The Bronx () is a
borough of New York City
New York City is composed of five boroughs: The Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island. Each borough is coextensive with a respective county of New York State, making New York City the largest U.S. municipality situated in ...
, coextensive with Bronx County, in the
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of
New York. It is south of
Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
; north and east of the New York City borough of
Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, across the
Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York, United States, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the New York mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyt ...
; and north of the New York City borough of
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, across the
East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
. The Bronx has a land area of and a population of 1,472,654 in the 2020 census.
[ If each borough were ranked as a city, the Bronx would rank as the ninth-most-populous in the U.S. Of the five boroughs, it has the fourth-largest area, fourth-highest population, and third-highest ]population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
.[New York State Department of Health]
''Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State – 2010''
retrieved on August 8, 2015. It is the only borough of New York City not primarily on an island. With a population that is 54.8% Hispanic as of 2020, it is the only majority-Hispanic county in the Northeastern United States and the fourth-most-populous nationwide.Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
into a hillier section in the west
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
, and a flatter eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
section. East and west street names are divided by Jerome Avenue
Jerome Avenue is one of the longest thoroughfares in the New York City borough of the Bronx, New York, United States. The road is long and stretches from Concourse to Woodlawn. Both of these termini are with the Major Deegan Expressway which r ...
. The West Bronx was annexed to New York City in 1874, and the areas east of the Bronx River in 1895.[On the start of business for Bronx County]
Bronx County In Motion. New Officials All Find Work to Do on Their First Day.
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', January 3, 1914 ( PDF retrieved on June 26, 2008):
:"Despite the fact that the new Bronx County Court House is not completed there was no delay yesterday in getting the court machinery in motion. All the new county officials were on hand and the County Clerk, the District Attorney, the Surrogate, and the County Judge soon had things in working order. The seal to be used by the new county was selected by County Judge Louis D. Gibbs. It is circular. In the center is a seated figure of Justice. To her right is an American shield and over the figure is written 'Populi Suprema.' ..."
:"Surrogate George M. S. Schulz, with his office force, was busy at the stroke of 9 o'clock. Two wills were filed in the early morning, but owing to the absence of a safe they were recorded and then returned to the attorneys for safe keeping. ..."
:"There was a rush of business to the new County Clerk's office. Between seventy-five and a hundred men applied for first naturalization papers. Two certificates of incorporation were issued, and seventeen judgments, seven lis pendens, three mechanics' liens and one suit for negligence were filed."
:"Sheriff O'Brien announced several additional appointments." About a quarter of the Bronx's area is open space,Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
, Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
, the New York Botanical Garden
The New York Botanical Garden (NYBG) is a botanical garden at Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York City. Established in 1891, it is located on a site that contains a landscape with over one million living plants; the Enid A. Haupt Conservatory, ...
, and the Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and is the largest metropolitan zoo in ...
in the borough's north and center. The Thain Family Forest at the New York Botanical Garden is thousands of years old; it is New York City's largest remaining tract of the original forest that once covered the city. These open spaces are primarily on land reserved in the late 19th century as urban development progressed north and east from Manhattan.
The word "Bronx" originated with Faroese-born (or Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
-born) Jonas Bronck
Jonas Bronck (alternatively Jonas Jonsson Brunk, Jonas Jonasson Bronk, or Jonas Jonassen Bronck) was born around year 1600 and died in 1643. Bronck was an immigrant to the Dutch colony of New Netherland after whom the Bronx River, and by extension ...
, who established the first settlement in the area as part of the New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
colony in 1639.Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
) and later from the Caribbean region (particularly Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
, Haiti, Guyana, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, and the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
), as well as immigrants from West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
(particularly from Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
), African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
migrants from the southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, Panamanians
Panamanians ( Spanish: ''Panameños'') are people identified with Panama, a transcontinental country in Central America (a region within North America) and South America, whose connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For ...
, Hondurans
Hondurans (Spanish: ''Hondureñas'' or ''Hondureños'') are the citizens of Honduras. Most Hondurans live in Honduras, although there is also a significant Honduran diaspora, particularly in the United States, Spain, and many smaller communiti ...
, and South Asians.
The Bronx contains the poorest congressional district in the United States, the 15th. There are, however, some upper-income, as well as middle-income neighborhoods such as Riverdale, Fieldston, Spuyten Duyvil, Schuylerville
Schuylerville () is a village in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The village is located in the northeastern part of the Town of Saratoga, east of Saratoga Springs. The Village of Victory is adjacent to Schuylerville to the southwes ...
, Pelham Bay, Pelham Gardens, Morris Park, and Country Club
A country club is a privately owned club, often with a membership quota and admittance by invitation or sponsorship, that generally offers both a variety of recreational sports and facilities for dining and entertaining. Typical athletic offe ...
.['' The Almanac of American Politics 2008'', edited by Michael Barone with Richard E. Cohen and Grant Ujifusa, National Journal Group, ]Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, 2008 (paperback) or (hardback), chapter on New York stateU.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, '' Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2003'', Section 31, Table 1384. Congressional District Profiles – 108th Congress: 2000urban decay
Urban decay (also known as urban rot, urban death or urban blight) is the sociological process by which a previously functioning city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude. There is no single process that leads to urban deca ...
. The borough began experiencing new population growth starting in the late 1990s and continuing to the present day.
Etymology and naming
Early names
 The Bronx was called '
The Bronx was called 'Siwanoy
The Siwanoy () were an Indigenous American band of Wappinger people, who lived in Long Island Sound along the coasts of what are now The Bronx, Westchester County, New York, and Fairfield County, Connecticut. They were one of the western bands of ...
band of Lenape (also known historically as ''the Delawares''), while other Native Americans knew the Bronx as ''Keskeskeck''.Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
}.
The Bronx was named after Jonas Bronck
Jonas Bronck (alternatively Jonas Jonsson Brunk, Jonas Jonasson Bronk, or Jonas Jonassen Bronck) was born around year 1600 and died in 1643. Bronck was an immigrant to the Dutch colony of New Netherland after whom the Bronx River, and by extension ...
(), a European settler whose precise origins are disputed. Documents indicate he was a Swedish-born immigrant from Komstad, Norra Ljunga parish, in Småland, Sweden, who arrived in New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
during the spring of 1639.[, excerpted a]
The Bronx ... Its History & Perspective
/ref>Mott Haven
Mott Haven is an American primarily residential neighborhood in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of the Bronx. Its boundaries, starting from the north and moving clockwise, are East 149th Street to the north, the Bruckner ...
. He leased land from the Dutch West India Company on the neck of the mainland immediately north of the Dutch settlement of New Haarlem (on Manhattan Island), and bought additional tracts from the local tribes. He eventually accumulated between the Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York, United States, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the New York mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyt ...
and the Aquahung, which became known as ''Bronck's River'' or ''the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
iver
Iver is a large civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England. In addition to the central clustered village, the parish includes the residential neighbourhoods of Iver Heath and Richings Park.
Geography, transport and economy
Part of the 43-square- ...
'. Dutch and English settlers referred to the area as ''Bronck's Land''.William Bronk
William Bronk (February 17, 1918 – February 22, 1999) was an American poet. For his book, ''Life Supports'' (1981), he won the National Book Award for Poetry.
He was also a veteran of World War II and a businessman. After teaching at Union Co ...
was a descendant of Pieter Bronck, either Jonas Bronck's son or his younger brother, but most probably a nephew or cousin, as there was an age difference of 16 years. Much work on the Swedish claim has been undertaken by Brian G. Andersson, former Commissioner of New York City's Department of Records, who helped organize a 375th Anniversary celebration in Bronck's hometown in 2014.
Use of definite article
The Bronx is referred to with the definite article
An article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech.
In English, both "the" and "a(n)" a ...
as "the Bronx" or "The Bronx", both legally and colloquially. The "County of Bronx" does not take "the" immediately before "Bronx" in formal references, unlike the coextensive "Borough of the Bronx". The United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
uses "Bronx, NY" for mailing addresses. The region was apparently named after the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
and first appeared in the "Annexed District of The Bronx" created in 1874 out of part of Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
. It was continued in the "Borough of The Bronx", which included a larger annexation from Westchester County in 1898. The use of the definite article is attributed to the style of referring to rivers. A time-worn story purportedly explaining the use of the definite article in the borough's name says it stems from the phrase "visiting the Broncks", referring to the settler's family.
The capitalization of the borough's name is sometimes disputed. Generally, the definite article is lowercase in place names ("the Bronx") except in some official references. The definite article is capitalized ("The Bronx") at the beginning of a sentence or in any other situation when a normally lowercase word would be capitalized. However, some people and groups refer to the borough with a capital letter at all times, such as Bronx Borough Historian Lloyd Ultan, The Bronx County Historical Society
The Bronx County Historical Society is a private non-profit organization that collects and disseminates historical material and information about the New York City borough of the Bronx, as well as southern Westchester County, New York.
The Socie ...
, and the Bronx-based organization Great and Glorious Grand Army of The Bronx, arguing the definite article is part of the proper name.
History
European colonization of the Bronx began in 1639. The Bronx was originally part of Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
, but it was ceded to New York County
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
in two major parts (West Bronx
The West Bronx is a region in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The region lies west of the Bronx River and roughly corresponds to the western half of the borough.
The West Bronx is more densely populated than the East Bronx, and is close ...
, 1874 and East Bronx
The East Bronx is the part of the New York City borough of the Bronx which lies east of the Bronx River; this roughly corresponds to the eastern half of the borough. Neighborhoods include: Baychester, Castle Hill, City Island, Co-op City, ...
, 1895) before it became Bronx County. Originally, the area was part of the Lenape's Lenapehoking territory inhabited by Siwanoy
The Siwanoy () were an Indigenous American band of Wappinger people, who lived in Long Island Sound along the coasts of what are now The Bronx, Westchester County, New York, and Fairfield County, Connecticut. They were one of the western bands of ...
of the Wappinger
The Wappinger () were an Eastern Algonquian Munsee-speaking Native American people from what is now southern New York and western Connecticut.
At the time of first contact in the 17th century they were primarily based in what is now Dutches ...
Confederacy. Over time, European colonists converted the borough into farmlands.
Before 1914
The Bronx's development is directly connected to its strategic location between New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
and New York (Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
). Control over the bridges across the Harlem River plagued the period of British colonial rule. The King's Bridge, built in 1693 where Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
reached the Spuyten Duyvil Creek
Spuyten Duyvil Creek () is a short tidal estuary in New York City connecting the Hudson River to the Harlem River Ship Canal and then on to the Harlem River. The confluence of the three water bodies separate the island of Manhattan from t ...
, was a possession of Frederick Philipse
Frederick Philipse (born Frederick Flypsen;Appleton, W.S. ''The Heraldic Journal, Recording the Amorial Bearings and Genealogies of American Families'', Wiggen & Lunt, Boston, 1867 1626 in Bolsward, Netherlands – December 23, 1702), first Lor ...
, lord of Philipse Manor.American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, the King's Bridge toll was abolished.Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
, one of the 12 original counties of the English Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the U ...
. The present Bronx County was contained in the town of Westchester and parts of the towns in Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
, Eastchester, and Pelham. In 1846, a new town was created by division of Westchester, called West Farms. The town of Morrisania
Morrisania ( ) is a residential neighborhood in the southwestern Bronx, New York City, New York. Its boundaries are the Cross-Bronx Expressway to the north, Crotona-Prospect Avenue to the east, East 161st Street to the south, and Webster Avenue ...
was created, in turn, from West Farms in 1855. In 1873, the town of Kingsbridge
Kingsbridge is a market town and tourist hub in the South Hams district of Devon, England, with a population of 6,116 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards bear the name of ''Kingsbridge'' (East & North). Their combined population at the ab ...
was established within the former borders of the town of Yonkers, roughly corresponding to the modern Bronx neighborhoods of Kingsbridge, Riverdale, and Woodlawn Heights, and included Woodlawn Cemetery.
Among famous settlers in the Bronx during the 19th and early 20th centuries were author Willa Cather
Willa Sibert Cather (; born Wilella Sibert Cather; December 7, 1873 – April 24, 1947) was an American writer known for her novels of life on the Great Plains, including '' O Pioneers!'', '' The Song of the Lark'', and '' My Ántonia''. In 192 ...
, tobacco merchant Pierre Lorillard, and inventor Jordan L. Mott, who established Mott Haven
Mott Haven is an American primarily residential neighborhood in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of the Bronx. Its boundaries, starting from the north and moving clockwise, are East 149th Street to the north, the Bruckner ...
to house the workers at his iron works.
The consolidation of the Bronx into New York City proceeded in two stages. In 1873, the state legislature annexed Kingsbridge, West Farms, and Morrisania to New York, effective in 1874; the three towns were soon abolished in the process.Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, and Staten Island. This included the Town of Westchester (which had voted against consolidation in 1894) and parts of Eastchester and Pelham.[Peck, Richard]
"In the Bronx, the Gentry Live On; The Gentry Live On"
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', December 2, 1973. Accessed July 17, 2008. "But the Harlem riverfront was industrializing, and in 1874 the city annexed the area west of the Bronx River: Morrisania, West Farms and Kingsbridge. A second annexation in 1894 gathered in Westchester and portions of Eastchester and Pelham." However, 1894 must refer to the referendum, since the enabling act was not passed or signed until 1895. The nautical community of City Island voted to join the city in 1896.
On January 1, 1898, the consolidated City of New York
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
was born, including the Bronx as one of the five distinct boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
(at the same time, the Bronx's territory moved from Westchester County into New York County
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, which already included Manhattan and the rest of pre-1874 New York City).
On April 19, 1912, those parts of New York County which had been annexed from Westchester County in previous decades were newly constituted as Bronx County, the 62nd and last county to be created by the state, effective in 1914.Marble Hill, Manhattan
Marble Hill is the northernmost neighborhood in the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is one of the few areas within the borough of Manhattan not located on Manhattan Island. Marble Hill was occupied as a Dutch colonial settlement in 1646, a ...
was now connected to the Bronx by filling in the former waterway, but it did not become part of the borough or county.[Steinhauer, Jennifer]
"F.Y.I."
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', October 10, 1993. Accessed August 23, 2021. "Marble Hill's Exile Q. Why is there a small piece of Manhattan in the Bronx?. ... A. Marble Hill was originally attached to the northern part of Manhattan, but was severed in 1895 when the city deepened and straightened the waterway that connected the Hudson River to what was known as Spuyten Duyvil Creek (Dutch for 'in Spite of the Devil', thought to be a reference to the trouble it took to cross it). ... Around 1914, Spuyten Duyvil Creek was filled in and the area became physically a part of the Bronx, but it remained politically part of Manhattan."
After 1914
The history of the Bronx during the 20th century may be divided into four periods: a boom period during 1900–1929, with a population growth by a factor of six from 200,000 in 1900 to 1.3 million in 1930. The Great Depression and post World War II years saw a slowing of growth leading into an eventual decline. The mid to late century were hard times, as the Bronx changed during 1950–1985 from a predominantly moderate-income to a predominantly lower-income area with high rates of violent crime and poverty in some areas. The Bronx has experienced an economic and developmental resurgence starting in the late 1980s that continues into today.
New York City expands
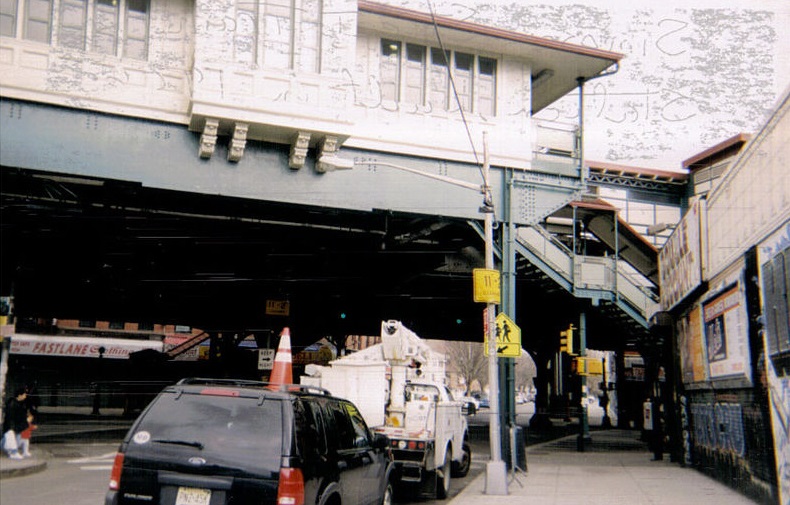
 The Bronx was a mostly rural area for many generations, with small farms supplying the city markets. In the late 19th century, however, it grew into a railroad suburb. Faster transportation enabled rapid population growth in the late 19th century, involving the move from horse-drawn street cars to elevated railways and the subway system, which linked to Manhattan in 1904.
The Bronx was a mostly rural area for many generations, with small farms supplying the city markets. In the late 19th century, however, it grew into a railroad suburb. Faster transportation enabled rapid population growth in the late 19th century, involving the move from horse-drawn street cars to elevated railways and the subway system, which linked to Manhattan in 1904.[Olmsted (1989); Olmsted (1998)]
The South Bronx was a manufacturing center for many years and was noted as a center of piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keybo ...
manufacturing in the early part of the 20th century. In 1919, the Bronx was the site of 63 piano factories employing more than 5,000 workers.World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Bronx hosted the rather small 1918 World's Fair at 177th Street and DeVoe Avenue.[Lloyd Ultann]
"History of the Bronx River"
Paper presented to the Bronx River Alliance, November 5, 2002 (notes taken by Maarten de Kadt, November 16, 2002), retrieved on August 29, 2008. This hour talk covers much of the early history of the Bronx as a whole, in addition to the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
.
The Bronx underwent rapid urban growth after World War I. Extensions of the New York City Subway contributed to the increase in population as thousands of immigrants came to the Bronx, resulting in a major boom in residential construction. Among these groups, many Irish Americans
, image = Irish ancestry in the USA 2018; Where Irish eyes are Smiling.png
, image_caption = Irish Americans, % of population by state
, caption = Notable Irish Americans
, population =
36,115,472 (10.9%) alone ...
, Italian Americans, and especially Jewish Americans
American Jews or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by culture, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Today the Jewish community in the United States consists primarily of Ashkenazi Jews, who descend from diaspora Je ...
settled here. In addition, French, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
, and other immigrants moved into the borough. As evidence of the change in population, by 1937, 592,185 Jews lived in the Bronx (43.9% of the borough's population), while only 54,000 Jews lived in the borough in 2011. Many synagogues still stand in the Bronx, but most have been converted to other uses.[Seymour J. Perlin]
"Remembrance of Synagogues Past: The Lost Civilization of the Jewish South Bronx"
(retrieved on August 10, 2008), citing population estimates in "The Jewish Community Study of New York: 2002", UJA nited Jewish AppealFederation of New York,
June 2004, and his own survey of synagogue sites.
Change
Bootleggers
Bootleg or bootlegging most often refers to:
* Bootleg recording, an audio or video recording released unofficially
* Rum-running, the illegal business of transporting and trading in alcoholic beverages, hence:
** Moonshine, or illicitly made ...
and gangs were active in the Bronx during Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
(1920–1933). Irish, Italian, Jewish, and Polish gangs smuggled in most of the illegal whiskey, and the oldest sections of the borough became poverty-stricken. Enright declared that speakeasies were home to "the vicious elements, bootleggers, gamblers and their friends in all walks of life" cooperating to "evade the law, escape punishment for their crimes, or to deter the police from doing their duty".
Between 1930 and 1960, moderate and upper income Bronxites (predominantly non-Hispanic Whites) began to relocate from the borough's southwestern neighborhoods. This migration has left a mostly poor African American and Hispanic (largely Puerto Rican) population in the West Bronx. One significant factor that shifted the racial and economic demographics was the construction of Co-op City
Co-op City (short for Cooperative City) is a cooperative housing development located in the northeast section of the borough of the Bronx in New York City. It is bounded by Interstate 95 to the southwest, west, and north and the Hutchinson River ...
, built to house middle-class residents in family-sized apartments. The high-rise complex played a significant role in draining middle-class residents from older tenement buildings in the borough's southern and western fringes. Most predominantly non-Hispanic White communities today are in the eastern and northwestern sections of the borough.
From the early 1960s to the early 1980s, the quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
changed for some Bronx residents. Historians and social scientists have suggested many factors, including the theory that Robert Moses' Cross Bronx Expressway destroyed existing residential neighborhoods and created instant slums, as put forward in Robert Caro
Robert Allan Caro (born October 30, 1935) is an American journalist and author known for his biographies of United States political figures Robert Moses and Lyndon B. Johnson.
After working for many years as a reporter, Caro wrote '' The Power ...
's biography ''The Power Broker
''The Power Broker: Robert Moses and the Fall of New York'' is a 1974 biography of Robert Moses by Robert Caro. The book focuses on the creation and use of power in New York local and state politics, as witnessed through Moses' use of unelected ...
''. Another factor in the Bronx's decline may have been the development of high-rise housing projects
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is usually owned by a government authority, either central or local. Although the common goal of public housing is to provide affordable housing, the details, terminology, d ...
, particularly in the South Bronx. Yet another factor may have been a reduction in the real estate listings and property-related financial services offered in some areas of the Bronx, such as mortgage loan
A mortgage loan or simply mortgage (), in civil law jurisdicions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any ...
s or insurance policies—a process known as redlining. Others have suggested a "planned shrinkage" of municipal services, such as fire-fighting. There was also much debate as to whether rent control laws had made it less profitable (or more costly) for landlords to maintain existing buildings with their existing tenants than to abandon or destroy those buildings.
In the 1970s, parts of the Bronx were plagued by a wave of arson. The burning of buildings was predominantly in the poorest communities, such as the South Bronx. One explanation of this event was that landlords decided to burn their low property-value buildings and take the insurance money, as it was easier for them to get insurance money than to try to refurbish a dilapidated building or sell a building in a severely distressed area. The Bronx became identified with a high rate of poverty and unemployment, which was mainly a persistent problem in the South Bronx.[Gonzalez (2004)] There were cases where tenants set fire to the building they lived in so they could qualify for emergency relocations by city social service agencies to better residences, sometimes being relocated to other parts of the city.
Out of 289 census tracts in the Bronx borough, 7 tracts lost more than 97% of their buildings to arson and abandonment between 1970 and 1980; another 44 tracts had more than 50% of their buildings meet the same fate. By the early 1980s, the Bronx was considered the most blighted urban area in the country, particularly the South Bronx which experienced a loss of 60% of the population and 40% of housing units. However, starting in the 1990s, many of the burned-out and run-down tenements were replaced by new housing units.
Revitalization
 Since the late 1980s, significant development has occurred in the Bronx, first stimulated by the city's "Ten-Year Housing Plan" and community members working to rebuild the social, economic and environmental infrastructure by creating affordable housing. Groups affiliated with churches in the South Bronx erected the Nehemiah Homes with about 1,000 units. The grass roots organization Nos Quedamos' endeavor known as Melrose Commons began to rebuild areas in the South Bronx. The IRT White Plains Road Line () began to show an increase in riders. Chains such as Marshalls, Staples Inc., Staples, and Target Corporation, Target opened stores in the Bronx. More bank branches opened in the Bronx as a whole (rising from 106 in 1997 to 149 in 2007), although not primarily in poor or minority neighborhoods, while the Bronx still has fewer branches per person than other boroughs.
Since the late 1980s, significant development has occurred in the Bronx, first stimulated by the city's "Ten-Year Housing Plan" and community members working to rebuild the social, economic and environmental infrastructure by creating affordable housing. Groups affiliated with churches in the South Bronx erected the Nehemiah Homes with about 1,000 units. The grass roots organization Nos Quedamos' endeavor known as Melrose Commons began to rebuild areas in the South Bronx. The IRT White Plains Road Line () began to show an increase in riders. Chains such as Marshalls, Staples Inc., Staples, and Target Corporation, Target opened stores in the Bronx. More bank branches opened in the Bronx as a whole (rising from 106 in 1997 to 149 in 2007), although not primarily in poor or minority neighborhoods, while the Bronx still has fewer branches per person than other boroughs.
 In 1997, the Bronx was designated an ''All America City'' by the National Civic League, acknowledging its comeback from the decline of the mid-century. In 2006, ''
In 1997, the Bronx was designated an ''All America City'' by the National Civic League, acknowledging its comeback from the decline of the mid-century. In 2006, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' reported that "construction cranes have become the borough's new visual metaphor, replacing the window decals of the 1980s in which pictures of potted plants and drawn curtains were placed in the windows of abandoned buildings."
Geography


Location and physical features
According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, Bronx County has a total area of , of which is land and (27%) is water.Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York, United States, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the New York mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyt ...
separates it from the island of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
to the southwest; the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
separates it from Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
to the southeast; and to the east, Long Island Sound separates it from Nassau County, New York, Nassau County in western Long Island. Directly north of the Bronx are (from west to east) the adjoining Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
communities of Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
, Mount Vernon, New York, Mount Vernon, Pelham Manor, New York, Pelham Manor and, though physically separated by water, New Rochelle, New York, New Rochelle. There is also a short southern land boundary with Marble Hill, Manhattan, Marble Hill in the Borough of Manhattan, over the filled-in former course of the Spuyten Duyvil Creek
Spuyten Duyvil Creek () is a short tidal estuary in New York City connecting the Hudson River to the Harlem River Ship Canal and then on to the Harlem River. The confluence of the three water bodies separate the island of Manhattan from t ...
; Marble Hill's postal ZIP code, telephonic area codes and fire service, however, are shared with the Bronx and not Manhattan.[
The ]Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
flows south from Westchester County through the borough, emptying into the East River; it is the only entirely freshwater river in New York City.East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
and Long Island Sound, such as City Island, New York, City Island and Hart Island (New York), Hart Island. Rikers Island in the East River, home to the large jail complex for the entire city, is also part of the Bronx.
The Bronx's highest elevation at is in the northwest corner, west of Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
and in the Chapel Farm area near the Riverdale Country School. The opposite (southeastern) side of the Bronx has four large low peninsulas or "necks" of low-lying land that jut into the waters of the East River and were once salt marsh: Hunt's Point, Clason's Point, Screvin's Neck and Throggs Neck. Further up the coastline, Rodman's Neck lies between Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
in the northeast and City Island, New York, City Island. The Bronx's irregular shoreline extends for .
Parks and open space

 Although Bronx County was the third most densely populated county in the United States as of 2006 (after
Although Bronx County was the third most densely populated county in the United States as of 2006 (after Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
and Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
),[Ladies and gentlemen, the Bronx is blooming!](_blank)
by Beth J. Harpaz, Travel Editor of The Associated Press (AP), June 30, 2008, retrieved on July 11, 2008 The vision of a system of major Bronx parks connected by park-like thoroughfares is usually attributed to John Mullaly.
Woodlawn Cemetery, one of the largest cemeteries in New York City, sits on the western bank of the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
near Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
. It opened in 1863, in what was then the town of Yonkers, at the time a rural area.
The borough's northern side includes the largest park in New York City—Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
, which includes Orchard Beach, New York, Orchard Beach—and the third-largest, Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
, which is west of Woodlawn Cemetery and borders Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
. Also in the northern Bronx, Wave Hill (New York), Wave Hill, the former estate of George Walbridge Perkins, George W. Perkins—known for a historic house, gardens, changing site-specific art installations and concerts—overlooks the New Jersey Palisades from a promontory on the Hudson River, Hudson in Riverdale. Nearer the borough's center, and along the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
, is Bronx Park; its northern end houses the New York Botanical Gardens, which preserve the last patch of the original Tsuga, hemlock forest that once covered the county, and its southern end the Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and is the largest metropolitan zoo in ...
, the largest urban zoological gardens in the United States.Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
is the Jerome Park Reservoir, surrounded by of stone walls and bordering several small parks in the Bedford Park, Bronx, Bedford Park neighborhood; the reservoir was built in the 1890s on the site of the former Jerome Park Racetrack. Further south is Crotona Park, home to a lake, 28 species of trees, and a large swimming pool. The land for these parks, and many others, was bought by New York City in 1888, while land was still open and inexpensive, in anticipation of future needs and future pressures for development.
Some of the acquired land was set aside for the Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse and Pelham Parkway, the first of a series of boulevards and parkways (thoroughfares lined with trees, vegetation and greenery). Later projects included the Bronx River Parkway, which developed a road while restoring the riverbank and reducing pollution, Mosholu Parkway and the Henry Hudson Parkway.
In 2006, a five-year, $220-million program of capital improvements and natural restoration in 70 Bronx parks was begun (financed by water and sewer revenues) as part of an agreement that allowed a Croton Water Filtration Plant, water filtration plant under Mosholu Golf Course in Van Cortlandt Park. One major focus is on opening more of the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
's banks and restoring them to a natural state.
Neighborhoods
The number, locations, and boundaries of the Bronx's neighborhoods (many of them sitting on the sites of 19th-century villages) have become unclear with time and successive waves of newcomers. In 2006, Manny Fernandez of ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' wrote,
According to a New York City Department of City Planning, Department of City Planning map of the city's neighborhoods, the Bronx has 49. The map publisher Hagstrom identifies 69. The borough president, Adolfo Carrión Jr., says 61. The Mayor's Community Assistance Unit, in a listing of the Bronx Community Board, borough's community boards, names 68.
Notable Bronx neighborhoods include the South Bronx; Little Italy on Arthur Avenue in the Belmont, Bronx, Belmont section; and Riverdale.
East Bronx
(Bronx Community Board, Bronx Community Districts 9 ''[south central]'', 10 ''[east]'', 11 ''[east central]'' and 12 ''[north central]'' )
 East of the
East of the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
, the borough is relatively flat and includes four large low peninsulas, or 'necks,' of low-lying land which jut into the waters of the East River and were once saltmarsh: Hunts Point, Clason's Point, Screvin's Neck (Castle Hill Point) and Throgs Neck. The East Bronx has older tenement buildings, low income public housing complexes, and multifamily homes, as well as single family homes. It includes New York City's largest park: Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
along the Westchester County, New York, Westchester-Bronx border.
Neighborhoods include: Clason's Point, Bronx, Clason's Point, Harding Park, Bronx, Harding Park, Soundview, Bronx, Soundview, Castle Hill, Bronx, Castle Hill, Parkchester, Bronx, Parkchester ''(Bronx Community Board 9, Community District 9)''; Throggs Neck, Country Club
A country club is a privately owned club, often with a membership quota and admittance by invitation or sponsorship, that generally offers both a variety of recreational sports and facilities for dining and entertaining. Typical athletic offe ...
, City Island, Pelham Bay, Edgewater Park (Bronx), Edgewater Park, Co-op City
Co-op City (short for Cooperative City) is a cooperative housing development located in the northeast section of the borough of the Bronx in New York City. It is bounded by Interstate 95 to the southwest, west, and north and the Hutchinson River ...
''(Bronx Community Board 10, Community District 10)''; Westchester Square, Bronx, Westchester Square, Van Nest, Pelham Parkway, Bronx, Pelham Parkway, Morris Park ''(Bronx Community Board 11, Community District 11)''; Williamsbridge, Bronx, Williamsbridge, Eastchester, Bronx, Eastchester, Baychester, Bronx, Baychester, Edenwald, Bronx, Edenwald and Wakefield, Bronx, Wakefield ''(Bronx Community Board 12, Community District 12)''.
=City Island and Hart Island
=
 (Bronx Community Board 10, Bronx Community District 10)
City Island is east of
(Bronx Community Board 10, Bronx Community District 10)
City Island is east of Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
in Long Island Sound and is known for its seafood restaurants and private waterfront homes. City Island's single shopping street, City Island Avenue, is reminiscent of a small New England town. It is connected to Rodman's Neck on the mainland by the City Island Bridge.
East of City Island is Hart Island (New York), Hart Island, which is uninhabited and not open to the public. It once served as a prison and now houses New York City's potter's field for unclaimed bodies.
West Bronx
 (Bronx Community Board, Bronx Community Districts 1 to 8, progressing roughly from south to northwest)
The western parts of the Bronx are hillier and are dominated by a series of parallel ridges, running south to north. The West Bronx has older apartment buildings, low income public housing complexes, multifamily homes in its lower income areas as well as larger single family homes in more affluent areas such as Riverdale and Fieldston. It includes New York City's third-largest park:
(Bronx Community Board, Bronx Community Districts 1 to 8, progressing roughly from south to northwest)
The western parts of the Bronx are hillier and are dominated by a series of parallel ridges, running south to north. The West Bronx has older apartment buildings, low income public housing complexes, multifamily homes in its lower income areas as well as larger single family homes in more affluent areas such as Riverdale and Fieldston. It includes New York City's third-largest park: Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
along the Westchester-Bronx border. The Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse, a wide boulevard, runs through it, north to south.
=Northwestern Bronx
=
(Bronx Community Board, Bronx Community Districts 7 ''[between the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
and Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York, United States, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the New York mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyt ...
s]'' and 8 ''[facing the Hudson River]'' – plus part of Board 12)
Neighborhoods include: Fordham-Bedford, Bedford Park, Bronx, Bedford Park, Norwood, Bronx, Norwood, Kingsbridge Heights ''(Bronx Community Board 7, Community District 7)'', Kingsbridge
Kingsbridge is a market town and tourist hub in the South Hams district of Devon, England, with a population of 6,116 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards bear the name of ''Kingsbridge'' (East & North). Their combined population at the ab ...
, Riverdale ''(Bronx Community Board 8, Community District 8)'', and Woodlawn Heights ''(Bronx Community Board 12, Community District 12)''.
(Marble Hill, Manhattan
Marble Hill is the northernmost neighborhood in the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is one of the few areas within the borough of Manhattan not located on Manhattan Island. Marble Hill was occupied as a Dutch colonial settlement in 1646, a ...
is now connected by land to the Bronx rather than Manhattan and is served by Bronx Community District 8.)
=South Bronx
=
(Bronx Community Board, Bronx Community Districts 1 to 6 plus part of CD 7—''progressing northwards, CDs 2, 3 and 6 border the Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
from its mouth to Bronx Park, while 1, 4, 5 and 7 face Manhattan across the Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York, United States, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the New York mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyt ...
'')
Like other neighborhoods in New York City, the South Bronx has no official boundaries. The name has been used to represent poverty in the Bronx and is applied to progressively more northern places so that by the 2000s, Fordham Road was often used as a northern limit. The Bronx River
The Bronx River (), approximately long, flows through southeast New York in the United States and drains an area of . It is named after colonial settler Jonas Bronck. Besides the Hutchinson River, the Bronx River is the only fresh water river in ...
more consistently forms an eastern boundary. The South Bronx has many high-density apartment buildings, low income public housing complexes, and multi-unit homes. The South Bronx is home to the Bronx County Courthouse, Borough Hall, and other government buildings, as well as Yankee Stadium. The Cross Bronx Expressway bisects it, east to west. The South Bronx has some of the poorest neighborhoods in the country, as well as very high crime areas.
Neighborhoods include: The Hub, Bronx, The Hub (a retail district at Third Avenue and East 149th Street), Port Morris, Bronx, Port Morris, Mott Haven
Mott Haven is an American primarily residential neighborhood in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of the Bronx. Its boundaries, starting from the north and moving clockwise, are East 149th Street to the north, the Bruckner ...
''(Bronx Community Board 1, Community District 1)'', Melrose, Bronx, Melrose ''(Bronx Community Board 1, Community District 1 & Bronx Community Board 3, Community District 3)'', Morrisania, East Morrisania, Bronx, East Morrisania [also known as Crotona Park East] ''(Bronx Community Board 3, Community District 3)'', Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point, Longwood, Bronx, Longwood ''(Bronx Community Board 2, Community District 2)'', Highbridge, Bronx, Highbridge, Concourse, Bronx, Concourse ''(Bronx Community Board 4, Community District 4)'', West Farms, Bronx, West Farms, Belmont, Bronx, Belmont, East Tremont, Bronx, East Tremont ''(Bronx Community Board 6, Community District 6)'', Tremont, Bronx, Tremont, Morris Heights, Bronx, Morris Heights ''(Bronx Community Board 5, Community District 5)'', University Heights, Bronx, University Heights. ''(Bronx Community Board 5, Community District 5 & Bronx Community Board 7, Community District 7)''.
Adjacent counties
The Bronx adjoins:
* Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
– north
* Nassau County, New York – southeast (across the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
)
* Queens, Queens County, New York (Queens) – south (across the East River)
* Manhattan, New York County, New York (Manhattan) – southwest
* Bergen County, New Jersey – west (across the Hudson River)
Climate
Demographics
Race, ethnicity, language, and immigration
2018 estimates
The borough's most populous racial group, white, declined from 99.3% in 1920 to 44.9% in 2018.
2010 census
According to the 2010 Census, 53.5% of Bronx's population was of Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin (they may be of any race); 30.1% non-Hispanic Black or African American, 10.9% of the population was non-Hispanic White, 3.4% non-Hispanic Asian, 0.6% from some other race (non-Hispanic) and 1.2% of two or more races (non-Hispanic).
As of 2010, 46.29% (584,463) of Bronx residents aged five and older spoke Spanish language, Spanish at home, while 44.02% (555,767) spoke English language, English, 2.48% (31,361) Languages of Africa, African languages, 0.91% (11,455) French language, French, 0.90% (11,355) Italian language, Italian, 0.87% (10,946) Indo-Aryan languages, various Indic languages, 0.70% (8,836) Indo-European languages, other Indo-European languages, and Chinese language, Chinese was spoken at home by 0.50% (6,610) of the population over the age of five. In total, 55.98% (706,783) of the Bronx's population age five and older spoke a language at home other than English. A Garifuna language, Garifuna-speaking community from Honduras and Guatemala also makes the Bronx its home.
2009 community survey
According to the 2009 American Community Survey, White Americans of both Hispanic and non-Hispanic origin represented over one-fifth (22.9%) of the Bronx's population. However, non-Hispanic whites formed under one-eighth (12.1%) of the population, down from 34.4% in 1980.
Older estimates
The 1930 United States Census, Census of 1930 counted only 1.0% (12,930) of the Bronx's population as Negro (while making no distinct counts of Hispanic or Spanish-surname residents).[Historical Census Browser](_blank)
University of Virginia, Geospatial and Statistical Data Center, retrieved on August 7, 2008, querying 1930 Census for New York State. "The data and terminology presented in the Historical Census Browser are drawn directly from historical volumes of the U.S. Census of Population and Housing."
Population and housing
 As of the 2010 Census, there were 1,385,108 people living in the Bronx, a 3.9% increase since 2000.
As of the United States Census
As of the 2010 Census, there were 1,385,108 people living in the Bronx, a 3.9% increase since 2000.
As of the United States Censuspopulation density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
was 31,709.3 inhabitants per square mile (12,242.2/km2). There were 490,659 housing units at an average density of 11,674.8 per square mile (4,507.4/km2).
Individual and household income
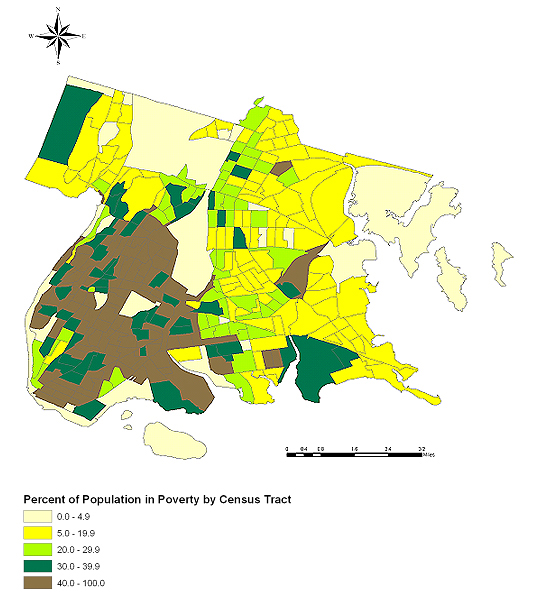
The 1999 median income for a household in the borough was $27,611, and the median family income was $30,682. Males had a median income of $31,178 versus $29,429 for females. The per capita income for the borough was $13,959. About 28.0% of families and 30.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 41.5% of those under age 18 and 21.3% of those age 65 or over. More than half of the neighborhoods in the Bronx are high poverty or extreme poverty areas.
From 2015 Census data, the median income for a household was (in 2015 dollars) $34,299. Per capita income in past 12 months (in 2015 dollars): $18,456 with persons in poverty at 30.3%. Per the 2016 Census data, the median income for a household was $35,302. Per capita income was cited at $18,896.
Culture and institutions

 Author Edgar Allan Poe spent the last years of his life (1846 to 1849) in the Bronx at Poe Cottage, now at
Author Edgar Allan Poe spent the last years of his life (1846 to 1849) in the Bronx at Poe Cottage, now at Kingsbridge
Kingsbridge is a market town and tourist hub in the South Hams district of Devon, England, with a population of 6,116 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards bear the name of ''Kingsbridge'' (East & North). Their combined population at the ab ...
Road and the Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse. A small wooden farmhouse built around 1812, the cottage once commanded unobstructed vistas over the rolling Bronx hills to the shores of Long Island. Poe moved there to get away from the Manhattan city air and crowding in hope that the then rural area would be beneficial for his wife's tuberculosis. It was in the Bronx that Poe wrote one of his most famous works, "Annabel Lee".
More than a century later, the Bronx would evolve from a hot bed of Latin jazz to an incubator of Hip hop music, hip hop as documented in the award-winning documentary, produced by City Lore and broadcast on Public Broadcasting Service, PBS in 2006, "From Mambo to Hip Hop: A South Bronx Tale." Hip hop first emerged in the South Bronx in the early 1970s. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' has identified 1520 Sedgwick Avenue "an otherwise unremarkable high-rise just north of the Cross Bronx Expressway and hard along the Major Deegan Expressway" as a starting point, where DJ Kool Herc presided over parties in the community room. The 2016 Netflix series ''The Get Down'' is based on the development of hip hop in 1977 in the South Bronx. Ten years earlier, the Bronx Opera had been founded.
Founding of hip-hop
On August 11, 1973, DJ Kool Herc was a D.J. and M.C. at a party in the recreation room of 1520 Sedgwick Avenue in the Bronx adjacent to the Cross Bronx Expressway.[Tukufu Zuberi ("detective"), "Birthplace of Hip Hop", ''History Detectives'', Season 6, Episode 11, New York City, found a]
PBS official website
Accessed February 24, 2009. While it was not the actual "Birthplace of Hip Hop" – the genre developed slowly in several places in the 1970s – it was verified to be the place where ''one of'' the pivotal and formative events occurred.
Sports
 The Bronx is the home of the New York Yankees, nicknamed "the Bronx Bombers", of Major League Baseball. The original Yankee Stadium (1923), Yankee Stadium opened in 1923 on 161st Street and River Avenue, a year that saw the Yankees bring home the first of their 27 World Series Championships. With the famous façade, the short right field porch and Monument Park, Yankee Stadium has been home to many of baseball's greatest players including Babe Ruth, Lou Gehrig, Joe DiMaggio, Whitey Ford, Yogi Berra, Mickey Mantle, Reggie Jackson, Thurman Munson, Don Mattingly, Derek Jeter and Mariano Rivera.
The original stadium was the scene of Lou Gehrig's Farewell Speech in 1939, Don Larsen's perfect game in the 1956 World Series, Roger Maris' record breaking 61st home run in 1961, and Reggie Jackson's 3 home runs to clinch Game 6 of the 1977 World Series. The Stadium was the former home of the New York Giants of the National Football League from 1956 to 1973.
The original Yankee Stadium closed in 2008 to make way for a new Yankee Stadium in which the team started play in 2009. It is north-northeast of the 1923 Yankee Stadium, on the former site of Macombs Dam Park. The current Yankee Stadium is also the home of New York City FC of Major League Soccer, who began play in 2015.
The Bronx is the home of the New York Yankees, nicknamed "the Bronx Bombers", of Major League Baseball. The original Yankee Stadium (1923), Yankee Stadium opened in 1923 on 161st Street and River Avenue, a year that saw the Yankees bring home the first of their 27 World Series Championships. With the famous façade, the short right field porch and Monument Park, Yankee Stadium has been home to many of baseball's greatest players including Babe Ruth, Lou Gehrig, Joe DiMaggio, Whitey Ford, Yogi Berra, Mickey Mantle, Reggie Jackson, Thurman Munson, Don Mattingly, Derek Jeter and Mariano Rivera.
The original stadium was the scene of Lou Gehrig's Farewell Speech in 1939, Don Larsen's perfect game in the 1956 World Series, Roger Maris' record breaking 61st home run in 1961, and Reggie Jackson's 3 home runs to clinch Game 6 of the 1977 World Series. The Stadium was the former home of the New York Giants of the National Football League from 1956 to 1973.
The original Yankee Stadium closed in 2008 to make way for a new Yankee Stadium in which the team started play in 2009. It is north-northeast of the 1923 Yankee Stadium, on the former site of Macombs Dam Park. The current Yankee Stadium is also the home of New York City FC of Major League Soccer, who began play in 2015.
Off-Off-Broadway
The Bronx is home to several Off-Off-Broadway theaters, many staging new works by immigrant playwrights from Latin America and Africa. The Pregones Theater, which produces Latin American work, opened a new 130-seat theater in 2005 on Walton Avenue in the South Bronx. Some artists from elsewhere in New York City have begun to converge on the area, and housing prices have nearly quadrupled in the area since 2002. However, rising prices directly correlate to a housing shortage across the city and the entire metro area.
Arts
The Bronx Academy of Arts and Dance, founded in 1998 by Arthur Aviles and Charles Rice-Gonzalez, provides dance, theatre and art workshops, festivals and performances focusing on contemporary and modern art in relation to race, gender and sexuality. It is home to the Arthur Aviles Typical Theatre, a contemporary dance company, and the Bronx Dance Coalition. The Academy was formerly in the American Bank Note Company Building before relocating to a venue on the grounds of St. Peter's Episcopal Church.
The Bronx Museum of the Arts, founded in 1971, exhibits 20th century and contemporary art through its central museum space and of galleries. Many of its exhibitions are on themes of special interest to the Bronx. Its permanent collection features more than 800 works of art, primarily by artists from Africa, Asia and Latin America, including paintings, photographs, prints, drawings, and mixed media. The museum was temporarily closed in 2006 while it underwent an expansion designed by the architectural firm Arquitectonica that would double the museum's size to .
The Bronx has also become home to a peculiar poetic tribute in the form of the "Heinrich Heine Memorial", better known as the Lorelei Fountain. After Heine's German birthplace of Düsseldorf had rejected, allegedly for anti-Semitic motives, a centennial monument to the radical German-Jewish poet (1797–1856), his incensed German-American admirers, including Carl Schurz, started a movement to place one instead in Midtown Manhattan, at Fifth Avenue and 59th Street. However, this intention was thwarted by a combination of ethnic antagonism, aesthetic controversy and political struggles over the institutional control of public art.[Christopher Gray]
"Sturm und Drang Over a Memorial to Heinrich Heine"
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', May 27, 2007, retrieved on July 3, 2008.. See als
Public Art in the Bronx: Joyce Kilmer Park
, from Lehman College In 1899, the memorial by Ernst Gustav Herter was placed in Joyce Kilmer Park, near the Yankee Stadium. In 1999, it was moved to 161st Street and the Concourse.
Maritime heritage
The peninsular borough's maritime heritage is acknowledged in several ways. The City Island Historical Society and Nautical Museum occupies a former public school designed by the New York City school system's turn-of-the-last-century master architect C. B. J. Snyder. The state's SUNY Maritime College, Maritime College in Fort Schuyler (on the southeastern shore) houses the Maritime Industry Museum. In addition, the Harlem River is reemerging as Sculling, "Scullers' Row" due in large part to the efforts of the Bronx River Restoration Project, a joint public-private endeavor of the city's parks department. Canoeing and kayaking on the borough's namesake river have been promoted by the Bronx River Alliance. The river is also straddled by the New York Botanical Gardens, its neighbor, the Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and is the largest metropolitan zoo in ...
, and a little further south, on the west shore, Bronx River Art Center.
Community celebrations
"Bronx Week", traditionally held in May, began as a one-day celebration. Begun by Bronx historian Lloyd Ultan and supported by then borough president Robert Abrams, the original one-day program was based on the "Bronx Borough Day" festival which took place in the 1920s. The following year, at the height of the decade's civil unrest, the festival was extended to a one-week event. In the 1980s the key event, the "Bronx Ball", was launched. The week includes the Bronx Week Parade as well as inductions into the "Bronx Walk of Fame."
Various Bronx neighborhoods conduct their own community celebrations. The Arthur Avenue "Little Italy" neighborhood conducts an annual Autumn Ferragosto Festival that celebrates Italian culture. Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point hosts an annual "Fish Parade and Summer Festival" at the start of summer. Edgewater Park (Bronx), Edgewater Park hosts an annual "Ragamuffin" children's walk in November. There are several events to honor the borough's veterans. Albanian Independence Day is also observed.
There are also parades to celebrate Dominican, Italian, and Irish heritage.
Press and broadcasting
The Bronx is home to several local newspapers and radio and television studios.
Newspapers
The Bronx has several local newspapers, including The Bronx Daily, ''The Bronx News'', ''Parkchester News'', ''City News'', ''The Norwood News'', ''The Riverdale Press'', ''Riverdale Review'', ''The Bronx Times Reporter'', ''Inner City Press'' (which now has more of a focus on national issues) and ''Co-op City Times''. Four non-profit news outlets, ''Norwood News'', ''Mount Hope Monitor'', ''Mott Haven Herald'' and ''The Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point Express'' serve the borough's poorer communities. The editor and co-publisher of ''The Riverdale Press'', Bernard Stein, won the Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Writing for his editorials about Bronx and New York City issues in 1998. (Stein graduated from the Bronx High School of Science in 1959.)
The Bronx once had its own daily newspaper, ''The Bronx Home News'', which started publishing on January 20, 1907, and merged into the ''New York Post'' in 1948. It became a special section of the ''Post'', sold only in the Bronx, and eventually disappeared from view.
Radio and television
One of New York City's major non-commercial radio broadcasters is WFUV, a National Public Radio-affiliated 50,000-watt station broadcasting from Fordham University's Rose Hill campus in the Bronx. The radio station's antenna was relocated to the top an apartment building owned by Montefiore Medical Center, which expanded the reach of the station's signal.
The City of New York has an official television station run by NYC Media and broadcasting from Bronx Community College, and Cablevision operates News 12 Networks, News 12 The Bronx, both of which feature programming based in the Bronx. Co-op City was the first area in the Bronx, and the first in New York beyond Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, to have its own cable television provider. The local public-access television station BronxNet originates from Herbert H. Lehman College, the borough's only four year CUNY school, and provides government-access television (GATV) public affairs programming in addition to programming produced by Bronx residents.
Economy
Shopping malls and markets in the Bronx include:
* Bay Plaza Shopping Center
* Bronx Terminal Market
* Hunts Point Cooperative Market
Shopping districts

 Prominent shopping areas in the Bronx include Fordham Road, Bay Plaza Shopping Center, Bay Plaza in Co-op City, The Hub, Bronx, The Hub, the Riverdale/
Prominent shopping areas in the Bronx include Fordham Road, Bay Plaza Shopping Center, Bay Plaza in Co-op City, The Hub, Bronx, The Hub, the Riverdale/Kingsbridge
Kingsbridge is a market town and tourist hub in the South Hams district of Devon, England, with a population of 6,116 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards bear the name of ''Kingsbridge'' (East & North). Their combined population at the ab ...
shopping center, and Bruckner Boulevard. Shops are also concentrated on streets aligned underneath elevated railroad lines, including Westchester Avenue, White Plains Road, Jerome Avenue
Jerome Avenue is one of the longest thoroughfares in the New York City borough of the Bronx, New York, United States. The road is long and stretches from Concourse to Woodlawn. Both of these termini are with the Major Deegan Expressway which r ...
, Southern Boulevard (Bronx), Southern Boulevard, and Broadway (Bronx), Broadway. The Bronx Terminal Market contains several big-box stores, which opened in 2009 south of Yankee Stadium.
The Bronx has three primary shopping centers: The Hub, Gateway Center and Southern Boulevard. The Hub–Third Avenue Business Improvement District (B.I.D.), in The Hub, Bronx, The Hub, is the retail heart of the South Bronx, where four roads converge: East 149th Street, Willis, Melrose and Third Avenues. It is primarily inside the neighborhood of Melrose, Bronx, Melrose but also lines the northern border of Mott Haven. The Hub has been called "the Broadway of the Bronx", being likened to Broadway (Bronx), the real Broadway in Manhattan and the northwestern Bronx. It is the site of both maximum traffic and architectural density. In configuration, it resembles a miniature Times Square, a spatial "bow-tie" created by the geometry of the street. The Hub is part of Bronx Community Board 1.
The Bronx Terminal Market, in the West Bronx
The West Bronx is a region in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The region lies west of the Bronx River and roughly corresponds to the western half of the borough.
The West Bronx is more densely populated than the East Bronx, and is close ...
, formerly known as Gateway Center, is a shopping center that encompasses less than one million square feet of retail space, built on a site that formerly held a wholesale fruit and vegetable market also named Bronx Terminal Market as well as the former Bronx House of Detention, south of Yankee Stadium. The $500 million shopping center, which was completed in 2009, saw the construction of new buildings and two smaller buildings, one new and the other a renovation of an existing building that was part of the original market. The two main buildings are linked by a six-level garage for 2,600 cars. The center's design has earned it a Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, LEED "Silver" designation.
Government and politics
Local government
Since New York City's consolidation in 1898, the New York City Charter that provides for a "strong" Mayor–council government, mayor–council system has governed the Bronx. The centralized New York City government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services in the Bronx.
The office of Borough President was created in the consolidation of 1898 to balance centralization with local authority. Each borough president had a powerful administrative role derived from having a vote on the New York City Board of Estimate, which was responsible for creating and approving the city's budget and proposals for land use. In 1989 the Supreme Court of the United States declared the Board of Estimate unconstitutional on the grounds that Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, the most populous borough, had no greater effective representation on the Board than Staten Island, the least populous borough, a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fourteenth Amendment's Equal Protection Clause pursuant to the high court's 1964 "one man, one vote" decision.[Cornell Law School Supreme Court Collection: Board of Estimate of City of New York v. Morris](_blank)
accessed June 12, 2006
Since 1990 the Borough President has acted as an advocate for the borough at the mayoral agencies, the New York City Council, City Council, the New York state government, and corporations.
Until March 1, 2009, the Borough President of the Bronx was Adolfo Carrión Jr., elected as a Democratic Party (United States), Democrat in 2001 and 2005 before retiring early to direct the White House Office of Urban Affairs Policy. His successor, Democratic New York State Assembly member Rubén Díaz Jr., Rubén Díaz, Jr. — after winning a special election on April 21, 2009 by a vote of 86.3% (29,420) on the "Bronx Unity" line to 13.3% (4,646) for the Republican district leader Anthony Ribustello on the "People First" line,[Trymaine Lee]
"Bronx Voters Elect Díaz as New Borough President"
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', New York edition, April 22, 2009, page A24, retrieved on May 13, 2009[The Board of Elections in the City of New York]
Bronx Borough President special election results, April 21, 2009
( PDF with details by Assembly District, April 29, 2009), retrieved on May 13, 2009 — became Borough President on May 1, 2009. In 2021, Rubén Díaz's Democratic successor, Vanessa Gibson was elected (to begin serving in 2022) with 79.9% of the vote against 13.4% for Janell King (Republican) and 6.5% for Sammy Ravelo (Conservative).
All of the Bronx's currently elected public officials have first won the nomination of the Democratic Party (U.S.), Democratic Party (in addition to any other endorsements). Local party platforms center on affordable housing, education and economic development. Controversial political issues in the Bronx include environmental issues, the cost of housing, and annexation of parkland for new Yankee Stadium.
Since its separation from New York County on January 1, 1914, the Bronx, has had, like each of the other 61 counties of New York State, its own criminal court system
Bronx votes for Mayor and President
Presidential vote
After becoming a separate county in 1914, the Bronx has supported only two Republican presidential candidates. It voted heavily for the winning Republican Warren G. Harding in 1920 United States presidential election in New York, 1920, but much more narrowly on a split vote for his victorious Republican successor Calvin Coolidge in 1924 United States presidential election in New York, 1924 (Coolidge 79,562; John W. Davis, Dem., 72,834; Robert M. La Follette, Sr., Robert La Follette, 62,202 equally divided between the Progressive Party (United States, 1924), Progressive and Socialist Party of America, Socialist lines).
Since then, the Bronx has always supported the Democratic Party's nominee for president, starting with a vote of 2–1 for the unsuccessful Al Smith in 1928, followed by four 2–1 votes for the successful Franklin D. Roosevelt. (Both had been Governors of New York, but Republican former Gov. Thomas E. Dewey won only 28% of the Bronx's vote in 1948 against 55% for Pres. Harry Truman, the winning Democrat, and 17% for Henry A. Wallace of the Progressive Party (United States, 1948), Progressives. It was only 32 years earlier, by contrast, that another Republican former Governor who narrowly lost the Presidency, Charles Evans Hughes, had won 42.6% of the Bronx's 1916 vote against Democratic President Woodrow Wilson's 49.8% and Socialist candidate Allan Benson's 7.3%.)
Elections for Mayor of New York
The Bronx has often shown striking differences from other boroughs in New York City mayoral elections, elections for Mayor. The only Republican to carry the Bronx since 1914 was Fiorello La Guardia in 1933, 1937 and 1941 (and in the latter two elections, only because his 30% to 32% vote on the American Labor Party line was added to 22% to 23% as a Republican). The Bronx was thus the only borough not carried by the successful Republican re-election campaigns of Mayors Rudolph Giuliani in 1997 and Michael Bloomberg in 2005. The anti-war Socialist Party of America, Socialist campaign of Morris Hillquit in the 1917 New York City mayoral election, 1917 mayoral election won over 31% of the Bronx's vote, putting him second and well ahead of the 20% won by the incumbent pro-war Fusion Mayor John P. Mitchel, who came in second (ahead of Hillquit) everywhere else and outpolled Hillquit citywide by 23.2% to 21.7%.
* Republican and Democratic columns for presidential elections also include their candidates' votes on other lines, such as the New York State Right to Life Party and the Working Families Party.
* For details of votes and parties in a particular election, click the year or see New York City mayoral elections.
Education
Education in the Bronx is provided by a large number of public and private institutions, many of which draw students who live beyond the Bronx. The New York City Department of Education manages the borough's public noncharter schools. In 2000, public schools enrolled nearly 280,000 of the Bronx's residents over 3 years old (out of 333,100 enrolled in all pre-college schools).[QT-P19. School Enrollment: 2000; Data Set: Census 2000 Summary File 3 (SF 3) – Sample Data; Geographic Area: Bronx County, New York](_blank)
United States Census Bureau, retrieved August 22, 2008 There are also several public charter schools. Private schools range from élite independent schools to religiously affiliated parochial schools#United States, schools run by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York and Jewish organizations.
A small portion of land between Pelham and Pelham Bay Park, with 35 houses, is a part of the Bronx, but is cut off from the rest of the borough due to the county boundaries; the New York City government pays for the residents' children to go to Pelham Union Free School District schools, including Pelham Memorial High School, since that is more cost effective than sending school buses to take the students to New York City schools. This arrangement has been in place since 1948.[ ()]
Educational attainment
In 2000, according to the United States Census, out of the nearly 800,000 people in the Bronx who were then at least 25 years old, 62.3% had graduated from high school and 14.6% held a bachelor's or higher college degree. These percentages were lower than those for New York's other boroughs, which ranged from 68.8% (Brooklyn) to 82.6% (Staten Island) for high school graduates over 24, and from 21.8% (Brooklyn) to 49.4% (Manhattan) for college graduates. (The respective state and national percentages were ''[NY]'' 79.1% & 27.4% and ''[US]'' 80.4% & 24.4%.)
High schools
 In the 2000 Census, 79,240 of the nearly 95,000 Bronx residents enrolled in high school attended public schools.
In the 2000 Census, 79,240 of the nearly 95,000 Bronx residents enrolled in high school attended public schools.
Colleges and universities
In 2000, 49,442 (57.5%) of the 86,014 Bronx residents seeking college, graduate or professional degrees attended public institutions.[In September 2008, Fordham University and its neighbor, the Wildlife Conservation Society, a global research organization which operates the ]Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and is the largest metropolitan zoo in ...
, will begin a joint program leading to a Master of Science degree in adolescent science education (biology grades 7–12).
Three campuses of the City University of New York are in the Bronx: Hostos Community College, Bronx Community College (occupying the former University Heights, Bronx, University Heights Campus of New York University) and Herbert H. Lehman College (formerly the uptown campus of Hunter College), which offers both undergraduate and graduate degrees.
The College of Mount Saint Vincent is a Catholic liberal arts college in Riverdale under the direction of the Sisters of Charity of New York. Founded in 1847 as a school for girls, the academy became a degree-granting college in 1911 and began admitting men in 1974. The school serves 1,600 students. Its campus is also home to the Academy for Jewish Religion (New York), Academy for Jewish Religion, a transdenominational rabbinical and cantorial school.
Manhattan College is a Catholic college in Riverdale which offers undergraduate programs in the arts, business, education, engineering, and science. It also offers graduate programs in education and engineering.
Albert Einstein College of Medicine, part of the Montefiore Medical Center, is in Morris Park.
The coeducational and non-sectarian Mercy College (New York), Mercy College—with its main campus in Dobbs Ferry, New York, Dobbs Ferry—has a Bronx campus near Westchester Square, Bronx, Westchester Square.
The State University of New York Maritime College in Fort Schuyler (Throggs Neck)—at the far southeastern tip of the Bronx—is the national leader in maritime education and houses the Maritime Industry Museum. (Directly across Long Island Sound is Kings Point, New York, Kings Point, Long Island, home of the United States Merchant Marine Academy and the American Merchant Marine Museum.) As of 2017, graduates from the university earned an average annual salary of $144,000, the highest of any university graduates in the United States.
In addition, the private, proprietary Monroe College, focused on preparation for business and the professions, started in the Bronx in 1933 and now has a campus in New Rochelle, New York, New Rochelle (Westchester County) as well the Bronx's Fordham, Bronx, Fordham neighborhood.
Transportation
Roads and streets

Surface streets
The Bronx street grid is irregular. Like the northernmost part of upper Manhattan, the West Bronx
The West Bronx is a region in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The region lies west of the Bronx River and roughly corresponds to the western half of the borough.
The West Bronx is more densely populated than the East Bronx, and is close ...
's hilly terrain leaves a relatively free-style street grid. Much of the West Bronx's street numbering carries over from upper Manhattan, but does not match it exactly; East 132nd Street is the lowest numbered street in the Bronx. This dates from the mid-19th century when the southwestern area of Westchester County
Westchester County is located in the U.S. state of New York. It is the seventh most populous county in the State of New York and the most populous north of New York City. According to the 2020 United States Census, the county had a population ...
west of the Bronx River, was incorporated into New York City and known as the Northside.
The East Bronx
The East Bronx is the part of the New York City borough of the Bronx which lies east of the Bronx River; this roughly corresponds to the eastern half of the borough. Neighborhoods include: Baychester, Castle Hill, City Island, Co-op City, ...
is considerably flatter, and the street layout tends to be more regular. Only the Wakefield, Bronx, Wakefield neighborhood picks up the street numbering, albeit at a misalignment due to Tremont Avenue's layout. At the same diagonal latitude, West 262nd Street in Riverdale matches East 237th Street in Wakefield.
Three major north–south thoroughfares run between Manhattan and the Bronx: Third Avenue, Park Avenue, and Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
. Other major north–south roads include the Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse, Jerome Avenue
Jerome Avenue is one of the longest thoroughfares in the New York City borough of the Bronx, New York, United States. The road is long and stretches from Concourse to Woodlawn. Both of these termini are with the Major Deegan Expressway which r ...
, Sedgwick Avenue, Webster Avenue, and White Plains Road. Major east-west thoroughfares include Mosholu Parkway, Gun Hill Road (Bronx), Gun Hill Road, Fordham Road, Pelham Parkway, and Tremont Avenue.
Most east–west streets are prefixed with either ''East'' or ''West'', to indicate on which side of Jerome Avenue they lie (continuing the similar system in Manhattan, which uses Fifth Avenue as the dividing line).
The historic Boston Post Road, part of the long pre-revolutionary road connecting Boston with other northeastern cities, runs east–west in some places, and sometimes northeast–southwest.
Mosholu Parkway, Mosholu and Pelham Parkways, with Bronx Park between them, Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
to the west and Pelham Bay Park
Pelham Bay Park is a municipal park located in the northeast corner of the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is, at , the largest public park in New York City. The park is more than three times the size of Manhattan's Central Park. The pa ...
to the east, are also linked by bridle paths.
As of the 2000 Census, approximately 61.6% of all Bronx households do not have access to a car. Citywide, the percentage of autoless households is 55%.
Highways
Several major limited access highways traverse the Bronx. These include:
* the Bronx River Parkway
* the Bruckner Expressway (Interstate 278, I-278/Interstate 95 in New York, I-95)
* the Cross Bronx Expressway (Interstate 95 in New York, I-95/Interstate 295 (New York), I-295)
* the New England Thruway (Interstate 95 in New York, I-95)
* the Henry Hudson Parkway (New York State Route 9A, NY-9A)
* the Hutchinson River Parkway
* the Major Deegan Expressway (Interstate 87 (New York), I-87)
Bridges and tunnels
 Thirteen bridges and three tunnels connect the Bronx to Manhattan, and three bridges connect the Bronx to
Thirteen bridges and three tunnels connect the Bronx to Manhattan, and three bridges connect the Bronx to Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
. These are, from west to east:
''To Manhattan:'' the Spuyten Duyvil Bridge, the Henry Hudson Bridge, the Broadway Bridge (Manhattan), Broadway Bridge, the University Heights Bridge, the Washington Bridge, the Alexander Hamilton Bridge, the High Bridge (New York City), High Bridge, the Concourse Tunnel, the Macombs Dam Bridge, the 145th Street Bridge, the 149th Street Tunnel, the Madison Avenue Bridge, the Park Avenue Bridge (New York City), Park Avenue Bridge, the Lexington Avenue Tunnel, the Third Avenue Bridge (Manhattan), Third Avenue Bridge (southbound traffic only), and the Willis Avenue Bridge (northbound traffic only).
''To both Manhattan and Queens:'' the Robert F. Kennedy Bridge, formerly known as the Triborough Bridge.
''To Queens:'' the Bronx–Whitestone Bridge and the Throgs Neck Bridge.
Mass transit
 The Bronx is served by seven New York City Subway services along six physical lines, with List of New York City Subway stations in the Bronx, 70 stations in the Bronx:
* IND Concourse Line ()
* IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line ()
* IRT Dyre Avenue Line ()
* IRT Jerome Avenue Line ()
* IRT Pelham Line ()
* IRT White Plains Road Line ()
There are also many MTA Regional Bus Operations bus routes in the Bronx. This includes List of bus routes in the Bronx, local and express routes as well as Bee-Line Bus System routes.
Two Metro-North Railroad commuter rail lines (the Harlem Line and the Hudson Line (Metro-North), Hudson Line) serve 11 stations in the Bronx. (Marble Hill (Metro-North station), Marble Hill, between the Spuyten Duyvil (Metro-North station), Spuyten Duyvil and University Heights (Metro-North station), University Heights stations, is actually in the only part of Manhattan connected to the mainland.) In addition, some trains serving the New Haven Line stop at Fordham (Metro-North station), Fordham Plaza. As part of Penn Station Access, the 2018 MTA budget funded construction of four new stops along the New Haven Line to serve Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point, Parkchester, Bronx, Parkchester, Morris Park, and
The Bronx is served by seven New York City Subway services along six physical lines, with List of New York City Subway stations in the Bronx, 70 stations in the Bronx:
* IND Concourse Line ()
* IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line ()
* IRT Dyre Avenue Line ()
* IRT Jerome Avenue Line ()
* IRT Pelham Line ()
* IRT White Plains Road Line ()
There are also many MTA Regional Bus Operations bus routes in the Bronx. This includes List of bus routes in the Bronx, local and express routes as well as Bee-Line Bus System routes.
Two Metro-North Railroad commuter rail lines (the Harlem Line and the Hudson Line (Metro-North), Hudson Line) serve 11 stations in the Bronx. (Marble Hill (Metro-North station), Marble Hill, between the Spuyten Duyvil (Metro-North station), Spuyten Duyvil and University Heights (Metro-North station), University Heights stations, is actually in the only part of Manhattan connected to the mainland.) In addition, some trains serving the New Haven Line stop at Fordham (Metro-North station), Fordham Plaza. As part of Penn Station Access, the 2018 MTA budget funded construction of four new stops along the New Haven Line to serve Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point, Parkchester, Bronx, Parkchester, Morris Park, and Co-op City
Co-op City (short for Cooperative City) is a cooperative housing development located in the northeast section of the borough of the Bronx in New York City. It is bounded by Interstate 95 to the southwest, west, and north and the Hutchinson River ...
.
In 2018, NYC Ferry's Soundview line opened, connecting the Soundview, Bronx, Soundview landing in Clason Point, Clason Point Park to three East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
locations in Manhattan. On December 28, 2021; the Throgs Neck Ferry landing at Ferry Point Park in Throgs Neck, Bronx, Throgs Neck was opened providing an additional stop on the Soundview line. The ferry is operated by Hornblower Cruises.
In popular culture
Film and television
Mid-20th century
Mid-20th century movies set in the Bronx portrayed densely settled, working-class, urban culture. ''From This Day Forward'' (1946), set in Highbridge, Bronx, Highbridge, occasionally delved into Bronx life. The most notable examinations of working class Bronx life were Paddy Chayefsky's Academy Awards, Academy Award-winning ''Marty (film), Marty'' and his 1956 film ''The Catered Affair.'' Other films that portrayed life in the Bronx are: the 1993 Robert De Niro/Chazz Palminteri film, ''A Bronx Tale'', Spike Lee's 1999 movie ''Summer of Sam'', which focused on an Italian-American Bronx community in the 1970's, 1994's ''I Like It Like That (film), I Like It Like That'' which takes place in the predominantly Puerto Rican people, Puerto Rican neighborhood of the South Bronx, and ''Doughboys'', the story of two Italian-American brothers in danger of losing their bakery thanks to one brother's gambling debts.
The Bronx's gritty urban life had worked its way into the movies even earlier, with depictions of the "Bronx cheer (gesture), Bronx cheer", a loud flatulent-like sound of disapproval, allegedly first made by New York Yankees fans. The sound can be heard, for example, on the Spike Jones and His City Slickers recording of "Der Fuehrer's Face" (from the 1942 Disney animated film of the Der Fuehrer's Face, same name), repeatedly lambasting Adolf Hitler with: "We'll Heil! (Bronx cheer) Heil! (Bronx cheer) Right in Der Fuehrer's Face!"
Symbolism
Starting in the 1970s, the Bronx often symbolized violence, decay, and urban ruin. The wave of arson in the South Bronx in the 1960s and 1970s inspired the observation that "The Bronx is burning": in 1974 it was the title of both a ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' editorial and a BBC documentary film. The line entered the pop-consciousness with Game Two of the 1977 World Series, when a fire broke out near Yankee Stadium (1923), Yankee Stadium as the team was playing the Los Angeles Dodgers. Many fires had broken out in the Bronx before this fire. As the fire was captured on live television, announcer Howard Cosell The Bronx Is Burning#Summary, is wrongly remembered to have said something like, "There it is, ladies and gentlemen: the Bronx is burning". Historians of New York City often point to Cosell's remark as an acknowledgement of both the city and the borough's decline. A new feature-length documentary film by Edwin Pagan called ''Bronx Burning'' is in production in 2006, chronicling what led up to the many arson-for-insurance fraud fires of the 1970s in the borough.
Bronx gang life was depicted in the 1974 novel ''The Wanderers'' by Bronx native Richard Price (writer), Richard Price and the The Wanderers (1979 film), 1979 movie of the same name. They are set in the heart of the Bronx, showing apartment life and the then-landmark Krums ice cream parlor. In the 1979 film ''The Warriors (film), The Warriors'', the eponymous gang go to a meeting in Van Cortlandt Park
Van Cortlandt Park is a park located in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. Owned by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, it is managed with assistance from the Van Cortlandt Park Alliance. The park, the city's third-lar ...
in the Bronx, and have to fight their way out of the borough and get back to Coney Island in Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
. ''A Bronx Tale'' (1993) depicts gang activities in the Belmont, Bronx, Belmont "Little Italy" section of the Bronx. The 2005 video game adaptation features levels called Pelham, Tremont, and "Gunhill" (a play off the name Gun Hill Road (Bronx), Gun Hill Road). This theme lends itself to the title of ''The Bronx Is Burning'', an eight-part ESPN TV mini-series (2007) about the New York Yankees' drive to winning baseball's 1977 World Series. The TV series emphasizes the team's boisterous nature, led by manager Billy Martin, catcher Thurman Munson and outfielder Reggie Jackson, as well as the malaise of the Bronx and New York City in general during that time, such as the blackout, the city's serious financial woes and near bankruptcy, the arson for insurance payments, and the election of Ed Koch as mayor.
The 1981 film ''Fort Apache, The Bronx'' is another film that used the Bronx's gritty image for its storyline. The movie's title is from the nickname for the 41st Police Precinct in the South Bronx which was nicknamed "Fort Apache". Also from 1981 is the horror film ''Wolfen (film), Wolfen'' making use of the rubble of the Bronx as a home for werewolf type creatures. ''Knights of the South Bronx'', a true story of a teacher who worked with disadvantaged children, is another film also set in the Bronx released in 2005. The Bronx was the setting for the 1983 film ''Fuga dal Bronx'', also known as ''Bronx Warriors 2'' and ''Escape 2000'', an Italian B-movie best known for its appearance on the television series ''Mystery Science Theater 3000''. The plot revolves around a sinister construction corporation's plans to depopulate, destroy and redevelop the Bronx, and a band of rebels who are out to expose the corporation's murderous ways and save their homes. The film is memorable for its almost incessant use of the phrase, "Leave the Bronx!" Many of the movie's scenes were filmed in Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, substituting as the Bronx. ''Rumble in the Bronx'', filmed in Vancouver, was a 1995 Jackie Chan kung-fu film, another which popularized the Bronx to international audiences. ''Last Bronx'', a 1996 Sega game played on the bad reputation of the Bronx to lend its name to an alternate version of post-Japanese bubble Tokyo, where crime and gang warfare is rampant.
Literature
Books
The Bronx has been featured significantly in fiction literature. All of the characters in Herman Wouk's City Boy: The Adventures of Herbie Bookbinder (1948) live in the Bronx, and about half of the action is set there. Kate Simon's ''Bronx Primitive: Portraits of a Childhood'' (1982) is directly autobiographical, a warm account of a Polish-Jewish girl in an immigrant family growing up before World War II, and living near Arthur Avenue and Tremont Avenue. In Jacob M. Appel's short story, "The Grand Concourse" (2007), a woman who grew up in the iconic Lewis Morris Building returns to the Morrisania neighborhood with her adult daughter. Similarly, in Avery Corman's book ''The Old Neighborhood'' (1980), an upper-middle class white protagonist returns to his birth neighborhood (Fordham Road and the Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse), and learns that even though the folks are poor, Hispanic and African-American, they are good people.
By contrast, Tom Wolfe's ''The Bonfire of the Vanities, Bonfire of the Vanities'' (1987) portrays a wealthy, white protagonist, Sherman McCoy, getting lost off the Bruckner Expressway in the South Bronx and having an altercation with locals. A substantial piece of the last part of the book is set in the resulting riotous trial at the Bronx County Courthouse. However, times change, and in 2007, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' reported that "the Bronx neighborhoods near the site of Sherman's accident are now dotted with townhouses and apartments." In the same article, the Reverend Al Sharpton (whose fictional analogue in the novel is "Reverend Bacon") asserts that "twenty years later, the cynicism of ''The Bonfire of the Vanities'' is as out of style as Tom Wolfe's wardrobe."
Don DeLillo's ''Underworld (DeLillo novel), Underworld'' (1997) is also set in the Bronx and offers a perspective on the area from the 1950s onward.
Poetry
In poetry, the Bronx has been immortalized by one of the world's shortest couplets:
The Bronx
No Thonx
: Ogden Nash, ''The New Yorker'', 1931
Nash repented 33 years after his calumny, penning in 1964 the following prose poem to the Dean of Bronx Community College:
I can't seem to escape
the sins of my smart-alec youth;
Here are my amends.
I wrote those lines, "The Bronx?
No thonx";
I shudder to confess them.
Now I'm an older, wiser man
I cry, "The Bronx?
God bless them!"
Bronx Memoir Project
''Bronx Memoir Project: Vol. 1'' is a published anthology by the Bronx Council on the Arts and brought forth through a series of workshops meant to empower Bronx residents and shed the stigma on the Bronx's burning past.
Songs
* "Jenny from the Block" (2002) byJennifer Lopez, from the album ''This Is Me... Then, This is me...Then'' is specifically about the South Bronx, where Lopez grew up.
* In Marc Ferris's 5-page, 15-column list of "Songs and Compositions Inspired by New York City" in ''The Encyclopedia of New York City'' (1995), only a handful refer to the Bronx; most refer to New York City proper, especially Manhattan and Brooklyn. Ferris's extensive but selective 1995 list mentions only four songs referring specifically to the Bronx: "On the Banks of the Bronx" (1919), by William LeBaron & Victor Jacobi; "Bronx Express" (1922), by Henry Creamer, Ossip Dymow & Turner Layton; "The Tremont Avenue Cruisewear Fashion Show" (1973), by Jerry Livingston & Mark David; and "I Love the New York Yankees" (1987), by Paula Lindstrom.
Theater
Clifford Odets’s play Awake and Sing!, Awake and Sing is set in 1933 in the Bronx. The play, first produced at the Belasco Theater in 1935, concerns a poor family living in small quarters, the struggles of the controlling parents and the aspirations of their children.
René Marqués La Carreta, The Oxcart (1959), concerns a rural Puerto Rican family who immigrate to the Bronx for a better life.
A Bronx Tale (play), A Bronx Tale is an autobiographical one-man show written and performed by Chazz Palminteri. It is a coming-of-age story set in the Bronx. It premiered in Los Angeles in the 1980s and then played on Off-Broadway. After a film version involving Palminteri and Robert DeNiro, Palminteri performed his one-man show on Broadway and on tour in 2007.
See also
* Bronx Borough Hall
* Bronx court system delays
* List of counties in New York
* List of people from the Bronx
* National Register of Historic Places listings in the Bronx
* Wildlife in the Bronx
References
Notes
Citations
Further reading
General
*
* Briggs, Xavier de Souza, Anita Miller and John Shapiro. 1996. "CCRP in the South Bronx." Planners' Casebook, Winter.
* Corman, Avery. "My Old Neighborhood Remembered, A Memoir." Barricade Books (2014)
* Chronopoulos, Themis. "Paddy Chayefsky's 'Marty' and Its Significance to the Social History of Arthur Avenue, The Bronx, in the 1950s." The Bronx County Historical Society Journal XLIV (Spring/Fall 2007): 50–59.
* Chronopoulos, Themis. "Urban Decline and the Withdrawal of New York University from University Heights, The Bronx." The Bronx County Historical Society Journal XLVI (Spring/Fall 2009): 4–24.
* de Kadt, Maarten. ''The Bronx River: An Environmental and Social History.'' The History Press (2011)
* DiBrino, Nicholas. ''The History of the Morris Park Racecourse and the Morris Family'' (1977)
* Jackson, Kenneth T., ed. ''The Encyclopedia of New York City'', (Yale University Press and the New-York Historical Society, (1995) ), has entries, maps, illustrations, statistics and bibliographic references on almost all of the significant topics in this article, from the entire borough to individual neighborhoods, people, events and artistic works.
* McNamara, John ''History In Asphalt: The Origin of Bronx Street and Place Names'' (1993)
* McNamara, John ''McNamara's Old Bronx'' (1989)
* Twomey, Bill and Casey, Thomas ''Images of America Series: Northwest Bronx'' (2011)
* Twomey, Bill and McNamara, John. ''Throggs Neck Memories'' (1993)
* Twomey, Bill and McNamara, John. ''Images of America Series: Throggs Neck-Pelham Bay'' (1998)
* Twomey, Bill and Moussot, Peter. ''Throggs Neck'' (1983), pictorial
* Twomey, Bill. ''Images of America Series: East Bronx'' (1999)
* Twomey, Bill. ''Images of America Series: South Bronx'' (2002)
* Twomey, Bill. ''The Bronx in Bits and Pieces'' (2007)
Bronx history
* Barrows, Edward, and Mike Wallace. ''Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898'' (1999)
*
* Federal Writers' Project. ''New York City Guide: A Comprehensive Guide to the Five Boroughs of the Metropolis: Manhattan, Brooklyn, the Bronx, Queens, and Richmond'' (1939
online edition
* Fitzpatrick Benedict. ''The Bronx and Its People; A History 1609–1927'' (The Lewis Historical Publishing Company, 1927. 3 volumes), Narrative history plus many biographies of prominent citizens
* Gonzalez, Evelyn. ''The Bronx''. (Columbia University Press, 2004. 263 ), scholarly history focused on the slums of the South Bron
online edition
* Goodman, Sam. "The Golden Ghetto: The Grand Concourse in the Twentieth Century", ''Bronx County Historical Society Journal'' 2004 41(1): 4–18 and 2005 42(2): 80–99
* Greene, Anthony C., "The Black Bronx: A Look at the Foundation of the Bronx's Black Communities until 1900", ''Bronx County Historical Society Journal'', 44 (Spring–Fall 2007), 1–18.
* Jackson, Kenneth T., ed. ''The Encyclopedia of New York City'', (Yale University Press and the New-York Historical Society, (1995) ), has entries, maps, illustrations, statistics and bibliographic references on almost all of the significant topics in this article, from the entire borough to individual neighborhoods, people, events and artistic works.
* Jonnes, Jull. ''South Bronx Rising: The Rise, Fall, and Resurrection of an American City'' (2002
online edition
by David Gonzalez (journalist), David Gonzales, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', published and retrieved on September 19, 2008
*
*
*
*
* Rodríguez, Clara E. ''Puerto Ricans: Born in the U.S.A'' (1991
online edition
* Samtur, Stephen M. and Martin A. Jackson. ''The Bronx: Lost, Found, and Remembered, 1935–1975'' (1999
online review
nostalgia
* Lloyd Ultan (historian), Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Northern Borough: A History Of The Bronx'' (2009), popular general history
* Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Bronx in the frontier era: from the beginning to 1696'' (1994)
* Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Beautiful Bronx (1920–1950)'' (1979), heavily illustrated
* Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Birth of the Bronx, 1609–1900'' (2000), popular
* Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Bronx in the innocent years, 1890–1925'' (1985), popular
* Ultan, Lloyd. ''The Bronx: It Was Only Yesterday, "The Bronx: It Was Only Yesterday 1935–1965'' (1992), heavily illustrated popular history
External links
Bronx Borough President's Office
*
Newspapers
The Bronx Times Reporter
The Bronx Daily
The Hunts Point Express
The Mott Haven Herald
Norwood News
The Riverdale Press
Associations
The Bronx River Alliance
Bronx Council for Environmental Quality
Throggs Neck Merchant Association
The Bronx Market
The South Bronx Overall Economic Development Corporation
Bronx County, NY Website
History
City Island Nautical Museum
East Bronx History Forum
Museum of Bronx History
The Bronx County Historical Society
The Bronx: A Swedish Connection
Report of the Bronx Parkway Commission, December 31, 1918
retrieved on July 24, 2008
Remembrance of Synagogues Past: The Lost Civilization of the Jewish South Bronx
by Seymour Perlin, retrieved on August 10, 2008
Forgotten New York: Relics of a Rich History in the Everyday Life of New York City
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bronx, The
The Bronx,
Boroughs of New York City
County seats in New York (state)
Populated coastal places in New York (state)
Populated places established in 1898
1898 establishments in New York City
Majority-minority counties in New York
Hispanic and Latino American culture in New York (state)
 The Bronx was called ' by the native
The Bronx was called ' by the native 
 The Bronx was a mostly rural area for many generations, with small farms supplying the city markets. In the late 19th century, however, it grew into a railroad suburb. Faster transportation enabled rapid population growth in the late 19th century, involving the move from horse-drawn street cars to elevated railways and the subway system, which linked to Manhattan in 1904.Olmsted (1989); Olmsted (1998)
The South Bronx was a manufacturing center for many years and was noted as a center of
The Bronx was a mostly rural area for many generations, with small farms supplying the city markets. In the late 19th century, however, it grew into a railroad suburb. Faster transportation enabled rapid population growth in the late 19th century, involving the move from horse-drawn street cars to elevated railways and the subway system, which linked to Manhattan in 1904.Olmsted (1989); Olmsted (1998)
The South Bronx was a manufacturing center for many years and was noted as a center of  In 1997, the Bronx was designated an ''All America City'' by the National Civic League, acknowledging its comeback from the decline of the mid-century. In 2006, ''
In 1997, the Bronx was designated an ''All America City'' by the National Civic League, acknowledging its comeback from the decline of the mid-century. In 2006, ''

 Although Bronx County was the third most densely populated county in the United States as of 2006 (after
Although Bronx County was the third most densely populated county in the United States as of 2006 (after  East of the
East of the  (Bronx Community Board 10, Bronx Community District 10)
City Island is east of
(Bronx Community Board 10, Bronx Community District 10)
City Island is east of 
 Author Edgar Allan Poe spent the last years of his life (1846 to 1849) in the Bronx at Poe Cottage, now at
Author Edgar Allan Poe spent the last years of his life (1846 to 1849) in the Bronx at Poe Cottage, now at 
 Prominent shopping areas in the Bronx include Fordham Road, Bay Plaza Shopping Center, Bay Plaza in Co-op City, The Hub, Bronx, The Hub, the Riverdale/
Prominent shopping areas in the Bronx include Fordham Road, Bay Plaza Shopping Center, Bay Plaza in Co-op City, The Hub, Bronx, The Hub, the Riverdale/ In the 2000 Census, 79,240 of the nearly 95,000 Bronx residents enrolled in high school attended public schools.
Many public High school (North America), high schools are in the borough including the elite Bronx High School of Science, Celia Cruz Bronx High School of Music, DeWitt Clinton High School, High School for Violin and Dance, Bronx Leadership Academy 2, Bronx International High School, the School for Excellence, the Morris Academy for Collaborative Study, Wings Academy for young adults, The Bronx School for Law, Government and Justice, Validus Preparatory Academy, The Eagle Academy For Young Men, Bronx Expeditionary Learning High School, Bronx Academy of Letters, Herbert H. Lehman High School and High School of American Studies at Lehman College, High School of American Studies. The Bronx is also home to three of New York City's most prestigious private, secular schools: Ethical Culture Fieldston School, Fieldston, Horace Mann School, Horace Mann, and Riverdale Country School.
High schools linked to the Catholic Church include: St. Raymond Academy, Saint Raymond's Academy for Girls, All Hallows High School, Fordham Preparatory School, Monsignor Scanlan High School, St. Raymond High School for Boys, Cardinal Hayes High School, Cardinal Spellman High School (New York City), Cardinal Spellman High School, Academy of Mount St. Ursula High School, The Academy of Mount Saint Ursula, Aquinas High School (New York City), Aquinas High School, Preston High School (New York City), Preston High School, St. Catharine Academy, Mount Saint Michael Academy, and St. Barnabas High School.
The SAR Academy and SAR High School are Modern Orthodox Jewish Yeshiva coeducational day schools in Riverdale, with roots in Manhattan's Lower East Side.
In the 1990s, New York City began closing the large, public high schools in the Bronx and replacing them with small high schools. Among the reasons cited for the changes were poor graduation rates and concerns about safety. Schools that have been closed or reduced in size include John F. Kennedy High School (Bronx, New York), John F. Kennedy, James Monroe High School (New York), James Monroe, William Howard Taft High School (New York City), Taft, Theodore Roosevelt High School (New York City), Theodore Roosevelt, Adlai E. Stevenson High School (New York City), Adlai Stevenson, Evander Childs High School, Evander Childs, Christopher Columbus High School (Bronx, New York), Christopher Columbus, Morris High School (Bronx, New York), Morris, Walton High School (New York City), Walton, and South Bronx High Schools.
In the 2000 Census, 79,240 of the nearly 95,000 Bronx residents enrolled in high school attended public schools.
Many public High school (North America), high schools are in the borough including the elite Bronx High School of Science, Celia Cruz Bronx High School of Music, DeWitt Clinton High School, High School for Violin and Dance, Bronx Leadership Academy 2, Bronx International High School, the School for Excellence, the Morris Academy for Collaborative Study, Wings Academy for young adults, The Bronx School for Law, Government and Justice, Validus Preparatory Academy, The Eagle Academy For Young Men, Bronx Expeditionary Learning High School, Bronx Academy of Letters, Herbert H. Lehman High School and High School of American Studies at Lehman College, High School of American Studies. The Bronx is also home to three of New York City's most prestigious private, secular schools: Ethical Culture Fieldston School, Fieldston, Horace Mann School, Horace Mann, and Riverdale Country School.
High schools linked to the Catholic Church include: St. Raymond Academy, Saint Raymond's Academy for Girls, All Hallows High School, Fordham Preparatory School, Monsignor Scanlan High School, St. Raymond High School for Boys, Cardinal Hayes High School, Cardinal Spellman High School (New York City), Cardinal Spellman High School, Academy of Mount St. Ursula High School, The Academy of Mount Saint Ursula, Aquinas High School (New York City), Aquinas High School, Preston High School (New York City), Preston High School, St. Catharine Academy, Mount Saint Michael Academy, and St. Barnabas High School.
The SAR Academy and SAR High School are Modern Orthodox Jewish Yeshiva coeducational day schools in Riverdale, with roots in Manhattan's Lower East Side.
In the 1990s, New York City began closing the large, public high schools in the Bronx and replacing them with small high schools. Among the reasons cited for the changes were poor graduation rates and concerns about safety. Schools that have been closed or reduced in size include John F. Kennedy High School (Bronx, New York), John F. Kennedy, James Monroe High School (New York), James Monroe, William Howard Taft High School (New York City), Taft, Theodore Roosevelt High School (New York City), Theodore Roosevelt, Adlai E. Stevenson High School (New York City), Adlai Stevenson, Evander Childs High School, Evander Childs, Christopher Columbus High School (Bronx, New York), Christopher Columbus, Morris High School (Bronx, New York), Morris, Walton High School (New York City), Walton, and South Bronx High Schools.

 Thirteen bridges and three tunnels connect the Bronx to Manhattan, and three bridges connect the Bronx to
Thirteen bridges and three tunnels connect the Bronx to Manhattan, and three bridges connect the Bronx to 
 The Bronx is served by seven New York City Subway services along six physical lines, with List of New York City Subway stations in the Bronx, 70 stations in the Bronx:
* IND Concourse Line ()
* IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line ()
* IRT Dyre Avenue Line ()
* IRT Jerome Avenue Line ()
* IRT Pelham Line ()
* IRT White Plains Road Line ()
There are also many MTA Regional Bus Operations bus routes in the Bronx. This includes List of bus routes in the Bronx, local and express routes as well as Bee-Line Bus System routes.
Two Metro-North Railroad commuter rail lines (the Harlem Line and the Hudson Line (Metro-North), Hudson Line) serve 11 stations in the Bronx. (Marble Hill (Metro-North station), Marble Hill, between the Spuyten Duyvil (Metro-North station), Spuyten Duyvil and University Heights (Metro-North station), University Heights stations, is actually in the only part of Manhattan connected to the mainland.) In addition, some trains serving the New Haven Line stop at Fordham (Metro-North station), Fordham Plaza. As part of Penn Station Access, the 2018 MTA budget funded construction of four new stops along the New Haven Line to serve Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point, Parkchester, Bronx, Parkchester, Morris Park, and
The Bronx is served by seven New York City Subway services along six physical lines, with List of New York City Subway stations in the Bronx, 70 stations in the Bronx:
* IND Concourse Line ()
* IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line ()
* IRT Dyre Avenue Line ()
* IRT Jerome Avenue Line ()
* IRT Pelham Line ()
* IRT White Plains Road Line ()
There are also many MTA Regional Bus Operations bus routes in the Bronx. This includes List of bus routes in the Bronx, local and express routes as well as Bee-Line Bus System routes.
Two Metro-North Railroad commuter rail lines (the Harlem Line and the Hudson Line (Metro-North), Hudson Line) serve 11 stations in the Bronx. (Marble Hill (Metro-North station), Marble Hill, between the Spuyten Duyvil (Metro-North station), Spuyten Duyvil and University Heights (Metro-North station), University Heights stations, is actually in the only part of Manhattan connected to the mainland.) In addition, some trains serving the New Haven Line stop at Fordham (Metro-North station), Fordham Plaza. As part of Penn Station Access, the 2018 MTA budget funded construction of four new stops along the New Haven Line to serve Hunts Point, Bronx, Hunts Point, Parkchester, Bronx, Parkchester, Morris Park, and