Nickel world production.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nickel is a
 Nickel is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge that takes a high polish. It is one of only four elements that are Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic at or near room temperature; the others are iron,
Nickel is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge that takes a high polish. It is one of only four elements that are Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic at or near room temperature; the others are iron,
To read the nickel atom levels, type "Ni I" in the Spectrum box and click on Retrieve data. However, each of these two configurations splits into several energy levels due to fine structure, and the two sets of energy levels overlap. The average energy of states with [Ar] 3d 4s is actually lower than the average energy of states with [Ar] 3d 4s. Therefore, the research literature on atomic calculations quotes the ground state configuration as [Ar] 3d 4s.
 On Earth, nickel occurs most often in combination with sulfur and iron in
On Earth, nickel occurs most often in combination with sulfur and iron in
 Nickel tetracarbonyl ), discovered by Ludwig Mond, is a volatile, highly toxic liquid at room temperature. On heating, the complex decomposes back to nickel and carbon monoxide:
:
This behavior is exploited in the Mond process for purifying nickel, as described above. The related nickel(0) complex bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is a useful catalyst in organonickel chemistry because the 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, cyclooctadiene (or ''cod'') ligands are easily displaced.
Nickel tetracarbonyl ), discovered by Ludwig Mond, is a volatile, highly toxic liquid at room temperature. On heating, the complex decomposes back to nickel and carbon monoxide:
:
This behavior is exploited in the Mond process for purifying nickel, as described above. The related nickel(0) complex bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is a useful catalyst in organonickel chemistry because the 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, cyclooctadiene (or ''cod'') ligands are easily displaced.
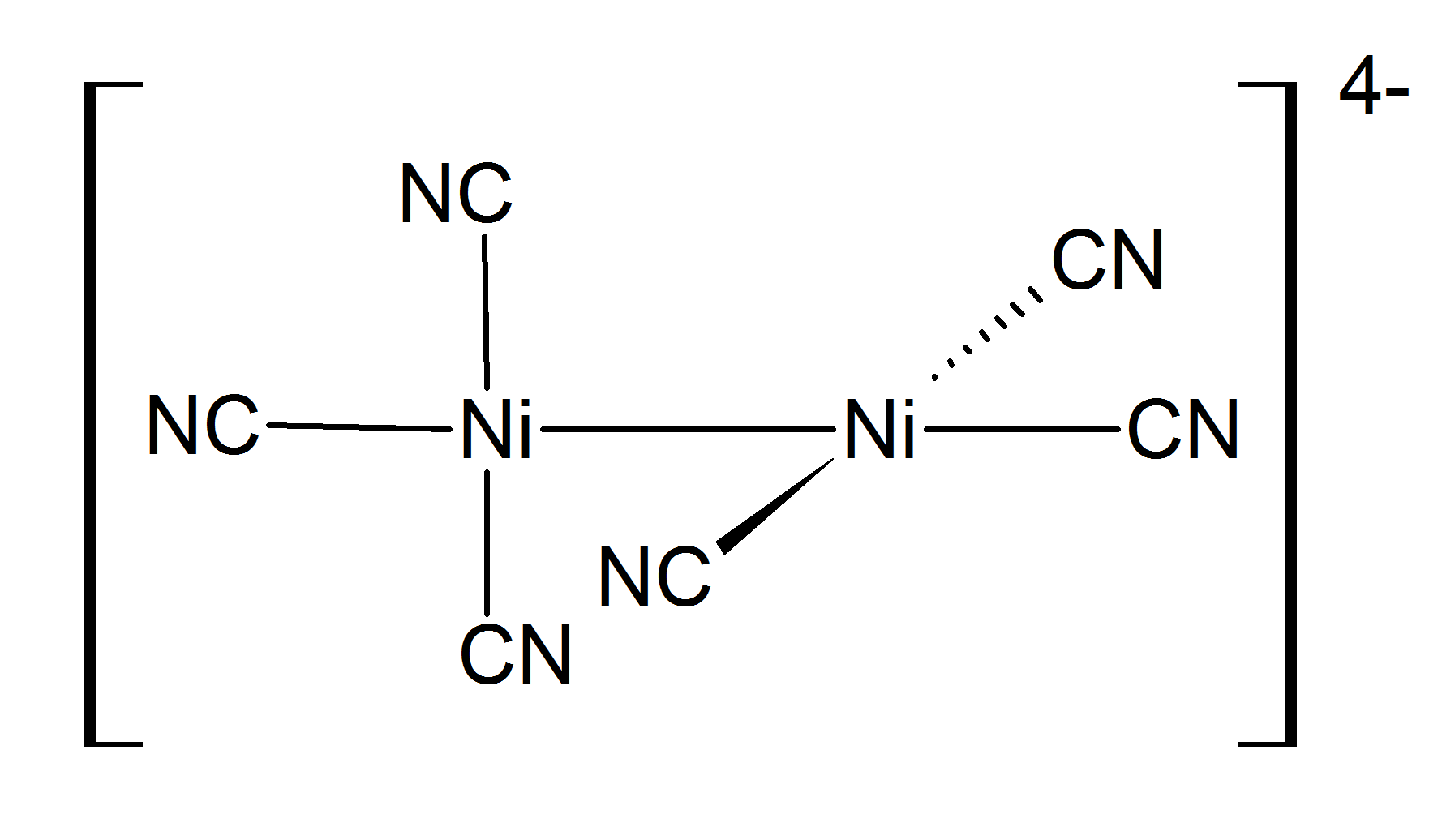 Nickel(I) complexes are uncommon, but one example is the tetrahedral complex . Many nickel(I) complexes have Ni–Ni bonding, such as the dark red diamagnetic prepared by reduction of with sodium amalgam. This compound is oxidized in water, liberating .
It is thought that the nickel(I) oxidation state is important to nickel-containing enzymes, such as NiFe Hydrogenase, [NiFe]-hydrogenase, which catalyzes the reversible reduction of protons to .
Nickel(I) complexes are uncommon, but one example is the tetrahedral complex . Many nickel(I) complexes have Ni–Ni bonding, such as the dark red diamagnetic prepared by reduction of with sodium amalgam. This compound is oxidized in water, liberating .
It is thought that the nickel(I) oxidation state is important to nickel-containing enzymes, such as NiFe Hydrogenase, [NiFe]-hydrogenase, which catalyzes the reversible reduction of protons to .

 Nickel(II) forms compounds with all common anions, including nickel sulfide, sulfide, nickel sulfate, sulfate, carbonate, hydroxide, carboxylates, and halides. Nickel(II) sulfate is produced in large amounts by dissolving nickel metal or oxides in sulfuric acid, forming both a hexa- and heptahydrateLascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David and Beyersmann, Detmar (2019) "Nickel Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. useful for nickel electroplating, electroplating nickel. Common salts of nickel, such as chloride, nitrate, and sulfate, dissolve in water to give green solutions of the metal aquo complex .
The four halides form nickel compounds, which are solids with molecules with octahedral Ni centres. Nickel(II) chloride is most common, and its behavior is illustrative of the other halides. Nickel(II) chloride is made by dissolving nickel or its oxide in hydrochloric acid. It is usually found as the green hexahydrate, whose formula is usually written . When dissolved in water, this salt forms the metal aquo complex . Dehydration of gives yellow anhydrous .
Some tetracoordinate nickel(II) complexes, e.g. bis(triphenylphosphine)nickel chloride, exist both in tetrahedral and square planar geometries. The tetrahedral complexes are paramagnetic; the square planar complexes are diamagnetic. In having properties of magnetic equilibrium and formation of octahedral complexes, they contrast with the divalent complexes of the heavier group 10 metals, palladium(II) and platinum(II), which form only square-planar geometry.
Nickelocene is known; it has an Electron counting, electron count of 20, making it relatively unstable.
Nickel(II) forms compounds with all common anions, including nickel sulfide, sulfide, nickel sulfate, sulfate, carbonate, hydroxide, carboxylates, and halides. Nickel(II) sulfate is produced in large amounts by dissolving nickel metal or oxides in sulfuric acid, forming both a hexa- and heptahydrateLascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David and Beyersmann, Detmar (2019) "Nickel Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. useful for nickel electroplating, electroplating nickel. Common salts of nickel, such as chloride, nitrate, and sulfate, dissolve in water to give green solutions of the metal aquo complex .
The four halides form nickel compounds, which are solids with molecules with octahedral Ni centres. Nickel(II) chloride is most common, and its behavior is illustrative of the other halides. Nickel(II) chloride is made by dissolving nickel or its oxide in hydrochloric acid. It is usually found as the green hexahydrate, whose formula is usually written . When dissolved in water, this salt forms the metal aquo complex . Dehydration of gives yellow anhydrous .
Some tetracoordinate nickel(II) complexes, e.g. bis(triphenylphosphine)nickel chloride, exist both in tetrahedral and square planar geometries. The tetrahedral complexes are paramagnetic; the square planar complexes are diamagnetic. In having properties of magnetic equilibrium and formation of octahedral complexes, they contrast with the divalent complexes of the heavier group 10 metals, palladium(II) and platinum(II), which form only square-planar geometry.
Nickelocene is known; it has an Electron counting, electron count of 20, making it relatively unstable.
 Many Ni(III) compounds are known. The first such compounds are , where X = chlorine, Cl, bromine, Br, iodine, I and R = Ethyl group, ethyl, propyl, butyl. Further, Ni(III) forms simple salts with fluoride or Nickel(III) oxide, oxide ions. Ni(III) can be stabilized by σ-donor ligands such as thiols and organophosphines.
Ni(III) occurs in nickel oxide hydroxide, which is used as the cathode in many Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries, including nickel-cadmium, nickel-iron battery, nickel-iron, Nickel hydrogen battery, nickel hydrogen, and nickel-metal hydride battery, nickel-metal hydride, and used by certain manufacturers in Li-ion batteries.
Ni(IV) occurs in the mixed oxide . Ni(IV) remains a rare oxidation state and very few compounds are known.
Many Ni(III) compounds are known. The first such compounds are , where X = chlorine, Cl, bromine, Br, iodine, I and R = Ethyl group, ethyl, propyl, butyl. Further, Ni(III) forms simple salts with fluoride or Nickel(III) oxide, oxide ions. Ni(III) can be stabilized by σ-donor ligands such as thiols and organophosphines.
Ni(III) occurs in nickel oxide hydroxide, which is used as the cathode in many Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries, including nickel-cadmium, nickel-iron battery, nickel-iron, Nickel hydrogen battery, nickel hydrogen, and nickel-metal hydride battery, nickel-metal hydride, and used by certain manufacturers in Li-ion batteries.
Ni(IV) occurs in the mixed oxide . Ni(IV) remains a rare oxidation state and very few compounds are known.
 In medieval Germany, a metallic yellow mineral was found in the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains) that resembled copper ore. But when miners were unable to get any copper from it, they blamed a mischievous sprite of German mythology, Nickel (similar to ''Devil in Christianity, Old Nick''), for besetting the copper. They called this ore ''Kupfernickel'' from German ''Kupfer'' 'copper'. This ore is now known as the mineral nickeline (formerly ''niccolite''), a nickel arsenide. In 1751, Baron
In medieval Germany, a metallic yellow mineral was found in the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains) that resembled copper ore. But when miners were unable to get any copper from it, they blamed a mischievous sprite of German mythology, Nickel (similar to ''Devil in Christianity, Old Nick''), for besetting the copper. They called this ore ''Kupfernickel'' from German ''Kupfer'' 'copper'. This ore is now known as the mineral nickeline (formerly ''niccolite''), a nickel arsenide. In 1751, Baron
 Aside from the aforementioned Bactrian coins, nickel was not a component of coins until the mid-19th century.
Aside from the aforementioned Bactrian coins, nickel was not a component of coins until the mid-19th century.
 In the United States, the term "nickel" or "nick" originally applied to the copper-nickel Flying Eagle cent, which replaced copper with 12% nickel 1857–58, then the Indian Head cent of the same alloy from 1859 to 1864. Still later, in 1865, the term designated the Three-cent piece (United States coin), three-cent nickel, with nickel increased to 25%. In 1866, the Nickel (United States coin)#Shield nickel (1866–1883), five-cent shield nickel (25% nickel, 75% copper) appropriated the designation, which has been used ever since for the subsequent 5-cent pieces. This alloy proportion is not ferromagnetic.
The Nickel (United States coin), US nickel coin contains of nickel, which at the April 2007 price was worth 6.5 cents, along with 3.75 grams of copper worth about 3 cents, with a total metal value of more than 9 cents. Since the face value of a nickel is 5 cents, this made it an attractive target for melting by people wanting to sell the metals at a profit. The United States Mint, anticipating this practice, implemented new interim rules on December 14, 2006, subject to public comment for 30 days, which criminalized the melting and export of cents and nickels. Violators can be punished with a fine of up to $10,000 and/or a maximum of five years in prison. As of September 19, 2013, the melt value of a US nickel (copper and nickel included) is $0.045 (90% of the face value).
In the United States, the term "nickel" or "nick" originally applied to the copper-nickel Flying Eagle cent, which replaced copper with 12% nickel 1857–58, then the Indian Head cent of the same alloy from 1859 to 1864. Still later, in 1865, the term designated the Three-cent piece (United States coin), three-cent nickel, with nickel increased to 25%. In 1866, the Nickel (United States coin)#Shield nickel (1866–1883), five-cent shield nickel (25% nickel, 75% copper) appropriated the designation, which has been used ever since for the subsequent 5-cent pieces. This alloy proportion is not ferromagnetic.
The Nickel (United States coin), US nickel coin contains of nickel, which at the April 2007 price was worth 6.5 cents, along with 3.75 grams of copper worth about 3 cents, with a total metal value of more than 9 cents. Since the face value of a nickel is 5 cents, this made it an attractive target for melting by people wanting to sell the metals at a profit. The United States Mint, anticipating this practice, implemented new interim rules on December 14, 2006, subject to public comment for 30 days, which criminalized the melting and export of cents and nickels. Violators can be punished with a fine of up to $10,000 and/or a maximum of five years in prison. As of September 19, 2013, the melt value of a US nickel (copper and nickel included) is $0.045 (90% of the face value).

 An estimated 2.7 million tonnes (t) of nickel per year are mined worldwide; Nickel mining in Indonesia, Indonesia (1,000,000 t), the Philippines (370,000 t),
An estimated 2.7 million tonnes (t) of nickel per year are mined worldwide; Nickel mining in Indonesia, Indonesia (1,000,000 t), the Philippines (370,000 t),
 Nickel is obtained through extractive metallurgy: it is extracted from ore by conventional roasting and reduction processes that yield metal of greater than 75% purity. In many stainless steel applications, 75% pure nickel can be used without further purification, depending on impurities.
Traditionally, most sulfide ores are processed using pyrometallurgical techniques to produce a Matte (metallurgy), matte for further refining. Recent advances in hydrometallurgy, hydrometallurgical techniques result in significantly purer metallic nickel product. Most sulfide deposits have traditionally been processed by concentration through a froth flotation process followed by pyrometallurgical extraction. In hydrometallurgical processes, nickel sulfide ores are concentrated with Froth flotation, flotation (differential flotation if Ni/Fe ratio is too low) and then smelted. The nickel matte is further processed with the Cobalt extraction techniques#Recovery from nickel-cobalt sulfide concentrates (Sherritt process), Sherritt-Gordon process. First, copper is removed by adding hydrogen sulfide, leaving a concentrate of cobalt and nickel. Then, solvent extraction is used to separate the cobalt and nickel, with the final nickel content greater than 99%.
Nickel is obtained through extractive metallurgy: it is extracted from ore by conventional roasting and reduction processes that yield metal of greater than 75% purity. In many stainless steel applications, 75% pure nickel can be used without further purification, depending on impurities.
Traditionally, most sulfide ores are processed using pyrometallurgical techniques to produce a Matte (metallurgy), matte for further refining. Recent advances in hydrometallurgy, hydrometallurgical techniques result in significantly purer metallic nickel product. Most sulfide deposits have traditionally been processed by concentration through a froth flotation process followed by pyrometallurgical extraction. In hydrometallurgical processes, nickel sulfide ores are concentrated with Froth flotation, flotation (differential flotation if Ni/Fe ratio is too low) and then smelted. The nickel matte is further processed with the Cobalt extraction techniques#Recovery from nickel-cobalt sulfide concentrates (Sherritt process), Sherritt-Gordon process. First, copper is removed by adding hydrogen sulfide, leaving a concentrate of cobalt and nickel. Then, solvent extraction is used to separate the cobalt and nickel, with the final nickel content greater than 99%.

 The purest metal is obtained from nickel oxide by the Mond process, which gives a purity of over 99.99%. The process was patented by Ludwig Mond and has been in industrial use since before the beginning of the 20th century. In this process, nickel is reacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a sulfur catalyst at around 40–80 °C to form nickel carbonyl. In a similar reaction with iron, iron pentacarbonyl can form, though this reaction is slow. If necessary, the nickel may be separated by distillation. Dicobalt octacarbonyl is also formed in nickel distillation as a by-product, but it decomposes to tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl at the reaction temperature to give a non-volatile solid.
Nickel is obtained from nickel carbonyl by one of two processes. It may be passed through a large chamber at high temperatures in which tens of thousands of nickel spheres (pellets) are constantly stirred. The carbonyl decomposes and deposits pure nickel onto the spheres. In the alternate process, nickel carbonyl is decomposed in a smaller chamber at 230 °C to create a fine nickel powder. The byproduct carbon monoxide is recirculated and reused. The highly pure nickel product is known as "carbonyl nickel".
The purest metal is obtained from nickel oxide by the Mond process, which gives a purity of over 99.99%. The process was patented by Ludwig Mond and has been in industrial use since before the beginning of the 20th century. In this process, nickel is reacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a sulfur catalyst at around 40–80 °C to form nickel carbonyl. In a similar reaction with iron, iron pentacarbonyl can form, though this reaction is slow. If necessary, the nickel may be separated by distillation. Dicobalt octacarbonyl is also formed in nickel distillation as a by-product, but it decomposes to tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl at the reaction temperature to give a non-volatile solid.
Nickel is obtained from nickel carbonyl by one of two processes. It may be passed through a large chamber at high temperatures in which tens of thousands of nickel spheres (pellets) are constantly stirred. The carbonyl decomposes and deposits pure nickel onto the spheres. In the alternate process, nickel carbonyl is decomposed in a smaller chamber at 230 °C to create a fine nickel powder. The byproduct carbon monoxide is recirculated and reused. The highly pure nickel product is known as "carbonyl nickel".
 Global use of nickel is currently 68% in stainless steel, 10% in nonferrous
Global use of nickel is currently 68% in stainless steel, 10% in nonferrous  Because nickel is resistant to corrosion, it was occasionally used as a substitute for decorative silver. Nickel was also occasionally used in some countries after 1859 as a cheap coinage metal (see above), but in the later years of the 20th century, it was replaced by cheaper stainless steel (i.e., iron) alloys, except in the United States and Canada.
Nickel is an excellent alloying agent for certain precious metals and is used in the Metallurgical assay, fire assay as a collector of Platinum group, platinum group elements (PGE). As such, nickel can fully collect all six PGEs from ores, and can partially collect gold. High-throughput nickel mines may also do PGE recovery (mainly platinum and palladium); examples are Norilsk, Russia and the Sudbury Basin, Canada.
Metal foam, Nickel foam or nickel mesh is used in gas diffusion electrodes for alkaline fuel cells.
Nickel and its alloys are often used as catalysts for hydrogenation reactions. Raney nickel, a finely divided nickel-aluminium alloy, is one common form, though related catalysts are also used, including Raney-type catalysts.
Nickel is naturally magnetostrictive: in the presence of a magnetic field, the material undergoes a small change in length. The magnetostriction of nickel is on the order of 50 ppm and is negative, indicating that it contracts.
Nickel is used as a binder in the cemented tungsten carbide or hardmetal industry and used in proportions of 6% to 12% by weight. Nickel makes the tungsten carbide magnetic and adds corrosion-resistance to the cemented parts, though the hardness is less than those with cobalt binder.
, with half-life 100.1 years, is useful in krytron devices as a beta particle (high-speed electron) emitter to make ionization by the keep-alive electrode more reliable. It is being investigated as a power source for Betavoltaic device, betavoltaic batteries.
Around 27% of all nickel production is used for engineering, 10% for building and construction, 14% for tubular products, 20% for metal goods, 14% for transport, 11% for electronic goods, and 5% for other uses.
Raney nickel is widely used for hydrogenation of Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated oils to make margarine, and substandard margarine and leftover oil may contain nickel as a contaminant. Forte et al. found that type 2 diabetic patients have 0.89 ng/mL of Ni in the blood relative to 0.77 ng/mL in control subjects.
Because nickel is resistant to corrosion, it was occasionally used as a substitute for decorative silver. Nickel was also occasionally used in some countries after 1859 as a cheap coinage metal (see above), but in the later years of the 20th century, it was replaced by cheaper stainless steel (i.e., iron) alloys, except in the United States and Canada.
Nickel is an excellent alloying agent for certain precious metals and is used in the Metallurgical assay, fire assay as a collector of Platinum group, platinum group elements (PGE). As such, nickel can fully collect all six PGEs from ores, and can partially collect gold. High-throughput nickel mines may also do PGE recovery (mainly platinum and palladium); examples are Norilsk, Russia and the Sudbury Basin, Canada.
Metal foam, Nickel foam or nickel mesh is used in gas diffusion electrodes for alkaline fuel cells.
Nickel and its alloys are often used as catalysts for hydrogenation reactions. Raney nickel, a finely divided nickel-aluminium alloy, is one common form, though related catalysts are also used, including Raney-type catalysts.
Nickel is naturally magnetostrictive: in the presence of a magnetic field, the material undergoes a small change in length. The magnetostriction of nickel is on the order of 50 ppm and is negative, indicating that it contracts.
Nickel is used as a binder in the cemented tungsten carbide or hardmetal industry and used in proportions of 6% to 12% by weight. Nickel makes the tungsten carbide magnetic and adds corrosion-resistance to the cemented parts, though the hardness is less than those with cobalt binder.
, with half-life 100.1 years, is useful in krytron devices as a beta particle (high-speed electron) emitter to make ionization by the keep-alive electrode more reliable. It is being investigated as a power source for Betavoltaic device, betavoltaic batteries.
Around 27% of all nickel production is used for engineering, 10% for building and construction, 14% for tubular products, 20% for metal goods, 14% for transport, 11% for electronic goods, and 5% for other uses.
Raney nickel is widely used for hydrogenation of Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated oils to make margarine, and substandard margarine and leftover oil may contain nickel as a contaminant. Forte et al. found that type 2 diabetic patients have 0.89 ng/mL of Ni in the blood relative to 0.77 ng/mL in control subjects.
"Nickel and nickel compounds"
in ''IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum''. Volume 100C. pp. 169–218..Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures, Amending and Repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 [OJ L 353, 31.12.2008, p. 1]
Annex VI
. Accessed July 13, 2017.Globally Harmonised System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
, 5th ed., United Nations, New York and Geneva, 2013..National Toxicology Program. (2016)
, 14th ed. Research Triangle Park, NC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service.. based on increased respiratory cancer risks observed in epidemiological studies of sulfidic ore refinery workers. This is supported by the positive results of the NTP bioassays with Ni sub-sulfide and Ni oxide in rats and mice. The human and animal data consistently indicate a lack of carcinogenicity via the oral route of exposure and limit the carcinogenicity of nickel compounds to respiratory tumours after inhalation. Nickel metal is classified as a suspect carcinogen; there is consistency between the absence of increased respiratory cancer risks in workers predominantly exposed to metallic nickel and the lack of respiratory tumours in a rat lifetime inhalation carcinogenicity study with nickel metal powder. In the rodent inhalation studies with various nickel compounds and nickel metal, increased lung inflammations with and without bronchial lymph node hyperplasia or fibrosis were observed. In rat studies, oral ingestion of water-soluble nickel salts can trigger perinatal mortality in pregnant animals. Whether these effects are relevant to humans is unclear as epidemiological studies of highly exposed female workers have not shown adverse developmental toxicity effects. People can be exposed to nickel in the workplace by inhalation, ingestion, and contact with skin or eye. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for the workplace at 1 mg/m per 8-hour workday, excluding nickel carbonyl. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) sets the recommended exposure limit (REL) at 0.015 mg/m per 8-hour workday. At 10 mg/m, nickel is immediately dangerous to life and health. Nickel carbonyl is an extremely toxic gas. The toxicity of metal carbonyls is a function of both the toxicity of the metal and the off-gassing of carbon monoxide from the carbonyl functional groups; nickel carbonyl is also explosive in air. Sensitization (immunology), Sensitized persons may show a skin contact Nickel allergy (nickel allergic contact dermatitis), allergy to nickel known as a contact dermatitis. Highly sensitized persons may also react to foods with high nickel content. Patients with Dyshidrosis, pompholyx may also be sensitive to nickel. Nickel is the top confirmed contact allergen worldwide, partly due to its use in jewelry for pierced ears. Nickel allergies affecting pierced ears are often marked by itchy, red skin. Many earrings are now made without nickel or with low-release nickel to address this problem. The amount allowed in products that contact human skin is now regulated by the European Union. In 2002, researchers found that the nickel released by 1 and 2 euro coins, far exceeded those standards. This is believed to be due to a Galvanization, galvanic reaction. Nickel was voted Allergen of the Year in 2008 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society. In August 2015, the American Academy of Dermatology adopted a position statement on the safety of nickel: "Estimates suggest that contact dermatitis, which includes nickel sensitization, accounts for approximately $1.918 billion and affects nearly 72.29 million people."Position Statement on Nickel Sensitivity
. American Academy of Dermatology(August 22, 2015) Reports show that both the nickel-induced activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and the up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible genes are caused by depletion of intracellular ascorbate. The addition of ascorbate to the culture medium increased the intracellular ascorbate level and reversed both the metal-induced stabilization of HIF-1- and HIF-1α-dependent gene expression.
Nickel
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
CDC – Nickel – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
An occupational hygiene assessment of dermal nickel exposures in primary production industries
by GW Hughson. Institute of Occupational Medicine Research Report TM/04/05
An occupational hygiene assessment of dermal nickel exposures in primary production and primary user industries. Phase 2 Report
by GW Hughson. Institute of Occupational Medicine Research Report TM/05/06
"The metal that brought you cheap flights"
BBC News {{Authority control Nickel, Chemical elements Transition metals Dietary minerals Ferromagnetic materials IARC Group 2B carcinogens Native element minerals Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with symbol Ni and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union ...
because a passivation layer of nickel oxide
Nickel oxide may refer to:
* Nickel(II) oxide, NiO, green, well-characterised oxide
* Nickel(III) oxide
Nickel (III) oxide is the inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydr ...
forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rock
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
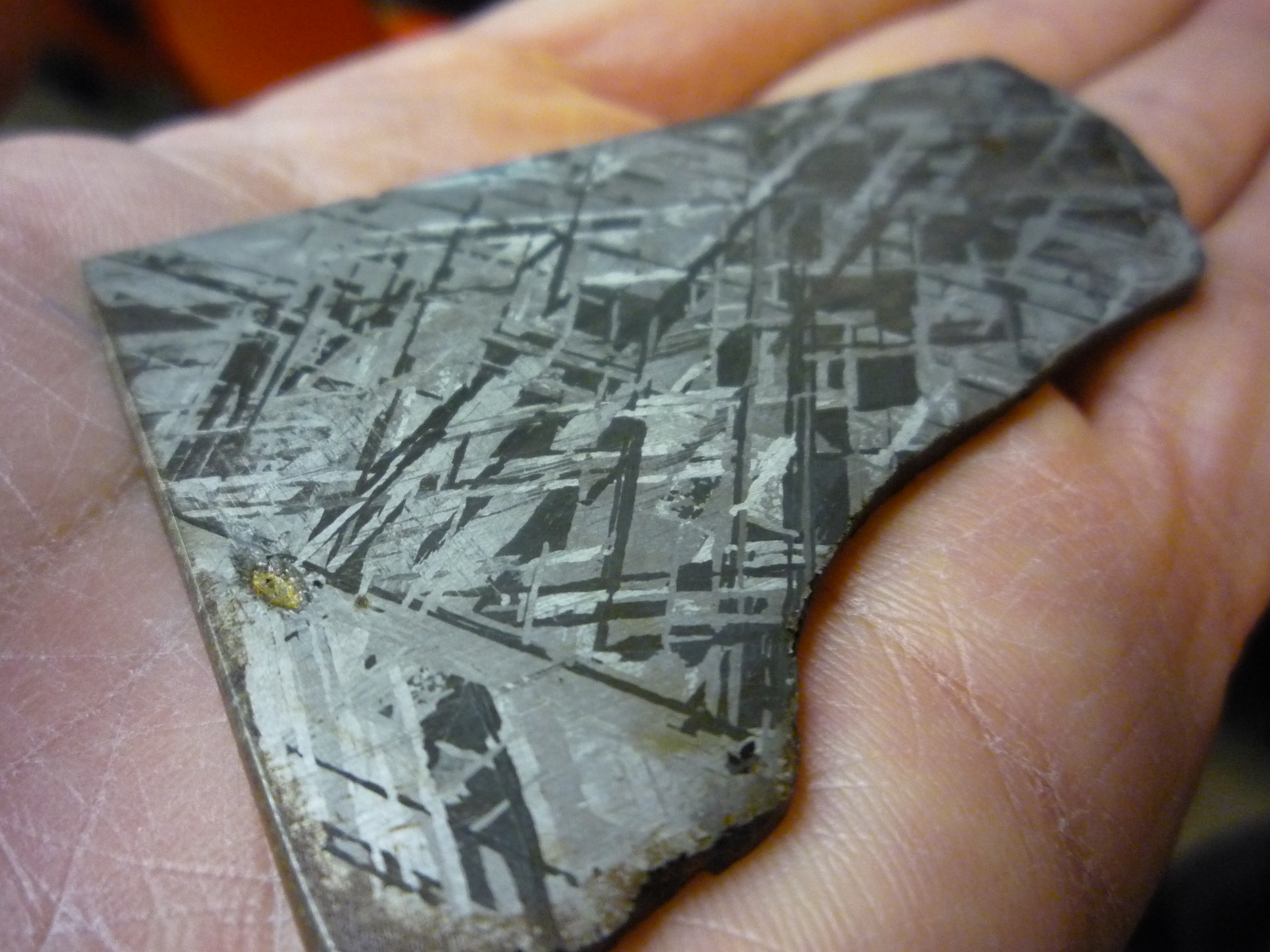
s, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere.
Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores.
Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an element in 1751 by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt
Baron Axel Fredrik Cronstedt (''/kroonstet/'' 23 December 1722 – 19 August 1765) was a Swedish mineralogist and chemist who discovered the element nickel in 1751 as a mining expert with the Bureau of Mines.
Cronstedt is considered a founder ...
, who initially mistook the ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 Apr ...
for a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
, in the cobalt mines of Los, Hälsingland, Sweden. The element's name comes from a mischievous sprite of German miner mythology, Nickel (similar to Old Nick), who personified the fact that copper-nickel ores resisted refinement into copper. An economically important source of nickel is the iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
ore limonite, which is often 1–2% nickel. Other important nickel ore minerals include pentlandite
Pentlandite is an iron–nickel sulfide with the chemical formula . Pentlandite has a narrow variation range in Ni:Fe but it is usually described as having a Ni:Fe of 1:1. It also contains minor cobalt, usually at low levels as a fraction of wei ...
and a mix of Ni-rich natural silicates known as garnierite
Garnierite is a general name for a green nickel ore which is found in pockets and veins within weathered and serpentinized ultramafic rocks. It forms by lateritic weathering of ultramafic rocks and occurs in many nickel laterite deposits in the ...
. Major production sites include the Sudbury region, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(which is thought to be of meteoric origin), New Caledonia in the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
, and Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk, ''Norílʹsk'') is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
Nickel is one of four elements (the others are iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
, and gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
) that are ferromagnetic at about room temperature. Alnico
Alnico is a family of iron alloys which in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co), hence the acronym ''al-ni-co''. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium. Alnico alloys are ferromagnetic, ...
permanent magnets
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel ...
based partly on nickel are of intermediate strength between iron-based permanent magnets and rare-earth magnets. The metal is used chiefly in alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s and corrosion-resistant plating. About 68% of world production is used in stainless steel. A further 10% is used for nickel-based and copper-based alloys, 9% for plating, 7% for alloy steels, 3% in foundries, and 4% in other applications such as in rechargeable batteries, including those in electric vehicles (EVs). Nickel is widely used in coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
, though nickel-plated objects sometimes provoke nickel allergy
Nickel allergy or nickel allergic contact dermatitis (Ni-ACD) is a form of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) caused by exposure to the chemical element nickel. It typically causes a rash that is red and itchy and that may be bumpy or scaly. The ...
. As a compound, nickel has a number of niche chemical manufacturing uses, such as a Raney nickel, catalyst for hydrogenation, cathodes for rechargeable batteries, pigments and metal surface treatments. Nickel is an essential nutrient for some microorganisms and plants that have enzymes with nickel as an active site.
Properties
Atomic and physical properties
 Nickel is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge that takes a high polish. It is one of only four elements that are Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic at or near room temperature; the others are iron,
Nickel is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge that takes a high polish. It is one of only four elements that are Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic at or near room temperature; the others are iron, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
and gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
. Its Curie temperature is , meaning that bulk nickel is non-magnetic above this temperature. The unit cell of nickel is a Cubic crystal system, face-centered cube with the lattice parameter of 0.352 nm, giving an atomic radius of 0.124 nm. This crystal structure is stable to pressures of at least 70 GPa. Nickel is hard, malleable and ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
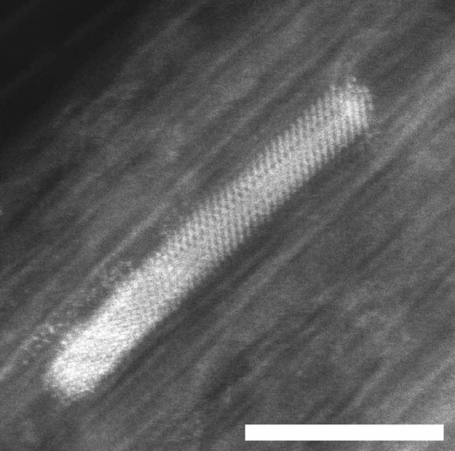
, and has a relatively high Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical and thermal conductivity for transition metals. The high compressive strength of 34 GPa, predicted for ideal crystals, is never obtained in the real bulk material due to formation and movement of dislocations. However, it has been reached in Ni nanoparticles.
Electron configuration dispute
Nickel has two atomic electron configurations, [Ar] 3d 4s and [Ar] 3d 4s, which are very close in energy; [Ar] denotes the complete argon core structure. There is some disagreement on which configuration has the lower energy. Chemistry textbooks quote nickel's electron configuration as [Ar] 4s 3d, also written [Ar] 3d 4s. This configuration agrees with the Madelung rule, Madelung energy ordering rule, which predicts that 4s is filled before 3d. It is supported by the experimental fact that the lowest energy state of the nickel atom is a 3d 4s energy level, specifically the 3d(F) 4s F, ''J'' = 4 level.NIST Atomic Spectrum DatabaseTo read the nickel atom levels, type "Ni I" in the Spectrum box and click on Retrieve data. However, each of these two configurations splits into several energy levels due to fine structure, and the two sets of energy levels overlap. The average energy of states with [Ar] 3d 4s is actually lower than the average energy of states with [Ar] 3d 4s. Therefore, the research literature on atomic calculations quotes the ground state configuration as [Ar] 3d 4s.
Isotopes
The isotopes of nickel range in atomic weight from 48 atomic mass unit, u () to 78 u (). Natural nickel is composed of five stable isotopes, , , , and , of which is the most abundant (68.077% natural abundance). Nickel-62 has the highest nuclear binding energy, binding energy per nucleon of any nuclide: 8.7946 MeV/nucleon. Its binding energy is greater than both iron-56, and iron-58, , more abundant nuclides often incorrectly cited as having the highest binding energy. Though this would seem to predict nickel as the most abundant heavy element in the universe, the high rate of photodisintegration of nickel in stellar interiors causes iron to be by far the most abundant. Nickel-60 is the daughter product of the extinct radionuclide iron-60, (half-life 2.6 million years). Due to the long half-life of , its persistence in materials in the Solar System may generate observable variations in the isotopic composition of . Therefore, the abundance of in extraterrestrial material may give insight into the origin of the Solar System and its early history. At least 26 nickel radioisotopes have been characterized; the most stable are with half-life 76,000 years, (100 years), and (6 days). All other radioisotopes have half-lives less than 60 hours and most these have half-lives less than 30 seconds. This element also has one meta state. Radioactive nickel-56 is produced by the silicon burning process and later set free in large amounts in Type Ia supernova, type Ia supernovae. The shape of the light curve of these supernovae at intermediate to late-times corresponds to the decay via electron capture of tocobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
-56 and ultimately to iron-56. Nickel-59 is a long-lived cosmogenic nuclide, cosmogenic radionuclide; half-life 76,000 years. has found many applications in isotope geology. has been used to date the terrestrial age of meteorites and to determine abundances of extraterrestrial dust in ice and sediment. The half-life of nickel-78 was recently measured at 110 milliseconds, and is believed an important isotope in supernova nucleosynthesis of elements heavier than iron. Ni, discovered in 1999, is the most proton-rich heavy element isotope known. With 28 protons and 20 neutrons, Ni is "doubly magic", as is Ni with 28 protons and 50 neutrons. Both are therefore unusually stable for nuclei with so large a neutron–proton ratio, proton–neutron imbalance.
Nickel-63 is a contaminant found in the support structure of nuclear reactors. It is produced through neutron capture by nickel-62. Small amounts have also been found near nuclear weapon test sites in the South Pacific.
Occurrence
 On Earth, nickel occurs most often in combination with sulfur and iron in
On Earth, nickel occurs most often in combination with sulfur and iron in pentlandite
Pentlandite is an iron–nickel sulfide with the chemical formula . Pentlandite has a narrow variation range in Ni:Fe but it is usually described as having a Ni:Fe of 1:1. It also contains minor cobalt, usually at low levels as a fraction of wei ...
, with sulfur in millerite, with arsenic in the mineral nickeline, and with arsenic and sulfur in nickel galena. Nickel is commonly found in iron meteorites as the alloys kamacite and taenite. Nickel in meteorites was first detected in 1799 by Joseph Proust, Joseph-Louis Proust, a French chemist who then worked in Spain. Proust analyzed samples of the meteorite from Campo del Cielo (Argentina), which had been obtained in 1783 by Miguel Rubín de Celis, discovering the presence in them of nickel (about 10%) along with iron.
The bulk of nickel is Nickel mine, mined from two types of ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 Apr ...
deposits. The first is laterite, where the principal ore mineral mixtures are nickeliferous limonite, (Fe,Ni)O(OH), and garnierite
Garnierite is a general name for a green nickel ore which is found in pockets and veins within weathered and serpentinized ultramafic rocks. It forms by lateritic weathering of ultramafic rocks and occurs in many nickel laterite deposits in the ...
(a mixture of various hydrous nickel and nickel-rich silicates). The second is magmatic sulfide deposits, where the principal ore mineral is pentlandite
Pentlandite is an iron–nickel sulfide with the chemical formula . Pentlandite has a narrow variation range in Ni:Fe but it is usually described as having a Ni:Fe of 1:1. It also contains minor cobalt, usually at low levels as a fraction of wei ...
: .
Indonesia and Australia have the biggest estimated reserves, at 43.6% of world total.
Identified land-based resources throughout the world averaging 1% nickel or greater comprise at least 130 million tons of nickel (about the double of known reserves). About 60% is in laterites and 40% in sulfide deposits.
On geophysics, geophysical evidence, most of the nickel on Earth is believed to be in Earth's outer core, outer and inner cores. Kamacite and taenite are naturally occurring alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s of iron and nickel. For kamacite, the alloy is usually in the proportion of 90:10 to 95:5, though impurities (such as cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
or carbon) may be present. Taenite is 20% to 65% nickel. Kamacite and taenite are also found in nickel iron meteorites.
Compounds
The most common oxidation state of nickel is +2, but compounds of , , and are well known, and the exotic oxidation states and have been produced and studied.Nickel(0)
 Nickel tetracarbonyl ), discovered by Ludwig Mond, is a volatile, highly toxic liquid at room temperature. On heating, the complex decomposes back to nickel and carbon monoxide:
:
This behavior is exploited in the Mond process for purifying nickel, as described above. The related nickel(0) complex bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is a useful catalyst in organonickel chemistry because the 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, cyclooctadiene (or ''cod'') ligands are easily displaced.
Nickel tetracarbonyl ), discovered by Ludwig Mond, is a volatile, highly toxic liquid at room temperature. On heating, the complex decomposes back to nickel and carbon monoxide:
:
This behavior is exploited in the Mond process for purifying nickel, as described above. The related nickel(0) complex bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is a useful catalyst in organonickel chemistry because the 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, cyclooctadiene (or ''cod'') ligands are easily displaced.
Nickel(I)
 Nickel(I) complexes are uncommon, but one example is the tetrahedral complex . Many nickel(I) complexes have Ni–Ni bonding, such as the dark red diamagnetic prepared by reduction of with sodium amalgam. This compound is oxidized in water, liberating .
It is thought that the nickel(I) oxidation state is important to nickel-containing enzymes, such as NiFe Hydrogenase, [NiFe]-hydrogenase, which catalyzes the reversible reduction of protons to .
Nickel(I) complexes are uncommon, but one example is the tetrahedral complex . Many nickel(I) complexes have Ni–Ni bonding, such as the dark red diamagnetic prepared by reduction of with sodium amalgam. This compound is oxidized in water, liberating .
It is thought that the nickel(I) oxidation state is important to nickel-containing enzymes, such as NiFe Hydrogenase, [NiFe]-hydrogenase, which catalyzes the reversible reduction of protons to .
Nickel(II)

 Nickel(II) forms compounds with all common anions, including nickel sulfide, sulfide, nickel sulfate, sulfate, carbonate, hydroxide, carboxylates, and halides. Nickel(II) sulfate is produced in large amounts by dissolving nickel metal or oxides in sulfuric acid, forming both a hexa- and heptahydrateLascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David and Beyersmann, Detmar (2019) "Nickel Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. useful for nickel electroplating, electroplating nickel. Common salts of nickel, such as chloride, nitrate, and sulfate, dissolve in water to give green solutions of the metal aquo complex .
The four halides form nickel compounds, which are solids with molecules with octahedral Ni centres. Nickel(II) chloride is most common, and its behavior is illustrative of the other halides. Nickel(II) chloride is made by dissolving nickel or its oxide in hydrochloric acid. It is usually found as the green hexahydrate, whose formula is usually written . When dissolved in water, this salt forms the metal aquo complex . Dehydration of gives yellow anhydrous .
Some tetracoordinate nickel(II) complexes, e.g. bis(triphenylphosphine)nickel chloride, exist both in tetrahedral and square planar geometries. The tetrahedral complexes are paramagnetic; the square planar complexes are diamagnetic. In having properties of magnetic equilibrium and formation of octahedral complexes, they contrast with the divalent complexes of the heavier group 10 metals, palladium(II) and platinum(II), which form only square-planar geometry.
Nickelocene is known; it has an Electron counting, electron count of 20, making it relatively unstable.
Nickel(II) forms compounds with all common anions, including nickel sulfide, sulfide, nickel sulfate, sulfate, carbonate, hydroxide, carboxylates, and halides. Nickel(II) sulfate is produced in large amounts by dissolving nickel metal or oxides in sulfuric acid, forming both a hexa- and heptahydrateLascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David and Beyersmann, Detmar (2019) "Nickel Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. useful for nickel electroplating, electroplating nickel. Common salts of nickel, such as chloride, nitrate, and sulfate, dissolve in water to give green solutions of the metal aquo complex .
The four halides form nickel compounds, which are solids with molecules with octahedral Ni centres. Nickel(II) chloride is most common, and its behavior is illustrative of the other halides. Nickel(II) chloride is made by dissolving nickel or its oxide in hydrochloric acid. It is usually found as the green hexahydrate, whose formula is usually written . When dissolved in water, this salt forms the metal aquo complex . Dehydration of gives yellow anhydrous .
Some tetracoordinate nickel(II) complexes, e.g. bis(triphenylphosphine)nickel chloride, exist both in tetrahedral and square planar geometries. The tetrahedral complexes are paramagnetic; the square planar complexes are diamagnetic. In having properties of magnetic equilibrium and formation of octahedral complexes, they contrast with the divalent complexes of the heavier group 10 metals, palladium(II) and platinum(II), which form only square-planar geometry.
Nickelocene is known; it has an Electron counting, electron count of 20, making it relatively unstable.
Nickel(III) and (IV)
 Many Ni(III) compounds are known. The first such compounds are , where X = chlorine, Cl, bromine, Br, iodine, I and R = Ethyl group, ethyl, propyl, butyl. Further, Ni(III) forms simple salts with fluoride or Nickel(III) oxide, oxide ions. Ni(III) can be stabilized by σ-donor ligands such as thiols and organophosphines.
Ni(III) occurs in nickel oxide hydroxide, which is used as the cathode in many Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries, including nickel-cadmium, nickel-iron battery, nickel-iron, Nickel hydrogen battery, nickel hydrogen, and nickel-metal hydride battery, nickel-metal hydride, and used by certain manufacturers in Li-ion batteries.
Ni(IV) occurs in the mixed oxide . Ni(IV) remains a rare oxidation state and very few compounds are known.
Many Ni(III) compounds are known. The first such compounds are , where X = chlorine, Cl, bromine, Br, iodine, I and R = Ethyl group, ethyl, propyl, butyl. Further, Ni(III) forms simple salts with fluoride or Nickel(III) oxide, oxide ions. Ni(III) can be stabilized by σ-donor ligands such as thiols and organophosphines.
Ni(III) occurs in nickel oxide hydroxide, which is used as the cathode in many Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries, including nickel-cadmium, nickel-iron battery, nickel-iron, Nickel hydrogen battery, nickel hydrogen, and nickel-metal hydride battery, nickel-metal hydride, and used by certain manufacturers in Li-ion batteries.
Ni(IV) occurs in the mixed oxide . Ni(IV) remains a rare oxidation state and very few compounds are known.
History
Because nickel ores are easily mistaken for ores of silver and copper, understanding of this metal and its use, is relatively recent. But unintentional use of nickel is ancient, and can be traced back as far as 3500 BCE. Bronzes from what is now Syria have been found to contain as much as 2% nickel. Some ancient Chinese manuscripts suggest that "white copper" (cupronickel, known as ''baitong'') was used there in 1700-1400 BCE. This Paktong white copper was exported to Britain as early as the 17th century, but the nickel content of this alloy was not discovered until 1822. Coins of nickel-copper alloy were minted by Bactrian kings Agathocles of Bactria, Agathocles, Euthydemus II, and Pantaleon in the 2nd century BCE, possibly out of the Chinese cupronickel. In medieval Germany, a metallic yellow mineral was found in the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains) that resembled copper ore. But when miners were unable to get any copper from it, they blamed a mischievous sprite of German mythology, Nickel (similar to ''Devil in Christianity, Old Nick''), for besetting the copper. They called this ore ''Kupfernickel'' from German ''Kupfer'' 'copper'. This ore is now known as the mineral nickeline (formerly ''niccolite''), a nickel arsenide. In 1751, Baron
In medieval Germany, a metallic yellow mineral was found in the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains) that resembled copper ore. But when miners were unable to get any copper from it, they blamed a mischievous sprite of German mythology, Nickel (similar to ''Devil in Christianity, Old Nick''), for besetting the copper. They called this ore ''Kupfernickel'' from German ''Kupfer'' 'copper'. This ore is now known as the mineral nickeline (formerly ''niccolite''), a nickel arsenide. In 1751, Baron Axel Fredrik Cronstedt
Baron Axel Fredrik Cronstedt (''/kroonstet/'' 23 December 1722 – 19 August 1765) was a Swedish mineralogist and chemist who discovered the element nickel in 1751 as a mining expert with the Bureau of Mines.
Cronstedt is considered a founder ...
tried to extract copper from kupfernickel at a cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
mine in the village of Los, Sweden, and instead produced a white metal that he named ''nickel'' after the spirit that had given its name to the mineral. In modern German, Kupfernickel or Kupfer-Nickel designates the alloy cupronickel.
Originally, the only source for nickel was the rare Kupfernickel. Beginning in 1824, nickel was obtained as a byproduct of cobalt blue production. The first large-scale smelting of nickel began in Norway in 1848 from nickel-rich pyrrhotite. The introduction of nickel in steel production in 1889 increased the demand for nickel; the nickel deposits of New Caledonia, discovered in 1865, provided most of the world's supply between 1875 and 1915. The discovery of the large deposits in the Sudbury Basin, Canada in 1883, in Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk, ''Norílʹsk'') is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk ...
-Talnakh, Russia in 1920, and in the Merensky Reef, South Africa in 1924, made large-scale nickel production possible.
Coinage
 Aside from the aforementioned Bactrian coins, nickel was not a component of coins until the mid-19th century.
Aside from the aforementioned Bactrian coins, nickel was not a component of coins until the mid-19th century.
Canada
Nickel (Canadian coin), 99.9% nickel five-cent coins were struck in Canada (the world's largest nickel producer at the time) during non-war years from 1922 to 1981; the metal content made these coins magnetic. During the war years 1942–45, most or all nickel was removed from Canadian and US coins to save it for making armor. Canada used 99.9% nickel from 1968 in its higher-value coins until 2000.Switzerland
Coins of nearly pure nickel were first used in 1881 in Switzerland.United Kingdom
Birmingham forged nickel coins in for trading in Malaysia.United States
 In the United States, the term "nickel" or "nick" originally applied to the copper-nickel Flying Eagle cent, which replaced copper with 12% nickel 1857–58, then the Indian Head cent of the same alloy from 1859 to 1864. Still later, in 1865, the term designated the Three-cent piece (United States coin), three-cent nickel, with nickel increased to 25%. In 1866, the Nickel (United States coin)#Shield nickel (1866–1883), five-cent shield nickel (25% nickel, 75% copper) appropriated the designation, which has been used ever since for the subsequent 5-cent pieces. This alloy proportion is not ferromagnetic.
The Nickel (United States coin), US nickel coin contains of nickel, which at the April 2007 price was worth 6.5 cents, along with 3.75 grams of copper worth about 3 cents, with a total metal value of more than 9 cents. Since the face value of a nickel is 5 cents, this made it an attractive target for melting by people wanting to sell the metals at a profit. The United States Mint, anticipating this practice, implemented new interim rules on December 14, 2006, subject to public comment for 30 days, which criminalized the melting and export of cents and nickels. Violators can be punished with a fine of up to $10,000 and/or a maximum of five years in prison. As of September 19, 2013, the melt value of a US nickel (copper and nickel included) is $0.045 (90% of the face value).
In the United States, the term "nickel" or "nick" originally applied to the copper-nickel Flying Eagle cent, which replaced copper with 12% nickel 1857–58, then the Indian Head cent of the same alloy from 1859 to 1864. Still later, in 1865, the term designated the Three-cent piece (United States coin), three-cent nickel, with nickel increased to 25%. In 1866, the Nickel (United States coin)#Shield nickel (1866–1883), five-cent shield nickel (25% nickel, 75% copper) appropriated the designation, which has been used ever since for the subsequent 5-cent pieces. This alloy proportion is not ferromagnetic.
The Nickel (United States coin), US nickel coin contains of nickel, which at the April 2007 price was worth 6.5 cents, along with 3.75 grams of copper worth about 3 cents, with a total metal value of more than 9 cents. Since the face value of a nickel is 5 cents, this made it an attractive target for melting by people wanting to sell the metals at a profit. The United States Mint, anticipating this practice, implemented new interim rules on December 14, 2006, subject to public comment for 30 days, which criminalized the melting and export of cents and nickels. Violators can be punished with a fine of up to $10,000 and/or a maximum of five years in prison. As of September 19, 2013, the melt value of a US nickel (copper and nickel included) is $0.045 (90% of the face value).
Current use
In the 21st century, the high price of nickel has led to some replacement of the metal in coins around the world. Coins still made with nickel alloys include one- and two-euro coins, 5¢, 10¢, 25¢, 50¢, and $1 Coins of the United States dollar, U.S. coins, and 20p, 50p, £1, and £2 coins of the pound sterling, UK coins. From 2012 on the nickel-alloy used for 5p and 10p UK coins was replaced with nickel-plated steel. This ignited a public controversy regarding the problems of people withnickel allergy
Nickel allergy or nickel allergic contact dermatitis (Ni-ACD) is a form of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) caused by exposure to the chemical element nickel. It typically causes a rash that is red and itchy and that may be bumpy or scaly. The ...
.
World production
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
(250,000 t), New Caledonia (France) (190,000 t), Australia (160,000 t) and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(130,000 t) are the largest producers as of 2021. The largest nickel deposits in non-Russian Europe are in Finland and Greece. Identified land-based sources averaging at least 1% nickel contain at least 130 million tonnes of nickel. About 60% is in laterites and 40% is in sulfide deposits. Also, extensive nickel sources are found in the depths of the Pacific Ocean, especially in an area called the Clarion Clipperton Zone in the form of polymetallic nodules peppering the seafloor at 3.5–6 km below sea level. These nodules are composed of numerous rare-earth metals and are estimated to be 1.7% nickel. With advances in science and engineering, regulation is currently being set in place by the International Seabed Authority to ensure that these nodules are collected in an environmentally conscientious manner while adhering to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
The one place in the United States where nickel has been profitably mined is Riddle, Oregon, with several square miles of nickel-bearing garnierite
Garnierite is a general name for a green nickel ore which is found in pockets and veins within weathered and serpentinized ultramafic rocks. It forms by lateritic weathering of ultramafic rocks and occurs in many nickel laterite deposits in the ...
surface deposits. The mine closed in 1987. The Eagle mine project is a new nickel mine in Michigan's Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula. Construction was completed in 2013, and operations began in the third quarter of 2014. In the first full year of operation, the Eagle Mine produced 18,000 t.
Production

Electrorefining
A second common refining process is leaching the metal matte into a nickel salt solution, followed by electrowinning the nickel from solution by plating it onto a cathode as electrolytic nickel.Mond process
 The purest metal is obtained from nickel oxide by the Mond process, which gives a purity of over 99.99%. The process was patented by Ludwig Mond and has been in industrial use since before the beginning of the 20th century. In this process, nickel is reacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a sulfur catalyst at around 40–80 °C to form nickel carbonyl. In a similar reaction with iron, iron pentacarbonyl can form, though this reaction is slow. If necessary, the nickel may be separated by distillation. Dicobalt octacarbonyl is also formed in nickel distillation as a by-product, but it decomposes to tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl at the reaction temperature to give a non-volatile solid.
Nickel is obtained from nickel carbonyl by one of two processes. It may be passed through a large chamber at high temperatures in which tens of thousands of nickel spheres (pellets) are constantly stirred. The carbonyl decomposes and deposits pure nickel onto the spheres. In the alternate process, nickel carbonyl is decomposed in a smaller chamber at 230 °C to create a fine nickel powder. The byproduct carbon monoxide is recirculated and reused. The highly pure nickel product is known as "carbonyl nickel".
The purest metal is obtained from nickel oxide by the Mond process, which gives a purity of over 99.99%. The process was patented by Ludwig Mond and has been in industrial use since before the beginning of the 20th century. In this process, nickel is reacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a sulfur catalyst at around 40–80 °C to form nickel carbonyl. In a similar reaction with iron, iron pentacarbonyl can form, though this reaction is slow. If necessary, the nickel may be separated by distillation. Dicobalt octacarbonyl is also formed in nickel distillation as a by-product, but it decomposes to tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl at the reaction temperature to give a non-volatile solid.
Nickel is obtained from nickel carbonyl by one of two processes. It may be passed through a large chamber at high temperatures in which tens of thousands of nickel spheres (pellets) are constantly stirred. The carbonyl decomposes and deposits pure nickel onto the spheres. In the alternate process, nickel carbonyl is decomposed in a smaller chamber at 230 °C to create a fine nickel powder. The byproduct carbon monoxide is recirculated and reused. The highly pure nickel product is known as "carbonyl nickel".
Market value
The market price of nickel surged throughout 2006 and the early months of 2007; , the metal was trading at United States dollar, US$52,300/tonne or $1.47/oz. The price later fell dramatically; , the metal was trading at $11,000/tonne, or $0.31/oz. During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, worries about sanctions on Russian nickel exports triggered a short squeeze, causing the price of nickel to quadruple in just two days, reaching US$100,000 per tonne. The London Metal Exchange cancelled contracts worth $3.9 billion and suspended nickel trading for over a week. Analyst Andy Home argued that such price shocks are exacerbated by the purity requirements imposed by metal markets: only Grade I (99.8% pure) metal can be used as a commodity on the exchanges, but most of the world's supply is either in ferro-nickel alloys or lower-grade purities.Applications
 Global use of nickel is currently 68% in stainless steel, 10% in nonferrous
Global use of nickel is currently 68% in stainless steel, 10% in nonferrous alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s, 9% electroplating, 7% alloy steel, 3% foundries, and 4% other (including batteries).
Nickel is used in many recognizable industrial and consumer products, including stainless steel, alnico magnets, coinage, Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries (e.g. nickel–iron battery, nickel-iron), electric guitar strings, microphone capsules, plating on plumbing fixtures, and special alloys such as permalloy, elinvar, and invar. It is used for plating and as a green tint in glass. Nickel is preeminently an alloy metal, and its chief use is in nickel steels and nickel cast irons, in which it typically increases the tensile strength, toughness, and elastic limit. It is widely used in many other alloys, including nickel brasses and bronzes and alloys with copper, chromium, aluminium, lead, cobalt, silver, and gold (Inconel, Incoloy, Monel, Nimonic).
 Because nickel is resistant to corrosion, it was occasionally used as a substitute for decorative silver. Nickel was also occasionally used in some countries after 1859 as a cheap coinage metal (see above), but in the later years of the 20th century, it was replaced by cheaper stainless steel (i.e., iron) alloys, except in the United States and Canada.
Nickel is an excellent alloying agent for certain precious metals and is used in the Metallurgical assay, fire assay as a collector of Platinum group, platinum group elements (PGE). As such, nickel can fully collect all six PGEs from ores, and can partially collect gold. High-throughput nickel mines may also do PGE recovery (mainly platinum and palladium); examples are Norilsk, Russia and the Sudbury Basin, Canada.
Metal foam, Nickel foam or nickel mesh is used in gas diffusion electrodes for alkaline fuel cells.
Nickel and its alloys are often used as catalysts for hydrogenation reactions. Raney nickel, a finely divided nickel-aluminium alloy, is one common form, though related catalysts are also used, including Raney-type catalysts.
Nickel is naturally magnetostrictive: in the presence of a magnetic field, the material undergoes a small change in length. The magnetostriction of nickel is on the order of 50 ppm and is negative, indicating that it contracts.
Nickel is used as a binder in the cemented tungsten carbide or hardmetal industry and used in proportions of 6% to 12% by weight. Nickel makes the tungsten carbide magnetic and adds corrosion-resistance to the cemented parts, though the hardness is less than those with cobalt binder.
, with half-life 100.1 years, is useful in krytron devices as a beta particle (high-speed electron) emitter to make ionization by the keep-alive electrode more reliable. It is being investigated as a power source for Betavoltaic device, betavoltaic batteries.
Around 27% of all nickel production is used for engineering, 10% for building and construction, 14% for tubular products, 20% for metal goods, 14% for transport, 11% for electronic goods, and 5% for other uses.
Raney nickel is widely used for hydrogenation of Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated oils to make margarine, and substandard margarine and leftover oil may contain nickel as a contaminant. Forte et al. found that type 2 diabetic patients have 0.89 ng/mL of Ni in the blood relative to 0.77 ng/mL in control subjects.
Because nickel is resistant to corrosion, it was occasionally used as a substitute for decorative silver. Nickel was also occasionally used in some countries after 1859 as a cheap coinage metal (see above), but in the later years of the 20th century, it was replaced by cheaper stainless steel (i.e., iron) alloys, except in the United States and Canada.
Nickel is an excellent alloying agent for certain precious metals and is used in the Metallurgical assay, fire assay as a collector of Platinum group, platinum group elements (PGE). As such, nickel can fully collect all six PGEs from ores, and can partially collect gold. High-throughput nickel mines may also do PGE recovery (mainly platinum and palladium); examples are Norilsk, Russia and the Sudbury Basin, Canada.
Metal foam, Nickel foam or nickel mesh is used in gas diffusion electrodes for alkaline fuel cells.
Nickel and its alloys are often used as catalysts for hydrogenation reactions. Raney nickel, a finely divided nickel-aluminium alloy, is one common form, though related catalysts are also used, including Raney-type catalysts.
Nickel is naturally magnetostrictive: in the presence of a magnetic field, the material undergoes a small change in length. The magnetostriction of nickel is on the order of 50 ppm and is negative, indicating that it contracts.
Nickel is used as a binder in the cemented tungsten carbide or hardmetal industry and used in proportions of 6% to 12% by weight. Nickel makes the tungsten carbide magnetic and adds corrosion-resistance to the cemented parts, though the hardness is less than those with cobalt binder.
, with half-life 100.1 years, is useful in krytron devices as a beta particle (high-speed electron) emitter to make ionization by the keep-alive electrode more reliable. It is being investigated as a power source for Betavoltaic device, betavoltaic batteries.
Around 27% of all nickel production is used for engineering, 10% for building and construction, 14% for tubular products, 20% for metal goods, 14% for transport, 11% for electronic goods, and 5% for other uses.
Raney nickel is widely used for hydrogenation of Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated oils to make margarine, and substandard margarine and leftover oil may contain nickel as a contaminant. Forte et al. found that type 2 diabetic patients have 0.89 ng/mL of Ni in the blood relative to 0.77 ng/mL in control subjects.
Biological role
It was not recognized until the 1970s, but nickel is known to play an important role in the biology of some plants, bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Nickel enzymes such as urease are considered virulence factors in some organisms. Urease catalyzes hydrolysis of urea to form ammonia and carbamate. NiFe hydrogenases can catalyze oxidation of to form protons and electrons; and also the reverse reaction, the reduction of protons to form hydrogen gas. A nickel-tetrapyrrole coenzyme, cofactor F430, is present in methyl coenzyme M reductase, which can catalyze the formation of methane, or the reverse reaction, in methanogenic archaea (in +1 oxidation state). One of the carbon monoxide dehydrogenase enzymes consists of an iron, Fe-Ni-sulfur, S cluster. Other nickel-bearing enzymes include a rare bacterial class of superoxide dismutase and glyoxalase I enzymes in bacteria and several eukaryotic Trypanosomatid, trypanosomal parasites (in other organisms, including yeast and mammals, this enzyme contains divalent ). Dietary nickel may affect human health through infections by nickel-dependent bacteria, but nickel may also be an essential nutrient for bacteria living in the large intestine, in effect functioning as a Prebiotic (nutrition), prebiotic. The US Institute of Medicine has not confirmed that nickel is an essential nutrient for humans, so neither a Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) nor an Adequate Intake have been established. The tolerable upper intake level of dietary nickel is 1 mg/day as soluble nickel salts. Estimated dietary intake is 70 to 100 µg/day; less than 10% is absorbed. What is absorbed is excreted in urine. Relatively large amounts of nickel – comparable to the estimated average ingestion above – Leaching (chemistry), leach into food cooked in stainless steel. For example, the amount of nickel leached after 10 cooking cycles into one serving of tomato sauce averages 88 µg. Nickel released from Siberian Traps volcanic eruptions is suspected of helping the growth of ''Methanosarcina'', a genus of euryarchaeote archaea that produced methane in the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the biggest known mass extinction.Toxicity
The major source of nickel exposure is oral consumption, as nickel is essential to plants. Typical background concentrations of nickel do not exceed 20 ng/m in air, 100 mg/kg in soil, 10 mg/kg in vegetation, 10 μg/L in freshwater and 1 μg/L in seawater. Environmental concentrations may be increased by human pollution. For example, nickel-plated faucets may contaminate water and soil; mining and smelting may dump nickel into wastewater; nickel–steelalloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
cookware and nickel-pigmented dishes may release nickel into food. Air may be polluted by nickel ore refining and fossil fuel combustion. Humans may absorb nickel directly from tobacco smoke and skin contact with jewelry, shampoos, detergents, and coins. A less common form of chronic exposure is through hemodialysis as traces of nickel ions may be absorbed into the plasma from the chelating action of albumin.
The average daily exposure is not a threat to human health. Most nickel absorbed by humans is removed by the kidneys and passed out of the body through urine or is eliminated through the gastrointestinal tract without being absorbed. Nickel is not a cumulative poison, but larger doses or chronic inhalation exposure may be toxic, even carcinogenic, and constitute an occupational hazard.
Nickel compounds are classified as human carcinogensIARC (2012)"Nickel and nickel compounds"
in ''IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum''. Volume 100C. pp. 169–218..Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures, Amending and Repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 [OJ L 353, 31.12.2008, p. 1]
Annex VI
. Accessed July 13, 2017.Globally Harmonised System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
, 5th ed., United Nations, New York and Geneva, 2013..National Toxicology Program. (2016)
, 14th ed. Research Triangle Park, NC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service.. based on increased respiratory cancer risks observed in epidemiological studies of sulfidic ore refinery workers. This is supported by the positive results of the NTP bioassays with Ni sub-sulfide and Ni oxide in rats and mice. The human and animal data consistently indicate a lack of carcinogenicity via the oral route of exposure and limit the carcinogenicity of nickel compounds to respiratory tumours after inhalation. Nickel metal is classified as a suspect carcinogen; there is consistency between the absence of increased respiratory cancer risks in workers predominantly exposed to metallic nickel and the lack of respiratory tumours in a rat lifetime inhalation carcinogenicity study with nickel metal powder. In the rodent inhalation studies with various nickel compounds and nickel metal, increased lung inflammations with and without bronchial lymph node hyperplasia or fibrosis were observed. In rat studies, oral ingestion of water-soluble nickel salts can trigger perinatal mortality in pregnant animals. Whether these effects are relevant to humans is unclear as epidemiological studies of highly exposed female workers have not shown adverse developmental toxicity effects. People can be exposed to nickel in the workplace by inhalation, ingestion, and contact with skin or eye. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for the workplace at 1 mg/m per 8-hour workday, excluding nickel carbonyl. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) sets the recommended exposure limit (REL) at 0.015 mg/m per 8-hour workday. At 10 mg/m, nickel is immediately dangerous to life and health. Nickel carbonyl is an extremely toxic gas. The toxicity of metal carbonyls is a function of both the toxicity of the metal and the off-gassing of carbon monoxide from the carbonyl functional groups; nickel carbonyl is also explosive in air. Sensitization (immunology), Sensitized persons may show a skin contact Nickel allergy (nickel allergic contact dermatitis), allergy to nickel known as a contact dermatitis. Highly sensitized persons may also react to foods with high nickel content. Patients with Dyshidrosis, pompholyx may also be sensitive to nickel. Nickel is the top confirmed contact allergen worldwide, partly due to its use in jewelry for pierced ears. Nickel allergies affecting pierced ears are often marked by itchy, red skin. Many earrings are now made without nickel or with low-release nickel to address this problem. The amount allowed in products that contact human skin is now regulated by the European Union. In 2002, researchers found that the nickel released by 1 and 2 euro coins, far exceeded those standards. This is believed to be due to a Galvanization, galvanic reaction. Nickel was voted Allergen of the Year in 2008 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society. In August 2015, the American Academy of Dermatology adopted a position statement on the safety of nickel: "Estimates suggest that contact dermatitis, which includes nickel sensitization, accounts for approximately $1.918 billion and affects nearly 72.29 million people."Position Statement on Nickel Sensitivity
. American Academy of Dermatology(August 22, 2015) Reports show that both the nickel-induced activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and the up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible genes are caused by depletion of intracellular ascorbate. The addition of ascorbate to the culture medium increased the intracellular ascorbate level and reversed both the metal-induced stabilization of HIF-1- and HIF-1α-dependent gene expression.
References
External links
Nickel
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
CDC – Nickel – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
An occupational hygiene assessment of dermal nickel exposures in primary production industries
by GW Hughson. Institute of Occupational Medicine Research Report TM/04/05
An occupational hygiene assessment of dermal nickel exposures in primary production and primary user industries. Phase 2 Report
by GW Hughson. Institute of Occupational Medicine Research Report TM/05/06
"The metal that brought you cheap flights"
BBC News {{Authority control Nickel, Chemical elements Transition metals Dietary minerals Ferromagnetic materials IARC Group 2B carcinogens Native element minerals Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure