Figurative system of human knowledge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
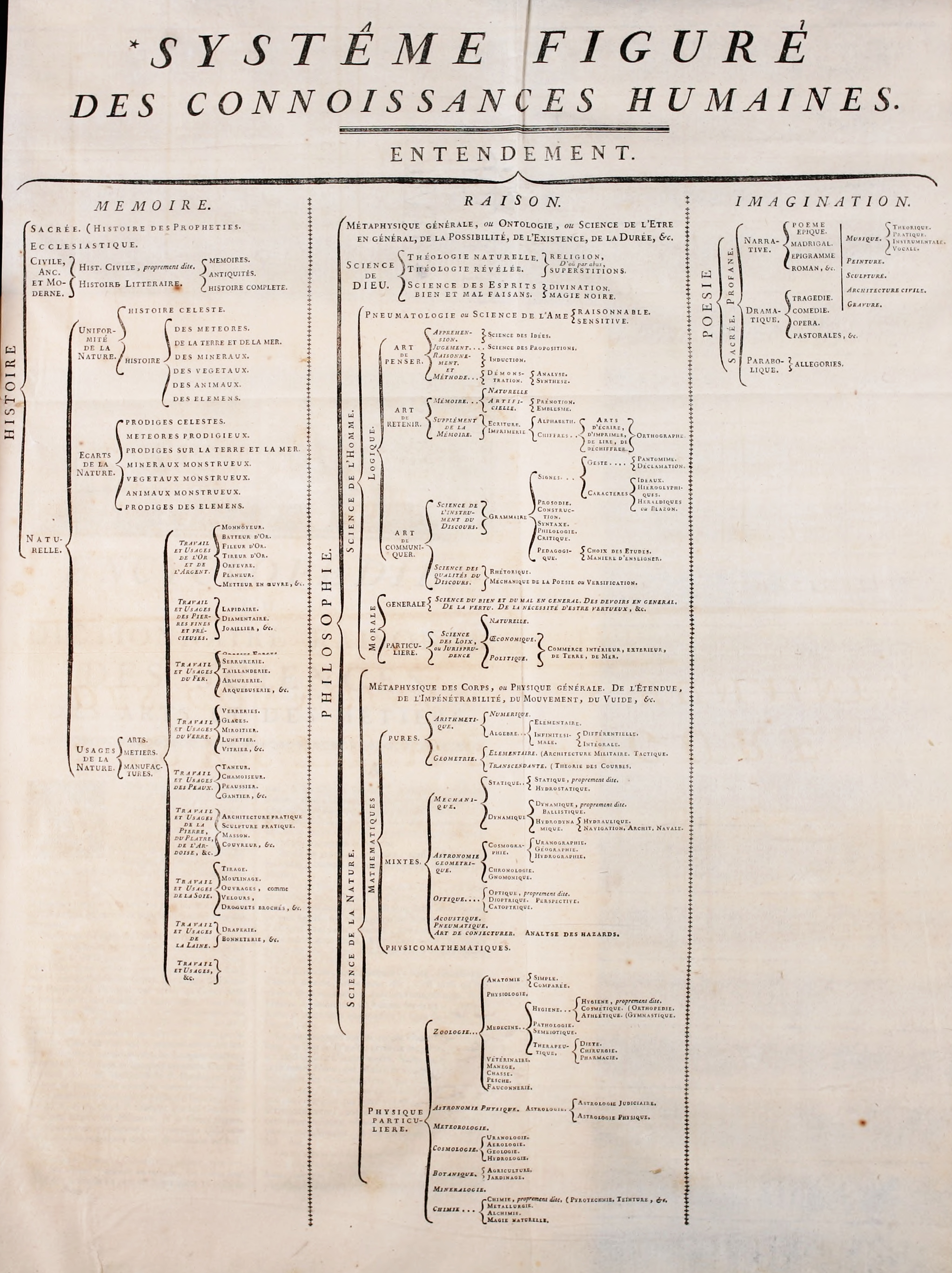 The "figurative system of human knowledge", sometimes known as the tree of Diderot and d'Alembert, was a tree developed to represent the structure of
The "figurative system of human knowledge", sometimes known as the tree of Diderot and d'Alembert, was a tree developed to represent the structure of
image of the diagram with English translations superimposed over the French text
is available. Another example of English translation of the tree is available in literature (see the reference by Schwab). Below is a version of it rendered in
The ''Tree'' translated into English
ESSAI D'UNE DISTRIBUTION GÉNÉALOGIQUE DES SCIENCES ET DES ARTS PRINCIPAUX, published as a fold-out frontispiece in volume 1 of Pierre Mouchon, ''Table analytique et raisonnée des matieres contenues dans les XXXIII volumes in-folio du Dictionnaire des sciences, des arts et des métiers, et dans son supplément'', Paris, Panckoucke 1780.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Figurative System Of Human Knowledge Taxonomy Age of Enlightenment Trees (data structures) Knowledge representation
 The "figurative system of human knowledge", sometimes known as the tree of Diderot and d'Alembert, was a tree developed to represent the structure of
The "figurative system of human knowledge", sometimes known as the tree of Diderot and d'Alembert, was a tree developed to represent the structure of knowledge
Knowledge can be defined as Descriptive knowledge, awareness of facts or as Procedural knowledge, practical skills, and may also refer to Knowledge by acquaintance, familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called pro ...
itself, produced for the ''Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
'' by Jean le Rond d'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert (; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the '' Encyclopéd ...
and Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the '' Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a promi ...
.
The tree was a taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
of human knowledge, inspired by Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
's '' The Advancement of Learning''. The three main branches of knowledge in the tree are: "Memory"/History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, "Reason"/ Philosophy, and "Imagination"/Poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
.
Notable is the fact that theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
is ordered under 'Philosophy'. The historian Robert Darnton
Robert Choate Darnton (born May 10, 1939) is an American cultural historian and academic librarian who specializes in 18th-century France.
He was director of the Harvard University Library from 2007 to 2016.
Life
Darnton was born in New York ...
has argued that this categorization of religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
as being subject to human reason, and not a source of knowledge in and of itself (revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing of some form of truth or knowledge through communication with a deity or other supernatural entity or entities.
Background
Inspiration – such as that bestowed by God on the ...
), was a significant factor in the controversy surrounding the work.Robert Darnton, "Philosophers Trim the Tree of Knowledge: The Epistemological Strategy of the ''Encyclopedie''," ''The Great Cat Massacre and Other Episodes in French Cultural History'' (New York: Basic Books, Inc., 1984), 191-213. Additionally notice that 'Knowledge of God' is only a few nodes away from 'Divination' and 'Black Magic'.
The original version, in French, can be seen in the graphic on the right. Aimage of the diagram with English translations superimposed over the French text
is available. Another example of English translation of the tree is available in literature (see the reference by Schwab). Below is a version of it rendered in
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
as a bulleted outline.
''The Tree of Diderot and d'Alembert''
"Detailed System of Human Knowledge" from theEncyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
.
* Understanding
Understanding is a psychological process related to an abstract or physical object, such as a person, situation, or message whereby one is able to use concepts to model that object.
Understanding is a relation between the knower and an object ...
:* Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
.
::* History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
.
:::* Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects ( ...
(History of Prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
s).
:::* Ecclesiastical.
:::* Civil
Civil may refer to:
*Civic virtue, or civility
*Civil action, or lawsuit
* Civil affairs
*Civil and political rights
*Civil disobedience
*Civil engineering
*Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism
*Civilian, someone not a membe ...
, Ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
and Modern.
::::* Civil History, properly said. ''(See also: History of civil society)''
::::* Literary History
The history of literature is the historical development of writings in prose or poetry that attempt to provide entertainment, enlightenment, or instruction to the reader/listener/observer, as well as the development of the literary techniques ...
.
:::::* Memoirs.
:::::* Antiquities
Antiquities are objects from antiquity, especially the civilizations of the Mediterranean: the Classical antiquity of Greece and Rome, Ancient Egypt and the other Ancient Near Eastern cultures. Artifacts from earlier periods such as the Meso ...
. ''(See also: Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
)''
:::::* Complete Histories.
:::* Natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
.
::::* Uniformity of Nature. ''(See: Uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in ...
)''
:::::* Celestial History.
:::::* History...
::::::* of Meteors
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
.
::::::* of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
and the Sea ''(See also: Origin of water on Earth
The origin of water on Earth is the subject of a body of research in the fields of planetary science, astronomy, and astrobiology. Earth is unique among the rocky planets in the Solar System in that it is the only planet known to have oceans of ...
)''
::::::* of Minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed ...
. ''(See also: Geological history of Earth
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
)''
::::::* of Vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
s. ''(See also: History of agriculture
Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin.
The development of agriculture a ...
)''
::::::* of Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s. ''(See also: Evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for ''gigaannum'') and evide ...
)''
::::::* of the Elements. ''(See also: Classical element, History of alchemy, and History of chemistry)''
::::* Deviations of Nature.
:::::* Celestial Wonders.
:::::* Large Meteors. ''(See also: Asteroids)''
:::::* Wonders of Land and Sea. ''(See: Wonders of the World
Various lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, in order to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural features and human-built structures.
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World is the o ...
)''
:::::* Monstrous Minerals.
:::::* Monstrous Vegetables. ''(See: Largest plants, Poisonous plant
Plants that produce toxins are referred to as poisonous plants. Plants that cause irritation on contact are also described as "poisonous".
The toxins in poisonous plants affect herbivores, and deter them from consuming the plants. Plants cannot ...
s, and Carnivorous plants)''
:::::* Monstrous Animals. (See: '' Largest animals and Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
s)''
:::::* Wonders of the Elements. ''(See: Natural disasters)''
::::* Uses of Nature (See ''Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and Reproducibility, reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in me ...
and Applied sciences)''
:::::* Arts, Craft
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pro ...
s, Manufactures.
::::::* Work and Uses of Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
and Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
.
:::::::* Minting
Minting is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The village is situated south from the A158 road. The population (including Gautby) at the 2011 census was 286.
Minting Priory was located here.
Mi ...
.
:::::::* Goldsmith
A goldsmith is a metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Nowadays they mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, goldsmiths have also made silverware, platters, goblets, decorative and servicea ...
.
:::::::* Gold Spinning.
:::::::* Gold Drawing.
:::::::* Silversmith
A silversmith is a metalworker who crafts objects from silver. The terms ''silversmith'' and ''goldsmith'' are not exactly synonyms as the techniques, training, history, and guilds are or were largely the same but the end product may vary grea ...
:::::::* Planisher, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Precious Stones.
:::::::* Lapidary
Lapidary (from the Latin ) is the practice of shaping stone, minerals, or gemstones into decorative items such as cabochons, engraved gems (including cameos), and faceted designs. A person who practices lapidary is known as a lapidarist. A lap ...
.
:::::::* Diamond cutting
Diamond cutting is the practice of shaping a diamond from a rough stone into a faceted gem. Cutting diamonds requires specialized knowledge, tools, equipment, and techniques because of its extreme difficulty.
The first guild of diamond cutters and ...
.
:::::::* Jeweler
A bench jeweler is an artisan who uses a combination of skills to make and repair jewelry. Some of the more common skills that a bench jeweler might employ include antique restoration, silversmith, Goldsmith, stone setting, engraving, fabrica ...
, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
.
:::::::* Large Forges.
:::::::* Locksmith.
:::::::* Tool Making.
:::::::* Armorer.
:::::::* Gun Making, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
.
:::::::* Glassmaking
Glass production involves two main methods – the float glass process that produces sheet glass, and glassblowing that produces bottles and other containers. It has been done in a variety of ways during the history of glass.
Glass container ...
.
:::::::* Plate-Glassmaking.
:::::::* Mirror Making.
:::::::* Optician.
:::::::* Glazier
A glazier is a tradesman responsible for cutting, installing, and removing glass (and materials used as substitutes for glass, such as some plastics).Elizabeth H. Oakes, ''Ferguson Career Resource Guide to Apprenticeship Programs'' ( Infobase: ...
, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Skin.
:::::::* Tanner.
:::::::* Chamois Maker.
:::::::* Leather Merchant.
:::::::* Glove Making, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
, Plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
, Slate, etc.
:::::::* Practical Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
.
:::::::* Practical Sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable ...
.
:::::::* Mason.
:::::::* Tiler, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
.
:::::::* Spinning.
:::::::* Milling.
:::::::* Work like.
:::::::* Velvet
Weave details visible on a purple-colored velvet fabric
Velvet is a type of woven tufted fabric in which the cut threads are evenly distributed, with a short pile, giving it a distinctive soft feel. By extension, the word ''velvety'' means ...
.
:::::::* Brocaded Fabrics, etc.
::::::* Work and Uses of Wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool. ...
.
:::::::* Cloth-Making.
:::::::* Bonnet-Making, etc.
::::::* Working and Uses, etc.
:* Reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, ...
::* Philosophy
:::* General Metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality, the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity, and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of conscio ...
, or Ontology
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exi ...
, or Science of Being in General, of Possibility, of Existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontological property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval Latin ''existentia/exsistentia' ...
, of Duration, etc.
:::* Science of God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
.
::::* Natural Theology.
::::* Revealed Theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
.
::::* Science of Good and Evil Spirits.
:::::* Divination.
:::::* Black Magic
Black magic, also known as dark magic, has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for evil and selfish purposes, specifically the seven magical arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 14 ...
.
:::* Science of Man.
::::* Pneumatology
Pneumatology refers to a particular discipline within Christian theology that focuses on the study of the Holy Spirit. The term is derived from the Greek word ''Pneuma'' ( πνεῦμα), which designates "breath" or "spirit" and metaphorica ...
or Science of the Soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest atte ...
.
:::::* Reasonable.
:::::* Sensible.
::::* Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premise ...
.
:::::* Art of Thinking
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, an ...
.
::::::* Apprehension.
:::::::* Science of Idea
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of bei ...
s
::::::* Judgement
Judgement (or US spelling judgment) is also known as ''adjudication'', which means the evaluation of evidence to make a decision. Judgement is also the ability to make considered decisions. The term has at least five distinct uses. Aristotle s ...
.
:::::::* Science of Proposition
In logic and linguistics, a proposition is the meaning of a declarative sentence. In philosophy, " meaning" is understood to be a non-linguistic entity which is shared by all sentences with the same meaning. Equivalently, a proposition is the no ...
s.
::::::* Reasoning.
:::::::* Induction.
::::::* Method
Method ( grc, μέθοδος, methodos) literally means a pursuit of knowledge, investigation, mode of prosecuting such inquiry, or system. In recent centuries it more often means a prescribed process for completing a task. It may refer to:
*Scien ...
.
:::::::* Demonstration.
::::::::* Analysis
Analysis ( : analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (3 ...
.
::::::::* Synthesis.
:::::* Art of Remembering.
::::::* Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
.
:::::::* Natural.
:::::::* Artificial
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotations
Artificiality ...
.
::::::::* Prenotion.
::::::::* Emblem.
::::::* Supplement to Memory.
:::::::* Writing
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
.
:::::::* Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
.
::::::::* Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllab ...
.
::::::::* Cipher.
:::::::::* Arts of Writing
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
, Printing, Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process involving such areas as word recognition, orthography (spelling ...
, Deciphering.
::::::::::* Orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
.
:::::* Art of Communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
::::::* Science of the Instrument of Discourse.
:::::::* Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domain ...
.
::::::::* Signs.
:::::::::* Gesture.
::::::::::* Pantomime
Pantomime (; informally panto) is a type of musical comedy stage production designed for family entertainment. It was developed in England and is performed throughout the United Kingdom, Ireland and (to a lesser extent) in other English-speaking ...
.
::::::::::* Declamation.
:::::::::* Characters.
::::::::::* Ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Greek "idea" and "to write") is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept, independent of any particular language, and specific words or phrases. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by famili ...
s.
::::::::::* Hieroglyphics
Egyptian hieroglyphs (, ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters.There were about 1,00 ...
.
::::::::::* Heraldry or Blazonry.
::::::::* Prosody.
::::::::* Construction.
::::::::* Syntax.
::::::::* Philology
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics (with especially strong ties to etymology). Philology is also defined as th ...
.
::::::::* Critique.
:::::::* Pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
.
::::::::* Choice of Studies.
::::::::* Manner of Teaching.
::::::* Science of Qualities of Discourse.
:::::::* Rhetoric.
:::::::* Mechanics of Poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
.
::::* Ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concer ...
.
:::::* General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
.
::::::* General Science of Good and Evil, of duties in general, of Virtue
Virtue ( la, virtus) is moral excellence. A virtue is a trait or quality that is deemed to be morally good and thus is valued as a foundation of principle and good moral being. In other words, it is a behavior that shows high moral standards ...
, of the necessity of being Virtuous, etc.
:::::* Particular
In metaphysics, particulars or individuals are usually contrasted with universals. Universals concern features that can be exemplified by various different particulars. Particulars are often seen as concrete, spatiotemporal entities as opposed to a ...
.
::::::* Science of Law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
s or Jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning a ...
.
:::::::* Natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
.
:::::::* Economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
. ''(See also commercial law)''
:::::::* Political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
. ''(See also political law)''
::::::::* Internal
Internal may refer to:
*Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism
*''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016
...
and External
External may refer to:
* External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra
* Externality
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party' ...
. ''(See also foreign policy)''
::::::::* Commerce
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, nation ...
on Land and Sea.
:::* Science of Nature
::::* Metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality, the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity, and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of conscio ...
of Bodies or, General Physics, of Extent, of Impenetrability, of Movement, of Word, etc.
::::* Mathematics.
:::::* Pure
Pure may refer to:
Computing
* A pure function
* A pure virtual function
* PureSystems, a family of computer systems introduced by IBM in 2012
* Pure Software, a company founded in 1991 by Reed Hastings to support the Purify tool
* Pure-FTPd, F ...
.
::::::* Arithmetic.
:::::::* Numeric.
:::::::* Algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
.
::::::::* Elementary
Elementary may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Elementary'' (Cindy Morgan album), 2001
* ''Elementary'' (The End album), 2007
* ''Elementary'', a Melvin "Wah-Wah Watson" Ragin album, 1977
Other uses in arts, entertainment, a ...
.
::::::::* Infinitesimal.
:::::::::* Differential.
:::::::::* Integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along wit ...
.
::::::* Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
.
:::::::* Elementary (Military Architecture, Tactics).
:::::::* Transcendental (Theory of Courses).
:::::* Mixed.
::::::* Mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to object ...
.
::::::::* Statics.
:::::::::* Statics, properly said.
:::::::::* Hydrostatics
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body "fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an imme ...
.
::::::::* Dynamics.
:::::::::* Dynamics, properly said.
:::::::::* Ballistics.
:::::::::* Hydrodynamics.
::::::::::* Hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
.
::::::::::* Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, Naval Architecture.
::::::* Geometric Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
.
:::::::* Cosmography
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-sca ...
.
::::::::* Uranography.
::::::::* Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
.
::::::::* Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primar ...
.
:::::::* Chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrónos'', "time"; and , ''-logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. I ...
.
:::::::* Gnomonics.
::::::* Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
.
:::::::* Optics, properly said.
:::::::* Dioptrics
Dioptrics is the branch of optics dealing with refraction, similarly the branch dealing with mirrors is known as catoptrics. Dioptrics is the study of the refraction of light, especially by lenses. Telescopes that create their image with an obj ...
, Perspective.
:::::::* Catoptrics
Catoptrics (from grc-gre, κατοπτρικός ''katoptrikós'', "specular", from grc-gre, κάτοπτρον ''katoptron'' "mirror") deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors. A catoptric s ...
.
::::::* Acoustics.
::::::* Pneumatics.
::::::* Art of Conjecture. Analysis of Chance.
:::::* Physicomathematics.
::::* Particular Physics.
:::::* Zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ...
.
::::::* Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
.
:::::::* Simple.
:::::::* Comparative
general linguistics, the comparative is a syntactic construction that serves to express a comparison between two (or more) entities or groups of entities in quality or degree - see also comparison (grammar) for an overview of comparison, as well ...
.
::::::* Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
.
::::::* Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
.
:::::::* Hygiene.
::::::::* Hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, properly said.
::::::::* Cosmetics (Orthopedics).
::::::::* Athletics (Gymnastics).
:::::::* Pathology.
:::::::* Semiotics.
:::::::* Treatment.
::::::::* Diete.
::::::::* Surgery.
::::::::* Pharmacy.
::::::* Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutri ...
.
::::::* Horse Management
There are many aspects to horse management. Horses, ponies, mules, donkeys and other domesticated equids require attention from humans for optimal health and long life.
Living environment
Horses require both shelter from natural elements like w ...
.
::::::* Hunting
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products ( fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, ...
.
::::::* Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
.
::::::* Falconry.
:::::* Physical Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
.
::::::* Astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
.
:::::::* Judiciary Astrology.
:::::::* Physical Astrology.
:::::* Meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
.
:::::* Cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
.
::::::* Uranology.
::::::* Aerology
Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of ...
.
::::::* Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
.
::::::* Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is call ...
.
:::::* Botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
.
::::::* Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
.
::::::* Gardening.
:::::* Mineralogy.
:::::* Chemistry.
::::::* Chemistry, properly said, ( Pyrotechnics, Dyeing, etc.).
::::::* Metallurgy.
::::::* Alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
.
::::::* Natural Magic.
:* Imagination.
::* Poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
.
:::* Sacred, Profane.
::::* Narrative.
:::::* Epic Poem
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants.
...
:::::* Madrigal
A madrigal is a form of secular vocal music most typical of the Renaissance music, Renaissance (15th–16th c.) and early Baroque music, Baroque (1600–1750) periods, although revisited by some later European composers. The Polyphony, polyphoni ...
:::::* Epigram
:::::* Novel, etc.
::::* Dramatic
:::::* Tragedy
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy ...
:::::* Comedy
Comedy is a genre of fiction that consists of discourses or works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. The term o ...
:::::* Pastoral, etc.
::::* Parable
:::::* Allegory
(NOTE: THIS NEXT BRANCH SEEMS TO BELONG TO BOTH THE NARRATIVE AND DRAMATIC TREE AS DEPICTED BY THE LINE DRAWN CONNECTING THE TWO.)
::::* Music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
:::::* Theoretical
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be ...
:::::* Practical ''(see also musical technique
Musical technique is the ability of instrumental and vocal musicians to exert optimal control of their instruments or vocal cords in order to produce the precise musical effects they desire. Improving one's technique generally entails practicin ...
)''
:::::** Instrumental
An instrumental is a recording normally without any vocals, although it might include some inarticulate vocals, such as shouted backup vocals in a big band setting. Through semantic widening, a broader sense of the word song may refer to inst ...
:::::** Vocal
::::* Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
::::* Sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable ...
::::* Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an in ...
See also
* Classification chart *Instauratio magna
The ''Novum Organum'', fully ''Novum Organum, sive Indicia Vera de Interpretatione Naturae'' ("New organon, or true directions concerning the interpretation of nature") or ''Instaurationis Magnae, Pars II'' ("Part II of The Great Instauration ...
* Propædia
The one-volume ''Propædia'' is the first of three parts of the 15th edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', intended as a compendium and topical organization of the 12-volume '' Micropædia'' and the 17-volume '' Macropædia,'' which are organ ...
* Pierre Mouchon
Pierre Mouchon (30 July 1733 – 20 August 1797) was an 18th-century Genevan pastor, best remembered for being the author of the ''Table analytique et raisonnée...'' (index) of the ''Encyclopédie'' by Diderot and D'Alembert.
Biography
The son ...
References
Further reading
* Robert Darnton, "Epistemological angst: From encyclopedism to advertising," in Tore Frängsmyr, ed., ''The structure of knowledge: classifications of science and learning since the Renaissance'' (Berkeley, CA: Office for the History of Science and Technology, University of California, Berkeley, 2001). * Adams, David (2006) 'The Système figuré des Connaissances humaines and the structure of Knowledge in the Encyclopédie', in Ordering the World, ed. Diana Donald and Frank O'Gorman, London: Macmillan, p. 190-215. * ''Preliminary discourse to the Encyclopedia of Diderot'', Jean Le Rond d'Alembert, translated by Richard N. Schwab, 1995.External links
The ''Tree'' translated into English
ESSAI D'UNE DISTRIBUTION GÉNÉALOGIQUE DES SCIENCES ET DES ARTS PRINCIPAUX, published as a fold-out frontispiece in volume 1 of Pierre Mouchon, ''Table analytique et raisonnée des matieres contenues dans les XXXIII volumes in-folio du Dictionnaire des sciences, des arts et des métiers, et dans son supplément'', Paris, Panckoucke 1780.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Figurative System Of Human Knowledge Taxonomy Age of Enlightenment Trees (data structures) Knowledge representation