Goupillon epicier.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
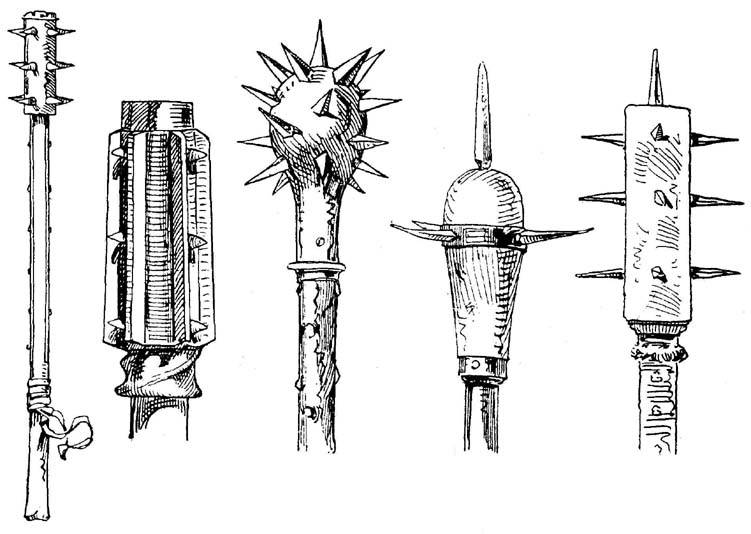
 A morning star (german: Morgenstern) is any of several medieval club-like weapons consisting of a shaft with an attached ball adorned with one or more spikes. Each used, to varying degrees, a combination of blunt-force and puncture attack to kill or wound the enemy.
A morning star (german: Morgenstern) is any of several medieval club-like weapons consisting of a shaft with an attached ball adorned with one or more spikes. Each used, to varying degrees, a combination of blunt-force and puncture attack to kill or wound the enemy.

 A morning star (german: Morgenstern) is any of several medieval club-like weapons consisting of a shaft with an attached ball adorned with one or more spikes. Each used, to varying degrees, a combination of blunt-force and puncture attack to kill or wound the enemy.
A morning star (german: Morgenstern) is any of several medieval club-like weapons consisting of a shaft with an attached ball adorned with one or more spikes. Each used, to varying degrees, a combination of blunt-force and puncture attack to kill or wound the enemy.
History
The morning star first came into widespread use around the beginning of the fourteenth century, particularly in Germany where it was known as ''Morgenstern''. The term is often confused with the military flail (''fléau d'armes'' in French and ''Kriegsflegel'' in German), which typically consists of a wooden shaft joined by a length of chain to one or more iron-shod wooden bars (heavysword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
pommels have also been used as weights). However, there are few depictions of such a ball-and-chain flail from the period, so the weapon of this type appears to have been uncommon.
Design
The morning star is a medieval weapon consisting of a spiked ball mounted on a shaft, resembling a mace, usually with a long spike extending straight from the top and many smaller spikes around the particle of the head. The spikes distinguish it from a mace, which can have, at most, flanges or small knobs. It was used by both infantry andcavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
; the horseman's weapon had a shorter shaft. The mace was a traditional knightly weapon that developed somewhat independently; as the mace transitioned to being constructed entirely of metal, the morning star retained its characteristic wooden shaft. Many surviving morning stars are of a longer two-handed form typically six feet in length, with some longer examples.
There were three types in existence, all differing in quality of workmanship. The first was the well crafted military type used by professional soldiers, made in series by expert weaponsmiths for stocking in town arsenals. The second and much simpler type would have been hand cut by peasant militia men, rather than turned on a lathe
A lathe () is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to c ...
, from wood they had gathered themselves and fitted with nails and spikes by the local blacksmith. The shaft and head were usually of one piece but sometimes reinforced at the top with an iron band. The third type was decorative in nature, usually short hafted and made of metal, one sixteenth century example being of steel and damascened
Damascening is the art of inlaying different metals into one another—typically, gold or silver into a darkly oxidized steel background—to produce intricate patterns similar to niello. The English term comes from a perceived resemblance to t ...
with inlaid gold and silver, in the Wallace Collection of London.
Holy water sprinkler
The holy water sprinkler (from its resemblance to the aspergillum used in the Catholic Mass), was a morning star used by the English army in the sixteenth century and made in series by professional smiths. One such weapon can be found in the Royal Armouries and has an all-steel head with six flanges forming three spikes each, reminiscent of a mace but with a short thick spike of square cross section extending from the top. The wooden shaft is reinforced with four langets and the overall length of the weapon is . The term holy water sprinkler is also used to describe a type of military flail, this being the name for the weapon in French ( ''goupillon''). It was (according to popular legend) the favored weapon ofKing John of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
, who was blind, and used to simply lay about himself on all sides.
Examples
Two examples of the military type are housed in the museums of Vienna, both from the 16th century. The first measures in length including the top spike which is . The head is a separate wooden cylinder slipped over the top of the shaft and reinforced with steel bands, with five metal spikes in symmetrical arrangement. The second example has an all-steel head of complex craftsmanship with four V-shaped spikes mounted on a long shaft that measures slightly less than two metres in length. A twisted and braided steel bar joins the socket to the base of the top spike. There are also 183 surviving specimens inGraz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the popul ...
, made in series and delivered to the arsenal in 1685. They are comparable in length to the previous examples and have three rows of spikes around the head. The wooden shafts of most morning stars of the military type are reinforced with metal Wiktionary:langet, langets extending down from the head. Still others can be found in the Swiss arsenals of Lucerne and Zurich.
In art
These types of morning stars are also depicted in medieval art. For instance, one is shown being carried by an armour, armored knight or soldier in the Caesar tapestry, Tapestries in the Historical Museum of Bern, depicting Julius Caesar's battle against the Germanic peoples, Germanic leader Ariovistus. These tapestries were woven in Tournai between 1465 and 1470, and taken as plunder from Charles the Bold after one of his defeats during the Burgundian Wars against the Swiss. In the poem ''Le Chevalier Délibéré'' written by Olivier de la Marche and first published in 1486, there is an anonymous woodcut depicting a knight carrying a rather simple morning star with spikes mounted in an asymmetrical pattern as well as a flail equipped with a single spiked ball, known in German as a "Flail (weapon), Kettenmorgenstern" (literally ''chain-morning star'') which is technically a military flail.Similar weapons
Goedendag
The ''goedendag'' (or variant spellings) was a Flanders, Flemish weapon which is often described in modern sources as similar to the morning star. However, this is a misconception; it was an infantry weapon in the form of a thick wooden shaft between in length, slightly thicker toward the top, topped with a stout iron spike. The weapon was used to great effect by the guildsmen of Flanders' wealthy cities against the French knights during the ''Guldensporenslag'' or Battle of the Golden Spurs near Kortrijk (Courtrai) on 11 July 1302; however, on account of superior but more expensive alternatives, it saw limited service from the fifteenth century on, being used exclusively by the Flemish "burgers." The goedendag was used to spear horses or knights,Kelly DeVries: ''Medieval Military Technology'', Broadview Press, 1998, but little is certain about its precise mode of use.See also
* Flail (weapon) * Pistol sword#Similar weapons, Henry VIII's Walking Staff * Mace (bludgeon) * Meteor hammerCitations
General references
* ''Dictionary of Medieval Knighthood and Chivalry'' by Bradford Broughton (NY, Greenwood Press, 1986, ) * ''Hafted Weapons in Medieval and Renaissance Europe: The Evolution of European Staff Weapons Between 1200 and 1650'' by John Waldman (Brill Publishers, Brill, 2005, ) * ''Medieval Military Technology'' by Kelly DeVries (Broadview Press, 1998, 0-921149-74-3)External links
* {{Commonscatinline Clubs (weapon) Medieval weapons