Burundi women's national football team.ogv on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a

 On 20 January 1959, Burundi's ruler Mwambutsa IV Bangiriceng of Burundi, Mwami Mwambutsa IV requested Burundi's independence from Belgium and dissolution of the Ruanda-Urundi union. In the following months, Burundian political parties began to advocate for the end of Belgian colonial rule and the separation of Rwanda and Burundi. The first and largest of these political parties was the Union for National Progress (UPRONA).
Burundi's push for independence was influenced by the Rwandan Revolution and the accompanying instability and ethnic conflict that occurred there. As a result of the Rwandan Revolution, many Rwandan Tutsi refugees arrived in Burundi during the period from 1959 to 1961.
Burundi's first Burundian legislative election, 1961, elections took place on 8 September 1961 and UPRONA, a multi-ethnic unity party led by Prince Louis Rwagasore won just over 80% of the electorate's votes. In the wake of the elections, on 13 October, the 29-year-old Prince Louis Rwagasore#Assassination in 1961, Prince Rwagasore was assassinated, robbing Burundi of its most popular and well-known nationalists.
The country claimed independence on 1 July 1962, and legally changed its name from Ruanda-Urundi to Burundi. Burundi became a constitutional monarchy with Mwami Mwambutsa IV, Prince Rwagasore's father, serving as the country's king. On 18 September 1962 Burundi joined the
On 20 January 1959, Burundi's ruler Mwambutsa IV Bangiriceng of Burundi, Mwami Mwambutsa IV requested Burundi's independence from Belgium and dissolution of the Ruanda-Urundi union. In the following months, Burundian political parties began to advocate for the end of Belgian colonial rule and the separation of Rwanda and Burundi. The first and largest of these political parties was the Union for National Progress (UPRONA).
Burundi's push for independence was influenced by the Rwandan Revolution and the accompanying instability and ethnic conflict that occurred there. As a result of the Rwandan Revolution, many Rwandan Tutsi refugees arrived in Burundi during the period from 1959 to 1961.
Burundi's first Burundian legislative election, 1961, elections took place on 8 September 1961 and UPRONA, a multi-ethnic unity party led by Prince Louis Rwagasore won just over 80% of the electorate's votes. In the wake of the elections, on 13 October, the 29-year-old Prince Louis Rwagasore#Assassination in 1961, Prince Rwagasore was assassinated, robbing Burundi of its most popular and well-known nationalists.
The country claimed independence on 1 July 1962, and legally changed its name from Ruanda-Urundi to Burundi. Burundi became a constitutional monarchy with Mwami Mwambutsa IV, Prince Rwagasore's father, serving as the country's king. On 18 September 1962 Burundi joined the
Death Tolls for the Major Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century: C. Burundi (1972–73, primarily Hutu killed by Tutsi) 120,000
International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi (2002). Paragraph 85. "The Micombero regime responded with a genocidal repression that is estimated to have caused over a hundred thousand victims and forced several hundred thousand Hutus into exile" In addition, several hundred thousand Hutu were estimated to have fled the killings into Zaïre, Rwanda and
 On 28 August 2000, a transitional government for Burundi was planned as a part of the Arusha Peace and Reconciliation Agreement. The transitional government was placed on a trial basis for five years. After several aborted cease-fires, a 2001 peace plan and power-sharing agreement has been relatively successful. A cease-fire was signed in 2003 between the Tutsi-controlled Burundian government and the largest Hutu rebel group, CNDD-FDD (National Council for the Defense of Democracy-Forces for the Defense of Democracy).
In 2003, FRODEBU leader Domitien Ndayizeye (Hutu) was elected president. In early 2005, ethnic quotas were formed for determining positions in Burundi's government. Throughout the year, elections for parliament and president occurred.
On 28 August 2000, a transitional government for Burundi was planned as a part of the Arusha Peace and Reconciliation Agreement. The transitional government was placed on a trial basis for five years. After several aborted cease-fires, a 2001 peace plan and power-sharing agreement has been relatively successful. A cease-fire was signed in 2003 between the Tutsi-controlled Burundian government and the largest Hutu rebel group, CNDD-FDD (National Council for the Defense of Democracy-Forces for the Defense of Democracy).
In 2003, FRODEBU leader Domitien Ndayizeye (Hutu) was elected president. In early 2005, ethnic quotas were formed for determining positions in Burundi's government. Throughout the year, elections for parliament and president occurred.
 Reconstruction efforts in Burundi started to practically take effect after 2006. The UN shut down its peacekeeping mission and re-focused on helping with reconstruction.Timeline Burundi
Reconstruction efforts in Burundi started to practically take effect after 2006. The UN shut down its peacekeeping mission and re-focused on helping with reconstruction.Timeline Burundi
BBC. . (accessed on 29 October 2008) Toward achieving economic reconstruction, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, D.R.Congo and Burundi relaunched the regional Economic Community of the Great Lakes Countries. In addition, Burundi, along with Rwanda, joined the East African Community in 2007. However, the terms of the September 2006 Ceasefire between the government and the last remaining armed opposition group, the National Liberation Front (Burundi), FLN (Forces for National Liberation, also called NLF or FROLINA), were not totally implemented, and senior FLN members subsequently left the truce monitoring team, claiming that their security was threatened. In September 2007, rival FLN factions clashed in the capital, killing 20 fighters and causing residents to begin fleeing. Rebel raids were reported in other parts of the country. The rebel factions disagreed with the government over disarmament and the release of political prisoners.Burundi: Release Civilians Detained Without Charge , Human Rights Watch
. Hrw.org (29 May 2008). Retrieved on 24 November 2012. In late 2007 and early 2008, FLN combatants attacked government-protected camps where former combatants were living. The homes of rural residents were also pillaged. The 2007 report of Amnesty International mentions many areas where improvement is required. Civilians are victims of repeated acts of violence done by the FLN. The latter also recruits child soldiers. The rate of violence against women is high. Perpetrators regularly escape prosecution and punishment by the state. There is an urgent need for reform of the judicial system. Genocide, war crimes and crimes against humanity continued to go unpunished. In late March 2008, the FLN sought for the parliament to adopt a law guaranteeing them 'provisional immunity' from arrest. This would cover ordinary crimes, but not grave violations of international humanitarian law like war crimes or crimes against humanity . Even though the government has granted this in the past to people, the FLN has been unable to obtain the provisional immunity. On 17 April 2008, the FLN bombarded Bujumbura. The Burundian army fought back and the FLN suffered heavy losses. A new ceasefire was signed on 26 May 2008. In August 2008, President Nkurunziza met with the FLN leader Agathon Rwasa, with the mediation of Charles Nqakula, South Africa's Minister for Safety and Security. This was the first direct meeting since June 2007. Both agreed to meet twice a week to establish a commission to resolve any disputes that might arise during the peace negotiations. The UN has attempted to evaluate the impact of its peace-building initiatives. In the early 2010s, the UN peacekeeping mission in Burundi sought to assess the success of its Disarmament, Demobilization and Reintegration program by counting the number of arms that had been collected, given the prevalence of arms in the country. However, these evaluations failed to include date from local populations, which are significant in impact evaluations of peacebuilding initiatives. As of 2012, Burundi was participating in African Union peacekeeping missions, including the African Union Mission to Somalia, mission to Somalia against Al-Shabaab militants. In 2014, the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Burundi), Truth and Reconciliation Commission was established, initially for four years and then extended for another four in 2018.
. CNN.com (15 May 2015). Retrieved on 29 June 2015. Following the attempted coup, protests however continued and over 100,000 people had fled the country by 20 May causing a humanitarian emergency. There are reports of continued and widespread abuses of human rights, including unlawful killings, torture, disappearances, and restrictions on freedom of expression. Despite calls by the
 Burundi's political system is that of a presidential system, presidential representative democracy, representative democratic republic based upon a multi-party state. The president of Burundi is the
Burundi's political system is that of a presidential system, presidential representative democracy, representative democratic republic based upon a multi-party state. The president of Burundi is the
United States Department of State. February 2008. Retrieved on 28 June 2008. For each of Burundi's eighteen provinces, one Hutu and one Tutsi senator are chosen. One term for the Transitional Senate is five years. Together, Burundi's legislative branch elect the president to a five-year term. Burundi's president appoints officials to his Council of Ministers, which is also part of the executive branch. The president can also pick fourteen members of the Transitional Senate to serve on the Council of Ministers. Members of the Council of Ministers must be approved by two-thirds of Burundi's legislature. The president also chooses two vice-presidents. Following the 2015 election, the president of Burundi was
 file:Hippos in Burundi.png, Hippos at Kibira National Park in northwest Burundi
One of the smallest countries in Africa, Burundi is landlocked and has an Tropical rainforest climate, equatorial climate. Burundi is a part of the Albertine Rift, the western extension of the East African Rift. The country lies on a rolling plateau in the centre of Africa. Burundi is bordered by Rwanda to the north,
file:Hippos in Burundi.png, Hippos at Kibira National Park in northwest Burundi
One of the smallest countries in Africa, Burundi is landlocked and has an Tropical rainforest climate, equatorial climate. Burundi is a part of the Albertine Rift, the western extension of the East African Rift. The country lies on a rolling plateau in the centre of Africa. Burundi is bordered by Rwanda to the north,
 Burundi is a landlocked, resource-poor country with an underdeveloped manufacturing sector. The economy is predominantly agricultural, accounting for 50% of GDP in 2017 and employing more than 90% of the population. Subsistence agriculture accounts for 90% of agriculture. Eggers, p. xlvii. Burundi's primary exports are coffee and tea, which account for 90% of foreign exchange earnings, though exports are a relatively small share of GDP. Other agricultural products include cotton, tea, maize, sorghum, sweet potatoes, bananas, manioc (tapioca); beef, milk and hides. Even though Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farming is highly relied upon, many people do not have the resources to sustain themselves. This is due to large population growth and no coherent policies governing land ownership. In 2014, the average farm size was about one acre.
Burundi is one of the world's poorest countries, owing in part to its landlocked geography, lack of access to education and the proliferation of HIV/AIDS. Approximately 80% of Burundi's population lives in poverty. Famines and food shortages have occurred throughout Burundi, most notably in the 20th century, and according to the World Food Programme, 56.8% of children under age five suffer from chronic malnutrition. Burundi's export earnings – and its ability to pay for imports – rests primarily on weather conditions and international coffee and tea prices.
Burundi is a landlocked, resource-poor country with an underdeveloped manufacturing sector. The economy is predominantly agricultural, accounting for 50% of GDP in 2017 and employing more than 90% of the population. Subsistence agriculture accounts for 90% of agriculture. Eggers, p. xlvii. Burundi's primary exports are coffee and tea, which account for 90% of foreign exchange earnings, though exports are a relatively small share of GDP. Other agricultural products include cotton, tea, maize, sorghum, sweet potatoes, bananas, manioc (tapioca); beef, milk and hides. Even though Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farming is highly relied upon, many people do not have the resources to sustain themselves. This is due to large population growth and no coherent policies governing land ownership. In 2014, the average farm size was about one acre.
Burundi is one of the world's poorest countries, owing in part to its landlocked geography, lack of access to education and the proliferation of HIV/AIDS. Approximately 80% of Burundi's population lives in poverty. Famines and food shortages have occurred throughout Burundi, most notably in the 20th century, and according to the World Food Programme, 56.8% of children under age five suffer from chronic malnutrition. Burundi's export earnings – and its ability to pay for imports – rests primarily on weather conditions and international coffee and tea prices.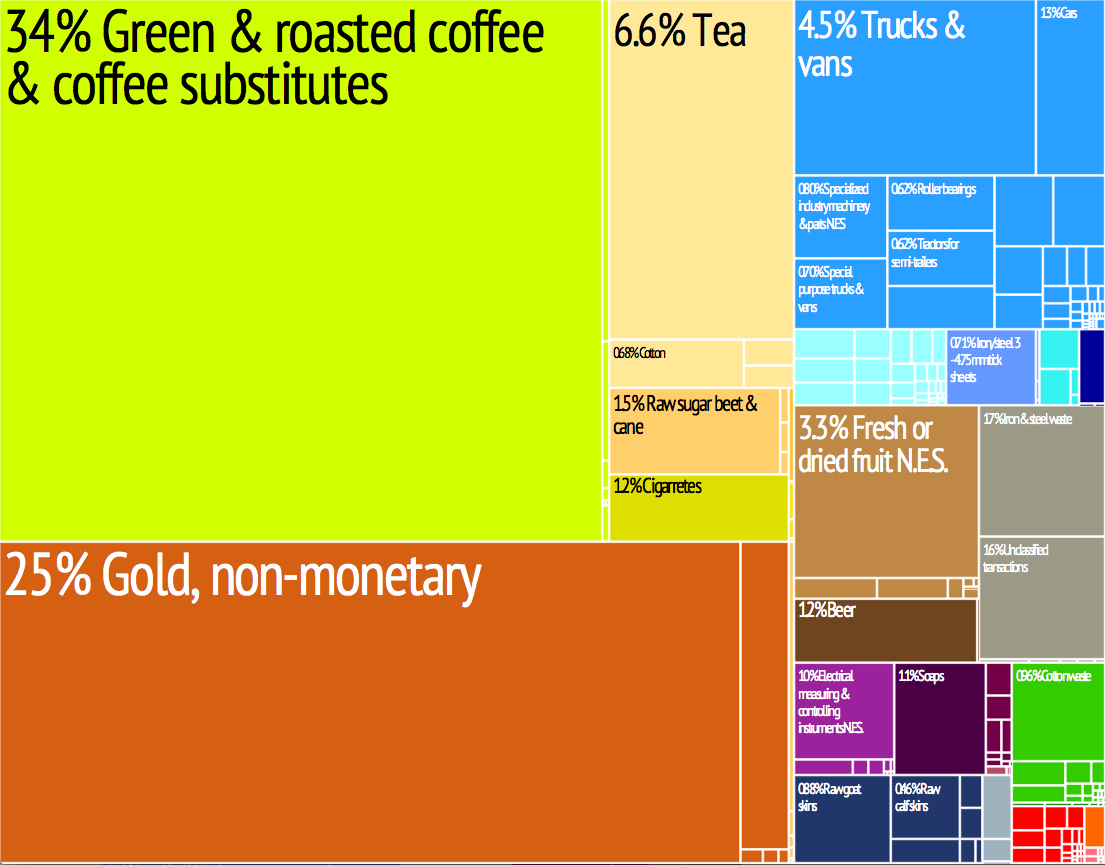 The purchasing power of most Burundians has decreased as wage increases have not kept up with inflation. As a result of deepening poverty, Burundi will remain heavily dependent on aid from bilateral and multilateral donors. Foreign aid represents 42% of Burundis national income, the second highest rate in Sub-Saharan Africa. Burundi joined the East African Community in 2009, which should boost its regional trade ties, and also in 2009 received $700 million in debt relief. Government corruption is hindering the development of a healthy private sector as companies seek to navigate an environment with ever-changing rules.
Studies since 2007 have shown Burundians to have extremely poor levels of Satisfaction with Life Index, satisfaction with life; the World Happiness Report, World Happiness Report 2018 rated them the world's least happy in 2018.
The purchasing power of most Burundians has decreased as wage increases have not kept up with inflation. As a result of deepening poverty, Burundi will remain heavily dependent on aid from bilateral and multilateral donors. Foreign aid represents 42% of Burundis national income, the second highest rate in Sub-Saharan Africa. Burundi joined the East African Community in 2009, which should boost its regional trade ties, and also in 2009 received $700 million in debt relief. Government corruption is hindering the development of a healthy private sector as companies seek to navigate an environment with ever-changing rules.
Studies since 2007 have shown Burundians to have extremely poor levels of Satisfaction with Life Index, satisfaction with life; the World Happiness Report, World Happiness Report 2018 rated them the world's least happy in 2018.
 Some of Burundi's natural resources include uranium, nickel, cobalt, copper and platinum. Besides agriculture, other industries include: assembly of imported components; public works construction; food processing and light consumer goods such as blankets, shoes and soap.
In regards to telecommunications infrastructure, Burundi is ranked second to last in the World Economic Forum's Network Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. Burundi ranked number 147 overall in the 2014 NRI ranking, down from 144 in 2013.
Lack of access to financial services is a serious problem for the majority of the population, particularly in the densely populated rural areas: only 2% of the total population holds bank accounts, and fewer than 0.5% use bank lending services. Microfinance, however, plays a larger role, with 4% of Burundians being members of microfinance institutions – a larger share of the population than that reached by banking and postal services combined. 26 licensed microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer savings, deposits and short- to medium-term credit. Dependence of the sector on donor assistance is limited.
Burundi is part of the East African Community and a potential member of the planned East African Federation. Economic growth in Burundi is relatively steady but Burundi is still behind neighbouring countries.
Some of Burundi's natural resources include uranium, nickel, cobalt, copper and platinum. Besides agriculture, other industries include: assembly of imported components; public works construction; food processing and light consumer goods such as blankets, shoes and soap.
In regards to telecommunications infrastructure, Burundi is ranked second to last in the World Economic Forum's Network Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. Burundi ranked number 147 overall in the 2014 NRI ranking, down from 144 in 2013.
Lack of access to financial services is a serious problem for the majority of the population, particularly in the densely populated rural areas: only 2% of the total population holds bank accounts, and fewer than 0.5% use bank lending services. Microfinance, however, plays a larger role, with 4% of Burundians being members of microfinance institutions – a larger share of the population than that reached by banking and postal services combined. 26 licensed microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer savings, deposits and short- to medium-term credit. Dependence of the sector on donor assistance is limited.
Burundi is part of the East African Community and a potential member of the planned East African Federation. Economic growth in Burundi is relatively steady but Burundi is still behind neighbouring countries.
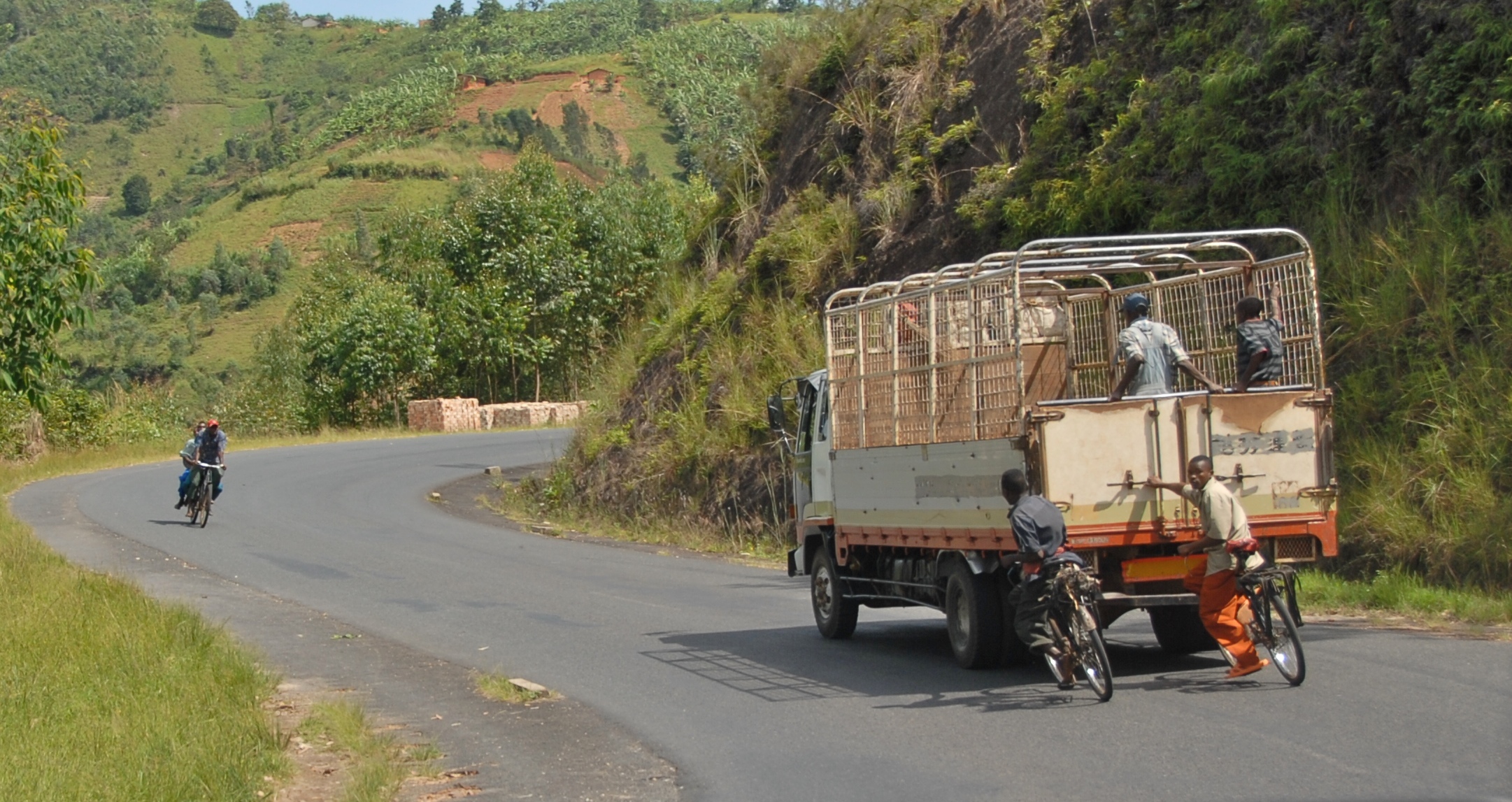
 Burundi's transport network is limited and underdeveloped. According to a 2012 ''DHL Global Connectedness Index'', Burundi is the least globalised of 140 surveyed countries. Bujumbura International Airport is the only airport with a paved runway and as of May 2017 it was serviced by four airlines (Brussels Airlines, Ethiopian Airlines, Kenya Airways and RwandAir). Kigali International Airport, Kigali is the city with the most daily flight connections to Bujumbura. The country has a road network but less than 10% of the country's roads were paved and private bus companies were the main operators of buses on the international route to Kigali; however, there were no bus connections to the other neighbouring countries (Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of Congo). Bujumbura is connected by a passenger and cargo ferry (the MV Mwongozo) to Kigoma in Tanzania. There is a East African Railway Master Plan, long-term plan to link the country via rail to Kigali and then onward to Kampala and Kenya.
Burundi's transport network is limited and underdeveloped. According to a 2012 ''DHL Global Connectedness Index'', Burundi is the least globalised of 140 surveyed countries. Bujumbura International Airport is the only airport with a paved runway and as of May 2017 it was serviced by four airlines (Brussels Airlines, Ethiopian Airlines, Kenya Airways and RwandAir). Kigali International Airport, Kigali is the city with the most daily flight connections to Bujumbura. The country has a road network but less than 10% of the country's roads were paved and private bus companies were the main operators of buses on the international route to Kigali; however, there were no bus connections to the other neighbouring countries (Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of Congo). Bujumbura is connected by a passenger and cargo ferry (the MV Mwongozo) to Kigoma in Tanzania. There is a East African Railway Master Plan, long-term plan to link the country via rail to Kigali and then onward to Kampala and Kenya.

 As of October 2021, Burundi was estimated by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs#Divisions, United Nations to have a population of 12,346,893 people, compared to only 2,456,000 in 1950. The population growth rate is 2.5 percent per year, more than double the average global pace, and a Burundian woman has on average 5.10 children, more than double the international fertility rate. Burundi had the tenth highest total fertility rate in the world, just behind Somalia, in 2021.
Many Burundians have migrated to other countries as a result of the civil war. In 2006, the United States accepted approximately 10,000 Burundian refugees.
Burundi remains an overwhelmingly rural society, with just 13% of the population living in urban areas in 2013. The population density of around 315 people per square kilometre (753 per sq mi) is the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Roughly 85% of the population are of
As of October 2021, Burundi was estimated by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs#Divisions, United Nations to have a population of 12,346,893 people, compared to only 2,456,000 in 1950. The population growth rate is 2.5 percent per year, more than double the average global pace, and a Burundian woman has on average 5.10 children, more than double the international fertility rate. Burundi had the tenth highest total fertility rate in the world, just behind Somalia, in 2021.
Many Burundians have migrated to other countries as a result of the civil war. In 2006, the United States accepted approximately 10,000 Burundian refugees.
Burundi remains an overwhelmingly rural society, with just 13% of the population living in urban areas in 2013. The population density of around 315 people per square kilometre (753 per sq mi) is the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Roughly 85% of the population are of
. Pew Research Center. 2010.Burundi
. U.S. Department of State. State.gov (17 November 2010). Retrieved on 24 November 2012.
The Blood Cries Out
. "In one of Africa's most densely populated countries, brothers are killing brothers over the right to farm mere acres of earth. There's just not enough land to go around in Burundi — and it could push the country into civil war." ''Foreign Policy (FP)'' The civil war in 1962 put a stop on the medical advancements in the country. Burundi, again, went into a violent cycle in 2015, jeopardising the citizens of Burundi's medical care. Like many Sub-Saharan Africa countries, Burundi uses indigenous medicine in addition to biomedicine. In the 1980s Burundi's health authorities asked the United Nations Development Program for support to develop quality control and begin new research on pharmaceuticals from medicinal plants. At the same time, the Burundi Association of Traditional Practitioners (ATRADIBU) was founded, which teamed up with the governments agency to set up the Centre for Research and Promotion of Traditional Medicine in Burundi (CRPMT). The recent influx of international aid has supported the work of biomedical health systems in Burundi. However, international aid workers have traditionally stayed away from indigenous medicine in Burundi. As of 2015, roughly 1 out of 10 children in Burundi die before the age of 5 from preventable and treatable illnesses such as pneumonia, diarrhoea, and malaria. The current violence in Burundi has limited the country's access to medication and hospital equipment. Burundi's life expectancy, as of 2015, was 60.1 years. In 2013, Burundi spent 8% of their GDP on healthcare. While Burundi's fertility rate is 6.1 children per women, the country's mortality rate is 61.9 deaths for every 1,000 live births. According to the WHO, the average life expectancy in the country is 58/62 years. Common diseases in Burundi include malaria and typhoid fever.
 Burundi's culture is based on local tradition and the influence of neighbouring countries, though cultural prominence has been hindered by civil unrest. Since farming is the main industry, a typical Burundian meal consists of sweet potatoes, maize, corn, rice and peas. Due to the expense, meat is eaten only a few times per month.
When several Burundians of close acquaintance meet for a gathering they drink ''impeke'', a beer, together from a large container to symbolise unity.
Notable Burundians include the footballer Mohammed Tchité and singer Jean-Pierre Nimbona, popularly known as Kidumu (who is based in Nairobi, Kenya).
Crafts are an important art form in Burundi and are attractive gifts to many tourists. Basket weaving is a popular craft for local artisans. Other crafts such as masks, shields, statues and pottery are made in Burundi. Cultural Profiles Project. Citizenship and Immigration Canada. Retrieved 30 June 2008.
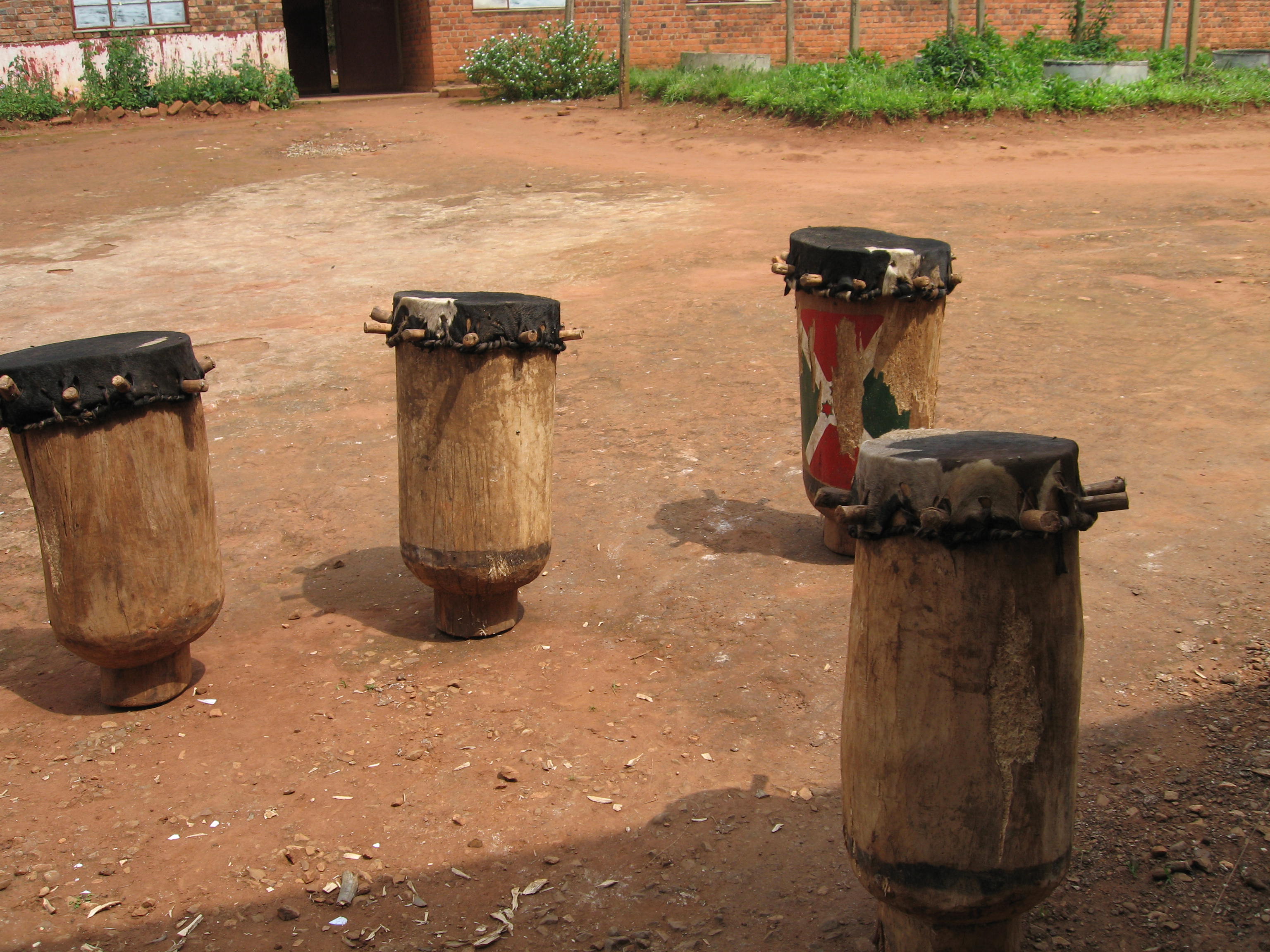
Drumming is an important part of the cultural heritage. The world-famous Royal Drummers of Burundi, who have performed for over 40 years, are noted for traditional drumming using the karyenda, amashako, ibishikiso and ikiranya drums. Dance often accompanies drumming performance, which is frequently seen in celebrations and family gatherings. The abatimbo, which is performed at official ceremonies and rituals and the fast-paced abanyagasimbo are some famous Burundian dances. Some musical instruments of note are the flute, zither, ikembe, indonongo, umuduri, inanga and the inyagara.
Burundi's culture is based on local tradition and the influence of neighbouring countries, though cultural prominence has been hindered by civil unrest. Since farming is the main industry, a typical Burundian meal consists of sweet potatoes, maize, corn, rice and peas. Due to the expense, meat is eaten only a few times per month.
When several Burundians of close acquaintance meet for a gathering they drink ''impeke'', a beer, together from a large container to symbolise unity.
Notable Burundians include the footballer Mohammed Tchité and singer Jean-Pierre Nimbona, popularly known as Kidumu (who is based in Nairobi, Kenya).
Crafts are an important art form in Burundi and are attractive gifts to many tourists. Basket weaving is a popular craft for local artisans. Other crafts such as masks, shields, statues and pottery are made in Burundi. Cultural Profiles Project. Citizenship and Immigration Canada. Retrieved 30 June 2008.
Drumming is an important part of the cultural heritage. The world-famous Royal Drummers of Burundi, who have performed for over 40 years, are noted for traditional drumming using the karyenda, amashako, ibishikiso and ikiranya drums. Dance often accompanies drumming performance, which is frequently seen in celebrations and family gatherings. The abatimbo, which is performed at official ceremonies and rituals and the fast-paced abanyagasimbo are some famous Burundian dances. Some musical instruments of note are the flute, zither, ikembe, indonongo, umuduri, inanga and the inyagara.
 The country's oral tradition is strong, relaying history and life lessons through storytelling, poetry and song. Imigani, indirimbo, amazina and ivyivugo are literary genres in Burundi.
Basketball and track and field are noted sports. Martial arts are popular, as well. There are five major judo clubs: Club Judo de l'Entente Sportive, in Downtown, and four others throughout the city. Association football is a popular pastime throughout the country, as are mancala games.
Most Christian holidays are celebrated, with Christmas being the largest. Burundian Independence Day is celebrated annually on 1 July. In 2005, the Burundian government declared Eid al-Fitr, an Islamic holiday, to be a public holiday.Burundi celebrates Muslim holiday
The country's oral tradition is strong, relaying history and life lessons through storytelling, poetry and song. Imigani, indirimbo, amazina and ivyivugo are literary genres in Burundi.
Basketball and track and field are noted sports. Martial arts are popular, as well. There are five major judo clubs: Club Judo de l'Entente Sportive, in Downtown, and four others throughout the city. Association football is a popular pastime throughout the country, as are mancala games.
Most Christian holidays are celebrated, with Christmas being the largest. Burundian Independence Day is celebrated annually on 1 July. In 2005, the Burundian government declared Eid al-Fitr, an Islamic holiday, to be a public holiday.Burundi celebrates Muslim holiday
. BBC. 3 November 2005. Retrieved on 30 June 2008.
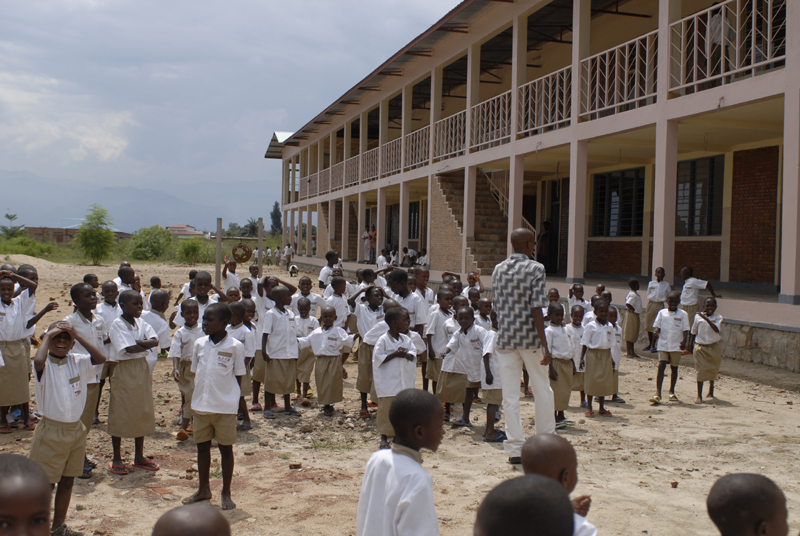 In 2009, the adult literacy rate in Burundi was estimated to be 67% (73% male and 61% female), with a literacy rate of 77% and 76%, respectively, for men and women between the ages of 15 to 24. By 2015, this had increased to 85.6% (88.2% male and 83.1% female). Literacy among adult women has increased by 17% since 2002. Burundi's literacy rate is relatively low due to low school attendance and because literacy in Kirundi only provides access to materials printed in that language, though it is higher than many other African countries. Ten percent of Burundian boys are allowed a secondary education.
Burundi has one public university, University of Burundi. There are museums in the cities, such as the Burundi Geological Museum in Bujumbura and the Burundi National Museum and the Burundi Museum of Life in
In 2009, the adult literacy rate in Burundi was estimated to be 67% (73% male and 61% female), with a literacy rate of 77% and 76%, respectively, for men and women between the ages of 15 to 24. By 2015, this had increased to 85.6% (88.2% male and 83.1% female). Literacy among adult women has increased by 17% since 2002. Burundi's literacy rate is relatively low due to low school attendance and because literacy in Kirundi only provides access to materials printed in that language, though it is higher than many other African countries. Ten percent of Burundian boys are allowed a secondary education.
Burundi has one public university, University of Burundi. There are museums in the cities, such as the Burundi Geological Museum in Bujumbura and the Burundi National Museum and the Burundi Museum of Life in Westwood Bridge to Burundi
. Facebook. Retrieved on 4 April 2014.
As of 2018, Burundi invested the equivalent of 5.1% of its GDP in education.
the United Nations International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi (UNICIB) (1995–1996)
at the United Nations Archives
Official Burundi government website
Official Website of the Ministry of Justice of Burundi
Burundi
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Burundi
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Burundi
from the BBC News *
Key Development Forecasts for Burundi
from International Futures {{Coord, 3, 30, S, 30, 00, E, type:country_region:BI, display=title Burundi, Central African countries East African countries French-speaking countries and territories Landlocked countries Least developed countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the African Union Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1962 Swahili-speaking countries and territories 1962 establishments in Burundi Countries in Africa Former monarchies
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
in the Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it ...
at the junction between the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
region and East Africa. It is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
to the east and southeast, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
to the west; Lake Tanganyika lies along its southwestern border. The capital cities are Gitega
Gitega (), formerly Kitega, is the political capital of Burundi. Located in the centre of the country, in the Burundian central plateau roughly east of Bujumbura (the largest city and former political capital), Gitega (the second largest city) ...
and Bujumbura, the latter being the country's largest city.
The Twa
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with ...
, Hutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the p ...
and Tutsi
The Tutsi (), or Abatutsi (), are an ethnic group of the African Great Lakes region. They are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group and the second largest of three main ethnic groups in Rwanda and Burundi (the other two being the largest Bantu ethnic ...
peoples have lived in Burundi for at least 500 years. For more than 200 of those years, Burundi was an independent kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
, until the beginning of the 20th century, when it became a German colony. After the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and Germany's defeat, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
"mandated" the territory to Belgium. After the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, this transformed into a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
Trust Territory
United Nations trust territories were the successors of the remaining League of Nations mandates and came into being when the League of Nations ceased to exist in 1946. All of the trust territories were administered through the United Nati ...
. Both Germans and Belgians ruled Burundi and Rwanda as a European colony known as Ruanda-Urundi. Burundi and Rwanda had never been under common rule until the time of European colonization of Africa.
Burundi gained independence in 1962 and initially had a monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restric ...
, but a series of assassinations, coups and a general climate of regional instability culminated in the establishment of a republic and a one-party state in 1966. Bouts of ethnic cleansing and ultimately two civil wars and genocides during the 1970s
File:1970s decade montage.jpg, Clockwise from top left: U.S. President Richard Nixon doing the V for Victory sign after his resignation from office following the Watergate scandal in 1974; The United States was still involved in the Vietnam War ...
and again in the 1990s resulted in hundreds of thousands of deaths, leaving the economy undeveloped and the population one of the world's poorest. Eggers, p. xlix. The year 2015 witnessed large-scale political strife as President Pierre Nkurunziza
Pierre Nkurunziza (18 December 19648 June 2020) was a Burundian politician who served as the ninth president of Burundi for almost 15 years from August 2005 until his death in June 2020.
A member of the Hutu ethnic group, Nkurunziza taught ph ...
opted to run for a third term in office, a coup attempt failed and the country's parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
and presidential elections were broadly criticised by members of the international community.
The sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
of Burundi's political system is that of a presidential representative democratic republic based upon a multi-party state. The president of Burundi is the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
. There are currently 21 registered parties in Burundi. On 13 March 1992, Tutsi coup leader Pierre Buyoya
Pierre Buyoya (24 November 1949 – 17 December 2020) was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.
An ...
established a constitution, International Center for Transitional Justice. Retrieved on 27 July 2008. which provided for a multi-party political process and reflected multi-party competition. From "The Financial Times World Desk Reference". Dorling Kindersley. 2004. Prentice Hall. Retrieved on 30 June 2008. Six years later, on 6 June 1998, the constitution was changed, broadening the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the rep ...
's seats and making provisions for two vice-presidents. Because of the Arusha Accord, Burundi enacted a transitional government in 2000. In October 2016, Burundi informed the UN of its intention to withdraw from the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
.
Burundi remains primarily a rural society, with just 13.4% of the population living in urban areas in 2019. The population density of around 315 people per square kilometre (753 per sq mi) is the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Roughly 85% of the population are of Hutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the p ...
ethnic origin, 15% are Tutsi
The Tutsi (), or Abatutsi (), are an ethnic group of the African Great Lakes region. They are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group and the second largest of three main ethnic groups in Rwanda and Burundi (the other two being the largest Bantu ethnic ...
, and fewer than 1% are indigenous Twa
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with ...
. Eggers, p. ix. The official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s of Burundi are Kirundi
Kirundi, also known as Rundi, is a Bantu language spoken by some 9 million people in Burundi and adjacent parts of Rwanda, Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, as well as in Kenya. It is the official language of Burundi. K ...
, French, and English, Kirundi being recognised officially as the sole national language.
One of the smallest countries in Africa, Burundi's land is used mostly for subsistence agriculture and grazing, which has led to deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
, soil erosion and habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
.Bermingham, Eldredge, Dick, Christopher W. and Moritz, Craig (2005). ''Tropical Rainforests: Past, Present, and Future''. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press, p. 146. , the country was almost completely deforested, with less than 6% of its land covered by trees and over half of that being commercial plantations.
Burundi is the poorest country in the world according to gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, with $292 in 2022, and a least developed country, facing widespread poverty, corruption, instability
In numerous fields of study, the component of instability within a system is generally characterized by some of the outputs or internal states growing without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be mar ...
, authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
, and List of countries by literacy rate, illiteracy.
Burundi is densely populated, and many young people emigrate in search of opportunities elsewhere. The World Happiness Report 2018 ranked the country as the world's least happy with a rank of 156. Burundi is a member of the African Union, Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa, United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
and the Non-Aligned Movement.
Etymology
Modern Burundi is named after the Kingdom of Burundi, King of Burundi, who ruled the region starting in the 16th century. It may ultimately derive its name from the Ha people of the region, whose place of origin was known as Buha.History
Burundi is one of the few countries in Africa, along with its neighbour Rwanda among others (such as Botswana, Lesotho, and Eswatini), to be a direct territorial continuation of a pre-colonial era African state. The early history of Burundi, and especially the role and nature of the country's three dominant ethnic groups, the Twa, Hutu and Tutsi, is highly debated amongst academics. However, it is important to note that the nature of culture and ethnic groups is always fluid and changing. While populations might have migrated to the area at different times and as distinctly different ethnic groups, the current distinctions are considered by some to be socio-cultural constructs. Initially the different ethnic groups lived together in relative peace. The first conflicts between ethnic groups can be dated back to the 17th century, when land was becoming ever more scarce because of the continuous growth in population.Kingdom of Burundi
The first evidence of the Burundian state dates back to the late 16th century where it emerged on the eastern foothills. Over the following centuries it expanded, annexing smaller neighbours. The Kingdom of Burundi, or Urundi, in the Great Lakes region was a polity ruled by a traditional monarch with several princes beneath him; succession struggles were common."Kingdom of Burundi". Encyclopædia Britannica (Online ed.). Retrieved 15 October 2016. The king, known as the ''mwami'' (translated as ruler) headed a princely aristocracy (''ganwa'') which owned most of the land and required a tribute, or tax, from local farmers (mainly Hutu) and herders (mainly Tutsi). The Kingdom of Burundi was characterised by a hierarchical political authority and tributary economic exchange. In the mid-18th century, the Tutsi royalty consolidated authority over land, production, and distribution with the development of the ubugabire—a patron-client relationship in which the populace received royal protection in exchange for tribute and land tenure. By this time, the royal court was made up of the Tutsi-Banyaruguru. They had higher social status than other pastoralists such as the Tutsi-Hima. In the lower levels of this society were generally Hutu people, and at the very bottom of the pyramid were the Twa. The system had some fluidity, however. Some Hutu people belonged to the nobility and in this way also had a say in the functioning of the state. The classification of Hutu or Tutsi was not merely based on ethnic criteria alone. Hutu farmers that managed to acquire wealth and livestock were regularly granted the higher social status of Tutsi, some even made it to become close advisors of the ''Ganwa''. On the other hand, there are also reports of Tutsi that lost all their cattle and subsequently lost their higher status and were called Hutu. Thus, the distinction between Hutu and Tutsi was also a socio-cultural concept, instead of a purely ethnic one.WEISSMAN, S., Preventing genocide in Burundi: lessons from international diplomacy, Washington D.C., United States Institute of Peace Press, 1998, p5. There were also many reports of marriages between Hutu and Tutsi people. In general, regional ties and power struggles played a far more determining role in Burundi's politics than ethnicity. Burundi ceased to be a monarchy when king Ntare V Ndizeye was deposed by his Prime Minister and Chief of Staff, Capt. Michel Micombero, who abolished the monarchy and declared a republic following the November 1966 Burundian coup d'état, November 1966 coup d'état.Rule by European powers
From 1884, the German East Africa Company was active in the African Great Lakes region. As a result of heightened tensions and border disputes between the German East Africa Company, the British Empire and the Sultanate of Zanzibar, the German Empire was called upon to put down the Abushiri revolts and protect the empire's interests in the region. The German East Africa Company transferred its rights to the German Empire in 1891, in this way establishing the German colony of German East Africa, which included Burundi (Urundi), Rwanda (Ruanda), and the mainland part ofTanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
(formerly known as Tanganyika (territory), Tanganyika). The German Empire stationed armed forces in Rwanda and Burundi during the late 1880s. The location of the present-day city of Gitega
Gitega (), formerly Kitega, is the political capital of Burundi. Located in the centre of the country, in the Burundian central plateau roughly east of Bujumbura (the largest city and former political capital), Gitega (the second largest city) ...
served as an administrative centre for the Ruanda-Urundi region.
During the World War I, First World War, the East African Campaign (World War I), East African Campaign greatly affected the African Great Lakes region. The Belgian Congo, Belgian and British Empire, British colonial forces of the Allies of World War I, allied powers launched a Tabora offensive, coordinated attack on the German colony. The German army stationed in Burundi was forced to retreat by the numerical superiority of the Belgian army and by 17 June 1916, Burundi and Rwanda were occupied. The Force Publique and the British Lake Force then started a thrust to capture Tabora, an administrative centre of central German East Africa. After the war, as outlined in the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was forced to cede "control" of the Western section of the former German East Africa to Belgium.
On 20 October 1924, Ruanda-Urundi, which consisted of modern-day Rwanda and Burundi, became a Belgian League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
League of Nations mandate, mandate territory, with Bujumbura, Usumbura as its capital. In practical terms it was considered part of the Belgian colonial empire. Burundi, as part of Ruanda-Urundi, continued its kingship dynasty despite the presence of European authorities.
The Belgians, however, preserved many of the kingdom's institutions; the Burundian monarchy succeeded in surviving into the post-colonial period. Following the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Ruanda-Urundi was classified as a United Nations Trust Territory under Belgian administrative authority. During the 1940s, a series of policies caused divisions throughout the country. On 4 October 1943, powers were split in the legislative division of Burundi's government between chiefdoms and lower chiefdoms. Chiefdoms were in charge of land, and lower sub-chiefdoms were established. Native authorities also had powers. In 1948, Belgium allowed the region to form political parties. These factions contributed to Burundi gaining its independence from Belgium, on 1 July 1962.
Independence
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
.
In 1963, King Mwambutsa appointed a Hutu prime minister, Pierre Ngendandumwe, but he was assassinated on 15 January 1965 by a Rwandan Tutsi employed by the US Embassy. The assassination occurred in the broader context of the Congo Crisis during which Western world, Western anti-communist countries were confronting the communist People's Republic of China as it attempted to make Burundi a logistics base for communist insurgents battling in Congo. Burundian legislative election, 1965, Parliamentary elections in May 1965 brought a majority of Hutu into the parliament, but when King Mwambutsa appointed a Tutsi prime minister, some Hutu felt this was unjust and ethnic tensions were further increased. In October 1965, an attempted 1965 Burundian coup d'état, coup d'état led by the Hutu-dominated police was carried out but failed. The Tutsi dominated army, then led by Tutsi officer Captain Michel Micombero purged Hutu from their ranks and carried out reprisal attacks which ultimately claimed the lives of up to 5,000 people in a precursor to the Ikiza, 1972 Burundian Genocide.
King Mwambutsa, who had fled the country during the October coup of 1965, was deposed by a July 1966 Burundian coup d'état, coup in July 1966 and his teenage son, Ntare V of Burundi, Prince Ntare V, claimed the throne. In November that same year, the Tutsi Prime Minister, then-Captain Michel Micombero, carried out another November 1966 Burundian coup d'état, coup, this time deposing Ntare, abolishing the monarchy and declaring the nation a republic, though his one-party government was effectively a military dictatorship. As president, Micombero became an advocate of African socialism and received support from the People's Republic of China. He imposed a staunch regime of law and order and sharply repressed Hutu militarism.
Civil war and genocides
In late April 1972, two events led to the outbreak of the Burundian genocide (1972), First Burundian Genocide. On 27 April 1972, a rebellion led byHutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the p ...
members of the gendarmerie broke out in the lakeside towns of Rumonge and Nyanza-Lac and the rebels declared the short-lived Martyazo Republic. The rebels attacked both Tutsi and any Hutu who refused to join their rebellion.
During this initial Hutu outbreak, anywhere from 800 to 1200 people were killed. At the same time, King Ntare V of Burundi returned from exile, heightening political tension in the country. On 29 April 1972, the 24-year-old Ntare V was murdered. In subsequent months, the Tutsi-dominated government of Michel Micombero used the army to combat Hutu rebels and commit genocide, murdering targeted members of the Hutu majority. The total number of casualties was never established, but contemporary estimates put the number of people killed between 80,000 and 210,000.White, MatthewDeath Tolls for the Major Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century: C. Burundi (1972–73, primarily Hutu killed by Tutsi) 120,000
International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi (2002). Paragraph 85. "The Micombero regime responded with a genocidal repression that is estimated to have caused over a hundred thousand victims and forced several hundred thousand Hutus into exile" In addition, several hundred thousand Hutu were estimated to have fled the killings into Zaïre, Rwanda and
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
.
Following the civil war and genocide, Micombero became mentally distraught and withdrawn. In 1976, Colonel Jean-Baptiste Bagaza, a Tutsi, led a 1976 Burundian coup d'état, bloodless coup to topple Micombero and set about promoting reform. His administration drafted a new constitution in 1981, which maintained Burundi's status as a one-party state. In August 1984, Bagaza was elected head of state. During his tenure, Bagaza suppressed political opponents and religious freedoms.
Major Pierre Buyoya
Pierre Buyoya (24 November 1949 – 17 December 2020) was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.
An ...
(Tutsi) 1987 Burundian coup d'état, overthrew Bagaza in 1987, suspended the constitution and dissolved political parties. He reinstated military rule by a Military Committee for National Salvation (CSMN). Anti-Tutsi ethnic propaganda disseminated by the remnants of the 1972 UBU, which had re-organized as PALIPEHUTU in 1981, led to killings of Tutsi peasants in the northern communes of Ntega and Marangara in August 1988. The government put the death toll at 5,000; some international NGOs believed this understated the deaths.
The new regime did not unleash the harsh reprisals of 1972. Its effort to gain public trust was eroded when it decreed an amnesty for those who had called for, carried out, and taken credit for the killings. Analysts have called this period the beginning of the "culture of impunity." Other analysts put the origins of the "culture of impunity" earlier, in 1965 and 1972, when a small number of identifiable Hutus unleashed massive killings of Tutsis.
In the aftermath of the killings, a group of Hutu intellectuals wrote an open letter to Pierre Buyoya
Pierre Buyoya (24 November 1949 – 17 December 2020) was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.
An ...
, asking for more representation of the Hutu in the administration. They were arrested and jailed. A few weeks later, Buyoya appointed a new government, with an equal number of Hutu and Tutsi ministers. He appointed Adrien Sibomana (Hutu) as Prime Minister. Buyoya also created a commission to address issues of national unity. In 1992, the government created a new constitution that provided for a multi-party system, but a civil war broke out.
An estimated total of 250,000 people died in Burundi from the various conflicts between 1962 and 1993.
Since Burundi's independence in 1962, two Burundi genocide (disambiguation), genocides have taken place in the country: the 1972 mass killings of Hutus by the Tutsi-dominated army, and the mass killings of Tutsis in 1993 by the Hutu majority. Both were described as genocides in the final report of the International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi presented in 2002 to the United Nations Security Council.
International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi (2002). Paragraphs 85,496.
First attempt at democracy and war between Tutsi National Army and Hutu population
In June 1993, Melchior Ndadaye, leader of the Hutu-dominated Front for Democracy in Burundi (FRODEBU), won the first democratic election. He became the first Hutu head of state, leading a pro-Hutu government. Though he attempted to smooth the country's bitter ethnic divide, his reforms antagonised soldiers in the Tutsi-dominated army, and he was assassinated amidst a failed military coup in October 1993, after only three months in office. The ensuing Burundian Civil War (1993–2005) saw persistent violence between Hutu rebels and the Tutsi majority army. It is estimated that some 300,000 people, mostly civilians, were killed in the years following the assassination. In early 1994, the parliament elected Cyprien Ntaryamira (Hutu) to the office of president. He and Juvénal Habyarimana, the president of Rwanda, both Hutus, died together Assassination of Habyarimana and Ntaryamira, when their aeroplane was shot down in April 1994. More refugees started fleeing to Rwanda. Speaker of Parliament, Sylvestre Ntibantunganya (Hutu), was appointed as president in October 1994. A coalition government involving 12 of the 13 parties was formed. A feared general massacre was averted, but violence broke out. A number of Hutu refugees in Bujumbura, the then-capital, were killed. The mainly Tutsi Union for National Progress withdrew from the government and parliament. In 1996,Pierre Buyoya
Pierre Buyoya (24 November 1949 – 17 December 2020) was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.
An ...
(Tutsi) again took power through a 1996 Burundian coup d'état, coup d'état. He suspended the constitution and was sworn in as president in 1998. This was the start of his second term as president, after his first term from 1987 to 1993. In response to rebel attacks, the government forced much of the population to move to refugee camps. Under Buyoya's rule, long peace talks started, mediated by South Africa. Both parties signed agreements in Arusha, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
and Pretoria, South Africa, to share power in Burundi. The agreements took four years to plan.
Pierre Nkurunziza
Pierre Nkurunziza (18 December 19648 June 2020) was a Burundian politician who served as the ninth president of Burundi for almost 15 years from August 2005 until his death in June 2020.
A member of the Hutu ethnic group, Nkurunziza taught ph ...
(Hutu), once a leader of a rebel group, was elected president in 2005. , the Burundian government was talking with the Hutu-led Palipehutu-National Liberation Forces (NLF) to bring peace to the country.
Peace agreements
African leaders began a series of peace talks between the warring factions following a request by the United Nations Secretary General Boutros Boutros-Ghali for them to intervene in the humanitarian crisis. Talks were initiated under the aegis of former Tanzanian President Julius Nyerere in 1995; following his death, South African President Nelson Mandela took the helm. As the talks progressed, South African President Thabo Mbeki and United States President Bill Clinton also lent their respective weight. The peace talks took the form of Track I mediations. This method of negotiation can be defined as a form of diplomacy involving governmental or intergovernmental representatives, who may use their positive reputations, mediation, or the "carrot and stick" method as a means of obtaining or forcing an outcome, frequently along the lines of "bargaining" or "win-lose". The main objective was to transform the Burundian government and military structurally in order to bridge the ethnic gap between the Tutsi and Hutu. It was to take place in two major steps. First, a transitional power-sharing government would be established, with the presidents holding office for three-year terms. The second objective involved a restructuring of the armed forces, where the two groups would be represented equally. As the protracted nature of the peace talks demonstrated, the mediators and negotiating parties confronted several obstacles. First, the Burundian officials perceived the goals as "unrealistic" and viewed the treaty as ambiguous, contradictory and confusing. Second, and perhaps most importantly, the Burundians believed the treaty would be irrelevant without an accompanying cease fire. This would require separate and direct talks with the rebel groups. The main Hutu party was skeptical of the offer of a power-sharing government; they alleged that they had been deceived by the Tutsi in past agreements. In 2000, the Burundian President signed the treaty, as well as 13 of the 19 warring Hutu and Tutsi factions. Disagreements persisted over which group would preside over the nascent government, and when the ceasefire would begin. The spoilers of the peace talks were the hardliner Tutsi and Hutu groups who refused to sign the accord; as a result, violence intensified. Three years later at a summit of African leaders in Tanzania, the Burundian president and the main opposition Hutu group signed an accord to end the conflict; the signatory members were granted ministerial posts within the government. However, smaller militant Hutu groups – such as the Forces for National Liberation – remained active.UN involvement
Between 1993 and 2003, many rounds of peace talks, overseen by regional leaders in Tanzania, South Africa and Uganda, gradually established power-sharing agreements to satisfy the majority of the contending groups. Initially the South African Protection Support Detachment was deployed to protect Burundian leaders returning from exile. These forces became part of the African Union Mission in Burundi, African Union Mission to Burundi, deployed to help oversee the installation of a transitional government. In June 2004, the UN stepped in and took over peacekeeping responsibilities as a signal of growing international support for the already markedly advanced peace process in Burundi.Howard, Lise Morje (2008). UN Peacekeeping in Civil Wars. New York: Cambridge University Press. The mission's mandate, under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, has been to monitor cease-fire, carry out disarmament, demobilisation and reintegration of former military personnel, support humanitarian assistance and refugee and IDP return, assist with elections, protect international staff and Burundian civilians, monitor Burundi's troublesome borders, including halting illicit arms flows, and assist in carrying out institutional reforms including those of the Constitution, judiciary, armed forces and police. The mission has been allotted 5,650 military personnel, 120 civilian police and about 1,000 international and local civilian personnel. The mission has been functioning well. It has greatly benefited from the transitional government, which has functioned and is in the process of transitioning to one that will be popularly elected. The main difficulty in the early stages was continued resistance to the peace process by the last Hutu nationalist rebel group. This organisation continued its violent conflict on the outskirts of the capital despite the UN's presence. By June 2005, the group had stopped fighting and its representatives were brought back into the political process. All political parties have accepted a formula for inter-ethnic power-sharing: no political party can gain access to government offices unless it is ethnically integrated. The focus of the UN's mission had been to enshrine the power-sharing arrangements in a popularly voted constitution, so that elections may be held and a new government installed. Disarmament, demobilisation and reintegration were done in tandem with elections preparations. In February 2005, the Constitution of Burundi, constitution was approved with over 90% of the popular vote. In May, June and August 2005, three separate elections were also held at the local level for the Parliament and the presidency. While there are still some difficulties with refugee returns and securing adequate food supplies for the war-weary population, the mission managed to win the trust and confidence of a majority of the formerly warring leaders, as well as the population at large. It was involved with several "quick effect" projects, including rehabilitating and building schools, orphanages, health clinics and rebuilding infrastructure such as water lines.2006 to 2018
 Reconstruction efforts in Burundi started to practically take effect after 2006. The UN shut down its peacekeeping mission and re-focused on helping with reconstruction.Timeline Burundi
Reconstruction efforts in Burundi started to practically take effect after 2006. The UN shut down its peacekeeping mission and re-focused on helping with reconstruction.Timeline BurundiBBC. . (accessed on 29 October 2008) Toward achieving economic reconstruction, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, D.R.Congo and Burundi relaunched the regional Economic Community of the Great Lakes Countries. In addition, Burundi, along with Rwanda, joined the East African Community in 2007. However, the terms of the September 2006 Ceasefire between the government and the last remaining armed opposition group, the National Liberation Front (Burundi), FLN (Forces for National Liberation, also called NLF or FROLINA), were not totally implemented, and senior FLN members subsequently left the truce monitoring team, claiming that their security was threatened. In September 2007, rival FLN factions clashed in the capital, killing 20 fighters and causing residents to begin fleeing. Rebel raids were reported in other parts of the country. The rebel factions disagreed with the government over disarmament and the release of political prisoners.Burundi: Release Civilians Detained Without Charge , Human Rights Watch
. Hrw.org (29 May 2008). Retrieved on 24 November 2012. In late 2007 and early 2008, FLN combatants attacked government-protected camps where former combatants were living. The homes of rural residents were also pillaged. The 2007 report of Amnesty International mentions many areas where improvement is required. Civilians are victims of repeated acts of violence done by the FLN. The latter also recruits child soldiers. The rate of violence against women is high. Perpetrators regularly escape prosecution and punishment by the state. There is an urgent need for reform of the judicial system. Genocide, war crimes and crimes against humanity continued to go unpunished. In late March 2008, the FLN sought for the parliament to adopt a law guaranteeing them 'provisional immunity' from arrest. This would cover ordinary crimes, but not grave violations of international humanitarian law like war crimes or crimes against humanity . Even though the government has granted this in the past to people, the FLN has been unable to obtain the provisional immunity. On 17 April 2008, the FLN bombarded Bujumbura. The Burundian army fought back and the FLN suffered heavy losses. A new ceasefire was signed on 26 May 2008. In August 2008, President Nkurunziza met with the FLN leader Agathon Rwasa, with the mediation of Charles Nqakula, South Africa's Minister for Safety and Security. This was the first direct meeting since June 2007. Both agreed to meet twice a week to establish a commission to resolve any disputes that might arise during the peace negotiations. The UN has attempted to evaluate the impact of its peace-building initiatives. In the early 2010s, the UN peacekeeping mission in Burundi sought to assess the success of its Disarmament, Demobilization and Reintegration program by counting the number of arms that had been collected, given the prevalence of arms in the country. However, these evaluations failed to include date from local populations, which are significant in impact evaluations of peacebuilding initiatives. As of 2012, Burundi was participating in African Union peacekeeping missions, including the African Union Mission to Somalia, mission to Somalia against Al-Shabaab militants. In 2014, the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Burundi), Truth and Reconciliation Commission was established, initially for four years and then extended for another four in 2018.
2015 unrest
In April 2015 protests broke out after the ruling party announced PresidentPierre Nkurunziza
Pierre Nkurunziza (18 December 19648 June 2020) was a Burundian politician who served as the ninth president of Burundi for almost 15 years from August 2005 until his death in June 2020.
A member of the Hutu ethnic group, Nkurunziza taught ph ...
would seek a third term in office. Protestors claimed Nkurunziza could not run for a third term in office but the country's constitutional court agreed with Nkurunziza (although some of its members had fled the country at the time of its vote).
2015 Burundian coup d'état attempt, An attempted coup d'état on 13 May failed to depose Nkurunziza.
He returned to Burundi, began purging his government, and arrested several of the coup leaders.Burundi arrests leaders of attempted coup. CNN.com (15 May 2015). Retrieved on 29 June 2015. Following the attempted coup, protests however continued and over 100,000 people had fled the country by 20 May causing a humanitarian emergency. There are reports of continued and widespread abuses of human rights, including unlawful killings, torture, disappearances, and restrictions on freedom of expression. Despite calls by the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the African Union, the United States, France, South Africa, Belgium, and various other governments, the ruling party Burundian legislative election, 2015, held parliamentary elections on 29 June, but these were boycotted by the opposition.
On 30 September 2016, the United Nations Human Rights Council established the Commission of Inquiry on Burundi through resolution 33/24. Its mandate is to "conduct a thorough investigation into human rights violations and abuses committed in Burundi since April 2015, to identify alleged perpetrators and to formulate recommendations." On 29 September 2017 the Commission of Inquiry on Burundi called on Burundian government to put an end to serious human rights violations. It further stressed that, "The Burundian government has so far refused to cooperate with the Commission of Inquiry, despite the Commission's repeated requests and initiatives." The violations the Commission documented include arrests, arbitrary arrests and detentions, acts of torture and cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment, extrajudicial executions, enforced disappearances, rape and other forms of sexual violence."
2018 to present
In a 2018 Burundian constitutional referendum, constitutional referendum in May 2018, Burundians voted by 79.08% to approve an amended constitution that ensured that Nkurunziza could remain in power until 2034. However, much to the surprise of most observers, Nkurunziza later announced that he did not intend to serve another term, paving the way for a new president to be elected in the 2020 Burundian general election, 2020 general election. On 20 May 2020, Évariste Ndayishimiye, Evariste Ndayishimiye, a candidate who was hand-picked as Nkurunziza's successor by the CNDD-FDD, won the election with 71.45% of the vote. Shortly after, on 9 June 2020, Nkurunziza died of a cardiac arrest, at the age of 55. There was some speculation that his death was COVID-19 related, though this is unconfirmed. As per the constitution, Pascal Nyabenda, the president of the national assembly, led the government until Ndayishimiye's inauguration on 18 June 2020. In December 2021, a Gitega prison fire, large prison fire killed dozens. Currently, Burundi remains as one of the poorest nations on Earth, based on a Gross National Income (GNI) of $270 per capita.Government
 Burundi's political system is that of a presidential system, presidential representative democracy, representative democratic republic based upon a multi-party state. The president of Burundi is the
Burundi's political system is that of a presidential system, presidential representative democracy, representative democratic republic based upon a multi-party state. The president of Burundi is the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
. There are currently 21 registered parties in Burundi. On 13 March 1992, Tutsi coup leader Pierre Buyoya
Pierre Buyoya (24 November 1949 – 17 December 2020) was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.
An ...
established a constitution, which provided for a multi-party political process and reflected multi-party competition. Six years later, on 6 June 1998, the constitution was changed, broadening National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the rep ...
's seats and making provisions for two vice-presidents. Because of the Arusha Accord, Burundi enacted a transitional government in 2000.
Burundi's legislative branch is a bicameral assembly, consisting of the Transitional National Assembly and the Senate of Burundi, Transitional Senate. , the Transitional National Assembly consisted of 170 members, with the Front for Democracy in Burundi holding 38% of seats, and 10% of the assembly controlled by UPRONA. Fifty-two seats were controlled by other parties. Burundi's constitution mandates representation in the Transitional National Assembly to be consistent with 60% Hutu, 40% Tutsi, and 30% female members, as well as three Batwa members. Members of the National Assembly are elected by popular vote and serve five-year terms.
The Transitional Senate has fifty-one members, and three seats are reserved for former presidents. Due to stipulations in Burundi's constitution, 30% of Senate members must be female. Members of the Senate are elected by electoral colleges, which consist of members from each of Burundi's provinces and communes.Background Note: BurundiUnited States Department of State. February 2008. Retrieved on 28 June 2008. For each of Burundi's eighteen provinces, one Hutu and one Tutsi senator are chosen. One term for the Transitional Senate is five years. Together, Burundi's legislative branch elect the president to a five-year term. Burundi's president appoints officials to his Council of Ministers, which is also part of the executive branch. The president can also pick fourteen members of the Transitional Senate to serve on the Council of Ministers. Members of the Council of Ministers must be approved by two-thirds of Burundi's legislature. The president also chooses two vice-presidents. Following the 2015 election, the president of Burundi was
Pierre Nkurunziza
Pierre Nkurunziza (18 December 19648 June 2020) was a Burundian politician who served as the ninth president of Burundi for almost 15 years from August 2005 until his death in June 2020.
A member of the Hutu ethnic group, Nkurunziza taught ph ...
. The first vice-president was Therence Sinunguruza, and the Second Vice-president was Gervais Rufyikiri.
On 20 May 2020, Evariste Ndayishimiye, a candidate who was hand-picked as Nkurunziza's successor by the CNDD-FDD, won 2020 Burundian general election, the election with 71.45% of the vote. Shortly after, on 9 June 2020, Nkurunziza died of a cardiac arrest, at the age of 55. As per the constitution, Pascal Nyabenda, the president of the national assembly, led the government until Ndayishimiye's inauguration on 18 June 2020.
The ''Cour Suprême'' (Supreme Court) is Burundi's highest court. There are three Courts of Appeals directly below the Supreme Court. Tribunals of First Instance are used as judicial courts in each of Burundi's provinces as well as 123 local tribunals.

Human rights
Burundi's government has been repeatedly criticised by human rights organisations including Human Rights Watch for the multiple arrests and trials of journalist Jean-Claude Kavumbagu for issues related to his reporting. Amnesty International (AI) named him a prisoner of conscience and called for his "immediate and unconditional release." In April 2009, the government of Burundi changed the law to criminalise homosexuality. Persons found guilty of consensual same-sex relations risk two to three years in prison and a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 Burundian francs. Amnesty International has condemned the action, calling it a violation of Burundi's obligations under international and regional human rights law, and against the constitution, which guarantees the right to privacy. Burundi officially left theInternational Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
(ICC) on 27 October 2017, the first country in the world to do so. The move came after the UN accused the country of various crimes and human rights violations, such as extrajudicial killings, torture and sexual violence, in a September 2017 report. The ICC announced on 9 November 2017 that human rights violations from the time Burundi was a member would still be prosecuted.
Subdivisions
Burundi is divided into 18 Provinces of Burundi, provinces, 119 Communes of Burundi, communes, and 2,638 Collines of Burundi, collines (hills). Provincial governments are structured upon these boundaries. Burundi’s provinces and communes were created on Christmas Day in 1959 by a Belgian colonial decree. They replaced the pre-existing system of chieftains. In 2000, the province encompassing Bujumbura was separated into two provinces, Bujumbura Rural and Bujumbura Mairie. The newest province, Rumonge Province, Rumonge, was created on 26 March 2015 from portions of Bujumbura Rural and Bururi. In July 2022, the government of Burundi announced a complete overhaul of the country’s territorial subdivisions. The proposed change would reduce the amounts of provinces from 18 to 5, and reduce the amount of communes from 119 to 42. The change needs the approval of the parliament of Burundi to take effect.Geography
 file:Hippos in Burundi.png, Hippos at Kibira National Park in northwest Burundi
One of the smallest countries in Africa, Burundi is landlocked and has an Tropical rainforest climate, equatorial climate. Burundi is a part of the Albertine Rift, the western extension of the East African Rift. The country lies on a rolling plateau in the centre of Africa. Burundi is bordered by Rwanda to the north,
file:Hippos in Burundi.png, Hippos at Kibira National Park in northwest Burundi
One of the smallest countries in Africa, Burundi is landlocked and has an Tropical rainforest climate, equatorial climate. Burundi is a part of the Albertine Rift, the western extension of the East African Rift. The country lies on a rolling plateau in the centre of Africa. Burundi is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
to the east and southeast, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
to the west. It lies within the Albertine Rift montane forests, Central Zambezian miombo woodlands, and Victoria Basin forest-savanna mosaic ecoregions.
The average elevation of the central plateau is , with lower elevations at the borders. The highest peak, Mount Heha at ,O'Mara, Michael (1999). ''Facts about the World's Nations''. Bronx, New York: H.W. Wilson, p. 150, lies to the southeast of the largest city and economic capital, Bujumbura. The source of the Nile River is in Bururi province, and is linked from Lake Victoria to its headwaters via the Ruvyironza River.Ash, Russell (2006). ''The Top 10 of Everything''. New York City: Sterling Publishing Company. Lake Victoria is also an important water source, which serves as a fork to the Kagera River. Another major lake is Lake Tanganyika, located in much of Burundi's southwestern corner.
There are two national parks: Kibira National Park to the northwest (a small region of rainforest, adjacent to Nyungwe Forest National Park in Rwanda), and Ruvubu National Park to the northeast (along the Rurubu River, also known as Ruvubu or Ruvuvu). Both were established in 1982 to conserve wildlife populations.East, Rob (1999). ''African Antelope Database 1998''. Gland, Switzerland: International Union for Conservation of Nature, p. 74. .
Wildlife
Economy
 The purchasing power of most Burundians has decreased as wage increases have not kept up with inflation. As a result of deepening poverty, Burundi will remain heavily dependent on aid from bilateral and multilateral donors. Foreign aid represents 42% of Burundis national income, the second highest rate in Sub-Saharan Africa. Burundi joined the East African Community in 2009, which should boost its regional trade ties, and also in 2009 received $700 million in debt relief. Government corruption is hindering the development of a healthy private sector as companies seek to navigate an environment with ever-changing rules.
Studies since 2007 have shown Burundians to have extremely poor levels of Satisfaction with Life Index, satisfaction with life; the World Happiness Report, World Happiness Report 2018 rated them the world's least happy in 2018.
The purchasing power of most Burundians has decreased as wage increases have not kept up with inflation. As a result of deepening poverty, Burundi will remain heavily dependent on aid from bilateral and multilateral donors. Foreign aid represents 42% of Burundis national income, the second highest rate in Sub-Saharan Africa. Burundi joined the East African Community in 2009, which should boost its regional trade ties, and also in 2009 received $700 million in debt relief. Government corruption is hindering the development of a healthy private sector as companies seek to navigate an environment with ever-changing rules.
Studies since 2007 have shown Burundians to have extremely poor levels of Satisfaction with Life Index, satisfaction with life; the World Happiness Report, World Happiness Report 2018 rated them the world's least happy in 2018.
 Some of Burundi's natural resources include uranium, nickel, cobalt, copper and platinum. Besides agriculture, other industries include: assembly of imported components; public works construction; food processing and light consumer goods such as blankets, shoes and soap.
In regards to telecommunications infrastructure, Burundi is ranked second to last in the World Economic Forum's Network Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. Burundi ranked number 147 overall in the 2014 NRI ranking, down from 144 in 2013.
Lack of access to financial services is a serious problem for the majority of the population, particularly in the densely populated rural areas: only 2% of the total population holds bank accounts, and fewer than 0.5% use bank lending services. Microfinance, however, plays a larger role, with 4% of Burundians being members of microfinance institutions – a larger share of the population than that reached by banking and postal services combined. 26 licensed microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer savings, deposits and short- to medium-term credit. Dependence of the sector on donor assistance is limited.
Burundi is part of the East African Community and a potential member of the planned East African Federation. Economic growth in Burundi is relatively steady but Burundi is still behind neighbouring countries.
Some of Burundi's natural resources include uranium, nickel, cobalt, copper and platinum. Besides agriculture, other industries include: assembly of imported components; public works construction; food processing and light consumer goods such as blankets, shoes and soap.
In regards to telecommunications infrastructure, Burundi is ranked second to last in the World Economic Forum's Network Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. Burundi ranked number 147 overall in the 2014 NRI ranking, down from 144 in 2013.
Lack of access to financial services is a serious problem for the majority of the population, particularly in the densely populated rural areas: only 2% of the total population holds bank accounts, and fewer than 0.5% use bank lending services. Microfinance, however, plays a larger role, with 4% of Burundians being members of microfinance institutions – a larger share of the population than that reached by banking and postal services combined. 26 licensed microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer savings, deposits and short- to medium-term credit. Dependence of the sector on donor assistance is limited.
Burundi is part of the East African Community and a potential member of the planned East African Federation. Economic growth in Burundi is relatively steady but Burundi is still behind neighbouring countries.
Currency
Burundi's currency is the Burundian franc (ISO 4217 code BIF). It is nominally subdivided into 100 centimes, though coins have never been issued in centimes in independent Burundi; centime coins were circulated only when Burundi used the congolese franc, Belgian Congo franc. Monetary policy is controlled by the central bank, Bank of the Republic of Burundi.Transport

 Burundi's transport network is limited and underdeveloped. According to a 2012 ''DHL Global Connectedness Index'', Burundi is the least globalised of 140 surveyed countries. Bujumbura International Airport is the only airport with a paved runway and as of May 2017 it was serviced by four airlines (Brussels Airlines, Ethiopian Airlines, Kenya Airways and RwandAir). Kigali International Airport, Kigali is the city with the most daily flight connections to Bujumbura. The country has a road network but less than 10% of the country's roads were paved and private bus companies were the main operators of buses on the international route to Kigali; however, there were no bus connections to the other neighbouring countries (Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of Congo). Bujumbura is connected by a passenger and cargo ferry (the MV Mwongozo) to Kigoma in Tanzania. There is a East African Railway Master Plan, long-term plan to link the country via rail to Kigali and then onward to Kampala and Kenya.
Burundi's transport network is limited and underdeveloped. According to a 2012 ''DHL Global Connectedness Index'', Burundi is the least globalised of 140 surveyed countries. Bujumbura International Airport is the only airport with a paved runway and as of May 2017 it was serviced by four airlines (Brussels Airlines, Ethiopian Airlines, Kenya Airways and RwandAir). Kigali International Airport, Kigali is the city with the most daily flight connections to Bujumbura. The country has a road network but less than 10% of the country's roads were paved and private bus companies were the main operators of buses on the international route to Kigali; however, there were no bus connections to the other neighbouring countries (Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of Congo). Bujumbura is connected by a passenger and cargo ferry (the MV Mwongozo) to Kigoma in Tanzania. There is a East African Railway Master Plan, long-term plan to link the country via rail to Kigali and then onward to Kampala and Kenya.
Demographics

 As of October 2021, Burundi was estimated by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs#Divisions, United Nations to have a population of 12,346,893 people, compared to only 2,456,000 in 1950. The population growth rate is 2.5 percent per year, more than double the average global pace, and a Burundian woman has on average 5.10 children, more than double the international fertility rate. Burundi had the tenth highest total fertility rate in the world, just behind Somalia, in 2021.
Many Burundians have migrated to other countries as a result of the civil war. In 2006, the United States accepted approximately 10,000 Burundian refugees.
Burundi remains an overwhelmingly rural society, with just 13% of the population living in urban areas in 2013. The population density of around 315 people per square kilometre (753 per sq mi) is the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Roughly 85% of the population are of
As of October 2021, Burundi was estimated by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs#Divisions, United Nations to have a population of 12,346,893 people, compared to only 2,456,000 in 1950. The population growth rate is 2.5 percent per year, more than double the average global pace, and a Burundian woman has on average 5.10 children, more than double the international fertility rate. Burundi had the tenth highest total fertility rate in the world, just behind Somalia, in 2021.
Many Burundians have migrated to other countries as a result of the civil war. In 2006, the United States accepted approximately 10,000 Burundian refugees.
Burundi remains an overwhelmingly rural society, with just 13% of the population living in urban areas in 2013. The population density of around 315 people per square kilometre (753 per sq mi) is the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Roughly 85% of the population are of Hutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the p ...
ethnic origin, 15% are Tutsi
The Tutsi (), or Abatutsi (), are an ethnic group of the African Great Lakes region. They are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group and the second largest of three main ethnic groups in Rwanda and Burundi (the other two being the largest Bantu ethnic ...
and fewer than 1% are indigenous Twa
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with ...
.
The official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s of Burundi are Kirundi
Kirundi, also known as Rundi, is a Bantu language spoken by some 9 million people in Burundi and adjacent parts of Rwanda, Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, as well as in Kenya. It is the official language of Burundi. K ...
, French, and English, the latter having been made an additional official language in 2014.
Religion
Sources estimate the Christian population at 80–90%, with Roman Catholics representing the largest group at 60–65%. Protestantism, Protestant and Anglicanism, Anglican practitioners constitute the remaining 15–25%. An estimated 5% of the population adheres to traditional indigenous religious beliefs. Muslims constitute 2–5%, the majority of whom are Sunni Islam, Sunnis and live in urban areas.Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Burundi. Pew Research Center. 2010.Burundi
. U.S. Department of State. State.gov (17 November 2010). Retrieved on 24 November 2012.
Health
Burundi has the worst hunger and malnourishment rates of all 120 countries ranked in the Global Hunger Index.Jillian KeenanThe Blood Cries Out
. "In one of Africa's most densely populated countries, brothers are killing brothers over the right to farm mere acres of earth. There's just not enough land to go around in Burundi — and it could push the country into civil war." ''Foreign Policy (FP)'' The civil war in 1962 put a stop on the medical advancements in the country. Burundi, again, went into a violent cycle in 2015, jeopardising the citizens of Burundi's medical care. Like many Sub-Saharan Africa countries, Burundi uses indigenous medicine in addition to biomedicine. In the 1980s Burundi's health authorities asked the United Nations Development Program for support to develop quality control and begin new research on pharmaceuticals from medicinal plants. At the same time, the Burundi Association of Traditional Practitioners (ATRADIBU) was founded, which teamed up with the governments agency to set up the Centre for Research and Promotion of Traditional Medicine in Burundi (CRPMT). The recent influx of international aid has supported the work of biomedical health systems in Burundi. However, international aid workers have traditionally stayed away from indigenous medicine in Burundi. As of 2015, roughly 1 out of 10 children in Burundi die before the age of 5 from preventable and treatable illnesses such as pneumonia, diarrhoea, and malaria. The current violence in Burundi has limited the country's access to medication and hospital equipment. Burundi's life expectancy, as of 2015, was 60.1 years. In 2013, Burundi spent 8% of their GDP on healthcare. While Burundi's fertility rate is 6.1 children per women, the country's mortality rate is 61.9 deaths for every 1,000 live births. According to the WHO, the average life expectancy in the country is 58/62 years. Common diseases in Burundi include malaria and typhoid fever.
Culture
 The country's oral tradition is strong, relaying history and life lessons through storytelling, poetry and song. Imigani, indirimbo, amazina and ivyivugo are literary genres in Burundi.
Basketball and track and field are noted sports. Martial arts are popular, as well. There are five major judo clubs: Club Judo de l'Entente Sportive, in Downtown, and four others throughout the city. Association football is a popular pastime throughout the country, as are mancala games.
Most Christian holidays are celebrated, with Christmas being the largest. Burundian Independence Day is celebrated annually on 1 July. In 2005, the Burundian government declared Eid al-Fitr, an Islamic holiday, to be a public holiday.Burundi celebrates Muslim holiday
The country's oral tradition is strong, relaying history and life lessons through storytelling, poetry and song. Imigani, indirimbo, amazina and ivyivugo are literary genres in Burundi.
Basketball and track and field are noted sports. Martial arts are popular, as well. There are five major judo clubs: Club Judo de l'Entente Sportive, in Downtown, and four others throughout the city. Association football is a popular pastime throughout the country, as are mancala games.
Most Christian holidays are celebrated, with Christmas being the largest. Burundian Independence Day is celebrated annually on 1 July. In 2005, the Burundian government declared Eid al-Fitr, an Islamic holiday, to be a public holiday.Burundi celebrates Muslim holiday. BBC. 3 November 2005. Retrieved on 30 June 2008.
Media
Education
 In 2009, the adult literacy rate in Burundi was estimated to be 67% (73% male and 61% female), with a literacy rate of 77% and 76%, respectively, for men and women between the ages of 15 to 24. By 2015, this had increased to 85.6% (88.2% male and 83.1% female). Literacy among adult women has increased by 17% since 2002. Burundi's literacy rate is relatively low due to low school attendance and because literacy in Kirundi only provides access to materials printed in that language, though it is higher than many other African countries. Ten percent of Burundian boys are allowed a secondary education.
Burundi has one public university, University of Burundi. There are museums in the cities, such as the Burundi Geological Museum in Bujumbura and the Burundi National Museum and the Burundi Museum of Life in
In 2009, the adult literacy rate in Burundi was estimated to be 67% (73% male and 61% female), with a literacy rate of 77% and 76%, respectively, for men and women between the ages of 15 to 24. By 2015, this had increased to 85.6% (88.2% male and 83.1% female). Literacy among adult women has increased by 17% since 2002. Burundi's literacy rate is relatively low due to low school attendance and because literacy in Kirundi only provides access to materials printed in that language, though it is higher than many other African countries. Ten percent of Burundian boys are allowed a secondary education.
Burundi has one public university, University of Burundi. There are museums in the cities, such as the Burundi Geological Museum in Bujumbura and the Burundi National Museum and the Burundi Museum of Life in Gitega
Gitega (), formerly Kitega, is the political capital of Burundi. Located in the centre of the country, in the Burundian central plateau roughly east of Bujumbura (the largest city and former political capital), Gitega (the second largest city) ...
.
In 2010 a new elementary school was opened in the small village of Rwoga that is funded by the pupils of Westwood High School, Quebec, Canada.. Facebook. Retrieved on 4 April 2014.
Science and technology
Burundi's ''Strategic Plan for Science, Technology, Research and Innovation'' (2013) covers the following areas: food technology; medical sciences; energy, mining and transportation; water; desertification; environmental biotechnology and indigenous knowledge; materials science; engineering and industry; ICTs; space sciences; mathematical sciences; and social and human sciences. With regard to material sciences, Burundi's publication intensity doubled from 0.6 to 1.2 articles per million inhabitants between 2012 and 2019, placing it in the top 15 for sub-Saharan Africa for this strategic technology. Medical sciences remain the main focus of research: medical researchers accounted for 4% of the country's scientists in 2018 but 41% of scientific publications between 2011 and 2019. The focus of the ''Strategic Plan for Science, Technology, Research and Innovation'' (2013) has been on developing an institutional framework and infrastructure, fostering greater regional and international co-operation and placing science in society. In October 2014, the EAC Secretariat designated the National Institute of Public Health a centre of excellence. Data are unavailable on output on nutritional sciences, the institute's area of specialization, but between 2011 and 2019, Burundi scientists produced seven articles on each of HIV and tropical communicable diseases and a further five on tuberculosis, all focus areas for the Sustainable Development Goals. The ''Strategic Plan'' has also focused on training researchers. Researcher density (in head counts) grew from 40 to 55 researchers per million inhabitants between 2011 and 2018. The amount of funding available to each researcher more than doubled from PPP$14,310 (constant 2005 values) to PPP$22,480, since the domestic research effort has also risen since 2012, from 0.11% to 0.21% of GDP. Burundi has almost tripled its scientific output since 2011 but the pace has not picked up since the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. With six scientific publications per million inhabitants, Burundi still has one of the lowest publication rate in Central and East Africa. Some 97.5% of publications involved foreign co-authorship between 2017 and 2019, with Ugandans figuring among the top five partners.See also
* Outline of Burundi * Index of Burundi-related articles * Wildlife of Burundi * National Defence Force (Burundi) * *Notes
References
Bibliography
* *Further reading
* Abdallah, Ahmedou Ould ''Burundi on the Brink, 1993–95: A UN Special Envoy Reflects on Preventive Diplomacy'' * * Bentley, Kristina and Southall, Roger ''An African Peace Process: Mandela, South Africa, and Burundi'' * Chrétien, Jean-Pierre ''The Great Lakes of Africa: Two Thousand Years of History'' * Patricia Daley, Daley, Patricia ''Gender and Genocide in Burundi: The Search for Spaces of Peace in the Great Lakes Region'' * * Ewusi, Kale and Akwanga, Ebenezer ''Burundi's Negative Peace: The Shadow of a Broken Continent in the Era of Nepad'' * Jennings, Christian ''Across the Red River: Rwanda, Burundi and the Heart of Darkness'' * Kayoya, Michel ''My Father's Footsteps'' (''Sur les traces de mon père'') East African Publishing House, 1973 * Kayoya, Michel ''Entre deux mondes'' (Between two worlds) Lavigerie Éditeurs, Bujumbura: 1971. Kayoya was murdered during the 1972 genocide. * Kidder, Tracy, ''Strength in What Remains'' (A biography of a Burundian immigrant to the US) * * Melady, Thomas Patrick ''Burundi: The Tragic Years'' * Nivonzima, David and Fendell, Len ''Unlocking Horns: Forgiveness and Reconciliation in Burundi'' * Uvin, Peter ''Life After Violence: A People's Story of Burundi'' * Watt, Nigel '' Burundi: The Biography of a Small African Country'' * 1st. edition.External links
* Records othe United Nations International Commission of Inquiry for Burundi (UNICIB) (1995–1996)
at the United Nations Archives
Official Burundi government website
Official Website of the Ministry of Justice of Burundi
Burundi
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Burundi
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Burundi
from the BBC News *
Key Development Forecasts for Burundi
from International Futures {{Coord, 3, 30, S, 30, 00, E, type:country_region:BI, display=title Burundi, Central African countries East African countries French-speaking countries and territories Landlocked countries Least developed countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the African Union Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1962 Swahili-speaking countries and territories 1962 establishments in Burundi Countries in Africa Former monarchies