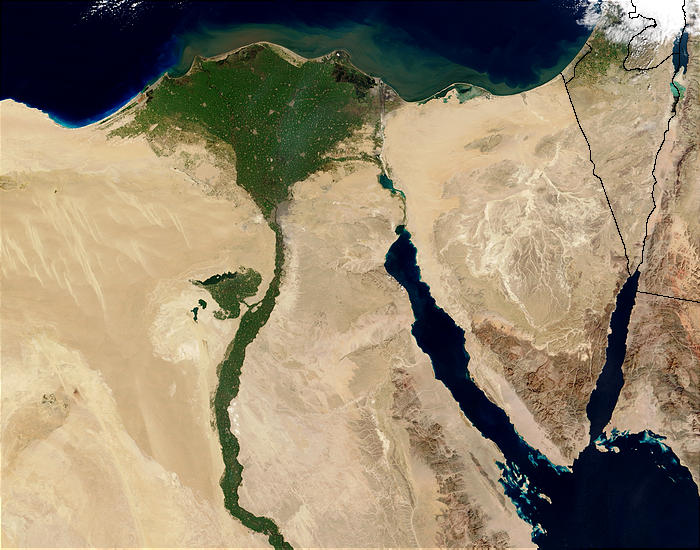
Nile River and delta from orbit.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nile, ,
Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its
 With a total length of about between the region of Lake Victoria and the
With a total length of about between the region of Lake Victoria and the
 The source of the Blue Nile is Lake Tana in the Gish Abay region in the Ethiopian Highlands.
The source of the White Nile, even after centuries of exploration, remains in dispute. The most remote source that is indisputably a source for the White Nile is the Kagera River; however, the Kagera has tributaries that are in contention for the farthest source of the White Nile. Two start in Burundi: the Ruvyironza River (also known as the Luvironza) and the Rurubu River. In addition, in 2010, an exploration party in Rwanda went to a place described as the source of the Rukarara River, Rukarara tributary, and by hacking a path up steep jungle-choked mountain slopes in the Nyungwe Forest found (in the dry season) an appreciable incoming surface flow for many kilometres upstream, and found a new source, giving the Nile a length of .
The source of the Blue Nile is Lake Tana in the Gish Abay region in the Ethiopian Highlands.
The source of the White Nile, even after centuries of exploration, remains in dispute. The most remote source that is indisputably a source for the White Nile is the Kagera River; however, the Kagera has tributaries that are in contention for the farthest source of the White Nile. Two start in Burundi: the Ruvyironza River (also known as the Luvironza) and the Rurubu River. In addition, in 2010, an exploration party in Rwanda went to a place described as the source of the Rukarara River, Rukarara tributary, and by hacking a path up steep jungle-choked mountain slopes in the Nyungwe Forest found (in the dry season) an appreciable incoming surface flow for many kilometres upstream, and found a new source, giving the Nile a length of .
 The White Nile leaves Lake Victoria at Ripon Falls near Jinja, Uganda, as the "Victoria Nile." It flows north for some to Lake Kyoga. The last part of the approximately river section starts from the western shores of the lake and flows at first to the west until just south of Masindi Port, where the river turns north, then makes a great half circle to the east and north to Karuma Falls. For the remaining part, it flows westerly through the Murchison Falls until it reaches the northern shores of Lake Albert (Africa), Lake Albert where it forms a significant river delta. Lake Albert is on the border of the
The White Nile leaves Lake Victoria at Ripon Falls near Jinja, Uganda, as the "Victoria Nile." It flows north for some to Lake Kyoga. The last part of the approximately river section starts from the western shores of the lake and flows at first to the west until just south of Masindi Port, where the river turns north, then makes a great half circle to the east and north to Karuma Falls. For the remaining part, it flows westerly through the Murchison Falls until it reaches the northern shores of Lake Albert (Africa), Lake Albert where it forms a significant river delta. Lake Albert is on the border of the
 The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At Aswan: 0.14 million tonnes of suspended load, suspended sediment and an additional 28% of bed load, bedload
* At Beni Sweif: 0.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 20% of bedload
* At Qena: 0.27 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 27% of bedload
* At Sohag: 1.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 13% of bedload
The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At Aswan: 0.14 million tonnes of suspended load, suspended sediment and an additional 28% of bed load, bedload
* At Beni Sweif: 0.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 20% of bedload
* At Qena: 0.27 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 27% of bedload
* At Sohag: 1.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 13% of bedload

 The Blue Nile ( am, ዓባይ, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile originates in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water from the Blue Nile (the rest being from the Tekezé River, Tekezé, Atbarah, Sobat River, Sobat, and small tributaries). The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian Wet season, rainy season when rainfall is especially high on the Ethiopian Highlands, Ethiopian Plateau; the rest of the year, the great rivers draining Ethiopia into the Nile have a weaker flow. In harsh and arid seasons and droughts, the Blue Nile dries out completely.
The flow of the Blue Nile varies considerably over its yearly cycle and is the main contribution to the large natural variation of the Nile flow. During the dry season the natural discharge of the Blue Nile can be as low as , although upstream dams regulate the flow of the river. During the wet season, the peak flow of the Blue Nile often exceeds in late August (a difference of a factor of 50).
Before the placement of dams on the river the yearly discharge varied by a factor of 15 at Aswan. Peak flows of over occurred during late August and early September, and minimum flows of about occurred during late April and early May.
The Blue Nile ( am, ዓባይ, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile originates in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water from the Blue Nile (the rest being from the Tekezé River, Tekezé, Atbarah, Sobat River, Sobat, and small tributaries). The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian Wet season, rainy season when rainfall is especially high on the Ethiopian Highlands, Ethiopian Plateau; the rest of the year, the great rivers draining Ethiopia into the Nile have a weaker flow. In harsh and arid seasons and droughts, the Blue Nile dries out completely.
The flow of the Blue Nile varies considerably over its yearly cycle and is the main contribution to the large natural variation of the Nile flow. During the dry season the natural discharge of the Blue Nile can be as low as , although upstream dams regulate the flow of the river. During the wet season, the peak flow of the Blue Nile often exceeds in late August (a difference of a factor of 50).
Before the placement of dams on the river the yearly discharge varied by a factor of 15 at Aswan. Peak flows of over occurred during late August and early September, and minimum flows of about occurred during late April and early May.
 The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the Ouaddaï highlands of eastern Chad to the Nile River Valley c. 8000 to c. 1000 BCE. Its remains are known as the Wadi Howar. The wadi passes through Gharb Darfur near the northern border with Chad and meets up with the Nile near the southern point of the Great Bend.
The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the Ouaddaï highlands of eastern Chad to the Nile River Valley c. 8000 to c. 1000 BCE. Its remains are known as the Wadi Howar. The wadi passes through Gharb Darfur near the northern border with Chad and meets up with the Nile near the southern point of the Great Bend.
 The Nile has been the lifeline of civilization in Egypt since the Stone Age, with most of the population and all of the cities of Egypt developing along those parts of the Nile valley lying north of Aswan. However, the Nile used to run much more westerly through what is now Wadi Hamim and Wadi al Maqar in Libya and flow into the Gulf of Sidra. As the sea level rose at the end of the Last Glacial Period, most recent ice age, the stream which is now the northern Nile Stream capture, captured the ancestral Nile near Asyut. This change in climate also led to the current extents of the Sahara desert, around 3400 BC.
The Nile has been the lifeline of civilization in Egypt since the Stone Age, with most of the population and all of the cities of Egypt developing along those parts of the Nile valley lying north of Aswan. However, the Nile used to run much more westerly through what is now Wadi Hamim and Wadi al Maqar in Libya and flow into the Gulf of Sidra. As the sea level rose at the end of the Last Glacial Period, most recent ice age, the stream which is now the northern Nile Stream capture, captured the ancestral Nile near Asyut. This change in climate also led to the current extents of the Sahara desert, around 3400 BC.
 The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile". An unending source of sustenance, it played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian civilization. Because the river overflowed its banks annually and deposited new layers of silt, the surrounding land was very fertile. The Ancient Egyptians cultivated and traded wheat, flax, papyrus and other crops around the Nile. Wheat was a crucial crop in the famine-plagued Middle East. This trading system secured Egypt's diplomatic relationships with other countries and contributed to economic stability. Far-reaching trade has been carried on along the Nile since ancient times. A tune, Hymn to the Nile, was created and sung by the ancient Egyptian peoples about the flooding of the Nile River and all of the miracles it brought to Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Water buffalo were introduced from Asia, and the Assyrian people, Assyrians introduced camels in the 7th century BC. These animals were raised for meat and were domesticated and used for ploughing—or in the camels' case, carriage. Water was vital to both people and livestock. The Nile was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.
The Nile was also an important part of ancient Egyptian spiritual life. Hapi (Nile god), Hapi was the god of the annual floods, and both he and the pharaoh were thought to control the flooding. The Nile was considered to be a causeway from life to death and the afterlife. The east was thought of as a place of birth and growth, and the west was considered the place of death, as the god Ra, the Sun, underwent birth, death, and resurrection each day as he crossed the sky. Thus, all tombs were west of the Nile, because the Egyptians believed that in order to enter the afterlife, they had to be buried on the side that symbolized death.
As the Nile was such an important factor in Egyptian life, the ancient calendar was even based on the three cycles of the Nile. These seasons, each consisting of four months of thirty days each, were called Season of the Inundation, Akhet, Season of the Emergence, Peret, and Season of the Harvest, Shemu. Akhet, which means inundation, was the time of the year when the Nile flooded, leaving several layers of fertile soil behind, aiding in agricultural growth. Peret was the growing season, and Shemu, the last season, was the harvest season when there were no rains.
The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile". An unending source of sustenance, it played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian civilization. Because the river overflowed its banks annually and deposited new layers of silt, the surrounding land was very fertile. The Ancient Egyptians cultivated and traded wheat, flax, papyrus and other crops around the Nile. Wheat was a crucial crop in the famine-plagued Middle East. This trading system secured Egypt's diplomatic relationships with other countries and contributed to economic stability. Far-reaching trade has been carried on along the Nile since ancient times. A tune, Hymn to the Nile, was created and sung by the ancient Egyptian peoples about the flooding of the Nile River and all of the miracles it brought to Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Water buffalo were introduced from Asia, and the Assyrian people, Assyrians introduced camels in the 7th century BC. These animals were raised for meat and were domesticated and used for ploughing—or in the camels' case, carriage. Water was vital to both people and livestock. The Nile was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.
The Nile was also an important part of ancient Egyptian spiritual life. Hapi (Nile god), Hapi was the god of the annual floods, and both he and the pharaoh were thought to control the flooding. The Nile was considered to be a causeway from life to death and the afterlife. The east was thought of as a place of birth and growth, and the west was considered the place of death, as the god Ra, the Sun, underwent birth, death, and resurrection each day as he crossed the sky. Thus, all tombs were west of the Nile, because the Egyptians believed that in order to enter the afterlife, they had to be buried on the side that symbolized death.
As the Nile was such an important factor in Egyptian life, the ancient calendar was even based on the three cycles of the Nile. These seasons, each consisting of four months of thirty days each, were called Season of the Inundation, Akhet, Season of the Emergence, Peret, and Season of the Harvest, Shemu. Akhet, which means inundation, was the time of the year when the Nile flooded, leaving several layers of fertile soil behind, aiding in agricultural growth. Peret was the growing season, and Shemu, the last season, was the harvest season when there were no rains.
 Owing to their failure to penetrate the Sudd wetlands of South Sudan, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Various expeditions failed to determine the river's source. Agatharchides records that in the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, a military expedition had penetrated far enough along the course of the Blue Nile to determine that the summer floods were caused by heavy seasonal rainstorms in the Ethiopian Highlands, but no European of antiquity is known to have reached Lake Tana. The ''Tabula Rogeriana'' depicted the source as three lakes in 1154.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the Middle East and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Society of Jesus, Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páez's account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páez's contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Blue Nile Falls, Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Cicero's ''De Republica''. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also uses his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder writes that the Nile had its origins "in a mountain of lower Mauretania", flowed above ground for "many days" distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground "for a distance of 20 days' journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians."
Owing to their failure to penetrate the Sudd wetlands of South Sudan, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Various expeditions failed to determine the river's source. Agatharchides records that in the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, a military expedition had penetrated far enough along the course of the Blue Nile to determine that the summer floods were caused by heavy seasonal rainstorms in the Ethiopian Highlands, but no European of antiquity is known to have reached Lake Tana. The ''Tabula Rogeriana'' depicted the source as three lakes in 1154.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the Middle East and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Society of Jesus, Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páez's account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páez's contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Blue Nile Falls, Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Cicero's ''De Republica''. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also uses his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder writes that the Nile had its origins "in a mountain of lower Mauretania", flowed above ground for "many days" distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground "for a distance of 20 days' journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians."
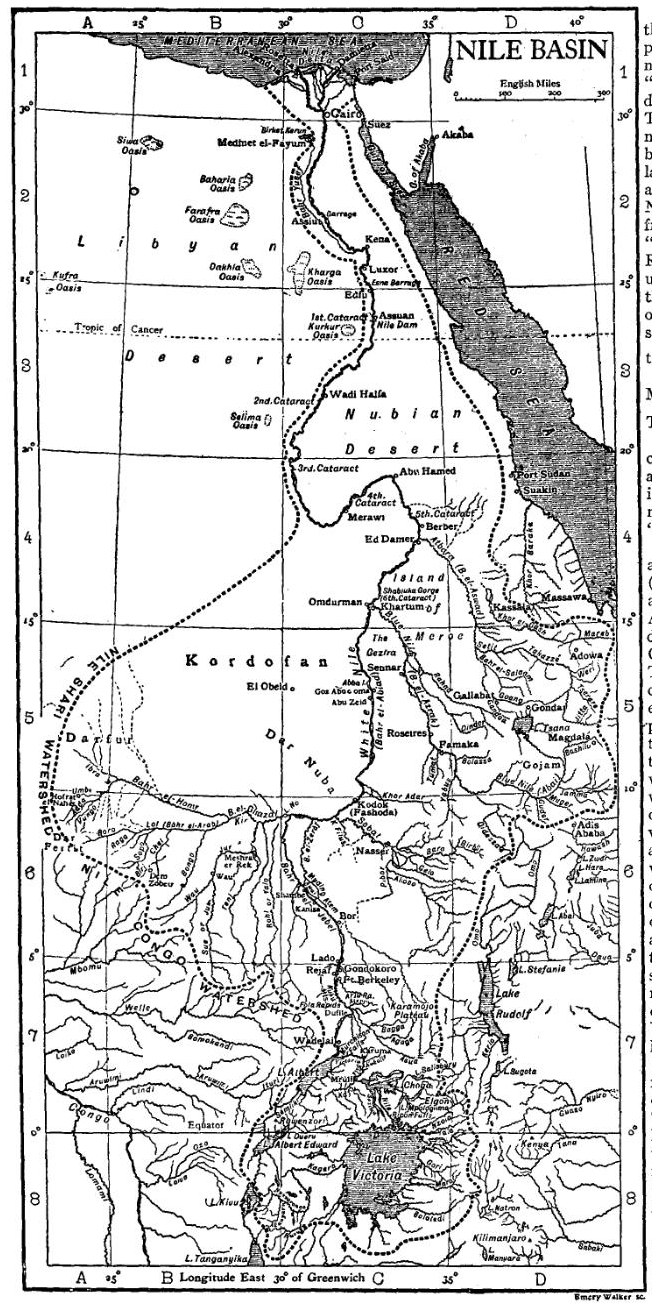 Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the Turco-Egyptian conquest of Sudan (1820–1824), conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, and his sons from 1821 onward. As a result of this, the Blue Nile was known as far as its exit from the Ethiopian foothills and the White Nile as far as the mouth of the Sobat River. Three expeditions under a Turkish officer, Selim Bimbashi, were made between 1839 and 1842, and two got to the point about beyond the present port of Juba, where the country rises and rapids make navigation very difficult.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proven his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A quarrel ensued which sparked intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Speke's discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.
Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the Turco-Egyptian conquest of Sudan (1820–1824), conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, and his sons from 1821 onward. As a result of this, the Blue Nile was known as far as its exit from the Ethiopian foothills and the White Nile as far as the mouth of the Sobat River. Three expeditions under a Turkish officer, Selim Bimbashi, were made between 1839 and 1842, and two got to the point about beyond the present port of Juba, where the country rises and rapids make navigation very difficult.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proven his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A quarrel ensued which sparked intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Speke's discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.


 The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the Jonglei Canal to bypass the swamp.
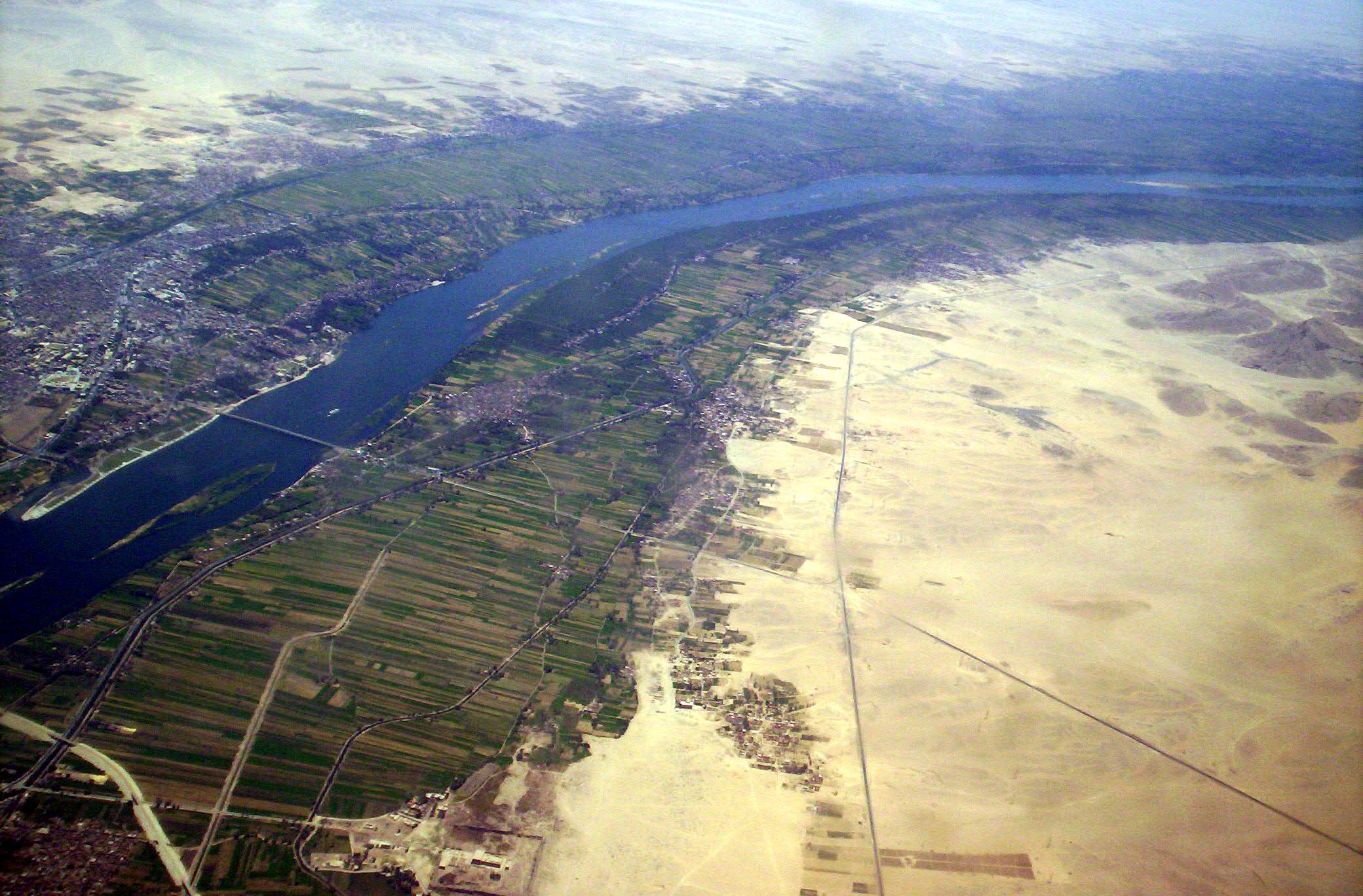
Nile cities include Khartoum, Aswan, Luxor (Thebes), and the GizaCairo conurbation. The first cataract, the closest to the mouth of the river, is at Aswan, north of the Aswan Dam. This part of the river is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as feluccas. Many cruise ships ply the route between Luxor and Aswan, stopping at Edfu and Kom Ombo along the way. Security concerns have limited cruising on the northernmost portion for many years.
A computer simulation study to plan the economic development of the Nile was directed by H.A.W. Morrice and W.N. Allan, for the Ministry of Hydro-power of Sudan, during 1955–57 Morrice was their hydrological adviser, and Allan his predecessor. The calculations were enabled by accurate monthly inflow data collected for 50 years. The underlying principle was the use of over-year storage, to conserve water from rainy years for use in dry years. Irrigation, navigation and other needs were considered. Each computer run postulated a set of reservoirs and operating equations for the release of water as a function of the month and the levels upstream. The behavior that would have resulted given the inflow data was modeled. Over 600 models were run. Recommendations were made to the Sudanese authorities. The calculations were run on an IBM 650 computer. Simulation studies to design water resources are discussed further in the article on hydrology transport models, which have been used since the 1980s to analyze water quality.
Despite the development of many reservoirs, drought during the 1980s led to widespread starvation in Ethiopia and Sudan, but Egypt was nourished by water impounded in Lake Nasser. Drought has proven to be a major cause of fatality in the Nile river basin. According to a report by the Strategic Foresight Group around 170 million people have been affected by droughts in the last century with half a million lives lost.Blue Peace for the Nile, 2009
The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the Jonglei Canal to bypass the swamp.
Nile cities include Khartoum, Aswan, Luxor (Thebes), and the GizaCairo conurbation. The first cataract, the closest to the mouth of the river, is at Aswan, north of the Aswan Dam. This part of the river is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as feluccas. Many cruise ships ply the route between Luxor and Aswan, stopping at Edfu and Kom Ombo along the way. Security concerns have limited cruising on the northernmost portion for many years.
A computer simulation study to plan the economic development of the Nile was directed by H.A.W. Morrice and W.N. Allan, for the Ministry of Hydro-power of Sudan, during 1955–57 Morrice was their hydrological adviser, and Allan his predecessor. The calculations were enabled by accurate monthly inflow data collected for 50 years. The underlying principle was the use of over-year storage, to conserve water from rainy years for use in dry years. Irrigation, navigation and other needs were considered. Each computer run postulated a set of reservoirs and operating equations for the release of water as a function of the month and the levels upstream. The behavior that would have resulted given the inflow data was modeled. Over 600 models were run. Recommendations were made to the Sudanese authorities. The calculations were run on an IBM 650 computer. Simulation studies to design water resources are discussed further in the article on hydrology transport models, which have been used since the 1980s to analyze water quality.
Despite the development of many reservoirs, drought during the 1980s led to widespread starvation in Ethiopia and Sudan, but Egypt was nourished by water impounded in Lake Nasser. Drought has proven to be a major cause of fatality in the Nile river basin. According to a report by the Strategic Foresight Group around 170 million people have been affected by droughts in the last century with half a million lives lost.Blue Peace for the Nile, 2009
; Report by Strategic Foresight Group From the 70 incidents of drought which took place between 1900 and 2012, 55 incidents took place in Ethiopia, Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya and Tanzania.
 The Nile's water has affected the politics of East Africa and the Horn of Africa for many decades. The dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the $4.5 billion Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam has become a national preoccupation in both countries, stoking patriotism, deep-seated fears and even murmurs of war. Countries including Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and Kenya have complained about Egyptian domination of its water resources. The Nile Basin Initiative promotes a peaceful cooperation among those states.
Several attempts have been made to establish agreements between the countries sharing the Nile waters. On 14 May 2010 at Entebbe, Uganda, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania signed a new agreement on sharing the Nile water even though this agreement raised strong opposition from Egypt and Sudan. Ideally, such international agreements should promote equitable and efficient usage of the Nile basin's water resources. Without a better understanding about the availability of the future water resources of the Nile, it is possible that conflicts could arise between these countries relying on the Nile for their water supply, economic and social developments.
The Nile's water has affected the politics of East Africa and the Horn of Africa for many decades. The dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the $4.5 billion Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam has become a national preoccupation in both countries, stoking patriotism, deep-seated fears and even murmurs of war. Countries including Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and Kenya have complained about Egyptian domination of its water resources. The Nile Basin Initiative promotes a peaceful cooperation among those states.
Several attempts have been made to establish agreements between the countries sharing the Nile waters. On 14 May 2010 at Entebbe, Uganda, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania signed a new agreement on sharing the Nile water even though this agreement raised strong opposition from Egypt and Sudan. Ideally, such international agreements should promote equitable and efficient usage of the Nile basin's water resources. Without a better understanding about the availability of the future water resources of the Nile, it is possible that conflicts could arise between these countries relying on the Nile for their water supply, economic and social developments.
Paddling the Blue Nile in Flood
. Retrieved 1 November 2014
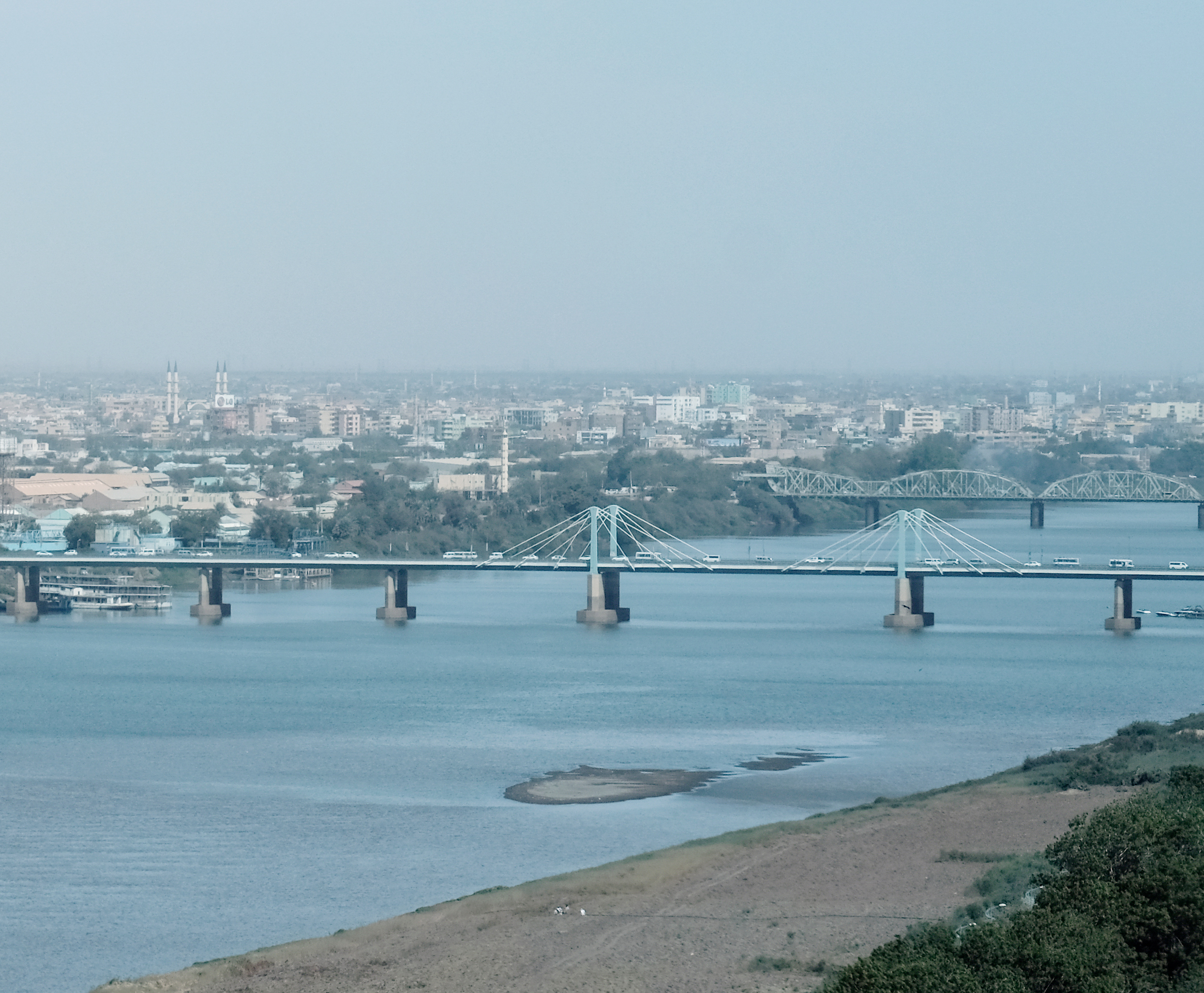
 The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
* Soba (city), Soba Bridge
The following bridges cross the White Nile and connect Khartoum to Omdurman:
* White Nile Bridge
* Fitayhab Bridge
* Al Dabbaseen Bridge (under construction)
* Omhuraz Bridge (proposed)
The following bridges cross from Omdurman: to Khartoum North:
* Shambat Bridge
* Halfia Bridge
The following bridges cross to Tuti from Khartoum state's three cities
* Tuti Bridge, Khartoum-Tuti Bridge
* Omdurman-Tuti Suspension Bridge (proposed)
* Khartoum North-Tuti Bridge (proposed)
Other bridges
* Shandi Bridge, Shendi
* Atbarah Bridge, Atbarah
* Merowe Dam, Merowe, Sudan, Merowe
* Merowe Bridge, Merowe
* Aswan Bridge, Aswan
* Luxor Bridge, Luxor
* Suhag Bridge, Suhag, Egypt, Suhag
* Assiut Bridge, Assiut
* Al Minya Bridge, Minya, Egypt, Minya
* Al Marazeek Bridge, Helwan
* First Ring Road Bridge (Moneeb Crossing),
The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
* Soba (city), Soba Bridge
The following bridges cross the White Nile and connect Khartoum to Omdurman:
* White Nile Bridge
* Fitayhab Bridge
* Al Dabbaseen Bridge (under construction)
* Omhuraz Bridge (proposed)
The following bridges cross from Omdurman: to Khartoum North:
* Shambat Bridge
* Halfia Bridge
The following bridges cross to Tuti from Khartoum state's three cities
* Tuti Bridge, Khartoum-Tuti Bridge
* Omdurman-Tuti Suspension Bridge (proposed)
* Khartoum North-Tuti Bridge (proposed)
Other bridges
* Shandi Bridge, Shendi
* Atbarah Bridge, Atbarah
* Merowe Dam, Merowe, Sudan, Merowe
* Merowe Bridge, Merowe
* Aswan Bridge, Aswan
* Luxor Bridge, Luxor
* Suhag Bridge, Suhag, Egypt, Suhag
* Assiut Bridge, Assiut
* Al Minya Bridge, Minya, Egypt, Minya
* Al Marazeek Bridge, Helwan
* First Ring Road Bridge (Moneeb Crossing),
A Struggle Over the Nile
– slideshow by ''The New York Times''
Thesis Analyzing Nile River Negotiations
*
Old maps of the Nile
from the Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel {{Authority control Nile, International rivers of Africa Nile basin, * Rivers of Egypt Rivers of Sudan Rivers of South Sudan Rivers of Uganda Geography of ancient Egypt Hebrew Bible rivers National parks of Egypt Water transport in Egypt Articles containing video clips Rivers of Africa
Bohairic
Coptic (Bohairic Coptic: , ) is a language family of closely related dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third-century AD in Roman Egypt. Copti ...
, lg, Kiira , Nobiin
Nobiin, or Mahas, is a Northern Nubian language of the Nilo-Saharan language family. "Nobiin" is the genitive form of ''Nòòbíí'' ("Nubian") and literally means "(language) of the Nubians". Another term used is ''Noban tamen'', meaning "the ...
: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
in northeastern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists SayOf the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Eritrea, South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the ...
, Republic of the Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.
The Nile has two major tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
– the White Nile and the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile (; ) is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water to ...
. The White Nile is traditionally considered to be the headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
stream. However, the Blue Nile is the source of most of the water of the Nile downstream, containing 80% of the water and silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
region. It begins at Lake Victoria and flows through Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet at the Sudanese capital of Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
.
The northern section of the river flows north almost entirely through the Nubian Desert
The Nubian Desert ( ar, صحراء النوبة, ''Şaḩrā’ an Nūbyah'') is in the eastern region of the Sahara Desert, spanning approximately 400,000 km2 of northeastern Sudan and northern Eritrea, between the Nile and the Red Sea. ...
to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
and its large delta, and the river flows into the Mediterranean Sea at Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
. Egyptian civilization and Sudanese kingdoms have depended on the river and its annual flooding since ancient times. Most of the population and cities of Egypt lie along those parts of the Nile valley north of Aswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan L ...
. Nearly all the cultural and historical sites of Ancient Egypt developed and are found along river banks. The Nile is, with the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
and Po, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge
In hydrology, discharge is the volumetric flow rate of water that is transported through a given cross-sectional area. It includes any suspended solids (e.g. sediment), dissolved chemicals (e.g. CaCO3(aq)), or biologic material (e.g. diatoms) in ad ...
.
Etymology
The standard English names "White Nile" and "Blue Nile" refer to the river's source, derived fromArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
names formerly applied to only the Sudanese stretches that meet at Khartoum.
In the ancient Egyptian language
The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian ( ) is a dead Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipher ...
, the Nile is called ''Ḥ'pī'' (Hapy) or ''Iteru'', meaning "river". In Coptic, the word ⲫⲓⲁⲣⲟ, pronounced ''piaro'' (Sahidic
Coptic (Bohairic Coptic: , ) is a language family of closely related dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third-century AD in Roman Egypt. Coptic ...
) or ''phiaro'' (Bohairic
Coptic (Bohairic Coptic: , ) is a language family of closely related dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third-century AD in Roman Egypt. Copti ...
), means "the river" (lit. p(h).iar-o "the.canal-great"), and comes from the same ancient name. In Nobiin
Nobiin, or Mahas, is a Northern Nubian language of the Nilo-Saharan language family. "Nobiin" is the genitive form of ''Nòòbíí'' ("Nubian") and literally means "(language) of the Nubians". Another term used is ''Noban tamen'', meaning "the ...
the river is called ''Áman Dawū'', meaning "the great water". In Luganda the river is called ''Kiira'' or ''Kiyira''. In Runyoro
The Nyoro language (autonym: ''Runyoro'') is a Bantu language spoken by the Nyoro people of Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by th ...
it is called ''Kihiira''. In Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian ( ar, العامية المصرية, ), or simply Masri (also Masry) (), is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic dialect in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and ...
, the Nile is called ''en-Nīl'', while in Standard Arabic it is called ''an-Nīl''. In Biblical Hebrew, it is , ''Ha-Ye'or'' or , ''Ha-Shiḥor''.
The English name ''Nile'' and the Arabic names ''en-Nîl'' and ''an-Nîl'' both derive from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
' and the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
. Beyond that, however, the etymology is disputed. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
called the river , ''Aiguptos'', but in subsequent periods, Greek authors referred to its lower course as ''Neilos''; this term became generalised for the entire river system. Thus, the name may derive from Ancient Egyptian expression ''n''ꜣ ''r''ꜣ''w-ḥ''ꜣ''w(t)'' (lit. 'the mouths of the front parts'), which referred specifically to the branches of the Nile transversing the Delta, and would have been pronounced ''ni-lo-he'' in the area around Memphis, Egypt, Memphis in the 8th century BCE. Hesiod at his ''Theogony'' refers to Nilus (mythology), Nilus (Νεῖλος) as one of the Potamoi (river gods), son of Oceanus and Tethys (mythology), Tethys.
Another derivation of ''Nile'' might be related to the term ''Nil'' ( sa, नील, wikt:nila, nila; arz, نيلة), which refers to ''Indigofera tinctoria'', one of the original sources of indigo dye. Another may be ''Nymphaea caerulea'', known as "The Sacred Blue Lily of the Nile", which was found scattered over Tutankhamun's corpse when it was excavated in 1922. Another possible etymology derives from the Semitic languages, Semitic term ''Nahal'', meaning "river". Proto-Berber language, Old Libyan has the term ''lilu'', meaning water (in modern Berber ''ilel'' ⵉⵍⴻⵍ means ''sea'').
Courses
 With a total length of about between the region of Lake Victoria and the
With a total length of about between the region of Lake Victoria and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
, the Nile is among the longest rivers on Earth. The drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Nile covers , about 10% of the area of Africa. Compared to other major rivers, though, the Nile carries little water (5% of the Congo River, for example). The Nile basin is complex, and because of this, the Discharge (hydrology), discharge at any given point along the main stem depends on many factors including weather, diversions, evaporation and evapotranspiration, and groundwater flow.
Upstream from Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
(to the south), the river is known as the White Nile, a term also used in a limited sense to describe the section between Lake No and Khartoum. At Khartoum, the river is joined by the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile (; ) is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water to ...
. The White Nile starts in equatorial East Africa, and the Blue Nile begins in Ethiopia. Both branches are on the western flanks of the East African Rift.
Sources
 The source of the Blue Nile is Lake Tana in the Gish Abay region in the Ethiopian Highlands.
The source of the White Nile, even after centuries of exploration, remains in dispute. The most remote source that is indisputably a source for the White Nile is the Kagera River; however, the Kagera has tributaries that are in contention for the farthest source of the White Nile. Two start in Burundi: the Ruvyironza River (also known as the Luvironza) and the Rurubu River. In addition, in 2010, an exploration party in Rwanda went to a place described as the source of the Rukarara River, Rukarara tributary, and by hacking a path up steep jungle-choked mountain slopes in the Nyungwe Forest found (in the dry season) an appreciable incoming surface flow for many kilometres upstream, and found a new source, giving the Nile a length of .
The source of the Blue Nile is Lake Tana in the Gish Abay region in the Ethiopian Highlands.
The source of the White Nile, even after centuries of exploration, remains in dispute. The most remote source that is indisputably a source for the White Nile is the Kagera River; however, the Kagera has tributaries that are in contention for the farthest source of the White Nile. Two start in Burundi: the Ruvyironza River (also known as the Luvironza) and the Rurubu River. In addition, in 2010, an exploration party in Rwanda went to a place described as the source of the Rukarara River, Rukarara tributary, and by hacking a path up steep jungle-choked mountain slopes in the Nyungwe Forest found (in the dry season) an appreciable incoming surface flow for many kilometres upstream, and found a new source, giving the Nile a length of .
In Uganda
 The White Nile leaves Lake Victoria at Ripon Falls near Jinja, Uganda, as the "Victoria Nile." It flows north for some to Lake Kyoga. The last part of the approximately river section starts from the western shores of the lake and flows at first to the west until just south of Masindi Port, where the river turns north, then makes a great half circle to the east and north to Karuma Falls. For the remaining part, it flows westerly through the Murchison Falls until it reaches the northern shores of Lake Albert (Africa), Lake Albert where it forms a significant river delta. Lake Albert is on the border of the
The White Nile leaves Lake Victoria at Ripon Falls near Jinja, Uganda, as the "Victoria Nile." It flows north for some to Lake Kyoga. The last part of the approximately river section starts from the western shores of the lake and flows at first to the west until just south of Masindi Port, where the river turns north, then makes a great half circle to the east and north to Karuma Falls. For the remaining part, it flows westerly through the Murchison Falls until it reaches the northern shores of Lake Albert (Africa), Lake Albert where it forms a significant river delta. Lake Albert is on the border of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, but the Nile is not a border river at this point. After leaving Lake Albert, the river continues north through Uganda and is known as the White Nile#Albert Nile, Albert Nile.
In South Sudan
The White Nile flows intoSouth Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the ...
just south of Nimule, where it is known as the ''Bahr al Jabal'' ("Mountain River"). Just south of the town is the confluence with the Achwa River. The Bahr el Ghazal River, Bahr al Ghazal, long, joins the Bahr al Jabal at a small lagoon called Lake No, after which the Nile becomes known as the ''Bahr al Abyad'', or the White Nile, from the whitish clay suspended in its waters. When the Flooding of the Nile, Nile floods it leaves a rich silty deposit which fertilizes the soil. The Nile no longer floods in Egypt since the completion of the Aswan Dam in 1970. An anabranch river, the Bahr el Zeraf, flows out of the Nile's Bahr al Jabal section and rejoins the White Nile.
The flow rate of the Bahr al Jabal at Mongalla, South Sudan, Mongalla is almost constant throughout the year and averages . After Mongalla, the Bahr Al Jabal enters the enormous swamps of the Sudd region. More than half of the Nile's water is lost in this swamp to evaporation and transpiration. The average flow rate of the White Nile at the tails of the swamps is about . From here it meets with the Sobat River at Malakal. On an annual basis, the White Nile upstream of Malakal contributes about 15% of the total outflow of the Nile.
The average flow of the White Nile at Lake Kawaki Malakal, just below the Sobat River, is ; the peak flow is approximately in October and minimum flow is about in April. This fluctuation is caused by the substantial variation in the flow of the Sobat, which has a minimum flow of about in March and a peak flow of over in October. During the dry season (January to June) the White Nile contributes between 70% and 90% of the total discharge from the Nile.
In Sudan
Below Renk, South Sudan, Renk, the White Nile enters Sudan, it flows north to Khartoum and meets the Blue Nile. The course of the Nile in Sudan is distinctive. It flows over Cataracts of the Nile, six groups of cataracts, from the sixth at Sabaloka Game Reserve, Sabaloka just north of Khartoum northward to Abu Hamad. The tectonic uplift of the Nubian Swell diverts the river south-west for over 300 km, following the structure of the Central African Shear Zone embracing the Bayuda Desert. At Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah it resumes its northward course towards the first cataract at Aswan forming the 'S'-shaped Great Bend of the Nile mentioned by Eratosthenes. In the north of Sudan, the river enters Lake Nasser (known in Sudan as Lake Nubia), the larger part of which is in Egypt.In Egypt
Below theAswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan L ...
, at the northern limit of Lake Nasser, the Nile resumes its historic course. North of Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, the Nile splits into two branches (or distributaries) that feed the Mediterranean: the Rosetta Branch to the west and the Damietta to the east, forming the Nile Delta.
Sediment transport
 The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At Aswan: 0.14 million tonnes of suspended load, suspended sediment and an additional 28% of bed load, bedload
* At Beni Sweif: 0.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 20% of bedload
* At Qena: 0.27 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 27% of bedload
* At Sohag: 1.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 13% of bedload
The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At Aswan: 0.14 million tonnes of suspended load, suspended sediment and an additional 28% of bed load, bedload
* At Beni Sweif: 0.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 20% of bedload
* At Qena: 0.27 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 27% of bedload
* At Sohag: 1.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 13% of bedload
Tributaries
Red Nile
Below the confluence with the Blue Nile the only major tributary is the Atbarah River, also known as the Red Nile, roughly halfway to the sea, which originates in Ethiopia north of Lake Tana, and is around long. The Atbarah flows only while there is rain in Ethiopia and dries very rapidly. During the dry period of January to June, it typically dries up north of Khartoum.Blue Nile

 The Blue Nile ( am, ዓባይ, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile originates in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water from the Blue Nile (the rest being from the Tekezé River, Tekezé, Atbarah, Sobat River, Sobat, and small tributaries). The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian Wet season, rainy season when rainfall is especially high on the Ethiopian Highlands, Ethiopian Plateau; the rest of the year, the great rivers draining Ethiopia into the Nile have a weaker flow. In harsh and arid seasons and droughts, the Blue Nile dries out completely.
The flow of the Blue Nile varies considerably over its yearly cycle and is the main contribution to the large natural variation of the Nile flow. During the dry season the natural discharge of the Blue Nile can be as low as , although upstream dams regulate the flow of the river. During the wet season, the peak flow of the Blue Nile often exceeds in late August (a difference of a factor of 50).
Before the placement of dams on the river the yearly discharge varied by a factor of 15 at Aswan. Peak flows of over occurred during late August and early September, and minimum flows of about occurred during late April and early May.
The Blue Nile ( am, ዓባይ, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile originates in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water from the Blue Nile (the rest being from the Tekezé River, Tekezé, Atbarah, Sobat River, Sobat, and small tributaries). The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian Wet season, rainy season when rainfall is especially high on the Ethiopian Highlands, Ethiopian Plateau; the rest of the year, the great rivers draining Ethiopia into the Nile have a weaker flow. In harsh and arid seasons and droughts, the Blue Nile dries out completely.
The flow of the Blue Nile varies considerably over its yearly cycle and is the main contribution to the large natural variation of the Nile flow. During the dry season the natural discharge of the Blue Nile can be as low as , although upstream dams regulate the flow of the river. During the wet season, the peak flow of the Blue Nile often exceeds in late August (a difference of a factor of 50).
Before the placement of dams on the river the yearly discharge varied by a factor of 15 at Aswan. Peak flows of over occurred during late August and early September, and minimum flows of about occurred during late April and early May.
Bahr el Ghazal and Sobat River
The Bahr el Ghazal River, Bahr al Ghazal and the Sobat River are the two most important tributaries of the White Nile in terms of discharge. The Bahr al Ghazal's drainage basin is the largest of any of the Nile's sub-basins, measuring in size, but it contributes a relatively small amount of water, about annually, because tremendous volumes of water are lost in the Sudd wetlands. The Sobat River, which joins the Nile a short distance below Lake No, drains about half as much land, , but contributes annually to the Nile. When in flood the Sobat carries a large amount of sediment, adding greatly to the White Nile's color.Yellow Nile
 The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the Ouaddaï highlands of eastern Chad to the Nile River Valley c. 8000 to c. 1000 BCE. Its remains are known as the Wadi Howar. The wadi passes through Gharb Darfur near the northern border with Chad and meets up with the Nile near the southern point of the Great Bend.
The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the Ouaddaï highlands of eastern Chad to the Nile River Valley c. 8000 to c. 1000 BCE. Its remains are known as the Wadi Howar. The wadi passes through Gharb Darfur near the northern border with Chad and meets up with the Nile near the southern point of the Great Bend.
History
Khufu branch
The Giza Pyramid Complex originally overlooked a branch of the Nile that no longer exists. This branch was highest during the African Humid Period.Ancient Niles
The existing Nile has five earlier phases; i) the Upper Miocenian Eonile, of about 6 million years Before Present, BP, ii) the Upper Pliocenian Paleonile, commencing about 3.32 million years BP, and during the Pleistocene, the Nile phases iii) Proto-Nile, commencing about 600,000 years BP, iv) Pre-Nile, transitioning at about 400,000 years BP to the v) Neo-Nile. Flowing north from the Ethiopian Highlands, satellite imagery was used to identify dry watercourses in the desert to the west of the Nile. A canyon, now filled by surface drift, represents the Eonile that flowed during 23–5.3 million years before present. The Eonile transported Clastic rock, clastic sediments to the Mediterranean; several natural gas fields have been discovered within these sediments. During the late-Miocene Messinian salinity crisis, when the Mediterranean Sea was a Endorheic basin, closed basin and evaporated to the point of being empty or nearly so, the Nile cut its course down to the new base level until it was several hundred metres below world ocean level at Aswan and below Cairo. This created a very long and deep canyon which was filled with sediment after the Mediterranean was recreated. At some point the sediments raised the riverbed sufficiently for the river to overflow westward into a depression to create Lake Moeris. Lake Tanganyika drained northwards into the Nile until the Virunga Mountains, Virunga Volcanoes blocked its course in Rwanda. The Nile was much longer at that time, with its furthest headwaters in northern Zambia. The currently existing Nile first flowed during the former parts of the Würm glaciation period.Integrated Nile
There are two theories about the age of the integrated Nile. One is that the integrated drainage of the Nile is of young age and that the Nile basin was formerly broken into series of separate basins, only the most northerly of which fed a river following the present course of the Nile in Egypt and Sudan. Rushdi Said postulates that Egypt supplied most of the waters of the Nile during the early part of its history.Said, R. (1981). ''The geological evolution of the River Nile''. Springer Verlag. The other theory is that the drainage from Ethiopia via rivers equivalent to the Blue Nile, the Atbara and the Takazze flowed to the Mediterranean via the Egyptian Nile since well back into Tertiary times.Williams, M.A.J.; Williams, F. (1980). ''Evolution of Nile Basin''. In M.A.J. Williams and H. Faure (eds). ''The Sahara and the Nile''. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 207–224. Salama suggests that during the Paleogene and Neogene Periods (66 million to 2.588 million years ago) a series of separate closed continental basins each occupied one of the major parts of the Sudanese Rift System: Melut Basin, Mellut rift, White Nile rift, Blue Nile rift, Atbara rift and Sag El Naam rift. The Mellut Basin is nearly deep at its central part. This rift is possibly still active, with reported Tectonics, tectonic activity in its northern and southern boundaries. The Sudd swamp which forms the central part of the basin may still be subsiding. The White Nile Rift system, although shallower than the Bahr el Arab rift, is about deep. Geophysical exploration of the Blue Nile Rift System estimated the depth of the sediments to be . These basins were not interconnected until their subsidence ceased, and the rate of sediment deposition was enough to fill and connect them. The Egyptian Nile connected to the Sudanese Nile, which captures the Ethiopian and Equatorial headwaters during the current stages of tectonic activity in the Eastern, Central and Sudanese Rift systems.Salama, R.B. (1997). ''Rift Basins of Sudan. African Basins, Sedimentary Basins of the World. 3.'' Edited by R.C. Selley (Series Editor K.J. Hsu) pp. 105–149. ElSevier, Amsterdam. The connection of the different Niles occurred during cyclic wet periods. The Atbarah overflowed its closed basin during the wet periods that occurred about 100,000 to 120,000 years ago. The Blue Nile connected to the main Nile during the 70,000–80,000 years B.P. wet period. The White Nile system in Bahr El Arab and White Nile Rifts remained a closed lake until the connection of the Victoria Nile to the main system some 12,500 years ago during the African humid period.Role in the founding of Egyptian civilization

 The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile". An unending source of sustenance, it played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian civilization. Because the river overflowed its banks annually and deposited new layers of silt, the surrounding land was very fertile. The Ancient Egyptians cultivated and traded wheat, flax, papyrus and other crops around the Nile. Wheat was a crucial crop in the famine-plagued Middle East. This trading system secured Egypt's diplomatic relationships with other countries and contributed to economic stability. Far-reaching trade has been carried on along the Nile since ancient times. A tune, Hymn to the Nile, was created and sung by the ancient Egyptian peoples about the flooding of the Nile River and all of the miracles it brought to Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Water buffalo were introduced from Asia, and the Assyrian people, Assyrians introduced camels in the 7th century BC. These animals were raised for meat and were domesticated and used for ploughing—or in the camels' case, carriage. Water was vital to both people and livestock. The Nile was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.
The Nile was also an important part of ancient Egyptian spiritual life. Hapi (Nile god), Hapi was the god of the annual floods, and both he and the pharaoh were thought to control the flooding. The Nile was considered to be a causeway from life to death and the afterlife. The east was thought of as a place of birth and growth, and the west was considered the place of death, as the god Ra, the Sun, underwent birth, death, and resurrection each day as he crossed the sky. Thus, all tombs were west of the Nile, because the Egyptians believed that in order to enter the afterlife, they had to be buried on the side that symbolized death.
As the Nile was such an important factor in Egyptian life, the ancient calendar was even based on the three cycles of the Nile. These seasons, each consisting of four months of thirty days each, were called Season of the Inundation, Akhet, Season of the Emergence, Peret, and Season of the Harvest, Shemu. Akhet, which means inundation, was the time of the year when the Nile flooded, leaving several layers of fertile soil behind, aiding in agricultural growth. Peret was the growing season, and Shemu, the last season, was the harvest season when there were no rains.
The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile". An unending source of sustenance, it played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian civilization. Because the river overflowed its banks annually and deposited new layers of silt, the surrounding land was very fertile. The Ancient Egyptians cultivated and traded wheat, flax, papyrus and other crops around the Nile. Wheat was a crucial crop in the famine-plagued Middle East. This trading system secured Egypt's diplomatic relationships with other countries and contributed to economic stability. Far-reaching trade has been carried on along the Nile since ancient times. A tune, Hymn to the Nile, was created and sung by the ancient Egyptian peoples about the flooding of the Nile River and all of the miracles it brought to Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Water buffalo were introduced from Asia, and the Assyrian people, Assyrians introduced camels in the 7th century BC. These animals were raised for meat and were domesticated and used for ploughing—or in the camels' case, carriage. Water was vital to both people and livestock. The Nile was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.
The Nile was also an important part of ancient Egyptian spiritual life. Hapi (Nile god), Hapi was the god of the annual floods, and both he and the pharaoh were thought to control the flooding. The Nile was considered to be a causeway from life to death and the afterlife. The east was thought of as a place of birth and growth, and the west was considered the place of death, as the god Ra, the Sun, underwent birth, death, and resurrection each day as he crossed the sky. Thus, all tombs were west of the Nile, because the Egyptians believed that in order to enter the afterlife, they had to be buried on the side that symbolized death.
As the Nile was such an important factor in Egyptian life, the ancient calendar was even based on the three cycles of the Nile. These seasons, each consisting of four months of thirty days each, were called Season of the Inundation, Akhet, Season of the Emergence, Peret, and Season of the Harvest, Shemu. Akhet, which means inundation, was the time of the year when the Nile flooded, leaving several layers of fertile soil behind, aiding in agricultural growth. Peret was the growing season, and Shemu, the last season, was the harvest season when there were no rains.
European search for the source
 Owing to their failure to penetrate the Sudd wetlands of South Sudan, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Various expeditions failed to determine the river's source. Agatharchides records that in the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, a military expedition had penetrated far enough along the course of the Blue Nile to determine that the summer floods were caused by heavy seasonal rainstorms in the Ethiopian Highlands, but no European of antiquity is known to have reached Lake Tana. The ''Tabula Rogeriana'' depicted the source as three lakes in 1154.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the Middle East and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Society of Jesus, Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páez's account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páez's contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Blue Nile Falls, Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Cicero's ''De Republica''. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also uses his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder writes that the Nile had its origins "in a mountain of lower Mauretania", flowed above ground for "many days" distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground "for a distance of 20 days' journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians."
Owing to their failure to penetrate the Sudd wetlands of South Sudan, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Various expeditions failed to determine the river's source. Agatharchides records that in the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, a military expedition had penetrated far enough along the course of the Blue Nile to determine that the summer floods were caused by heavy seasonal rainstorms in the Ethiopian Highlands, but no European of antiquity is known to have reached Lake Tana. The ''Tabula Rogeriana'' depicted the source as three lakes in 1154.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the Middle East and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Society of Jesus, Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páez's account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páez's contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Blue Nile Falls, Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Cicero's ''De Republica''. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also uses his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder writes that the Nile had its origins "in a mountain of lower Mauretania", flowed above ground for "many days" distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground "for a distance of 20 days' journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians."
 Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the Turco-Egyptian conquest of Sudan (1820–1824), conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, and his sons from 1821 onward. As a result of this, the Blue Nile was known as far as its exit from the Ethiopian foothills and the White Nile as far as the mouth of the Sobat River. Three expeditions under a Turkish officer, Selim Bimbashi, were made between 1839 and 1842, and two got to the point about beyond the present port of Juba, where the country rises and rapids make navigation very difficult.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proven his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A quarrel ensued which sparked intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Speke's discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.
Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the Turco-Egyptian conquest of Sudan (1820–1824), conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, and his sons from 1821 onward. As a result of this, the Blue Nile was known as far as its exit from the Ethiopian foothills and the White Nile as far as the mouth of the Sobat River. Three expeditions under a Turkish officer, Selim Bimbashi, were made between 1839 and 1842, and two got to the point about beyond the present port of Juba, where the country rises and rapids make navigation very difficult.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proven his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A quarrel ensued which sparked intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Speke's discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.
Since 1950


 The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the Jonglei Canal to bypass the swamp.
Nile cities include Khartoum, Aswan, Luxor (Thebes), and the GizaCairo conurbation. The first cataract, the closest to the mouth of the river, is at Aswan, north of the Aswan Dam. This part of the river is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as feluccas. Many cruise ships ply the route between Luxor and Aswan, stopping at Edfu and Kom Ombo along the way. Security concerns have limited cruising on the northernmost portion for many years.
A computer simulation study to plan the economic development of the Nile was directed by H.A.W. Morrice and W.N. Allan, for the Ministry of Hydro-power of Sudan, during 1955–57 Morrice was their hydrological adviser, and Allan his predecessor. The calculations were enabled by accurate monthly inflow data collected for 50 years. The underlying principle was the use of over-year storage, to conserve water from rainy years for use in dry years. Irrigation, navigation and other needs were considered. Each computer run postulated a set of reservoirs and operating equations for the release of water as a function of the month and the levels upstream. The behavior that would have resulted given the inflow data was modeled. Over 600 models were run. Recommendations were made to the Sudanese authorities. The calculations were run on an IBM 650 computer. Simulation studies to design water resources are discussed further in the article on hydrology transport models, which have been used since the 1980s to analyze water quality.
Despite the development of many reservoirs, drought during the 1980s led to widespread starvation in Ethiopia and Sudan, but Egypt was nourished by water impounded in Lake Nasser. Drought has proven to be a major cause of fatality in the Nile river basin. According to a report by the Strategic Foresight Group around 170 million people have been affected by droughts in the last century with half a million lives lost.Blue Peace for the Nile, 2009
The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the Jonglei Canal to bypass the swamp.
Nile cities include Khartoum, Aswan, Luxor (Thebes), and the GizaCairo conurbation. The first cataract, the closest to the mouth of the river, is at Aswan, north of the Aswan Dam. This part of the river is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as feluccas. Many cruise ships ply the route between Luxor and Aswan, stopping at Edfu and Kom Ombo along the way. Security concerns have limited cruising on the northernmost portion for many years.
A computer simulation study to plan the economic development of the Nile was directed by H.A.W. Morrice and W.N. Allan, for the Ministry of Hydro-power of Sudan, during 1955–57 Morrice was their hydrological adviser, and Allan his predecessor. The calculations were enabled by accurate monthly inflow data collected for 50 years. The underlying principle was the use of over-year storage, to conserve water from rainy years for use in dry years. Irrigation, navigation and other needs were considered. Each computer run postulated a set of reservoirs and operating equations for the release of water as a function of the month and the levels upstream. The behavior that would have resulted given the inflow data was modeled. Over 600 models were run. Recommendations were made to the Sudanese authorities. The calculations were run on an IBM 650 computer. Simulation studies to design water resources are discussed further in the article on hydrology transport models, which have been used since the 1980s to analyze water quality.
Despite the development of many reservoirs, drought during the 1980s led to widespread starvation in Ethiopia and Sudan, but Egypt was nourished by water impounded in Lake Nasser. Drought has proven to be a major cause of fatality in the Nile river basin. According to a report by the Strategic Foresight Group around 170 million people have been affected by droughts in the last century with half a million lives lost.Blue Peace for the Nile, 2009; Report by Strategic Foresight Group From the 70 incidents of drought which took place between 1900 and 2012, 55 incidents took place in Ethiopia, Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya and Tanzania.
Water sharing dispute
 The Nile's water has affected the politics of East Africa and the Horn of Africa for many decades. The dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the $4.5 billion Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam has become a national preoccupation in both countries, stoking patriotism, deep-seated fears and even murmurs of war. Countries including Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and Kenya have complained about Egyptian domination of its water resources. The Nile Basin Initiative promotes a peaceful cooperation among those states.
Several attempts have been made to establish agreements between the countries sharing the Nile waters. On 14 May 2010 at Entebbe, Uganda, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania signed a new agreement on sharing the Nile water even though this agreement raised strong opposition from Egypt and Sudan. Ideally, such international agreements should promote equitable and efficient usage of the Nile basin's water resources. Without a better understanding about the availability of the future water resources of the Nile, it is possible that conflicts could arise between these countries relying on the Nile for their water supply, economic and social developments.
The Nile's water has affected the politics of East Africa and the Horn of Africa for many decades. The dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the $4.5 billion Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam has become a national preoccupation in both countries, stoking patriotism, deep-seated fears and even murmurs of war. Countries including Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and Kenya have complained about Egyptian domination of its water resources. The Nile Basin Initiative promotes a peaceful cooperation among those states.
Several attempts have been made to establish agreements between the countries sharing the Nile waters. On 14 May 2010 at Entebbe, Uganda, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania signed a new agreement on sharing the Nile water even though this agreement raised strong opposition from Egypt and Sudan. Ideally, such international agreements should promote equitable and efficient usage of the Nile basin's water resources. Without a better understanding about the availability of the future water resources of the Nile, it is possible that conflicts could arise between these countries relying on the Nile for their water supply, economic and social developments.
Modern achievements and exploration
White Nile
In 1951, American John Goddard (adventurer), John Goddard together with two French explorers became the first to successfully navigate the entire Nile from its source in Burundi at the potential headsprings of the Kagera River in Burundi to its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, a journey of approximately . Their 9-month journey is described in the book ''Kayaks down the Nile''. The White Nile Expedition, led by South African national Hendrik Coetzee, navigated the White Nile's entire length of approximately . The expedition began at the White Nile's beginning at Lake Victoria in Uganda, on 17 January 2004 and arrived at the Mediterranean in Rosetta, four and a half months later.Blue Nile
The Blue Nile Expedition, led by geologist Pasquale Scaturro and his partner, kayaker and documentary filmmaker Gordon Brown became the first known people to descend the entire Blue Nile, from Lake Tana in Ethiopia to the beaches of Alexandria on the Mediterranean. Their approximately journey took 114 days, from 25 December 2003 to 28 April 2004. Though their expedition included others, Brown and Scaturro were the only ones to complete the entire journey. Although they descended whitewater manually, the team used Outboard motor, outboard motors for much of their journey. On 29 January 2005, Canadian Les Jickling and New Zealander Mark Tanner completed the first human-powered transit of Ethiopia's Blue Nile. Their journey of over took five months. They recount that they paddled through two war zones, regions notorious for bandits, and were arrested at gunpoint.Mark TannerPaddling the Blue Nile in Flood
. Retrieved 1 November 2014
Crossings
Crossings from Khartoum to the Mediterranean Sea
 The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
* Soba (city), Soba Bridge
The following bridges cross the White Nile and connect Khartoum to Omdurman:
* White Nile Bridge
* Fitayhab Bridge
* Al Dabbaseen Bridge (under construction)
* Omhuraz Bridge (proposed)
The following bridges cross from Omdurman: to Khartoum North:
* Shambat Bridge
* Halfia Bridge
The following bridges cross to Tuti from Khartoum state's three cities
* Tuti Bridge, Khartoum-Tuti Bridge
* Omdurman-Tuti Suspension Bridge (proposed)
* Khartoum North-Tuti Bridge (proposed)
Other bridges
* Shandi Bridge, Shendi
* Atbarah Bridge, Atbarah
* Merowe Dam, Merowe, Sudan, Merowe
* Merowe Bridge, Merowe
* Aswan Bridge, Aswan
* Luxor Bridge, Luxor
* Suhag Bridge, Suhag, Egypt, Suhag
* Assiut Bridge, Assiut
* Al Minya Bridge, Minya, Egypt, Minya
* Al Marazeek Bridge, Helwan
* First Ring Road Bridge (Moneeb Crossing),
The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
* Soba (city), Soba Bridge
The following bridges cross the White Nile and connect Khartoum to Omdurman:
* White Nile Bridge
* Fitayhab Bridge
* Al Dabbaseen Bridge (under construction)
* Omhuraz Bridge (proposed)
The following bridges cross from Omdurman: to Khartoum North:
* Shambat Bridge
* Halfia Bridge
The following bridges cross to Tuti from Khartoum state's three cities
* Tuti Bridge, Khartoum-Tuti Bridge
* Omdurman-Tuti Suspension Bridge (proposed)
* Khartoum North-Tuti Bridge (proposed)
Other bridges
* Shandi Bridge, Shendi
* Atbarah Bridge, Atbarah
* Merowe Dam, Merowe, Sudan, Merowe
* Merowe Bridge, Merowe
* Aswan Bridge, Aswan
* Luxor Bridge, Luxor
* Suhag Bridge, Suhag, Egypt, Suhag
* Assiut Bridge, Assiut
* Al Minya Bridge, Minya, Egypt, Minya
* Al Marazeek Bridge, Helwan
* First Ring Road Bridge (Moneeb Crossing), Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
* Abbas Bridge, Cairo
* University Bridge, Cairo
* Qasr al-Nil Bridge, Cairo
* 6th October Bridge, Cairo
* Boulak Bridge, Abu El Ela Bridge, Cairo (removed in 1998)
* New Abu El Ela Bridge, Cairo
* Imbaba Bridge, Cairo
* Rod Elfarag Bridge, Cairo
* Second Ring Road Bridge, Cairo
* Banha Bridge, Banha
* Samanoud Bridge, Samanoud
* Mansoura 2 Bridges, Mansoura
* Talkha Bridge, Talkha
* Shirbine high Bridge
* Shirbine Bridge
* Kafr Sad – Farscor Bridge
* International Coastal Road Bridge
* Damietta high Bridge, Damietta
* Damietta Bridge, Damietta
* Kafr El Zayat Bridges, Kafr El Zayat
* Zefta Bridge, Zefta
Crossings from Jinja, Uganda to Khartoum
* Source of the Nile Bridge, Jinja District, Jinja, Uganda * River Nile Railway Bridge, Jinja District, Jinja, Uganda * Nalubaale Bridge, Jinja, Uganda (Formerly Owen Falls, Owen Falls Bridge) * Karuma Bridge, Karuma, Uganda * Pakwach Bridge, UgandaSee also
* Bujagali Hydroelectric Power Station * Egyptian Public Works * Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station * Water politics in the Nile Basin * Merowe Dam * Nalubaale Hydroelectric Power Station * Orders of magnitude (length), Orders of magnitude * Vid Flumina, a river of liquid methane and ethane on Saturn's moon Titan * ''The River War'' (1899), Winston Churchill's second book, an account of steaming up the Nile to the Battle of Omdurman, Sudan, in 1898Notes and references
;Notes ;References ;SourcesFurther reading
* * Tim Jeal, Jeal, Tim (2011). ''Explorers of the Nile: The Triumph and Tragedy of a Great Victorian Adventure''. * Moorehead, Alan, "The White Nile" (Hamish Hamilton, 1960; revised and illustrated edition, 1971). Abridged illustrated edition, as The Story of the White Nile (Harper & Row, 1967) * Moorehead, Alan, "The Blue Nile" (Hamish Hamilton, 1962; revised and illustrated edition, 1972). Abridged illustrated edition, as The Story of the Blue Nile (Harper & Row, 1966) * Tvedt, Terje, ed. ''The River Nile in the Post-Colonial Age: Conflict and Cooperation Among the Nile Basin Countries'' (I.B. Tauris, 2010) 293 pages; studies of the river's finite resources as shared by multiple nations in the post-colonial era; includes research by scholars from Burundi, Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. * Tvedt, Terje, (2004) "The Nile: An Annotated Bibliography", London/New York,External links
A Struggle Over the Nile
– slideshow by ''The New York Times''
Thesis Analyzing Nile River Negotiations
*
Old maps of the Nile
from the Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel {{Authority control Nile, International rivers of Africa Nile basin, * Rivers of Egypt Rivers of Sudan Rivers of South Sudan Rivers of Uganda Geography of ancient Egypt Hebrew Bible rivers National parks of Egypt Water transport in Egypt Articles containing video clips Rivers of Africa