that they would not have seasons as Earth has.
See also
* Milankovitch cycles * Polar motion * Rotation around a fixed axis *True polar wander
True polar wander is a solid-body rotation of a planet or moon with respect to its spin axis, causing the geographic locations of the north and south poles to change, or "wander". Unless the body is totally rigid (which the Earth is not) its sta ...
References
External links
National Space Science Data Center
*
Obliquity of the Ecliptic Calculator
{{Climate oscillations Precession Planetary science