Ieper Grote Markt R01.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a
 Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the
Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the
 Ieper railway station run by NMBS has hourly trains to Kortrijk railway station, Kortrijk.
It can also be accessed from Brussels, linking to Eurostar, and takes about 75 minutes with two stops.
Ieper railway station run by NMBS has hourly trains to Kortrijk railway station, Kortrijk.
It can also be accessed from Brussels, linking to Eurostar, and takes about 75 minutes with two stops.
Association for World War Archaeology; information about World War I excavations near YpresIn Flanders Fields MuseumLast Post AssociationPilgrimage to Ypres and Sanctuary Wood
at Library and Archives Canada *[http://2020visioncampaign.org Mayors For Peace International Secretariat Ypres]
Webpage about the fortificationsCoat of arms of Ieper (Ypres)
* – Information available in Dutch language, Dutch and limited information available in English
Ypres Travel Guide
– A comprehensive English language guide to Ypres (Ieper); includes history, sightseeing and Belgian beer culture. {{Authority control Ypres, Ypresian, Municipalities of West Flanders World War I memorials in Belgium Recipients of the Military Cross Vauban fortifications in Belgium
Belgian
Belgian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to, Belgium
* Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent
* Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German
*Ancient Belgian language, an extinct languag ...
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of West Flanders
)
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of West Flanders.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van West-Vlaanderen.svg
, shield_size =
, image_map ...
. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge
Boezinge (; vls, Boezienge) is a village in the municipality of Ypres in the Belgian province of West Flanders. Boezinge can be reached via the N369 road in the direction of Diksmuide. It was an independent municipality until 1977.
History
Boezi ...
, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge
Elverdinge is a village in the Flemish province of West Flanders in Belgium. The village is part of the municipality of Ypres.
In World War I, the village was part of the Ypres Salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of ...
, Hollebeke Hollebeke is a Flemish village in the Belgian province of West Vlaanderen, now part of Ypres city.
History
In World War I, it was the site of allied heroism (like other neighbouring parts of Ypres, such as Klein Zillebeke) that won Khudadad Khan t ...
, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge
Vlamertinge is a village in the Belgian province of West Flanders and a borough of the city of Ypres. The village center of Vlamertinge lies just outside the city center of Ypres, along the main road N38 to the nearby town of Poperinge.
In addit ...
, Voormezele, Zillebeke
Zillebeke (also known as Zellebeck) is a village in the Flemish province of West Flanders in Belgium. It is a former municipality which is now part of Ypres.
History
On 3 March 1914 the then municipality was granted the arms of the last Lords o ...
, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants.
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas ...
) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres
The Battle of Ypres was a series of engagements during the First World War, near the Belgian city of Ypres, between the German and the Allied armies (Belgian, French, British Expeditionary Force and Canadian Expeditionary Force). During the five ...
between German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and Allied forces.
History
Origins before First World War
 Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the
Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee
The Ieperlee (or ''Ypres-Ijzer Canal'') is a canalized river that rises in Heuvelland in the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows via the city of Ypres (Ieper) into the Yser at Fort Knokke.
The river is long. Its name is derived from '' ...
on the banks of which it was founded.
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
city with a population of 40,000 in 1200 AD, renowned for its linen trade with England, which was mentioned in the ''Canterbury Tales
''The Canterbury Tales'' ( enm, Tales of Caunterbury) is a collection of twenty-four stories that runs to over 17,000 lines written in Middle English by Geoffrey Chaucer between 1387 and 1400. It is widely regarded as Chaucer's ''magnum opus ...
''.
As the third largest city in the County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Yp ...
(after Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
and Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the country by population.
The area of the whole city a ...
) Ypres played an important role in the history of the textile industry. Textiles from Ypres could be found in the markets of Novgorod in Kievan Rus' in the early 12th century. In 1241, a major fire ruined much of the old city. The powerful city was involved in important treaties and battles, including the Battle of the Golden Spurs, the Battle at Mons-en-Pévèle, the Peace of Melun, and the Battle of Cassel.
The famous Cloth Hall
A cloth hall or linen hall (german: Gewandhaus; pl, Sukiennice; french: Halle aux draps; nl, Lakenhal) is a historic building located in the centre of the main marketplace of a European town. Cloth halls were built from medieval times into the 18 ...
was built in the 13th century. Also during this time cats, then the symbol of the devil and witchcraft, were thrown off Cloth Hall, possibly because of the belief that this would get rid of evil demons. Today, this act is commemorated with a triennial
An anniversary is the date on which an event took place or an institution was founded in a previous year, and may also refer to the commemoration or celebration of that event. The word was first used for Catholic feasts to commemorate saints. ...
Cat Parade through town.
In 1377, when textile workers held guns against their bosses, they were hanged, accused of rebellion and burned in the bonfire by Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
accused of heresy (N Cohn, 1981:86)
During the Norwich Crusade, led by the English bishop Henry le Despenser
Henry le Despenser ( 1341 – 23 August 1406) was an English nobleman and Bishop of Norwich whose reputation as the 'Fighting Bishop' was gained for his part in suppressing the Peasants' Revolt in East Anglia and in defeating the peasants at t ...
, Ypres was besieged from May to August 1383, until French relief forces arrived. After the destruction of Thérouanne
Thérouanne (; vls, Terenburg; Dutch ''Terwaan'') is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located west of Aire-sur-la-Lys and south of Saint-Omer, on the D 157 and D 341 road junction. Loca ...
, Ypres became the seat of the new Diocese of Ypres in 1561, and Saint Martin's Church was elevated to cathedral.
On 25 March 1678 Ypres was conquered by the forces of Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of ...
. It remained French under the Treaty of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen ('; german: Friede von Nimwegen) were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Repub ...
, and Vauban constructed his typical fortifications that can still be seen today. In 1697, after the Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Gran ...
, Ypres was returned to the Spanish Crown.
During the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
, the Duke of Marlborough
General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 O.S.) was an English soldier and statesman whose career spanned the reign ...
in 1709 intended to capture Ypres, at the time a major French fortress, but changed his mind owing to the long time and effort it had taken him to capture Tournai and apprehension of disease spreading in his army in the poorly drained land around Ypres (see Battle of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet took place on 11 September 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession and was fought between a French army commanded by the Duke of Villars and a Grand Alliance force under the Duke of Marlborough. In one of the blo ...
). In 1713 it was handed over to the Habsburgs, and became part of the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
.
In 1782 the Habsburg Emperor Joseph II
Joseph II (German: Josef Benedikt Anton Michael Adam; English: ''Joseph Benedict Anthony Michael Adam''; 13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg lands from November 29, 1780 un ...
ordered parts of the walls torn down. This destruction, which was only partly repaired, made it easier for the French to capture the city in the 1794 Siege of Ypres during the War of the First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition (french: Guerre de la Première Coalition) was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797 initially against the constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French Republic that suc ...
.
In 1850 the Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian ...
Age of the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
Epoch was named on the basis of geology in the region by Belgian
Belgian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to, Belgium
* Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent
* Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German
*Ancient Belgian language, an extinct languag ...
geologist André Hubert Dumont
André — sometimes transliterated as Andre — is the French and Portuguese form of the name Andrew, and is now also used in the English-speaking world. It used in France, Quebec, Canada and other French-speaking countries. It is a variation ...
.
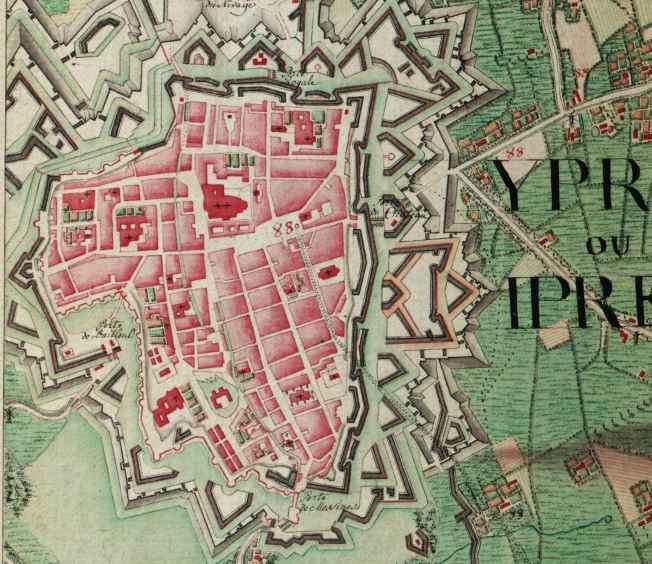
Ypres had long been fortified to keep out invaders. Parts of the early ramparts, dating from 1385, still survive near the Rijselpoort (Lille Gate). Over time, the earthworks were replaced by sturdier masonry and earth structures and a partial moat. Ypres was further fortified in the 17th and 18th centuries while under the occupation of the Habsburgs and the French. Major works were completed at the end of the 17th century by the French military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban.
First World War
Ypres occupied a strategic position during the First World War because it stood in the path of Germany's planned sweep across the rest of Belgium and into France from the north (theSchlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on ...
). The neutrality of Belgium, established by the First Treaty of London,
was guaranteed by Britain; Germany's invasion of Belgium brought the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
into the war. The German army surrounded the city on three sides, bombarding it throughout much of the war. To counterattack, British, French, and allied forces made costly advances from the Ypres Salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of several battles and an extremely important part of the Western front during the First World War.
Ypres district
Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee ...
into the German lines on the surrounding hills.
In the First Battle of Ypres (19 October to 22 November 1914), the Allies captured the town from the Germans. The Germans had used tear gas at the Battle of Bolimov on 3 January 1915. Their use of poison gas for the first time on 22 April 1915 marked the beginning of the Second Battle of Ypres, which continued until 25 May 1915. They captured high ground east of the town. The first gas attack occurred against Canadian, British, and French soldiers, including both metropolitan French soldiers as well as Senegalese and Algerian tirailleurs (light infantry) from French Africa. The gas used was chlorine. Mustard gas, also called Yperite from the name of this town, was also used for the first time near Ypres, in the autumn of 1917.
Of the battles, the largest, best-known, and most costly in human suffering was the Third Battle of Ypres (31 July to 10 November 1917, also known as the Battle of Passchendaele), in which the British, Canadian, ANZAC, and French forces recaptured the Passchendaele Ridge east of the city at a terrible cost of lives. After months of fighting, this battle resulted in nearly half a million casualties to all sides, and only a few miles of ground won by Allied forces. During the course of the war the town was all but obliterated by the artillery fire.
English-speaking soldiers often referred to Ieper/Ypres by the deliberate mispronunciation "Wipers". British soldiers even published a wartime newspaper called ''The Wipers Times''. The same style of deliberate mispronunciation was applied to other Flemish place names in the Ypres area for the benefit of British troops, such as Capture of Wytschaete, Wytschaete becoming "White Sheet" and Ploegsteert becoming "Plug Street".
Ypres was one of the sites that hosted an unofficial Christmas Truce in 1914 between German and British soldiers.
During World War Two, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) would fight the Germans in a delaying action at the Battle of the Ypres–Comines Canal, Ypres-Comines Canal, one of the actions that allowed the Allied retreat to Dunkirk. Adolf Hitler (later Chancellor of Germany) fought at Ypres in the First World War and later visited the town during the Battle of France.
War memory and memorial
On 12 February 1920 King George V awarded the Military Cross to the City of Ypres, one of only two awards of this decoration to a municipality during World War I, the other being to Verdun. In May 1920 John French, 1st Earl of Ypres, Field Marshal French presented the Cross in a special ceremony in the city, and in 1925 it was added to the city's coat of arms, along with the French Croix de Guerre. Historian Mark Connelly states that in the 1920s, British veterans set up the Ypres League and made the city the symbol of all that they believed Britain was fighting for and gave it a holy aura in their minds. The Ypres League sought to transform the horrors of trench warfare into a spiritual quest in which British and imperial troops were purified by their sacrifice. In 1920 Henry Beckles Willson, Lieutenant-Colonel Beckles Willson's guide book, ''The Holy Ground of British Arms'' captured the mood of the Ypres League:There is not a single half-acre in Ypres that is not sacred. There is not a single stone which has not sheltered scores of loyal young hearts, whose one impulse and desire was to fight and, if need be, to die for England. Their blood has drenched its cloisters and its cellars, but if never a drop had been spilt, if never a life had been lost in defence of Ypres still would Ypres have been hallowed, if only for the hopes and the courage it has inspired and the scenes of valour and sacrifice it has witnessed.Ypres became a pilgrimage destination for Britons to imagine and share the sufferings of their men and gain a spiritual benefit. After the war, Winston Churchill proposed to leave Ypres as a mausoleum, with the rightful owners to be deprived from regaining their land. By early March 1919, the Belgian scheme was to leave the Cathedral and Cloth Hall and the buildings around them in ruins. By November 1919, the Belgian government was seriously considering two schemes, both of which would have kept the Cloth Hall and the Cathedral in ruins, but one scheme would allow rebuilding houses around the Grand Place, whereas the other would have created a belt of trees surrounding the Hall and Cathedral. By early September 1920, the decision had been made by the British Government that the Menin Gate and its immediate surroundings would be used as a memorial, by which time, the Belgians had already begun to rebuild the area. In the 100th anniversary period more attempts are being made to preserve the First World War heritage in and around Ypres.
Second World War
On September 6th 1944, the 1st Polish Armoured Division liberated the town of Ypres after 4 years of occupation, and the nightly 'Last_Post#Menin_Gate, Last Post' ceremony was resumed at the #Menin Gate, Menin Gate; the Germans had forbidden the ceremony when they occupied Ypres in 1940; from January 1941 until the liberation, the daily commemoration took place in Brookwood_Cemetery#Brookwood_Military_Cemetery_and_memorials, Brookwood Military Cemetery.Ypres today
After the war the town was extensively rebuilt using money paid by Germany in World War I reparations, reparations, with the main square, including the Cloth Hall and town hall, being rebuilt as close to the original designs as possible (the rest of the rebuilt town is more modern in appearance). The Cloth Hall today is home to In Flanders Fields Museum, dedicated to Ypres's role in the First World War and named for the In Flanders Fields, poem by John McCrae. Ypres is a small city in the very western part of Belgium, the so-called ''Westhoek''. Ypres these days has the title of "city of peace" and maintains a close friendship with another town on which war had a profound impact: Hiroshima. Both towns witnessed warfare at its worst: Ypres was one of the first places where chemical warfare was Second Battle of Ypres, employed, while Hiroshima suffered the debut of nuclear warfare. The city governments of Ypres and Hiroshima advocate that cities should never be targets again and campaign for the abolition of nuclear weapons. Ypres hosts the international campaign secretariat of Mayors for Peace, an international Mayoral organization mobilizing cities and citizens worldwide to abolish and eliminate nuclear weapons by 2020.Sights
Town centre
The imposingCloth Hall
A cloth hall or linen hall (german: Gewandhaus; pl, Sukiennice; french: Halle aux draps; nl, Lakenhal) is a historic building located in the centre of the main marketplace of a European town. Cloth halls were built from medieval times into the 18 ...
was built in the 13th century and was one of the largest commercial buildings of the Middle Ages. The structure which stands today is the exact copy of the original medieval building, rebuilt after the war. The Belfries of Belgium and France, belfry that surmounts the hall houses a 49-bell carillon. The whole complex was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1999.
The Gothic architecture, Gothic-style Saint Martin's Cathedral, built in 1221, was also completely reconstructed after the war, but now with a higher spire. It houses the tombs of Jansenius, bishop of Ypres and father of the religious movement known as Jansenism, and of Robert III of Flanders, Robert of Bethune, nicknamed "The Lion of Flanders", who was Count of Nevers (1273–1322) and Count of Flanders (1305–1322).
Menin Gate
The Menin Gate, Menin Gate Memorial to the Missing commemorates those soldiers of the British Commonwealth – with the exception of Newfoundland and New Zealand – who fell in theYpres Salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of several battles and an extremely important part of the Western front during the First World War.
Ypres district
Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee ...
during the First World War before 16 August 1917 and who have no known grave. United Kingdom and New Zealand servicemen who died after that date are named on the memorial at Tyne Cot, a site which marks the farthest point reached by Commonwealth forces in Belgium until nearly the end of the war. Other New Zealand casualties are commemorated on memorials at Buttes New British Cemetery and Messines Ridge (New Zealand) Memorial, Messines Ridge British Cemetery. The Menin Gate records only soldiers for whom there is no known grave. As graves are identified, the names of those buried in them are removed from the Gate.
The memorial, designed by Sir Reginald Blomfield with sculpture by Sir William Reid Dick, was unveiled by Herbert Plumer, 1st Viscount Plumer, Lord Plumer on 24 July 1927. It was built and is maintained by The Commonwealth War Graves Commission.
The memorial's location is especially poignant, as it lies on the eastward route from the town, which Entente Cordiale, Entente soldiers would have taken heading towards the fighting – many never to return. Every evening since 1929, at precisely eight o'clock, traffic around the imposing arches of the Menin Gate Memorial has been stopped while the "Last Post" is sounded beneath the gate by the buglers of the Last Post Association in honour of the memory of British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
soldiers who fought and died there. During the Second World War the ceremony was prohibited by the occupying German forces, but was resumed on the very evening of liberation – 6 September 1944 – notwithstanding the heavy fighting still underway in other parts of the town. The Last Post ceremony was, instead, hosted daily at Brookwood Military Cemetery in England for the duration of that period.
The stone lions bearing the Ypres coat-of-arms, which once flanked the original gate, were presented to Australia in 1936 by the people of Belgium, as acknowledgement of Australia's sacrifice during the war. They now reside in the Australian War Memorial in Canberra. In 2017, for the 100th anniversary memorial services of the Third Battle of Ypres, or Passendale, in a joint effort by the Belgian, Flemish and Australian governments, the lions were temporarily returned to the Menin Gate. Exact replicas are now installed, in their original position, guarding the approach to Menin Gate on its eastern side.
:::"Who will remember, passing through this Gate,
:::The unheroic Dead who fed the guns?"
::::-- Siegfried Sassoon, ''On Passing the Menin Gate''
War graves
War graves, both of the Allied side and the Central Powers, cover the landscape around Ypres. The largest number of dead are at Langemark German war cemetery and Tyne Cot, Tyne Cot Commonwealth war cemetery. The countryside around Ypres is featured in the famous poem by John McCrae, ''In Flanders Fields''. Saint George's Memorial Church, Ypres, Saint George's Memorial Church commemorates the British and Commonwealth soldiers who died in the five battles fought for Ypres during First World War.Events
*The Cat Parade ("Kattenstoet") takes place every three years on the second Sunday of May. It involves the throwing of stuffed toy cats from the belfry and a colourful parade of cats and witches. The latest Cat Parade took place on 13 May 2018. *Ypres is also the home of the Belgium Ypres Westhoek Rally since its creation in 1965. It is organized by the Auto Club Targa Florio. Some of the drivers to have taken part are among the best-known names in rallying, such as Juha Kankkunen, Bruno Thiry, Henri Toivonen, Colin McRae, Jimmy McRae, Marc Duez, François Duval, Craig Breen and Freddy Loix among others. *Ypres holds an annual canoe polo tournament in which teams come from all over Europe to play. *On 9 July 2014, the 101st Tour de France started stage 5 in Ypres. *During the last weekend of August each year, Ypres hosts the ''Ieperfest'', one of the biggest European festivals in the hardcore metal subculture.Economy
Though Ypres is an historic city, and generates significant income from tourism, it also has a number of industrial areas. The biggest one is along theIeperlee
The Ieperlee (or ''Ypres-Ijzer Canal'') is a canalized river that rises in Heuvelland in the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows via the city of Ypres (Ieper) into the Yser at Fort Knokke.
The river is long. Its name is derived from '' ...
canal, which hosts room for around 120 companies and a wind farm in the north of Ypres.
The office area known as Ieper Business Park is connected to the industrial area. That office area started as the site of speech recognition company Lernout & Hauspie, and was named "Flanders Language Valley" (mimicking Silicon Valley), until the company went bankrupt. Since then, the office area had many difficult years, where a big share of the offices were unused. However, those years are mostly over, and currently, the area offers about 1000 employees a job.
Then there are also various other, smaller industrial areas like the area around Picanol in the south of Ypres.
Transport
 Ieper railway station run by NMBS has hourly trains to Kortrijk railway station, Kortrijk.
It can also be accessed from Brussels, linking to Eurostar, and takes about 75 minutes with two stops.
Ieper railway station run by NMBS has hourly trains to Kortrijk railway station, Kortrijk.
It can also be accessed from Brussels, linking to Eurostar, and takes about 75 minutes with two stops.
Notable people
*William of Ypres, a commander of Flemish mercenaries in England who was reckoned among the more able of the military commanders fighting for Stephen of England, King Stephen of England in his The Anarchy, 19-year civil war with the Empress Matilda. *Jacob Clemens non Papa (c. 1510–1556), Renaissance composer *Georg Robin (1522–1595), architect *Cornelius Jansen (1585–1638), bishop of Ypres and father of the Jansenism movement *Jan Thomas van Ieperen (1617–1673), Baroque painter, draughtsman and printmaker. He was first active in Antwerp, where he worked in the workshop of Rubens, and later became court painter at the Habsburg court in Vienna. *Clementine Lynch (1754– 1799), Abbess of the Ypres Benedictine convent during the French Revolution. *Jules Malou (1810–1886), politician, Prime Minister of Belgium from 1871 to 1878 and in 1884 * (1812–1884), politician, minister * (1855–1901) Minister of Industry and Labour, Lawyer, University Professor, *Julien Nyssens (1859–1910) engineer, builder of Zeebrugge harbour. *Albert Devèze (1881–1959), politician, minister *Camille Durutte (1803–1881), music theorist *Edward Phillips (cricketer, born 1883), Edward Phillips (1883–1915), cricketer * (1895–1954), university professor *Simona Noorenbergh (1907–1990), nun, social worker, co-founder of Fane, Papua New Guinea, Fane, Papua New Guinea *John French, 1st Earl of Ypres *Antoon Verschoot (1925–2017), from 1954 to 2015 chief bugler at the Menin Gate for the daily Last Post ceremony. *Walter Fiers (1931–2019), molecular biologist *Marc Vervenne (born 1949), emeritus dean Leuven university *Jo Lernout and Pol Hauspie, founders of the speech technology company Lernout & Hauspie *Henk Lauwers (born 1956), classical baritone singer *Catherine Verfaillie (born, 1957), MD and stem cell pioneer *Nicholas Lens (born 1957), opera composer *Edouard Vermeulen (born 1957), fashion designer *Renaat Landuyt (born 1959), politician, Belgian minister *Erik Vermeulen (born 1959), jazz pianist *Isaac Delahaye (born 1982), lead guitarist of Epica (band), Epica *Emma Meesseman (born 1993), professional basket playerTwin cities
*: Semey (since 2012) *: Sittingbourne, Kent (since 1964) *: Siegen, Westfalen, Westphalia (since 1967) *: Saint-Omer, Pas-de-Calais (since 1969) * Ghana: Wa, Ghana, Wa, Upper West RegionNotes
References
*External links
Association for World War Archaeology; information about World War I excavations near Ypres
at Library and Archives Canada *[http://2020visioncampaign.org Mayors For Peace International Secretariat Ypres]
Webpage about the fortifications
* – Information available in Dutch language, Dutch and limited information available in English
Ypres Travel Guide
– A comprehensive English language guide to Ypres (Ieper); includes history, sightseeing and Belgian beer culture. {{Authority control Ypres, Ypresian, Municipalities of West Flanders World War I memorials in Belgium Recipients of the Military Cross Vauban fortifications in Belgium