Manchukuo Hsinking avenue.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a
 The
The

 After the
After the
 China did not recognize Manchukuo but the two sides established official ties for trade, communications, and transportation. In 1933, the
China did not recognize Manchukuo but the two sides established official ties for trade, communications, and transportation. In 1933, the
 Before World War II, the Japanese colonized Manchukuo and used it as a base from which to invade China. The Manchu General Tong Linge was killed in action by the Japanese in the
Before World War II, the Japanese colonized Manchukuo and used it as a base from which to invade China. The Manchu General Tong Linge was killed in action by the Japanese in the
The Soviet Union and the Manchurian Revolutionary Base (1945–1949)
'. Moscow, Progress Publishers. The
 Historians generally consider Manchukuo a
Historians generally consider Manchukuo a  The Kwantung Army for its part tolerated the talk of social revolution in Manchukuo as the best way of gaining support from the Han majority of Manchukuo, who did not want Manchuria to be severed from China. Even more active in going to Manchukuo were the products of ''
The Kwantung Army for its part tolerated the talk of social revolution in Manchukuo as the best way of gaining support from the Han majority of Manchukuo, who did not want Manchuria to be severed from China. Even more active in going to Manchukuo were the products of ''
 In 1908, the number of residents was 15,834,000, which rose to 30,000,000 in 1931 and 43,000,000 for the Manchukuo state. The population balance remained 123 men to 100 women and the total number in 1941 was 50,000,000. Other statistics indicate that in Manchukuo the population rose by 18,000,000.
In early 1934, the total population of Manchukuo was estimated as 30,880,000, with 6.1 persons the average family, and 122 men for each 100 women. These numbers included 29,510,000 Chinese (96%, which should have included the Manchu people), 590,760 Japanese (2%), 680,000
In 1908, the number of residents was 15,834,000, which rose to 30,000,000 in 1931 and 43,000,000 for the Manchukuo state. The population balance remained 123 men to 100 women and the total number in 1941 was 50,000,000. Other statistics indicate that in Manchukuo the population rose by 18,000,000.
In early 1934, the total population of Manchukuo was estimated as 30,880,000, with 6.1 persons the average family, and 122 men for each 100 women. These numbers included 29,510,000 Chinese (96%, which should have included the Manchu people), 590,760 Japanese (2%), 680,000  The Japanese Ueda Kyōsuke labeled all 30 million people in Manchuria as "Manchus", including Han Chinese, despite the fact that most of them were not ethnic Manchu, and the Japanese written, "Great Manchukuo" built upon Ueda's argument to claim that all 30 million "Manchus" in Manchukuo had the right to independence to justify splitting Manchukuo from China. In 1942 the Japanese wrote "Ten Year History of the Construction of Manchukuo" which attempted to emphasize the right of ethnic Japanese to the land of Manchukuo while attempting to delegitimize the Manchu's claim to Manchukuo as their native land, noting that most Manchus moved out during the Qing period and only returned later.
The Japanese Ueda Kyōsuke labeled all 30 million people in Manchuria as "Manchus", including Han Chinese, despite the fact that most of them were not ethnic Manchu, and the Japanese written, "Great Manchukuo" built upon Ueda's argument to claim that all 30 million "Manchus" in Manchukuo had the right to independence to justify splitting Manchukuo from China. In 1942 the Japanese wrote "Ten Year History of the Construction of Manchukuo" which attempted to emphasize the right of ethnic Japanese to the land of Manchukuo while attempting to delegitimize the Manchu's claim to Manchukuo as their native land, noting that most Manchus moved out during the Qing period and only returned later.
 In 1931–2, there were 100,000 Japanese farmers; other sources mention 590,760 Japanese inhabitants. Other figures for Manchukuo speak of a Japanese population 240,000 strong, later growing to 837,000. In Xinjing, they made up 25% of the population. Accordingly, to the census of 1936, of the Japanese population of Manchukuo, 22% were civil servants and their families; 18% were working for the South Manchurian Railroad company; 25% had come to Manchukuo to establish a business, and 21% had come to work in industry. The Japanese working in the fields of transportation, the government, and in business tended to be middle class, white-collar people such as executives, engineers, and managers, and those Japanese who working in Manchukuo as blue collar employees tended to be skilled workers. In 1934, it was reported that a Japanese carpenter working in Manchukuo with its growing economy could earn twice as much as he could in Japan. With its gleaming modernist office buildings, state of the art transport networks like the famous Asia Express railroad line, and modern infrastructure that was going up all over Manchukuo, Japan's newest colony become a popular tourist destination for middle-class Japanese, who wanted to see the "Brave New Empire" that was going up in the mainland of Asia. The Japanese government had official plans projecting the emigration of 5 million Japanese to Manchukuo between 1936 and 1956. Between 1938 and 1942 a batch of young farmers of 200,000 arrived in Manchukuo; joining this group after 1936 were 20,000 complete families. Of the Japanese settlers in Manchukuo, almost half came from the rural areas of Kyushu. When Japan lost sea and air control of the Yellow Sea in 1943–44, this migration stopped.
In 1931–2, there were 100,000 Japanese farmers; other sources mention 590,760 Japanese inhabitants. Other figures for Manchukuo speak of a Japanese population 240,000 strong, later growing to 837,000. In Xinjing, they made up 25% of the population. Accordingly, to the census of 1936, of the Japanese population of Manchukuo, 22% were civil servants and their families; 18% were working for the South Manchurian Railroad company; 25% had come to Manchukuo to establish a business, and 21% had come to work in industry. The Japanese working in the fields of transportation, the government, and in business tended to be middle class, white-collar people such as executives, engineers, and managers, and those Japanese who working in Manchukuo as blue collar employees tended to be skilled workers. In 1934, it was reported that a Japanese carpenter working in Manchukuo with its growing economy could earn twice as much as he could in Japan. With its gleaming modernist office buildings, state of the art transport networks like the famous Asia Express railroad line, and modern infrastructure that was going up all over Manchukuo, Japan's newest colony become a popular tourist destination for middle-class Japanese, who wanted to see the "Brave New Empire" that was going up in the mainland of Asia. The Japanese government had official plans projecting the emigration of 5 million Japanese to Manchukuo between 1936 and 1956. Between 1938 and 1942 a batch of young farmers of 200,000 arrived in Manchukuo; joining this group after 1936 were 20,000 complete families. Of the Japanese settlers in Manchukuo, almost half came from the rural areas of Kyushu. When Japan lost sea and air control of the Yellow Sea in 1943–44, this migration stopped.  About 2% of the Japanese population worked in agriculture. Many had been young, land-poor farmers in Japan that were recruited by the Patriotic Youth Brigade to colonize new settlements in Manchukuo. The Manchukuo government had seized great portions of these land through "price manipulation, coerced sales and forced evictions". Some Japanese settlers gained so much land that they could not farm it themselves and had to hire Chinese or Korean laborers for help, or even lease some of it back to its former Chinese owners, leading to uneasy, sometimes hostile relations between the groups.
When the
About 2% of the Japanese population worked in agriculture. Many had been young, land-poor farmers in Japan that were recruited by the Patriotic Youth Brigade to colonize new settlements in Manchukuo. The Manchukuo government had seized great portions of these land through "price manipulation, coerced sales and forced evictions". Some Japanese settlers gained so much land that they could not farm it themselves and had to hire Chinese or Korean laborers for help, or even lease some of it back to its former Chinese owners, leading to uneasy, sometimes hostile relations between the groups.
When the
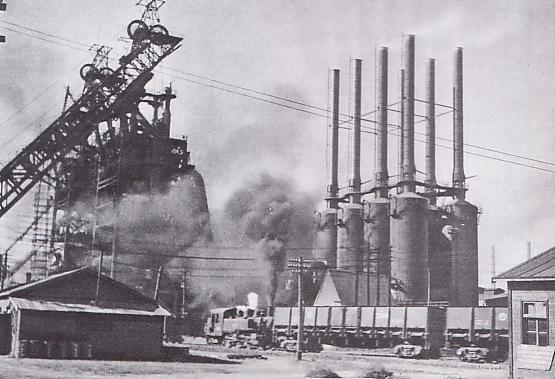 Manchukuo experienced rapid economic growth and progress in its social systems. During the 1920s, the Japanese Army under the influence of the ''Wehrstaat'' (Defense State) theories popular with the ''
Manchukuo experienced rapid economic growth and progress in its social systems. During the 1920s, the Japanese Army under the influence of the ''Wehrstaat'' (Defense State) theories popular with the ''
 The
The 
 The other two branches, the
The other two branches, the
 In 2007, an article by Reiji Yoshida in ''
In 2007, an article by Reiji Yoshida in ''
. Eventually, Japanese became the official language in addition to the Chinese taught in Manchukuo schools.
online
*Mitter, Rana. ''The Manchurian Myth: Nationalism, Resistance, and Collaboration in Modern China'' (2000)
Manchukuo Propaganda Posters & BillsManchu Money Museum
*[http://www.e.okayama-u.ac.jp/~matsu/index-en.html "Toshiro Matsumoto s research over Manchukuo"]
"Vaticano-Manchukuo no sirve de mea culpa" by Gianni Valente
* Mukden Incident photos
World War II database (1)
World War II database (2)
{{coord, 43, 53, N, 125, 19, E, source:kolossus-svwiki, display=title Manchukuo, History of Manchuria Client states of the Empire of Japan Former countries in East Asia Former countries in Chinese history Former Japanese colonies Former monarchies Former monarchies of Asia Former unrecognized countries Military history of China during World War II Second Sino-Japanese War States and territories established in 1932 States and territories disestablished in 1945 1932 establishments in China 1945 disestablishments in China 1932 establishments in the Japanese colonial empire 1945 disestablishments in the Japanese colonial empire Former monarchies of East Asia Axis powers Collaboration with the Axis Powers Chinese collaborators with Imperial Japan, Totalitarian states Former countries of the interwar period Former empires
puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sove ...
of the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of Japan, 1947 constitu ...
in Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until the ...
, and in 1934 it became a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
under the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' control of Japan. It had limited international recognition
Diplomatic recognition in international law is a unilateral declarative political act of a state that acknowledges an act or status of another state or government in control of a state (may be also a recognized state). Recognition can be accord ...
.
The area was the homeland of the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, including the emperors of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
. In 1931, Japan seized the region following the Mukden Incident. A pro-Japanese government was installed one year later with Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
, the last Qing emperor, as the nominal regent and later emperor. Manchukuo's government was dissolved in 1945 after the surrender of Imperial Japan at the end
End, END, Ending, or variation, may refer to:
End
*In mathematics:
** End (category theory)
** End (topology)
**End (graph theory)
** End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
**End (endomorphism)
*In sports and games
**End (gridiron footbal ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The territories claimed by Manchukuo were first seized in the Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian strategic offensive operation (russian: Манчжурская стратегическая наступательная операция, Manchzhurskaya Strategicheskaya Nastu ...
in August 1945, and then formally transferred to Chinese administration in the following year.
Demographically, Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
formed a minority in Manchukuo; the largest ethnic group was Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
. The Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
population increased immensely under this period, largely in part due to Japan's settlement efforts to move young, land-poor farmers from the inner islands to colonize new land. By 1945, there were more than a million Japanese settlers. The population of Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
also increased during this Manchukuo period, and there were also Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, and other minorities. The Mongol regions of western Manchukuo were ruled under a slightly different system in acknowledgment of the Mongolian traditions there. The southern tip of the Liaodong Peninsula
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River ...
(present-day Dalian) continued to be directly ruled by Japan as the Kwantung Leased Territory until the end of World War II.
Names
"Manchukuo" is a variant of the Wade-Gilesromanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
''Man-chou-kuo'' of the Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
pronunciation ''Mǎnzhōuguó'' of the original Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
name of the state, ''Manshūkoku'' In Japanese, the name refers to the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, the ''region'' of the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
. The English name, adapted to incorporate the word ''Manchu'', would mean the state of the Manchu people. Indeed, Manchukuo was often referred to in English as simply "Manchuria", a name for Northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
which had been particularly employed by the Imperial Japanese to promote its separation from the rest of the country. Other European languages used equivalent terms: Manchukuo was known to its allies as in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
and or in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
. In present-day Chinese, Manchukuo's name is still often prefaced by the word ''wěi'' (, "so-called", "false", "pseudo-
The prefix pseudo- (from Greek ψευδής, ''pseudes'', "false") is used to mark something that superficially appears to be (or behaves like) one thing, but is something else. Subject to context, ''pseudo'' may connote coincidence, imitation, ...
", etc.) to stress its perceived illegitimacy.
The formal name of the country was changed to the "''Empire of Manchuria''" (sometimes referred to as "Manchutikuo"), after the establishment of Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
as the ''Kangde Emperor'' in 1934. In Chinese and Japanese, the names were ''Dà Mǎnzhōu dìguó'' and ''Dai Manshū teikoku''. The ''Dà/Dai'' ("big", "great") were added after the model of the formal names of the ''Great'' Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
and Qing dynasties
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
, but this was unused in English.
The Japanese had their own motive for deliberately spreading the usage of the term Manchuria. The historian Norman Smith wrote that "The term 'Manchuria' is controversial". Professor Mariko Asano Tamanoi said that she should "use the term in quotation marks" when referring to Manchuria. Herbert Giles
Herbert Allen Giles (, 8 December 184513 February 1935) was a British diplomat and sinologist who was the professor of Chinese at the University of Cambridge for 35 years. Giles was educated at Charterhouse School before becoming a British ...
wrote that "Manchuria" was unknown to the Manchus themselves as a geographical expression. In his doctoral thesis of 2012, Professor Chad D. Garcia noted that usage of the term "Manchuria" was out of favor in "current scholarly practice" and preferred the term "the northeast".
History
Background
 The
The Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
, which replaced the Shun
Shun may refer to one of the following:
*To shun, which means avoiding association with an individual or group
* Shun (given name), a masculine Japanese given name
*Seasonality in Japanese cuisine (''shun'', 旬)
Emperor Shun
* Emperor Shun (� ...
and Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
dynasties in China, was founded by Manchus from Manchuria (modern Northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
). The Manchu emperors separated their homeland in Jilin
Jilin (; alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea ( Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, Ryanggang and Chagang) and Russia (Prim ...
and Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
from the Han Liaoning province with the Willow Palisade
Willow Palisade (; mnc, m=, v=Biregen Jase, ᠠ=Biregen Jase) was a system of ditches and embankments planted with willows intended to restrict movement into Manchuria (including Inner Manchuria and Outer Manchuria), built by the Qing dynasty of ...
. This ethnic division continued until the Qing dynasty encouraged the massive immigration of Han in the 19th century during Chuang Guandong
''Chuang Guandong'' (; IPA: ; literally "Crashing into Guandong" with ''Guandong'' being an older name for Manchuria) is descriptive of the rush of Han people into Manchuria, mainly from the Shandong Peninsula and Zhili, during the hundred-year pe ...
to prevent the Russians from seizing the area from the Qing. After conquering the Ming, the Qing identified their state as "China" (中國, Zhongguo; "Central Realm") and referred to it as "Dulimbai Gurun" in Manchu. The Qing equated the lands of the Qing state (including present day Manchuria, Xinjiang, Mongolia, Tibet and other areas) as "China" in both the Chinese and Manchu languages, defining China as a multi-ethnic state, rejecting the idea that China only meant Han areas, and proclaiming that both Han and non-Han peoples were part of "China". The Qing state used "China" to refer to the Qing in official documents, international treaties, and foreign affairs; the "Chinese language" () referred to Chinese, Manchu, and Mongol languages; and the term "Chinese people" (中國人 Zhongguo ren; Manchu: Dulimbai gurun i niyalma) referred to all Han, Manchu and Mongol subjects of the Qing. The lands in Manchuria were explicitly stated by the Qing to belong to "China" (Zhongguo, ) in Qing edicts and in the Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk () of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River ...
.
During the Qing dynasty, the area of Manchuria was known as the "three eastern provinces" (三東省; ''Sān dōng shěng''): in 1683 Jilin and Heilongjiang were separated even though it was not until 1907 that they were turned into actual provinces. The area of Manchuria was then converted into three provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
by the late Qing government in 1907. From that time the "Three Northeast Provinces" () was officially used by the Qing government in China to refer to this region, and the post of Viceroy of Three Northeast Provinces
The Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Three Northeast Provinces and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Generals of the Three Provinces, Director of Civil Affairs of Fengtian ...
was established to take charge of these provinces.
As the power of the court in Beijing weakened, many outlying areas either broke free (such as Kashgar) or fell under the control of Imperialist powers. In the 19th century, Imperial Russia was most interested in the northern lands of the Qing Empire. In 1858, Russia gained control over a huge tract of land called Outer Manchuria
Outer Manchuria (russian: Приаму́рье, translit=Priamurye; zh, s=外满洲, t=外滿洲, p=Wài Mǎnzhōu), or Outer Northeast China ( zh, s=外东北, t=外東北, p=Wài Dōngběi), refers to a territory in Northeast Asia that is now ...
thanks to the Supplementary Treaty of Beijing that ended the Second Opium War. But Russia was not satisfied and, as the Qing dynasty continued to weaken, it made further efforts to take control of the rest of Manchuria. Inner Manchuria came under strong Russian influence in the 1890s with the building of the Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (als ...
through Harbin to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, c ...
.
The Japanese far-right, ultra-nationalist Black Dragon Society
The , or the Amur River Society, was a prominent paramilitary, ultranationalist group in Japan.
History
The ''Kokuryūkai'' was founded in 1901 by martial artist Uchida Ryohei as a successor to his mentor Mitsuru Tōyama's '' Gen'yōsha''. I ...
supported Sun Yat-sen's activities against the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, believing that overthrowing the Qing would help the Japanese take over the Manchu homeland and that Han Chinese would not oppose the takeover. The Society's Gen'yōsha
The was an influential Pan-Asianist group and secret society active in the Empire of Japan, and was considered to be an ultranationalist group by General Headquarters in the International Military Tribunal for the Far East.
Foundation as the ...
leader Tōyama Mitsuru
was a Japanese right wing and ultranationalist founder of Genyosha (''Black Ocean Society'') and Kokuryukai (''Black Dragon Society''). Tōyama was a strong advocate of Pan Asianism (Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere).
Early life
Tōyama ...
believed that the Japanese could easily take over Manchuria and Sun Yat-sen and other anti-Qing revolutionaries would not resist and help the Japanese take over and enlargen the opium trade in China while the Qing was trying to destroy the opium trade. The Japanese Black Dragons supported Sun Yat-sen and anti-Manchu revolutionaries until the Qing collapsed. Toyama supported anti-Manchu, anti-Qing revolutionary activities including by Sun Yat-sen and supported Japan taking over Manchuria. The anti-Qing Tongmenghui
The Tongmenghui of China (or T'ung-meng Hui, variously translated as Chinese United League, United League, Chinese Revolutionary Alliance, Chinese Alliance, United Allegiance Society, ) was a secret society and underground resistance movement ...
was founded and based in exile in Japan where many anti-Qing revolutionaries gathered.
The Japanese had been trying to unite anti-Manchu groups made out of Han people to take down the Qing. Japanese were the ones who helped Sun Yat-sen unite all anti-Qing, anti-Manchu revolutionary groups together and there were Japanese like Tōten Miyazaki inside of the anti-Manchu Tongmenghui revolutionary alliance. The Black Dragon Society hosted the Tongmenghui in its first meeting. The Black Dragon Society had very intimate relations with Sun Yat-sen and promoted pan-Asianism and Sun sometimes passed himself off as Japanese. That had connections with Sun for a long time. Japanese groups like the Black Dragon Society had a large impact on Sun Yat-sen. According to an American military historian, Japanese military officers were part of the Black Dragon Society. The Yakuza and Black Dragon Society helped arrange in Tokyo for Sun Yat-sen to hold the first Kuomintang meetings, and were hoping to flood China with opium and overthrow the Qing and deceive Chinese into overthrowing the Qing to Japan's benefit. After the revolution was successful, the Japanese Black Dragons started infiltrating China and spreading opium and anti-Communist sentiment. The Black Dragons pushed for the takeover of Manchuria by Japan in 1932.
Origins
As a direct result of theRusso-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
(1904–05), Japanese influence replaced that of Russia in Inner Manchuria. During the war with Russia, Japan had mobilized one million soldiers to fight in Manchuria, meaning that one in eight families in Japan had a member fighting in Manchuria. During the Russo-Japanese War, the losses were heavy, with Japan losing a half-million dead or wounded. From the time of the Russian-Japanese war onward, many Japanese people came to have a proprietary attitude to Manchuria, taking the viewpoint that a land where so much Japanese blood had been lost meant that it in some way now belonged to them. Japanese publications from 1905 onward often described Manchuria as a "sacred" and "holy" land where so many Japanese had lost their lives. The war with Russia had almost bankrupted Japan, forcing the Japanese to accept the compromise Treaty of Portsmouth
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
mediated by President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
of the United States, under which Japan made gains, but nowhere to the extent that the Japanese public had been expecting. The Treaty of Portsmouth set off an anti-American riot in Tokyo between 5–7 September 1905 as the general viewpoint in Japan was that the Japanese had won the war, but lost the peace. The perception in Japan was the Treaty of Portsmouth was a humiliating diplomatic disaster that did not place all of Manchuria into the Japanese sphere of influence as widely expected, and the question of Manchuria was still "unfinished business" that would one day be resolved by the Imperial Army. In 1906, Japan established the South Manchurian Railway
The South Manchuria Railway ( ja, 南満州鉄道, translit=Minamimanshū Tetsudō; ), officially , Mantetsu ( ja, 満鉄, translit=Mantetsu) or Mantie () for short, was a large of the Empire of Japan whose primary function was the operatio ...
on the former Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (als ...
built by Russia from Manzhouli
Manzhouli (; mn, Манжуур хот; ) is a sub-prefectural city located in Hulunbuir prefecture-level city, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Located on the border with Russia, it is a major land port of entry. It has an area of and ...
to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, c ...
via Harbin with a branch line from Harbin to Port Arthur (Japanese: Ryojun), today's Dalian.
Under the terms of the Treaty of Portsmouth, the Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
had the right to occupy southern Manchuria while the region fell into the Japanese economic sphere of influence. The Japanese-owned South Manchurian Railroad company had a market capitalization of 200 million yen, making it Asia's largest corporation, which went beyond just running the former Russian railroad network in southern Manchuria to owning the ports, mines, hotels, telephone lines, and sundry other businesses, dominating the economy of Manchuria. With the growth of the South Manchuria Railroad (''Mantetsu'') company went a growth in number of Japanese living in Manchuria from 16,612 Japanese civilians in 1906 to 233,749 in 1930. The majority of blue-collar employees for the ''Mantetsu'' were Chinese, and the Japanese employees were mostly white-collar, meaning most of the Japanese living in Manchuria were middle-class people who saw themselves as an elite. In Japan, Manchuria was widely seen as a Japanese counterpart to the "Wild West", a dangerous frontier region full of bandits, revolutionaries, and warlords, but also a place it was possible for ordinary Japanese living there to become very well-off. As part of this "Wild East" image was the picture of Manchuria as a land of boundless wealth and promise, which became the prevalent view of Manchuria in Japan. Between World War I and World War II Manchuria became a political and military battleground between Russia, Japan, and China. Japan moved into Outer Manchuria
Outer Manchuria (russian: Приаму́рье, translit=Priamurye; zh, s=外满洲, t=外滿洲, p=Wài Mǎnzhōu), or Outer Northeast China ( zh, s=外东北, t=外東北, p=Wài Dōngběi), refers to a territory in Northeast Asia that is now ...
(that is, Russia's Far East) as a result of the chaos following the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
. A combination of Soviet military successes and American economic pressure forced the Japanese to withdraw from the area, however, and Outer Manchuria returned to Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
control by 1925.
During the Warlord Era in China, the warlord Marshal Zhang Zuolin
Zhang Zuolin (; March 19, 1875 June 4, 1928), courtesy name Yuting (雨亭), nicknamed Zhang Laogang (張老疙瘩), was an influential Chinese bandit, soldier, and warlord during the Warlord Era in China. The warlord of Manchuria from 1916 to ...
established himself in Inner Manchuria with Japanese backing. Later, the Japanese Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
found him too independent, so he was assassinated in 1928. In assassinating Marshal Zhang, the "Old Marshal" the Kwantung Army generals expected Manchuria to descend into anarchy, providing the pretext for seizing the region. Marshal Zhang was killed when the bridge his train was riding across was blown up while three Chinese men were murdered and explosive equipment placed on their corpses to make it appear that they were the killers, but the plot was foiled when Zhang's son Zhang Xueliang, the "Young Marshal" succeeded him without incident while the cabinet in Tokyo refused to send additional troops to Manchuria. Given that the Kwantung Army had assassinated his father, the "Young Marshal"—who unlike his father was a Chinese nationalist—had strong reasons to dislike Japan's privileged position in Manchuria. Marshal Zhang knew his forces were too weak to expel the Kwantung Army, but his relations with the Japanese were unfriendly right from the start.

 After the
After the Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until the ...
in 1931, Japanese militarists moved forward to separate the region from Chinese control and to create a Japanese-aligned puppet state. To create an air of legitimacy, the last Emperor of China, Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
, was invited to come with his followers and act as the head of state for Manchuria. One of his faithful companions was Zheng Xiaoxu
Zheng Xiaoxu (Cheng Hsiao-hsu; ; Hepburn: ''Tei Kōsho'') (2 April 1860 – 28 March 1938) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat and calligrapher. He served as the first Prime Minister of Manchukuo.
Early life and diplomatic career
Although Zhe ...
, a Qing reformist and loyalist.Reginald Fleming Johnston, p. 438.
The "Northeast Supreme Administrative Council" (東北最高行政委員會, or the Northeast Administrative Committee/東北行政委員會) was established as a puppet government
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sover ...
established by the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of Japan, 1947 constitu ...
in Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
following the Mukden Incident. On 16 February 16 1932 the Imperial Army hosted the "Founding Conference" or the "Big Four Conference" with governor of Liaoning Zang Shiyi, commander of the Kirin Provincial Army Xi Qia
Aisin-Gioro Xiqia (Aisin-Gioro Hsi-hsia; ; 1883–1950), commonly known as Xi Qia or Xi Xia (Hsi Hsia; ; Hepburn: ''Ki Kō''), was a general in command of the Kirin Provincial Army of the Republic of China, who defected to the Japanese during t ...
, Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
governor Zhang Jinghui
Zhang Jinghui (Chang Ching-hui; ; Hepburn: ''Chō Keikei''); (1871 – 1 November 1959) was a Chinese general, warlord and politician during the Warlord era. He is noted for his role in the Japanese puppet regime of Manchukuo in which he serve ...
, and general Ma Zhanshan
Ma Zhanshan (Ma Chan-shan; ; November 30, 1885 – November 29, 1950) was a Chinese general who initially opposed the Imperial Japanese Army in the invasion of Manchuria, briefly defected to Manchukuo, and then rebelled and fought against the ...
to establish the Northeast Administrative Committee. On its second meeting, the committee appointed the previous four and Tang Yulin, Ling Sheng, and Qimote Semupilei as chairmen. On the 18th, the Council issued a statement announcing that "the Northeast provinces are completely independent", all territories of whom are within the hands of the Council.
On 18 February 1932 Manchukuo ("The Manchurian State") was proclaimed by the Northeast Supreme Administrative Council, nominally in control of Manchuria. On February 25th, the Council decided that the name of the new country name (Manchukuo), the national flag, era name, and more. Manchuko was formally established on 1 March in Hsinking
Changchun (, ; ), also romanized as Ch'angch'un, is the capital and largest city of Jilin Province, People's Republic of China. Lying in the center of the Songliao Plain, Changchun is administered as a , comprising 7 districts, 1 county and 3 c ...
, and the Council was abolished. It was recognized by Japan on 15 September 1932 through the Japan–Manchukuo Protocol, after the assassination of Japanese Prime Minister
The prime minister of Japan ( Japanese: 内閣総理大臣, Hepburn: ''Naikaku Sōri-Daijin'') is the head of government of Japan. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Japan and has the ability to select and dismiss its Ministers of Stat ...
Inukai Tsuyoshi
Inukai Tsuyoshi ( ja, 犬養 毅, 4 June 1855 – 15 May 1932) was a Japanese politician, cabinet minister, and Prime Minister of Japan from 1931 to his assassination in 1932. Inukai was Japan's second oldest prime minister while serving, as he ...
. The city of Changchun, renamed Xinjing (), became the capital of the new entity. Chinese in Manchuria organized volunteer armies to oppose the Japanese and the new state required a war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
lasting several years to pacify the country.
The Japanese initially installed Puyi as head of state in 1932, and two years later he was declared Emperor of Manchukuo with the era name
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year of ...
of ''Kangde'' w''Kang-te'', "Tranquility and Virtue"). Manchukuo thus became Manchutikuo ("The Manchurian Empire"). Zheng Xiaoxu
Zheng Xiaoxu (Cheng Hsiao-hsu; ; Hepburn: ''Tei Kōsho'') (2 April 1860 – 28 March 1938) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat and calligrapher. He served as the first Prime Minister of Manchukuo.
Early life and diplomatic career
Although Zhe ...
served as Manchukuo's first prime minister until 1935, when Zhang Jinghui
Zhang Jinghui (Chang Ching-hui; ; Hepburn: ''Chō Keikei''); (1871 – 1 November 1959) was a Chinese general, warlord and politician during the Warlord era. He is noted for his role in the Japanese puppet regime of Manchukuo in which he serve ...
succeeded him. Puyi was nothing more than a figurehead and real authority rested in the hands of the Japanese military officials. An imperial palace was specially built for the emperor. The Manchu ministers all served as front-men for their Japanese vice-ministers, who made all decisions.
In this manner, Japan formally detached Manchukuo from China over the course of the 1930s. With Japanese investment and rich natural resources, the area became an industrial powerhouse. Manchukuo had its own issued banknotes
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
and postage stamps
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail), who then affix the stamp to the f ...
. Several independent banks were founded as well.
The conquest of Manchuria proved to be extremely popular with the Japanese people who saw the conquest as providing a much-needed economic "lifeline" to their economy which had been badly hurt by the Great Depression. The very image of a "lifeline" suggested that Manchuria—which was rich in natural resources—was essential for Japan to recover from the Great Depression, which explains why the conquest was so popular at the time and later why the Japanese people were so completely hostile towards any suggestion of letting Manchuria go. At the time, censorship in Japan was nowhere near as stringent as it would later become, and the American historian Louise Young noted: "Had they wished, it would have been possible in 1931 and 1932 for journalists and editors to express anti-war sentiments". The popularity of the conquest meant that newspapers such as the ''Asahi Shimbun
is one of the four largest newspapers in Japan. Founded in 1879, it is also one of the oldest newspapers in Japan and Asia, and is considered a newspaper of record for Japan. Its circulation, which was 4.57 million for its morning edition a ...
'' which initially opposed the war swiftly changed to supporting the war as the best way of improving sales. The conquest of Manchuria was also presented as resolving the "unfinished business" left over the Russo-Japanese war that finally undid one of the key terms of the Treaty of Portsmouth. The most popular song in Japan in 1932 was the ''Manchuria March'' whose verses proclaimed that the seizing of Manchuria in 1931–32 was a continuation of what Japan had fought for against Russia in 1904–05, and the ghosts of the Japanese soldiers killed in the Russo-Japanese war could now rest at ease as their sacrifices had not been in vain.
In 1935, Manchukuo bought the Chinese Eastern Railway from the Soviet Union.
Diplomatic recognition
 China did not recognize Manchukuo but the two sides established official ties for trade, communications, and transportation. In 1933, the
China did not recognize Manchukuo but the two sides established official ties for trade, communications, and transportation. In 1933, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
adopted the Lytton Report, declaring that Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
remained rightfully part of China, leading Japan to resign its membership. The Manchukuo case persuaded the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
to articulate the so-called Stimson Doctrine
The Stimson Doctrine is the policy of nonrecognition of states created as a result of a war of aggression. The policy was implemented by the United States government, enunciated in a note of January 7, 1932, to the Empire of Japan and the Repub ...
, under which international recognition was withheld from changes in the international system created by the force of arms.
In spite of the League's approach, the new state was diplomatically recognized by El Salvador (3 March 1934) and the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
(1934), Costa Rica (23 September 1934), Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
(29 November 1937), Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
(2 December 1937), Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
(12 May 1938) and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
(9 January 1939). The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
extended de facto recognition on 23 March 1935, but explicitly noted that this did not mean de jure recognition. However, upon signing the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact on 13 April 1941, the Soviet Union recognized Manchukuo de jure in exchange for Japan recognizing the integrity of the neighboring Mongolian People's Republic
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It w ...
. The USSR did maintain five consulates-general in Manchukuo initially, although in 1936–37 these were reduced to just two: one in Harbin and another in Manzhouli
Manzhouli (; mn, Манжуур хот; ) is a sub-prefectural city located in Hulunbuir prefecture-level city, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Located on the border with Russia, it is a major land port of entry. It has an area of and ...
. Manchukuo opened consulates in Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur and the Zeya Rivers, o ...
(September 1932) and in Chita (February 1933).
It is commonly believed that the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
established diplomatic relations with Manchukuo in 1934, but the Holy See never did so. This belief is partly due to the erroneous reference in Bernardo Bertolucci
Bernardo Bertolucci (; 16 March 1941 – 26 November 2018) was an Italian film director and screenwriter with a career that spanned 50 years. Considered one of the greatest directors in Italian cinema, Bertolucci's work achieved international ...
's 1987 film ''The Last Emperor
''The Last Emperor'' ( it, L'ultimo imperatore) is a 1987 epic biographical drama film about the life of Puyi, the final Emperor of China. It is directed by Bernardo Bertolucci from a screenplay he co-wrote with Mark Peploe, which was adapted ...
'' that the Holy See diplomatically recognized Manchukuo. Bishop Auguste Ernest Pierre Gaspais was appointed as "representative ''ad tempus'' of the Holy See and of the Catholic missions of Manchukuo to the government of Manchukuo" by the Congregation De Propaganda Fide (a purely religious body responsible for missions) and not by the Secretariat of State responsible for diplomatic relations with states. In the 1940s the Vatican established full diplomatic relations with Japan, but it resisted Japanese and Italian pressure to recognize Manchukuo and the Nanjing regime.
After the outbreak of World War II, the state was recognized by Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
(1 June 1940), Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
(12 July 1940), Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
(1 December 1940), Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
(10 May 1941), Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
(17 July 1941), Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
(August 1941), Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
(2 August 1941)—all controlled or influenced by Japan's ally Germany—as well as by Wang Jingwei
Wang Jingwei (4 May 1883 – 10 November 1944), born as Wang Zhaoming and widely known by his pen name Jingwei, was a Chinese politician. He was initially a member of the left wing of the Kuomintang, leading a government in Wuhan in oppositi ...
's Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China
The Wang Jingwei regime or the Wang Ching-wei regime is the common name of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China ( zh , t = 中華民國國民政府 , p = Zhōnghuá Mínguó Guómín Zhèngfǔ ), the government of the pup ...
(30 November 1940), Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
(5 August 1941) and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
(1943)—all under the control or influence of Japan.
World War II and aftermath
 Before World War II, the Japanese colonized Manchukuo and used it as a base from which to invade China. The Manchu General Tong Linge was killed in action by the Japanese in the
Before World War II, the Japanese colonized Manchukuo and used it as a base from which to invade China. The Manchu General Tong Linge was killed in action by the Japanese in the Battle of Beiping–Tianjin
The Battle of Beiping–Tianjin (), also known as the Battle of Beiping, Battle of Peiping, Battle of Beijing, Battle of Peiking, the Peiking-Tientsin Operation, and by the Japanese as the (25–31 July 1937) was a series of battles of the Sec ...
, which marked the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War. In the summer of 1939 a border dispute between Manchukuo and the Mongolian People's Republic
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It w ...
resulted in the Battle of Khalkhin Gol
The Battles of Khalkhin Gol (russian: Бои на Халхин-Голе; mn, Халхын голын байлдаан) were the decisive engagements of the undeclared Soviet–Japanese border conflicts involving the Soviet Union, Mongolia, ...
. During this battle, a combined Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
-Mongolian force defeated the Japanese Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
('' Kantōgun'') supported by limited Manchukuoan forces.
On 8 August 1945, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
declared war on Japan, in accordance with the agreement at the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
, and invaded Manchukuo from outer Manchuria and Outer Mongolia. During the Soviet offensive, the Manchukuo Imperial Army
The Manchukuo Imperial Army ( zh, s=滿洲國軍, p=Mǎnzhōuguó jūn) was the ground force of the military of the Empire of Manchukuo, a puppet state established by Imperial Japan in Manchuria, a region of northeastern China. The force was pri ...
, on paper a 200,000-man force, performed poorly and whole units surrendered to the Soviets without firing a single shot; there were even cases of armed riots and mutinies against the Japanese forces. Emperor Kangde abdicate on 17 August and had hoped to escape to Japan to surrender to the Americans, but the Soviets captured him and eventually extradited him to the government of China, when the Chinese Communist Party came to power in 1949, where the authorities had him imprisoned as a war criminal along with all other captured Manchukuo officials.
From 1945 to 1948, Manchuria (Inner Manchuria) served as a base area for the People's Liberation Army in the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
against the National Revolutionary Army.Borisov, O. (1977). The Soviet Union and the Manchurian Revolutionary Base (1945–1949)
'. Moscow, Progress Publishers. The
Chinese Communists
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
used Manchuria as a staging ground until the final Nationalist retreat to Taiwan in 1949. Many Manchukuo army and Japanese Kantōgun personnel served with the communist troops during the Chinese Civil War against the Nationalist forces. Most of the 1.5 million Japanese who had been left in Manchukuo at the end of World War II were sent back to their homeland in 1946–1948 by U.S. Navy ships in the operation now known as the Japanese repatriation from Huludao.
Administrative divisions
During its short-lived existence, Manchukuo was divided into between five (in 1932) and 19 (in 1941)provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, one special ward of Beiman () and two special cities which were Xinjing () and Harbin (). Each province was divided into four (Xing'an dong) and 24 (Fengtian) prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
. Beiman lasted less than 3 years (1 July 1933 – 1 January 1936) and Harbin was later incorporated into Binjiang province. Longjiang also existed as a province in 1932 before being divided into Heihe
Heihe (; ; Russian: Хэйхэ) is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1 ...
, Longjiang, and Sanjiang in 1934. Andong and Jinzhou provinces separated themselves from Fengtian while Binjiang and Jiandao separated themselves from Jilin in the same year.
Politics
 Historians generally consider Manchukuo a
Historians generally consider Manchukuo a puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sove ...
of Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
because of the Japanese military's strong presence and strict control of the government administration. Chinese historians generally refer to the state as ''Wei Manzhouguo'' ("false state of Manchuria"). Some historians see Manchukuo as an effort at building a glorified Japanese state in mainland Asia that deteriorated due to the pressures of war.
The independence of Manchuria was proclaimed on 18 February 1932 and officially founded on 1 March. The Japanese commander-in-chief appointed Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
as regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
(reign name
A regnal name, or regnant name or reign name, is the name used by monarchs and popes during their reigns and, subsequently, historically. Since ancient times, some monarchs have chosen to use a different name from their original name when they ac ...
Datong) for the time being, stating that he would become Emperor of Manchukuo but could not reign using the title of Emperor of the Great Qing Empire as he once held. Manchukuo was proclaimed a monarchy on 1 March 1934, with Puyi assuming the throne under the reign name of Emperor Kang-de. Puyi was assisted in his executive duties by a Privy Council (), and a General Affairs State Council (). This State Council was the center of political power, and consisted of several cabinet ministers, each assisted by a Japanese vice-minister. The commander-in-chief of the Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
(the army of Manchukuo) also served as the official Japanese ambassador to the state. He functioned in a manner similar to resident officers in European colonial empires, with the added ability to veto decisions by the emperor. The Kwantung Army leadership placed Japanese vice ministers in his cabinet, while all Chinese advisors gradually resigned or were dismissed.
The Legislative Council () was largely a ceremonial body, existing to rubber-stamp decisions issued by the State Council. The only authorized political party was the government-sponsored Concordia Association
The Concordia Association ( Japanese Shinjitai: 満州国協和会, Hepburn: ''Manshū-koku Kyōwakai'') was a political party in Manchukuo. Established to promote the ideals of Pan-Asianism and the creation of a multi-ethnic nation-state and ...
, although various émigré groups were permitted their own political associations such as the White Russian Russian Fascist Party
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
* Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and pe ...
.
The American historian Louise Young noted that one of the most striking aspects of Manchukuo was that many of the young Japanese civil servants who went to work in Manchukuo were on the left, or at least had once been. In the 1920s, much of the younger ''intelligentsia'' in Japan had rejected their parents' values and had become active in various left-wing movements. Starting with the Peace Preservation Law of 1925, which made the very act of thinking about "altering the ''kokutai
is a concept in the Japanese language translatable as " system of government", "sovereignty", "national identity, essence and character", "national polity; body politic; national entity; basis for the Emperor's sovereignty; Japanese constitu ...
'' a crime, the government had embarked on a sustained campaign to stomp out all left-wing thought in Japan. However, many of the bright young university graduates active in left-wing movements in Japan were needed to serve as civil servants in Manchukuo, which Young noted led the Japanese state to embark upon a contradictory policy of recruiting the same people active in the movements that it was seeking to crush." To rule Manchukuo, which right from the start had a very statist economy, the Japanese state needed university graduates who were fluent in Mandarin Chinese, and the 1920s–30s, many of the university graduates in Japan who knew Mandarin were "progressives" involved in left-wing causes. The fact that young Japanese civil servants in Manchukuo with their degrees in economics, sociology, etc., who had once been active in left-wing movements helps explain the decidedly leftist thrust of social and economic policies in Manchukuo with the state playing an increasingly large role in society. Likewise, much of the debate between Japanese civil servants about the sort of social-economic policies Japan should follow in Manchukuo in the 1930s was framed in Marxist terms, with the civil servants arguing over whether Manchuria prior to September 1931 had a "feudal" or a "capitalist" economy. The American historian Joshua Fogel wrote about the young servants of Manchukuo: "Tremendous debates transpired on such things as the nature of the Chinese economy, and the lingua franca of these debates was always Marxism". To resolve this debate, various research teams of five or six young civil servants, guarded by detachments from the Kwantung Army of about 20 or 30 men, went out to do field research in Manchukuo, gathering material about the life of ordinary people, to determine Manchukuo was in the "feudal" or "capitalist" stage of development. Starting in 1936, the Manchukuo state launched Five Year Plans for economic development, which were closely modeled after the Five Year Plans in the Soviet Union.
In Manchukuo, the Japanese were creating a brand new state that was in theory independent, which meant that there were no limits upon the sort of policies that the new state could carry out, and many university graduates in Japan, who despite being opposed to the social system that existed in Japan itself, went to work in Manchukuo, believing that they could carry out reforms there that might inspire similar reforms in Japan. This was especially the case since it was impossible to effect any reforms in Japan itself as the very act of thinking about "altering the ''kokutai''" was a crime, which led many leftist Japanese university graduates to go work in Manchukuo, where they believed they could achieve the sort of social revolution that was impossible in Japan. By 1933, the Japanese state had essentially destroyed both the Japanese Socialist Party and the Japanese Communist Party via mass arrests and ''Tenkō is a Japanese term referring to the coerced ideological conversions of Japanese socialists and communists who, between 1925 and 1945, were induced to renounce leftist ideologies and enthusiastically embrace the Emperor-centric, capitalist, and imp ...
'' with both parties reduced down to mere rumps, which caused many Japanese student leftists to draw the conclusion that change was impossible in Japan, but still possible in Manchukuo, where paradoxically the Kwantung Army was sponsoring the sort of policies that were unacceptable in Japan. Moreover, the Great Depression had made it very difficult for university graduates in Japan to find work, which made the prospect of a well-paying job in Manchukuo very attractive to otherwise underemployed Japanese university graduates. In Manchukuo, the Japanese state was creating an entire state anew, which meant that Manchukuo had a desperate need for university graduates to work in its newly founded civil service. In addition, the Pan-Asian rhetoric of Manchukuo and the prospect of Japan helping ordinary people in Manchuria greatly appealed to the idealistic youth of Japan. Young wrote about the young Japanese people who went to work in Manchukuo: "The men, and in some cases, the women, who answered the call of this land of opportunity, brought with them tremendous drive and ambition. In their efforts to remake their own lives, they remade an empire. They invested it with their preoccupations of modernity and their dreams of a Utopian future. They pushed it to embrace idealist rhetoric of social reform and justified itself in terms of Chinese nationalist aspiration. They turned it to architectural ostentation and the heady luxury of colonial consumption. They made it into a project of radical change, experimentation and possibility".
Tenkō is a Japanese term referring to the coerced ideological conversions of Japanese socialists and communists who, between 1925 and 1945, were induced to renounce leftist ideologies and enthusiastically embrace the Emperor-centric, capitalist, and imp ...
'' ("Changing directions"), a process of brainwashing by the police of left-wing activists to make them accept that the Emperor was a god after all, whom they were best to serve. ''Tenkō'' was a very successful process that turned young Japanese who once had been ardent liberals or leftists who rejected the idea that the Emperor was a god into fanatical rightists, who made up for their previous doubts about the divinity of the Emperor with militant enthusiasm. One ''tenkōsha'' was Tachibana Shiraki, who once been a Marxist Sinologist who after his arrest and undergoing ''Tenkō'' became a fanatical right-winger. Tachibana went to Manchukuo in 1932, proclaiming that the theory of the "five races" working together was the best solution to Asia's problems and argued in his writings that only Japan could save China from itself, which was a complete change from his previous policies, where he criticized Japan for exploiting China. Other left-wing activists like Ōgami Suehiro did not undergo ''Tenkō'', but still went to work in Manchukuo, believing it was possible to effect social reforms that would end the "semi-feudal" condition of the Chinese peasants of Manchukuo, and that he could use the Kwantung Army to effect left-wing reforms in Manchukuo. Ōgami went to work in the "agricultural economy" desk of the Social Research Unit of the South Manchurian Railroad company, writing up reports about the rural economy of Manchukuo that were used by the Kwantung Army and the Manchukuo state. Ōgami believed that his studies helped ordinary people, citing one study he did about water use in rural Manchukuo, where he noted a correlation between villages that were deprived of water and "banditry" (the codeword for anti-Japanese guerrillas), believing that the policy of improving water supply in villages was due to his study. The outbreak of the war with China in 1937 caused the state in Manchukuo to grow even bigger as a policy of "total war" came in, which meant there was a pressing demand for people with university degrees trained to think "scientifically". Fogel wrote that almost all of the university graduates from Japan who arrived in Manchukuo in the late 1930s were "largely left-wing Socialists and Communists. This was precisely at the time when Marxism had been all but banned in Japan, when (as Yamada Gōichi put) "if the expression ''shakai'' (social) appeared in the title of a book, it was usually confiscated".
Young also noted—with reference to Lord Acton's dictum that "Absolute power corrupts absolutely"—that for many of the idealistic young Japanese civil servants, who believed that they could affect a "revolution from above" that would make the lives of ordinary people better, that the absolute power that they enjoyed over millions of people "went to their heads", causing them to behave with abusive arrogance towards the very people that they had gone to Manchukuo to help. Young wrote that it was a "monumental conceit" of the part of the young idealists to believe that they could use the Kwantung Army to achieve a "revolution from above" when it was the Kwantung Army that was using them. The ambitious plans for land reform in Manchukuo were vetoed by the Kwantung Army for precisely the reason that it might inspire similar reforms in Japan. The landlords in Japan tended to come from families who once belonged to the samurai caste, and almost all of the officers in the Imperial Japanese Army came from samurai families, which made the Kwantung Army very hostile towards any sort of land reform which might serve as an example for Japanese peasants. In October 1941, the Soviet spy ring headed by Richard Sorge
Richard Sorge (russian: Рихард Густавович Зорге, Rikhard Gustavovich Zorge; 4 October 1895 – 7 November 1944) was a German-Azerbaijani journalist and Soviet military intelligence officer who was active before and during Wo ...
was uncovered in Tokyo, which caused the authorities to become paranoid about Soviet espionage, and led to a new crackdown on the left. In November 1941, the Social Research Unit of the South Manchurian Railroad Company, which was well known as a hotbed of Marxism since the early 1930s, was raided by the ''Kenpeitai
The , also known as Kempeitai, was the military police arm of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1881 to 1945 that also served as a secret police force. In addition, in Japanese-occupied territories, the Kenpeitai arrested or killed those suspecte ...
'', who arrested 50 of those working in the Social Research Unit. At least 44 of those working in the Social Research Unit were convicted of violating the Peace Preservation Law, which made thinking about "altering the ''kokutai''" a crime in 1942–43 and were given long prison sentences, of whom four died due to the harsh conditions of prisons in Manchukuo. As the men working in the Social Research Unit had played important roles in Manchukuo's economic policy and were university graduates from good families, the Japanese historian Hotta Eri wrote that the ''Kenpeitai'' was ordered to "handle them with care", meaning no torture of the sort that the ''Kenpeitai'' normally employed in its investigations.
When the Japanese surrender
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy ( ...
was announced on 15 August 1945, Puyi agreed to abdicate.
Head of state
Prime Minister
Demographics
Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
(2%), and 98,431 (<1%) of other nationality: White Russians, Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, etc. Around 80% of the population was rural. During the existence of Manchukuo, the ethnic balance did not change significantly, except that Japan increased the Korean population in China. From Japanese sources come these numbers: in 1940 the total population in Manchukuo of Lungkiang, Jehol, Kirin, Liaoning (Fengtian) and Xing'an provinces at 43,233,954; or an Interior Ministry figure of 31,008,600. Another figure of the period estimated the total population as 36,933,000 residents. The majority of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
in Manchukuo believed that Manchuria was rightfully part of China, who both passively and violently resisted Japan's propaganda that Manchukuo was a "multinational state".
After the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
(1917–1922), thousands of Russians fled to Manchuria to join the Russian community already there. The Russians living in Manchuria were stateless and as whites had an ambiguous status in Manchukuo, which was meant to be a Pan-Asian state, whose official "five races" were the Chinese, Mongols, Manchus, Koreans, and Japanese. At various times, the Japanese suggested that the Russians might be a "sixth race" of Manchukuo, but this was never officially declared. In 1936, the ''Manchukuo Almanac'' reported that were 33,592 Russians living in the city of Harbin—the "Moscow of the Orient"—and of whom only 5,580 had been granted Manchukuo citizenship. Japanese imperialism was to a certain extent based on racism with the Japanese as the "great Yamato race", but there was always a certain dichotomy in Japanese thinking between an ideology based on racial differences based on bloodlines versus the idea of Pan-Asianism with Japan as the natural leader of all the Asian peoples. In 1940, ethnic Russians were included among the other nationalities of Manchukuo as candidates for conscription into the Manchukuo military.
The British writer Peter Fleming visited Manchukuo in 1935, and while riding a train through the countryside of Manchukuo, a group of Japanese colonists mistook his Swiss traveling companion Kini for a Russian refugee, and began to beat her up. It was only after Fleming was able to prove to the Japanese that she was Swiss, not Russian, that the Japanese stopped and apologized, saying that they would never had beaten her up if they had known she was Swiss, saying that they sincerely believed she was a Russian when they assaulted her. Fleming observed that in Manchukuo: "you can beat White Russians up till you are blue in the face, because they are people without status in the world, citizens of nowhere". Fleming further noted that the Japanese in Manchukuo had a strong dislike of all white people, and because the Russians in Manchukuo were stateless without an embassy to issue protests if they were victimized, the Japanese liked to victimize them. Until World War II, the Japanese tended to leave alone those travelling to Manchukuo with a passport as they did not like to deal with protests from embassies in Tokyo about the mistreatment of their citizens. The Kwantung Army operated a secret biological-chemical warfare unit based in Pinfang, Unit 731, that performed gruesome experiments on people involving much visceration of the subjects to see the effects of chemicals and germs on the human body. In the late 1930s, the doctors of Unit 731 demanded more white subjects to experiment upon in order to test the efficiency the strains of anthrax and plague that they were developing leading to a great many of the Russians living in Manchukuo becoming the unwilling human guinea pigs of Unit 731. The Russian Fascist Party
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
* Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and pe ...
, which worked with the Japanese was used to kidnap various "unreliable" Russians living in Manchukuo for Unit 731 to experiment upon.
The children of the Russian exiles often married Han Chinese, and the resulting children were always known in Manchukuo as "mixed water" people, who were shunned by both the Russian and Chinese communities. Chinese accounts, both at the time and later, tended to portray the Russians living in Manchuria as all prostitutes and thieves, and almost always ignored the contributions made by middle-class Russians to community life. Mindful of the way that Americans and most Europeans enjoyed extraterritorial rights in China at the time, accounts in Chinese literature about the Russians living in Manchukuo and their "mixed water" children often display a certain ''schadenfreude'' recounting how the Russians in Manchukuo usually lived in poverty on the margins of Manchukuo society with the local Chinese more economically successful. The South Korean historian Bong Inyoung noted when it came to writing about the "mixed water" people, Chinese writers tended to treat them as not entirely Chinese, but on the other hand were willing to accept these people as Chinese provided that would totally embrace Chinese culture by renouncing their Russian heritage, thus making Chineseness as much a matter of culture as of race.
Around the same time the Soviet Union was advocating the Siberian Jewish Autonomous Oblast
The Jewish Autonomous Oblast (JAO; russian: Евре́йская автоно́мная о́бласть, (ЕАО); yi, ייִדישע אװטאָנאָמע געגנט, ; )In standard Yiddish: , ''Yidishe Oytonome Gegnt'' is a federal subject ...
across the Manchukuo-Soviet border, some Japanese officials investigated a plan (known as the Fugu Plan
Shortly prior to and during World War II, and coinciding with the Second Sino-Japanese War, tens of thousands of Jewish refugees were resettled in the Japanese Empire. The onset of the European war by Nazi Germany involved the lethal mass persecuti ...
) to attract Jewish refugees to Manchukuo as part of their colonisation efforts which was never adopted as official policy. The Jewish community in Manchukuo was not subjected to the official persecution that Jews experienced under Japan's ally Nazi Germany, and Japanese authorities were involved in closing down local anti-Semitic publications such as the Russian periodical ''Nashput''. However, Jews in Manchukuo were victims of harassment by antisemitic elements among the White Russian population, one notable incident being the murder of Simon Kaspé. In 1937 the Far Eastern Jewish Council was created, chaired by the Harbin Jewish community leader Dr. Abraham Kaufman. Between 1937 and 1939 the city of Harbin in Manchukuo was the location of the Conference of Jewish Communities in the Far East. Following the Russian Red Army's invasion of Manchuria in 1945, Dr. Kaufman and several other Jewish community leaders were arrested by the Soviets and charged with anti-Soviet activities, resulting in Kaufman's imprisonment for ten years in a Soviet labor camp.
 The Japanese Ueda Kyōsuke labeled all 30 million people in Manchuria as "Manchus", including Han Chinese, despite the fact that most of them were not ethnic Manchu, and the Japanese written, "Great Manchukuo" built upon Ueda's argument to claim that all 30 million "Manchus" in Manchukuo had the right to independence to justify splitting Manchukuo from China. In 1942 the Japanese wrote "Ten Year History of the Construction of Manchukuo" which attempted to emphasize the right of ethnic Japanese to the land of Manchukuo while attempting to delegitimize the Manchu's claim to Manchukuo as their native land, noting that most Manchus moved out during the Qing period and only returned later.
The Japanese Ueda Kyōsuke labeled all 30 million people in Manchuria as "Manchus", including Han Chinese, despite the fact that most of them were not ethnic Manchu, and the Japanese written, "Great Manchukuo" built upon Ueda's argument to claim that all 30 million "Manchus" in Manchukuo had the right to independence to justify splitting Manchukuo from China. In 1942 the Japanese wrote "Ten Year History of the Construction of Manchukuo" which attempted to emphasize the right of ethnic Japanese to the land of Manchukuo while attempting to delegitimize the Manchu's claim to Manchukuo as their native land, noting that most Manchus moved out during the Qing period and only returned later.
Population of main cities
*Niuzhuang
Yingkou () is a coastal prefecture-level city of central southern Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, on the northeastern shore of Liaodong Bay. It is the third-smallest city in Liaoning with a total area of , and the ninth most populo ...
(119,000 or 180,871 in 1940)
*Mukden
Shenyang (, ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly known as Fengtian () or by its Manchu name Mukden, is a major Chinese sub-provincial city and the provincial capital of Liaoning province. Located in central-north Liaoning, it is the prov ...
(339,000 or 1,135,801 in 1940)
* Xinjing (126,000 or 544,202 in 1940)
* Harbin (405,000 or 661,948 in 1940)
* Andong (92,000 or 315,242 in 1940)
* Kirin (119,000 or 173,624 in 1940)
*Tsitsihar
Qiqihar () is the second-largest city in the Heilongjiang province of China, in the west central part of the province. The built-up (or metro) area made up of Longsha, Tiefeng and Jianhua districts had 959,787 inhabitants, while the total popula ...
(75,000 in 1940)
Source:
Japanese population
 In 1931–2, there were 100,000 Japanese farmers; other sources mention 590,760 Japanese inhabitants. Other figures for Manchukuo speak of a Japanese population 240,000 strong, later growing to 837,000. In Xinjing, they made up 25% of the population. Accordingly, to the census of 1936, of the Japanese population of Manchukuo, 22% were civil servants and their families; 18% were working for the South Manchurian Railroad company; 25% had come to Manchukuo to establish a business, and 21% had come to work in industry. The Japanese working in the fields of transportation, the government, and in business tended to be middle class, white-collar people such as executives, engineers, and managers, and those Japanese who working in Manchukuo as blue collar employees tended to be skilled workers. In 1934, it was reported that a Japanese carpenter working in Manchukuo with its growing economy could earn twice as much as he could in Japan. With its gleaming modernist office buildings, state of the art transport networks like the famous Asia Express railroad line, and modern infrastructure that was going up all over Manchukuo, Japan's newest colony become a popular tourist destination for middle-class Japanese, who wanted to see the "Brave New Empire" that was going up in the mainland of Asia. The Japanese government had official plans projecting the emigration of 5 million Japanese to Manchukuo between 1936 and 1956. Between 1938 and 1942 a batch of young farmers of 200,000 arrived in Manchukuo; joining this group after 1936 were 20,000 complete families. Of the Japanese settlers in Manchukuo, almost half came from the rural areas of Kyushu. When Japan lost sea and air control of the Yellow Sea in 1943–44, this migration stopped.
In 1931–2, there were 100,000 Japanese farmers; other sources mention 590,760 Japanese inhabitants. Other figures for Manchukuo speak of a Japanese population 240,000 strong, later growing to 837,000. In Xinjing, they made up 25% of the population. Accordingly, to the census of 1936, of the Japanese population of Manchukuo, 22% were civil servants and their families; 18% were working for the South Manchurian Railroad company; 25% had come to Manchukuo to establish a business, and 21% had come to work in industry. The Japanese working in the fields of transportation, the government, and in business tended to be middle class, white-collar people such as executives, engineers, and managers, and those Japanese who working in Manchukuo as blue collar employees tended to be skilled workers. In 1934, it was reported that a Japanese carpenter working in Manchukuo with its growing economy could earn twice as much as he could in Japan. With its gleaming modernist office buildings, state of the art transport networks like the famous Asia Express railroad line, and modern infrastructure that was going up all over Manchukuo, Japan's newest colony become a popular tourist destination for middle-class Japanese, who wanted to see the "Brave New Empire" that was going up in the mainland of Asia. The Japanese government had official plans projecting the emigration of 5 million Japanese to Manchukuo between 1936 and 1956. Between 1938 and 1942 a batch of young farmers of 200,000 arrived in Manchukuo; joining this group after 1936 were 20,000 complete families. Of the Japanese settlers in Manchukuo, almost half came from the rural areas of Kyushu. When Japan lost sea and air control of the Yellow Sea in 1943–44, this migration stopped.  About 2% of the Japanese population worked in agriculture. Many had been young, land-poor farmers in Japan that were recruited by the Patriotic Youth Brigade to colonize new settlements in Manchukuo. The Manchukuo government had seized great portions of these land through "price manipulation, coerced sales and forced evictions". Some Japanese settlers gained so much land that they could not farm it themselves and had to hire Chinese or Korean laborers for help, or even lease some of it back to its former Chinese owners, leading to uneasy, sometimes hostile relations between the groups.
When the
About 2% of the Japanese population worked in agriculture. Many had been young, land-poor farmers in Japan that were recruited by the Patriotic Youth Brigade to colonize new settlements in Manchukuo. The Manchukuo government had seized great portions of these land through "price manipulation, coerced sales and forced evictions". Some Japanese settlers gained so much land that they could not farm it themselves and had to hire Chinese or Korean laborers for help, or even lease some of it back to its former Chinese owners, leading to uneasy, sometimes hostile relations between the groups.
When the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
invaded Manchukuo, they captured 850,000 Japanese settlers. With the exception of some civil servants and soldiers, these were repatriated to Japan in 1946–7. Many Japanese orphans in China were left behind in the confusion by the Japanese government and were adopted by Chinese families. Many, however, integrated well into Chinese society. In the 1980s Japan began to organize a repatriation program for them but not all chose to go back to Japan.
The majority of Japanese left behind in China were women, and these Japanese women mostly married Chinese men and became known as "stranded war wives" (zanryu fujin). Because they had children fathered by Chinese men, the Japanese women were not allowed to bring their Chinese families back with them to Japan, so most of them stayed. Japanese law allowed children fathered only by Japanese to become Japanese citizens.
Legal system
Though Manchukuo itself was a product of illegality, as theLeague of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
ruled that Japan had broken international law by seizing Manchuria, the Japanese invested much effort into giving Manchukuo a legal system, believing that this was the fastest way for international recognition of Manchukuo. A particular problem for the Japanese was that Manchukuo was always presented as a new type of state: a multi-ethnic Pan-Asian state comprising Japanese, Koreans, Manchus, Mongols and Chinese to mark the birth of the "New Order in Asia". Typical of the rhetoric surrounding Manchukuo was always portrayed as the birth of a glorious new civilization was the press release issued by the Japanese Information Service on 1 March 1932 announcing the "glorious advent" of Manchukuo with the "eyes of the world turned on it" proclaimed that the birth of Manchukuo was an "epochal event of far-reaching consequences in world history, marking the birth of a new era in government, racial relations, and other affairs of general interest. Never in the chronicles of the human race was any State born with such high ideals, and never has any State accomplished so much in such a brief space of its existence as Manchukuo".
The Japanese went out of their way to try to ensure that Manchukuo was the embodiment of modernity in all of its aspects, as it was intended to prove to the world what the Asian peoples could accomplish if they worked together. Manchukuo's legal system was based upon the Organic Law of 1932, which featured a 12 article Human Rights Protection Law and a supposedly independent judiciary to enforce the law. The official ideology of Manchukuo was the ''wangdao'' ("Kingly Way") devised by a former mandarin under the Qing turned Prime Minister of Manchukuo Zheng Xiaoxu
Zheng Xiaoxu (Cheng Hsiao-hsu; ; Hepburn: ''Tei Kōsho'') (2 April 1860 – 28 March 1938) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat and calligrapher. He served as the first Prime Minister of Manchukuo.
Early life and diplomatic career
Although Zhe ...
calling for an ordered Confucian society that would promote justice and harmony that was billed at the time as the beginning of a new era in world history. The purpose of the law in Manchukuo was not the protection of the rights of the individual, as the ''wangdao'' ideology was expressly hostile towards individualism, which was seen as a decadent Western concept inimical to Asia, but rather the interests of the state by ensuring that subjects fulfilled their duties to the emperor. The ''wangdao'' favored the collective over the individual, as the ''wangdao'' called for all people to put the needs of society ahead of their own needs. Zheng together with the Japanese legal scholar Ishiwara Kanji in a joint statement attacked the Western legal tradition for promoting individualism, which they claimed led to selfishness, greed and materialism, and argued that the ''wangdao'' with its disregard for the individual was a morally superior system. The seemingly idealistic Human Rights Protection Law counterbalanced the "rights" of the subjects with their "responsibilities" to the state with a greater emphasis on the latter, just as was the case in Japan. The ''wangdao'' promoted Confucian morality and spirituality, which was seen as coming down from Emperor Puyi, and as such, the legal system existed to serve the needs of the state headed by Emperor Puyi, who could change the laws as he saw fit. In this regard it is noteworthy that Legislative Yuan had only the power of ''assisting'' the Emperor with making laws, being endowed with far fewer powers than even the Imperial Diet in Japan had, which had the power to reject or approve laws. It was often suggested at the time that the Legislative Yuan of Manchukuo was a model for the Imperial Diet in Japan, an idea Hirohito, the Japanese emperor, was sympathetic to, but never took up. Hirohito in the end preferred the Meiji constitution passed by his grandfather in 1889 as it gave the Emperor of Japan ultimate power, while at the same time the fictitious nature of the Imperial Diet together with a Prime Minister and his cabinet governing Japan gave the Emperor a scapegoat when things went wrong.
Initially, the judges who had served the Zhangs were retained, but in 1934, the Judicial Law College headed by the Japanese judge Furuta Masatake was opened in Changchun, to be replaced by a larger Law University in 1937. Right from the start, the new applicants vastly exceeded the number of openings as the first class of the Law College numbered only 100, but 1,210 students had applied. The legal system that the students were trained was closely modeled after the Japanese legal system, which in its turn was modeled after the French legal system, but there were a number of particularities unique to Manchukuo. Law students were trained to write essays on such topics as the "theory of the harmony of the five races f Manchukuo, the "political theory of the Kingly Way", "practical differences between consular jurisdiction and extraterritoriality", and how best to "realize the governance of the Kingly Way". The Japanese professors were "astonished" by the "enthusiasm" which the students wrote their essays on these subjects as the students expressed the hope that the ''wangdao'' was a uniquely Asian solution to the problems of the modern world, and that Manchukuo represented nothing less than the beginning of a new civilization that would lead to a utopian society in the near future. The Japanese professors were greatly impressed with the Confucian idealism of their students, but noted that their students all used stock phrases to the extent it was hard to tell their essays apart, cited examples of wise judges from ancient China while ignoring more recent legal developments, and were long on expressing idealistic statements about how the ''wangdao'' would lead to a perfect society, but were short on how explaining just how this was to be done in practice.
An example of the extent of Japanese influence on the legal system of Manchukuo was that every issue of the ''Manchukuo Legal Advisory Journal'' always contained a summary of the most recent rulings by the Supreme Court of Japan, and the reasons why the Japanese Supreme Court had ruled in these cases. However, there were some differences between the Manchukuo and Japanese legal systems. In Japan itself, corporal punishment had been abolished as part of the successful effort to end the extraterritorial rights enjoyed by citizens of the Western powers, but retained for the Japanese colonies of Korea and Taiwan. However, corporal punishment, especially flogging, was a major part of the Manchukuo legal system with judges being very much inclined to impose floggings on low-income Chinese men convicted of minor offenses that would normally merit only a fine or a short prison sentence in Japan. Writing in a legal journal in 1936, Ono Jitsuo, a Japanese judge serving in Manchukuo, regretted having to impose floggings as a punishment for relatively minor crimes but argued that it was necessary of Manchukuo's 30 million people "more than half are ignorant and completely illiterate barbarians" who were too poor to pay fines and too numerous to imprison. In Taiwan and Korea, Japanese law was supreme, but judges in both colonies had to respect "local customs" in regards to family law. In the case of Manchukuo, a place with a Han majority, but that ideology proclaimed the "five races" of Japanese, Chinese, Koreans, Manchus, and Mongols as all equal, this led in effect to several family laws for each of the "five races" respecting their "local customs" plus the Russian and Hui Muslim minorities.
The Manchukuo police had the power to arrest without charge anyone who was engaged in the vaguely defined crime of "undermining the state". Manchukuo had an extensive system of courts at four levels staffed by a mixture of Chinese and Japanese judges. All of the courts had both two Japanese and two Chinese judges with the Chinese serving as the nominal superior judges and the Japanese the junior judges, but in practice the Japanese judges were the masters and the Chinese judges puppets. Despite the claims that the legal system of Manchukuo was a great improvement over the legal system presided over by Marshal Zhang Xueliang
Chang Hsüeh-liang (, June 3, 1901 – October 15, 2001), also romanized as Zhang Xueliang, nicknamed the "Young Marshal" (少帥), known in his later life as Peter H. L. Chang, was the effective ruler of Northeast China and much of northern ...
the "Young Marshal", the courts in Manchukuo were inefficient and slow, and ignored by the authorities whenever it suited them. In Asia, the rule of law and an advanced legal system are commonly seen as one of the marks of "civilization", which is why the chaotic and corrupt legal system run by Marshal Zhang was denigrated so much by the Japanese and Manchukuo media. In the early 1930s, Manchukuo attracted much legal talent from Japan as Japanese Pan-Asian idealists went to Manchuria with the goal of establishing a world-class legal system. As the Kwangtung Army had the ultimate power in Manchukuo, the best Japanese judges by the late 1930s preferred not to go to Manchukuo where their decisions could be constantly second-guessed, and instead only the second-rate judges went to Manchukuo. By 1937 the Japanese judges and lawyers in Manchukuo were either disillusioned Pan-Asian idealists or more commonly cynical opportunists and mediocre hacks who lacked the talent to get ahead in Japan. By contrast, the best of the ethnic Chinese law schools graduates in Manchukuo chose to work as part of Manchukuo's judicial system, suggesting many middle-class Chinese families were prepared to accept Manchukuo.
Starting with the Religions Law of May 1938, a cult of Emperor-worship closely modeled after the Imperial cult in Japan where Hirohito was worshiped as a living god, began in Manchukuo. Just as in Japan, schoolchildren began their classes by praying to a portrait of the emperor while imperial rescripts and the imperial regalia become sacred relics imbued with magical powers by being associated with the god-emperor. As the Emperor Puyi was considered to be a living god, his will could not be limited by any law, and the purpose of the law was starkly reduced down to serving the will of the emperor rather than upholding values and rules. As in Japan, the idea governing the legal philosophy in Manchukuo was the Emperor was a living god who was responsible to no-one and who delegated some of his powers down to mere human beings who had the duty of obeying the will of the god-emperors. In Japan and Manchukuo, the actions of the god-emperors were always just and moral because gods could never do wrong, rather than because the god-emperors were acting to uphold moral values that existed ''a priori''.
And again following the Japanese system, in 1937 a new category of "thought crime" was introduced declaring that certain thoughts were now illegal and those thinking these forbidden thoughts were "thought criminals". People were thus convicted not for their actions, but merely for their thoughts. After the war with China began in July 1937, an "emergency law" was declared in Manchukuo, placing it under a type of martial law that suspended the theoretical civil liberties that existed up to that point, ordered the mobilization of society for total war, and increased the tempo of repression with the law on "thought crimes" being merely the most dramatic example. In April 1938, a new type of Special Security Courts were created for those charged with the five types of "thought crime". On 26 August 1941, a new security law ruled that those tried before the Special Security Courts had no right of appeal or to a defense lawyer. One Special Security Court in Jinzhou
Jinzhou (, ), formerly Chinchow, is a coastal prefecture-level city in central-west Liaoning province, China. It is a geographically strategic city located in the Liaoxi Corridor, which connects most of the land transports between North Chin ...
between 1942 and 1945 sentenced about 1,700 people to death and another 2,600 for life imprisonment for "thought crimes", a figure that appears to be typical of the special courts. The police frequently used torture to obtain confessions and those tried in the Special Security Courts had no right to examine the evidence against them. Starting in 1943 the number of those tried and convicted by the courts rose drastically, though the number of death sentences remained stable. The rise in the number of convictions was due to the need for slave labor for the factories and mines of Manchukuo as the traditional supplies of slave labor from northern China were disturbed by World War II as most of those convicted were sentenced to work in the factories and mines. The American historian Thomas David Dubois wrote the legal system of Manchukuo went through two phases: the first lasting from 1931 to 1937, when the Japanese wanted to show the world a state with an ultra-modern legal system that was meant to be a shining tribute to Asians working together in brotherhood; and the second from 1937 to 1945 when the legal system becomes more of a tool for the totalitarian mobilization of society for total war.
Economy
Reichswehr
''Reichswehr'' () was the official name of the German armed forces during the Weimar Republic and the first years of the Third Reich. After Germany was defeated in World War I, the Imperial German Army () was dissolved in order to be reshape ...
'' had started to advocate their own version of the ''Wehrstaat'', the totalitarian "national defense state" which would mobilize an entire society for war in peacetime. An additional influence on the Japanese "total war" school who tended to be very anti-capitalist was the First Five Year Plan in the Soviet Union, which provided an example of rapid industrial growth achieved without capitalism. At least part of the reason why the Kwangtung Army seized Manchuria in 1931 was to use it as an laboratory for creating an economic system geared towards the "national defense state"; colonial Manchuria offered up possibilities for the army carrying out drastic economic changes that were not possible in Japan. From the beginning, the Army intended to turn Manchukuo into the industrial heartland of the empire, and starting in 1932, the Army sponsored a policy of forced industrialization that was closely modeled after the Five Year Plan in the Soviet Union. Reflecting a dislike of capitalism, the ''Zaibatsu
is a Japanese term referring to industrial and financial vertically integrated business conglomerates in the Empire of Japan, whose influence and size allowed control over significant parts of the Japanese economy from the Meiji period unt ...
'' were excluded from Manchukuo and all of the heavy industrial factories were built and owned by Army-owned corporations. In 1935, there was a change when the "reform bureaucrat" Nobusuke Kishi was appointed Deputy Minister of Industrial Development. Kishi persuaded the Army to allow the ''zaibatsu'' to invest in Manchukuo, arguing that having the state carry out the entire industrialization of Manchukuo was costing too much money. Kishi pioneered an elitist system where bureaucrats such as himself developed economic plans, which the ''zaibatsu'' had to then carry out. Kishi succeeded in marshaling private capital in a very strongly state-directed economy to achieve his goal of vastly increased industrial production while at the same time displaying utter indifference to the exploited Chinese workers toiling in Manchukuo's factories; the American historian Mark Driscoll described Kishi's system as a "necropolitical" system where the Chinese workers were literally treated as dehumanized cogs within a vast industrial machine. The system that Kishi pioneered in Manchuria of a state-guided economy where corporations made their investments on government orders later served as the model for Japan's post-1945 development, albeit not with same level of brutal exploitation as in Manchukuo. By the 1930s, Manchukuo's industrial system was among the most advanced making it one of the industrial powerhouses in the region. Manchukuo's steel production exceeded Japan's in the late 1930s. Many Manchurian cities were modernized during the Manchukuo era. However, much of the country's economy was often subordinated to Japanese interests and, during the war, raw material flowed into Japan to support the war effort. Traditional lands were taken and redistributed to Japanese farmers with local farmers relocated and forced into collective farming
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
units over smaller areas of land.
Transport
The Japanese built an efficient and impressive railway system that still functions well today. Known as theSouth Manchuria Railway
The South Manchuria Railway ( ja, 南満州鉄道, translit=Minamimanshū Tetsudō; ), officially , Mantetsu ( ja, 満鉄, translit=Mantetsu) or Mantie () for short, was a large of the Empire of Japan whose primary function was the operatio ...
or ''Mantetsu'', this large corporation came to own large stakes in many industrial projects throughout the region. ''Mantetsu'' personnel were active in the pacification of occupied China during World War II. However, most railway lines in Manchukuo were owned by the Manchukuo National Railway, which, though theoretically independent, was managed and operated entirely by Mantetsu.
Military
Manchukuo Imperial Army
The Manchukuo Imperial Army ( zh, s=滿洲國軍, p=Mǎnzhōuguó jūn) was the ground force of the military of the Empire of Manchukuo, a puppet state established by Imperial Japan in Manchuria, a region of northeastern China. The force was pri ...
was the ground component of the Empire of Manchukuo's armed forces and consisted of as many as 170,000 to 220,000 troops at its peak in 1945 by some estimates, having formally been established by the Army and Navy Act of 15 April 1932. The force included members of all the major ethnic groups of Manchukuo, which were trained and led by Japanese instructors and advisors. Despite the numerous attempts by the Japanese to improve the combat capability of the Imperial Army and instill a Manchukuoan patriotic spirit among its troops, the majority of its units were regarded as unreliable by Japanese officers. Their main role was to fight Nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
and Communist insurgents that continued to resist the Japanese occupation of northeastern China, and occasionally the Manchukuo Imperial Army took part in operations against the Chinese National Revolutionary Army and the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
(usually in support of the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
). Initially its members were former soldiers of Marshal Zhang Xueliang
Chang Hsüeh-liang (, June 3, 1901 – October 15, 2001), also romanized as Zhang Xueliang, nicknamed the "Young Marshal" (少帥), known in his later life as Peter H. L. Chang, was the effective ruler of Northeast China and much of northern ...
's warlord army who had surrendered to Japan during the Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until the ...
. But since the Young Marshal's former troops were largely not loyal to the new regime and performed poorly against partisans, the new government of Manchukuo took efforts to recruit—and later draft—new soldiers. In 1934 a law was passed stating that only those that had been trained by the government of Manchukuo could serve as officers. The Military Supplies Requisition Law of 13 May 1937 allowed Japanese and Manchukuo authorities to draft forced laborers. The actual calling up of conscripts for the army did not begin until 1940, at which point all youths received a physical and 10% were to be selected for service. Between 1938 and 1940, several military academies were established to provide a new officer corps for the Imperial Army, including a specific school for ethnic Mongols.
After fighting against insurgents during the early to mid-1930s, the Manchukuo Imperial Army played mainly a supporting role during the actions in Inner Mongolia against Chinese forces, with news reports stating that some Manchukuoan units performed fairly well. Later it fought against the Soviet Red Army during the Soviet–Japanese border conflicts
The Soviet–Japanese border conflicts, also known as the Soviet-Japanese Border War or the First Soviet-Japanese War,was a series of minor and major conflicts fought between the Soviet Union (led by Joseph Stalin), Mongolia (led by Khorloo ...
. A skirmish between Manchukuoan and Mongolian cavalry in May 1939 escalated as both sides brought in reinforcements and began the Battle of Khalkhin Gol
The Battles of Khalkhin Gol (russian: Бои на Халхин-Голе; mn, Халхын голын байлдаан) were the decisive engagements of the undeclared Soviet–Japanese border conflicts involving the Soviet Union, Mongolia, ...
. Although they did not perform well in the battle overall, the Japanese considered their actions decent enough to warrant expansion of the Manchukuo Army. Throughout the 1940s the only action it saw was against Communist guerrilla fighters and other insurgents, although the Japanese chose to rely only on the more elite units while the majority were used for garrison and security duty. Although Japan took the effort of equipping the Manchukuoan forces with some artillery (in addition to the wide variety it had inherited from Zhang Xueliang's army) along with some elderly tankette
A tankette is a tracked armoured fighting vehicle that resembles a small tank, roughly the size of a car. It is mainly intended for light infantry support and scouting.
s and armored cars, the cavalry was the Imperial Army's most effective and developed branch. This was the force that was confronted by 76 battle-hardened Red Army divisions transferred from the European front in August 1945 during the Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian strategic offensive operation (russian: Манчжурская стратегическая наступательная операция, Manchzhurskaya Strategicheskaya Nastu ...
. The cavalry branch saw the most action against the Red Army, but the Manchukuo Army and their depleted Japanese Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
allies were quickly swept aside by the Soviet offensive. While some units remained loyal to their Japanese allies and put up a resistance, many mutinied against their Japanese advisors while others simply melted away into the countryside. Many of these Manchukuo Army troops would later join the Communists since the Chinese Nationalists would execute former collaborators with Japan, which became an important source of manpower and equipment for the Communists in the region.
Manchukuo Imperial Air Force
The Manchukuo Imperial Air Force (') ( was the air force of the Empire of Manchuria, a puppet state of Imperial Japan. The air force's predecessor was the Manchukuo Air Transport Company (later renamed the Manchukuo National Airways), a paramilit ...
and the Manchukuo Imperial Navy, were small and underdeveloped, largely existing as token forces to give legitimacy to the Manchukuo regime. An Air Force was established in February 1937 with 30 men selected from the Manchukuo Imperial Army who were trained at the Japanese Kwantung Army aircraft arsenal in Harbin (initially the Kwantung Army did not trust the Manchukuoans enough to train a native air force for them). The Imperial Air Force's predecessor was the Manchukuo Air Transport Company (later renamed the Manchukuo National Airways), a paramilitary airline formed in 1931, which undertook transport and reconnaissance missions for the Japanese military. The first air unit was based in Xinjing (Changchun) and equipped with just one Nieuport-Delage NiD 29
The Nieuport-Delage NiD.29 was a French single-seat biplane fighter (C.I category) designed and built by Nieuport-Delage for the French Air Force.
Design and development
The prototype NiD.29 was an equal-span biplane with ailerons on both u ...
and was later expanded with Nakajima Army Type 91 Fighter
The Nakajima Army Type 91 Fighter was a Japanese fighter of the 1930s. It was a single-engine, single-seat parasol monoplane with a fixed, tailwheel undercarriage.
Development
Designed in response to an Army requirement of 1927, the Type 91 w ...
s and Kawasaki Type 88 light bombers. Two more air units were established, but they suffered a setback when one hundred pilots took their aircraft and defected to insurgents after murdering their Japanese instructors. Nonetheless, three fighter squadrons were formed in 1942 from the first batch of cadets, being equipped with Nakajima Ki-27
The was the main fighter aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service up until 1940. Its Allied nickname was "Nate", although it was called "Abdul" in the "China Burma India" (CBI) theater by many post war sources; Allied Intellige ...
fighters in addition to Tachikawa Ki-9s and Tachikawa Ki-55
The Tachikawa Ki-55 was a Japanese advanced trainer.
Design and development
The excellent characteristics of the Tachikawa Ki-36 made it potentially ideal as a trainer. This led to the development of the Ki-55 with a single machine gun. Afte ...
trainers, along with some Mitsubishi Ki-57
The Mitsubishi Ki-57 was a Japanese passenger transport aircraft, developed from the Ki-21 bomber, during the early 1940s.
Development
In 1938, when the Ki-21 heavy bomber began to enter service with the Imperial Japanese Army, its capability ...
transports. In 1945, because of American bombing raids, they were issued with Nakajima Ki-43
The Nakajima Ki-43 ''Hayabusa'' (, "Peregrine falcon", "Army Type 1 Fighter" ) is a single-engine land-based tactical fighter used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service in World War II.
The Allied reporting name was "Oscar", but it was o ...
fighters to have a better chance of intercepting B-29 Superfortresses. Some pilots saw action against the American bombers and at least one Ki-27 pilot downed a B-29 by ramming his plane into it in a kamikaze
, officially , were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who flew suicide attacks for the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, intending t ...
attack. The air force practically ceased to exist by the Soviet invasion but there were isolated instances of Manchukuoan planes attacking Soviet forces. The Imperial Navy of Manchukuo existed mainly as a small river flotilla and consisted mainly of small gunboats and patrol boats, both captured Chinese ships and some Japanese additions. The elderly Japanese destroyer ''Kashi'' was lent to the Manchukuoan fleet from 1937 to 1942 as the ''Hai Wei'' before returning to the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrend ...
. These ships were mostly crewed by Japanese sailors.
In addition, several specialized units functioned outside of the main command structure of the military also existed. The Manchukuo Imperial Guard was formed out of soldiers of ethnic Manchu descent, charged with the protection of the Kangde Emperor (Puyi) and senior officials, as well as to function as an honor guard
A guard of honour ( GB), also honor guard ( US), also ceremonial guard, is a group of people, usually military in nature, appointed to receive or guard a head of state or other dignitaries, the fallen in war, or to attend at state ceremonials, ...
. Despite this it took part in combat and was considered to be an effective unit. Throughout the 1930s a "Mongolian Independence Army" was established out of about 6,000 ethnic Mongolian recruits and fought its own war against bandits with some success. It was expanded in 1938 but merged with the regular Imperial Army in 1940, although Mongol units continued to perform well. A special Korean detachment was formed in 1937 on the personal initiative of a businessman of Korean descent. The unit was small but distinguished itself in combat against Communist guerrillas and was noted by the Japanese for its martial spirit, becoming one of the few puppet units to earn the respect of its Japanese superiors.
Police
The Manchukuo government also established apolice force
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and th ...
for general law-enforcement activities. It also included a Marine Police.
Human rights abuses
War crimes in Manchukuo
According to a joint study by historians Zhifen Ju, Mitsuyochi Himeta, Toru Kubo, and Mark Peattie, more than ten million Chinese civilians were used by the Kwantung Army for slave labor in Manchukuo under the supervision of the Kōa-in. The Chinese slave laborers often suffered illness due to high-intensity manual labor. Some badly ill workers were directly pushed intomass grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact ...
s in order to avoid the medical expenditure and the world's most serious mine disaster, at Benxihu Colliery
Benxihu (Honkeiko) Colliery (), located in Benxi, Liaoning, China, was first mined in 1905. Originally an iron and coal mining project under joint Japanese and Chinese control, the mine came under predominantly Japanese control. In the early 1930s, ...
, happened in Manchukuo.
Bacteriological weapons were experimented on humans by the infamous Unit 731
, short for Manshu Detachment 731 and also known as the Kamo Detachment and Ishii Unit, was a covert Biological warfare, biological and chemical warfare research and development unit of the Imperial Japanese Army that engaged in unethical h ...
located near Harbin in Beinyinhe from 1932 to 1936 and to Pingfan until 1945. Victims, mostly Chinese, Russians and Koreans, were subjected to vivisection
Vivisection () is surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure. The word is, more broadly, used as a pejorative catch-all term for Animal testi ...
, sometimes without anesthesia.
Abuse of ethnic minorities
The Oroqen suffered a significant population decline under Japanese rule. The Japanese distributed opium among them and subjected some members of the community to human experiments, and combined with incidents of epidemic diseases this caused their population to decline until only 1,000 remained. The Japanese banned Oroqen from communicating with other ethnicities, and forced them to hunt animals for them in exchange for rations and clothing which were sometimes insufficient for survival, which led to deaths from starvation and exposure. Opium was distributed to Oroqen adults older than 18 as a means of control. After 2 Japanese troops were killed in Alihe by an Oroqen hunter, the Japanese poisoned 40 Oroqen to death. The Japanese forced Oroqen to fight for them in the war which led to a population decrease of Oroqen people. Even those Oroqen who avoided direct control by the Japanese found themselves facing conflict from anti-Japanese forces of the Chinese Communists, which contributed to their population decline during this period. Between 1931 and 1945, theHezhen
The Nanai people are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Jurchens of northernmost Manch ...
population declined by 80% or 90%, due to heavy opium use and deaths from Japanese cruelty, such as slave labor and relocation by the Japanese.
Drug trafficking
 In 2007, an article by Reiji Yoshida in ''
In 2007, an article by Reiji Yoshida in ''The Japan Times
''The Japan Times'' is Japan's largest and oldest English-language daily newspaper. It is published by , a subsidiary of News2u Holdings, Inc.. It is headquartered in the in Kioicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo.
History
''The Japan Times'' was launched b ...
'' argued that Japanese investments in Manchukuo were partly financed by selling drugs. According to the article, a document found by Yoshida shows that the Kōa-in was directly implicated in providing funds to drug dealers in China for the benefit of the puppet governments of Manchukuo, Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. This document corroborates evidence analyzed earlier by the Tokyo tribunal
The International Military Tribunal for the Far East (IMTFE), also known as the Tokyo Trial or the Tokyo War Crimes Tribunal, was a military trial convened on April 29, 1946 to try leaders of the Empire of Japan for crimes against peace, conve ...
which stated that
Society and culture
National symbols
Aside from the national flag, the orchid, reportedly Puyi's favorite flower, became the royal flower of the country, similar to the chrysanthemum in Japan. The sorghum flower also became a national flower by decree in April 1933. "Five Races Under One Union
Five Races Under One Union was one of the major principles upon which the Republic of China was founded in 1911 at the time of the Xinhai Revolution. Its central tenet was the harmonious existence under one nation of what were considered the f ...
" was used as a national motto.
Education
Manchukuo developed an efficient public education system. The government established many schools and technical colleges, 12,000 primary schools in Manchukuo, 200 middle schools, 140 normal schools (for preparing teachers), and 50 technical and professional schools. In total the system had 600,000 children and young pupils and 25,000 teachers. Local Chinese children and Japanese children usually attended different schools, and the ones who did attend the same school were segregated by ethnicity, with the Japanese students assigned to better-equipped classes. Confucius's teachings also played an important role in Manchukuo's public school education. In rural areas, students were trained to practice modern agricultural techniques to improve production. Education focused on practical work training for boys and domestic work for girls, all based on obedience to the "Kingly Way" and stressing loyalty to the Emperor. The regime used numerous festivals, sports events, and ceremonies to foster loyalty of citizens.Japan Focus. Eventually, Japanese became the official language in addition to the Chinese taught in Manchukuo schools.
Film
The Photographic Division, part of the public relations section of the South Manchurian Railway was created in 1928 to produce short documentary films about Manchuria to Japanese audiences. In 1937, theManchukuo Film Association
or (Chinese: 株式會社滿洲映畫協會) was a Japanese film studio in Manchukuo during the 1930s and 1940s.
Background
Man'ei was established by the Kwantung Army in the occupied northeast part of China in 1937. Man'ei controlled the en ...
was established by the government and the South Manchurian Railway in a studio in Jilin province. It was founded by Masahiko Amakasu
was an officer in the Imperial Japanese Army imprisoned for his involvement in the Amakasu Incident, the extrajudicial execution of anarchists after the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, who later became head of the Manchukuo Film Association.
B ...
, who also helped the career of Yoshiko Ōtaka
was a Japanese singer, actress, journalist, and politician. Born in China, she made an international career in film in China, Hong Kong, Japan and the United States.
Early in her career, the Manchukuo Film Association concealed her Japanese ori ...
, also known as Ri Koran. He also tried to ensure that Manchukuo would have its own industry and would be catering mainly to Manchurian audiences. The films for the most part usually promote pro-Manchukuo and pro-Japanese views. General Amakasu shot various "documentaries" showing carefully choreographed scenes worthy of Hollywood of Emperor Puyi in his capital of Hsinking (modern Changchun) being cheered by thousands of subjects and reviewing his troops marching in parades that were intended to help legitimize Manchukuo's independence. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the archives and the equipment of the association were used by the Changchun Film Studio of the People's Republic of China.
Dress
TheChangshan
(; ), also known as (), and (), is a form of , Chinese robe, which was derived from the Qing dynasty , the traditional dress of the Manchu people, which were worn by Manchu men. The was actually developed by the Han Chinese through the modi ...
and the Qipao
''Cheongsam'' (, ), also known as the ''qipao'' () and sometimes referred to as the mandarin gown, is a Chinese dress worn by women which takes inspiration from the , the ethnic clothing of the Manchu people. The cheongsam is most often se ...
, both derived from traditional Manchu dress, were considered national dresses in Manchukuo.
In a meeting with the Concordia Association
The Concordia Association ( Japanese Shinjitai: 満州国協和会, Hepburn: ''Manshū-koku Kyōwakai'') was a political party in Manchukuo. Established to promote the ideals of Pan-Asianism and the creation of a multi-ethnic nation-state and ...
, the organizers devised what was termed Concordia Costume, or the ''kyōwafuku'', in 1936. Even Japanese such as Masahiko Amakasu and Kanji Ishiwara adopted it. It was gray and a civilianized version of the Imperial Japanese Army uniform. It was similar to the National Clothes ''(kokumin-fuku)'' worn by Japanese civilians in World War II as well as the Zhongshan suit
Zhongshan (; ) is a prefecture-level city in the south of the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong province, China. As of the 2020 census, the whole city with 4,418,060 inhabitants is now part of the Guangzhou–Shenzhen conurbation with 65,565,622 i ...
. A pin of either a Manchukuo flag or a five-pointed, five colored star with the Manchukuo national colors were worn on the collars. Court dress resembled those of Meiji-era Japan at that time.
Sport
The Manchukuo National Physical Education Association was established in 1932 to promote sports. Manchukuo also had a national football team, and football was considered the country's de facto national sport; the Football Association of Manchukuo was formed around it. Manchukuo hosted and participated in baseball matches with Japanese teams. Some of the games of the Intercity baseball tournament were held in the country, and played with local teams. Manchukuo was to compete in the 1932 Summer Olympics, but one of the athletes who intended to represent Manchukuo,Liu Changchun
Liu Changchun (; listed in official Olympic records as "Liu, Cheng-Chun";''The Games of the Xth Olympiad, Los Angeles, 1932: Official Report'', The Xth Olympiade Committee of the Games of Los Angeles, U.S.A. 1932 Ltd., 1933.http://www.la84founda ...
, refused to join the team and instead joined as the first Chinese representative in the Olympics. There were attempts by Japanese authorities to let Manchukuo join the 1936 games, but the Olympic Committee persisted in the policy of not allowing an unrecognized state to join the Olympics. Manchukuo had a chance to participate in the planned 1940 Helsinki Olympics, but the onset of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
prevented the games from taking place. Manchukuo instead sent athletes to compete at the 1940 East Asian Games
The East Asian Games ( ja, 東亜競技大会, links=no, ''Tōa Kyōgi Taikai''), also known as the Asian Development Games ( ja, 興亜競技大会, links=no, ''Kōa Kyōgi Taikai'') were multi-sport events organized by the Japan Association of ...
in Tokyo organised by the Japanese Empire, as a replacement for the cancelled 1940 Summer Olympics.
Stamps and postal history
Manchukuo issuedpostage stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail), who then affix the stamp to the f ...
s from 28 July 1932 until its dissolution following the surrender of the Empire of Japan in August 1945. The last issue of Manchukuo was on 2 May 1945.
Notable figures
Local Administration: *Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
: Emperor of Manchukuo (1934–1945); formerly the last Emperor of China and the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
*Pujie
Pujie (; 16 April 1907 – 28 February 1994) was a Qing dynasty imperial prince of the Aisin-Gioro. Pujie was the younger brother of Puyi, the last Emperor of China. After the fall of the Qing dynasty, Pujie went to Japan, where he was educated ...
: Head of the Manchukuo Imperial Guards (1933–1945), younger brother of Puyi, and former Qing prince
*Empress Wanrong
Wanrong (; 13 November 1906 – 20 June 1946), of the Manchu Plain White Banner Gobulo clan, was the wife and empress consort of Puyi, the last Emperor of China, sometimes anachronistically called the “Xuantong Empress”, referring to Puy ...
: Empress of Manchukuo (1934–1945) and Empress Consort of Puyi
*Jin Yunying
Jin is a toneless pinyin romanization of various Chinese names and words. These have also been romanized as Kin and Chin (Wade–Giles). "Jin" also occurs in Japanese and Korean.
It may refer to:
States Jìn 晉
* Jin (Chinese state) (晉國) ...
: Younger sister of Puyi and former Qing princess
*Yoshiko Kawashima
was a Qing dynasty princess of the Aisin-Gioro clan. She was raised in Japan and served as a spy for the Japanese Kwantung Army and Manchukuo during the Second Sino-Japanese War. She is sometimes known in fiction under the pseudonym "Eastern Ma ...
: Spy for the Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
and Manchukuo and former Qing princess
*Zheng Xiaoxu
Zheng Xiaoxu (Cheng Hsiao-hsu; ; Hepburn: ''Tei Kōsho'') (2 April 1860 – 28 March 1938) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat and calligrapher. He served as the first Prime Minister of Manchukuo.
Early life and diplomatic career
Although Zhe ...
: First Prime Minister of Manchukuo (1932–1935) and close advisor and tutor to Puyi
*Luo Zhenyu
Luo Zhenyu or Lo Chen-yü (August 8, 1866 – May 14, 1940), courtesy name Shuyun (叔蘊), was a Chinese classical scholar, philologist, epigrapher, antiquarian and Qing loyalist.
Biography
A native of Huai'an, Luo began to publish works ...
: Chairman of the Japan-Manchukuo Cultural Cooperation Society, tutor and advisor to Puyi, and Qing loyalist
*Zhang Jinghui
Zhang Jinghui (Chang Ching-hui; ; Hepburn: ''Chō Keikei''); (1871 – 1 November 1959) was a Chinese general, warlord and politician during the Warlord era. He is noted for his role in the Japanese puppet regime of Manchukuo in which he serve ...
: Second and last Prime Minister of Manchukuo (1935–1945), Foreign Minister (1937), and Minister of Defense (1932–1935)
*Ma Zhanshan
Ma Zhanshan (Ma Chan-shan; ; November 30, 1885 – November 29, 1950) was a Chinese general who initially opposed the Imperial Japanese Army in the invasion of Manchuria, briefly defected to Manchukuo, and then rebelled and fought against the ...
: Minister of Defense (1932) and governor of Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
province (1931–1933); former Chinese general who was one of the main leaders against the Japanese during the invasion of Manchuria
*Xi Qia
Aisin-Gioro Xiqia (Aisin-Gioro Hsi-hsia; ; 1883–1950), commonly known as Xi Qia or Xi Xia (Hsi Hsia; ; Hepburn: ''Ki Kō''), was a general in command of the Kirin Provincial Army of the Republic of China, who defected to the Japanese during t ...
: Imperial Household Minister and Interior Minister (1935–1945) and later Minister of Finance (1932–1935)
* Zang Shiyi: Governor of Liaoning province, Speaker of the Senate (1935–1945), Vice Minister for Home Affairs, and ambassador to the Reorganized National Government of China
The Wang Jingwei regime or the Wang Ching-wei regime is the common name of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China ( zh , t = 中華民國國民政府 , p = Zhōnghuá Mínguó Guómín Zhèngfǔ ), the government of the pup ...
* Xie Jieshi: Foreign Minister (1932–1935), ambassador to Japan, and Minister of Industry
*Yu Zhishan
Yu Zhishan (; Hepburn: ''U Shizan''; 1882 – May 1951), was a military officer under the Beiyang Government and the Fengtian clique, subsequently becoming a cabinet minister in the Empire of Manchukuo.
Biography
A native of Liaoning Province, ...
: Minister of Defense (1935–1939), commander-in-chief of the 1st Army, and Army Minister
*Sun Qichang
Sun Qichang (; Hepburn: ''Son Kishō''; 1885–1954), was a politician in the early Republic of China who subsequently served as a cabinet minister in the Empire of Manchukuo.
Biography
A native of Liaoyang Liaoning Province, Sun studied at t ...
: Director of the Spirits and Tobacco State Monopoly, governor of Heilongjiang province, governor of Longjiang province, Minister of Finance, and Minister of Civil Affairs
* Liu Menggeng: Governor of Rehe province (1934–1937)
* Bao Guancheng: Mayor of Harbin and ambassador to Japan
* Zhang Yanqing: Foreign Minister (1935–1937), Industry Minister, and Co-Director of the Concordia Association
*Li Shaogeng
Li Shaogeng (; Hepburn: ''Ri Shōkō''; b. 1896), was a politician in the early Republic of China who subsequently served in a number of cabinet posts of the Empire of Manchuria.
Biography
A native of Liaoyang Liaoning Province, Li graduated ...
: Foreign Minister (1942–1944), Minister of Transportation, and Special Envoy to the Reorganized National Government of China
* Ruan Zhenduo: Chief Secretary for Liaoning province, co-founder of the Concordia Association, Foreign Minister (1944–1945), Minister of Education (1935–1937), Minister of Transportation (1940–1942), and Minister of Finance (1942–1944)
* Ding Jianxiu: Minister of Transportation (1934–1935) and Minister of Enterprises (1935–1937)
* Lü Ronghuan: Mayor of Harbin, Governor of Harbin Special Municipality (1933–1935), Governor of Binjiang Province (1934–1935), Minister of Civil Affairs (1935–1937) (1940–1941), Minister of Enterprises (1937), Minister of Industries (1937–1940), and special envoy to the Reorganized National Government of China (1941–1944)
* Yuan Jinkai: Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal
*Li Yuan
Emperor Gaozu of Tang (7 April 566 – 25 June 635, born Li Yuan, courtesy name Shude) was the founding emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 618 to 626. Under the Sui dynasty, Li Yuan was the governor in the area of modern-da ...
: Co-founder of the East Hebei Autonomous Council
The East Hebei Autonomous Government (),Japanese also known as the East Ji Autonomous Government and the East Hebei Autonomous Anti-Communist Government, was a short-lived late-1930s state in northern China. It has been described by historians ...
* Tong Jixu: Chief of Security to the Imperial Household Department
The Imperial Household Department (; mnc, , v=dorgi baita be uheri kadalara yamun) was an institution of the Qing dynasty of China. Its primary purpose was to manage the internal affairs of the Qing imperial family and the activities of the inn ...
*Zhang Haipeng
Zhang Haipeng (, Hepburn: ''Chō Kaihō''; 1867–1949), was a Chinese Northeastern Army general, who went over to the Japanese during the Invasion of Manchuria and became a general in the Manchukuo Imperial Army of the State of Manchuria.
Bio ...
: Governor of Rehe province (1933–1934), Commander of the Taoliao Army, Commander of the Rehe Guard Army
*Li Chi-chun Li Jizhun (1875–?), a Chinese general from the beginning of the Republic of China, leader of a Japanese puppet force in southeast Manchukuo from 1933 -1935.
Li Jizhun, born in Hubei in 1875, became a general after serving in the Republican Army ...
: General and commander of the National Salvation Army (A Japanese puppet force)
* Liu Guitang: Manchukuo soldier and commander, involved in the actions in Inner Mongolia (1933–1936)
The Inner Mongolian campaign in the period from 1933 to 1936 were part of the ongoing invasion of northern China by the Empire of Japan prior to the official start of hostilities in the Second Sino-Japanese War. In 1931, the invasion of Manchur ...
* Cui Xingwu: Officer in the 55th army of Jehol under Tang Yulin and commanded the 9th Cavalry brigade during the Battle of Rehe
The Battle of Rehe (, sometimes called the Battle of Jehol) was the second part of Operation Nekka, a campaign by which the Empire of Japan successfully captured the Inner Mongolian province of Rehe from the Chinese warlord Zhang Xueliang and an ...
before subsequently defecting to the Japanese; later involved in the actions in Inner Mongolia
* Yangsanjab: Head of the Khorchin Left Wing Middle Banner and a Mongol prince from Southeastern Mongolia
Culture:
* Jue Qing: Writer; later labeled as a "traitor to the Chinese nation"
White Russian leaders:
* Vladimir Kislitsin: Former Imperial Russian Army officer and later a commander of the White movement
*Grigory Mikhaylovich Semyonov
Grigory Mikhaylovich Semyonov, or Semenov (russian: Григо́рий Миха́йлович Семёнов; September 25, 1890 – August 30, 1946), was a Japanese-supported leader of the White movement in Transbaikal and beyond from December ...
: Former Imperial Russian Army soldier and general of the White movement; employed by Puyi, the Emperor of Manchukuo
* Urzhin Garmaev: White movement general who served in the Manchukuo Imperial Army
The Manchukuo Imperial Army ( zh, s=滿洲國軍, p=Mǎnzhōuguó jūn) was the ground force of the military of the Empire of Manchukuo, a puppet state established by Imperial Japan in Manchuria, a region of northeastern China. The force was pri ...
as a lieutenant general
*Konstantin Petrovich Nechaev
Konstantin Petrovich Nechaev (russian: Константин Петрович Нечаев, pl, Konstantin Pietrowicz Nieczajew; 31 May 1883 – 5 February 1946) was an Imperial Russian Army officer and White movement leader, who commanded a larg ...
: Former Imperial Russian Army officer and general of the White movement; lived in Manchukuo after its founding
*Konstantin Rodzaevsky
Konstantin Vladimirovich Rodzaevsky (russian: Константи́н Влади́мирович Родзае́вский; – 30 August 1946) was the leader of the Russian Fascist Party, which he led in exile from Manchuria. Rodzaevsky was also ...
: Leader of the Russian Fascist Party based in Manzhouli
Manzhouli (; mn, Манжуур хот; ) is a sub-prefectural city located in Hulunbuir prefecture-level city, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Located on the border with Russia, it is a major land port of entry. It has an area of and ...
, Manchukuo
Notable Koreans:
* Park Chung-hee: Enlisted and served in the Manchukuo Imperial Army during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
as a lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often ...
; later served in the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
and became a general in the Republic of Korea Army
The Republic of Korea Army (ROKA; ko, 대한민국 육군; Hanja: 大韓民國 陸軍; RR: ''Daehanminguk Yuk-gun''), also known as the ROK Army or South Korean Army, is the army of South Korea, responsible for ground-based warfare. It is the l ...
and the 3rd President of South Korea
The president of the Republic of Korea (), also known as the president of South Korea (often abbreviated to POTROK or POSK; ), is the head of state and head of government of the Republic of Korea. The president leads the State Council, and is ...
; assassinated in 1979
* Chung Il-kwon: Served in the Manchukuo Imperial Army as a captain during World War II; later served in the Korean War and became a South Korean Army General and subsequently served as Foreign Minister and the 8th Prime Minister of South Korea
The prime minister of the Republic of Korea (PMOTROK or PMOSK; ) is the deputy head of government and the second highest political office of South Korea who is appointed by the President of the Republic of Korea, with the National Assembly's app ...
*Paik Sun-yup
Paik Sun-yup (; November 23, 1920 – July 10, 2020) was a South Korean military officer. Paik is best known for his service during the Korean War, for being the first four-star general in the history of the South Korean military, and for his ...
: Enlisted in the Manchukuo Imperial Army during World War II as a first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a ...
and served with the Gando Special Force; later joined the South Korean Army and served in the Korean War as a general; passed away on July 10, 2020
*Kim Chang-ryong
Kim Chang-ryong (July 18, 1920 – January 30, 1956) was a high-ranking officer in the Republic of Korea Army, the head of the Korean Counter Intelligence Corps, and South Korean President Syngman Rhee's most trusted right-hand man. He was assas ...
: Joined the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
in Manchukuo and served in the Military police as a detective to hunt down moles in the Kenpeitai
The , also known as Kempeitai, was the military police arm of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1881 to 1945 that also served as a secret police force. In addition, in Japanese-occupied territories, the Kenpeitai arrested or killed those suspecte ...
and Communists; later joined the South Korean Army as a high-ranking officer and became the head of the National Intelligence Service; assassinated in 1956 by army colleagues
In popular culture
InMasaki Kobayashi
was a Japanese film director and screenwriter, best known for the epic trilogy ''The Human Condition'' (1959–1961), the samurai films '' Harakiri'' (1962) and '' Samurai Rebellion'' (1967), and the horror anthology ''Kwaidan'' (1964). ''Sens ...
's ''The Human Condition
''The Human Condition'', first published in 1958, is Hannah Arendt's account of how "human activities" should be and have been understood throughout Western history. Arendt is interested in the ''vita activa'' (active life) as contrasted with ...
'' (1959), Kaji, the main protagonist, is a labor supervisor assigned to a workforce consisting of Chinese prisoners in a large mining operation in Japanese-colonized Manchuria.
Bernardo Bertolucci
Bernardo Bertolucci (; 16 March 1941 – 26 November 2018) was an Italian film director and screenwriter with a career that spanned 50 years. Considered one of the greatest directors in Italian cinema, Bertolucci's work achieved international ...
's 1987 film ''The Last Emperor
''The Last Emperor'' ( it, L'ultimo imperatore) is a 1987 epic biographical drama film about the life of Puyi, the final Emperor of China. It is directed by Bernardo Bertolucci from a screenplay he co-wrote with Mark Peploe, which was adapted ...
'' presented a portrait of Manchukuo through the memories of Emperor Puyi
Aisin-Gioro Puyi (; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), courtesy name Yaozhi (曜之), was the last emperor of China as the eleventh and final Qing dynasty monarch. He became emperor at the age of two in 1908, but was forced to abdicate on 1 ...
, during his days as a political prisoner in the People's Republic of China.
Haruki Murakami
is a Japanese writer. His novels, essays, and short stories have been bestsellers in Japan and internationally, with his work translated into 50 languages and having sold millions of copies outside Japan. He has received numerous awards for his ...
's 1995 novel ''The Wind-Up Bird Chronicle
is a novel published in 1994–1995 by Japanese author Haruki Murakami. The American translation and its British adaptation, dubbed the "only official translations" ( English), are by Jay Rubin and were first published in 1997. For this novel, M ...
'' deals greatly with Manchukuo through the character of Lieutenant Mamiya. Mamiya recalls, in person and in correspondence, his time as an officer in the Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
in Manchukuo. While the period covered in these recollections extends over many years, the focus is on the final year of the war and the Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian strategic offensive operation (russian: Манчжурская стратегическая наступательная операция, Manchzhurskaya Strategicheskaya Nastu ...
.
The 2008 South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
n western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
''The Good, the Bad, the Weird
''The Good, the Bad, the Weird'' () is a 2008 South Korean Western action film directed by Kim Jee-woon and starring Song Kang-ho, Lee Byung-hun, and Jung Woo-sung.' The film is inspired by the 1966 Italian Spaghetti Western ''The Good, the Bad ...
'' is set in the desert wilderness of 1930s Manchuria.
Michael Chabon
Michael Chabon ( ;
born May 24, 1963) is an American novelist, screenwriter, columnist, and short story writer. Born in Washington, DC, he spent a year studying at Carnegie Mellon University before transferring to the University of Pittsburgh, gr ...
's 2007 novel ''The Yiddish Policemen's Union
''The Yiddish Policemen's Union'' is a 2007 novel by American author Michael Chabon. The novel is a detective story set in an alternative history version of the present day, based on the premise that during World War II, a temporary settlement f ...
''; in this alternative 2007 Manchukuo has broken off from the rest of China and is an independent nation in its own right, and has its own Space Programme.
See also
*Battle of Lake Khasan *Collaborationist Chinese Army *Fengtian clique *History of the Republic of China *Japanization *List of East Asian leaders in the Japanese sphere of influence (1931–1945) *Manchukuo Temporary Government *Marco Polo Bridge Incident *Mengjiang *Nomonhan *Northeast Anti-Japanese United Army *Manchukuo Imperial Army
The Manchukuo Imperial Army ( zh, s=滿洲國軍, p=Mǎnzhōuguó jūn) was the ground force of the military of the Empire of Manchukuo, a puppet state established by Imperial Japan in Manchuria, a region of northeastern China. The force was pri ...
* Gando Special Force
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Toshihiko Kishi, Mitsuhiro MATSUSHIGE and MATSUMURA Fuminori MATSUMURA, eds, 20 Seiki Manshu Rekishi Jiten [Encyclopedia of 20th Century Manchuria History], Tokyo: Yoshikawa Kobunkan, 2012, *Toshihiko Kishi. "Manchuria's Visual Media Empire (Manshukoku no Visual Media): Posters, Pictorial Post Cards, Postal Stamps", Tokyo: Yoshikawa Kobunkan, 10 June 2010. *Reginald Fleming Johnston. "Twilight in the Forbidden City". Soul Care Publishing, 18 March 2008. . *Fleming, Peter, Travel's in Tartary: One's Company and News from Tartary: 1941 (Part one: Manchukuo) *Smith, Lloyd (January 1940). Everybody's Complete Encyclopedia. Whitman Publishing, Whitman Publishing Company. Racine, Wisconsin. p. 462 *Clauss, Errol MacGregor. "The Roosevelt Administration and Manchukuo, 1933–1941", ''Historian'' (1970), 32#4 pp 595–611. *Duara, Prasenjit. ''Sovereignty and Authenticity: Manchukuo and the East Asian Modern'' (2004) * *Power, Brian. ''Puppet Emperor: The Life of Pu Yi, Last Emperor of China'' (1988) *Yamamuro, Shin'ichi. ''Manchuria under Japanese Dominion'' (U. of Pennsylvania Press, 2006) **Review in ''The Journal of Japanese Studies'' 34.1 (2007) 109–11online
*Mitter, Rana. ''The Manchurian Myth: Nationalism, Resistance, and Collaboration in Modern China'' (2000)
External links
Manchukuo Propaganda Posters & Bills
*[http://www.e.okayama-u.ac.jp/~matsu/index-en.html "Toshiro Matsumoto s research over Manchukuo"]
"Vaticano-Manchukuo no sirve de mea culpa" by Gianni Valente
* Mukden Incident photos
World War II database (1)
World War II database (2)
{{coord, 43, 53, N, 125, 19, E, source:kolossus-svwiki, display=title Manchukuo, History of Manchuria Client states of the Empire of Japan Former countries in East Asia Former countries in Chinese history Former Japanese colonies Former monarchies Former monarchies of Asia Former unrecognized countries Military history of China during World War II Second Sino-Japanese War States and territories established in 1932 States and territories disestablished in 1945 1932 establishments in China 1945 disestablishments in China 1932 establishments in the Japanese colonial empire 1945 disestablishments in the Japanese colonial empire Former monarchies of East Asia Axis powers Collaboration with the Axis Powers Chinese collaborators with Imperial Japan, Totalitarian states Former countries of the interwar period Former empires