Coral Browne in 1931.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
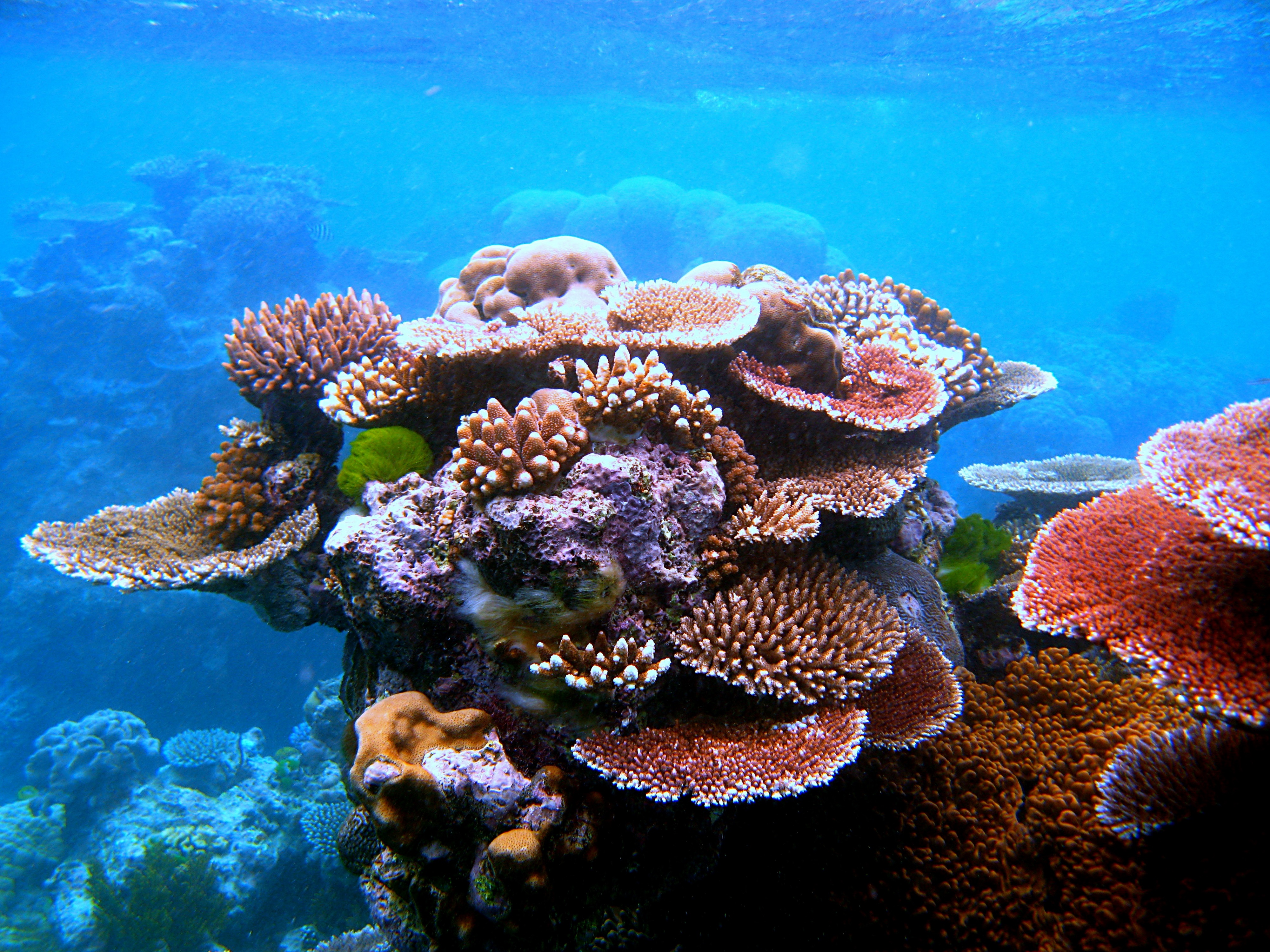 Corals are
Corals are
delineation
Ā of coral species is challenging as hypotheses based on morphological traits contradict hypotheses formed via molecular tree-based processes. ┬Ā As of 2020, there are 2175 identified separate coral species, 237 of which are currently endangered, making distinguishing corals to be the utmost of importance in efforts to curb extinction.┬Ā Adaptation and delineation continues to occur in species of coral in order to combat the dangers posed by the climate crisis. Corals ar
colonial modular organisms
formed by asexually produced and genetically identical modules calle
polyps
Polyps are connected by living tissue to produce the full organism.┬Ā The living tissue allows for inter module communication (interaction between each polyp), which appears in colony morphologies produced by corals, and is one of the main identifying characteristics for┬Āa species of coral. ┬Ā There are 2 main classifications for corals: 1. Hard coral (scleractinian and stony coral) which form reefs by a calcium carbonate base, with polyps with 6 stiff tentacles, and 2. Soft coral (Alcyonacea and ahermatypic coral) which are bendable and formed by a colony of polyps with 8 feather like tentacles.┬Ā These two classifications arose fro
differentiation in gene expressions
in their branch tips and bases that arose through developmental signaling pathways such as Hox,
BMP
etc. Scientists typically select ''Acropora'' as research models since they are the most diverse genus of hard coral, having over 120 species.┬Ā Most species within this genus have polyps which ar
axial
polyps grow rapidly and have lighter coloration, whil
radial
polyps are small and are darker in coloration. In the ''Acropora'' genus, gamete synthesis and
basal
polyps, growth occurs mainly at the radial polyps. Growth at the site of the radial polyps encompasses two processes: asexual reproduction vi
mitotic cell proliferation
and skeleton deposition of the calcium carbonate via
differentially expressed (DE) signaling genes
ref name=":2" /> between both branch tips and bases.┬Ā These processes lead t
colony differentiation
which is the most accurate distinguisher between coral species. In the Acropora genus, colony differentiation through Downregulation and upregulation, up-regulation and down-regulation of DEs. Systematic studies of soft coral species have faced challenges due to a lack of Taxonomy, taxonomic knowledge.┬Ā Researchers have not found enough variability within the genus to confidently delineate similar species, due to a low rate in mutation of mitochondrial DNA. Environmental factors, such as the rise of temperatures and acid levels in our oceans account for some speciation of corals in the form of Species loss, species lost.┬Ā Various coral species have heat shock proteins (HSP) that are also in the category of DE across species.┬Ā These HSPs help corals combat the increased temperatures they are facing which lead to protein denaturing, growth loss, and eventually coral death.┬Ā Approximately 33% of coral species are on the International Union for Conservation of NatureŌĆÖs endangered species list and at risk of species loss.┬Ā Ocean acidification (falling pH levels in the oceans) is threatening the continued species growth and differentiation of corals.┬Ā Mutation rates of ''Vibrio shilonii'', the reef pathogen responsible for coral bleaching, heavily outweigh the┬Ā typical reproduction rates of coral colonies when pH levels fall. Thus, corals are unable to mutate their HSPs and other climate change preventative genes to combat the increase in temperature and decrease in pH at a competitive rate to these pathogens responsible for coral bleaching, resulting in species loss.
 For most of their life corals are Sessility (motility), sessile animals of
For most of their life corals are Sessility (motility), sessile animals of
 The polyps of stony corals have six-fold symmetry. In stony corals, the tentacles are cylindrical and taper to a point, but in soft corals they are pinnate with side branches known as pinnules. In some tropical species, these are reduced to mere stubs and in some, they are fused to give a paddle-like appearance.
Coral skeletons are biocomposites (mineral + organics) of calcium carbonate, in the form of calcite or aragonite. In scleractinian corals, "centers of calcification" and fibers are clearly distinct structures differing with respect to both morphology and chemical compositions of the crystalline units. The organic matrices extracted from diverse species are acidic, and comprise proteins, sulphated sugars and lipids; they are species specific. The soluble organic matrices of the skeletons allow to differentiate
The polyps of stony corals have six-fold symmetry. In stony corals, the tentacles are cylindrical and taper to a point, but in soft corals they are pinnate with side branches known as pinnules. In some tropical species, these are reduced to mere stubs and in some, they are fused to give a paddle-like appearance.
Coral skeletons are biocomposites (mineral + organics) of calcium carbonate, in the form of calcite or aragonite. In scleractinian corals, "centers of calcification" and fibers are clearly distinct structures differing with respect to both morphology and chemical compositions of the crystalline units. The organic matrices extracted from diverse species are acidic, and comprise proteins, sulphated sugars and lipids; they are species specific. The soluble organic matrices of the skeletons allow to differentiate

 Corals predominantly reproduce sexual reproduction, sexually. About 25% of hermatypic corals (reef building stony corals) form single sex (gonochoristic) colonies, while the rest are hermaphroditic. It is estimated more than 67% of coral are Simultaneous hermaphroditism, simultaneous hermaphrodites.
Corals predominantly reproduce sexual reproduction, sexually. About 25% of hermatypic corals (reef building stony corals) form single sex (gonochoristic) colonies, while the rest are hermaphroditic. It is estimated more than 67% of coral are Simultaneous hermaphroditism, simultaneous hermaphrodites.
 Reproductive synchrony, Synchronous spawning is very typical on the coral reef, and often, even when multiple species are present, all corals spawn on the same night. This synchrony is essential so male and female gametes can meet. Corals rely on environmental cues, varying from species to species, to determine the proper time to release gametes into the water. The cues involve temperature change, Lunar phase, lunar cycle, day length, and possibly chemical signalling. Synchronous spawning may form hybrids and is perhaps involved in coral speciation. The immediate cue is most often sunset, which cues the release. The spawning event can be visually dramatic, clouding the usually clear water with gametes.
Reproductive synchrony, Synchronous spawning is very typical on the coral reef, and often, even when multiple species are present, all corals spawn on the same night. This synchrony is essential so male and female gametes can meet. Corals rely on environmental cues, varying from species to species, to determine the proper time to release gametes into the water. The cues involve temperature change, Lunar phase, lunar cycle, day length, and possibly chemical signalling. Synchronous spawning may form hybrids and is perhaps involved in coral speciation. The immediate cue is most often sunset, which cues the release. The spawning event can be visually dramatic, clouding the usually clear water with gametes.

 Within a coral head, the genetically identical polyps reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually, either by budding (gemmation) or by dividing, whether longitudinally or transversely.
Budding involves splitting a smaller polyp from an adult. As the new polyp grows, it forms :Image:Coral polyp.jpg, its body parts. The distance between the new and adult polyps grows, and with it, the coenosarc (the common body of the colony). Budding can be intratentacular, from its oral discs, producing same-sized polyps within the ring of tentacles, or extratentacular, from its base, producing a smaller polyp.
Division forms two polyps that each become as large as the original. Longitudinal division begins when a polyp broadens and then divides its coelenteron (body), effectively splitting along its length. The mouth divides and new tentacles form. The two polyps thus created then generate their missing body parts and exoskeleton. Transversal division occurs when polyps and the exoskeleton divide transversally into two parts. This means one has the basal disc (bottom) and the other has the oral disc (top); the new polyps must separately generate the missing pieces.
Asexual reproduction offers the benefits of high reproductive rate, delaying senescence, and replacement of dead modules, as well as geographical distribution.
Within a coral head, the genetically identical polyps reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually, either by budding (gemmation) or by dividing, whether longitudinally or transversely.
Budding involves splitting a smaller polyp from an adult. As the new polyp grows, it forms :Image:Coral polyp.jpg, its body parts. The distance between the new and adult polyps grows, and with it, the coenosarc (the common body of the colony). Budding can be intratentacular, from its oral discs, producing same-sized polyps within the ring of tentacles, or extratentacular, from its base, producing a smaller polyp.
Division forms two polyps that each become as large as the original. Longitudinal division begins when a polyp broadens and then divides its coelenteron (body), effectively splitting along its length. The mouth divides and new tentacles form. The two polyps thus created then generate their missing body parts and exoskeleton. Transversal division occurs when polyps and the exoskeleton divide transversally into two parts. This means one has the basal disc (bottom) and the other has the oral disc (top); the new polyps must separately generate the missing pieces.
Asexual reproduction offers the benefits of high reproductive rate, delaying senescence, and replacement of dead modules, as well as geographical distribution.
 Corals are one of the more common examples of an animal host whose symbiosis with microalgae can turn to dysbiosis, and is visibly detected as bleaching. Coral microbiomes have been examined in a variety of studies, which demonstrate how oceanic environmental variations, most notably temperature, light, and inorganic nutrients, affect the abundance and performance of the microalgal symbionts, as well as calcification and physiology of the host.Apprill, A. (2017) "Marine animal microbiomes: toward understanding hostŌĆōmicrobiome interactions in a changing ocean". ''Frontiers in Marine Science'', 4: 222. .
Corals are one of the more common examples of an animal host whose symbiosis with microalgae can turn to dysbiosis, and is visibly detected as bleaching. Coral microbiomes have been examined in a variety of studies, which demonstrate how oceanic environmental variations, most notably temperature, light, and inorganic nutrients, affect the abundance and performance of the microalgal symbionts, as well as calcification and physiology of the host.Apprill, A. (2017) "Marine animal microbiomes: toward understanding hostŌĆōmicrobiome interactions in a changing ocean". ''Frontiers in Marine Science'', 4: 222. .  Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Studies have also suggested that resident bacteria, archaea, and fungi additionally contribute to nutrient and organic matter cycling within the coral, with viruses also possibly playing a role in structuring the composition of these members, thus providing one of the first glimpses at a multi-domain marine animal symbiosis. The gammaproteobacterium ''Endozoicomonas'' is emerging as a central member of the coral's microbiome, with flexibility in its lifestyle.Neave, M.J., Apprill, A., Ferrier-Pag├©s, C. and Voolstra, C.R. (2016) "Diversity and function of prevalent symbiotic marine bacteria in the genus ''Endozoicomonas''". ''Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology'', 100(19): 8315ŌĆō8324. . Given the recent mass bleaching occurring on reefs, corals will likely continue to be a useful and popular system for symbiosis and dysbiosis research. ''Astrangia poculata'', the northern star coral, is a temperate stony coral, widely documented along the eastern coast of the United States. The coral can live with and without Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License


 At certain times in the geological past, corals were very abundant. Like modern corals, these ancestors built reefs, some of which ended as great structures in sedimentary rocks. Fossils of fellow reef-dwellers algae, sponges, and the remains of many Echinoderm, echinoids, brachiopods, bivalves, gastropods, and trilobites appear along with coral fossils. This makes some corals useful index fossils. Coral fossils are not restricted to reef remnants, and many solitary fossils are found elsewhere, such as ''Cyclocyathus'', which occurs in England's Gault clay formation.
At certain times in the geological past, corals were very abundant. Like modern corals, these ancestors built reefs, some of which ended as great structures in sedimentary rocks. Fossils of fellow reef-dwellers algae, sponges, and the remains of many Echinoderm, echinoids, brachiopods, bivalves, gastropods, and trilobites appear along with coral fossils. This makes some corals useful index fossils. Coral fossils are not restricted to reef remnants, and many solitary fossils are found elsewhere, such as ''Cyclocyathus'', which occurs in England's Gault clay formation.
File:Syringoporid.jpg, Tabulate coral (a syringoporid); Boone limestone (Lower Carboniferous) near Hiwasse, Arkansas, scale bar is 2.0 cm
File:AuloporaDevonianSilicaShale.jpg, Tabulate coral ''Aulopora'' from the Devonian period
File:RugosaOrdovician.jpg, Solitary rugose coral (''Grewingkia'') in three views; Ordovician, southeastern Indiana
 Coral reefs are under stress around the world. In particular, coral mining, agricultural runoff, agricultural and urban runoff, pollution (organic and inorganic), overfishing, blast fishing, disease, and the digging of canals and access into islands and bays are localized threats to coral ecosystems. Broader threats are sea temperature rise, sea level rise and pH changes from ocean acidification, all associated with greenhouse gas emissions. In 1998, 16% of the world's reefs died as a result of increased water temperature.
Approximately 10% of the world's coral reefs are dead. About 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to human-related activities. The threat to reef health is particularly strong in Southeast Asia, where 80% of reefs are endangered species, endangered. Over 50% of the world's
Coral reefs are under stress around the world. In particular, coral mining, agricultural runoff, agricultural and urban runoff, pollution (organic and inorganic), overfishing, blast fishing, disease, and the digging of canals and access into islands and bays are localized threats to coral ecosystems. Broader threats are sea temperature rise, sea level rise and pH changes from ocean acidification, all associated with greenhouse gas emissions. In 1998, 16% of the world's reefs died as a result of increased water temperature.
Approximately 10% of the world's coral reefs are dead. About 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to human-related activities. The threat to reef health is particularly strong in Southeast Asia, where 80% of reefs are endangered species, endangered. Over 50% of the world's
NINO 3.4 SSTA
NINO 3.4 SSTA
time can be correlated to coral strontium/calcium and Δ18O, δ18O variations. To confirm the accuracy of the annual relationship between Sr/Ca and Δ18O, δ18O variations, a perceptible association to annual coral growth rings confirms the age conversion. Geochronology is established by the blending of Sr/Ca data, growth rings, and Stable isotope ratio, stable isotope data. El Nino-Southern Oscillation, El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is directly related to climate fluctuations that influence coral Δ18O, δ18O ratio from local salinity variations associated with the position of the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) and can be used for El Niño Southern Oscillation, ENSO modeling.
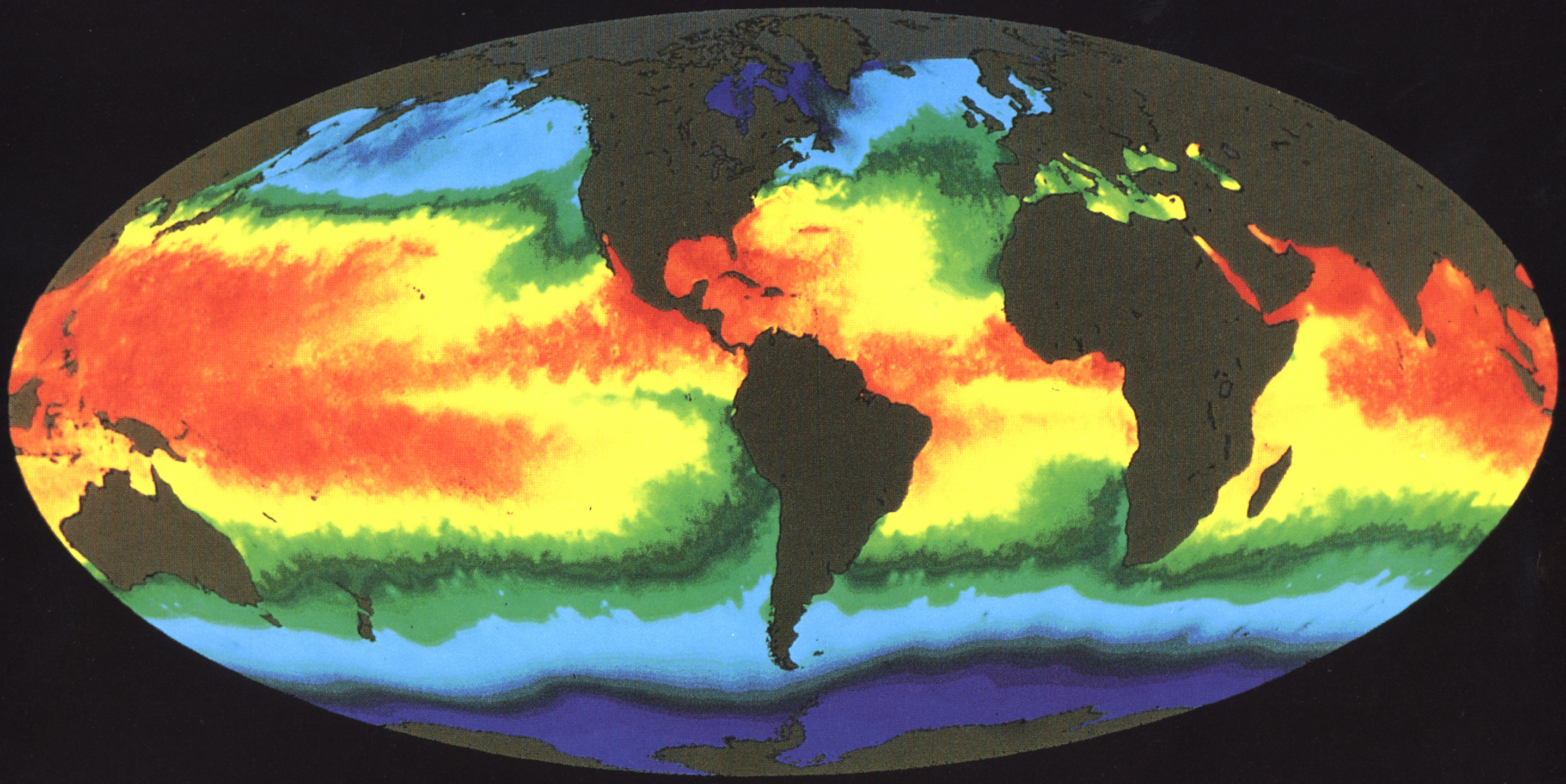 The global moisture budget is primarily being influenced by tropical sea surface temperatures from the position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). The Southern Hemisphere has a unique meteorological feature positioned in the southwestern Pacific Basin called the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ), which contains a perennial position within the Southern Hemisphere. During El Ni├▒o Southern Oscillation, ENSO warm periods, the South Pacific convergence zone, SPCZ reverses orientation extending from the equator down south through Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji and towards the French Polynesian islands, Polynesian Islands; and due east towards South America affecting geochemistry of corals in tropical regions.
Geochemical analysis of skeletal coral can be linked to sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature (SST), fro
The global moisture budget is primarily being influenced by tropical sea surface temperatures from the position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). The Southern Hemisphere has a unique meteorological feature positioned in the southwestern Pacific Basin called the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ), which contains a perennial position within the Southern Hemisphere. During El Ni├▒o Southern Oscillation, ENSO warm periods, the South Pacific convergence zone, SPCZ reverses orientation extending from the equator down south through Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji and towards the French Polynesian islands, Polynesian Islands; and due east towards South America affecting geochemistry of corals in tropical regions.
Geochemical analysis of skeletal coral can be linked to sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature (SST), fro
El Nino 3.4 SSTA
data, of tropical oceans to seawater Δ18O, δ18O ratio anomalies from corals. El Niño Southern Oscillation, ENSO phenomenon can be related to variations in sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature, sea surface temperature (SST) that can help model tropical climate activities.
 Climate research on live coral species is limited to a few studied species. Studying ''Porites'' coral provides a stable foundation for geochemical interpretations that is much simpler to physically extract data in comparison to ''Platygyra'' species where the complexity of ''Platygyra'' species skeletal structure creates difficulty when physically sampled, which happens to be one of the only multidecadal living coral records used for coral paleoclimate modeling.
Climate research on live coral species is limited to a few studied species. Studying ''Porites'' coral provides a stable foundation for geochemical interpretations that is much simpler to physically extract data in comparison to ''Platygyra'' species where the complexity of ''Platygyra'' species skeletal structure creates difficulty when physically sampled, which happens to be one of the only multidecadal living coral records used for coral paleoclimate modeling.
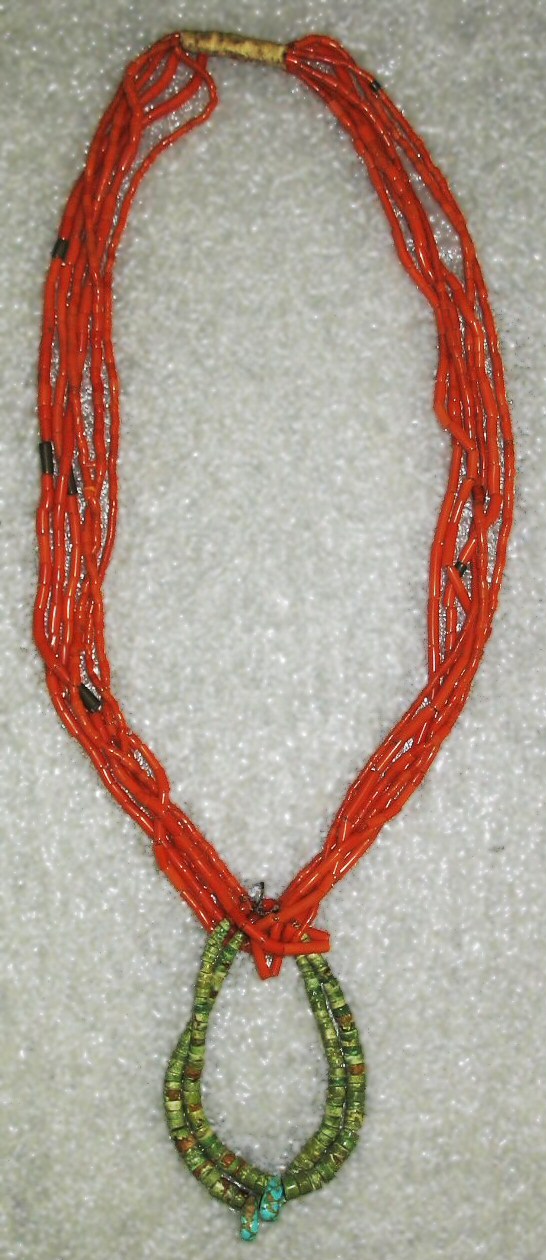 Corals' many colors give it appeal for necklaces and other jewelry. Intensely red coral is prized as a gemstone. Sometimes called fire coral, it is not the same as fire coral. Red coral is very rare because of overharvesting. In general, it is inadvisable to give coral as gifts since they are in decline from stressors like climate change, pollution, and unsustainable fishing.
Always considered a precious mineral, "the Chinese have long associated red coral with auspiciousness and longevity because of its color and its resemblance to deer antlers (so by association, virtue, long life, and high rank". It reached its height of popularity during the Manchu or Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) when it was almost exclusively reserved for the emperor's use either in the form of coral beads (often combined with pearls) for court jewelry or as decorative Penjing (decorative miniature mineral trees). Coral was known as ''shanhu'' in Chinese. The "early-modern 'coral network' [began in] the Mediterranean Sea [and found its way] to Qing China via the English East India Company". There were strict rules regarding its use in a code established by the Qianlong Emperor in 1759.
Corals' many colors give it appeal for necklaces and other jewelry. Intensely red coral is prized as a gemstone. Sometimes called fire coral, it is not the same as fire coral. Red coral is very rare because of overharvesting. In general, it is inadvisable to give coral as gifts since they are in decline from stressors like climate change, pollution, and unsustainable fishing.
Always considered a precious mineral, "the Chinese have long associated red coral with auspiciousness and longevity because of its color and its resemblance to deer antlers (so by association, virtue, long life, and high rank". It reached its height of popularity during the Manchu or Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) when it was almost exclusively reserved for the emperor's use either in the form of coral beads (often combined with pearls) for court jewelry or as decorative Penjing (decorative miniature mineral trees). Coral was known as ''shanhu'' in Chinese. The "early-modern 'coral network' [began in] the Mediterranean Sea [and found its way] to Qing China via the English East India Company". There were strict rules regarding its use in a code established by the Qianlong Emperor in 1759.
 The saltwater fishkeeping hobby has expanded, over recent years, to include Reef aquarium, reef tanks, fish tanks that include large amounts of live rock on which coral is allowed to grow and spread. These tanks are either kept in a natural-like state, with algae (sometimes in the form of an algae scrubber) and a deep sand bed providing filtration, or as "show tanks", with the rock kept largely bare of the algae and microfauna that would normally populate it, in order to appear neat and clean.
The most popular kind of coral kept is
The saltwater fishkeeping hobby has expanded, over recent years, to include Reef aquarium, reef tanks, fish tanks that include large amounts of live rock on which coral is allowed to grow and spread. These tanks are either kept in a natural-like state, with algae (sometimes in the form of an algae scrubber) and a deep sand bed providing filtration, or as "show tanks", with the rock kept largely bare of the algae and microfauna that would normally populate it, in order to appear neat and clean.
The most popular kind of coral kept is Coral Reefs
. Marinebio.org. Retrieved on 2016-06-13. More serious fishkeepers may keep small polyp stony coral, which is from open, brightly lit reef conditions and therefore much more demanding, while large polyp stony coral is a sort of compromise between the two.
File:Mushroom Coral (Fungia) Top Macro 91.JPG, ''Fungia'' sp. skeleton
File:Eusmilia fastigiata large.jpg, Polyps of ''Eusmilia fastigiata''
File:Dendrogyra cylindrus (pillar coral) (San Salvador Island, Bahamas) 1 (15513345363).jpg, Pillar coral, ''Dendrogyra cylindricus''
File:Brain coral.jpg, Brain coral, ''Diploria labyrinthiformis''
File:Brain coral spawning.jpg, Brain coral spawning
File:Stony coral spawning 3.jpg, Brain coral releasing eggs
File:EilatFringingReef.jpg, Fringing
Coral Reefs
The Ocean Portal by the Smithsonian Institution * NOAA
Coral Reef Conservation Program
* NOAA CoRIS ŌĆ
Coral Reef Biology
* NOAA Office for Coastal Management
Fast Facts - Coral Reefs
* NOAA Ocean Service Education ŌĆ
Corals
* {{Authority control Anthozoa Coral reefs,
 Corals are
Corals are marine invertebrates
Marine invertebrates are the invertebrates that live in marine habitats. Invertebrate is a blanket term that includes all animals apart from the vertebrate members of the chordate phylum. Invertebrates lack a vertebral column, and some have ev ...
within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
. They typically form compact colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processesŌĆö deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock o ...
builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.
A coral "group" is a colony of very many genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work ma ...
s surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''├®x┼Ź'' "outer" and ''skelet├│s'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquat ...
: polyps of the same species release gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
s simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180┬░). This means ...
. Fertilized eggs form planulae, a mobile early form of the coral polyp which, when mature, settles to form a new colony.
Although some corals are able to catch plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
and small fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
using stinging cells on their tentacles, most corals obtain the majority of their energy and nutrients from photosynthetic unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
dinoflagellates of the genus ''Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)''
''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicell ...
'' that live within their tissues. These are commonly known as zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
and give the coral color. Such corals require sunlight and grow in clear, shallow water, typically at depths less than . Corals are major contributors to the physical structure of the coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
s that develop in tropical and subtropical waters, such as the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
off the coast of Australia. These corals are increasingly at risk of bleaching
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
events where polyps expel the zooxanthellae in response to stress such as high water temperature or toxins.
Other corals do not rely on zooxanthellae and can live globally in much deeper water, such as the cold-water genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Lophelia
''Lophelia pertusa'', the only species in the genus ''Lophelia'', is a cold-water coral that grows in the deep waters throughout the North Atlantic ocean, as well as parts of the Caribbean Sea and Alboran Sea. Although ''L. pertusa'' reefs are h ...
'' which can survive as deep as . Some have been found as far north as the Darwin Mounds, northwest of Cape Wrath, Scotland, and others off the coast of Washington state
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George WashingtonŌĆöthe first U.S. presidentŌĆöthe state was formed from the western part of the Washington ...
and the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,ŌĆØLand of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large v ...
.
Taxonomy
The classification of corals has been discussed for millennia, owing to having similarities to both plants and animals.Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽü╬╣ŽāŽä╬┐Žä╬Ł╬╗╬ĘŽé ''Aristot├®l─ōs'', ; 384ŌĆō322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
's pupil Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, ╬ś╬ĄŽīŽåŽü╬▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žé ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
described the red coral
Precious coral, or red coral, is the common name given to a genus of marine corals, ''Corallium''. The distinguishing characteristic of precious corals is their durable and intensely colored red or pink-orange skeleton, which is used for ma ...
, ''korallion'', in his book on stones, implying it was a mineral, but he described it as a deep-sea plant in his ''Enquiries on Plants'', where he also mentions large stony plants that reveal bright flowers when under water in the Gulf of Heroes. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
stated boldly that several sea creatures including sea nettles and sponges "are neither animals nor plants, but are possessed of a third nature (''tertia natura'')". Petrus Gyllius
Petrus Gyllius or Gillius (or Pierre Gilles) (1490ŌĆō1555) was a French natural scientist, topographer and translator.
Gilles was born in Albi, southern France. A great traveller, he studied the Mediterranean and Orient, producing such works as ...
copied Pliny, introducing the term ''zoophyta'' for this third group in his 1535 book ''On the French and Latin Names of the Fishes of the Marseilles Region''; it is popularly but wrongly supposed that Aristotle created the term. Gyllius further noted, following Aristotle, how hard it was to define what was a plant and what was an animal. The Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talm┼½ßĖÅ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cent ...
refers to coral among a list of types of trees, and the 11th century French commentator Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, ū©ūæūÖ ū®ū£ū×ūö ūÖū”ūŚū¦ūÖ; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 ŌĆō 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a compre ...
describes it as "a type of tree (ū×ūÖū¤ ūóūź) that grows underwater that goes by the (French) name "coral."
The Persian polymath Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 ŌĆō after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(d.1048) classified sponges and corals as animals, arguing that they respond to touch. Nevertheless, people believed corals to be plants until the eighteenth century, when William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 ŌĆō 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline ...
used a microscope to establish that coral had the characteristic thin cell membranes of an animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
.
Presently, corals are classified as species of animals within the sub-classes Hexacorallia
Hexacorallia is a class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as al ...
and Octocorallia
Octocorallia (also known as Alcyonaria) is a class of Anthozoa comprising around 3,000 species of water-based organisms formed of colonial polyps with 8-fold symmetry. It includes the blue coral, soft corals, sea pens, and gorgonians (sea fans ...
of the class Anthozoa in the phylum Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
. Hexacorallia includes the stony corals and these groups have polyps that generally have a 6-fold symmetry. Octocorallia includes blue coral
Blue coral (''Heliopora coerulea'') is a species of colonial coral. It is the only octocoral known to produce a massive skeleton. This skeleton is formed of aragonite, similar to that of scleractinia. Individual polyps live in tubes within the ...
and soft coral
Alcyonacea, or soft corals, are an order of corals. In addition to the fleshy soft corals, the order Alcyonacea now contains all species previously known as "gorgonian corals", that produce a more or less hard skeleton, though quite different f ...
s and species of Octocorallia have polyps with an eightfold symmetry, each polyp having eight tentacles and eight mesenteries
In zoology, a mesentery is a membrane inside the body cavity of an animal. The term identifies different structures in different phyla: in vertebrates it is a double fold of the peritoneum enclosing the intestines; in other organisms it forms com ...
. The group of corals is paraphyletic because the sea anemones are also in the sub-class Hexacorallia.
Systematics
Thdelineation
Ā of coral species is challenging as hypotheses based on morphological traits contradict hypotheses formed via molecular tree-based processes. ┬Ā As of 2020, there are 2175 identified separate coral species, 237 of which are currently endangered, making distinguishing corals to be the utmost of importance in efforts to curb extinction.┬Ā Adaptation and delineation continues to occur in species of coral in order to combat the dangers posed by the climate crisis. Corals ar
colonial modular organisms
formed by asexually produced and genetically identical modules calle
polyps
Polyps are connected by living tissue to produce the full organism.┬Ā The living tissue allows for inter module communication (interaction between each polyp), which appears in colony morphologies produced by corals, and is one of the main identifying characteristics for┬Āa species of coral. ┬Ā There are 2 main classifications for corals: 1. Hard coral (scleractinian and stony coral) which form reefs by a calcium carbonate base, with polyps with 6 stiff tentacles, and 2. Soft coral (Alcyonacea and ahermatypic coral) which are bendable and formed by a colony of polyps with 8 feather like tentacles.┬Ā These two classifications arose fro
differentiation in gene expressions
in their branch tips and bases that arose through developmental signaling pathways such as Hox,
Hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introductio ...
, WntBMP
etc. Scientists typically select ''Acropora'' as research models since they are the most diverse genus of hard coral, having over 120 species.┬Ā Most species within this genus have polyps which ar
polyps grow rapidly and have lighter coloration, whil
radial
polyps are small and are darker in coloration. In the ''Acropora'' genus, gamete synthesis and
photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
occur at thbasal
polyps, growth occurs mainly at the radial polyps. Growth at the site of the radial polyps encompasses two processes: asexual reproduction vi
mitotic cell proliferation
and skeleton deposition of the calcium carbonate via
extra cellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide str ...
(EMC) proteins acting adifferentially expressed (DE) signaling genes
ref name=":2" /> between both branch tips and bases.┬Ā These processes lead t
colony differentiation
which is the most accurate distinguisher between coral species. In the Acropora genus, colony differentiation through Downregulation and upregulation, up-regulation and down-regulation of DEs. Systematic studies of soft coral species have faced challenges due to a lack of Taxonomy, taxonomic knowledge.┬Ā Researchers have not found enough variability within the genus to confidently delineate similar species, due to a low rate in mutation of mitochondrial DNA. Environmental factors, such as the rise of temperatures and acid levels in our oceans account for some speciation of corals in the form of Species loss, species lost.┬Ā Various coral species have heat shock proteins (HSP) that are also in the category of DE across species.┬Ā These HSPs help corals combat the increased temperatures they are facing which lead to protein denaturing, growth loss, and eventually coral death.┬Ā Approximately 33% of coral species are on the International Union for Conservation of NatureŌĆÖs endangered species list and at risk of species loss.┬Ā Ocean acidification (falling pH levels in the oceans) is threatening the continued species growth and differentiation of corals.┬Ā Mutation rates of ''Vibrio shilonii'', the reef pathogen responsible for coral bleaching, heavily outweigh the┬Ā typical reproduction rates of coral colonies when pH levels fall. Thus, corals are unable to mutate their HSPs and other climate change preventative genes to combat the increase in temperature and decrease in pH at a competitive rate to these pathogens responsible for coral bleaching, resulting in species loss.
Anatomy
 For most of their life corals are Sessility (motility), sessile animals of
For most of their life corals are Sessility (motility), sessile animals of colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of genetically identical polyps. Each polyp varies from millimeters to centimeters in diameter, and colonies can be formed from many millions of individual polyps. Stony coral, also known as hard coral, polyps produce a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate to strengthen and protect the organism. This is deposited by the polyps and by the coenosarc, the living tissue that connects them. The polyps sit in cup-shaped depressions in the skeleton known as corallites. Colonies of stony coral are markedly variable in appearance; a single species may adopt an encrusting, plate-like, bushy, columnar or massive solid structure, the various forms often being linked to different types of habitat, with variations in light level and water movement being significant.
The body of the polyp may be roughly compared in a structure to a wikt:sac, sac, the wall of which is composed of two layers of cell (biology), cells. The outer layer is known technically as the germ layer, ectoderm, the inner layer as the germ layer, endoderm. Between ectoderm and endoderm is a supporting layer of gelatinous substance termed mesogloea, mesoglea, secreted by the cell layers of the body wall. The mesoglea can contain endoskeleton, skeletal elements derived from cells cell migration, migrated from the ectoderm.
The sac-like body built up in this way is attached to a hard surface, which in hard corals are cup-shaped depressions in the skeleton known as corallites. At the center of the upper end of the sac lies the only opening called the mouth, surrounded by a circle of tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work ma ...
s which resemble glove fingers. The tentacles are organ (anatomy), organs which serve both for tactile sense and for the capture of food. Polyps extend their tentacles, particularly at night, often containing coiled stinging cells (cnidocytes) which pierce, poison and firmly hold living prey paralyzing or killing them. Polyp prey includes plankton such as copepods and fish larvae. Longitudinal muscular fibers formed from the cells of the ectoderm allow tentacles to contract to convey the food to the mouth. Similarly, circularly disposed muscular fibres formed from the endoderm permit tentacles to be protracted or thrust out once they are contracted. In both stony and soft corals, the polyps can be retracted by contracting muscle fibres, with stony corals relying on their hard skeleton and cnidocytes for defense. Soft corals generally secrete terpenoid toxins to ward off predators.
In most corals, the tentacles are retracted by day and spread out at night to catch plankton and other small organisms. Shallow-water species of both stony and soft corals can be zooxanthellate, the corals supplementing their plankton diet with the products of photosynthesis produced by these Symbiosis, symbionts. The polyps interconnect by a complex and well-developed system of gastrovascular canals, allowing significant sharing of nutrients and symbionts.
The external form of the polyp varies greatly. The column may be long and slender, or may be so short in the axial direction that the body becomes disk-like. The tentacles may number many hundreds or may be very few, in rare cases only one or two. They may be simple and unbranched, or feathery in pattern. The mouth may be level with the surface of the peristome, or may be projecting and trumpet-shaped.
Soft corals
Soft corals have no solid exoskeleton as such. However, their tissues are often reinforced by small supportive elements known as sclerites made of calcium carbonate. The polyps of soft corals have eight-fold symmetry, which is reflected in the ''Octo'' in Octocorallia. Soft corals vary considerably in form, and most are colonial. A few soft corals are stolonate, but the polyps of most are connected by sheets of tissue called coenosarc, and in some species these sheets are thick and the polyps deeply embedded in them. Some soft corals encrust other sea objects or form lobes. Others are tree-like or whip-like and have a central axial skeleton embedded at their base in the matrix of the supporting branch. These branches are composed of a fibrous protein called gorgonin or of a calcified material.Stony corals
 The polyps of stony corals have six-fold symmetry. In stony corals, the tentacles are cylindrical and taper to a point, but in soft corals they are pinnate with side branches known as pinnules. In some tropical species, these are reduced to mere stubs and in some, they are fused to give a paddle-like appearance.
Coral skeletons are biocomposites (mineral + organics) of calcium carbonate, in the form of calcite or aragonite. In scleractinian corals, "centers of calcification" and fibers are clearly distinct structures differing with respect to both morphology and chemical compositions of the crystalline units. The organic matrices extracted from diverse species are acidic, and comprise proteins, sulphated sugars and lipids; they are species specific. The soluble organic matrices of the skeletons allow to differentiate
The polyps of stony corals have six-fold symmetry. In stony corals, the tentacles are cylindrical and taper to a point, but in soft corals they are pinnate with side branches known as pinnules. In some tropical species, these are reduced to mere stubs and in some, they are fused to give a paddle-like appearance.
Coral skeletons are biocomposites (mineral + organics) of calcium carbonate, in the form of calcite or aragonite. In scleractinian corals, "centers of calcification" and fibers are clearly distinct structures differing with respect to both morphology and chemical compositions of the crystalline units. The organic matrices extracted from diverse species are acidic, and comprise proteins, sulphated sugars and lipids; they are species specific. The soluble organic matrices of the skeletons allow to differentiate zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
and non-zooxanthellae specimens.
Ecology

Feeding
Polyps feed on a variety of small organisms, from microscopic zooplankton to small fish. The polyp's tentacles immobilize or kill prey using stinging cells called nematocysts. These cells carry venom which they rapidly release in response to contact with another organism. A dormant nematocyst discharges in response to nearby prey touching the trigger (Cnidocil). A flap (Operculum (animal), operculum) opens and its stinging apparatus fires the barb into the prey. The venom is injected through the hollow filament to immobilise the prey; the tentacles then manoeuvre the prey into the stomach. Once the prey is digested the stomach reopens allowing the elimination of waste products and the beginning of the next hunting cycle.Intracellular symbionts
Many corals, as well as other cnidarian groups such as sea anemones form a symbiotic relationship with a class of dinoflagellate algae,zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
of the genus ''Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)''
''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicell ...
'', which can form as much as 30% of the tissue of a polyp. Typically, each polyp harbors one species of alga, and coral species show a preference for ''Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)''
''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicell ...
''. Young corals are not born with zooxanthellae, but acquire the algae from the surrounding environment, including the water column and local sediment. The main benefit of the zooxanthellae is their ability to photosynthesize which supplies corals with the products of photosynthesis, including glucose, glycerol, and amino acids, which the corals can use for energy. Zooxanthellae also benefit corals by aiding in calcification, for the coral skeleton, and waste removal. In addition to the soft tissue, microbiomes are also found in the coral's mucus and (in stony corals) the skeleton, with the latter showing the greatest microbial richness.
The zooxanthellae benefit from a safe place to live and consume the polyp's carbon dioxide, phosphate and nitrogenous waste. Stressed corals will eject their zooxanthellae, a process that is becoming increasingly common due to strain placed on coral by rising ocean temperatures. Mass ejections are known as coral bleaching because the algae contribute to coral coloration; some colors, however, are due to host coral pigments, such as green fluorescent proteins (GFPs). Ejection increases the polyp's chance of surviving short-term stress and if the stress subsides they can regain algae, possibly of a different species, at a later time. If the stressful conditions persist, the polyp eventually dies. Zooxanthellae are located within the coral cytoplasm and due to the algae's photosynthetic activity the internal pH of the coral can be raised; this behavior indicates that the zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
are responsible to some extent for the metabolism of their host corals. Stony Coral Tissue Loss Disease has been associated with the breakdown of host-zooxanthellae physiology. Moreover, Vibrio bacterium are known to have virulence traits used for host coral tissue damage and photoinhibition of algal symbionts.Therefore, both coral and their symbiotic microorganisms could have evolved to harbour traits resistant to disease and transmission.
Reproduction
Corals can be both Gonochorism, gonochoristic (unisexual) and Hermaphroditism, hermaphroditic, each of which can reproduce sexually and asexually. Reproduction also allows coral to settle in new areas. Reproduction is coordinated by chemical communication.Sexual
Broadcasters
About 75% of all hermatypic corals "broadcast spawn" by releasinggamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
sŌĆöegg (biology), eggs and spermŌĆöinto the water to spread offspring. A genetic ability to detect blue light allows these sightless organisms to detect a full moon, triggering the simultaneous release. The gametes fertilize at the water's surface to form a microscopic larva called a planula, typically pink and elliptical in shape. A typical coral colony forms several thousand larvae per year to overcome the odds against formation of a new colony.
 Reproductive synchrony, Synchronous spawning is very typical on the coral reef, and often, even when multiple species are present, all corals spawn on the same night. This synchrony is essential so male and female gametes can meet. Corals rely on environmental cues, varying from species to species, to determine the proper time to release gametes into the water. The cues involve temperature change, Lunar phase, lunar cycle, day length, and possibly chemical signalling. Synchronous spawning may form hybrids and is perhaps involved in coral speciation. The immediate cue is most often sunset, which cues the release. The spawning event can be visually dramatic, clouding the usually clear water with gametes.
Reproductive synchrony, Synchronous spawning is very typical on the coral reef, and often, even when multiple species are present, all corals spawn on the same night. This synchrony is essential so male and female gametes can meet. Corals rely on environmental cues, varying from species to species, to determine the proper time to release gametes into the water. The cues involve temperature change, Lunar phase, lunar cycle, day length, and possibly chemical signalling. Synchronous spawning may form hybrids and is perhaps involved in coral speciation. The immediate cue is most often sunset, which cues the release. The spawning event can be visually dramatic, clouding the usually clear water with gametes.
Brooders
Brooding species are most often ahermatypic (not reef-building) in areas of high current or wave action. Brooders release only sperm, which is negatively buoyant, sinking onto the waiting egg carriers that harbor unfertilized eggs for weeks. Synchronous spawning events sometimes occur even with these species. After fertilization, the corals release planula that are ready to settle.Planulae
The time from spawning to larval settlement is usually two to three days, but can occur immediately or up to two months. Broadcast-spawned planula larvae develop at the water's surface before descending to seek a hard surface on the benthos to which they can attach and begin a new colony. The larvae often need a biological cue to induce settlement such as specific crustose coralline algae species or microbial biofilms. High failure rates afflict many stages of this process, and even though thousands of eggs are released by each colony, few new colonies form. During settlement, larvae are inhibited by physical barriers such as sediment, as well as chemical (allelopathic) barriers. The larvae metamorphose into a single polyp and eventually develops into a juvenile and then adult by asexual budding and growth.Asexual
 Within a coral head, the genetically identical polyps reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually, either by budding (gemmation) or by dividing, whether longitudinally or transversely.
Budding involves splitting a smaller polyp from an adult. As the new polyp grows, it forms :Image:Coral polyp.jpg, its body parts. The distance between the new and adult polyps grows, and with it, the coenosarc (the common body of the colony). Budding can be intratentacular, from its oral discs, producing same-sized polyps within the ring of tentacles, or extratentacular, from its base, producing a smaller polyp.
Division forms two polyps that each become as large as the original. Longitudinal division begins when a polyp broadens and then divides its coelenteron (body), effectively splitting along its length. The mouth divides and new tentacles form. The two polyps thus created then generate their missing body parts and exoskeleton. Transversal division occurs when polyps and the exoskeleton divide transversally into two parts. This means one has the basal disc (bottom) and the other has the oral disc (top); the new polyps must separately generate the missing pieces.
Asexual reproduction offers the benefits of high reproductive rate, delaying senescence, and replacement of dead modules, as well as geographical distribution.
Within a coral head, the genetically identical polyps reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually, either by budding (gemmation) or by dividing, whether longitudinally or transversely.
Budding involves splitting a smaller polyp from an adult. As the new polyp grows, it forms :Image:Coral polyp.jpg, its body parts. The distance between the new and adult polyps grows, and with it, the coenosarc (the common body of the colony). Budding can be intratentacular, from its oral discs, producing same-sized polyps within the ring of tentacles, or extratentacular, from its base, producing a smaller polyp.
Division forms two polyps that each become as large as the original. Longitudinal division begins when a polyp broadens and then divides its coelenteron (body), effectively splitting along its length. The mouth divides and new tentacles form. The two polyps thus created then generate their missing body parts and exoskeleton. Transversal division occurs when polyps and the exoskeleton divide transversally into two parts. This means one has the basal disc (bottom) and the other has the oral disc (top); the new polyps must separately generate the missing pieces.
Asexual reproduction offers the benefits of high reproductive rate, delaying senescence, and replacement of dead modules, as well as geographical distribution.
Colony division
Whole colonies can reproduce asexually, forming two colonies with the same genotype. The possible mechanisms include fission, bailout and fragmentation. Fission occurs in some corals, especially among the family Fungiidae, where the colony splits into two or more colonies during early developmental stages. Bailout occurs when a single polyp abandons the colony and settles on a different substrate to create a new colony. Fragmentation involves individuals broken from the colony during storms or other disruptions. The separated individuals can start new colonies.Coral microbiome
 Corals are one of the more common examples of an animal host whose symbiosis with microalgae can turn to dysbiosis, and is visibly detected as bleaching. Coral microbiomes have been examined in a variety of studies, which demonstrate how oceanic environmental variations, most notably temperature, light, and inorganic nutrients, affect the abundance and performance of the microalgal symbionts, as well as calcification and physiology of the host.Apprill, A. (2017) "Marine animal microbiomes: toward understanding hostŌĆōmicrobiome interactions in a changing ocean". ''Frontiers in Marine Science'', 4: 222. .
Corals are one of the more common examples of an animal host whose symbiosis with microalgae can turn to dysbiosis, and is visibly detected as bleaching. Coral microbiomes have been examined in a variety of studies, which demonstrate how oceanic environmental variations, most notably temperature, light, and inorganic nutrients, affect the abundance and performance of the microalgal symbionts, as well as calcification and physiology of the host.Apprill, A. (2017) "Marine animal microbiomes: toward understanding hostŌĆōmicrobiome interactions in a changing ocean". ''Frontiers in Marine Science'', 4: 222. . Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Studies have also suggested that resident bacteria, archaea, and fungi additionally contribute to nutrient and organic matter cycling within the coral, with viruses also possibly playing a role in structuring the composition of these members, thus providing one of the first glimpses at a multi-domain marine animal symbiosis. The gammaproteobacterium ''Endozoicomonas'' is emerging as a central member of the coral's microbiome, with flexibility in its lifestyle.Neave, M.J., Apprill, A., Ferrier-Pag├©s, C. and Voolstra, C.R. (2016) "Diversity and function of prevalent symbiotic marine bacteria in the genus ''Endozoicomonas''". ''Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology'', 100(19): 8315ŌĆō8324. . Given the recent mass bleaching occurring on reefs, corals will likely continue to be a useful and popular system for symbiosis and dysbiosis research. ''Astrangia poculata'', the northern star coral, is a temperate stony coral, widely documented along the eastern coast of the United States. The coral can live with and without
zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
(algal symbionts), making it an ideal model organism to study microbial community interactions associated with symbiotic state. However, the ability to develop Primer (molecular biology), primers and Molecular probe, probes to more specifically target key microbial groups has been hindered by the lack of full length 16S rRNA sequences, since sequences produced by the Illumina platform are of insufficient length (approximately 250 base pairs) for the design of primers and probes. In 2019, Goldsmith et al demonstrated Sanger sequencing was capable of reproducing the biologically-relevant diversity detected by deeper next-generation sequencing, while also producing longer sequences useful to the research community for probe and primer design (see diagram on right). Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Holobiont
Reef-building corals are well-studied holobionts that include the coral itself together with its symbiontzooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
(photosynthetic dinoflagellates), as well as its associated bacteria and viruses.Knowlton, N. and Rohwer, F. (2003) "Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: the host as a habitat". ''The American Naturalist'', 162(S4): S51-S62. . Co-evolutionary patterns exist for coral microbial communities and coral phylogeny.
Cophylogeny and phylosymbiosis
It is known that the coral's microbiome and symbiont influence host health, however the historic influence of each member on others is not well understood. Scleractinian corals have been diversifying for longer than many other symbiotic systems, and their microbiomes are known to be partially species-specific. It has been suggested that ''Endozoicomonas'', a commonly highly abundant bacterium in corals, has exhibited codiversification with its host. This hints at an intricate set of relationships between the members of the coral holobiont that have been developing as evolution of these members occurs. A study published in 2018 revealed evidence of phylosymbiosis between corals and their tissue and skeleton microbiomes. The coral skeleton, which represents the most diverse of the three coral microbiomes, showed the strongest evidence of phylosymbiosis. Coral microbiome composition and Species richness, richness were found to reflect coral phylogeny. For example, interactions between bacterial and eukaryotic coral phylogeny influence the abundance of ''Endozoicomonas'', a highly abundant bacterium in the coral holobiont. However, host-microbial cophylogeny appears to influence only a subset of coral-associated bacteria.
Reefs
Many corals in the order Scleractinia are Hermatypic coral, hermatypic, meaning that they are involved in building reefs. Most such corals obtain some of their energy fromzooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''S ...
in the genus ''Symbiodinium''. These are symbiosis, symbiotic photosynthetic dinoflagellates which require sunlight; reef-forming corals are therefore found mainly in shallow water. They secrete calcium carbonate to form hard skeletons that become the framework of the reef. However, not all reef-building corals in shallow water contain zooxanthellae, and some deep water species, living at depths to which light cannot penetrate, form reefs but do not harbour the symbionts.
There are various types of shallow-water coral reef, including fringing reefs, barrier reefs and atolls; most occur in tropical and subtropical seas. They are very slow-growing, adding perhaps one centimetre (0.4 in) in height each year. The Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
is thought to have been laid down about two million years ago. Over time, corals fragment and die, sand and rubble accumulates between the corals, and the shells of clams and other molluscs decay to form a gradually evolving calcium carbonate structure. Coral reefs are extremely diverse marine ecosystems hosting over 4,000 species of fish, massive numbers of cnidarians, Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and many other animals.
Evolution
 At certain times in the geological past, corals were very abundant. Like modern corals, these ancestors built reefs, some of which ended as great structures in sedimentary rocks. Fossils of fellow reef-dwellers algae, sponges, and the remains of many Echinoderm, echinoids, brachiopods, bivalves, gastropods, and trilobites appear along with coral fossils. This makes some corals useful index fossils. Coral fossils are not restricted to reef remnants, and many solitary fossils are found elsewhere, such as ''Cyclocyathus'', which occurs in England's Gault clay formation.
At certain times in the geological past, corals were very abundant. Like modern corals, these ancestors built reefs, some of which ended as great structures in sedimentary rocks. Fossils of fellow reef-dwellers algae, sponges, and the remains of many Echinoderm, echinoids, brachiopods, bivalves, gastropods, and trilobites appear along with coral fossils. This makes some corals useful index fossils. Coral fossils are not restricted to reef remnants, and many solitary fossils are found elsewhere, such as ''Cyclocyathus'', which occurs in England's Gault clay formation.
Early corals
Corals first appeared in the Cambrian about . Fossils are extremely rare until the Ordovician period, 100 million years later, when Heliolitida, Rugosa, rugose, and tabulata, tabulate corals became widespread. Paleozoic corals often contained numerous endobiotic symbionts. Tabulate corals occur in limestones and calcareous shales of the Ordovician period, with a gap in the fossil record due to OrdovicianŌĆōSilurian extinction events, extinction events at the end of the Ordovician. Corals reappeared some millions of years later during the Silurian period, and tabulate corals often form low cushions or branching masses of calcite alongside rugose corals. Tabulate coral numbers began to decline during the middle of the Silurian period. Rugose or horn corals became dominant by the middle of the Silurian period, and during the Devonian, corals flourished with more than 200 genera. The rugose corals existed in solitary and colonial forms, and were also composed of calcite. Both rugose and tabulate corals became extinct in the PermianŌĆōTriassic extinction event (along with 85% of marine species), and there is a gap of tens of millions of years until new forms of coral evolved in the Triassic.Modern corals
The currently ubiquitous stony corals, Scleractinia, appeared in the Middle Triassic to fill the niche vacated by the extinct rugose and tabulate orders, and is not closely related to the earlier forms. Unlike the corals prevalent before the Permian extinction, which formed skeletons of a form of calcium carbonate known as calcite, modern stony corals form skeletons composed of the aragonite. Their fossils are found in small numbers in rocks from the Triassic period, and become common in the Jurassic and later periods. Although they are geologically younger than the tabulate and rugose corals, the aragonite of their skeletons is less readily preserved, and their fossil record is accordingly less complete.Status
Threats
 Coral reefs are under stress around the world. In particular, coral mining, agricultural runoff, agricultural and urban runoff, pollution (organic and inorganic), overfishing, blast fishing, disease, and the digging of canals and access into islands and bays are localized threats to coral ecosystems. Broader threats are sea temperature rise, sea level rise and pH changes from ocean acidification, all associated with greenhouse gas emissions. In 1998, 16% of the world's reefs died as a result of increased water temperature.
Approximately 10% of the world's coral reefs are dead. About 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to human-related activities. The threat to reef health is particularly strong in Southeast Asia, where 80% of reefs are endangered species, endangered. Over 50% of the world's
Coral reefs are under stress around the world. In particular, coral mining, agricultural runoff, agricultural and urban runoff, pollution (organic and inorganic), overfishing, blast fishing, disease, and the digging of canals and access into islands and bays are localized threats to coral ecosystems. Broader threats are sea temperature rise, sea level rise and pH changes from ocean acidification, all associated with greenhouse gas emissions. In 1998, 16% of the world's reefs died as a result of increased water temperature.
Approximately 10% of the world's coral reefs are dead. About 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to human-related activities. The threat to reef health is particularly strong in Southeast Asia, where 80% of reefs are endangered species, endangered. Over 50% of the world's coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
s may be destroyed by 2030; as a result, most nations protect them through environmental laws.
In the Caribbean and tropical Pacific, direct contact between ~40ŌĆō70% of common seaweeds and coral causes bleaching and death to the coral via transfer of lipid-soluble metabolites. Seaweed and algae proliferate given adequate nutrients and limited grazing by herbivores such as parrotfish.
Water temperature changes of more than or salinity changes can kill some species of coral. Under such environmental stresses, corals expel their Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)''
''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicell ...
; without them coral tissues reveal the white of their skeletons, an event known as coral bleaching.
Submarine springs found along the coast of Mexico's Yucat├Īn Peninsula produce water with a naturally low pH (relatively high acidity) providing conditions similar to those expected to become widespread as the oceans absorb carbon dioxide. Surveys discovered multiple species of live coral that appeared to tolerate the acidity. The colonies were small and patchily distributed, and had not formed structurally complex reefs such as those that compose the nearby Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System.
Coral health
To assess the threat level of coral, scientists developed a coral imbalance ratio, Log (Average abundance of disease associated taxa / Average abundance of healthy associated taxa). The lower the ratio the healthier the microbial community is. This ratio was developed after the microbial mucus of coral was collected and studied.Climate change impacts
Increasing Sea surface temperature, sea surface temperatures in tropical regions (~) the last century have caused major coral bleaching, death, and therefore shrinking coral populations. Although coral are able to adapt and acclimate, it is uncertain if this evolutionary process will happen quickly enough to prevent major reduction of their numbers. Annual growth bands in some corals, such as the deep sea bamboo corals (''Isididae''), may be among the first signs of the effects of ocean acidification on marine life. The growth rings allow geologists to construct year-by-year chronologies, a form of incremental dating, which underlie high-resolution records of past paleoclimatology, climatic and paleoecology, environmental changes using geochemistry, geochemical techniques. Certain species form communities called microatolls, which are colonies whose top is dead and mostly above the water line, but whose perimeter is mostly submerged and alive. Average tide level limits their height. By analyzing the various growth morphologies, microatolls offer a low resolution record of sea level change. Fossilized microatolls can also be dated using Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon dating. Such methods can help to reconstruct Holocene sea levels. Though coral have large sexually-reproducing populations, their evolution can be slowed by abundant asexual reproduction. Gene flow is variable among coral species. According to the biogeography of coral species, gene flow cannot be counted on as a dependable source of adaptation as they are very stationary organisms. Also, coral longevity might factor into their adaptivity. However, adaptation to climate change has been demonstrated in many cases, which is usually due to a shift in coral and zooxanthellae genotypes. These shifts in allele frequency have progressed toward more tolerant types of zooxanthellae. Scientists found that a certain scleractinian zooxanthella is becoming more common where sea temperature is high. Symbionts able to tolerate warmer water seem to photosynthesise more slowly, implying an evolutionary trade-off. In the Gulf of Mexico, where sea temperatures are rising, cold-sensitive Staghorn coral, staghorn and elkhorn coral have shifted in location. Not only have the symbionts and specific species been shown to shift, but there seems to be a certain growth rate favorable to selection. Slower-growing but more heat-tolerant corals have become more common. The changes in temperature and acclimation are complex. Some reefs in current shadows represent a Refugium (population biology), refugium location that will help them adjust to the disparity in the environment even if eventually the temperatures may rise more quickly there than in other locations. This vicariance, separation of populations by climatic barriers causes a realized niche to shrink greatly in comparison to the old fundamental niche.Geochemistry
Corals are shallow, colonial organisms that integrate oxygen and trace elements into their skeletal aragonite (Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcite) crystalline structures as they grow. Geochemical anomalies within the crystalline structures of corals represent functions of temperature, salinity and oxygen isotopic composition. Such geochemical analysis can help with climate modeling. The ╬┤18O, ratio of oxygen-18 to oxygen-16 (╬┤18O), for example, is a proxy for temperature.=Strontium/calcium ratio anomaly
= Time can be attributed to coral geochemistry anomalies by correlating strontium/calcium minimums with sea surface temperature, sea surface temperature (SST) maximums to data collected froNINO 3.4 SSTA
=Oxygen isotope anomaly
= The comparison of coral strontium/calcium minimums with sea surface temperature maximums, data recorded froNINO 3.4 SSTA
time can be correlated to coral strontium/calcium and Δ18O, δ18O variations. To confirm the accuracy of the annual relationship between Sr/Ca and Δ18O, δ18O variations, a perceptible association to annual coral growth rings confirms the age conversion. Geochronology is established by the blending of Sr/Ca data, growth rings, and Stable isotope ratio, stable isotope data. El Nino-Southern Oscillation, El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is directly related to climate fluctuations that influence coral Δ18O, δ18O ratio from local salinity variations associated with the position of the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) and can be used for El Niño Southern Oscillation, ENSO modeling.
=Sea surface temperature and sea surface salinity
= The global moisture budget is primarily being influenced by tropical sea surface temperatures from the position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). The Southern Hemisphere has a unique meteorological feature positioned in the southwestern Pacific Basin called the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ), which contains a perennial position within the Southern Hemisphere. During El Ni├▒o Southern Oscillation, ENSO warm periods, the South Pacific convergence zone, SPCZ reverses orientation extending from the equator down south through Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji and towards the French Polynesian islands, Polynesian Islands; and due east towards South America affecting geochemistry of corals in tropical regions.
Geochemical analysis of skeletal coral can be linked to sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature (SST), fro
The global moisture budget is primarily being influenced by tropical sea surface temperatures from the position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). The Southern Hemisphere has a unique meteorological feature positioned in the southwestern Pacific Basin called the South Pacific convergence zone, South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ), which contains a perennial position within the Southern Hemisphere. During El Ni├▒o Southern Oscillation, ENSO warm periods, the South Pacific convergence zone, SPCZ reverses orientation extending from the equator down south through Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji and towards the French Polynesian islands, Polynesian Islands; and due east towards South America affecting geochemistry of corals in tropical regions.
Geochemical analysis of skeletal coral can be linked to sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature (SST), froEl Nino 3.4 SSTA
data, of tropical oceans to seawater Δ18O, δ18O ratio anomalies from corals. El Niño Southern Oscillation, ENSO phenomenon can be related to variations in sea surface salinity (SSS) and sea surface temperature, sea surface temperature (SST) that can help model tropical climate activities.
=Limited climate research on current species
= Climate research on live coral species is limited to a few studied species. Studying ''Porites'' coral provides a stable foundation for geochemical interpretations that is much simpler to physically extract data in comparison to ''Platygyra'' species where the complexity of ''Platygyra'' species skeletal structure creates difficulty when physically sampled, which happens to be one of the only multidecadal living coral records used for coral paleoclimate modeling.
Climate research on live coral species is limited to a few studied species. Studying ''Porites'' coral provides a stable foundation for geochemical interpretations that is much simpler to physically extract data in comparison to ''Platygyra'' species where the complexity of ''Platygyra'' species skeletal structure creates difficulty when physically sampled, which happens to be one of the only multidecadal living coral records used for coral paleoclimate modeling.
Protection
Marine Protected Areas, Biosphere reserves, marine parks, national monuments world heritage status, Fisheries management, fishery management and habitat (ecology), habitat protection can protect reefs from anthropogenic damage. Many governments now prohibit removal of coral from reefs, and inform coastal residents about reef protection and ecology. While local action such as habitat restoration and herbivore protection can reduce local damage, the longer-term threats of acidification, temperature change and sea-level rise remain a challenge. Protecting networks of diverse and healthy reefs, not only climate Refugium (population biology), refugia, helps ensure the greatest chance of genetic diversity, which is critical for coral to adapt to new climates. A variety of conservation methods applied across marine and terrestrial threatened ecosystems makes coral adaption more likely and effective. To eliminate destruction of corals in their indigenous regions, projects have been started to grow corals in non-tropical countries.Relation to humans
Local economies near major coral reefs benefit from an abundance of fish and other marine creatures as a food source. Reefs also provide recreational scuba diving and snorkeling tourism. These activities can damage coral but international projects such as Green Fins that encourage dive and snorkel centres to follow a Code of Conduct have been proven to mitigate these risks.Jewelry
 Corals' many colors give it appeal for necklaces and other jewelry. Intensely red coral is prized as a gemstone. Sometimes called fire coral, it is not the same as fire coral. Red coral is very rare because of overharvesting. In general, it is inadvisable to give coral as gifts since they are in decline from stressors like climate change, pollution, and unsustainable fishing.
Always considered a precious mineral, "the Chinese have long associated red coral with auspiciousness and longevity because of its color and its resemblance to deer antlers (so by association, virtue, long life, and high rank". It reached its height of popularity during the Manchu or Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) when it was almost exclusively reserved for the emperor's use either in the form of coral beads (often combined with pearls) for court jewelry or as decorative Penjing (decorative miniature mineral trees). Coral was known as ''shanhu'' in Chinese. The "early-modern 'coral network' [began in] the Mediterranean Sea [and found its way] to Qing China via the English East India Company". There were strict rules regarding its use in a code established by the Qianlong Emperor in 1759.
Corals' many colors give it appeal for necklaces and other jewelry. Intensely red coral is prized as a gemstone. Sometimes called fire coral, it is not the same as fire coral. Red coral is very rare because of overharvesting. In general, it is inadvisable to give coral as gifts since they are in decline from stressors like climate change, pollution, and unsustainable fishing.
Always considered a precious mineral, "the Chinese have long associated red coral with auspiciousness and longevity because of its color and its resemblance to deer antlers (so by association, virtue, long life, and high rank". It reached its height of popularity during the Manchu or Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) when it was almost exclusively reserved for the emperor's use either in the form of coral beads (often combined with pearls) for court jewelry or as decorative Penjing (decorative miniature mineral trees). Coral was known as ''shanhu'' in Chinese. The "early-modern 'coral network' [began in] the Mediterranean Sea [and found its way] to Qing China via the English East India Company". There were strict rules regarding its use in a code established by the Qianlong Emperor in 1759.
Medicine
In medicine, chemical compounds from corals can potentially be used to treat cancer, AIDS, pain, and for other therapeutic uses. Coral skeletons, e.g. ''Isididae'' are also used for bone grafting in humans. Coral Calx, known as Praval Bhasma in Sanskrit, is widely used in traditional system of Ayurveda, Indian medicine as a supplement in the treatment of a variety of bone metabolic disorders associated with calcium deficiency. In classical times ingestion of pulverized coral, which consists mainly of the weak base calcium carbonate, was recommended for calming stomach ulcers by Galen and Dioscorides.Construction
Coral reefs in places such as the East African coast are used as a source of building material. Ancient (fossil) coral limestone, notably including the Coral Rag Formation of the hills around Oxford (England), was once used as a building stone, and can be seen in some of the oldest buildings in that city including the Saxon tower of St Michael at the Northgate, St. George's Tower of Oxford Castle, and the medieval walls of the city.Shoreline protection
Healthy coral reefs absorb 97 percent of a wave's energy, which buffers shorelines from currents, waves, and storms, helping to prevent loss of life and property damage. Coastlines protected by coral reefs are also more stable in terms of erosion than those without.Local economies
Coastal communities near coral reefs rely heavily on them. Worldwide, more than 500 million people depend on coral reefs for food, income, coastal protection, and more. The total economic value of coral reef services in the United States - including fisheries, tourism, and coastal protection - is more than $3.4 billion a year.Aquaria
 The saltwater fishkeeping hobby has expanded, over recent years, to include Reef aquarium, reef tanks, fish tanks that include large amounts of live rock on which coral is allowed to grow and spread. These tanks are either kept in a natural-like state, with algae (sometimes in the form of an algae scrubber) and a deep sand bed providing filtration, or as "show tanks", with the rock kept largely bare of the algae and microfauna that would normally populate it, in order to appear neat and clean.
The most popular kind of coral kept is
The saltwater fishkeeping hobby has expanded, over recent years, to include Reef aquarium, reef tanks, fish tanks that include large amounts of live rock on which coral is allowed to grow and spread. These tanks are either kept in a natural-like state, with algae (sometimes in the form of an algae scrubber) and a deep sand bed providing filtration, or as "show tanks", with the rock kept largely bare of the algae and microfauna that would normally populate it, in order to appear neat and clean.
The most popular kind of coral kept is soft coral
Alcyonacea, or soft corals, are an order of corals. In addition to the fleshy soft corals, the order Alcyonacea now contains all species previously known as "gorgonian corals", that produce a more or less hard skeleton, though quite different f ...
, especially zoanthids and mushroom corals, which are especially easy to grow and propagate in a wide variety of conditions, because they originate in enclosed parts of reefs where water conditions vary and lighting may be less reliable and direct.. Marinebio.org. Retrieved on 2016-06-13.
Aquaculture
Aquaculture of coral, Coral aquaculture, also known as ''coral farming'' or ''coral gardening'', is the cultivation of corals for commercial purposes or coral reef restoration. Aquaculture is showing promise as a potentially effective tool for restoringcoral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
s, which have been declining around the world. The process bypasses the early growth stages of corals when they are most at risk of dying. Coral fragments known as "seeds" are grown in nurseries then replanted on the reef. Coral is farmed by coral farmers who live locally to the reefs and farm for reef Conservation movement, conservation or for income. It is also farmed by scientists for research, by businesses for the supply of the live and ornamental coral trade and by private aquarium hobbyists.
Gallery
''Further images: commons:Coral reefs and commons:Corals''coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
off the coast of Eilat, Israel.
File:000324-Corals-IMG 0418-2.jpg, Corals, Tis Beach, Chabahar, Iran
File:000407-Corals-IMG 0693-2.jpg, Corals, Tis Beach, Chabahar, Iran
See also
*Keystone species *Ringstead Coral BedReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Coral Reefs
The Ocean Portal by the Smithsonian Institution * NOAA
Coral Reef Conservation Program
* NOAA CoRIS ŌĆ
Coral Reef Biology
* NOAA Office for Coastal Management
Fast Facts - Coral Reefs
* NOAA Ocean Service Education ŌĆ
Corals
* {{Authority control Anthozoa Coral reefs,