Badgers carrying Paul Bunyan's Axe.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family
 Badgers have been trapped commercially for their pelts, which have been used for centuries to make
Badgers have been trapped commercially for their pelts, which have been used for centuries to make
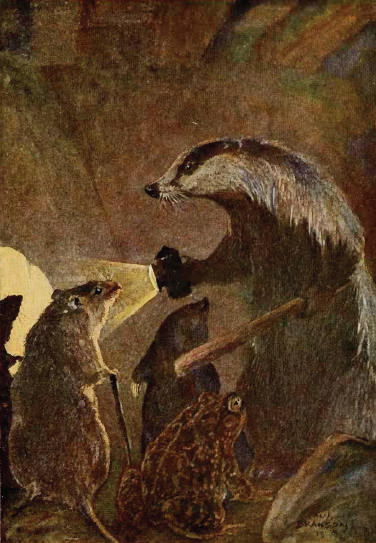 In Europe during the medieval period, accounts of badgers in bestiaries described badgers as working together to dig holes under mountains. They were said to lie down at the entrance of the hole holding a stick in their mouths, while other badgers piled dirt on their bellies. Two badgers would then take hold of the stick in the badger's mouth, and drag the animal loaded with dirt away, almost in the fashion of a wagon. The moralizing component of Bestiaries often took precedence over their function as natural history texts, and this description of badgers most likely reflects an allegorical exemplar rather than what everyday people in the Middle Ages might or might not have believed about how badgers behave in the wild.
The 19th-century poem "The Badger" by
In Europe during the medieval period, accounts of badgers in bestiaries described badgers as working together to dig holes under mountains. They were said to lie down at the entrance of the hole holding a stick in their mouths, while other badgers piled dirt on their bellies. Two badgers would then take hold of the stick in the badger's mouth, and drag the animal loaded with dirt away, almost in the fashion of a wagon. The moralizing component of Bestiaries often took precedence over their function as natural history texts, and this description of badgers most likely reflects an allegorical exemplar rather than what everyday people in the Middle Ages might or might not have believed about how badgers behave in the wild.
The 19th-century poem "The Badger" by
Badgerland – The Definitive On-Line Guide to Badgers in the UK
Durham County Badger Group
Badger Facts
www.ontariobadgers.org – Information about American Badgers
YouTube video of examples of Badger scratching trees
* {{Authority control Mammal common names Paraphyletic groups
Mustelidae
The Mustelidae (; from Latin ''mustela'', weasel) are a family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, ferrets, martens, minks and wolverines, among others. Mustelids () are a diverse group and form the largest family in th ...
(which also includes the otters, wolverine
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscul ...
s, martens, minks, polecat
Polecat is a common name for several mustelid species in the order Carnivora and subfamilies Ictonychinae and Mustelinae. Polecats do not form a single taxonomic rank (i.e. clade). The name is applied to several species with broad similarities ...
s, weasel
Weasels are mammals of the genus ''Mustela'' of the family Mustelidae. The genus ''Mustela'' includes the least weasels, polecats, stoats, ferrets and European mink. Members of this genus are small, active predators, with long and slender b ...
s, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of conver ...
rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by their squat bodies and adaptions for fossorial activity. All belong to the caniform
Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs (wolves, foxes, etc.), bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia (seals, walruses and sea lions) are also assigned to this group. ...
suborder of carnivoran
Carnivora is a monophyletic order of placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all cat-like and dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are formally referred to as carnivorans, ...
mammals.
The fifteen species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of mustelid badgers are grouped in four subfamilies: four species of Melinae (genera ''Meles'' and ''Arctonyx'') including the European badger
The European badger (''Meles meles''), also known as the Eurasian badger, is a badger species in the family Mustelidae native to almost all of Europe. It is classified as least concern on the IUCN Red List as it has a wide range and a large stab ...
, five species of Helictidinae (genus ''Melogale'') or ferret-badger
Ferret-badgers are the six species of the genus ''Melogale'', which is the only genus of the monotypic mustelid subfamily Helictidinae.
* Bornean ferret-badger (''Melogale everetti'')
* Chinese ferret-badger (''Melogale moschata'')
*Formosan fer ...
, the honey badger
The honey badger (''Mellivora capensis''), also known as the ratel ( or ), is a mammal widely distributed in Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Because of its wide range and occurrence in a variety of habitats, it is liste ...
or ratel Mellivorinae (genus ''Mellivora''), and the American badger
The American badger (''Taxidea taxus'') is a North American badger similar in appearance to the European badger, although not closely related. It is found in the western, central, and northeastern United States, northern Mexico, and south-cent ...
Taxideinae (genus ''Taxidae''). Badgers include the most basal mustelids; the American badger is the most basal of all, followed successively by the ratel and the Melinae; the estimated split dates are about 17.8, 15.5 and 14.8 million years ago, respectively.
The two species of Asiatic stink badgers of the genus ''Mydaus'' were formerly included within Melinae (and thus Mustelidae), but more recent genetic evidence indicates these are actually members of the skunk family (Mephitidae).
Badger mandibular condyle
The condyloid process or condylar process is the process on the human and other mammalian species' mandibles that ends in a condyle, the mandibular condyle. It is thicker than the coronoid process of the mandible and consists of two portions: the ...
s connect to long cavities in their skulls, which gives resistance to jaw dislocation and increases their bite grip strength. This in turn limits jaw movement to hinging open and shut, or sliding from side to side, but it does not hamper the twisting movement possible for the jaws of most mammals.
Badgers have rather short, wide bodies, with short legs for digging. They have elongated, weasel-like heads with small ears. Their tails vary in length depending on species; the stink badger has a very short tail, while the ferret-badger's tail can be long, depending on age. They have black faces with distinctive white markings, grey bodies with a light-coloured stripe from head to tail, and dark legs with light-coloured underbellies. They grow to around in length including tail.
The European badger is one of the largest; the American badger, the hog badger, and the honey badger are generally a little smaller and lighter. Stink badgers are smaller still, and ferret-badgers are the smallest of all. They weigh around , while some Eurasian badgers weigh around .
Etymology
The word "badger", originally applied to theEuropean badger
The European badger (''Meles meles''), also known as the Eurasian badger, is a badger species in the family Mustelidae native to almost all of Europe. It is classified as least concern on the IUCN Red List as it has a wide range and a large stab ...
(''Meles meles''), comes from earlier ''bageard'' (16th century), presumably referring to the white mark borne like a badge on its forehead. Similarly, a now archaic synonym was ''bauson'' 'badger' (1375), a variant of ''bausond'' 'striped, piebald', from Old French ''bausant'', ''baucent'' 'id.'.
The less common name ''brock'' (Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
: ''brocc''), ( Scots: ''brock'') is a Celtic loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
(cf. Gaelic ''broc'' and Welsh ''broch'', from Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celti ...
''*brokkos'') meaning "grey". The Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
term was ''*þahsuz'' (cf. German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
''Dachs'', Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
''das'', Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
svin''toks''; Early Modern English
Early Modern English or Early New English (sometimes abbreviated EModE, EMnE, or ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle E ...
''dasse''), probably from the PIE root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
''*tek'-'' "to construct," so the badger would have been named after its digging of sett
A sett or set is a badger's den. It usually consists of a network of tunnels and numerous entrances. The largest setts are spacious enough to accommodate 15 or more animals with up to of tunnels and as many as 40 openings. Such elaborate setts ...
s (tunnels); the Germanic term ''*þahsuz'' became ''taxus'' or ''taxō'', -''ōnis'' in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
glosses, replacing ''mēlēs'' (" marten" or "badger"), and from these words the common Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
terms for the animal evolved (Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
''tasso'', French ''taisson''—''blaireau'' is now more common—Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
''toixó'', Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
''tejón'', Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
''texugo'').
A male European badger is a boar, a female is a sow, and a young badger is a cub. However, in North America the young are usually called kits, while the terms male and female are generally used for adults. A collective name suggested for a group of colonial badgers is a cete, but badger colonies are more often called clans. A badger's home is called a sett.
Classification
The following list shows where the various species with the common name of badger are placed in the Mustelidae and Mephitidae classifications. The list ispolyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of conver ...
and the species commonly called badgers do not form a valid clade.
* Family Mustelidae
The Mustelidae (; from Latin ''mustela'', weasel) are a family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, ferrets, martens, minks and wolverines, among others. Mustelids () are a diverse group and form the largest family in th ...
** Subfamily Melinae
*** Genus ''Arctonyx
Hog badgers are three species of mustelid in the genus ''Arctonyx''. They represent one of the two genera in the subfamily Melinae, alongside the true badgers (genus '' Meles'').
Taxonomy
''Arctonyx'' was formerly considered a monotypic genus ...
''
**** Northern hog badger
The northern hog badger (''Arctonyx albogularis'') is a species of mustelid native to South and East Asia.
Taxonomy
It was formerly considered a subspecies of the greater hog badger (''A. collaris'') when ''A. collaris'' was considered the on ...
, ''Arctonyx albogularis''
****Greater hog badger
The greater hog badger (''Arctonyx collaris'') is a very large terrestrial mustelid native to Southeast Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species because the global population is thought to be declining due to h ...
, ''Arctonyx collaris''
****Sumatran hog badger
The Sumatran hog badger (''Arctonyx hoevenii'') is a species of Mustelidae, mustelid Endemism, endemic to the island of Sumatra in Indonesia.
Taxonomy
It was formerly considered a subspecies of the greater hog badger (''A. collaris''), when it ...
, ''Arctonyx hoevenii''
*** Genus '' Meles''
**** Japanese badger
The Japanese badger (''Meles anakuma'') is a species of carnivoran of the family Mustelidae, the weasels and their kin. Endemic to Japan, it is found on Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku, and Shōdoshima. It shares the genus '' Meles'' with its close re ...
, ''Meles anakuma''
**** Asian badger
The Asian badger (''Meles leucurus''), also known as the sand badger, is a species of badger native to Mongolia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Korean Peninsula and Russia.
Characteristics
The Asian badger is mostly lighter in colour than ...
, ''Meles leucurus''
**** European badger
The European badger (''Meles meles''), also known as the Eurasian badger, is a badger species in the family Mustelidae native to almost all of Europe. It is classified as least concern on the IUCN Red List as it has a wide range and a large stab ...
, ''Meles meles''
****Caucasian badger
The Caucasian badger (''Meles canescens'') or Southwest Asian badger is a species of badger native to Western Asia and some islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
Taxonomy
The Caucasian badger was formerly thought to be a subspecies of the European ...
, ''Meles canescens''
** Subfamily Helictidinae
*** Genus '' Melogale''
**** Burmese ferret-badger, ''Melogale personata''
**** Javan ferret-badger
The Javan ferret-badger (''Melogale orientalis'') is a mustelid endemic to Java and Bali, Indonesia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List and occurs from at least elevation in or close to forested areas.
Description
An adult Javan ...
, ''Melogale orientalis''
**** Chinese ferret-badger
The Chinese ferret-badger (''Melogale moschata''), also known as the small-toothed ferret-badger is a member of the Mustelidae, and widely distributed in Southeast Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List and considered tolerant ...
, ''Melogale moschata''
****Formosan ferret-badger
The Formosan ferret-badger (''Melogale subaurantiaca'') is a mustelid species endemic to Taiwan.
Taxonomy
It was formerly thought to be conspecific with the Chinese ferret-badger (''M. moschata''), but a 2019 genetic study found it to represent ...
, ''Melogale subaurantiaca''
**** Bornean ferret-badger
The Bornean ferret badger (''Melogale everetti''), also known as Everett's ferret badger or the Kinabalu ferret badger, is a small, nocturnal and omnivorous mammal that is endemic to the island of Borneo. It is a member of the family Mustelidae a ...
, ''Melogale everetti''
**** Vietnam ferret-badger
The Vietnam ferret-badger (''Melogale cucphuongensis'') is a member of the family Mustelidae native to Vietnam. It was described in 2011 and is known from only two specimens.
Taxonomy
The Vietnam ferret-badger is a member of the genus '' Melogal ...
, ''Melogale cucphuongensis''
** Subfamily Mellivorinae
*** Honey badger
The honey badger (''Mellivora capensis''), also known as the ratel ( or ), is a mammal widely distributed in Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Because of its wide range and occurrence in a variety of habitats, it is liste ...
, ''Mellivora capensis''
** Subfamily Taxidiinae:
*** †'' Chamitataxus avitus''
*** †''Pliotaxidea nevadensis''
*** †''Pliotaxidea garberi''
*** American badger
The American badger (''Taxidea taxus'') is a North American badger similar in appearance to the European badger, although not closely related. It is found in the western, central, and northeastern United States, northern Mexico, and south-cent ...
, ''Taxidea taxus''
* Family Mephitidae
Mephitidae is a family of mammals comprising the skunks and stink badgers. They are noted for the great development of their anal scent glands, which they use to deter predators. Skunks were formerly classified as a subfamily of the Mustelidae ...
** Subfamily Mydainae
*** Genus ''Mydaus
Stink badgers, also known as false badgers are a genus (''Mydaus'') of the skunk family of carnivorans, the Mephitidae. They resemble the better-known members of the family Mustelidae also termed 'badgers' (which are themselves a polyphyletic g ...
''
**** Indonesian or Sunda stink badger
The Sunda stink badger (''Mydaus javanensis''), also called the Javan stink badger, teledu, Malay stink badger, Malay badger, Indonesian stink badger and Sunda skunk, is a mammal native to Indonesia and Malaysia. Despite the common name, stink b ...
(''teledu''), ''Mydaus javanensis''
**** Palawan stink badger
The Palawan stink badger (''Mydaus marchei''), pantot or tuldo in the Batak language, is a carnivoran of the western Philippines named for its resemblance to badgers, its powerful smell, and the largest island to which it is native, Palawan. Like ...
, ''Mydaus marchei''
Distribution
Badgers are found in much of North America,Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
and most of the rest of Europe as far north as southern Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
. They live as far east as Japan and China. The Javan ferret-badger lives in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of data deficient and the Bornean ferret-badger lives in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of data deficient. The honey badger is found in most of sub-Saharan Africa, the Arabian Desert, southern Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.
Behaviour
The behaviour of badgers differs by family, but all shelter underground, living in burrows calledsett
A sett or set is a badger's den. It usually consists of a network of tunnels and numerous entrances. The largest setts are spacious enough to accommodate 15 or more animals with up to of tunnels and as many as 40 openings. Such elaborate setts ...
s, which may be very extensive. Some are solitary, moving from home to home, while others are known to form clans called cetes. Cete size is variable from two to 15.
Badgers can run or gallop
The canter and gallop are variations on the fastest gait that can be performed by a horse or other equine. The canter is a controlled three-beat gait, while the gallop is a faster, four-beat variation of the same gait. It is a natural gait pos ...
at for short periods of time. They are nocturnal.
In North America, coyotes sometimes eat badgers and vice versa, but the majority of their interactions seem to be mutual or neutral. American badgers and coyotes have been seen hunting together in a cooperative fashion.
Diet
The diet of the Eurasian badger consists largely ofearthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. T ...
s (especially ''Lumbricus terrestris
''Lumbricus terrestris'' or the ''common earthworm'' is a large, reddish worm species thought to be native to Western Europe, now widely distributed around the world (along with several other lumbricids). In some areas where it is an introduce ...
''), insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s, grubs, and the eggs and young of ground-nesting bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s. They also eat small mammals, amphibians, reptiles and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, as well as root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s and fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
. In Britain, they are the main predator of hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introductio ...
s, which have demonstrably lower populations in areas where badgers are numerous, so much so that hedgehog rescue societies do not release hedgehogs into known badger territories. They are occasional predators of domestic chickens, and are able to break into enclosures that a fox cannot. In southern Spain, badgers feed to a significant degree on rabbits.
American badgers are fossorial carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other s ...
s – i.e. they catch a significant proportion of their food underground, by digging. They can tunnel after ground-dwelling rodents at speed.
The honey badger of Africa consumes honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, porcupines
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethiz ...
, and even venomous snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s (such as the puff adder
The puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') is a viper species found in savannahs and grasslands from Morocco and western Arabia throughout Africa except for the Sahara and rainforest regions.U.S. Navy. 1991. ''Venomous Snakes of the World''. US Govt. ...
); they climb trees to gain access to honey from bees' nests.
Badgers have been known to become intoxicated with alcohol after eating rotting fruit.
Relation with humans
Hunting
Hunting badgers for sport has been common in many countries. The Dachshund (German for "badger hound")dog breed
A dog breed is a particular strain of dog that was purposefully bred by humans to perform specific tasks, such as herding, hunting, and guarding. Dogs are the most variable mammal on Earth, with artificial selection producing around 450 globall ...
was bred for this purpose. Badger-baiting
Badger-baiting is a form of blood sport in which badgers are baited with dogs. A baiting session typically results in the death of the badger, and possibly serious injuries to the dogs.
Background
The badger is a usually quiet and docile creat ...
was formerly a popular blood sport
A blood sport or bloodsport is a category of sport or entertainment that involves bloodshed. Common examples of the former include combat sports such as cockfighting and dog fighting, and some forms of hunting and fishing. Activities char ...
. Although badgers are normally quite docile, they fight fiercely when cornered. This led people to capture and box badgers and then wager on whether a dog could succeed in removing the badger from its refuge. In England, opposition from naturalists led to its ban under the Cruelty to Animals Act of 1835 and the Protection of Badgers Act of 1992 made it an offence to kill, injure, or take a badger or to interfere with a sett unless under license from a statutory authority. The Hunting Act of 2004 further banned fox hunt
Fox hunting is an activity involving the tracking, chase and, if caught, the killing of a fox, traditionally a red fox, by trained foxhounds or other scent hounds. A group of unarmed followers, led by a "master of foxhounds" (or "master of hou ...
ers from blocking setts during their chases.
 Badgers have been trapped commercially for their pelts, which have been used for centuries to make
Badgers have been trapped commercially for their pelts, which have been used for centuries to make shaving brush
A shaving brush or shave brush is a small brush with a handle parallel to the bristles used to make lather from shaving soap or shaving cream and apply it to the face when shaving. Shave brushes are often decorative; antique handles are often mad ...
es, a purpose to which it is particularly suited owing to its high water retention. Virtually all commercially available badger hair now comes from mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
, though, which has farms for the purpose. The Chinese supply three grades of hair to domestic and foreign brush makers. Village cooperatives are also licensed by the national government to hunt and process badgers to avoid their becoming a crop nuisance in rural northern China. The European badger is also used as trim for some traditional Scottish clothing
Highland dress is the traditional, regional dress of the Highlands and Isles of Scotland. It is often characterised by tartan (''plaid'' in North America). Specific designs of shirt, jacket, bodice and headwear may also be worn along with clan ...
. The American badger is also used for paintbrush
A paintbrush is a brush used to apply paint or ink. A paintbrush is usually made by clamping bristles to a handle with a ferrule. They are available in various sizes, shapes, and materials. Thicker ones are used for filling in, and thinner on ...
es and as trim for some Native American garments.
Culling
Controlling the badger population is prohibited in many European countries since badgers are listed in theBerne Convention
The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, was an international assembly held in 1886 in the Swiss city of Bern by ten European countries with the goal to agree on a set of leg ...
, but they are not otherwise the subject of any international treaty or legislation. Many badgers in Europe were gassed during the 1960s and 1970s to control rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ...
.
Until the 1980s, badger culling in the United Kingdom was undertaken in the form of gassing, allegedly to control the spread of bovine tuberculosis
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship betwee ...
(bTB). Limited culling resumed in 1998 as part of a 10-year randomised trial cull, which was considered by John Krebs
John Richard Krebs, Baron Krebs, Kt FRS (born 11 April 1945) is an English zoologist researching in the field of behavioural ecology of birds. He was the principal of Jesus College, Oxford, from 2005 until 2015."Elliott Coues Award, 1999: Si ...
and others to show that culling was ineffective. Some groups called for a selective cull, whilst others favoured a programme of vaccination. Wales and Northern Ireland are currently (2013) conducting field trials of a badger vaccination programme. In 2012 the government authorised a limited cull led by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. However it was later deferred and a wide range of reasons given. In August 2013 a full culling programme began, whereby it was expected that about 5,000 badgers would be killed over six weeks in West Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
using a mixture of controlled shooting and free shooting (some badgers were to be trapped in cages first). The cull caused many protests, with emotional, economic and scientific reasons being cited. The badger is considered an iconic species of the British countryside and it has been claimed by shadow ministers that "The government's own figures show it will cost more than it saves...", and Lord Krebs, who led the Randomised Badger Culling Trial in the 1990s, said the two pilots "will not yield any useful information".
Food
Although rarely eaten today in the United States or the United Kingdom, badgers were once a primary meat source for the diets of Native Americans and European colonists. Badgers were also eaten in Britain duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
and the 1950s. In some areas of Russia, the consumption of badger meat is still widespread. Shish kebab
Shish kebab is a popular meal of skewered and grilled cubes of meat. It can be found in Mediterranean cuisine and is similar to or synonymous with dishes called shashlik and khorovats, found in the Caucasus region.
It is one of the many types o ...
s made from badger, along with dog meat and pork, are a major source of trichinosis
Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the '' Trichinella'' type. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of ...
outbreaks in the Altai Region of Russia. In Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
badger meat is rarely eaten, but when it is, it is usually smoked, dried, or served in goulash
Goulash ( hu, gulyás) is a soup or stew of meat and vegetables seasoned with paprika and other spices. Originating in Hungary, goulash is a common meal predominantly eaten in Central Europe but also in other parts of Europe. It is one of the n ...
. In France, badger meat was used in the preparation of several dishes, such as ''Blaireau au sang'', and it was a relatively common ingredient in countryside cuisine. Badger meat was eaten in some parts of Spain until recently.
Pets
Badgers are sometimes kept as pets. Keeping a badger as a pet or offering one for sale is an offence in the United Kingdom under the 1992 Protection of Badgers Act.In popular culture
John Clare
John Clare (13 July 1793 – 20 May 1864) was an English poet. The son of a farm labourer, he became known for his celebrations of the English countryside and sorrows at its disruption. His work underwent major re-evaluation in the late 20th ce ...
describes a badger hunt and badger-baiting
Badger-baiting is a form of blood sport in which badgers are baited with dogs. A baiting session typically results in the death of the badger, and possibly serious injuries to the dogs.
Background
The badger is a usually quiet and docile creat ...
. The character Frances in Russell Hoban
Russell Conwell Hoban (February 4, 1925 – December 13, 2011) was an American expatriate writer. His works span many genres, including fantasy, science fiction, mainstream fiction, magical realism, poetry, and children's books.
He lived in ...
's children's books, beginning with ''Bedtime for Frances'' (1948–1970), is depicted as a badger. Trufflehunter is a heroic badger in the ''Chronicles of Narnia
''The Chronicles of Narnia'' is a series of seven high fantasy novels by British author C. S. Lewis. Illustrated by Pauline Baynes and originally published between 1950 and 1956, ''The Chronicles of Narnia'' has been adapted for radio, telev ...
'' book ''Prince Caspian
''Prince Caspian'' (originally published as ''Prince Caspian: The Return to Narnia'') is a high fantasy novel for children by C. S. Lewis, published by Geoffrey Bles in 1951. It was the second published of seven novels in ''The Chronicles of N ...
'' (1951) by C. S. Lewis
Clive Staples Lewis (29 November 1898 – 22 November 1963) was a British writer and Anglican lay theologian. He held academic positions in English literature at both Oxford University (Magdalen College, 1925–1954) and Cambridge Univers ...
.
Badger characters are featured in author Brian Jacques
James Brian Jacques (, as in "Jakes"; 15 June 1939 – 5 February 2011) was an English novelist known for his '' Redwall'' series of novels and '' Castaways of the Flying Dutchman'' series. He also completed two collections of short stories ent ...
' ''Redwall
''Redwall'' is a series of children's fantasy novels by British writer Brian Jacques, published from 1986 to 2011. It is also the title of the first book of the series, published in 1986, as well as the name of the abbey featured in the book, ...
'' series (1986–2011), they are depicted as feared warriors most often falling under the title of Badger Lord or Badger Mother. A badger character is featured in '' The Immortals'' (1992–1996) by Tamora Pierce
Tamora Pierce (born December 13, 1954) is an American writer of fantasy fiction for teenagers, known best for stories featuring young heroines. She made a name for herself with her first book series, '' The Song of the Lioness'' (1983–1988), w ...
and "The Badger" is a comic book hero created by Mike Baron
Mike Baron (born July 1, 1949) is an American comic book writer. He is the creator of ''Badger'' and the co-creator of ''Nexus'' with Steve Rude.
Biography
Mike Baron entered the comics industry with an illustrated text piece in ''Weird Trips ...
. The badger is the emblem of the Hufflepuff
Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry () is a fictional Scottish boarding school of magic for students aged eleven to eighteen, and is the primary setting for the first six books in J. K. Rowling's ''Harry Potter'' series and serves as a majo ...
house of the Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry
Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry () is a fictional Scottish boarding school of magic for students aged eleven to eighteen, and is the primary setting for the first six books in J. K. Rowling's ''Harry Potter'' series and serves as a m ...
in the J. K. Rowling
Joanne Rowling ( "rolling"; born 31 July 1965), also known by her pen name J. K. Rowling, is a British author and philanthropist. She wrote ''Harry Potter'', a seven-volume children's fantasy series published from 1997 to 2007. The ser ...
's '' Harry Potter'' book series (1997–2007), it is chosen as such because the badger is an animal that is often underestimated, because it lives quietly until attacked, but which, when provoked, can fight off animals much larger than itself, which resembles the Hufflepuff house in several ways.
Many other stories featuring badgers as characters include Kenneth Grahame
Kenneth Grahame ( ; 8 March 1859 – 6 July 1932) was a British writer born in Edinburgh, Scotland. He is most famous for ''The Wind in the Willows'' (1908), a classic of children's literature, as well as '' The Reluctant Dragon''. Both books w ...
's children's novel ''The Wind in the Willows
''The Wind in the Willows'' is a children's novel by the British novelist Kenneth Grahame, first published in 1908. It details the story of Mole, Ratty, and Badger as they try to help Mr. Toad, after he becomes obsessed with motorcars and get ...
'' (1908), Beatrix Potter
Helen Beatrix Potter (, 28 July 186622 December 1943) was an English writer, illustrator, natural scientist, and conservationist. She is best known for her children's books featuring animals, such as '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'', which was ...
's '' The Tale of Mr. Tod'' (1912; featuring badger Tommy Brock), the Rupert Bear
Rupert Bear is a British children's comic strip character and franchise created by artist Mary Tourtel and first appearing in the ''Daily Express'' newspaper on 8 November 1920. Rupert's initial purpose was to win sales from the rival ''D ...
adventures by Mary Tourtel (appearing since 1920), T. H. White's Arthurian fantasy novels ''The Once and Future King
''The Once and Future King'' is a collection of fantasy novels by T. H. White about the legend of King Arthur. It is loosely based upon the 1485 work ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' by Sir Thomas Malory. It was first published in 1958 as a collection ...
'' (1958, written 1938–41) and '' The Book of Merlyn'' (1977), ''Fantastic Mr. Fox
''Fantastic Mr Fox'' is a children's literature, children's novel written by British author Roald Dahl. It was published in 1970, by Allen & Unwin, George Allen & Unwin in the UK and Alfred A. Knopf in the U.S., with illustrations by Donald Ch ...
'' (1970) by Roald Dahl, Richard Adams's ''Watership Down
''Watership Down'' is an adventure novel by English author Richard Adams, published by Rex Collings Ltd of London in 1972. Set in Berkshire in southern England, the story features a small group of rabbits. Although they live in their natura ...
'' (1972), Colin Dann
Colin Dann (born 10 March 1943) is an English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of ...
's ''The Animals of Farthing Wood
The Animals of Farthing Wood is a series of books about a group of woodland animals. It originated with the 1979 book, ''The Animals of Farthing Wood'', by Colin Dann, and was followed by six sequels and a prequel by Dann. An animated ''Anim ...
'' (1979), and Erin Hunter
Erin Hunter is a collective pseudonym used by the authors Victoria Holmes, Kate Cary, Cherith Baldry, Clarissa Hutton, Inbali Iserles, Tui T. Sutherland, and Rosie Best in the writing of several juvenile fantasy novel series, which focus on anim ...
's '' Warriors'' (appearing since 2003). In the historic novel ''Incident at Hawk's Hill
''Incident at Hawk's Hill'' is a Newbery Honor book by naturalist and writer Allan W. Eckert published in 1971. Supposedly based on a true event, it is a historical novel centering on a six-year-old boy who gets lost on the Canadian prairie and ...
'' (1971) by Allan W. Eckert a badger is one of the main characters.
Badgers are also featured in films and animations: a flash video
Flash Video is a container file format used to deliver digital video content (e.g., TV shows, movies, etc.) over the Internet using Adobe Flash Player version 6 and newer. Flash Video content may also be embedded within SWF files. There ar ...
called ''Badgers
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by the ...
'' shows a cete doing calisthenics
Calisthenics (American English) or callisthenics (British English) ( /ˌkælɪsˈθɛnɪks/) is a form of strength training consisting of a variety of movements that exercise large muscle groups (gross motor movements), such as standing, graspi ...
. The 1973 Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
animated film ''Robin Hood
Robin Hood is a legendary heroic outlaw originally depicted in English folklore and subsequently featured in literature and film. According to legend, he was a highly skilled archer and swordsman. In some versions of the legend, he is dep ...
'' depicts the character of Friar Tuck
Friar Tuck is one of the legendary Merry Men, the band of heroic outlaws in the folklore of Robin Hood.
History
The figure of the jovial friar was common in the May Games festivals of England and Scotland during the 15th through 17th centur ...
as a badger. In the '' Doctor Snuggles'' series, Dennis the handyman was a badger.
In Europe, badgers were traditionally used to predict the length of winter.
The badger is the state animal of the U.S. state of Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, though this is a reference to the state's early miners rather than the animal itself, and Bucky Badger is the mascot of the athletic teams at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
. The badger is also the official mascot of Brock University in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada; The University of Sussex, England; and St Aidan's College at the University of Durham
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate university, collegiate public university, public research university in Durham, England, Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by royal charte ...
.
In 2007, the appearance of honey badgers around the British base at Basra, Iraq
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, fueled rumours among the locals that British forces deliberately released "man-eating" and "bear-like" badgers to spread panic. These allegations were denied by the British army and the director of Basra's veterinary hospital.
On 28 August 2013, the PC video game ''Shelter
Shelter is a small building giving temporary protection from bad weather or danger.
Shelter may also refer to:
Places
* Port Shelter, Hong Kong
* Shelter Bay (disambiguation), various locations
* Shelter Cove (disambiguation), various locatio ...
'' was released by developers Might and Delight
Might and Delight is a Swedish video game development studio and publisher based in Stockholm. The studio was established in 2010 and is best known for the ''Shelter'' series.
History
Might and Delight formed in 2010, comprising a team of 11 wh ...
in which players control a mother badger protecting her cubs.
As a sub-series of the ''Sonic the Hedgehog'' franchise, Sticks the Badger is one of the main characters of the ''Sonic Boom'' series.
References
External links
Badgerland – The Definitive On-Line Guide to Badgers in the UK
Durham County Badger Group
Badger Facts
www.ontariobadgers.org – Information about American Badgers
YouTube video of examples of Badger scratching trees
* {{Authority control Mammal common names Paraphyletic groups